1. Introduction
Diabetes is a common clinical endocrine disease that may lead to a series of complications. The incidence of diabetes in China is increasing year by year, and there are currently about 120 million diabetics in China. One of the major complications of diabetes is the diabetic foot (DF). Studies have shown that about one-fifth of diabetic patients develop foot ulcers during the disease, and severe infection even leads to amputation, which seriously affects the quality of life and safety of diabetic patients [
1,
2]. DF is a refractory disease, with high morbidity, high amputation rates, high treatment costs, and a mortality rate 11% higher than that of malignant tumors. The main manifestations of DF are peripheral neuropathy, vasculopathy and infection, resulting in chronic progressive lesions of the skin, muscle and connective tissue and even bone [
3], and improper management is associated with aggravated lesions or serious consequences such as foot gangrene or systemic infections. In addition, peripheral vasculopathy and nerve damage are the main pathological features of DF. Chronic neuropathy in the foot may cause foot deformity, the skin at its high pressure is prone to ulcer formation, and vascular lesions induce microcirculatory disorders in the foot, resulting in trauma hypoxia and ischemia [
4,
5].
Active glycemic control, complete removal of necrotic tissue, prevention of local infection spread, and improvement of blood supply to the affected limb are critical to the management of DF [
6]. Debridement plus topical application of autologous platelet-rich plasma was mostly adopted in the early management of DF, which reduces the microorganisms in the foot ulcer wound by cleaning the infected material and increases the growth factor growth in the wound by topical application of platelet plasma, resulting in healing of the wound. However, external treatment is prone to infection, poor prognosis, and recurrent episodes [
7]. Data show that diabetic patients account for 40% to 60% of non-traumatic low amputations, and 85% are found after foot ulcers. Lower extremity arterial disease (LEAD) is one of the main causes of disability and death due to foot ulcers in diabetic patients, and currently, severe LEAD is mainly treated by interventional or lower extremity artery bypass graft surgery, while mild to moderate LEAD is mainly treated with medical drugs. Nonetheless, the long-term outcome leaves much to be desired [
8,
9].
In the 1980s, Ilizarov first proposed the tibial lateral bone repositioning procedure. To evaluate the effects of retraction rate and retraction frequency on osteogenesis during limb lengthening, different retraction rates (0.5 mm/d, 1.0 mm/d, 2.0 mm/d) and different retraction frequencies (1 step/d, 4 steps/d, 60 steps/d) were used in the tibia of the canine leg for experimental studies, in which retraction was performed to study skeletal muscle, bone tissue, smooth muscle, fascia, skin, nerves and blood vessels after open osteotomy and closed osteotomy. After nearly 20 years of development, lateral bone repositioning has achieved breakthroughs in basic research and clinical practice for the treatment of lower limb ischemic diseases [
10,
11]. The mechanism of lateral bone repositioning microvascular regeneration is still unclear. It has been suggested that bone marrow is the source of microvascular regeneration, and other studies have suggested that periosteal retraction induced microvascular regeneration. Antibiotic bone cement possesses good mechanical strength and barrier effect, releases antibiotics locally and is independent of blood flow conditions. Thus, antibiotic bone cement has been promoted for DF management, especially in trauma involving bone tissue. As one of the main manifestations of DF patients, the pain will increase the psychological burden and aggravate the condition of patients, and the improvement of the patient condition can be reflected through pain assessment. Tibial nerve motor conduction velocity and common peroneal nerve sensory conduction velocity, as common lower limb function indicators, reflect the improvement of lower limb nerve conduction function in patients with DF [
13]. Peak flow rate, blood flow, and intravascular diameter are common hemodynamic indices that can indicate the improvement of dorsalis pedis artery hemodynamics and microcirculation in patients, and wound area, transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen, and wound PH are common healing indices that reflect the improvement of ulcer wounds in patients [
14]. To this end, the current study was undertaken to evaluate the clinical efficacy of antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning for severe DF and its impact on wound healing rate.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Participants
Sixty patients with hemodialysis anemia admitted to the endocrinology department of our hospital from July 2020 to July 2021 were included and randomly assigned to receive antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning (observation group) or vacuum sealing drainage (VSD) (control group). Informed permission was obtained from the patients and informed consent was signed prior to enrollment in the study. The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Renmin Hospital,Hubei University of Medicine, and all processes complied with the Declaration of Helsinki ethical guidelines for clinical research. (
Table 1)
2.2. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: (1) patients with diabetic foot, lower extremity atherosclerosis-occlusive disease and thrombo-occlusive vasculitis with chronic infection of the foot and ankle, which may include deep soft tissue infection of the foot and ankle, chronic osteomyelitis and septic arthritis and other refractory infections; (2) who received tibial lateral bone repositioning technique combined with antibiotic bone cement treatment; (3) lower extremity vascular ultrasound or CT angiography shows popliteal artery and proximal blood flow.
Exclusion criteria: (1) with uncontrolled systemic infections; (2) with underlying diseases that resulted in intolerance to surgery; (3) with psychiatric disorders that prevented cooperation with treatment; (4) with complete obstruction of the popliteal artery and above. (5) with severe cardiac insufficiency; (6) with severe renal insufficiency; (7) patients and family members did not accept the treatment plan.
2.3. Treatment methods
The control group was treated with conventional ulcer wound debridement combined with vacuum sealing drainage (VSD) under nerve block anesthesia. After irrigation of the ulcer wound, the obvious necrotic tissues were removed by electric knife and the inter-ecological tissues were preserved as appropriate. After hemostasis, the diabetic foot wound was repeatedly irrigated with iodine peroxide solution and saline, and the VSD material (Shandong Weigao Group Co., Ltd.) was trimmed appropriately and completely covered the diabetic foot ulcer wound, followed by the connection of a negative pressure suction device, with the negative pressure ranging from -0.017 to -0.06 MPa in intermittent suction mode. The dressing was changed promptly in about 1 week depending on the oozing condition of the external trauma dressing. The growth of granulation at the base of the trauma was closely monitored. In the case of diabetic foot ulcers with localized granulomatous punctate bleeding and no obvious necrotic septic tissue, the VSD material was removed, and the wound was cleaned and dressed. A free skin graft was used to restore the residual wound, or a conservative dressing change was used to promote the healing of the residual wound.
The observation group received antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning. (1) Thorough debridement: After anesthesia, the debridement method was selected according to the condition of the wound, necrotic and blackened tissues were removed, pus-soaked tendon tissues were excised, tissues without necrotic muscles or bleeding after scraping were preserved, tissues with osteomyelitis changes were cleared, and the skin was preserved to the maximum extent possible. The second stage of debridement was indicated for late necrosis. The wound was repeatedly irrigated with hydrogen peroxide, dilute iodophor and saline several times during the trauma debridement. (2) Antibiotic bone cement to fill the trauma: Antibiotic bone cement was prepared according to the area of the trauma, with vancomycin to bone cement ratio of 1:20, using four 500 mg vancomycin to one 40 g packet of bone cement (PALACOS, Heraeus Medical, China). The bone cement was sufficiently mixed into a drawn shape and then filled the trauma without leaving a dead cavity. A Kirschner needle was used to facilitate the injection of the bone cement. For wounds with more necrotic tissue and exudate, the bone cement was covered with VSD (Type III-PU, Shandong Weigao, China) for negative pressure drainage, and the air pressure for negative pressure suction was 0.04-0.06 MPa. The cement was removed 4 weeks after trauma debridement bone cement filling, and secretions were obtained every three days for review. Three consecutive bacterial cultures were performed, and closure of the wound was conducted. In the event of continued bacterial growth from the discharge, a second antibiotic bone cement filling was performed. (3) Installation of a tibial lateral bone repositioning scaffold: After successful anesthesia, the osteotomy range was designed about 1 cm below the tibial tuberosity (the traditional osteotomy zone is in the middle and lower third of the tibia). Two 3mm external fixation pins were inserted into the repositioned bone block, and the bone was osteotomized using an osteotomy mould. The holes were drilled with an electric drill (saline was used to cool the holes), and then the continuous bone between the holes was truncated with a thin bone cutter, with caution to protect the periosteum. The periosteal holes were repaired with sutures after drilling. Two to three 4mm external fixation pins were inserted into the distal and proximal ends of the displaced bone block, and the bone repositioning frame was installed and adjusted. The direction of bone repositioning was marked, followed by hemostasis of the incision by intra-incisional electrocoagulation and suturing of the incision after saline irrigation. (4) Postoperative precautions: Bone repositioning was performed 1 week after bone repositioning stenting by pulling the bone repositioning block outward 1mm per day (bone repositioning turntable was turned 90° every 6h and 360° every 24h), back repositioning was usually performed after 2 weeks, back repositioning also lasted 2 weeks, and a course of treatment was performed for 1 month. Depending on the patient condition, the treatment was repeated for 2 to 3 sessions. Another debridement and bone cement filling were required for a long interval of disease. The external fixation stent was removed 1 month after cessation of repositioning, and the area around the fixation pins of the external fixation stent was disinfected and changed daily to prevent infection of the nail tract. The repositioning was discontinued immediately to prevent skin necrosis should the tension be too high. The repositioning was stopped in the event of severe infection, and the external fixation could be removed.
2.4. Outcome measures
2.4.1. Clinical evaluation indices
Clinical evaluation indices include limb preservation rate, postoperative ulcer healing, recurrence rate, mortality rate, and the degree of resting pain of the affected limb after 1h of rest in the flat position. Postoperative follow-up was performed to monitor the occurrence of complications.
2.4.2. Skin temperature, ankle-brachial index, and sensory threshold of the affected limb
(1) The wound healing was closely monitored postoperatively; (2) Before and after surgery, the patient's skin temperature was monitored at 8:00 a.m. daily during the check-in, and the selected site was the end of the lesser toe or the toe end of other toes, and the skin temperature of the affected limb was measured via a skin temperature gun; (3) A sensory threshold detector was used to measure superficial sensation in the affected limb, with values >25 Volt indicating a high risk of diabetic foot ulcer, 16-25 Volt a moderate risk, and <15 Volt a low risk.
2.4.3. Foot wound healing
The wound area before and after treatment, the transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen in the skin at 3 cm around the wound, and the pH of the wound were compared between the two groups of patients.
2.4.4. Dorsal pedis artery hemodynamics
The ultrasound detector was used to examine the arteries of both lower limbs of the patients before and after different treatments. The ultrasound probe was used on the patient's foot to measure the bilateral dorsalis pedis arteries, and the indices included blood flow, peak flow velocity and intravascular diameter.
2.4.5. Lower limb function
The nerve conduction function of the affected limb before and after treatment was measured by KeypointIV electromyographic evoked potential instrument with the patient in the lying position, including the indices of sensory nerve conduction velocity and motor nerve conduction velocity.
2.4.6. Clinical efficacy
Markedly effective: clinical symptoms and signs completely disappeared or significantly reduced, and trauma healing exceeded 90%; Effective: clinical symptoms and signs significantly reduced, and trauma healing was 60%-90%; Ineffective: clinical symptoms and signs did not improve or even worsened, and trauma healing was less than 10%. Total efficiency = markedly effective + effective.
2.5. Statistical analysis
SPSS23.0 was used for data analyses. The count data were expressed as N (%) and tested with the chi-square test. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (Mean ± SD); an independent sample t-test was used for intergroup comparisons and paired sample t-test was used for intragroup comparisons. A difference in statistical significance was indicated by P < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Perioperative indices
Patients in the observation group had significantly better perioperative indices versus those in the control group (P<0.05). (
Table 2)
3.2. Skin temperature of the affected limb, ankle-brachial indices, and sensory threshold
Antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning resulted in significantly higher skin temperature of the affected limb and lower ankle-brachial indices and sensory threshold versus VSD (P<0.05). (
Table 3)
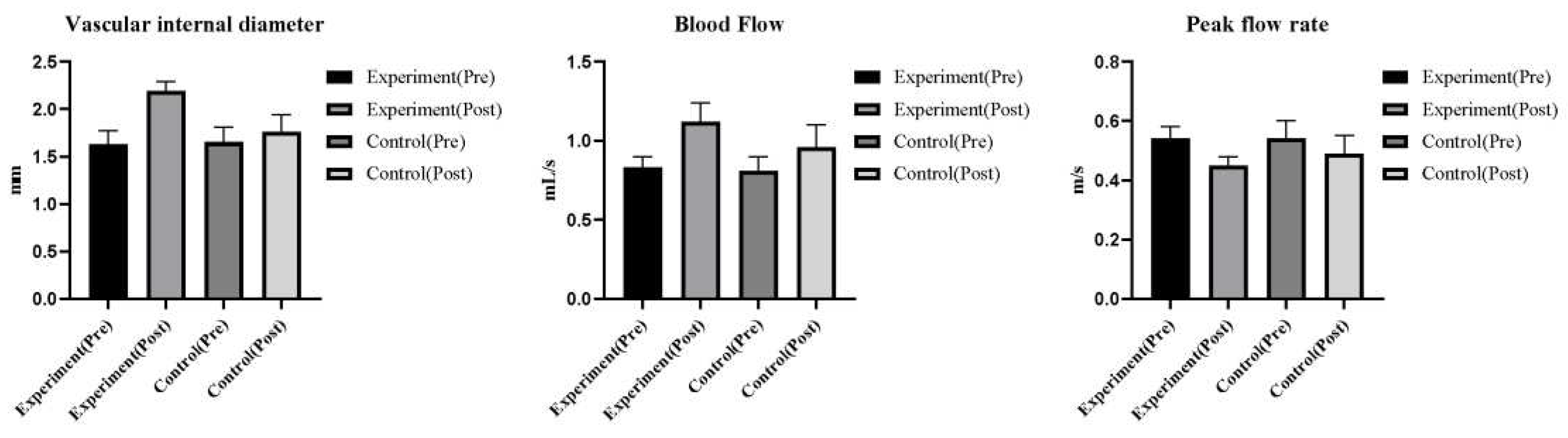
3.3. Dorsalis pedis artery hemodynamics
The differences in dorsalis pedis artery vascular internal diameter, blood flow and peak flow velocity between the two groups were not statistically significant before treatment (P>0.05). In both groups after treatment, the dorsalis pedis arteriosus internal diameter and blood flow increased and the peak flow velocity decreased (P<0.05), with significantly greater results in the observation group, and a lower peak flow velocity was observed in the observation group than in the control group (P<0.05). (
Figure 1)
3.4. Wound healing
Before treatment, the difference in trauma area, transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen and trauma pH between the two groups did not come up to the statistical standard (P>0.05). After treatment, the observation group showed a significantly smaller trauma area, a lower trauma pH and higher transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen than the control group (P<0.05). (
Table 4)
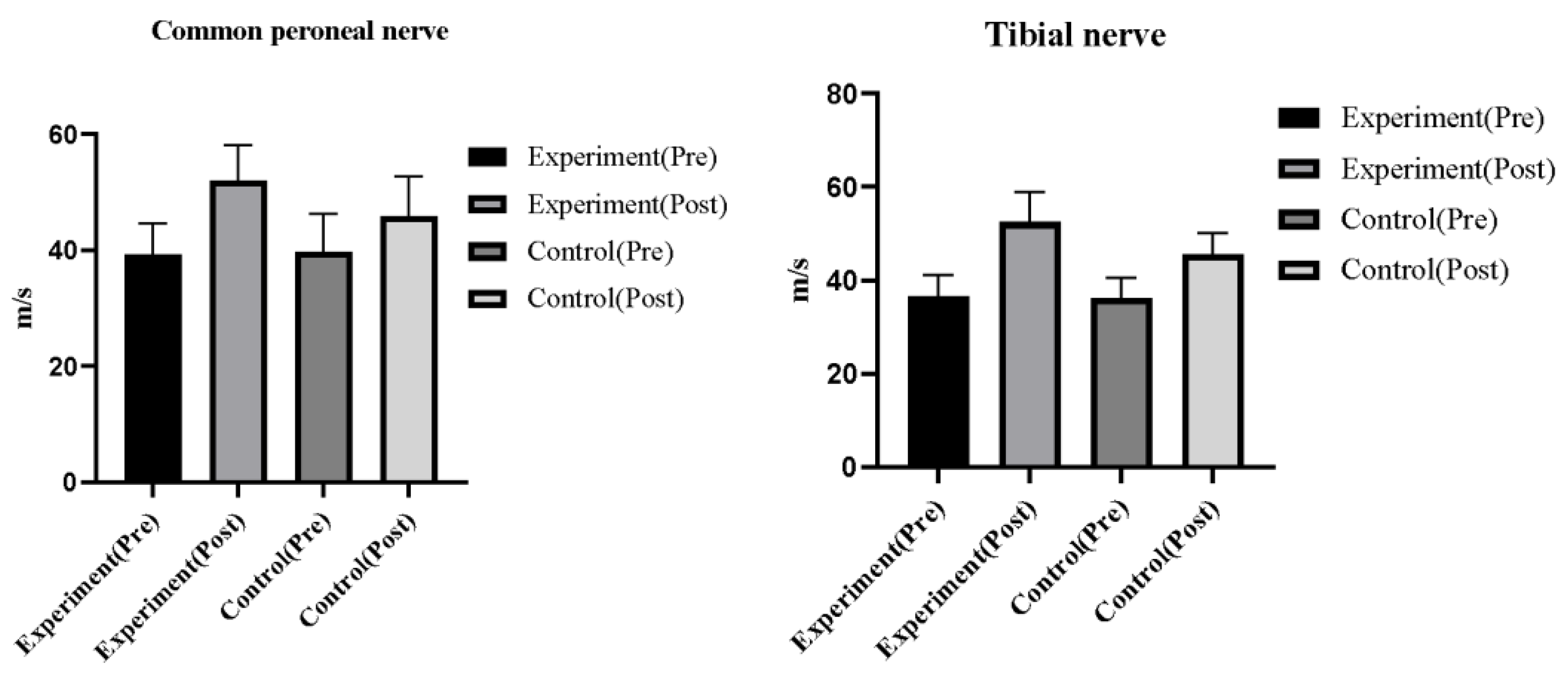
3.5. Lower extremity nerve conduction function
There was no statistically significant difference in common peroneal nerve sensory conduction velocity and tibial nerve motor conduction velocity between the two groups of patients before treatment (P>0.05). Compared with before treatment, the sensory conduction velocity of the common peroneal nerve and the motor conduction velocity of the tibial nerve increased in both groups after treatment (P<0.05), with better outcomes in the observation group versus the control group (P<0.05). (
Figure 2)
3.6. Clinical efficacy
Antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning resulted in significantly higher treatment efficiency versus VSD (P<0.05). (
Table 5)
4. Discussion
Diabetic foot is a foot ulcer, infection and tissue destruction caused by neurological and vascular lesions in diabetic patients with high morbidity, mortality and amputation rates [
15,
16]. The prevalence of DF in diabetic patients is 12 to 25%, and the International Diabetes Federation reports an estimated 9.1 to 26.1 million new DF cases each year. Patients with DF have a 2.5-fold increased risk of death compared to diabetic patients without foot trauma [
17], and DF is poorly treated with a high risk of recurrence. It has been reported that the recurrence rate is 40%, 60%, and 65% within 1, 3, and 5 years, respectively. In addition, research has shown that the risk of amputation in diabetic patients is 10 to 30 times higher than in non-diabetic patients [
18]. Hence, there exists an urgent need to explore more effective treatment methods for DF.
The results of the present study showed that antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning resulted in significantly higher treatment efficiency and transcutaneous partial pressure of oxygen, smaller wound, and lower trauma pH versus VSD, suggesting that antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning contributes to potentiating the treatment efficacy and reducing the foot ulcer trauma, thereby facilitating rapid recovery. Patients given antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning had larger vascular internal diameter and blood flow and better sensory conduction velocity of the common peroneal nerve and the motor conduction velocity of the tibial nerve versus those given VSD, indicating its vascular and neurological benefits. The reason may be that tibial lateral bone repositioning reduces damage to all surrounding tissues including the periosteum, bone tissue and surrounding soft tissues [
19]. By laterally pulling the tibial bone fragment, a continuous, slow and steady pulling stress was given to the living tissue to stimulate the simultaneous regeneration of bones, muscles, blood vessels and nerves in the body. This technique effectively improves lower limb blood flow and neuropathy, promotes microcirculation regeneration in the affected limb, restores blood flow to the foot and ankle trauma, and also activates the regenerative potential of traumatic soft tissues to improve the healing rate of infected wounds [
20]. Antibiotic bone cement on the surface of diabetic foot ulcers can form an induced membrane, from which multiple cytokines, such as vascular endothelial growth factor, angiogenesis-related factors and TGF-β, can be secreted to promote the repair and healing of ulcer wounds. In addition, the rich vascular network system formed around the ulcer by the induced membrane can play a great role in improving the blood supply to the diabetic foot wound, increasing the local resistance to infection, and promoting the survival of the later implant or flap repair of the diabetic foot wound [
21,
22]. Chinese doctors were the first in the world to adopt tibial lateral bone repositioning for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers and vasculitis ulcers and achieved good results with a low recurrence rate. In this study, tibial lateral bone repositioning combined with antibiotic bone cement resulted in successful limb preservation and disease healing. However, this technique is still under development, progress and improvement, and there remain various issues to be addressed. The issues are mainly focused on the unclear mechanisms and principles of the technique, the unstable effect, and the presence of serious complications such as flap necrosis, medically induced fractures, and even death. Some elderly patients with diabetic foot were long-term bedridden after fracture and died during treatment with complications such as thrombosis and pulmonary infection [
23]. The main technical mechanism of the procedure is the provision of a controlled and adjustable trauma stimulus. The body produces a repair response to trauma when it is exposed to trauma, and this trauma-repair response allows for the repair of trauma, mainly by cytokines at the molecular level, whose possible factors include but are not limited to multiple inflammatory factors, growth factors, bone morphogenetic proteins, and stem cell mobilization [
24,
25].
The advantages of antibiotic bone cement: (1) Antibiotic bone cement covered on the ulcer wound induces the formation of an induced membrane, which secretes a series of factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor, angiogenesis-related factor, and transforming growth factor-β. These factors accelerate wound healing, and the induced membrane creates a rich vascular system that improves local blood supply, enhances anti-infection effects, and promotes rapid wound healing [
26]. (2) Compared with intravenous or oral antibiotics, antibiotic bone cement releases a significantly higher concentration of antibiotics, longer duration of action, has more significant local bactericidal ability, and prevents the development of drug-resistant bacteria, thereby creating a good antibacterial environment, contributing to the control of traumatic infections and reducing the adverse effects produced by prolonged systemic administration [
27]. (3) The antibiotic bone cement provides close apposition to the ulcerated wound, removes the ineffective cavity, enhances the antibiotic efficacy, and creates a better environment for wound healing, with easy operation, short operation time, and lower difficulty of second stage wound closure [
28]. This study has the following limitations: (1) the sample size of this study was small and only a single-center trial was conducted, which is subject to selective bias; (2) it was not possible to evaluate the test results blindly during the study, which was subject to measurement bias; (3) long-term efficacy evaluation was absent.
5. Conclusion
Antibiotic bone cement plus lateral bone repositioning enhances the treatment efficiency, boosts trauma healing, and promotes postoperative functional recovery of patients. The research provides new solutions to improve efficiency and avoid complications. The theory of "trauma-repair and regeneration-reconstruction system" can well explain the surgical mechanism and the principle of action, and put forward new ideas for the repair of trauma at the molecular level, such as inflammatory factors, regenerative factors, stem cell mobilization and information transfer. Regardless of the confirmation and falsification, there is a wide space and research prospect for further active exploration. It is expected that a large number of investigators and patients will cooperate to conduct clinical studies with larger samples in the future to provide more clinical evidence for the research and application of this method.
Author Contributions
Wei Shang and Peichao Liu designed the research study. Xinhua Cheng and Xiaotao Wang performed the research. Yonggui Yu conducted the experiments, analyzed the data. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Guiding project of Shiyan Science and Technology Bureau, No.22Y51. Hubei Provincial Health Commission's 2021-2022 Health Research General Project, No: WJ2021M052.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate; The protocol was approved by the ethics committee of Renmin Hospital,Hubei University of Medicine. Ethical No.:1591792.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
References
- T. L. Coye, C. Foote, P. Stasko, "Prevalence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in diabetic foot infections in the United States: A systematic review and meta-analysis," Foot & Ankle Surgery: Techniques, Reports & Cases, vol. 2, no. 2,2022.
- B. L. Gwilym, E. Mazumdar, G. Naik, T. Tolley, K. Harding, D. Bosanquet, "Initial reduction in ulcer size as a prognostic indicator for complete wound healing: a systematic review of diabetic foot and venous leg ulcers.," Advances in Wound Care, vol., no.,2022.
- E. Imre, E. Imre, "Polypharmacy is Associated with Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Type 2 Diabetes mellitus.," The international journal of lower extremity wounds, vol., no.,2022.
- Z. Fan, D. Liu, "Impairment characteristics of static balance and pedis load distribution of patients undergoing tibial cortex transverse distraction for diabetic foot ulcers.," Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, vol. 17, no. 1,2022.
- C. E. Holterman, R. L. Myette, D. Burger, C. R. Kennedy, "A letter to the editor about “dopamine 1 receptor activation protects mouse diabetic podocytes injury via regulating the PKA/NOX-5/p38 MAPK axis”," EXPERIMENTAL CELL RESEARCH, vol., no. prepublish,2022.
- A. Bal, S. K. Jain, Jagannath et al., "Efficacy and Safety of Topical Solution of Diperoxochloric Acid for Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcer: Results from a Phase 3, Multicentre, Randomized, Active-controlled, Parallel-group Study.," The international journal of lower extremity wounds, vol., no.,2022.
- I. A. Anaya, D. M. Zequera, "Fourier transform-based data augmentation in deep learning for diabetic foot thermograph classification," Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, vol., no. prepublish,2022.
- S. Pandey, M. Shaif, T. M. Ansari, A. Shamim, P. Kushwaha, "Leveraging Potential of Nanotherapeutics in Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcer.," Experimental and clinical endocrinology & diabetes : official journal, German Society of Endocrinology [and] German Diabetes Association, vol., no.,2022.
- H. M. Badahdah, T. Zgonis, "External Fixation for Surgical Offloading of the Diabetic Foot," Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery, vol. 39, no. 2,2022.
- S. Ou, C. Xu, Y. Yang et al., "Transverse Tibial Bone Transport Enhances Distraction Osteogenesis and Vascularization in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot.," Orthopaedic Surgery, vol., no.,2022.
- S. Ou, C. Xu, G. Li et al., "[Effect of transverse tibial bone transport on expression of serum angiogenesis-related growth factors].," Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi = Zhongguo xiufu chongjian waike zazhi = Chinese journal of reparative and reconstructive surgery, vol. 34, no. 1,2020.
- B. Wang, Z. P. Gong, Y. J. Liu et al., "[A case of diabetic foot treated with fibula transversal bone transfer and micro-vascular network regeneration].," Zhonghua yi xue za zhi, vol. 100, no. 9,2020.
- M. Lapray, J. M. Petit, C. Fourmont, A. Rouland, B. Vergès, B. Bouillet, "Healing of diabetic foot ulcers is independently associated with the use of angiotensin receptor blockers but not with those of diuretics and angiotensin conversion enzyme inhibitors," DIABETES & METABOLISM, vol., no. prepublish,2022.
- M. Lapray, J. M. Petit, C. Fourmont, A. Rouland, B. Vergès, B. Bouillet, "Healing of diabetic foot ulcers is independently associated with the use of angiotensin receptor blockers but not with those of diuretics and angiotensin conversion enzyme inhibitors," DIABETES & METABOLISM, vol., no. prepublish,2022.
- L. Qiu, Y. Li, C. Yang et al., "Influence of Foot Ulceration on All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Diabetic Patients: A Case-Control Study," Journal of Wound, Ostomy & Continence Nursing, vol. 49, no. 2,2022.
- K. Mnif, F. Smaoui, H. Chaabouni et al., "Diabetic foot osteitis: more than double trouble," METABOLISM-CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL, vol. 128, no. S,2022.
- J. Bonnet, A. Sultan, "Narrative Review of the Relationship Between CKD and Diabetic Foot Ulcer," Kidney International Reports, vol. 7, no. 3,2022.
- W. Yu, T. Zhang, H. Xu, "Role of Dipeptidyl Dipeptidase 4 Inhibitors in the Management of Diabetic Foot.," The international journal of lower extremity wounds, vol., no.,2022.
- H. Li, J. You, C. Liu, Y. Ma, "[Effectiveness of transverse tibial bone transport in treatment of diabetic foot ulcer].," Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi = Zhongguo xiufu chongjian waike zazhi = Chinese journal of reparative and reconstructive surgery, vol. 33, no. 1,2019.
- X. J. Cao, Z. W. Jia, X. S. Guo et al., "[Experimental study on the improvement of Ilizarov transverse tibial bone transport and microcirculation reconstruction technique].," Zhonghua yi xue za zhi, vol. 99, no. 45,2019.
- E. R. E. Mendame, H. Zhang, B. Qi, A. Yu, "Application and Clinical Effectiveness of Antibiotic-Loaded Bone Cement to Promote Soft Tissue Granulation in the Treatment of Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Ulcers Complicated by Osteomyelitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial," Journal of Diabetes Research, vol. 2021, no.,2021.
- X. Ding, Y. Yuan, H. Lu et al., "Analysis of the Effect of Antibiotic Bone Cement in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer through Tibia Transverse Transport.," Orthopaedic Surgery, vol., no.,2022.
- Q. Zuo, F. Gao, H. Song, J. Zhou, "Application of Ilizarov transverse tibial bone transport and microcirculation reconstruction in the treatment of chronic ischemic diseases in lower limbs.," Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, vol. 16, no. 2,2018.
- Y. Sun, Y. Xiao, H. Wang, "[Transverse tibial bone movement for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers].," Zhongguo gu shang = China journal of orthopaedics and traumatology, vol. 31, no. 10,2018.
- B. Wang, W. Liu, Y. Huo et al., "[Application of femoral-femoral artery bypass grafting combined with transverse tibial bone transporting for lower extremity arteriosclerosis obliterans or combined with diabetic foot].," Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi = Zhongguo xiufu chongjian waike zazhi = Chinese journal of reparative and reconstructive surgery, vol. 32, no. 12,2018.
- C. Huankai, J. L. Wu, T. N. Mok, L. Simin, "Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer with Tibial Transverse Transport Combined with Antibiotic Bone Cement, a Case Report," Journal of Surgery, vol. 9, no. 2,2021.
- H. J. Huang, X. H. Niu, G. L. Yang et al., "[Clinical effects of application of antibiotic bone cement in wounds of diabetic foot ulcers].," Zhonghua shao shang za zhi = Zhonghua shaoshang zazhi = Chinese journal of burns, vol. 35, no. 6,2019.
- S. J. Park, S. Song, "Risk Factors for the Treatment Failure of Antibiotic-Loaded Cement Spacer Insertion in Diabetic Foot Infection," Journal of Korean Foot and Ankle Society, vol. 23, no. 2,2019.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).