1. Introduction
According to a recent report published by the United Nations, in 2050, the global population will include over 9 billion people [
1]. The fast growth of the world population is a great preoccupation since the production of food from animal sources cannot follow this increase [
2]. Hence alternative protein sources are required [
3,
4]. In this regard, insect rearing has been considered in recent years due to a lower space requirement, the possibility of using organic side streams as feed and its lower greenhouse gas emissions, which makes it much more environmentally friendly compared to traditional animal production [
5]. In addition, insects have a high nutritional value, with protein content ranging, by dry matter, from 13% to 77%, including a high level of essential amino acids (EAA) that could reach, depending on the species, 46-96% of the total amount [
6]. The lipid content varies depending on the life stage, from 10% to 60% in dry matter, often showing a high content of linoleic, oleic and α-linolenic acid [
7].
It is estimated that nearly 2000 insect species are consumed by approximately 2 billion people on a regular basis globally, mostly in Africa, Thailand and Australia [
5]. Nonetheless, the practice of eating insects is far less common in European countries. In this regard, the European Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [
8], established on the first of January of 2018 by the European Union, was a significant breakthrough in the direction of introducing edible insects in European countries. Through this regulation, edible insects have come to be considered a novel food, allowing them to be commercialised in the European Union upon their approval. Despite the large range of products from insects that are consumed, such as honey or cochineal that is used as a colourant in food manufacture, in Western societies, eating insects is seen by many people as “disgusting”, “unclean” and “disease-transmitters” due to sanitary, cultural or even religious reasons, often driven by fear of the unknown [
9]. However, appropriate information and the gradual introduction of insects in food products could lead to a change in the mentality of consumers, as has already been observed for other products previously [
10].
The amino acid and fatty acid profiles of many edible insects have been described [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. In addition, a limited number of more detailed lipidomic studies have been conducted [
18,
19,
20,
21]. Nevertheless, the distribution of fatty acids over the respective lipid classes, namely, neutral, glycolipids and phospholipids, remains unknown. To the best of our knowledge, only Guil-Guerrero et al. [
22] reported the fatty acid composition of the lipid classes in a number of insects. But, this distribution is important since it could influence the response to lipid oxidation, as well as the bioavailability of (essential) fatty acids. For instance, although there is no general consensus, there are some studies in which neutral lipids have been observed to undergo auto-oxidation at a faster rate, whereas phospholipids have been observed to be oxidised at a higher level by photo-oxidation. [
23,
24]. It has also been observed that essential fatty acids such as EPA have a higher bioaccessibility in the intestine when they are present in the phospholipid fraction, probably due to a more stable emulsification due to the emulsifying properties of phospholipids [
25].
As commented before, together with lipid content, the protein content of various edible insects has been widely reported. However, the protein content reported in the literature is commonly calculated based on the nitrogen content by applying a conversion factor that typically corresponds to 6.25. Due to the presence of non-protein nitrogen, this index may result in an overestimation of the protein content. The use of a correct conversion factor allows a more accurate estimation of protein content, which is essential for further applications in food technology. To date, this species-specific conversion factor has been determined for a limited number of edible insect species, including
Alphitobius diaperinus (ALD) [
26,
27],
Acheta domesticus (ACD) [
26,
28,
29],
Locusta migratoria (LM) [
28] and
Tenebrio molitor (TM) [
26,
27,
28]. Conversely, there is no direct data on other commonly consumed insects such
Blaptica dubia (BD),
Galleria mellonera (GM) or
Zophobas morio (ZM).
This work tries to fill these gaps by providing novel data regarding fatty acid distribution among lipid classes, as well as the species-specific protein conversion factor (Kp) of a large range of insects, in an attempt to further contribute to improve the nutritional characterisation of insects as food.
Additionally, the generated fatty acid and amino acid profiles were used to calculate several indices to assess the nutritional quality of lipids and protein.
The selected insects include
A. domesticus,
A. diaperinus,
B. dubia,
G. mellonella,
L. migratoria,
T. molitor and
Z. morio, which belong to the orders Orthoptera, Coleoptera, Blattodea and Lepidoptera, which cover the worldwide most consumed orders [
30].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Edible insect samples
All insects used in this study were purchased from a local producer (Nusect living nutrition, Belgium). ZM, TM, ALD and GM were obtained in the larvae form, whereas BD, ACD and LM were collected in their adult stage. After overnight starvation, all insects were freeze-killed by keeping them at -20 °C for 24 h. One fraction of each insect was stored frozen at -20 °C while the other fraction was lyophilised, ground and vacuum stored at -20 °C until further analysis.
2.2. Total lipids and Lipid Classes
Total lipids were extracted from 100 mg of insect powder following the method described by Ryckebosch et al. [
31] using chloroform/methanol (1:1) and the total lipid content is determined gravimetrically after evaporation of solvent by a Laborota 4000 efficient rotavapor (Heidolph, Schwabach, Germany).
From these lipid extracts, the content of different lipid classes (neutral lipids, glycolipids and phospholipids) was determined following the method described by Christie & Han [
32] through separation on a J.T.Baker silica SPE column (Avantor Inc, Pennsylvania, USA). The column was conditioned using two times 5 mL of chloroform, after which approximately 10 mg lipid, previously dissolved in 100 µL of chloroform, was added to the column. A total of 10 mL of chloroform, followed by 10 mL of acetone and finally 10 mL of methanol, was used to elute fractions of neutral lipids, glycolipids and phospholipids, respectively. The content of all fractions was determined gravimetrically after evaporation of the solvent on a rotavapor. Ten replicates per insect were done, and after separation, replicates of the same fraction of each insect were pooled and stored at -18 °C until further analyses of the fatty acid composition of each fraction.
2.3. Fatty acids profile and nutritional indices
For fatty acid analysis, 5 mg of the lipid from each lipid class was used. Methylation and analysis by gas chromatography with flame ionisation detection (GC/FID) were carried out following the method described by Ryckebosch et al. [
31]. For methylation, lipid extracts were dissolved in 1 mL of toluene and 2 mL of sulfuric acid in methanol (1%), keeping the mixtures overnight at 50 °C. After the addition of 5 mL of water with NaCl (5%), the formed fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) were extracted with hexane and quantified using GC/FID. An EC_Wax column (Restek, Belgium) was used for the analysis with the following temperature-time program: 70 ºC to 180 ºC at 10 ºC/min, 180 ºC to 235 ºC at 4 ºC/min and 235 ºC during 4.75 min. Peak areas were quantified with Chromcard for Windows software (Interscience, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium). Standards (Nu-check, Elysian, USA) of 35 different FAMEs were analysed for peak identification. Results were expressed as a percentage of the total FAMEs in each lipid class. FAMEs of the total lipids were calculated from the FAMEs in the three lipid classes and the corresponding percentage that each class represents.
Total saturated fatty acids (SFA), total monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), total polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), total PUFA n-3 and PUFA n-6, as well as the PUFA/SFA and n-6/n-3 ratios, were calculated. For all insects, the index of atherogenic (IA), index of thrombogenic (IT) and hypocholesterolemic/hypercholesterolemic ratio (h/H) were also determined for the total lipid content according to the following equations [
33,
34,
35,
36]:
2.4. Amino acid composition and conversion factor (Kp)
Amino acids were hydrolysed by the addition of 25 ml of HCl 6 M to 50 mg of freshly ground insect and keeping it at 110 °C in an oven for 22 h. Next, derivatisation was carried out with the use of the AccQ•Tag Derivatization Kit. Amino acids (with the exception of tryptophan) were determined using an Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC) separation system by Waters (Waters, USA) with an AccQ•Tag Ultra column (2.1 i.d. x 100 mm from Waters, USA). The column temperature was 60 °C, the gradient elution was applied according to the AccQ•Tag Ultra method, the flow rate was 0.7 mL/min, and the time of separation was 9.5 min. Three replicates per insect were done and data processing was carried out by using Empower 2 Software.
After analysing the amino acids, the true protein content was calculated using equation 1, described by Biancarosa et al. [
37]:
where,
is the mass of each single amino acid residue in a protein, that is its true fraction after the loss of one molecule of H2O expressed as g/100 g of dry matter (DM),
is the mass of each single amino acid expressed as g/100 g of DM and
is the molecular weight of each single amino acid.
In order to determine the species-specific conversion factor (Kp), the total nitrogen content in each insect was analysed following the Kjeldahl method, in which an initial digestion stage is undertaken using a K-437 Buchi-Digest System (Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland) coupled to a scrubber B-414 (Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland), followed by distillation through the use of a K-350 Buchi distillation unit (Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland) and finally by titration with a 785 DMP Titrino (Metrohm AG, Herisau, Switzerland). The Kp was calculated following equation 5 as presented by Mariotti et al. [
38], in which
represents the mass of a single amino acid residue (true protein, see equation 4) expressed as g/100 g of DM, and
represents the total nitrogen (g/100 g of DM).
2.5. Amino acid-based nutritional indices
The ratio of essential to total amino acids was calculated as E/T (%) and the essential amino acid index (EAAI) was evaluated by the formula described by Kavle et al. [
39] which is based on the content of all EAA except tryptophan in comparison to the reference protein:
where n is the number of EAA, EAAi is the mass of each single EAA expressed as mg/g of protein and EAAis is the mass of each corresponding EAA in standard expressed as mg/g of protein. The reference substance used was the whole egg in accordance with Yu et al. [
16].
The essential amino acid score (AAS) expressed in percentage was calculated by the method of FAO/WHO [
40] as shown below:
The AAS is the lowest value obtained from the calculations of all amino acids and the corresponding amino acid is the limiting amino acid.
The predicted protein efficiency ratio (PER) values were calculated from their amino acid composition based on the following equations [
41]:
2.6. Statistical analysis
The values are presented in terms of mean values and the standard error of the means. Differences among insects were examined using a one-way ANOVA, where insect species was set as a factor. When a significant effect (P < 0.05) was detected, means were compared using Tukey’s posthoc test. All analyses were conducted using the IBM SPSS Statistics 28.0 program (IBM Corporation, NY, USA) software package.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Total lipid content and fatty acid composition
The highest total lipid content (
Supplementary Table S1), by far, was found in GM (53.63 g/100 g DM), which was followed by ZM and LM (33.97 and 32.28 g/100 g DM, respectively), TM, ALD and ACD (22.61, 21.82 and 21.32 g/100 g DM, respectively), and finally BD (13.96 g/100 g DM). The percentage obtained for ACD was comparable with the range described in literature [
42], as was the content of ALD and BD [
20]. Likewise, similar values for GM and LM were previously reported [
43,
44,
45]. In contrast, the values observed in TM were slightly lower than the ones reported by Finke [
11] and Tzompa-Sosa et al. [
20].
The fatty acid profiles of the total lipid of the selected seven edible insects are presented in
Table 1. A total of nine fatty acids were detected in amounts above 1% of the total fatty acid content, including three SFAs (C14:0 or myristic acid, C16:0 or palmitic acid and C18:0 or stearic acid), four MUFAs (C16:1 or palmitoleic acid, C18:1 or oleic acid, C20:1 or 11-eicosanoic acid and C24:1 or nervonic acid) and two PUFAs (C18:2 or linoleic acid and C18:3n-3 or α-linolenic acid).
Among SFA, a low percentage of myristic acid was present only in LM and TM (1.67 and 3.57% of the total FA, respectively), while palmitic acid and stearic acid were found in all insects [
20]. According to previous findings, this can be explained by the de novo system, whereby insects can synthesise certain saturated fatty acids from other resources, such as carbohydrates and proteins [
46]. The total amount of SFAs differed among all insects being the highest in LM (39.21%) and the lowest in BD (24.64%), values that are higher than the ones reported previously [
20]. With regard to MUFAs, high amounts of oleic acid were found in all insects (ranging from 23.30% to 54.26% of the total FA), being the most abundant fatty acid in all insects except for ACD. Palmitoleic acid was only observed in BD (2.90%) and TM (1.32%), as well as, 11-eicosenoic acid in GM (2.36%) and nervonic acid in TM (1.08%). Previous studies have also shown higher proportions of 11-eicosenoic acid in triglycerides from males of GM compared to other insects [
47]. Due to the high content of oleic acid, a remarkable amount of total MUFAs was found in BD, which reached 58.28% of the total FA, followed by GM with a value of 46.57% of the total FA. A much lower percentage was found in ACD, which was only 25.06%. Linoleic acid was the only PUFA present in all samples, for which the highest value was shown in ACD (36.67%). This may be due to the fact that ACD is able to biosynthesise linoleic acid thanks to the enzyme ∆12 desaturase, which is naturally present in its body [
48]. In contrast, α-linolenic acid was present in values above 1% in four out of seven insects, having the highest value by far in LM (10.47%). The latter value is somewhat in line with that observed by Ramos-Bueno et al. [
14] (11.5-14.4%) making this species particularly attractive within the food industry as a source for the production of products enriched with n-3 oils for nutritional and medicinal uses. In line with previous findings, only trace amounts (<1%) of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, C20:5n-3) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, C22:6n-3) were found in ACD, ALD and LM, and GM, LM and TM, respectively [
12,
20,
45,
49]. The highest values of total PUFAs were found in ACD (39.76%), followed by TM (30.41%) and LM (27.77%), while the minimum was shown in BD (17.08%) and GM (18.64%).
3.2. Nutritional quality of the lipids
From the fatty acid profile, it is possible to estimate the nutritional quality of the lipid and the possible effects that its intake may have on the health of consumers. For this purpose, different indices can be used, among which PUFA/SFA and n-6/-n-3 ratios, IA, IT and h/H have been considered in this study (
Table 1). For a healthy diet, the consumption of lipids with a PUFA/SFA ratio close to 1 is recommended since it has been observed that the consumption of food with values higher than 1 is related to cardiovascular risk reduction [
50]. The consumption of lipids with ratios above 3 could promote the formation of tumours, while ratios below 0.33 in the diet could have an atherogenic effect [
51]. Accordingly, edible insects can be considered a healthy lipid source, among which ACD and TM provided the best PUFA/SFA ratio among the species studied (1.1 and 0.98, respectively), which are slightly below the ones reported by Otero et al. [
52]. Together with that, a high dietary n-6/n-3 value may be related to the risk of developing coronary heart disease and cancer, among others, ratios below 4 being advisable [
53]. Of the edible insects examined in this work, only LM exhibits a value below the recommendation (1.59), mainly due to its high α-linolenic acid content, as mentioned above. Still, our results were far lower than the ones obtained by Paul et al. [
54] for TM, with reported values of approximately 200, which the authors suggested to be due to the low intake of n-3 fatty acid in the feed. While Cito et al. [
54] showed values ranging between 1.98 and 4.86 for GM, which were in line with those obtained by Francardi et al. [
55], our sample reached a value of 13.76, even substantially higher than the 7.3 reported by Guil-Guerrero et al. [
22]. As stated before, there have been suggestions that these differences may be due to the fact that fatty acid profiles depend on extrinsic factors such as feed [
11,
48,
54]. However, more recent studies have revealed that, regardless of the diet of the insects, the concentration of the main fatty acids remained relatively stable, and changes were essentially limited to n-3 PUFAs [
49]. Furthermore, it has been observed that TM has the ability to self-select nutrients from the feed, based on its physiological needs. Thus, a higher availability of particular nutrients in the feed does not necessarily result in an increased level of these nutrients in the insect [
56]. It is reasonable to assume that more species may also have that ability which could suggest that physiological aspects may play a more important role in the lipid profile compared to the feed.
The IA, IT and h/H index also showed significant differences among species. While lower values of IA and IT are related to a lower risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, higher levels of h/H are considered desirable [
57]. In this study, the IA index ranged from 0.26 to 0.58, which is comparable to those reported for meat and fish and lower than those observed for dairy products while the IT, ranging from 0.57 to 1.08, was higher than those reported for most fish, in the same range as those reported for most meat and lower than those observed for dairy [
57]. Likewise, the h/H ranged from 1.86 to 4.20, which is in line with values previously reported in insects [
33,
34]) and are higher than those reported for dairy products and in the same range as most meat and fish [
57]. BD reached the lowest IA and IT indices (0.26 and 0.57, respectively) with a considerably higher value of h/H (4.20), suggesting the fatty acid profile of this insect could be the healthiest among the insects studied. In contrast, LM exhibited higher IA (0.58) compared to the other insects and a rather low h/H (1.96). ZM showed the highest IT (1.08), a rather high IA (0.52) and a rather low h/H (2.06). Even so, the IT value obtained for ZM was slightly below that previously reported for 60-day-old larvae (1.19) [
58]. On the other hand, the IT value obtained for ALD was somewhat higher than that reported by Mohammad Taghi Gharibzahedi and Altintas [
33], but for TM, it was considerably higher than that obtained by Lawal et al. [
34]. According to the evidence reported by Mohammad Taghi Gharibzahedi and Altintas [
33], these indices may be influenced by the solvent used during lipid extraction, explaining the variation among these different reports. In our study, lipids were extracted with chloroform/methanol, which allows a quantitative extraction of all lipids [
59], hence indices most accurately reflect the lipid composition of the entire insect as a whole. More importantly, as mentioned above, diet may also be a factor to consider in such differences.
3.3. Analysis of lipid classes
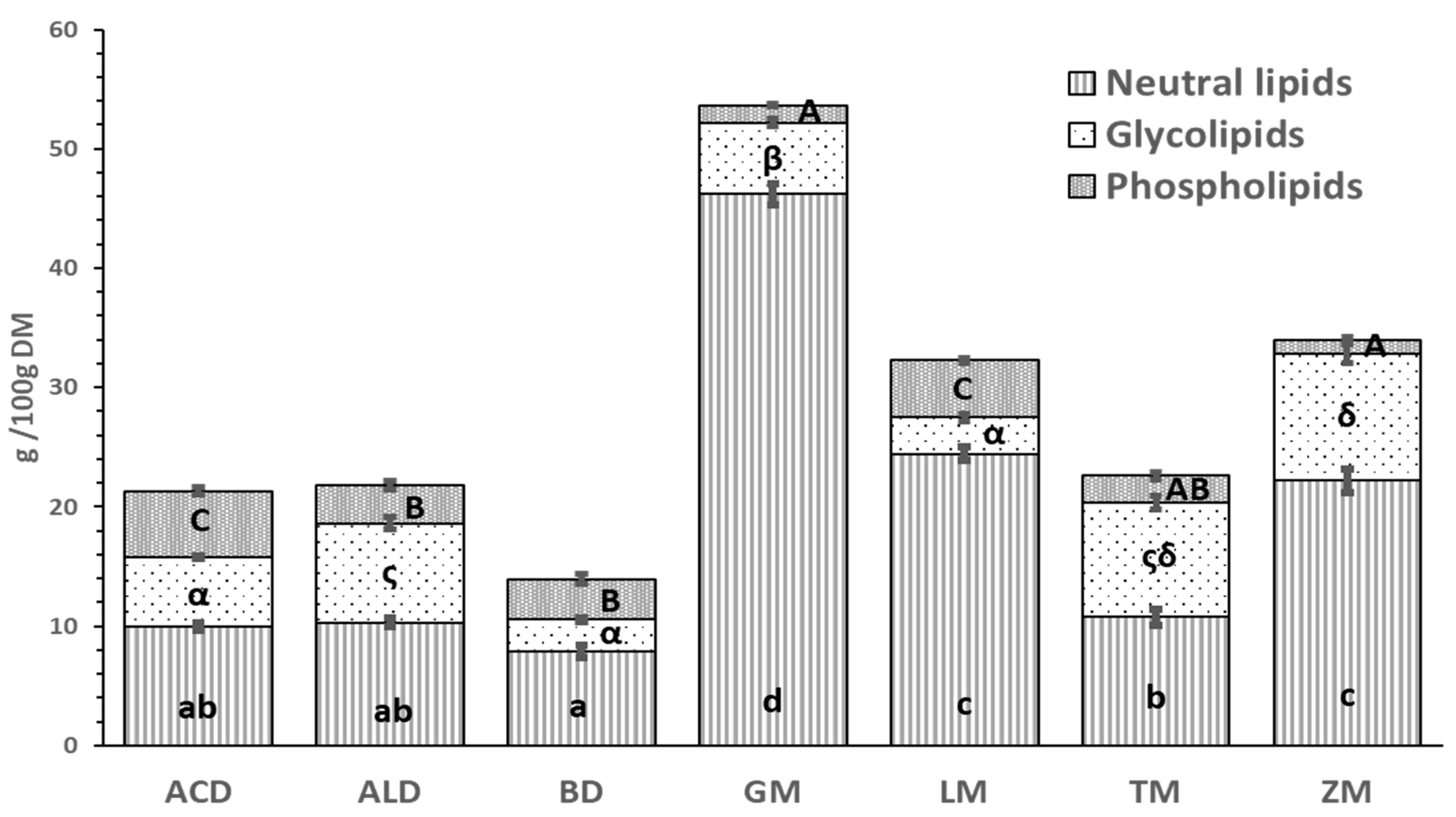
Lipids were separated into lipid classes in order to have a more detailed knowledge of the lipid composition of the selected edible insects. In
Figure 1, the amount of neutral lipids, glycolipids and phospholipids that constitute the total lipid is presented, expressed in g/100 g DM (average values and the corresponding SEM are also provided in ST1). Non-polar or neutral lipids, with values ranging between 46.56% in ACD and 86.15% in GM of total lipid content, were the highest fraction in all insects as this lipid group serves as an energy deposit in the form of triacylglycerols [
19] The content of polar fractions, glycolipids and phospholipids, reached values up to 10.61 g/100 g DM of glycolipids in ZM and 5.54 g/g 100 DM of phospholipids in ACD. Phospholipids play a fundamental role in the structures of cell membranes. This lipid fraction represented 9.9% of the total lipids in TM, a significantly lower percentage than previously reported by Gowda et al. [
18] (51%). Nevertheless, it has been shown on insects typically consumed in Nigeria that although phospholipid fraction was the second most abundant, values remained below 20% [
60]. Among the insects used in this study, only BD and LM displayed a phospholipid fraction as the second most abundant (24.64 and 14.79% of total lipid content, respectively). The presence of phospholipids has also been confirmed by Tzompa-Sosa et al. [
20] in lipid extracts of ACD, ALD, BD and TM. They observed that the extraction method affects the composition of the extracts as the phospholipids become water-soluble and remain in the aqueous layer, thus not being isolated when lipid separation in aqueous conditions is applied. Hence, using organic solvents in this study allows us to obtain the phospholipidic fraction. On the other hand, TM, ALD and ZM, which belong to the family Tenebrionidae, were the insects with the highest percentage of glycolipids with respect to total lipids (42, 38 and 31%, respectively), which could be interesting, not only for agrifood uses but also for the cosmetics industries for the development of skin treatment products [
61].
It has been suggested that the sensitivity of fatty acids to oxidation may depend on their incorporation in the lipids, i.e., either free or esterified in the form of triacylglycerols or other complex lipids, such as phospholipids and glycolipids [
23,
24,
62]. Similarly, the digestion and absorption of fatty acid may vary depending on the lipid class in which it is incorporated [
63]. Since there is limited research on the issue, it was considered valuable to know the specific fatty acid composition of the lipid classes as a basis for further understanding of their oxidative stability and bioavailability. The fatty acid profiles obtained from the neutral lipid, glycolipid and phospholipid fractions, expressed as the ratio of the specific fatty acid against the sum of all FAMEs in the lipid class, are shown in
Table 2,
Table 3 and
Table 4, respectively. As expected, since it is the major class (from 46.56% in ACD to 86.15% in GM of the total lipids), the fatty acid composition of the neutral fraction is similar to the composition of the total lipids, only small differences can be observed. Likewise, the glycolipids showed slight variations in fatty acid composition compared to the total lipids. However, the phospholipid fraction showed the greatest variation relative to the total lipid fraction. All insects presented a considerably lower content of oleic acid in the phospholipid fraction but a higher percentage of stearic acid compared to the total lipid fraction. Linoleic acid showed higher percentages in the phospholipid fraction in most of the insects, except for ALD and TM. While in ALD similar values were recorded, the phospholipid fraction of TM, in contrast to the rest of the insects studied, was the only one that exhibited strikingly lower values of linoleic acid as well as a higher content of palmitic acid in comparison to the total lipid profile. LM showed a considerably high content of α-linolenic acid, which is an essential fatty acid, in the phospholipid fraction. In addition, the phospholipid fraction was the only fraction in which DHA content was higher than 1%, more specifically in TM, suggesting that the trace levels observed in the total lipid profile were derived from its phospholipid fraction. It is known that the bioavailability of fatty acids depends on many factors, such as their chemical structure and the food matrix, among others, and may even be influenced by the lipid class to which it belongs [
64]. However, there is still substantial debate on this, and further research, including in vivo studies, is needed to substantiate the role of lipid class in the bioavailability of (semi-)essential fatty acids such as α-linolenic acid, EPA and DHA.
As noted above, lipid oxidation is one of the main reasons for chemical food degradation. Unsaturated fatty acids, and especially PUFA, are more susceptible to oxidation than saturated fatty acids due to their lower energy of activation at the initial stage when free radicals are formed [
65]. Despite the presence of PUFA in all three fractions, in most of the insects studied, they were the most abundant in the phospholipid fraction (except for ALD and TM). The same pattern has been previously reported in vegetables [
23]. According to previous studies [
23,
66], the phospholipid fraction may be more protective against autoxidation than the neutral and glycolipid fractions, but more rapidly oxidised by photo-oxidation and lipoxygenase-catalysed oxidation [
24].
3.4. Amino acid composition and estimation of protein quality
The total amounts and composition of amino acids are shown in
Table 5, except for tryptophan as alkaline hydrolysis was not performed. As previous studies reported, insects were considered rich in glutamic acid, and in general, present great amounts of alanine and aspartic acid, but are poor in cysteine [
11,
12,
15]. According to that, in all the samples analysed, cysteine was the AA with the lowest values (0.73-1.46 g/100 g of protein), whilst the sum of glutamic acid and glutamine showed the highest content (11.28-13.74 g/100 g of protein) followed by alanine in ACD, BD and LM (9.17-12.73 g/100 g of protein), asparagine and aspartic acid in ALD and GM (9.47 and 10.14 g/100 g of protein, respectively) and tyrosine in TM and ZM (8.11 and 9.23 g/100 g of protein, respectively). The total sulphur-containing and the total aromatic amino acid content in all insects reached 2.29-3.65 g/100 g of protein for the former and 8.87-14.11 g/100 g of protein for the latter. Among insects, ZM showed the greatest content of aromatic amino acids (tyrosine and phenylalanine), while ACD presented the highest content of sulphur amino acids (methionine and cysteine).
Protein quality relies on both constituent amino acids and the protein digestibility [
67]. While studying digestibility was beyond the scope of this paper, the amino acid composition of the studied insects was investigated together with common nutritional ratios based on the amino acid profile, which include total EAA content, E/T (%), EAAI, PER and AAS (
Table 5).
The total EAA content ranged between 39.57 g/100g of protein in GM and 49.28 g/100g of protein in ZM. Among them, values for ACD, BD and LM were comparable to those in the literature [
11,
12,
15,
45,
68]. In contrast, while Finke [
11] reported similar values for ZM and TM (about 48% for both insects), Yi et al. [
15] reported lower content (44%) for ZM and, to a lesser extent in TM (46%). On the other hand, the EAA values in GM and ALD were slightly lower than those previously reported (39.57 and 46.44% versus 43 and 48%, respectively) [
11,
12,
15]. Apart from that, while EAA values were in line with those reported for other insect species, such as A. mellifera and S. gregaria (43.8 and 39.6 g/100 g of protein, respectively), the reported values of conventional protein sources such as egg (43.6 g/100 g of protein) or milk (42.6 g/100 g of protein) were lower than those obtained for insects like ZM, TM and ALD. This highlights their relevance as alternative protein sources [
69], together with the fact that the percentage ratios of essential to total amino acids (% E/T) reached values from 39.57% in GM to 49.28% in ZM, all values higher than the 36% which was considered appropriate for an ideal protein [
70].
Regarding EAAI, a higher value represents a higher protein efficiency and quality [
71]. Our data presented values ranging between 2.43-2.51. While these values were lower than those reported for other insects, such as P. reticularis (3.3-3.4) [
40], all were higher than 1, which suggested that insect amino acid composition is superior to FAO/WHO [
40] standard and thus insect protein can be considered as good-quality protein [
40].
In addition, AAS is an index to evaluate the protein and amino acid efficiency that is required for the various population groups, based on the fact that the protein synthesis in the body cells does not take place unless the necessary amino acids are provided by the diet. Therefore, the AAS represents the protein quality regarding the EAA proportion present in a food [
72]. Based on our analysis, Leu was the limiting amino acid for ALD, DB and GM, whereas, for ACD, LM and TM, the limiting amino acid was Lys and Met+Cys for ZM. Despite this, the AAS for all insects (111%-159%) could reach the FAO/WHO requirements [
40] for older children, adolescents and adults.
Lastly, PER estimates the dietary value of different proteins by calculating it based on the interaction between Leu-Pro and Leu-Tyr (PER-1 and PER-2). According to Sommano et al. [
72], PER values lower than 1.5 correspond to low-quality proteins, while those higher than 2 correspond to high-quality proteins. The values obtained for PER-1 ranged between 1.94 and 2.78, while those for PER-2 varied from 1.83 to 2.77. In this regard, noteworthy was the score of LM (2.78 and 2.77 for PER-1 and PER-2, respectively), which was higher than those of other insects, suggesting that LM might have higher digestibility [
73]. Even so, the predicted PER-1 and PER-2 values of all insects were above 1.5, even in most cases above 2, which makes insect protein among the high-quality proteins. However, these marks were slightly lower than those previously observed for meat products and much lower than those for fish (2-7-3.2 and 3.1-3.7, respectively) [
67].
Nevertheless, amino acid availability varies according to protein source, processing and interaction with other food constituents, which all affect protein digestibility [
74]. Hence, it should be noted that these data only provide an overview of the potential nutritional value of the protein and should be confirmed by further experimental trials in vivo [
75], which were not the focus of the present study.
3.5. True protein content
Based on the amino acid content, the true protein content was calculated (ST1). Our findings showed that the highest protein content was found in BD (61.49 g/100 g DM), followed by ALD (55.74 g/100 g DM) and TM and LM (44.68 g/100 g and 44.23 g/100 g DM, respectively). A lower amount was found in ACD (39.37 g/100 g DM), followed by ZM (34.57 g/100 g DM) and the lowest values were shown in GM with 28.69 g/100 g DM. As was expected, these true protein values are, in general, lower than the crude protein contents reported previously by other authors since, in most studies, crude protein calculation was based on the application of Jones’ conversion factor (6.25) to the total nitrogen content [
44,
45,
58], as discussed further below.
3.6. Protein conversion factor (Kp)
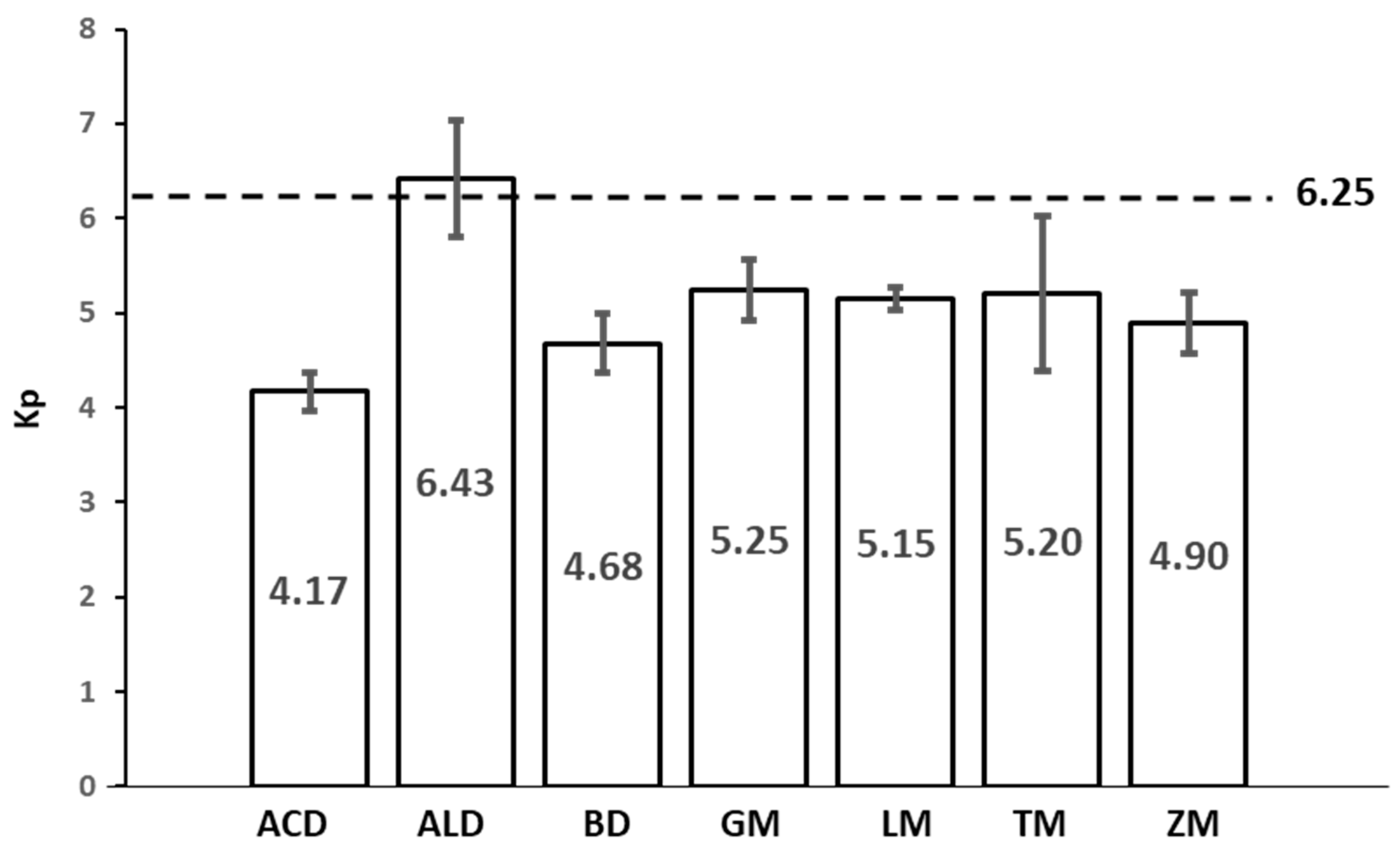
There is some controversy concerning the Kp that should be used to calculate protein content from nitrogen analysis. Previous research, due to insufficient data, often used the default value for animal protein (6.25). However, for insects, the total protein value could be overestimated owing to the non-protein nitrogen derived from other compounds, such as chitin [
39]. In order to give a precise and accurate result, the true protein content reported above was used to calculate the specific Kp for each insect (
Figure 2). As already pointed out, the calculated Kp showed lower values than the commonly used 6.25, with the exception of ALD (Kp = 6.43). Apart from ALD, GM, TM and LM showed the highest values (5.25, 5.20 and 5.15, respectively), while the lowest values were found in ACD, BD and ZM, with comparable Kp values in the range of 4.17 to 4.90. As stated before, it is clear that the use of the common Jones’ factor (6.25) significantly overestimates the protein content in six of the seven insects studied, from 19% in the case of GM up to as much as 50% in the case of ACD. Values for LM were similar to those obtained previously by Boulos et al. [
28] (5.33). By contrast, values for ACD were slightly lower than those obtained by Belghit et al. [
26] (4.53-4.80) and substantially lower than the 5.09 reported by Ritvanen et al. [
29] and the 5.25 showed by Boulos et al. [
28]. On the other hand, the values for TM were similar to those obtained previously by Boulos et al. [
28] (5.41) but were slightly higher than those obtained by Belghit et al. [
26], as well as those obtained by Janssen et al. [
27], who observed Kp of 4.64-4.86. Likewise, also somewhat larger values were obtained by Belghit et al. [
26] and Janssen et al. [
27] for ALD, which reached 4.86-5.05. These higher values could be explained by the different methods used for total nitrogen determination. Both studies, Belghit et al. [
26] and Janssen et al. [
27] analysed total nitrogen by the Dumas method, which has been observed to lead to higher nitrogen levels than when the Kjeldahl method is used [
36], whereby a higher total nitrogen results in a lower Kp.
To the best of our knowledge, our study is the first publication in which Kp of BD, GM and ZM is calculated, which provides useful input when used as an alternative source of protein. Apart from that, the range of Kp found in all these insects was in line with those reported for other insects, such as Apis mellifera pupae (4.9) and Schistocerca gregaria (4.5), [
27,
39,
76]. Boulos et al. [
28] suggested an average of 5.33 as the factor that was the most accurate indicator of the total protein content of the insects. Conversely, this study showed that even insects of the same family do not display comparable values. Therefore, it would be inadequate to assume a single value for all insects, making further studies required.
4. Conclusions
In recent years, research on insects as food has been increasing. This work studied fatty acid (among lipid classes) and amino acid profiles, from which various nutritional indices as well as technological (Kp) data were deduced. The nutritional quality indices revealed lipid with an overall favourable AI, TI and h/H, combined with a good PUFA/SFA ratio, making them a healthy novel lipid source. In terms of these indices, BD can overall be considered to have the most healthy fatty acid composition of the species studied. Furthermore, concerning protein, it was confirmed that all the insects studied exceeded the EAA requirements, with LM showing the best PER values. Still, it is important to emphasize that the fatty acid composition also depends on extrinsic factors, such as the feed. In contrast, the amino acid composition generally showed less variation.
In addition, the innovative aspect of this study involved, on one hand, the distribution of fatty acids across the lipid classes and, on the other hand, the determination of the species-specific Kp of these edible insect species. As far as the former is concerned, as expected, neutral lipids constituted the largest fraction. Although the overall low percentage of phospholipids, BD and LM and, to a lesser extent, ACD presented remarkably higher values than the other insects. Apart from ALD and TM, higher percentages of linoleic acid were observed in the phospholipid fraction compared to the total lipid fraction. In addition, LM showed a considerably high proportion of α-linolenic acid in the phospholipid fraction. In TM, DHA was quantifiable in the phospholipid fraction. The presence of these (semi-)essential fatty acids in phospholipids is noteworthy given that their absorption may be facilitated when it is found in this class of lipids. Similarly, it has been suggested that PUFA may be somewhat protected against autoxidation when they are contained in phospholipids, an interesting fact since most insects have a higher PUFA content in phospholipids than in the rest of the lipid classes. On the other hand, regarding the species-specific Kp, it was confirmed that using the Jones’ factor leads to overestimation of the protein content, which could reach even 50%. It was also found that Kp is independent of the insect family, resulting in a wide range from 4.17 in ACD to 6.43 in ALD. Additionally, data regarding Kp of BD, GM and ZM, which corresponded to 4.68, 5.25 and 4.9, respectively, were, for the first time, provided.
Overall, these data should be complemented by in vivo studies to investigate (semi-)essential fatty acid bio-availability and protein digestibility.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica, Ilse van de Voorde and Ilse Fraeye; methodology Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica, Ilse van de Voorde and Ilse Fraeye; software, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica; validation, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica, Ilse van de Voorde and Ilse Fraeye; formal analysis, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica and Ilse de Pril; investigation, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica; resources, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica and Ilse Fraeye; data curation, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica; writing—original draft preparation, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica; writing—review and editing, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica, Ilse van de Voorde and Ilse Fraeye; supervision, Ilse van de Voorde and Ilse Fraeye; project administration, Ilse Fraeye; funding acquisition, Cristina Perez-Santaescolastica and Ilse Fraeye. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Research Foundation of Flanders, grant number 1222921N.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Research Foundation of Flanders (grant number 1222921N). The authors gratefully acknowledge Prof. Imogen Foubert and Bsc. Céline Dejonghe (Food & Lipids, KU Leuven Kulak) for their valuable support in performing all lipid-related analyses and interpreting the outcomes.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, P. D. (2022). World Population Prospects 2022 Summary of Results. UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO. 3.
- Flachowsky, G., Meyer, U., & Südekum, K. H. (2017). Land use for edible protein of animal origin: A review. In Animals (Vol. 7, Issue 3). MDPI AG. [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. (2020). Edible insects: An overview on nutritional characteristics, safety, farming, production technologies, regulatory framework, and socio-economic and ethical implications. In Trends in Food Science and Technology (Vol. 100, pp. 35–50). Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Henchion, M., Hayes, M., Mullen, A. M., Fenelon, M., & Tiwari, B. (2017). Future protein supply and demand: Strategies and factors influencing a sustainable equilibrium. Foods, 6(7), 1–21. [CrossRef]
- van Huis, A., van Itterbeeck, J., Klunder, H., Mertens, E., Halloran, A., Muir, G., & Vantomme, P. (2013). Edible insects: Future prospects for food and feed security. Food And AgrIculture OrganizatIon of the UnIted NatIons.
- Kouřimská, L., & Adámková, A. (2016). Nutritional and sensory quality of edible insects. In NFS Journal (Vol. 4, pp. 22–26). Elsevier GmbH. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S., Lee, S. M., Jung, C., & Meyer-Rochow, V. B. (2017). Nutritional composition of five commercial edible insects in South Korea. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 20(2), 686–694. [CrossRef]
- European Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament of and of the Council of 25 November 2015 concerning novel foods and novel food ingredients, Pub. L. No. 2015/2283, 2015 (2015).
- Giordano, S., Clodoveo, M. L., Gennaro, B. de, & Corbo, F. (2018). Factors determining neophobia and neophilia with regard to new technologies applied to the food sector: A systematic review. In International Journal of Gastronomy and Food Science (Vol. 11, pp. 1–19). AZTI-Tecnalia. [CrossRef]
- Telfser, K. (2015). Creating a market for a more sustainable alternative: entomophagy businesses in Europe.
- Finke, M. D. (2002). Complete nutrient composition of commercially raised invertebrates used as food for insectivores. Zoo Biology, 21(3), 269–285. [CrossRef]
- Finke, M. D. (2015). Complete nutrient content of four species of commercially available feeder insects fed enhanced diets during growth. Zoo Biology, 34(6), 554–564. [CrossRef]
- Kulma, M., Plachý, V., Kouřimská, L., Vrabec, V., Bubová, T., Adámková, A., & Hučko, B. (2016). Nutritional value of three Blattodea species used as feed for animals. Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 25(4), 354-360. [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Bueno, R. P., González-Fernández, M. J., Sánchez-Muros-Lozano, M. J., García-Barroso, F., & Guil-Guerrero, J. L. (2016). Fatty acid profiles and cholesterol content of seven insect species assessed by several extraction systems. European Food Research and Technology, 242(9), 1471–1477. [CrossRef]
- Yi, L., Lakemond, C. M. M., Sagis, L. M. C., Eisner-Schadler, V., Huis, A. van, & Boekel, M. A. J. S. V. (2013). Extraction and characterisation of protein fractions from five insect species. Food Chemistry, 141(4), 3341–3348. [CrossRef]
- Yu, X., He, Q., & Wang, D. (2021). Dynamic Analysis of Major Components in the Different Developmental Stages of Tenebrio molitor. Frontiers in Nutrition, 8. [CrossRef]
- Smets, R. (2021). On the Compositional Analysis and Biorefinery of the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens). Resolving Uncertainties & Towards More Sustainable Processing. KU LEUVEN, Science, Engineering & Technology. Dissertation.
- Gowda, S. G. B., Sasaki, Y., Hasegawa, E., Chiba, H., & Hui, S. P. (2022). Lipid fingerprinting of yellow mealworm Tenebrio molitor by untargeted liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 8(2), 157-168. [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, M., & Komiya, Y. (2021). Detection of edible insect derived phospholipids with polyunsaturated fatty acids by thin-layer chromatography, gas chromatography, and enzymatic methods. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 99. [CrossRef]
- Tzompa-Sosa, D. A., Yi, L., van Valenberg, H. J. F., van Boekel, M. A. J. S., & Lakemond, C. M. M. (2014). Insect lipid profile: Aqueous versus organic solvent-based extraction methods. Food Research International, 62, 1087–1094. [CrossRef]
- Tzompa-Sosa, D. A., Dewettinck, K., Provijn, P., Brouwers, J. F., de Meulenaer, B., & Oonincx, D. G. A. B. (2021). Lipidome of cricket species used as food. Food Chemistry, 349. [CrossRef]
- Guil-Guerrero, J. L., Ramos-Bueno, R. P., González-Fernández, M. J., Fabrikov, D., Sánchez-Muros, M. J., & Barroso, F. G. (2018). Insects as Food: Fatty Acid Profiles, Lipid Classes, and sn-2 Fatty Acid Distribution of Lepidoptera Larvae. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 120(6). [CrossRef]
- Lee, J., Park, K., Lee, S., & Choe, E. (2000). Lipid changes of freeze-dried spinach by various kinds of oxidation. Journal of Food Science, 65(8), 1290–1295. [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T., Sugimura, R., Shimajiri, J., Suda, M., Abe, M., Hosokawa, M., & Miyashita, K. (2012). Oxidative stability of glyceroglycolipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acids. Journal of oleo science, 61(9), 505-513.
- Domoto, N., Koenen, M. E., Havenaar, R., Mikajiri, A., & Chu, B. S. (2013). The bioaccessibility of eicosapentaenoic acid was higher from phospholipid food products than from mono-and triacylglycerol food products in a dynamic gastrointestinal model. Food science & nutrition, 1(6), 409-415. [CrossRef]
- Belghit, I., Lock, E. J., Fumière, O., Lecrenier, M. C., Renard, P., Dieu, M., Berntssen, M. H. G., Palmblad, M., & Rasinger, J. D. (2019). Species-specific discrimination of insect meals for aquafeeds by direct comparison of tandem mass spectra. Animals, 9(5). [CrossRef]
- Janssen, R. H., Vincken, J. P., van den Broek, L. A. M., Fogliano, V., & Lakemond, C. M. M. (2017). Nitrogen-to-Protein Conversion Factors for Three Edible Insects: Tenebrio molitor, Alphitobius diaperinus, and Hermetia illucens. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 65(11), 2275–2278. [CrossRef]
- Boulos, S., Tännler, A., & Nyström, L. (2020). Nitrogen-to-Protein Conversion Factors for Edible Insects on the Swiss Market: T. molitor, A. domesticus, and L. migratoria. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7. [CrossRef]
- Ritvanen, T., Pastell, H., Welling, A., & Raatikainen, M. (2020). The nitrogen-to-protein conversion factor of two cricket species-Acheta domesticus and Gryllus bimaculatus. https://ec.europa.eu/food/safety/novel_food/authorisations/summary-appli-.
- EFSA Scientific Committee. (2015). Risk profile related to production and consumption of insects as food and feed. EFSA Journal, 13(10). [CrossRef]
- Ryckebosch, E., Muylaert, K., & Foubert, I. (2012). Optimization of an analytical procedure for extraction of lipids from microalgae. JAOCS, Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 89(2), 189–198. [CrossRef]
- Christie, W. W., & Han, X. (2003). Lipid analysis isolation, separation, identification and lipidomic analysis (Fourth, Vol. 24). Woodhead Publishing Limited.
- Mohammad Taghi Gharibzahedi, S., & Altintas, Z. (2023). Lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus L.) larvae oils extracted by pure and binary mixed organic solvents: Physicochemical and antioxidant properties, fatty acid composition, and lipid quality indices. Food Chemistry, 408. [CrossRef]
- Lawal, K. G., Kavle, R. R., Akanbi, T. O., Mirosa, M., & Agyei, D. (2022). Lipid nutritional indices, regioisomeric distribution, and thermal properties of Tenebrio molitor and Hermetia illucens larvae fat. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 25(3). [CrossRef]
- Santos-Silva, J., Bessa, R., & Santos-Silvã, F. (2002). Effect of genotype, feeding system and slaughter weight on the quality of light lambs II. Fatty acid composition of meat. Livestock Production Science, 77, 187–194. www.elsevier.com/locate/livprodsci.
- Ulbricht, T. L. V., & Southgate, D. A. T. (1991). Coronary heart disease: seven dietary factors. The Lancet, 338, 985–992.
- Biancarosa, I., Espe, & M., Bruckner, C. G., Heesch, & S., Liland, & N., Waagbø, & R., Torstensen, & B., & Lock, E. J. (2016). Amino acid composition, protein content, and nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors of 21 seaweed species from Norwegian waters. Journal of Applied Phycology, 29, 1001-1009. [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, F., Tomé, D., & Mirand, P. P. (2008). Converting nitrogen into protein - Beyond 6.25 and Jones’ factors. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 48(2), 177–184. [CrossRef]
- Kavle, R. R., Nolan, P. J., Bekhit, A. E. D. A., Carne, A., Morton, J. D., & Agyei, D. (2023). Physicochemical Characteristics, Techno-Functionalities, and Amino Acid Profile of Prionoplus reticularis (Huhu) Larvae and Pupae Protein Extracts. Foods, 12(2). [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, & United Nations University. (2007). Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition (Vol. 935).
- Chavan, U. D., Mckenzie, D. B., & Shahidi, F. (2001). Functional properties of protein isolates from beach pea (Lathyrus maritimus L.). Food Chemistry, 74, 177–187. [CrossRef]
- Rumpold, B. A., & Schlüter, O. K. (2013). Nutritional composition and safety aspects of edible insects. In Molecular Nutrition and Food Research (Vol. 57, Issue 5, pp. 802–823). [CrossRef]
- Barker, D., Fitzpatrick, M. P., & Dierenfeld, E. S. (1998). Nutrient Composition of Selected Whole Invertebrates. In Zoo Biology (Vol. 17).
- Dobermann, D., Swift, J. A., & Field, L. M. (2017). Opportunities and hurdles of edible insects for food and feed. In Nutrition Bulletin (Vol. 42, Issue 4, pp. 293–308). Blackwell Publishing Ltd. [CrossRef]
- Osimani, A., Garofalo, C., Milanović, V., Taccari, M., Cardinali, F., Aquilanti, L., Pasquini, M., Mozzon, M., Raffaelli, N., Ruschioni, S., Riolo, P., Isidoro, N., & Clementi, F. (2017). Insight into the proximate composition and microbial diversity of edible insects marketed in the European Union. European Food Research and Technology, 243(7), 1157–1171. [CrossRef]
- Rutaro, K., Malinga, G. M., Lehtovaara, V. J., Opoke, R., Valtonen, A., Kwetegyeka, J., Nyeko, P., & Roininen, H. (2018). The fatty acid composition of edible grasshopper Ruspolia differens (Serville) (Orthoptera: Tettigoniidae) feeding on diversifying diets of host plants. Entomological Research, 48(6), 490–498. [CrossRef]
- Stanley-Samuelson, D. W., Jurenka, R. A., Cripps, C., Blomquist, G. J., & de Renobales, M. (1988). Fatty Acids in Insects: Composition, Metabolism, and Biological Significance. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 9, 1–33.
- Paul, A., Frederich, M., Megido, R. C., Alabi, T., Malik, P., Uyttenbroeck, R., Francis, F., Blecker, C., Haubruge, E., Lognay, G., & Danthine, S. (2017). Insect fatty acids: A comparison of lipids from three Orthopterans and Tenebrio molitor L. larvae. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 20(2), 337–340. [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G., Mattioli, S., Rondoni, G., Bosco, A. D., Servili, M., Castellini, C., & Conti, E. (2022). Characterisation of fatty acid profiles of Tenebrio molitor larvae reared on diets enriched with edible oils. Journal of Insects as Food and Feed, 8(8), 901–912. [CrossRef]
- Czernichow, S., Thomas, D., & Bruckert, E. (2010). N-6 Fatty acids and cardiovascular health: A review of the evidence for dietary intake recommendations. In British Journal of Nutrition (Vol. 104, Issue 6, pp. 788–796). [CrossRef]
- Turley, J., & Thompson, J. (2015). Nutrition: your life science. Cengage Learning.
- Otero, P., Gutierrez-Docio, A., Navarro del Hierro, J., Reglero, G., & Martin, D. (2020). Extracts from the edible insects Acheta domesticus and Tenebrio molitor with improved fatty acid profile due to ultrasound assisted or pressurized liquid extraction. Food Chemistry, 314. [CrossRef]
- Milićević, D., Vranić, D., Mašić, Z., Parunović, N., Trbović, D., Nedeljković-Trailović, J., & Petrović, Z. (2014). The role of total fats, saturated/unsaturated fatty acids and cholesterol content in chicken meat as cardiovascular risk factors. Lipids in Health and Disease, 13(1). [CrossRef]
- Cito, A., Dreassi, E., Frosinini, R., Zanfini, A., Pianigiani, C., Botta, M., & Francardi, V. (2017). The potential beneficial effects of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera Tenebrionidae) and Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera Pyralidae) on human health. Redia, 100, 125–133. [CrossRef]
- Francardi, V., Frosinini, R., Pichini, C., Botta, M., Cito, A., & Dreassi, E. (2017). Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera pyralidae): an edible insect of nutraceutical interest. Redia, 3, 285-294. [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ramos, J. A., Rojas, M. G., Shapiro-Ilan, D. I., & Tedders, W. L. (2011). Self-selection of two diet components by tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) larvae and its impact on fitness. Environmental Entomology, 40(5), 1285–1294. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., & Liu, H. (2020). Nutritional indices for assessing fatty acids: A mini-review. In International Journal of Molecular Sciences (Vol. 21, Issue 16, pp. 1–24). MDPI AG. [CrossRef]
- Kulma, M., Kouřimská, L., Homolková, D., Božik, M., Plachý, V., & Vrabec, V. (2020). Effect of developmental stage on the nutritional value of edible insects. A case study with Blaberus craniifer and Zophobas morio. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 92. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. J., Yoon, B. D., & Oh, H. M. (1998). Rapid method for the determination of lipid from the green alga Botryococcus braunii. Biotechnology techniques, 12(7), 553-556.
- Ekpo, K. E., Onigbinde, A. O., & Asia, I. O. (2009). Pharmaceutical potentials of the oils of some popular insects consumed in southern Nigeria. African Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 3(2), 51–057. http://www.academicjournals.org/ajpp.
- Traversier, M., Gaslondes, T., Milesi, S., Michel, S., & Delannay, E. (2018). Polar lipids in cosmetics: Recent trends in extraction, separation, analysis and main applications. Phytochemistry Reviews, 17, 1179-1210. [CrossRef]
- Hazahari, N. Y. B., Hosokawa, M., & Miyashita, K. (2018). Comparison of Oxidative Stability of Monogalactosyl Diacylglycerol, Digalactosyl Diacylglycerol, and Triacylglycerol Containing Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Food and Nutrition Sciences, 09(03), 221–234. [CrossRef]
- Lordan, R., Tsoupras, A., & Zabetakis, I. (2017). Phospholipids of animal and marine origin: Structure, function, and anti-inflammatory properties. Molecules, 22(11). [CrossRef]
- Bordoni, L., Petracci, I., Zhao, F., Min, W., Pierella, E., Assmann, T. S., Martinez, J. A., & Gabbianelli, R. (2021). Nutrigenomics of dietary lipids. Antioxidants, 10(7). [CrossRef]
- Min, D. B., & Boff, J. M. (2002). Chemistry and reaction of singlet oxygen in foods. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 1(2), 58–72. [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, O., & Oido, H. (1969). Changes of Lipid and Pigment Compositions in Spinach Leaves during Their Storage. Journal of the Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan, 43(7), 423–428.
- Friedman, M. (1996). Nutritional Value of Proteins from Different Food Sources. A Review. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 44, 6–29.
- Purschke, B., Tanzmeister, H., Meinlschmidt, P., Baumgartner, S., Lauter, K., & Jäger, H. (2018). Recovery of soluble proteins from migratory locust (Locusta migratoria) and characterisation of their compositional and techno-functional properties. Food Research International, 106, 271–279. [CrossRef]
- Paul, A. A., Southgate, D. A., & Russell, J. (1980). The Composition of Foods. HM Stationery Office, London.
- FAO/WHO. (1973). Energy and protein requirements. Report of FAO Nutritional Meetings Series No.52.
- Bártová, V., Bárta, J., Brabcová, A., Zdráhal, Z., & Horáčková, V. (2015). Amino acid composition and nutritional value of four cultivated South American potato species. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 40, 78–85. [CrossRef]
- Sommano, S. R., Bhat, F. M., Wongkeaw, M., Sriwichai, T., Sunanta, P., Chuttong, B., & Burgett, M. (2020). Amino Acid Profiling and Chemometric Relations of Black Dwarf Honey and Bee Pollen. Frontiers in Nutrition, 7. [CrossRef]
- Yang, F., Huang, X., Zhang, C., Zhang, M., Huang, C., & Yang, H. (2018). Amino acid composition and nutritional value evaluation of Chinese chestnut (: Castanea mollissima Blume) and its protein subunit. RSC Advances, 8(5), 2653–2659. [CrossRef]
- Boye, J., Wijesinha-Bettoni, R., & Burlingame, B. (2012). Protein quality evaluation twenty years after the introduction of the protein digestibility corrected amino acid score method. British Journal of Nutrition, 108(SUPPL. 2). [CrossRef]
- Wang, P., Huang, J., Sun, J., Liu, R., Jiang, T., & Sun, G. (2022). Evaluating the Nutritional Properties of Food: A Scoping Review. In Nutrients (Vol. 14, Issue 11). MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Mishyna, M., Martinez, J. J. I., Chen, J., & Benjamin, O. (2019). Extraction, characterization and functional properties of soluble proteins from edible grasshopper (Schistocerca gregaria) and honey bee (Apis mellifera). Food Research International, 116, 697–706. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).