Submitted:
15 October 2023
Posted:
18 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
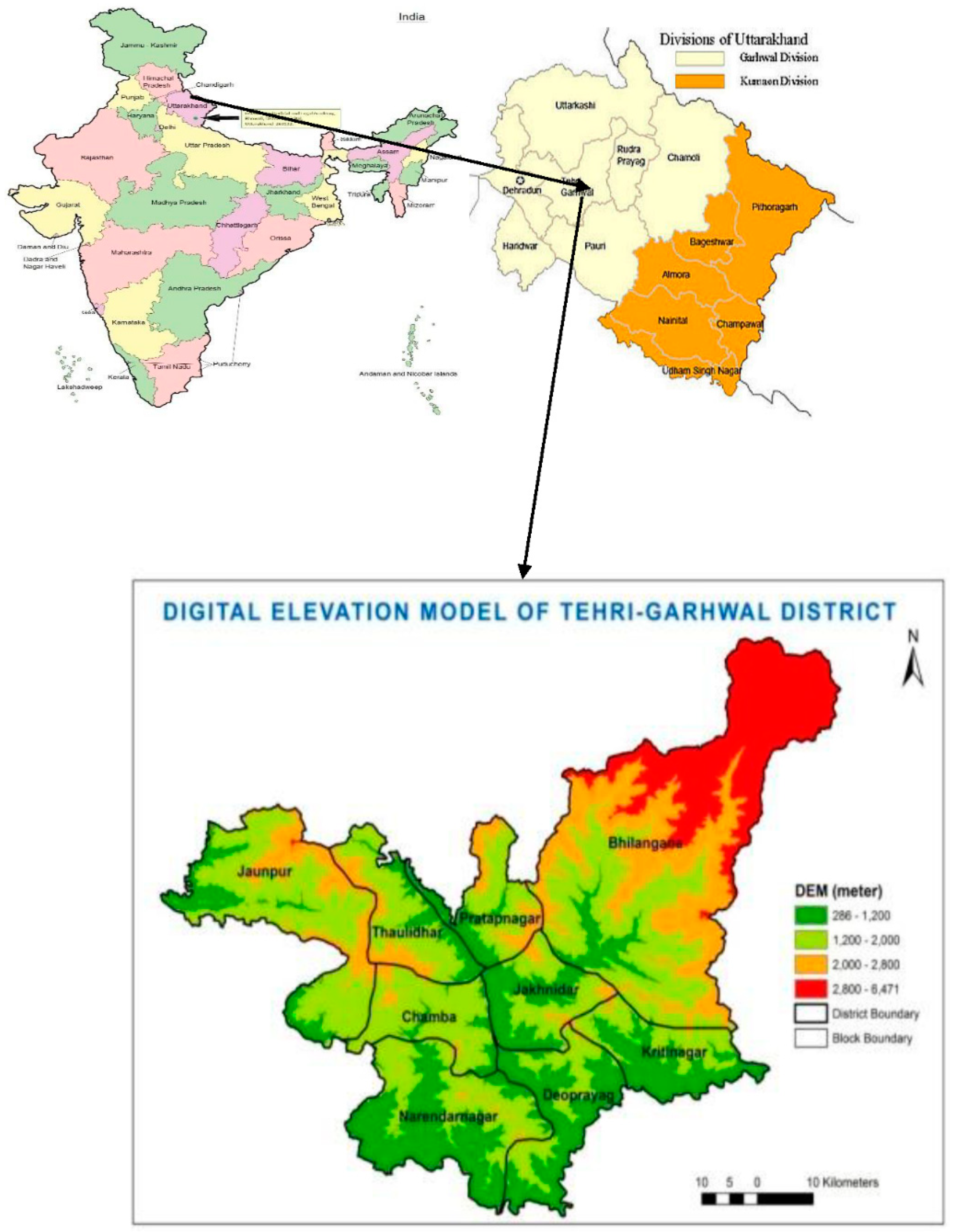
2.1. Study area
2.2. Methodology
3. Results
6. Discussion:
7. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Stephanie, C. Importance of agroforestry systems in carbon sequestration, Penn State University, Forest science database, https://www.cabi.org/forestscience/news/65086 (accessed on 20 October 2022). 2018.
- Parti, M . U.S. and India launch a new initiative to increase tree coverage in India, US Agency for international development, https://www.usaid.gov/india/ (accessed on 24 November 2022). 2022.
- Rizvi, RH., Dhyani, SK., Ram, N, et al. Mapping agroforestry area in India through remote sensing and preliminary estimates. Indi Farmi. 2014; 63(11): 62–64.
- NAPCC. National Action Plan on Climate Change, Government of India. 2021; 1-56.
- Jain, N. Harnessing the unrealized potential of agroforestry in curbing climate change in India, Monogaby News and inspiration from nature frontline in India, https://india.mongabay.com/ (accessed on 28 November 2022). 2021.
- Jose, S., Bardhan, S. Agroforestry for biomass production and carbon sequestration. Agro Sys.2012; 86: 105-111. [CrossRef]
- ISFR. Indian State of Forest Report, Forest survey of India, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate change, Government of India, Dehradun, Uttarakhand. 2019.
- Singh, JS., Singh, SP. Forests of Himalaya: Structure, Functioning and Impact of Man. Gyanodaya Prakashan, Nainital, Uttarakhand, India. 1992; 294.
- Muller, D., Ellenberg, H. Aims and methods of vegetation ecology. John Wiley & Sons, New York.1974.
- Pressler, M. Das Gestz der Stammformbildung. Leipzig: Verlag Arnold.1865.
- Bitterlich, W.The Relaskop idea. Farnham Royal: Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau. 1984.
- IPCC. Guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2006.
- Smith, DM. Maximum moisture content method for determining specific gravity of small wood samples. United states Department of Agriculture Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory Report No. 2014, Madison and Wisconsin.1954.
- Chidumayo, EN. Above-ground woody biomass structure and productivity in Zambezian woodland. For Ecol Manag. 1990; 36: 33-46. [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Revised IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.1996.
- Woomer PL. Impact of cultivation of carbon fluxes in woody savannas of Southern Africa. Wat Ai So Poll. 1999; 70: 403–412. [CrossRef]
- Pearson, TR., Brown, SL., Birdsey, RA. Measurement guidelines for the sequestration of Forest carbon: USDA Forest Service 19073-3294. 2007. [CrossRef]
- Singh RA.Soil physical analysis. New Delhi: Kalyani Publishers.1980.
- Walkley, AJ., Black, I. Estimation of soil organic carbon by chromic acid titration method. Soil Science.1934; 37: 29–38.
- Dadhwal, KS., Narain, P., Dhyani, SK. Agroforestry systems in the Garhwal Himalayas of India. Agrofor Sys. 1989; 7: 213–225.
- Toky, OP., Kumar, P., Khosla, PK. Structure and function of traditional agroforestry systems in Western Himalaya. I. Biomass and productivity. Agroforestry System.1989; 9(1): 47-70. [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S., Verma. KS., Kaushal, R. Biomass and carbon sequestration in different agroforestry systems of a Western Himalayan Watershed. Biol Agri Horti. 2014; 30 (2): 88-96. [CrossRef]
- Vikrant, KK., Chauhan. DS., Rizvi, RH, et al. (2018) Mapping the extent of agroforestry area in different elevations of Tehri district, North Western Himalaya, India through GIS and Remote sensing data. J of Ind Soci of Re Sens. 2018; 46:1-12. [CrossRef]
- Lal, R., Kimble, J., Follett, RF. Pedospheric processes and the carbon cycle. In: Soil process and the carbon cycle, Lal et al. (eds.) CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1998; 1-8.
- Rajput, BS. Status of Soil Organic Carbon Stocks Under Different Land Use Systems in Wet Temperate North Western Himalaya. J of T Sci. 2013; 32: (1&2).
- IPCC. Land use and land use change and forestry. A special report, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 2000.
- Vikrant. Carbon stock along elevations in traditional agroforestry system in Garhwal Himalaya, Ph.D thesis awarded HNB Garhwal University, Srinagar Garhwal, UK, India.2019; 199.
- Albrecht, A., Kandji, ST. Carbon sequestration in tropical agroforestry systems. Agri Ecosys Envir. 2003; 99: 15–27. [CrossRef]
| Components | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dominants tree species (forest tree + fruit) | Dominants annual crops (crop+ grass+ weed) | |||||
| Elevations (m) | Agrisilviculture system (AS) |
Agrihortisilviculture system (AHS) |
Agrihorticulture system (AH) | Agrisilviculture system (AS) | Agrihortisilviculture system (AHS) |
Agrihorticulture system (AH) |
| 286-1200 |
Grewia oppositifolia, Melia azedarach, Celtis australis, Boehmeria regulosa, Ficus auriculata,Toona ciliata, Prunus cerasoides, Bauhinia variegata, Ficus roxburghii |
Citrus limon, Psidium guajava, Mangifera indica, Musa paradisica, Citrus sinensis, Grewia oppositifolia, Melia azedarach, Toona ciliata, Celtis australis, Ficus roxburghii | Mangifera indica, Citrus limon, Carica papaya, Citrus aurentium, Embilica officinalis, Prunus persica, Psidium guajava, Punica granatum |
Echinochloa frumentacea, Eleusine coracana, , Zea mays, ,Triticum aestivum , Agreatum cenozoides, Cynodon dactylon, Lantana camara |
Echinochloa frumentacea, Eleusine coracana, Oryza sativa, Glycine max, Cajanus spp., Cynodon dactylon, Lantana camara, Allium cepa, Solanum tuberosum, Brassica compestris, Raphanus sativus | Glycine max, Pisum sativum, Ehinochloa frumentacea, Eleusine coracana, Allium cepa, Solanum tuberosum, Brassica compestris, Raphanus sativus |
| 1200-2000 | Celtis australis, Bauhinia variegata, Ficus roxburghii, Grewia oppositifolia, Melia azedirach, Morus alba, Quercus leucotrichophora, Toona ciliata | Celtis australis, Ficus roxburghii, Grewia oppositifolia, Melia azedirach, Morus alba, Citrus aurentium, Psidium guajava, Embilica officinalis, Mangifera indica, Musa paradisiacia, Malus domestica |
Citrus aurentium, Psidium guajava , Embilica officinalis, Mangifera indica, Musa paradisiaca, Malus domestica |
Amarnathusblitum, Ehinochloa frumentacea, Eleusine coracana, Oryza sativa, Glycine max, Cicer arientinum, Cajanus spp., Triticum aestivum , Cynodon dactylon, Lantana camara |
Fagopyrumesculentum, Oryza sativa, Ehinochloa frumentacea,Eleusine coracana, Chenopodium album, Allium cepa, Solanum tuberosum, Brassica compestris, Raphanus sativus, Cynodon dactylon, Lantana camara |
Glycine max, Pisum sativum, Ehinochloa frumentacea.Eleusine coracana, Allium cepa, Solanum tuberosum, Brassica compestris, Raphanus sativus. |
| 2000-2800 | Quercus leucotrichophora, Rhododendron arboretum, Myrica esculenta, Grewia oppositifolia |
Grewia oppositifolia ,Quercus leucotrichophora, Rhododendron arboreum, Myrica esculenta, Citrus limon, C. sinensis, Juglans regia, Malus domestica. |
Pyrus communis, Prunus persica, Prunus armenica, Juglanse regia, Pyrus communi, Citrus limon, C. sinensis, Malus domestica |
Triticum aestivum, Eleusine coracana, Fagopyrum esculentum, Amarnathusblitum, Ehinochloa frumentacea, Lantana camara |
Triticum aestivum, Amarnathus blitum, Fagopyrum esculentum, Ehinochloa frumentacea, Eleusine coracana, Solanum tuberosum, Amranthus virdius | Triticum aestivum, Amarnathus blitum, Ehinochloa frumentacea, Eleusine coracana, Solanum tuberosum, Cynodon dactylon |
| Density (trees ha-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevations | Forest species | Agrisilviculture system (AS) | Agrihortisilviculture system (AHS) |
Agrihorticulture system (AH) |
| 286- 1200 m | Adina cardifolia | 6 | NA | NA |
| Anogeissus latifolia | 6 | NA | NA | |
| Acacia catechu | 4 | 8 | NA | |
| Bahunia verigata | 5 | NA | NA | |
| Bombax ceiba | 8 | NA | NA | |
| Celtisaustralis | 40 | 41 | NA | |
| Ficus palamata | 11 | NA | NA | |
| Ficus roxburghii | 10 | NA | NA | |
| Ficus semicordata | 6 | NA | NA | |
| Grewia oppositifolia | 60 | 55 | NA | |
| Hoplia integrifolia | 5 | 10 | NA | |
| Melia azedirach | 20 | 22 | NA | |
| Morus alba | 5 | 10 | NA | |
| Pinus roxburghii | 7 | 6 | NA | |
| Prunus cerasoides | 6 | NA | NA | |
| Pyrus pashia | 8 | 9 | NA | |
| Rhus parviflora. | 4 | NA | NA | |
| Toona ciliata | 5 | 8 | NA | |
| Woodfordia fruticosa | 3 | NA | NA | |
| Total | 227 | 169 | NIL | |
| 1200- 2000 m | Celtis australis | 32 | 25 | NA |
| Ficus roxburghii | 45 | 24 | NA | |
| Grewia oppositifolia | 77 | 90 | NA | |
| Melia azedirach | 15 | 22 | NA | |
| Morus alba | 11 | NA | NA | |
| Pinus roxburghii | 6 | NA | NA | |
| Quercusleucotrichophora | 15 | 17 | NA | |
| Rhus parviflora | 5 | NA | NA | |
| Toona ciliata | 6 | NA | NA | |
| Woodfordia fruticosa | 4 | NA | NA | |
| Total | 216 | 178 | NIL | |
| 2000-2800 m | Grewia oppositifolia | 40 | 18 | NA |
| Myrica esculenta | 35 | 32 | NA | |
| Quercus leucotrichophora | 58 | 51 | NA | |
| Rhododendron arboreum | 19 | 19 | NA | |
| Total | 152 | 120 | NIL | |
| Fruit species | ||||
| 286- 1200 m | Carica papaya | NA | 7 | 24 |
| Citrus aurentium | NA | NA | 22 | |
| Citrus limon | NA | NA | 25 | |
| Embilica officinalis | NA | 15 | NA | |
| Mangifera indica | NA | 12 | 37 | |
| Musa paradisiacia | NA | 11 | 34 | |
| Psidium guajava | NA | 10 | 17 | |
| Punica granatum | NA | 6 | 22 | |
| Total | NIL | 61 | 181 | |
| Grand total (forest + fruit) | 227 | 230 | 181 | |
| 1200- 2000 m | Citrus aurentium | NA | 5 | 14 |
| Citrus limon | NA | NA | 14 | |
| Citrus sinensis | NA | 10 | 35 | |
| Embilica officinalis | NA | 5 | 18 | |
| Mangifera indica | NA | 13 | 35 | |
| Musa paradisiacia | NA | 15 | 23 | |
| Prunus armenica | NA | 7 | 19 | |
| Prunus persica | NA | 7 | 23 | |
| Psidiumguajava | NA | NA | 12 | |
| Punica granatum | NA | 3 | 11 | |
| Pyrus communis | NA | NA | 29 | |
| Total | NIL | 65 | 233 | |
| Grand total (forest + fruit) | 216 | 243 | 233 | |
| 2000-2800 m | Citrus limon | NA | NA | 21 |
| Citrus sinensis | NA | 25 | 32 | |
| Juglanse regia | NA | 17 | 12 | |
| Malus domestica | NA | 28 | 32 | |
| Prunus armenica | NA | NA | 13 | |
| Prunus persica | NA | NA | 22 | |
| Pyrus communis | NA | 16 | 16 | |
| Total | NIL | 86 | 148 | |
| Grand total (forest + fruit) | 152 | 206 | 148 | |
| Elevations (m) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 286-1200 m | 1200-2000 m | 2000-2800 m | |||||||
| AFS | Total Biomass |
Biomass Carbon stocks |
CO2 Mitigation | Total Biomass | Biomass Carbon stocks | CO2 Mitigation | Total Biomass | Biomass carbon stocks |
CO2 Mitigation |
| AS | 3.81 | 1.71 | 6.27 | 3.62 | 1.62 | 5.94 | 2.45 | 1.10 | 4.03 |
| AHS | 6.36 | 2.86 | 10.49 | 4.37 | 1.96 | 7.19 | 3.77 | 1.69 | 6.20 |
| AH | 3.54 | 1.59 | 5.83 | 2.69 | 1.21 | 4.44 | 1.81 | 0.81 | 2.97 |
| LSD | 0.86 | 0.39 | 1.43 | 0.77 | 0.35 | 1.28 | 0.60 | 0.27 | 1.11 |
| Carbon (Mg ha-1) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevations (m) | |||||||||
| AFS | 286-1200 m | 1200-2000 m | 2000-2800 m | ||||||
| Plant | Soil (0-30 cm) | Total | Plant | Soil (0-30 cm) | Total | Plant | Soil (0-30 cm) | Total | |
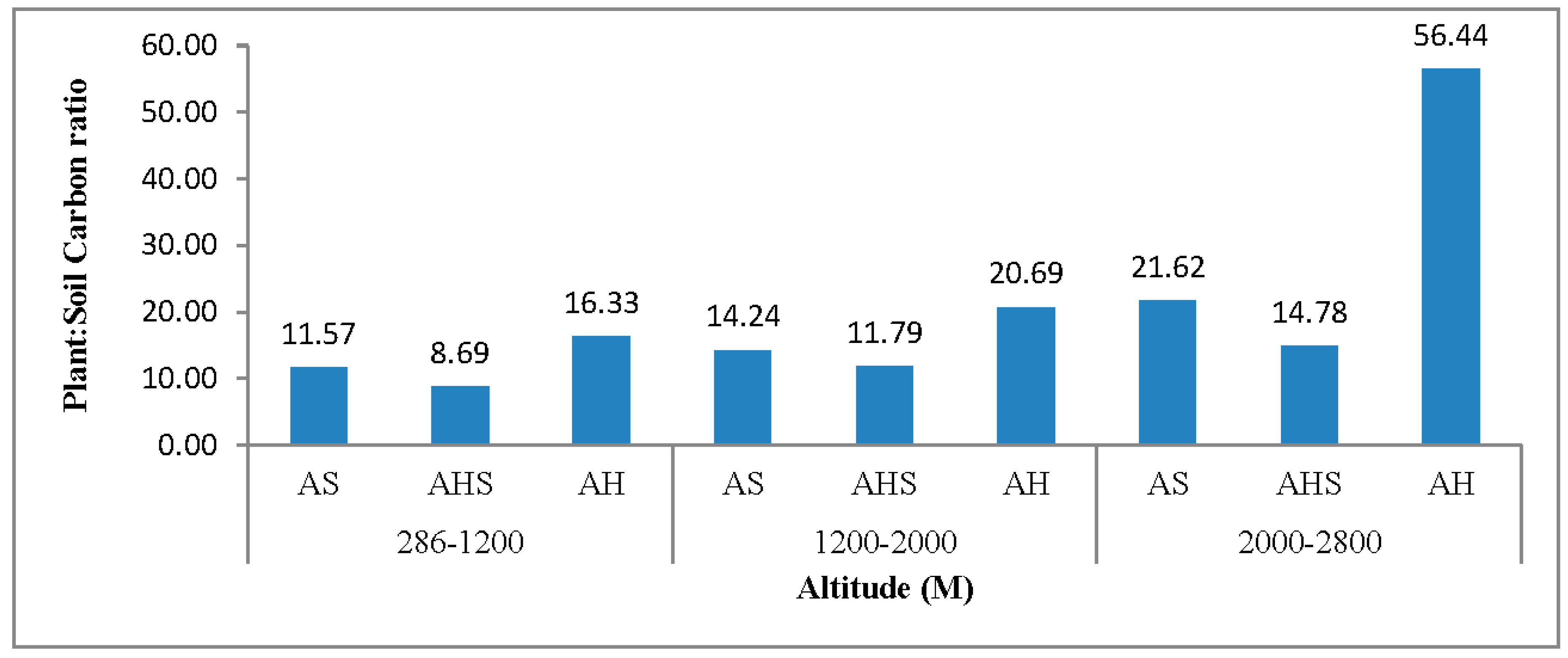
| AS | 1.71 | 19.78 | 21.49 | 1.62 | 23.07 | 24.69 | 1.10 | 23.78 | 24.88 |
| AHS | 2.86 | 24.85 | 27.71 | 1.96 | 23.11 | 25.07 | 1.69 | 24.98 | 26.67 |
| AH | 1.59 | 25.97 | 27.56 | 1.21 | 25.03 | 26.24 | 0.81 | 45.72 | 46.53 |
| LSD | 0.39 | 17.21 | 19.60 | 0.35 | 20.21 | 20.56 | 0.27 | 21.29 | 21.56 |
| Carbon credits | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elevations (m) | Estimated agroforestry area (ha)* | Mitigated carbon (Mg) | Total | ha-1 | Value of carbon credits (€)c |
| 286-1200 | 2231.26 | 4574.08 | 16786.87 | 7.52 | 50360.61 |
| 1200-2000 | 3707.36 | 5894.13 | 21631.45 | 5.83 | 64894.35 |
| 2000-2800 | 1038.65 | 1246.38 | 4574.21 | 4.40 | 13722.63 |
| 2800-6471 | 52.11 | Not estimated | |||
| Total | 7029.06 | 11714.59 | 42992.53 | 128977.59 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





