1. Introduction
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common type of nonskin malignancy and one of the leading causes of cancer-related death in men [
1,
2]. Owing to PCa heterogeneity, patients in different clinical states benefit from different treatments [
3,
4]. Surgery and radiation therapy are common forms of treatment for localized PCa [
5]. Considering that 25~35% of PCa patients will relapse and develop to advanced PCa, androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is recognized as the cornerstone therapy for recurrent PCa. However, almost all patients will develop resistance to androgen deprivation therapy and inevitably relapse into the hormone-independent stage, that is, castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) within a few years [
2,
6,
7]. In this case, a considerable number of studies have focused on the mechanism and therapeutic potential of inhibiting the androgen receptor (AR) pathway. Nevertheless, therapies targeting the AR pathway have gradually been shown to be resistant [
8]. PCD has been a hot spot in the spotlight in recent years. Mechanisms underlying apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis and PANoptosis in PCa are perfect subjects with which to study the role of PCD in PCa.
Cell death is as important as cell proliferation in the development and homeostasis of multicellular organisms [
9,
10]. As a crucial member of cell death, PCD plays an indispensable role in maintaining biological balance in cells and tissues and responding to infection, tumors and some other pathologies [
11,
12]. Apoptosis, pyroptosis and necroptosis are three extensively studied and understood forms of PCD. As the earliest form of PCD to be discovered, apoptosis is a nonlytic PCD with an integral cellular membrane and is considered immunologically silent [
9]. Necrosis is a lytic and inflammatory form of unregulated and accidental cell death. However, studies have revealed that some subtypes of necrosis are driven by specific molecules, and these molecules determine the cell death modality named programmed necrosis or necroptosis [
13]. Necroptotic cells undergo swelling and membrane rupture, which causes the release of intracellular damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) into the extracellular microenvironment [
14,
15]. Pyroptosis is characterized by a series of events initiated by rapid caspase-dependent plasma membrane rupture and the release of inflammation-inducing intracellular contents [
16,
17,
18]. Apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis are mediated by specific pathways and molecules that eliminate damage factors. Furthermore, these pathways can interact and cooperate with each other [
19,
20]. Notably, PANoptosis, a novel complex form of PCD, is a combination of the three aforementioned forms of cell death and is triggered in people with infectious diseases and cancer [
21,
22]. PANoptosis reveals the importance of these three forms of death and may contribute to anticancer drug development. Furthermore, therapy targeting the mechanism underlying apoptosis has led to brilliant results in patients with PCa, which also shows the importance of continuing to develop drugs that target necroptosis and pyroptosis pathways. In this review, the mechanisms of several characteristic forms of PCD are elaborated. The emerging representative treatment and targets for the four forms of PCD are summarized.
2. The Mechanisms of Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis and Their Connection
2.1. Mechanisms of Apoptosis
First proposed by Kerr et al. [
23] in 1972, apoptosis is characterized by shrinkage and condensation of cells, crumbling of the nuclear envelope, condensation of chromatin with fragmentation of DNA, and the formation of small apoptotic vesicles known as ApoBDs [
24]. Apoptotic cells do not release cellular contents into their surroundings and activate no inflammatory response, which makes apoptosis a mild type of PCD [
25].
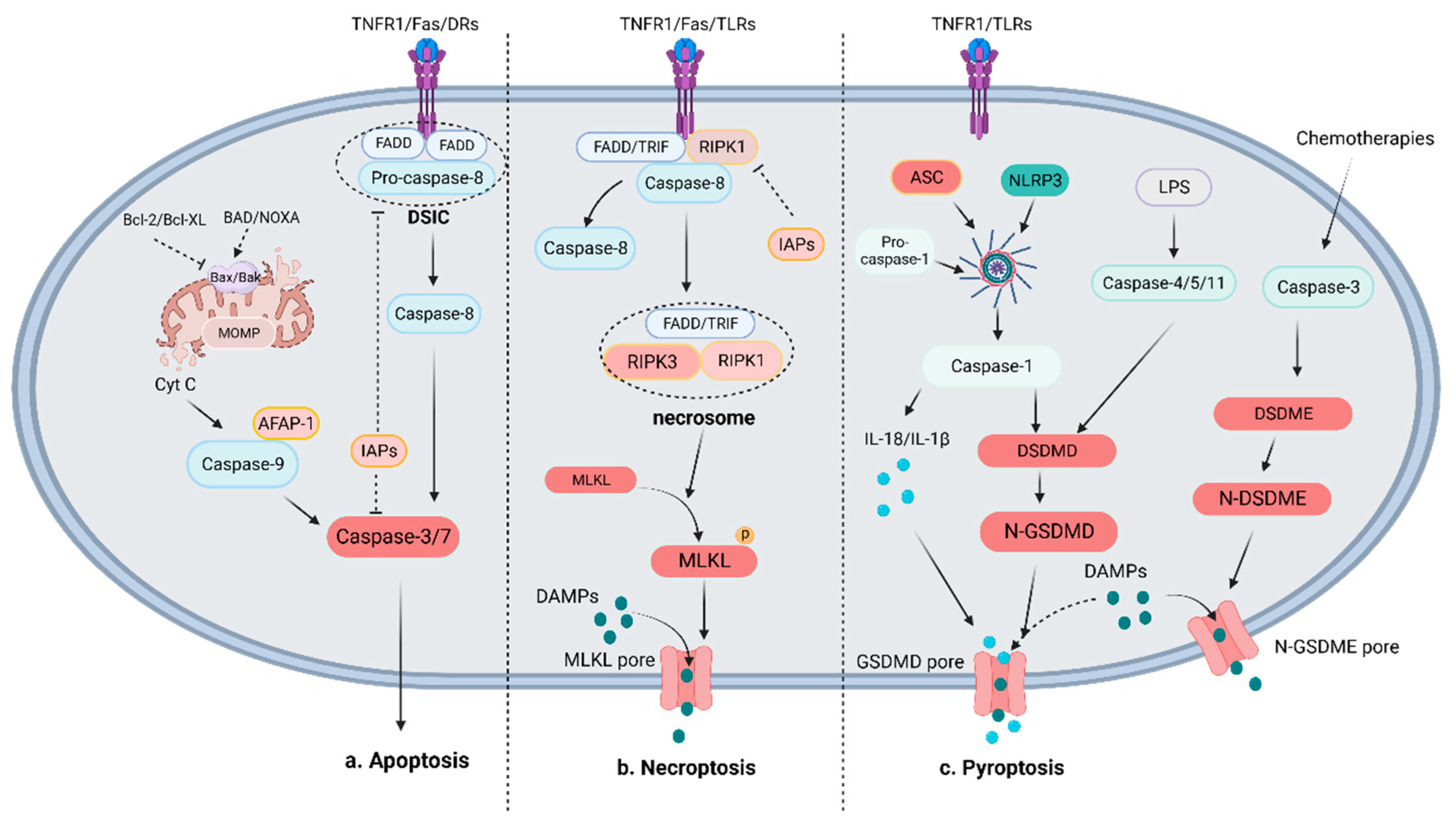
Two major pathways contribute to cell apoptosis: the intrinsic pathway involving B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) family proteins and the extrinsic pathway mediated by death receptor (DR) ligands [
19] (
Figure 1). The extrinsic pathway is initiated by the activation of apoptotic death receptors, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 (TNFR1), Fas and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptors (DR4 and DR5), when bound to their ligands (TNFα, FasL and TRAIL) [
26,
27,
28]. Then, adaptor proteins are recruited, namely, TNF receptor-associated death domain (TRADD) and Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD), which activate the downstream interactor procaspase-8/10 and form the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) [
29]. Activated caspase-8 initiates the execution phase of apoptosis by cleaving the downstream effector caspase-3 or caspase-7 [
30]. Inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) proteins such as XIAP and IAP1/2 can bind to and inhibit the activation of caspase-3/9 [
31]. In the intrinsic pathway, stimuli such as toxicity-inducing substances or DNA damage dysregulate intracellular homeostasis and cause mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), which leads to the release of cytochrome c into the cytosol. Cytochrome-c regulated by the Bcl-2 family recruits procaspase-9 by binding to apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 (APAF-1), which triggers the formation of apoptosomes [
32,
33]. Through the apoptosome, procaspase-9 is cleaved to generate activated caspase-9, which then activates the effector, caspase-3 [
34]. The Bcl-2 family plays an indispensable role in regulating mitochondrion-related apoptosis and can be divided into proapoptotic proteins (such as Bax and Bak) and antiapoptotic proteins (such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL) [
35]. Another important proapoptotic protein, namely, BH3-only proteins, shares a homologous BH3 region, through which they bind and directly activate Bax and/or Bak-1 or inhibit antiapoptotic proteins to mediate apoptosis [
36,
37]. The transcription factor p53, encoded by the TP53 gene, can be detected in normal conditions but is silenced or mutated in cancer. DNA damage and oncogene activation can increase cellular p53 levels by phosphorylation and acetylation. p53 induces the extrinsic pathway and the mitochondrial pathway by regulating DRs and Bcl-2 proteins such as Bax and PUMA [
38]. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are regulators of cell-cycle progression and transcription. CDK transcriptionally enhances the activity of antiapoptotic BH3-only proteins such as myeloid cell leukemia (Mcl-1) while repressing sensitizers [
39].
a. Mechanism of apoptosis: The apoptotic pathway is mainly initiated by the death receptor-mediated extrinsic pathway and the Bcl-mediated intrinsic pathway. ExtrinsicThe extrinsic pathway activatedactivates the effector caspase-3/7 to decompose cells by the formation of the DISC, which includes pro-caspase-8 and FADD, to cleave caspase-8. IntrinsicThe intrinsic pathway is characterized by the release of mitochondrial Cyt C mediated by pro-apoptotic proteins (such as Bax and Bak) or anti-apoptotic proteins (such as Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, BAD, NOXA). The combination of Cyt C, AFAP-1 and caspase-9 activateactivates effector caspase-3/7 to crack cells. b. Mechanism of necroptosis: The necroptotic pathway is initiated when caspase-8 is absent by RIPK1-mediated RIPK3 activation. MLKL is then is recruited and phosphorylated to form porepores in the membrane and release of DAMPs. c. Mechanism of pyroptosis: The pyroptotic pathway can be divided into the NLRP3-induced canonical pathway and the LPS-induced noncanonical pathway, which activeactivate caspase-1 and GSDMD to cause the release of IL-18, and IL-1β and DAMPs. In addition to the above two main pathways, chemotherapies induce caspase-3 -mediated GSDME cleavage to crack cellcleave cells and release of DAMPs.
2.2. Mechanism of Necroptosis
As a counterpart of apoptosis, necrosis was long thought to be an unregulated form of cell death. However, in 2005, as suggested by Degterev et al. [
40], necroptosis was reconsidered to be a necrotic form of PCD. The morphology of necroptotic cells is the same as that of necrotic cells, including a disrupted plasma membrane, and both types of cells passively release intracellular contents [
41].
In necroptotic cells, death receptors (such as TNFR1 and Fas) and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) such as Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) are activated by binding to their cognate ligands [
15]. Then, these activated receptors recruit interacting kinase 1 (RIPK1) and a series of proteins to form an oligomeric complex, in which RIPK1 is polyubiquitinated and cleaved [
42,
43]. The NF-κB-dependent proinflammatory pathway and prosurvival pathway are involved in most of the abovementioned activities to promote cell survival [
44]. An oligomeric complex, which consists of RIPK1, FADD, and CASP8, then exerts proapoptotic effects after dimerization by activating CASP8. However, in the absence of CASP8, active RIPK1 recruits and phosphorylates receptor-interacting kinase 3 (RIPK3) to form a RIPK1/RIPK3 complex, which then recruits and phosphorylates mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL) to form the necrosome [
42,
45,
46,
47]. Phosphorylated MLKL can increase plasma membrane permeability by opening calcium or sodium ion channels or by directly forming pores in the plasma membrane, which leads to membrane rupture and the release of DAMPs. The released DAMPs inevitably cause inflammation and trigger immune responses [
48,
49].
2.3. Mechanism of Pyroptosis
Pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of PCD that was first observed in 1986 in primary mouse macrophages undergoing anthrax-induced lethality, which causes the rapid release of cell contents and cell death [
50,
51]. A series of caspase families are involved in pyroptosis in an inflammasome-dependent manner and are considered to play an indispensable role in the occurrence and development of cancer [
51].
Pyroptosis is mediated through two main mechanisms: canonical and noncanonical pathways that trigger the gasdermin family [
51,
52]. In the canonical pathway, pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or DAMPs are detected by PRRs, such as TLRs and Nod-like receptors (NLRs), which activate inflammasome sensors, such as Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3), AIM2, and pyrin [
51,
53,
54]. Activated inflammasome sensors recruit the adapter protein apoptosis-related speck-like protein (ASC) and pro-caspase-1 to form inflammasomes [
55]. Procaspase-1 is then cleaved, which yields activated caspase-1, which can process procytokines interleukin (IL)-1β/18 to generate mature IL-1β/18. Activated IL-18/1β are secreted outside a cell through membrane pores and amplify the inflammatory response [
56]. Activated caspase-1 can also process gasdermin D (GSDMD), thereby releasing the N-terminal fragment of GSDMD (GSDMD-N), which contributes to the nonselective formation of pores on the cell membrane and eventually results in cell swelling and lysis [
57,
58]. In the noncanonical pathway, gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) triggers pyroptosis by activating caspase-4/5 in humans or caspase-11 in mice to cleave GSDMD [
58]. GSDMD-N positively regulates pyroptosis by activating the NLRP3 or NLRC4 inflammasome [
59]. In addition to the abovementioned pyroptosis pathways, the caspase-3-mediated GSDME pathway has also been shown to play an essential role in inducing pyroptosis, especially during chemotherapeutic treatment [
60].
2.4. The Connection between Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis
The apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis pathways have long been considered to function in parallel but have recently been shown to be tightly connected and to interact with each other. Acting as a bridge between apoptotic and necroptotic pathways, caspase-8 was a well-known PCD mediator. It can not only activate the downstream executioner caspase-3/7 in the apoptosis pathway but also cleave RIPK1 and RIPK3 in the ripoptosome in the necroptosis pathway, thereby preventing necroptosis and facilitating apoptosis [
61,
62,
63]. In addition, FADD and caspase-8 mediate caspase-1 processing, NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and GSDMD activation, indicative of crosstalk between apoptosis and pyroptosis pathways [
64,
65,
66]. In a recent discovery, pannexin-1, a channel-forming glycoprotein in macrophages, promoted NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways [
67]. Necroptosis can also play an important role in initiating pyroptosis. For example, RNA viruses upregulate the expression of NLRP3 inflammasome components in a RIPK1/RIPK3-dependent and MLKL-independent manner [
68]. Furthermore, the PANoptosome, the set of activated apoptosis, necroptosis and pyroptosis components that converge within the same period, was recently proposed and has received significant attention [
69,
70]. In PANoptosis, the connection between apoptosis, necroptosis and pyroptosis is particularly tight, and the specific mechanisms will become clearer as relevant literature is published in the future.
3. Role of Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis in PCa
3.1. Role of Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer
Previous studies have shown that the normal growth and function of the prostate gland as well as the growth and progression of PCa largely depend on signaling by androgen-induced AR pathway activation [
71]. After treatment with androgen deprivation therapy or castration, prostate glands undergo marked involution characterized by apoptotic cell death, which significantly inhibits the progression of PCa. Furthermore, intrinsic pathways induced by mitochondrial or extrinsic death pathway receptors are both involved in the apoptosis of prostate epithelial cells after androgen deprivation therapy or castration [
72].
Activation of death receptors initiates the extrinsic death pathway. Among the death receptors, TRAIL-R2 (DR5) is a member of the TNFR family, and drugs targeting DR5 are the most advanced [
73]. TRAIL-R2 was downregulated in PCa cell lines and was markedly reduced in high-grade tumors [
74]. The agonistic monoclonal antibody lexatumumab targeting DR5 have been the subject of early-phase investigations for use against several solid malignancies including PCa [
37]. The extrinsic death pathway can also be activated in immune responses. A recent study cocultured human NK cells (KHYG-1) with human prostate cancer stem-like cells. They discovered that NK cells exerted a killing effect by initiating the TRAIL/DR5 cell death pathway [
75]. In another study, a selenium-bearing ruthenium complex (RuSe) was designed. RuSe potentiated NK cell-mediated killing of PC3 cells by activating TRAIL-R and FasL [
76].
Bcl-2 family proteins and their regulators are also key molecules in PCa progression and therapy resistance. Initially, researchers discovered that the expression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2 was decreased in PCa epithelial cells but increased after castration [
77,
78]. Moreover, increased levels of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-X and Mcl-1 were identified in prostate tumor cells, especially in high grade and metastatic tumors [
79,
80]. Increased expression of antiapoptotic proteins contributes to PCa cell resistance to apoptosis mediated by androgen independence and metastasis [
80,
81]. The expression of the proapoptotic effector protein Bax was increased in castrated mice and was associated with poor outcomes, while the other Bcl-2 family member, Bak, was detected in PCa cell lines, and its level was increased in therapeutic assays [
72]. In addition, BH3-only protein (such as BAD) levels were dysregulated in PCa cells, and this dysregulation was correlated with biochemical recurrence (BCR) and overall survival (OS) [
82]. The aforementioned data indicate that the normal balance between antiapoptosis and proapoptosis pathway activation was disrupted in PCa, and as tumor progression increased, PCa cells gradually exhibited resistance to apoptosis. In addition, Bcl-2 family members can be regulated by transcription factors such as NF-κB and p53 and signaling pathways such as the PI3K/AKT and RAS/ERK signaling pathways. The direct or indirect regulation of the intrinsic pathway leads to significant benefits for the development of drugs that reduce PCa resistance to apoptosis [
72,
73].
3.2. Role of Necroptosis in Prostate Cancer
Necroptosis is considered a programmed form of necrosis characterized by mitochondrial alterations and plasma membrane permeabilization, which results in the release of cytoplasmic content into the extracellular space leading to inflammatory reactions [
52]. Accumulated evidence emphasizes the importance of necroptosis in PCa, and greater comprehension of the necroptotic mechanism might be helpful in creating novel strategies for controlling PCa [
83].
A study performed bioinformatics analyses using a dataset from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and identified necroptosis-related genes that were closely associated with PCa prognosis. Using them as a gene signature to construct a prognostic model led to the accurate prediction of 1-, 3- and 5-year OS in prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) patients [
84]. For one study, researchers collected sixty-seven prostate tissues that had been used to histologically diagnose PCa and categorized them into different tumor progression stages. RNA expression, tumor growth, etc., were measured. The results showed that the expression of RIPK3 was significantly elevated in the early stage but profoundly decreased in the final cancer stage [
85]. This finding demonstrated that necroptosis was activated in the early stages of tumor progression but was resisted by tumor cells during disease progression into the late stage. Another study reported research on the biological role and clinical significance of RIP3 in the PCa context. They discovered that RIP3 was significantly downregulated in PCa cell lines and clinical prostate tumor samples. Upregulated RIP3 alleviates PCa progression by activating the RIP3/MLKL signaling pathway. Furthermore, RIP3 inhibits the proliferation and tumorigenicity of PCa cells in an MLKL-dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo [
86]. These studies indicate that necroptosis is closely related to the progression in PCa and that inducing necroptosis of PCa cells is a feasible treatment strategy; however, a larger number of experimental and clinical studies are needed to confirm these conclusions and optimize the therapeutic approach.
3.3. Role of Pyroptosis in Prostate Cancer
Pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of PCD that can affect the tumor immune environment. The abnormal expression of pyroptosis-related genes (PRGs) may be closely related to the tumor immune microenvironment and thus promote the occurrence and development of PCa. By analyzing data collected in an online database, Hu and colleagues discovered that the expression levels of PRGs were significantly different between tumor and normal tissues. They constructed a prognostic signature based on these PRGs; their expression profile; a clinical database that can be used to precisely predict BCR after radical intervention, which is a determining risk factor for PCa specificity and distant metastasis; and the progression-free survival (PFS) rate [
87]. Other researchers, who repeated this work, verified that the identified PRGs were closely related to carcinogenesis, tumor cell invasion and the immune microenvironment in PCa [
88,
89].
Inflammation is an important prerequisite for the development of PCa [
90]. The NLRP3 inflammasome is a well-studied inflammasome that induces pyroptosis in PCa. A recent study demonstrated that the expression level of NLRP3 was upregulated in LNCaP and PC3 cell lines. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by LPS + ATP promoted the proliferation and migration of prostate tumor cell lines in vivo. NLRP3 knockdown inhibited malignant progression of PCa cell lines [
91]. Another study revealed a relationship between NLRP3 inflammasome and AR levels in high-grade PCa tumors. Compared with AR-dependent low-grade PCa cells, high-grade PCa cells showed increased NLRP3 levels. Furthermore, they identified an AR-related circular RNA (circRNA) named circAR-3-a, which can acetylate NLRP3 and promote NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly. Disrupting NLRP3 acetylation or blocking inflammasome assembly with an inhibitor suppressed the progression of PCa xenograft tumors. [
92]. The NLRP12 inflammasome level was also shown to be significantly higher in malignant prostate tissues than in adjacent benign tissues, as indicated by immunostaining intensity [
93].
Another pore-forming effector protein from the gasdermin family, GSDME, which is expressed in most normal tissue cells, is activated by apoptotic caspase (caspase 3), and its activation can switch the PCD from apoptosis to pyroptosis [
94]. In contrast to NLRP3/caspase-1-mediated DSDMD cleavage, caspase-3-mediated DSDME cleavage plays a crucial role in the chemotherapeutic treatment of PCa. Tian et al. discovered that the expression level of GSDME in PCa cells did not significantly change, but its activity was profoundly increased by the poly polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib. Simply upregulating GSDME conferred cells with sensitivity to olaparib but did not inhibit tumor cell proliferation [
95]. These findings indicate that the DSDME level is physiologically low in both normal and PCa cells and that upregulation of DSDME may increase the sensitivity of PCa cells to chemotherapeutic drugs.
3.4. Role of PANoptosis in Tumors and PCa
PANoptosis is a recently proposed PCD that highlights the crosstalk and coordination among apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis pathways, which are interconnected via shared regulatory proteins and signaling pathways [
96]. In combination with inflammatory cytokine-induced signaling through death domain-containing receptors, activated PRRs initiate this highly interconnected form of cell death, PANoptosis. PANoptosis has been linked to the development of multiple systemic diseases, including infectious diseases, cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammatory diseases [
97]. An accumulation of recent studies performed bioinformatics analysis of expression data of PANoptosis-related genes (PRGs) based on online databases. They identified several PRGs correlated with patient survival, immune responses and/or cancer-related biological processes. PRGs were used to construct PANoptosis signatures and significantly predicted the prognosis and immunotherapeutic response of several cancers, including pancreatic cancer, colon cancer, gastric cancer and prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) [
22,
98,
99,
100]. However, in vivo and in vitro experiments on prostate cancer and PANoptosis have not been performed. These discoveries demonstrate the close connection between PANoptosis and tumors and lay the foundation for our deeper and systematic research into the regulatory mechanisms underlying PANoptosis effects on PCa.
4. Therapeutic Potential of Compounds and Targets That Induce More than a Single Form of Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis in PCa
A growing number of treatments have been found to induce more than just a single type of PCD. Compounds and targets previously thought to only induce apoptosis have been shown to have a positive effect in inducing pyroptosis and necroptosis. A series of newly discovered compounds and potential targets that can induce two or even three forms of PCD in cancers. However, no compounds and targets have been found to induce PANoptosis (apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis) in PCa. Compounds and targets that induced both apoptosis and necroptosis or apoptosis and pyroptosis are listed in
Table 1 and
Table 2. Compounds and targets that induce PANoptosis in nonprostatic cancers are shown in
Table 3.
4.1. Compounds and Targets That Induce Both Apoptosis and Necroptosis in PCa
Selenium, a fundamental and essential trace mineral for the biological activities of mammals, has been proven to be closely but negatively correlated with cancer risk and mortality [
101]. A previous study showed that sodium selenite, an inorganic form of selenium compounds, sensitized LNCaP cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in a ROS/p53/Bax-mediated manner [
102]. Recently, a study found that sodium selenite induced necrosis-like morphologic changes in PC-3 cells and DU145 cells, which is not caspase-mediated apoptosis, pyroptosis, or autophagic cell death. A RIP3 inhibitor protected PC-3 cells from selenite-induced cell death by inducting ATP depletion and inhibiting PFK activity [
103]. Another study developed biogenic selenium nanoparticles, and oral administration of selenium nanoparticles induced markedly lower toxicity than the major natural food-form of selenium (L-selenomethionine) in mice. At a minimal concentration of 2 μg Se/ml could induce necroptosis in LNCaP-FGC cells though upregulation of TNF and interferon regulatory factor (IRF1) [
104].
The natural compound tocotrienol (TT) is a member of the vitamin E family and is expressed in four isoforms (α-TT, β-TT, γ-TT and δ-TT), in which γ-TT and δ-TT specifically exert antitumoral activity affecting proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis in different types of tumors [
105]. Previous studies have proven that δ-tocotrienols (δ-TTs) exert antitumor effects by inducing apoptosis in PC3 and DU145 cells via triggering the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress [
106]. Another study revealed the involvement of the necroptosis pathway in the anticancer treatment of δ-TT in PCa cells (DU145 and PC3 cells). Inhibition of necroptosis prevents δ-TT-induced PCa cell death. In addition, the combined effect of δ-TT and docetaxel was evaluated, and this combination has been approved for PCa treatment. Furthermore, δ-TT induced death in DU145 cells that had developed docetaxel resistance by activating necroptosis. In conclusion, δ-TT shows the ability to induce necroptosis in the PC3, DU145 and DU-DXR cell lines, which indicates that the induction of necroptosis in PCa is a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome DTX chemoresistance [
107].
Ophiopogonin D’ (OPD’) is a natural compound extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Ophiopogon japonicus. Ophiopogonin D exerts potential anticancer effects by inducing cell cycle arrest and activating apoptosis and autophagy [
108]. OPD’ was shown to exert potent antitumor activity against PC3 cells. It induced apoptosis via a RIPK1-related pathway, increased the protein expression levels of RIPK1 and Bim, and decreased the levels of cleaved-RIPK1, caspase 8, cleaved-caspase 8, Bid, caspase 10, and cleaved-caspase 10. OPD’ also increased the mRNA expression of Bim. The protein expression of Bim was decreased when cells were pretreated with necrostatin-1. Treatment with OPD’ inhibited the growth of PC3 and DU145 xenograft tumors in BALB/c nude mice [
109].A previous study indicated that OPD’ exhibited antitumor activity against AR-independent PCa [
109]. In a recent study, OPD’ induced RIPK1-mediated necroptosis in AR-dependent LNCaP cells in a FasL-dependent manner. The RIPK1 inhibitor necrostatin-1 and the MLKL inhibitor necrosulfonamide both inhibited OPD’-activated necroptosis in LNCaP cells in a synergistic manner. Furthermore, OPD’ increased the Fas-associated necroptosis rate in LNCaP cells and regulated the expression levels of FasL, AR and prostate-specific antigen in a RIPK1-dependent manner [
110]. These results suggested that OPD’ may exhibit potential as an anti-PCa agent by inducing RIPK1- and MLKL-dependent necroptosis.
Shikonin, a natural compound extracted from the roots of
Lithospermum erythrorhizon, has several protective effects, including anti-inflammatory and antitumor functions [
111]. A study showed that exposure to SHI resulted in an accumulation of apoptotic events in parental and DX-resistant PC3 and DU145 cells. Although apoptosis was undetectable in parental LNCaP cells, the concentration of 0.7 µM SHI or higher contributed to apoptosis in the DX-resistant LNCaP cells. Furthermore, exposure to SHI showed an increase in pRIP1 and/or pRIP3 activation in PC3 and DU145 cells, which are indicative of necroptosis. However, SHI-induced necroptosis was more dominant than apoptosis in both parental and DX-resistant PCa cells for enhanced pRIP1 and pRIP3 expression and remarkable reversal of SHI’s antigrowth effect after applying the necroptosis inhibitor necrostatin-1 [
112].
The sirtuin (SIRT) family of proteins, highly conserved NAD
+-dependent histone deacetylases, are involved in several biological processes (such as oxidative stress responses, apoptosis and inflammation), which makes SIRTs promising therapeutic targets for PCa [
113]. A recent study found that SIRT6 was overexpressed in prostate tumors, compared with normal or paratumor prostate tissues. Tissue microarray studies confirmed the higher levels of SIRT6 in both prostate tumor tissues and prostate cancer cells than in their normal counterparts. Knockdown of SIRT6 in human prostate cancer cells led to sub-G1 phase arrest of the cell cycle, increased apoptosis, elevated DNA damage levels and decreased BCL2 gene expression [
114]. A study discovered that the expression levels of SIRT6 were significantly increased in PCa patients and were associated with patients’ Gleason score and nodal metastasis number. SIRT6 promoted PCa progression by inhibiting RIPK3-mediated necroptosis and the innate immune response. Knockdown of SIRT6 not only activated TNF-induced necroptosis but also reestablished the corresponding recruitment of macrophages and neutrophils [
115].
Reticulocalbin 1 (RCN1), an ER-resident Ca
2+-binding protein, is essential for an accumulation of cell bioactivity. The dystegulation of RCN1 is correlated with cancers [
116]. A recent study showed that reticulocalbin 1 is highly expressed in prostate cancer. RCN1 depletion led to the activation of caspase-3 and PARP in DU145 cells, which are markers of apoptosis. An inhibitor of necroptosis, necrostatin-1, evidently attenuated cell death in LNCaP cells treated with siRCN1, which suggested that necroptosis may partially contributeto siRCN1-mediated LNCaP cell death [
117].
Table 1.
Compounds and targets that induce both apoptosis and necroptosis in PCa.
Table 1.
Compounds and targets that induce both apoptosis and necroptosis in PCa.
| Compound/Target |
Induced Cell Death |
In Vivo/Vitro |
Cell Lines/Animals |
Mechanisms |
References |
| Sodium Selenite |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro |
LNCaP Cells |
Sensitized LNCaP Cells to TRAIL in a ROS/p53/Bax-mediated manner |
[102] |
| Necroptosis |
In Vitro |
PC-3, DU145 Cells |
Induced RIP3/MLKL-independent necroptosis |
[103] |
| Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles |
Necroptosis |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
LNCaP-FGC Cells/Mice |
Upregulated the expression of TNF and IRF1 |
[104] |
| δ-TT |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro |
DU145, PC3 Cells |
Triggers endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress |
[106] |
| Necroptosis |
In Vitro |
DU145, PC3 and DU-DXR Cells |
Activation of the RIP3/MLKL pathway |
[107] |
| Ophiopogonin D’ |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
PC3, DU145 Cells/Mice |
Increased the expression of RIPK1 and Bim |
[109] |
| Necroptosis |
In Vitro |
LNCaP Cells |
Induced the RIPK1/MLKL-mediated necroptosis in a FasL-dependent manner. |
[110] |
| Shikonin |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro |
Parental and DXR PC3 and DU145 Cells, DXR LNCaP Cells |
Increased the expression of PARP, caspase 3, and caspase 8 |
[112] |
| Necroptosis |
In Vitro |
PC3, DU145 Cells |
Increased the expression of pRIP1 and/or pRIP3 |
[112] |
| SIRT6 |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
PC3 Cells/Mice |
Elevated DNA damage level and decreased BCL2 gene expression |
[114] |
| Necroptosis |
In Vitro |
LNCaP Cells |
Inhibited the expression of RIPK3 |
[115] |
| Reticulocalbin 1 |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
DU145 Cells/Mice |
Activated caspase-3, PARP and ER stress |
[117] |
| Necroptosis |
In Vitro |
LNCaP Cells |
Necrostatin-1 (inhibitor of necroptosis) reversed the cell death in siRCN1-treated LNCaP cells |
[117] |
4.2. Compounds and Targets That Induce Apoptosis and Pyroptosis in PCa
Targeting pyroptosis therapeutic regulation induce pyroptosis mainly by inhibiting the formation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and DSDME-related pathway in PCa.
Ulinastatin (UTI), a serine protease inhibitor, is a glycoprotein composed of 143 amino acids. In humans, the precursor of UTI is an inactive interalpha-trypsin inhibitor synthesized by the liver. Ulinastatin exerts clear anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic effects [
118]. A recent experiment showed that UTI tended to suppress proliferation, migration, and invasion of cells but promoted apoptosis in PC-3 cells at higher concentrations. Moreover, UTI blocked RhoA and ROCK mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation in PC-3 cells [
119].
Chalcones, which are flavones, possess two phenyl rings (the A- and B-rings) connected by a three-carbon α, β-unsaturated carbonyl bridge. A novel 3′,5′-diprenylated chalcone (C10), in the chalcone family, exhibited anti-inflammatory and anticancer pharmacological functions in the context of leukemia. In one study, C10 profoundly inhibited the proliferation of human leukemia cell lines via its effect on the apoptosis and autophagy pathways [
120]. In a recent study of the effects of C10 on PCa, C10 significantly reduced the proliferation and viability of PC3 cells by inducing caspase-dependent apoptosis and GSDME-dependent pyroptosis by activating PKCδ/JNK signaling [
121].
Cell division cycle protein 20 (CDC20), the adaptor subunit and activator of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC) exerts clear effects on the cell cycle and tumorigenesis [
122]. Previous findings indicated that oncogenic CDC20 was overexpressed in PCa. We demonstrated that the expression of CDC20 was increased in PCa cells by irradiation, and knockdown of CDC20 resulted in inhibition of cell proliferation, migration and tumor formation, induced cell apoptosis and increased radiosensitivity in PCa in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, we observed that CDC20 regulated the Twist1 pathway, influencing cell proliferation and migration. These results suggest that targeting CDC20 and Twist1 may be an effective way to improve the radiosensitivity of PCa [
123]. In one study, a set of PCa and mPCa data was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), and an integrated analysis was performed to identify differentially expressed genes. Higher expression of the CDC20 and PTTG1 genes was shown in mPCa samples and was significantly associated with poorer prognosis. In addition, these activated genes promoted the migration of PCa cells [
124]. Another study reported the discovery of CDC20 upregulation mediated by ubiquitination and the proteolysis of GSDME. Knockdown of CDC20 increased the level of GSDME by switching the PCD pathway from apoptosis to pyroptosis. Furthermore, depletion of CDC20 significantly enhanced antitumor immunity in a CD8+ T lymphocyte-dependent manner. Administration of a CDC20 inhibitor, such Apcin, with α-PD-1 led to synergistic antitumor effects mediated via immunotherapy in murine models in vivo [
125].
Table 2.
Compounds and targets that induce both apoptosis and pyroptosis in PCa.
Table 2.
Compounds and targets that induce both apoptosis and pyroptosis in PCa.
| Compound/Target |
Cell Death |
In Vivo /Vitro |
Cell Lines/Animals |
Mechanisms |
References |
| Ulinastatin |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro |
PC-3 Cells |
Downregulation of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and upregulation of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax, caspase3, and caspase-9) |
[102] |
| Pyroptosis |
In Vitro |
PC-3 Cells |
Blocked the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome |
[102] |
| 3′,5′-diprenylated chalcone |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro |
PC3 Cells |
Cleavage of PARP, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, Caspase-9, Bax, and cytochrome C |
[121] |
| Pyroptosis |
In Vitro |
PC-3 Cells |
Activation of GSDME |
[121] |
| CDC20 |
Apoptosis |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
PC3, DU145 Cells/Mice |
Increased the expression of RIPK1 and BIM |
[109] |
| Pyroptosis |
In Vitro |
Prostate Cancer Stem-like Cells |
Downregulation of CDC20 increased the level of GSDME by transforming apoptosis to pyroptosis |
[125] |
Table 3.
Compounds and targets that induce three of PANoptosis (apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis) in nonprostatic cancers.
Table 3.
Compounds and targets that induce three of PANoptosis (apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis) in nonprostatic cancers.
| Compound/Target |
Cancers |
In Vivo/Vitro |
Cell Lines/Animals |
Mechanisms |
References |
| NFS1 |
Colorectal Cancer |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
Colorectal Cancer Cells/Mice |
Increased the intracellular levels of ROS. |
[126] |
| IRF1 |
Colorectal Cancer |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
Bone marrow–derived macrophages/Mice |
Knockout of IRF1 attenuated PANoptosis |
[127] |
| CDK1 |
Adrenocortical Carcinoma |
In Vitro and In Vivo |
SW-13 cells, NCI-H295R Cells/Mice |
Binded with the PANoptosome in a ZBP1-dependent way |
[128] |
| APE1 |
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
In Vitro |
A549, NCI-460 Cells |
Inhibited APE1 induced DNA damage and PANoptosis |
[129] |
| Sulconazole |
Esophageal Cancer |
In Vitro |
KYSE30, KYSE150 Cells |
Triggered oxidative stress and inhibited glycolysis |
[130] |
4.3. Compounds and Targets That Induce PANoptosis (Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis) in Nonprostatic Cancers
Although PANoptosis has not been mentioned in PCa, a series of novel studies confirmed its existence in several nonprostatic cancers, which sets a precursor for research into PANoptosis in PCa. Cysteine desulfurase (NFS1) is an iron–sulfur (Fe–S) cluster biosynthetic enzyme. A study revealed that depletion of NFS1 significantly augmented the sensitivity of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells to oxaliplatin by triggering PANoptosis in a ROS-mediated manner in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, a high expression level of NFS1 was correlated with poor survival and reduced sensitivity to chemotherapy in CRC patients [
126]. Interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1) is a transcription factor induced in response to interferons. A study found that IRF1, which was downregulated in tumor tissues, prevents colitis-associated tumorigenesis in vivo in colorectal cancer. Mice with IRF1 knockout showed attenuated PANoptosis cell death in colon. However, the specific regulatory mechanism has not been further studied [
127]. Cyclin-dependent kinase-1 (CDK1) is significantly related to the adverse clinical outcomes of adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC). A CDK1 inhibitor repressed the proliferation of ACC cells by triggering PANoptosis in a ZBP1-mediated manner [
128]. Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) is an enzyme that is broadly associated with a series of critical base excision repair pathways, including DNA repair, cancer cell growth, and drug resistance. A study revealed that APE1 is overexpressed in NSCLCs and correlates with malignancy. They identified an APE1 inhibitor named NO.0449-0145, with which induced DNA damage, apoptosis, necroptosis, and pyroptosis in the NSCLC cell lines A549 and NCI-H460 [
129]. Sulconazole had a broad spectrum of anticancer effects including inhibiting the proliferation and migration of esophageal cancer cells. A study found that sulconazole induced not only PANoptosis, but also ferroptosis by triggering mitochondrial oxidative stress and inhibiting glycolysis [
130]. These studies suggest that PANoptosis may be a promising therapeutic target for anticancer therapy in cancers, including PCa.
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Programmed cell death has attracted increasing attention from researchers globally and is a promising target for the treatment of PCa. In this review, apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis and PANoptosis, which are considered the main forms of PCD, play their own significant roles in the progression and therapeutic potential of PCa. Targets and compounds target on not only apoptosis, but also necroptosis, pyroptosis and PANoptosis may effectively contribute to the development of new drugs to overcome the apoptosis resistance of PCa cells. However, compared with apoptosis, research on pyroptosis, necroptosis and PANoptosis in PCa are still in the basic experimental stage. Therefore, in addition to improving their relevant mechanisms of action, clinical trials are needed to evaluate the feasibility of using agents targeting pyroptosis and necroptosis in clinical applications. Combining traditional Chinese medicine and its specific components with multidisciplinary approaches to identify drugs that can effectively induce PCD of cells in tumor sites may effectively promote the research and development of drugs related to PCa treatment. The efficiency and safety of drugs that induce apoptosis, necroptosis, pyroptosis, and PANoptosis in PCa urgently need to be evaluated. We hope that in the future, through cooperation among researchers in various disciplines and the development of biotechnology, feasible methods for targeting and precisely killing PCa cells will be proposed and put to use.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z. (Minggang Zhu) and F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z. (Minggang Zhu); writing—review and editing, M.Z. (Minggang Zhu), G.L., D.L., M.Z. (Mingrui Zhang); visualization, M.Z. (Minggang Zhu); supervision, F.P.; project administration, F.P.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81873854).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| PCD |
Programmed cell death |
| PCa |
Prostate cancer |
| ADT |
Androgen deprivation therapy |
| AR |
Androgen receptor |
| DAMPs |
Damage-associated molecular patterns |
| BCL-2 |
B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| DR |
Death receptor |
| TNFR1 |
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 |
| TRAIL |
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand |
| TRADD |
TNF receptor-associated death domain |
| FADD |
Fas-associated death domain protein |
| DISC |
Death-inducing signaling complex |
| IAP |
Inhibitor of apoptosis |
| MOMP |
Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization |
| APAF-1 |
Apoptotic protease-activating factor-1 |
| CDKs |
Cyclin-dependent kinases |
| Mcl-1 |
Myeloid cell leukemia-1 |
| PRR |
Pattern recognition receptors |
| TLR3 |
Toll-like receptor3 |
| RIPK1 |
Receptors recruit interacting kinase 1 |
| RIPK3 |
Receptor-interacting kinase 3 |
| MLKL |
Mixed lineage kinase domain like proteins |
| PAMPs |
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| NLRs |
Nod-like receptors |
| ASC |
Apoptosis-related speck-like protein |
| IL |
Interleukin |
| NLRP3 |
Nod-like receptor protein 3 |
| GSDMD |
Gasdermin D |
| TRAIL-R2 |
TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2 |
| RuSe |
Selenium-Bearing Ruthenium Complex |
| BCR |
Biochemical recurrence |
| OS |
Overall survival |
| TCGA |
The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| PRAD |
Prostate adenocarcinoma |
| PRGs |
Pyroptosis-related genes |
| PFS |
Progression-free survival |
| PARP |
Poly polymerase |
| IRF1 |
Interferon regulatory factor 1 |
| TT |
Tocotrienol |
| δ-TTs |
δ-tocotrienols |
| OPD’ |
Ophiopogonin D’ |
| Shikonin |
SHI |
| SIRT |
Sirtuin |
| RCN1 |
Reticulocalbin 1 |
| UTI |
Ulinastatin |
| C10 |
3′,5′-diprenylated chalcone |
| CDC20 |
Cell division cycle protein 20 |
| NFS1 |
Cysteine desulfurase |
| CRC |
cColorectal Cancer |
| CDK1 |
Cyclin-dependent kinase-1 |
| APE1 |
Apurinic endonuclease 1 |
References
- Rebello, R.J.; et al. Prostate cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, R.; Wang, Z.; Montironi, R.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, M.; Santoni, M.; Huang, K.; Massari, F.; Lu, X.; Cimadamore, A.; et al. Epigenetic modulations and lineage plasticity in advanced prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Shen, M.M. Prostate cancer cell heterogeneity and plasticity: Insights from studies of genetically-engineered mouse models. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 82, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, M.C.; Zwart, W.; Roudier, M.P.; True, L.D.; Nelson, W.G.; Epstein, J.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Nelson, P.S.; Yegnasubramanian, S. Genomic and phenotypic heterogeneity in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 18, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippou, Y.; Sjoberg, H.; Lamb, A.D.; Camilleri, P.; Bryant, R.J. Harnessing the potential of multimodal radiotherapy in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 17, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Alabi, B.R.; Yin, Q.; Stoyanova, T. Molecular mechanisms underlying the development of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, K.; McManus, J.M.; Sharifi, N. Hormonal Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Endocr Rev 2021, 42, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Garzón, V.; Kypta, R. WNT signalling in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketelut-Carneiro, N.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Necroptosis-Oh My! The Many Ways a Cell Can Die. J Mol Biol 2022, 434, 167378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Kang, J.; Fu, C. The independence of and associations among apoptosis, autophagy, and necrosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, H.; Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; Shao, W.; Zhong, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. Insights into N6-methyladenosine and programmed cell death in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Lam, H.C.; Lei, X. Dissecting Programmed Cell Death with Small Molecules. Accounts Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkermann, A.; Green, D.R. Necroptosis. N Engl J Med 2014, 370, 455–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Luedde, T. Apoptosis and necroptosis in the liver: a matter of life and death. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Inuzuka, H.; Wei, W. Necroptosis pathways in tumorigenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsbaken, T.; Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Pyroptosis: host cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Gao, W.; Shao, F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Huang, B. Pyroptosis: A road to next-generation cancer immunotherapy. Semin. Immunol. 2023, 68, 101782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertheloot, D.; Latz, E.; Franklin, B.S. Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1106–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Ramos, A.M.; Ortiz, A. Regulated cell death pathways in kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Place, D.; Lee, S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. PANoptosis in microbial infection. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2020, 59, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Pan, J.; Li, P.; Gao, J. Characterization of PANoptosis patterns predicts survival and immunotherapy response in gastric cancer. Clin. Immunol. 2022, 238, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, J.F.; Wyllie, A.H.; Currie, A.R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 1972, 26, 239–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, R.A.; Treherne, J.; Furness, L.; Hajimohamadreza, I. The pharmacology of apoptosis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999, 20, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christgen, S.; Tweedell, R.E.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Programming inflammatory cell death for therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 232, 108010–108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gon, S.; Gatanaga, T.; Sendo, F. Involvement of Two Types of TNF Receptor in TNF-α Induced Neutrophil Apoptosis. Microbiol. Immunol. 1996, 40, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, P.; et al. TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappaB. Immunity 1997, 7, 831–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.M.; et al. Death receptor 5, a new member of the TNFR family, and DR4 induce FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate the NF-kappaB pathway. Immunity 1997, 7, 821–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.; Shu, H.-B.; Pan, M.-G.; Goeddel, D.V. TRADD–TRAF2 and TRADD–FADD Interactions Define Two Distinct TNF Receptor 1 Signal Transduction Pathways. Cell 1996, 84, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Pan, D.; Li, G.; Chen, K.; Hu, X. Regulation of programmed cell death by Brd4. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveraux, Q.L.; Reed, J.C. IAP family proteins---suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Kim, C.N.; Yang, J.; Jemmerson, R.; Wang, X. Induction of Apoptotic Program in Cell-Free Extracts: Requirement for dATP and Cytochrome c. Cell 1996, 86, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Benedict, M.A.; Ding, L.; Núñez, G. Role of cytochrome c and dATP/ATP hydrolysis in Apaf-1-mediated caspase-9 activation and apoptosis. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3586–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acehan, D.; Jiang, X.; Morgan, D.G.; E Heuser, J.; Wang, X.; Akey, C.W. Three-Dimensional Structure of the Apoptosome: Implications for Assembly, Procaspase-9 Binding, and Activation. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, Y. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in apoptosis: apoptosomes or mitochondria? Genes Cells 1998, 3, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerflinger, M.; Glab, J.A.; Puthalakath, H. BH3-only proteins: a 20-year stock-take. Febs j 2015, 282, 1006–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Simpson, E.R.; Brown, K.A. p53: Protection against Tumor Growth beyond Effects on Cell Cycle and Apoptosis. Cancer Res 2015, 75, 5001–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; et al. CDK inhibitors upregulate BH3-only proteins to sensitize human myeloma cells to BH3 mimetic therapies. Cancer Res 2012, 72, 4225–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degterev, A.; et al. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat Chem Biol 2005, 1, 112–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, M.K.; Gupta, K.; Franco, S.R.; Liu, B. Necroptosis in the Pathophysiology of Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 190, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Jitkaew, S.; Cai, Z.; Choksi, S.; Li, Q.; Luo, J.; Liu, Z.-G. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like is a key receptor interacting protein 3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 5322–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenev, T.; et al. The Ripoptosome, a signaling platform that assembles in response to genotoxic stress and loss of IAPs. Mol Cell 2011, 43, 432–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; et al. Anti-proliferation and anti-inflammation effects of corilagin in rheumatoid arthritis by downregulating NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 2022, 284, 114791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheau, O.; Tschopp, J. Induction of TNF receptor I-mediated apoptosis via two sequential signaling complexes. Cell 2003, 114, 181–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, W.J.; Sridharan, H.; Huang, C.; Mandal, P.; Upton, J.W.; Gough, P.J.; Sehon, C.A.; Marquis, R.W.; Bertin, J.; Mocarski, E.S. Toll-like Receptor 3-mediated Necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31268–31279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Challa, S.; Moquin, D.; Genga, R.; Ray, T.D.; Guildford, M.; Chan, F.K.-M. Phosphorylation-Driven Assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 Complex Regulates Programmed Necrosis and Virus-Induced Inflammation. Cell 2009, 137, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, A.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V. Necroptosis: The Release of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Its Physiological Relevance. Immunity 2013, 38, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Cramer, S.D.; Thorburn, A. The interplay of autophagy and non-apoptotic cell death pathways. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 2020, 352, 159–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, A.M. Macrophages are sensitive to anthrax lethal toxin through an acid-dependent process. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 7123–7126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, X. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y. Autophagy, ferroptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in tumor immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liston, A.; Masters, S.L. Homeostasis-altering molecular processes as mechanisms of inflammasome activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, W.; Pilato, J.L.; Kay, C.; Man, S.M. Activation mechanisms of inflammasomes by bacterial toxins. Cell. Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.-T.; Wan, H.; Hu, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Z.-H.; Zhong, C.-Q.; Han, J. Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1β secretion. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, K.; et al. Caspase 1-independent IL-1beta release and inflammation induced by the apoptosis inducer Fas ligand. Nat Med 1998, 4, 1287–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, F. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015, 526, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayagaki, N.; et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 2015, 526, 666–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Mei, P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, S.; Xu, X.-W.; Gan, J.; et al. TRIM21 regulates pyroptotic cell death by promoting Gasdermin D oligomerization. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 29, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Zhao, C.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H.; Dai, H. Chemotherapy-induced pyroptosis is mediated by BAK/BAX-caspase-3-GSDME pathway and inhibited by 2-bromopalmitate. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Du, F.; Wang, X. TNF-α Induces Two Distinct Caspase-8 Activation Pathways. Cell 2008, 133, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Yang, Y.; Mei, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhu, D.-E.; Hoti, N.; Castanares, M.; Wu, M. Cleavage of RIP3 inactivates its caspase-independent apoptosis pathway by removal of kinase domain. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 2056–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Wickliffe, K.E.; Dugger, D.L.; Maltzman, A.; Roose-Girma, M.; Dohse, M.; Kőműves, L.; Webster, J.D.; Dixit, V.M. Cleavage of RIPK1 by caspase-8 is crucial for limiting apoptosis and necroptosis. Nature 2019, 574, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, N.H.; et al. Caspase-8 mediates caspase-1 processing and innate immune defense in response to bacterial blockade of NF-κB and MAPK signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 7385–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, P.; et al. FADD and caspase-8 mediate priming and activation of the canonical and noncanonical Nlrp3 inflammasomes. J Immunol 2014, 192, 1835–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhan, J.; Liu, B.C.; Muendlein, H.I.; Li, P.; Nilson, R.; Tang, A.Y.; Rongvaux, A.; Bunnell, S.C.; Shao, F.; Green, D.R.; et al. Caspase-8 induces cleavage of gasdermin D to elicit pyroptosis during Yersinia infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2018, 115, E10888–E10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.W.; Demarco, B.; Heilig, R.; Shkarina, K.; Boettcher, A.; Farady, C.J.; Pelczar, P.; Broz, P. Extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis activate pannexin-1 to drive NLRP 3 inflammasome assembly. EMBO J. 2019, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Yan, Y.; Gong, T.; Han, J.; Tian, Z.; Zhou, R. RNA viruses promote activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome through a RIP1-RIP3-DRP1 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christgen, S.; Zheng, M.; Kesavardhana, S.; Karki, R.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Banoth, B.; Place, D.E.; Briard, B.; Sharma, B.R.; Tuladhar, S.; et al. Identification of the PANoptosome: A Molecular Platform Triggering Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PANoptosis). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kesavardhana, S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. ZBP1 and TAK1: Master Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome/Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PAN-optosis). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.H.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E.-L. Androgen receptor: structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Kulik, G. Signaling Pathways That Control Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielinski, R.R.; Eigl, B.J.; Chi, K.N. Targeting the Apoptosis Pathway in Prostate Cancer. Cancer J. 2013, 19, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Cueto, A.; Hernandez-Cueto, D.; Antonio-Andres, G.; Mendoza-Marin, M.; Jimenez-Gutierrez, C.; Sandoval-Mejia, A.L.; Mora-Campos, R.; Gonzalez-Bonilla, C.; Vega, M.I.; Bonavida, B.; et al. Death receptor 5 expression is inversely correlated with prostate cancer progression. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Ishii, K.; Takahama, Y.; Kato, K.; Yano, T. NK Cells Can Preferentially Target Prostate Cancer Stem-like Cells via the TRAIL/DR5 Signaling Pathway. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Zeng, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, T. Selenium-containing ruthenium complex synergizes with natural killer cells to enhance immunotherapy against prostate cancer via activating TRAIL/FasL signaling. Biomaterials 2019, 219, 119377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.W.; Walsh, K.; Buttyan, R. An elevated bax/bcl-2 ratio corresponds with the onset of prostate epithelial cell apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.; Shin, E.A.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.B.; Kim, S.-H. Implications of Bcl-2 and its interplay with other molecules and signaling pathways in prostate cancer progression. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, C.; et al. Bcl-xL is overexpressed in hormone-resistant prostate cancer and promotes survival of LNCaP cells via interaction with proapoptotic Bak. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4960–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajewska, M.; Krajewski, S.; I Epstein, J.; Shabaik, A.; Sauvageot, J.; Song, K.; Kitada, S.; Reed, J.C. Immunohistochemical analysis of bcl-2, bax, bcl-X, and mcl-1 expression in prostate cancers. Am J Pathol 1996, 148, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, T.; Shiina, H.; Urakami, S.; Kikuno, N.; Yoneda, T.; Shigeno, K.; Igawa, M. Bcl-2 Expression as a Predictive Marker of Hormone-Refractory Prostate Cancer Treated with Taxane-Based Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6116–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, K.; Gemmell, L.; Mukherjee, R.; Traynor, P.; Edwards, J. Bad expression influences time to androgen escape in prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2007, 100, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beretta, G.L.; Zaffaroni, N. Necroptosis and Prostate Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Cells 2022, 11, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Y.; You, J.-X.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Su, L.-X.; Yang, X.-T. A Novel Model Based on Necroptosis-Related Genes for Predicting Prognosis of Patients With Prostate Adenocarcinoma. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 9, 814813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidaryan, F.; et al. The Trend of ripk1/ripk3 and mlkl Mediated Necroptosis Pathway in Patients with Different Stages of Prostate Cancer as Promising Progression Biomarkers. Clin Lab 2020, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.J.; et al. Up-Regulation of RIP3 Alleviates Prostate Cancer Progression by Activation of RIP3/MLKL Signaling Pathway and Induction of Necroptosis. Front Oncol 2020, 10, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Cao, Q.; Tong, M.; Ji, C.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Jin, Y.; Tong, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; et al. A novel defined risk signature based on pyroptosis-related genes can predict the prognosis of prostate cancer. BMC Med Genom. 2022, 15, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Wan, S.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; Tian, J.; Mi, J. A novel signature based on pyroptosis-related genes for predicting prognosis and treatment response in prostate cancer patients. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1006151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Li, G.; Luo, R.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y. Classification of pyroptosis patterns and construction of a novel prognostic model for prostate cancer based on bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1003594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denk, D.; Greten, F.R. Inflammation: the incubator of the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Qin, Z.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, L.; Xu, L.; Jia, R. NLRP3 inflammasome promoted the malignant progression of prostate cancer via the activation of caspase-1. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; Shi, B.; Zhang, H.; Bai, Y.; Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Disturbing NLRP3 acetylation and inflammasome assembly inhibits androgen receptor-promoted inflammatory responses and prostate cancer progression. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, D.; Tawfik, O.; Dubey, S. Expression analysis of inflammasome sensors and implication of NLRP12 inflammasome in prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, Z.-X.; Chen, H.; Lan, R.; Wang, Z.; Lai, K.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Zou, Z.; et al. GSDME-mediated pyroptosis promotes inflammation and fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2333–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, A.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Sha, J.; Xia, W. Triggering pyroptosis enhances the antitumor efficacy of PARP inhibitors in prostate cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2023, 46, 1855–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. The regulation of the ZBP1-NLRP3 inflammasome and its implications in pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis). Immunol Rev 2020, 297, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Ke, Z.-R.; Chen, J.-X.; Li, S.-J.; Ma, T.-L.; Fan, X.-L. Advances in mechanism and regulation of PANoptosis: Prospects in disease treatment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1120034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Xu, H.; Liao, D.; Zhang, T.; Wei, Q.; Li, H.; Peng, J.; Ai, J. Construction of PANoptosis signature: Novel target discovery for prostate cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Ther. - Nucleic Acids 2023, 33, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Song, H.; Shang, D. PANoptosis-related molecular subtype and prognostic model associated with the immune microenvironment and individualized therapy in pancreatic cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1217654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, R.; Chan, S.; Meng, L.; Xu, Y.; Zuo, X.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X.; Han, Q.; Dai, L.; et al. PANoptosis-based molecular clustering and prognostic signature predicts patient survival and immune landscape in colon cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 955355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; et al. Inorganic selenium sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through superoxide/p53/Bax-mediated activation of mitochondrial pathway. Mol Cancer Ther 2006, 5, 1873–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Yan, M.; Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Lu, S.; Fan, L.; Hu, H. Inorganic Selenium Induces Nonapoptotic Programmed Cell Death in PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells Associated with Inhibition of Glycolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10637–10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkusre, P. Specificity of Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles for Prostate Cancer Therapy With Reduced Risk of Toxicity: An in vitro and in vivo Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailo, B.L.; Banik, K.; Padmavathi, G.; Javadi, M.; Bordoloi, D.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Tocotrienols: The promising analogues of vitamin E for cancer therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, F.; Moretti, R.M.; Raimondi, M.; Marzagalli, M.; Beretta, G.; Procacci, P.; Sartori, P.; Marelli, M.M.; Limonta, P. δ-Tocotrienol induces apoptosis, involving endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy, and paraptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marelli, M.M.; Beretta, G.; Moretti, R.M. Necroptosis Induced by Delta-Tocotrienol Overcomes Docetaxel Chemoresistance in Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lu, J.-J.; Hong, H.-J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.-J. Ophiopogon japonicus and its active compounds: A review of potential anticancer effects and underlying mechanisms. Phytomedicine 2023, 113, 154718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.; Song, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, C.; Kong, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; et al. Ophiopogonin D′, a Natural Product From Radix Ophiopogonis, Induces in Vitro and in Vivo RIPK1-Dependent and Caspase-Independent Apoptotic Death in Androgen-Independent Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhu, M.; Song, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Li, N.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Ophiopogonin D' induces RIPK1-dependent necroptosis in androgen-dependent LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 56, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulos, J.C.; Rahama, M.; Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Efferth, T. Shikonin derivatives for cancer prevention and therapy. Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitsch, S.D.; Juetter, K.M.; Schupp, P.; Hauschulte, K.; Vakhrusheva, O.; Slade, K.S.; Thomas, A.; Tsaur, I.; Cinatl, J.; Michaelis, M.; et al. Shikonin Reduces Growth of Docetaxel-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells Mainly through Necroptosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.-J.; Zhang, T.-N.; Chen, H.-H.; Yu, X.-F.; Lv, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, J.-Q.; Wei, Y.-F.; et al. The sirtuin family in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Q.R.; Wang, B.; Shao, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, T.; Huang, G.; Xia, W. Inhibition of SIRT6 in prostate cancer reduces cell viability and increases sensitivity to chemotherapeutics. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Li, H.; Fu, H.; Zhao, S.; Shi, W.; Sun, M.; Li, Y. The SIRT3 and SIRT6 Promote Prostate Cancer Progression by Inhibiting Necroptosis-Mediated Innate Immune Response. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, B. Reticulocalbin 1 is required for proliferation and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells regulated by osteoblast-conditioned medium. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 11198–11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, D.; Zhu, D.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Qian, L.; Niu, H.; Lu, Y.; Ren, G.; et al. Downregulation of reticulocalbin-1 differentially facilitates apoptosis and necroptosis in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, L.; Long, M.; Du, Y. Recent research progress on the role of ulinastatin in chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2021, 26, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Xu, C.; Min, F.; Yu, G.; Chen, C. Ulinastatin ameliorates the malignant progression of prostate cancer cells by blocking the RhoA/ROCK/NLRP3 pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 84, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; et al. A novel synthesized 3’, 5’-diprenylated chalcone mediates the proliferation of human leukemia cells by regulating apoptosis and autophagy pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 106, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; et al. A novel 3’,5’-diprenylated chalcone induces concurrent apoptosis and GSDME-dependent pyroptosis through activating PKCδ/JNK signal in prostate cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 2020, 12, 9103–9124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, V.; Alex, A.; Stege, P.; Maffini, S.; Stoppiello, G.A.; Veld, P.J.H.I.; Vetter, I.R.; Musacchio, A. CDC20 assists its catalytic incorporation in the mitotic checkpoint complex. Science 2021, 371, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ge, Y.; Zang, Y.; Xu, M.; Jin, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xue, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. CDC20 promotes radioresistance of prostate cancer by activating Twist1 expression. Apoptosis 2023, 28, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Song, Z.-X.; Wei, D.-P.; Zhang, J.-D.; Liang, J.-Q.; Wang, B.-B.; Ma, W.-T.; Li, L.-Y.; Dang, Y.-L.; Zhao, L.; et al. CDC20 and PTTG1 are Important Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 2973–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, M.; Zhong, T.; Xiao, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, M.; Yu, J.; Chen, D. Inhibition of CDC20 potentiates anti-tumor immunity through facilitating GSDME-mediated pyroptosis in prostate cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.F.; et al. Phosphorylated NFS1 weakens oxaliplatin-based chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer by preventing PANoptosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Sharma, B.R.; Lee, E.; Banoth, B.; Malireddi, R.S.; Samir, P.; Tuladhar, S.; Mummareddy, H.; Burton, A.R.; Vogel, P.; et al. Interferon regulatory factor 1 regulates PANoptosis to prevent colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; et al. CDK1 serves as a therapeutic target of adrenocortical carcinoma via regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition, G2/M phase transition, and PANoptosis. J Transl Med 2022, 20, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.; Gu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, E.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Pan, F.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Z. Small-molecule inhibition of APE1 induces apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-X.; Heng, J.-H.; Deng, D.-X.; Zhao, H.; Zheng, Z.-Y.; Liao, L.-D.; Lin, W.; Xu, X.-E.; Li, E.-M.; Xu, L.-Y. Sulconazole Induces PANoptosis by Triggering Oxidative Stress and Inhibiting Glycolysis to Increase Radiosensitivity in Esophageal Cancer. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2023, 22, 100551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).