1. Introduction
Set design has gained recognition in recent years and has established itself in the 21st century as a strong means for corporate promotion, particularly in terms of communicating products and services. In this context, it is observed that companies and major brands require creative strategic planning to survive in increasingly competitive markets, hence the prudent application of scenographic design to enhance product visibility and trust. This has become necessary due to the competitive nature of advertising and marketing in most sectors of the economy, as a result of globalization, modernity, and technological advancement [
1].
The application of scenography production occurs in all fields where a scenic language is needed to present a spectacle, recording set, Tailor Made (TM) - customized adaptation of a project for a client/brand. Its use takes place in the artistic realm, in TV, theater, cinema, as well as in the consumer environment, in commercial stands, shops, bars, restaurants, and also in marketing and advertising, with brand establishment activations, shows, and events. In Brazil today, there is a very special configuration for the scenographic market and all forms of culture, which provides a very attractive moment for this market niche.
In a cultural context, good branding practices provide brand recognition and preference [
1]. This implies that customers remember and choose a brand over others due to the value and visual appeal of the produced product. This idea is an organizational tool whose successful implementation largely depends on meeting the strategic, organizational, and communicational context in which it is used. In both cases, the corporate brand brings to marketing the ability to explicitly use the company’s vision and culture as part of its unique selling proposition [
2].
This unique and personalized vision underscores the need for qualified and well-prepared professionals to execute Tailor Made projects within the more complex and lucrative scenographic environment.
This study aims primarily to reduce cognitive load in reading Technical Drawings (TD) of TM projects. Secondly, it can identify the spatial abilities of the participants, thus diagnosing facilitating factors that will allow for better communication between scenography and creative teams (project clients - marketing/promotional agencies, in general).
In addition, studies [
3] [
4] [
5] related to the importance of detailing and organizing TDs reveal improvements in quality control, production agility, cost reduction, documentation, and even project safety. The study can also identify the impact of inadequate drawings in the company’s current production processes, as well as the perception of results obtained from the use of technical drawings developed with the assistance of specific programs integrated with AR to facilitate the interpretation of technical information.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 lists the existing works directly related to the topic of this research.
Section 3 describes the development process of the proposed artifact.
Section 4 describes the experiment performed and
Section 5 how the artifact was validated, while
Section 6 discusses its main findings. Finally,
Section 7 draws conclusions about the work and lists future work directions.
2. Related Work
In this section, the functionalities and characteristics of AR-based tools for the project are analyzed based on the literature review. Some of these tools are unavailable as they were developed exclusively for experimentation/scientific studies. Therefore, their analysis is based solely on the information obtained from the literature.
The category of AR tools with purposes to mediate cognitive activities of reading/interpreting TD encompasses artifacts that allow for the representation of 3D models, visualization of object/product information, interaction with models and/or their information, animations, and instructions (teaching/learning activities). Some tools are linked to pedagogical models, such as the Virtual Augmented Book [
6], which allows for visualizing three-dimensional objects and completing tasks aimed at developing spatial skills in engineering students.
Other tools enable similar approaches to the same activity or workflow, such as AR-Dehaes [
6,
7], as well as studies on the relationship between AR and traditional educational materials [
4], all directed towards engineering students. Among the analyzed similar artifacts, only TaDiMA and the "self-disassembly" experiment in AR [
5,
8] have industrial applications, respectively focused on Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and artifact assembly lines. Furthermore, these two studies are also the only ones that utilize RAM.
Each tool was analyzed, and the results are presented in Table 1 of Appendix A. This analysis of similar tools aims to contribute to the elicitation of design requirements for the digital artifact.
3. Artifact Development
In this stage, the design of an artifact that aims to meet the needs elicited in this research takes place. Based on the obtained information, the development process of the artifact was initiated, aiming to fulfill the requirements.
Despite the different approaches used in the analyzed similar artifacts, what was sought in each of them can be summarized, in general, in two characteristics: improving spatial ability components through the use of AR for training and teaching purposes, and optimizing access to product information in TD, meaning implementing AR with only minor changes to the company’s product lifecycle process. Only one of the tools, TaDiMa, encompassed these objectives as a relatively intuitive system that mostly met the project requirements. TaDiMa is based on a flexible access database for Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), using a tangible/graphical user interface and AR. The user can introduce a tangible element with visual markers in their workspace (office desk, meeting table, production bench, etc.). These markers can be printed or attached as stickers on paper, in this case, technical drawings. The solution utilizes a flexible combination of benefits from a Graphical Interface (GI) and a Tangible Interface (TI), taking advantage of each approach’s strengths. The user can explore the TI for intuitive navigation of the model and the GI for precise control of information (e.g., through touch screen, digital pen, mouse, keyboard).
This stage aimed to develop a web-based instantiation of AR to provide elements that will allow for future implementation in the TD system of scenography warehouses, thus becoming a feasible alternative for future adoption in the development process of new products in these scenarios. The following are the alternatives developed during the interactions, presented and analyzed.
3.1. Configuration of the 3D Model and TD
This alternative was developed using Autodesk Maya 2018 and Adobe Illustrator. Its main characteristic was the development of the 3D model from the original SVG files of the Plywood Chair, its texturing and animation for Web AR platforms, as well as the definition of physical content - inserted in the TD, and the integration of AR through delivery methods in the TD.
Thus, the starting point for the development of the proposed mediating artifact was the choice of the model to be used for the study. To do so, the product proposed for the study had to meet two main characteristics: having more than one construction/assembly stage and belonging to the scenographic production repertoire. Therefore, a furniture item - the Plywood Chair - was used for automated execution in a CNC Router, which improves automation and flexibility in the warehouse, with multiple parts and fitting and assembly stages. The files contained are SVG files to be cut directly with CNC or printed and cut with a bandsaw. The SVG files are exported from the chair modeled in 18mm plywood or 3/4 inch (19.05mm). The SVG files cannot be used with any other plywood thickness. To use thinner or thicker plywood, the model needs to be modified according to that thickness.
Figure 1 shows the final optimized 3D model of the Plywood Chair for use in Web AR, respecting the previously established requirements.
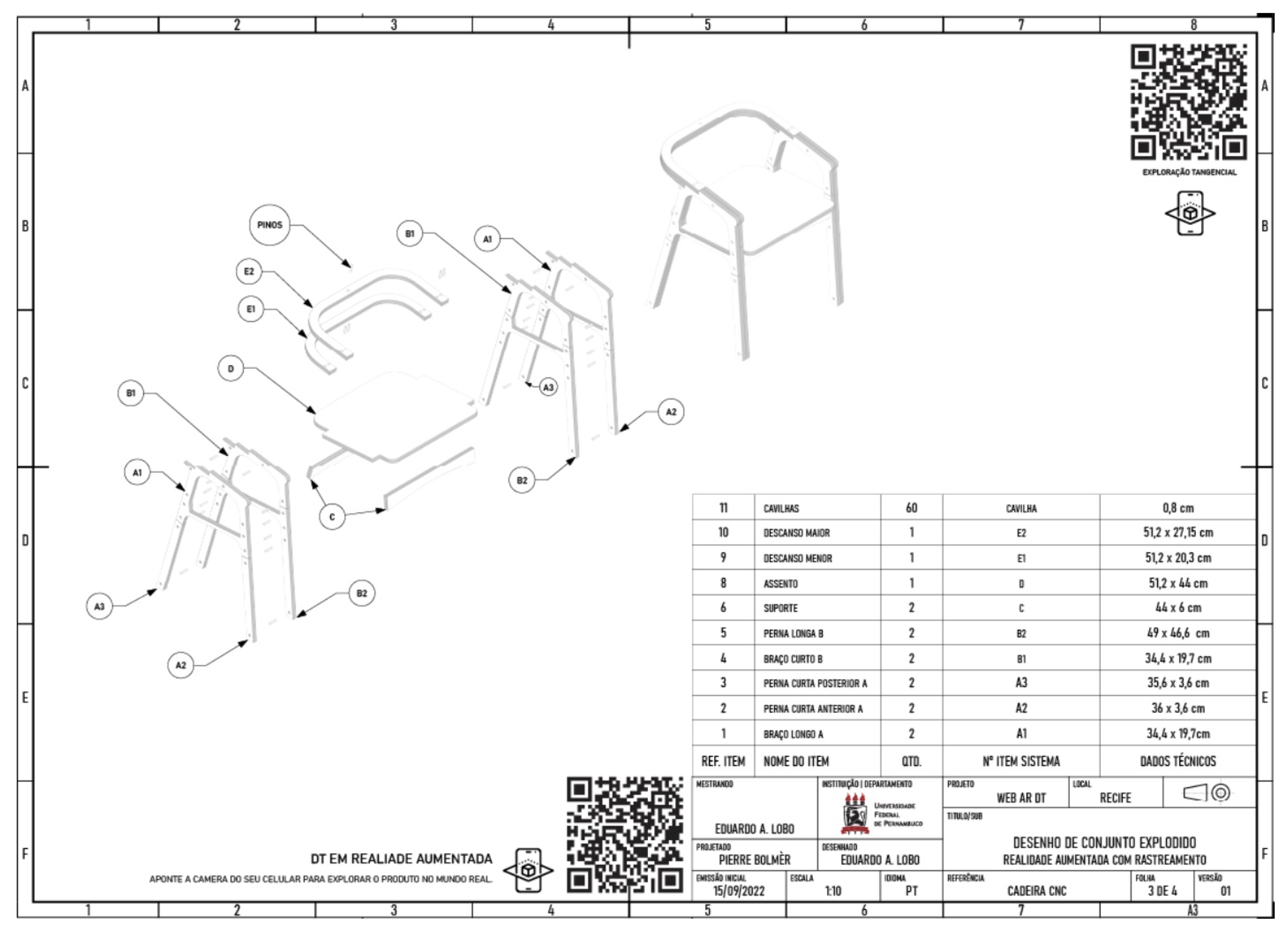
After defining the 3D model, the TD Sheets were created. Four technical sheets were configured - see Appendix B, to address the model in its fullest understanding, with the following content defined:
Sheet 1: Introduction to the model;
Sheet 2: Orthographic views;
Sheet 3: Exploded view with markings;
Sheet 4: Assembly stages.
Figure 2 shows the final result of the TD sheet designed for the A3 format. The use of QR Code was chosen as the method to deliver AR seamlessly in the scenographic environment. In addition, brief instructions for QR code usage were included, considering the possibility of low familiarity with the technology among some participants.
3.2. Augmented TD Implementation
This stage is aimed at configuring the 3D models, animations accessible to Web AR platforms, and integration capabilities. This interaction was developed using the MyWebAR and Vectary platforms. MyWebAR is an online Web AR service that allows the use of online editors to build interactions compatible with various mobile browsers and operating systems through a project. The motivation for using this platform lies in its ability to support the playback of videos and 3D animations, as well as more advanced interactive implementations, such as starting/pausing an animation through the implementation of augmented buttons (virtually projected onto the real world).
Additionally, the platform encompasses multiple tracking features, such as Image Tracking, Surface Tracking (Instant Tracking), and VSLAM, allowing for the association of multiple types of AR associated with the usage intentions of this research to mediate each spatial skills capability.
3.3. Animated Models
After previous iteration, some limitations regarding Web AR providers and the study’s hardware were identified.
Therefore, for Sheet 2, an animation was developed for the folding present in the TD, considering the ABNT format (First Angle Projection). To maintain visual coherence and address new solution parameters, the model was applied with native material and hexadecimal color (without the use of textures). This resulted in a scene loading time of less than 5 seconds, even with the animation included. Additionally, simulated lighting was used, where an invisible plane is created over the TD map to capture the object’s shadow. This creates a perception that the model is truly integrated into the TD and the real world.
For this sheet, the applied AR used hybrid tracking, benefiting from VSLAM, which combines the advantages of IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units) and mobile device cameras. When scanning the QR code, the user positions the 100% augmented (holographic) TD in the real world. Once positioned, it is possible to rotate, zoom in, or zoom out the TD. This solution simulates a traditional view of the TD but with the benefits of enlarging the TD sheet to a more comfortable size for studying the object. Additionally, a button located in the center of the TD allows for the initiation of the 3D model’s animation, illustrating a folding motion between views. This process also aims to instruct workers on the spatial orientation relationship between the parts (a problem identified during the initial visits to the scenography warehouses, explained in the problem awareness stage).
3.4. Direct Hand Manipulation
Having verified the use of tangential and direct manipulation with hands in all similar artifacts, an artifact was developed for manipulating the 3D model in AR. Despite all the similar artifacts having tangential experience, many had limitations because the projection was mirrored on monitor screens, causing cognitive dissonance [
9] [
10].
Figure 3 shows the final model of the tangible artifact, with an ergonomic flap for manipulating the board, made of triplex paper/cardboard sheet. For the purposes of this research, the flap provides a preview of the final model, without a QR code. The delivery method is enabled through Sheets 3 and 4, Exploded View and Assembly Steps, respectively. This allows participants to explore through more than one spatial valence, considering moderating factors among users, such as media expertise, which makes model rotation more intuitive for some individuals.
4. Experiment
This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of UFPE. The individuals who participated in the research signed the Informed Consent Form and provided permissions for the use of their image and testimonial.
A total of 15 participants were involved in the research, divided into 2 analysis groups with distinct objectives. Group 1 consisted of 9 participants and focused on the awareness stage, while Group 2 had 6 participants and focused on evaluating the prescribed artifact as a mediating tool. Their participation contributed to the development of heuristics and project requirements, as well as the understanding of the surrounding behavioral conjectures. The participants were professionals working in the scenographic industry, involved in theater projects, both in the production line (project execution) and in the creative activities of the sector (project development).
In this context, the proposed artifact was tested under conditions similar to those observed in the scenographic warehouses using the observation framework. The demonstration setup encompassed the main spatial characteristics, including natural/artificial lighting, a restricted workspace (a 75 cm support table), and evaluation periods during both day and night. Working with augmented reality in low-light environments was considered a challenge, as it could cause the virtual model to shift in the real world.
Figure 4 shows the arrangement of the Augmented TD, composed of 4 Sheets printed on A3 75g paper, along with the tangible manipulation board with a printed usable area of 20x20 cm, attached to a rigid cardboard panel.
The demonstration of the 4 sheets was performed using the Galaxy S10 Plus, with a 4G connection. The demonstration of Sheet 1 - Introduction to the model verified important parameters for the execution of AR such as: estimation of the real distance of the 3D model in scale in the real world, estimated by ARCore. This capability was confirmed by measuring the model in real size projected with a ruler placed under the object (with a margin of error of 0.5 to 1 cm). The tracking and occlusion of objects capability. The platform was able to recognize objects and surfaces with delays of 1 to 2 seconds when exposed in the foreground, i.e., closer than the positioning of the artifact - generally quite satisfactory. Regarding the functional integration, the artifact can (in the demonstration) maintain the same conventional reading behaviors of the physical design template, except for the fact that it is viewed through the smartphone, resulting in little change in the operating mode.
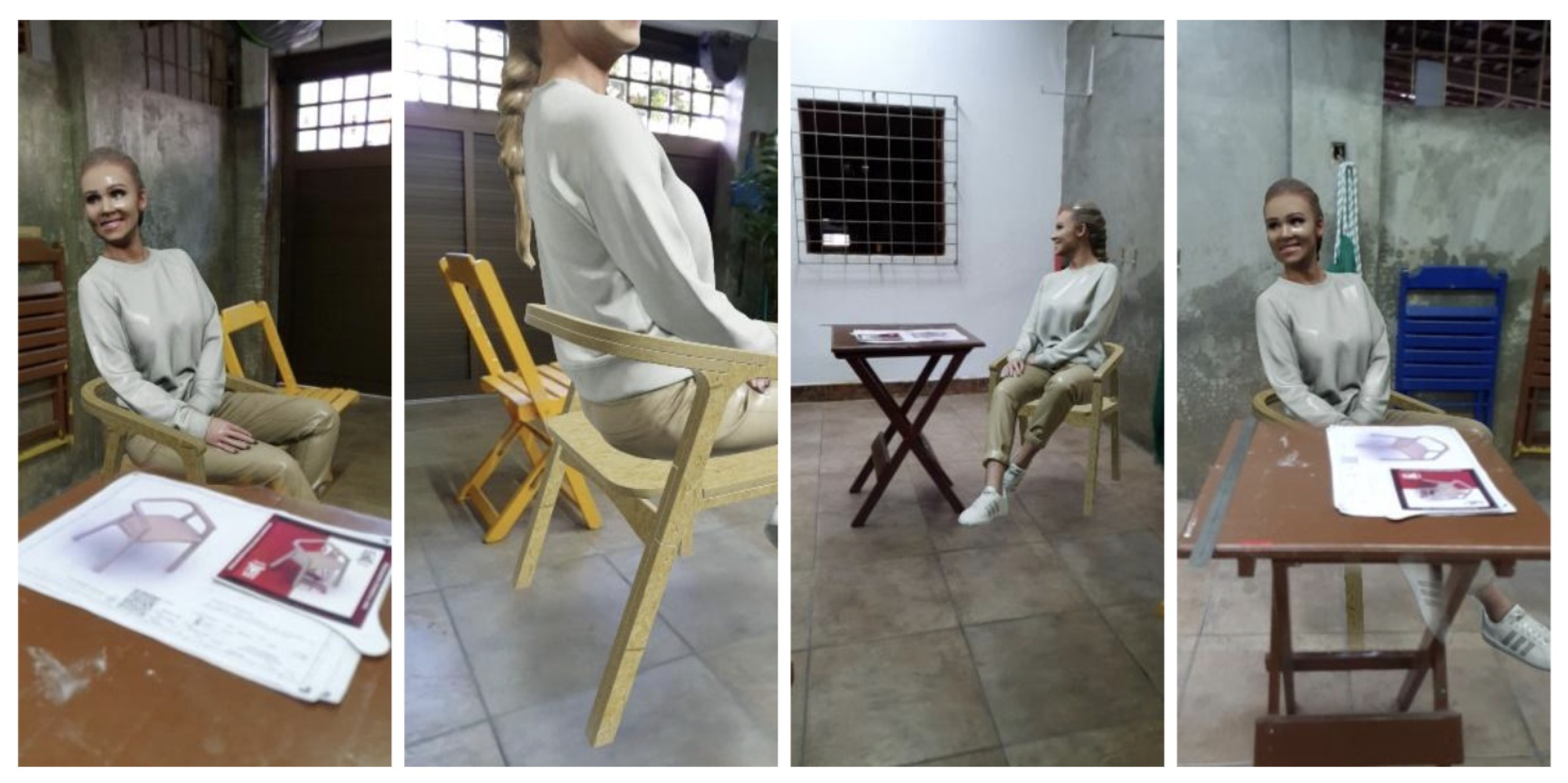
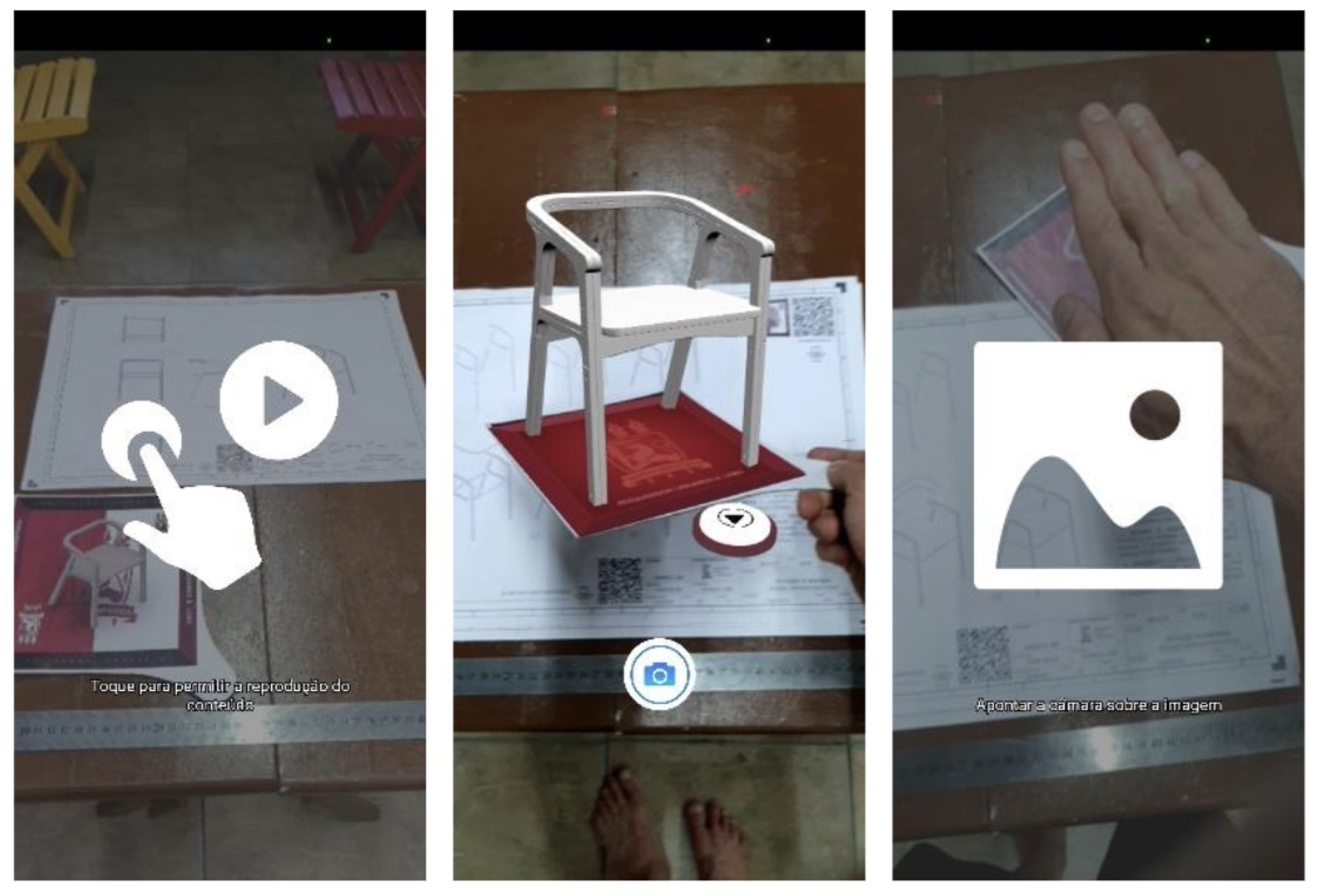
Figure 5 demonstrates the use of AR for Sheet 1, visualizing the projected product in the real world.
Figure 6 demonstrates the AR experience using a female reference model measuring 1.70 m. The tests positively evaluated the responsiveness of the algorithm in interpreting foreground objects, further integrating the projected 3D model and the intended use of the artifact. The use of the ergonomic reference contributed to the understanding of the product, as there was an initial perception that the artifact would be excessively smaller or in a reduced scale.
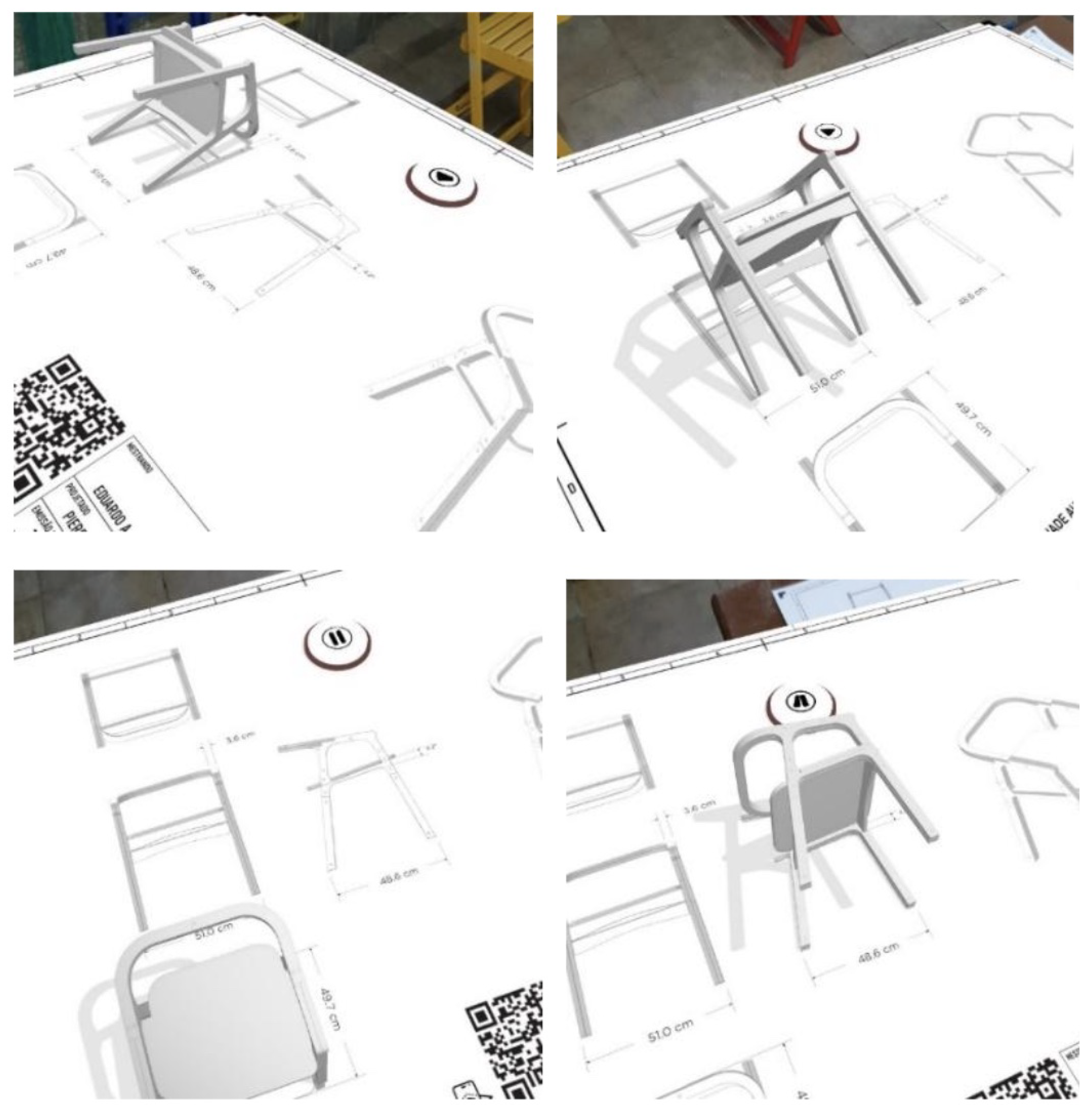
Sheet 2 addressed important aspects of spatial capabilities. The folding animation of the model on the conventional sheet of the TD allowed for instruction and assistance in the assimilation process of more complex products through the tool.
Figure 7 shows the static primitive interaction (rotation and scale of the projected TD) and dynamic interaction (exploration from different angles and positioning of the mobile device).
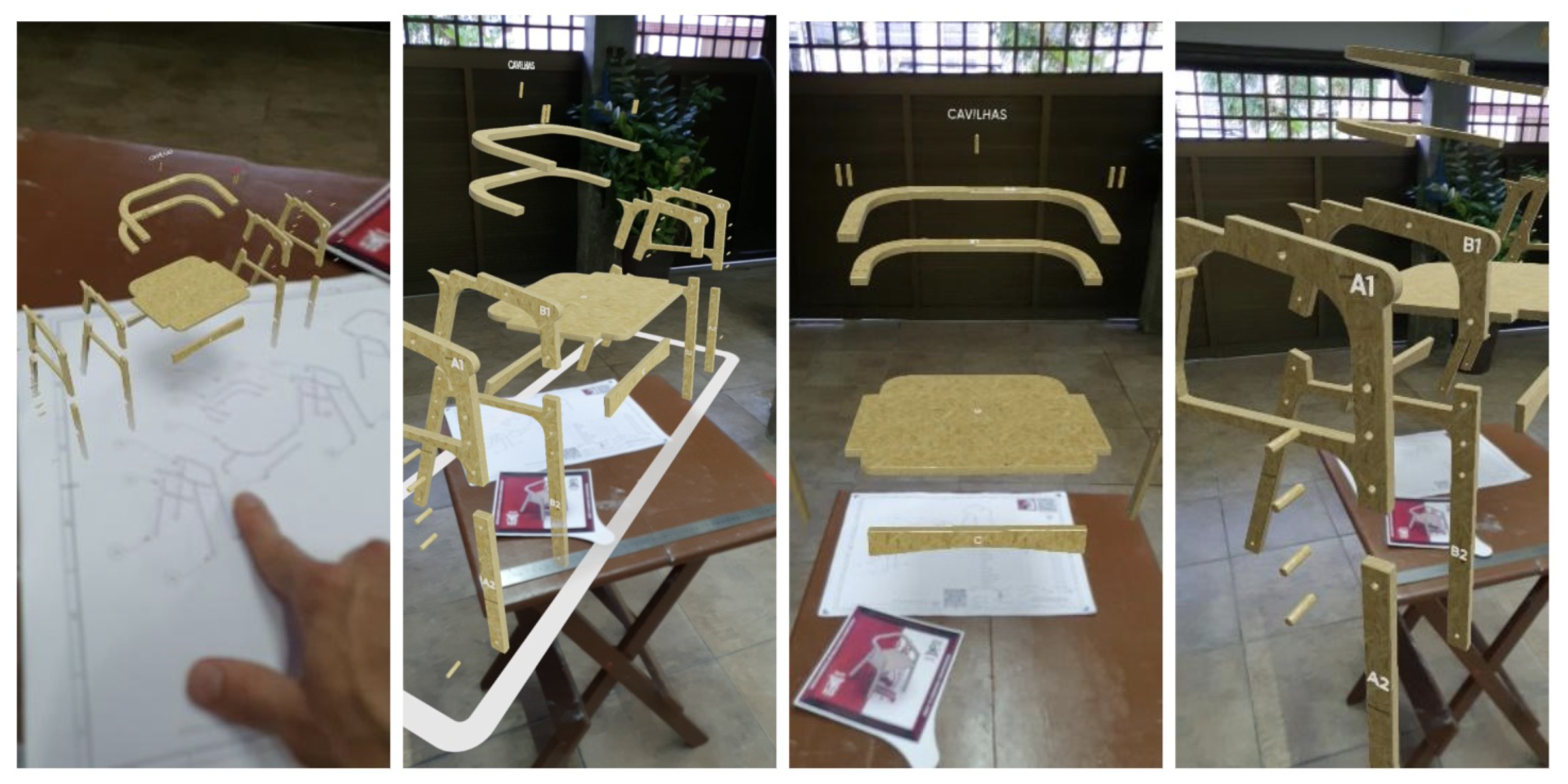
Sheet 3 utilized surface tracking system, which allowed the artifact to be (re)positioned throughout space using Instant Tracking, enabling various inferences of the model - in conjunction with the physical TD or projected throughout the environment. This allowed for exploring the product from different angles with multiple integration possibilities, optimizing work environments (
Figure 8).
The following demonstrations were performed during the nighttime to test the quality of camera tracking and possible image tracking failures.
Sheet 4, which considers assembly instructions for the model, includes animation and the use of VSLAM. The results were satisfactory.
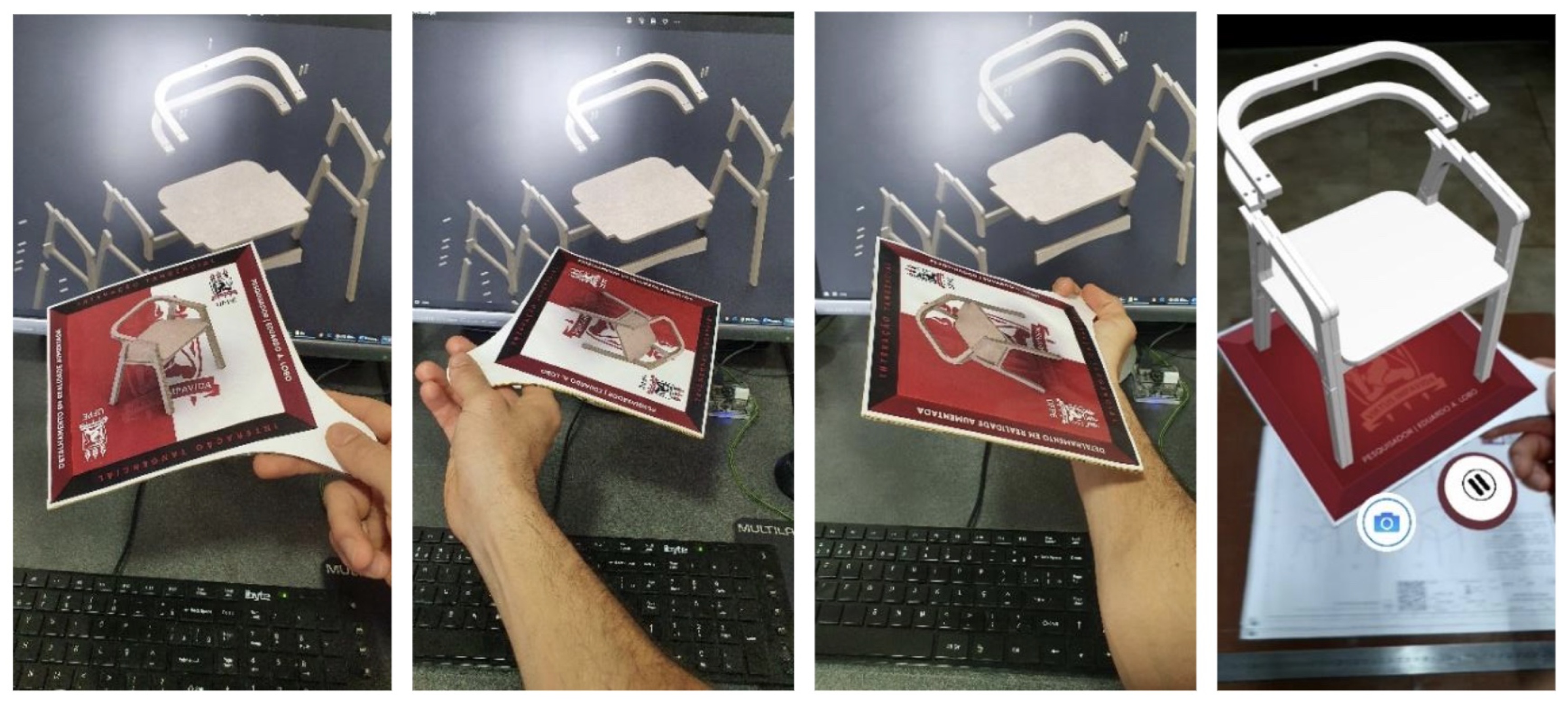
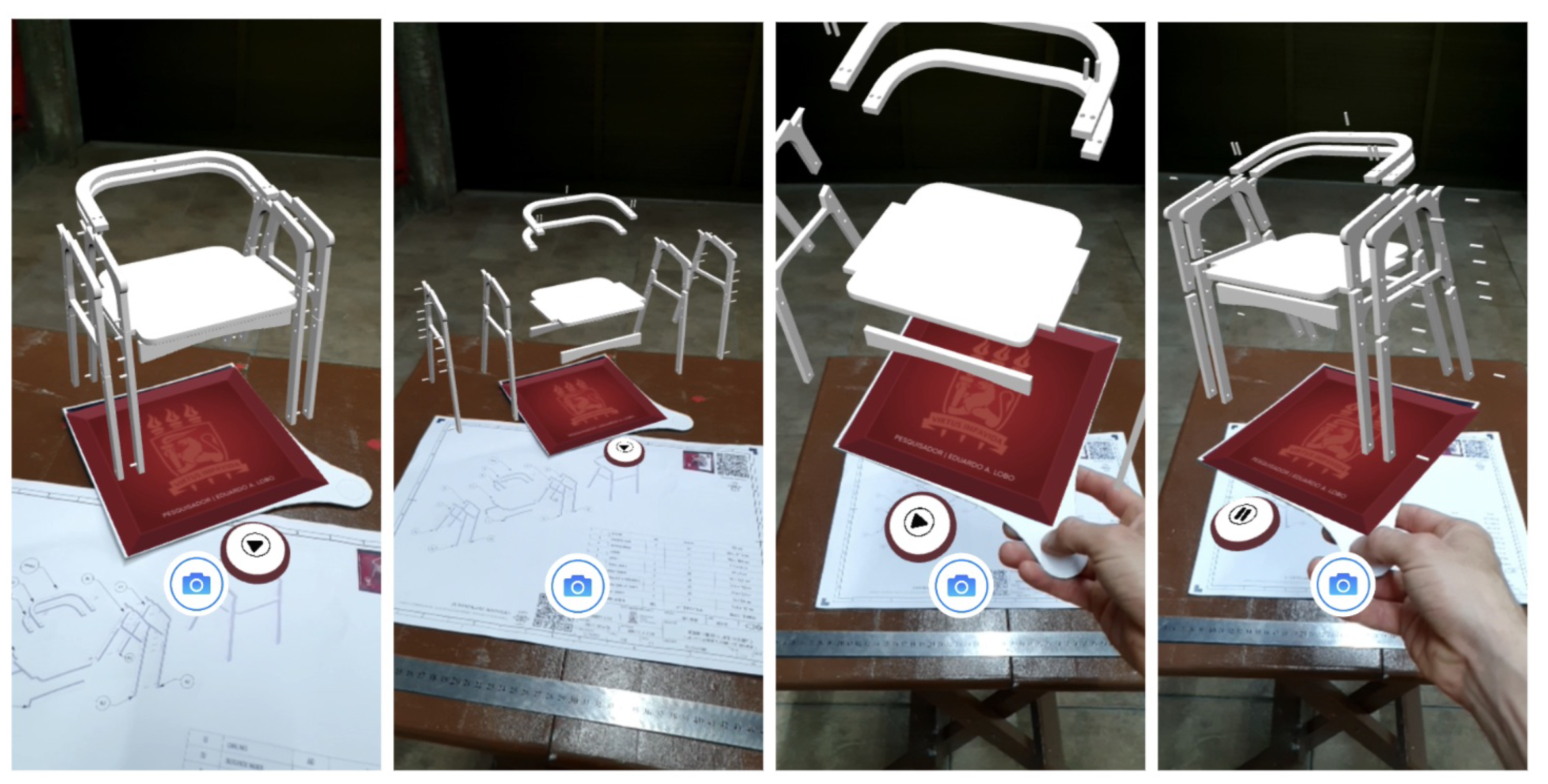
Next, demonstrations of the Augmented TD using the tangible board are performed, allowing for free exploration of the model with one hand. The quality of tracking, integration of the Play/Pause button, recording (saving the visualization as photo and video), and responsive screens to tracking errors were verified (
Figure 9).
All the above-mentioned features performed satisfactorily, except for the recording modes. Considering that the registration is done via WebRTC (meaning that the recording takes place through screen recording on the server and in real-time, causing network overload), it caused the mobile device to freeze in all attempts, preventing the recording of videos longer than 3 seconds. On the other hand, the photo capture feature continued to work properly (with only a 1-second lag at the moment of capturing). It was also observed that the registration process causes a displacement of the key reference point, which can cognitively overload the understanding of the interface for new users.
The following demonstration aimed to verify the animated 3D model of Sheet 3 - exploded view. The animation transitions between the object and the exploded view, seeking to drastically reduce cognitive load [
11]. As previously mentioned, the model with native material and a visual appearance similar to the detail sheet was used, along with the Play/Pause button.
Figure 10 shows the simulations of using the tangential board in relation to the TD sheet and the workspace. The user can pause the model explosion at any point during the transition to study the relationship between the parts or the fittings of each item, relying on the intuition of static or dynamic interactions.
In a complementary manner, possible ways of exploring the 3D model in combination with the TD sheet were investigated. Thus, dynamic interactions were evaluated through manipulation using either the mobile phone or the tangential board - fixed on the surface, which served as a second form of exploration (aimed at individuals with less AR expertise). This approach allows for viewing the model by rotating it around the vertical axis (component of spatial rotation) while interacting with the mobile phone (spatial orientation), thereby segmenting the amount of information accommodated for the user.
The conducted demonstrations of the instantiation artifact demonstrated solidity in recognizing the key points configured for use in the physical interaction with the tangential board (there was no leakage or deviation of the image on the texture, indicating a good contrast construction of the reference image). Furthermore, the final configuration defined, combining static realistic models with animated texture-less models, proved to be relevant as the instantiation artifact gains connectivity (with loading time less than 5 seconds) and robustness (with excellent image tracking performance, no leakage, even during nighttime, including simultaneous movement of the physical artifact and parts of the model).
5. Evaluation
The evaluation of the artifact took place in two dimensions:
To assess the acceptance, intention, and use of the technology, as well as the workload, an empirical study was conducted using the artifact. The study was carried out in two scenography companies in Recife - Baluarte and Ceno Mais. Four evaluations were conducted in one scenography, and two evaluations in the other, respectively.
The data were compiled as a single evaluation group, comprising a total of 6 participants in this final evaluation. In each scenography, activities of reading and interpreting the TD were carried out for the evaluation designed for the use of Augmented TD - the mediation tool. The evaluation sessions were recorded or documented in the form of images and videos, respecting the users’ comfort regarding the recording methods. In addition to observations, acceptance, intention, and technology usage questionnaires were administered to the participants, as well as the NASA TLX, to obtain specific data in a systematic manner.
The following describes the empirical evaluations carried out in the scenography environments. Subsequently, the evaluated data is presented.
The evaluation involved participants from different sectors of scenography, such as executive management, production coordination, carpentry, machine control, and 3D modeling. Each participant was instructed to read and interpret the Augmented TD, which included the proposed study piece - a plywood chair executed with CNC Router. The 4 physical forms in A3 format were provided to each participant in their respective work environment for observation and behavioral analysis of their interactions with the artifact. The first 30 seconds of reading and manipulation of each Sheet (4) were narratively guided to help participants understand the tool’s usage possibilities and the different types of applied AR.
The A3 format forms were well accepted due to the better dimension of the information contained, compared to the conventional A4 format used in the environment. In general, conventional form readings were quickly performed by participants when compared to exploration using AR triggers, due to the novelty effect [
12] and the wow factor [
13] of using the platform.
One of the most frequently used features of the platform to assist in understanding the chair project was the use of AR to verify the real size of the model and comprehend the purpose of the product, which also encompasses the structural and functional perception of the model.
It was observed that all participants had little to no prior experience with AR technology. Therefore, brief instructions were provided on the interaction gestures to position, rotate, and scale the object in AR.
Sheet 2 - Orthographic Views received positive feedback from participants due to the fact that it displayed the TD itself in AR. This allowed them to scale the physical form to the desired dimension and interact with the animated 3D model on top of it. Participants responded positively to the technique of viewing and pausing the model animation, stating that it facilitated memorizing the relationships of each object side to the TD.
The exploration of the exploded model in AR preferably involved placing it on the floor rather than the table, considering the distance between the model items. Participants also used this configuration to better understand the product’s fittings, as the animated stages did not have labeling of the components.
The direct hand interaction approach using the tangible board in Sheets 3 and 4 made a great impression on the participants, with positive feedback and comments about the ease of manipulating the 3D model, exploring it from any angle - even considered easier than on-screen interaction, which was also possible in Sheets 1 and 3.
In general, the use of the tangible board allowed for greater freedom of use and applications, as it was a more intuitive navigation feature compared to dynamic and static interaction on a mobile device. It is important to note that regardless of the available space, AR could be used effectively in all study environments - indoor, outdoor, with natural and artificial lighting, as well as during daytime and nighttime shifts.
The relationships between people, practices, problems, and artifacts corroborated with the practices of the Augmented TD. The artifact, in addition to offering its intended functions, also had side effects on this practice as well as on other practices [
14].
5.1. NASA TLX (POST-EXPERIMENT)
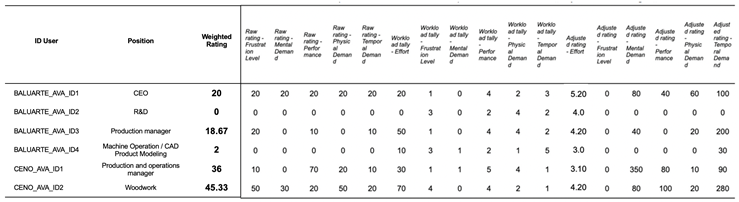
The application of NASA-TLX (POST-EXPERIMENT) took place immediately after the activity of reading and interpreting the Augmented TD. This evaluation allowed for a subjective analysis of the degree of impact of the tool in the scenography environment. The data extracted from the method are described in
Table 1. The evaluation of the tool’s usage encompassed both scenography companies, compiling the data jointly to obtain a result that reflects the participants’ performance in using the Augmented TD, regardless of the company. This aims to visualize the effectiveness of the mediation tool at the sector level, not just the organizational level.
The high production demand within the scenography settings, driven by tight production deadlines, contributed to the inconsistent availability of some participants. In other words, the evaluation of workload conducted with the Augmented TD (NASA-TLX POST-EXPERIMENT) was also performed with new individuals.
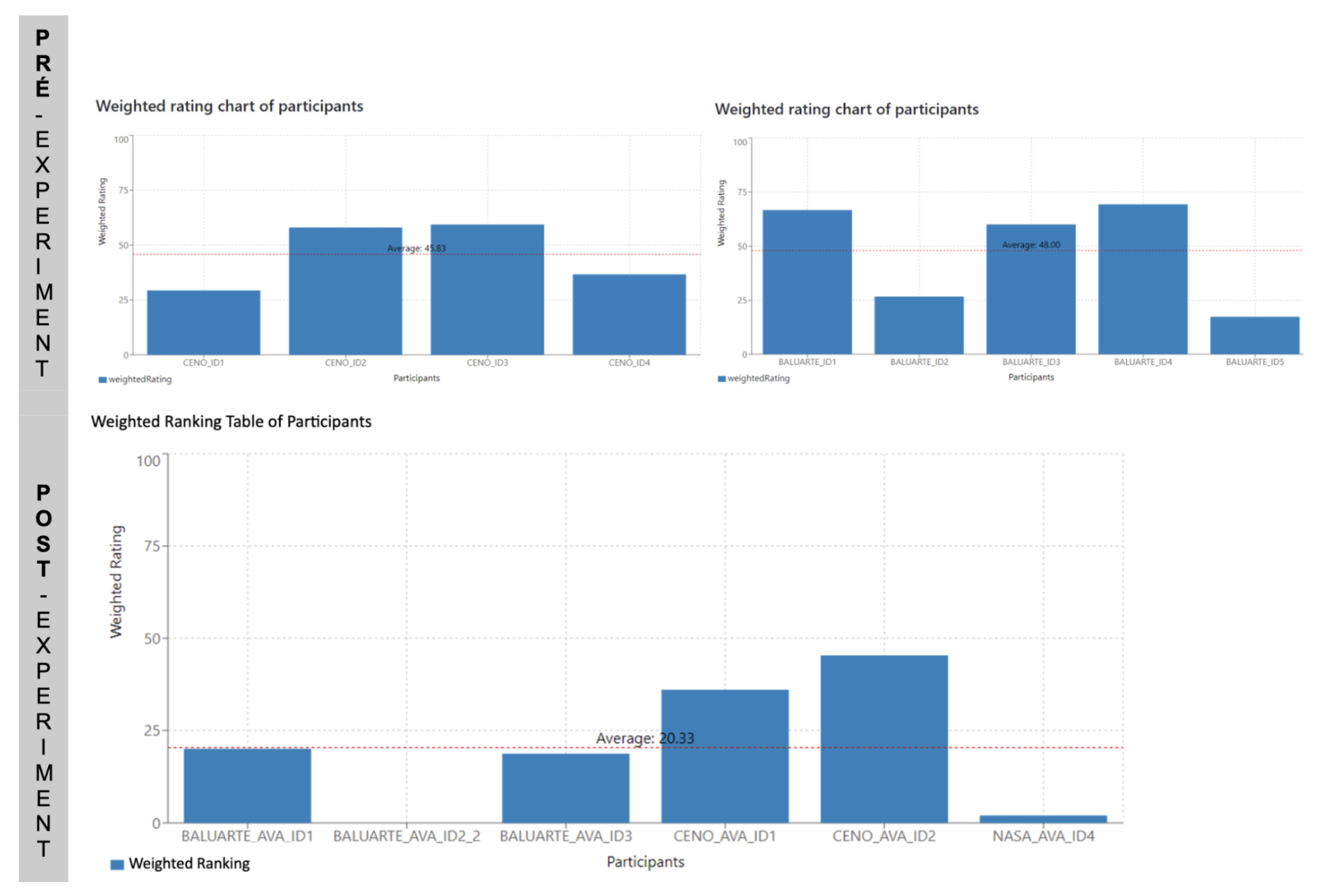
The data from the table above is illustrated in
Figure 11. In the top row, it can be observed that the weighted index of participants was 45.8 and 48 points in the evaluation of workload using conventional TDs (NASA-TLX PRE-EXPERIMENT). This is higher than the index recorded in the second test (NASA-TLX POST-EXPERIMENT), which was 20.3 points. This corresponds to a significant average reduction of 56.7% in the overall workload related to TD reading in scenography.
Despite this second NASA-TLX test not having the same participants, it was possible to analyze the data in this format. Figure 96 illustrates some of these data. The figure shows the data from the Production and Operations Manager of Ceno Mais and the Executive Director of Baluarte Group. The weighted ratings show an average reduction of 37.9% (from 58 to 36) in the participant’s workload index, primarily impacting effort, frustration, and temporal demands. On the other hand, the analysis of individual data showed that the new tool increased mental demand significantly, with a lesser impact on performance demand. This aligns with some characteristics predicted in the literature [
12], such as moderating factors of AR expertise that can increase cognitive processes, in this case, the mental demand for using the tool. Thus, despite being the first contact with this type of technology, the participant reported good usability and intuitiveness of the platform, as well as an intention to use the tool in the future. Despite the increase in mental demand due to the use of a new platform in the operational ecosystem, the ratings were quite satisfactory.
Among the recurring individuals in Groups 1 and 2 are the participants: Production Manager (Ceno Mais), Production Manager (Baluarte), and Executive Director (Baluarte), as illustrated in Figure 96. The weighted ratings from NASA-TLX (POST-EXPERIMENT) were 36, 18.67, and 20 points, respectively. These were significantly lower than the ratings in NASA-TLX (PRE-EXPERIMENT): 58, 26, and 67 points, respectively. This illustrates reductions of 62%, 70%, and 29.9%, respectively, in the workload index. With these data, a general weighted average reduction of 53.9% is observed among the recurring participants.
Further analysis of the data from these participants reveals that the Augmented TD tool, by adding a new layer of interaction (the Web AR interface) to the reading activity, had an impact on the participants’ mental demand. This demonstrates the additional efforts required to assimilate new information associated with the use of the new interface while performing the same type of task. However, the benefits generated by this extra effort outweigh the gains in overall demand in other work scales, with the most significant benefits observed in the demand for time and mental effort. This mental effort is associated with how much the individual had to work (mentally and physically) to achieve their performance level. As for temporal demand, it is associated with how pressured the individual felt (or would feel) due to the pace at which tasks or task elements occurred (would occur in daily life) with the use of the Augmented TD.
5.2. Technology Acceptance, Intention, and Use Questionnaire
The objective questionnaire, consisting of 37 items, was administered to evaluate user satisfaction with the Augmented TD. It was given after the interaction with the artifact, allowing participants to express their agreement. The questions are structured using a 7-point scale. Low scores are better than high scores due to the anchor points used (completely agree / completely disagree), except for the Anxiety construct (where higher scores are better, due to the phrasing of the negative statements).
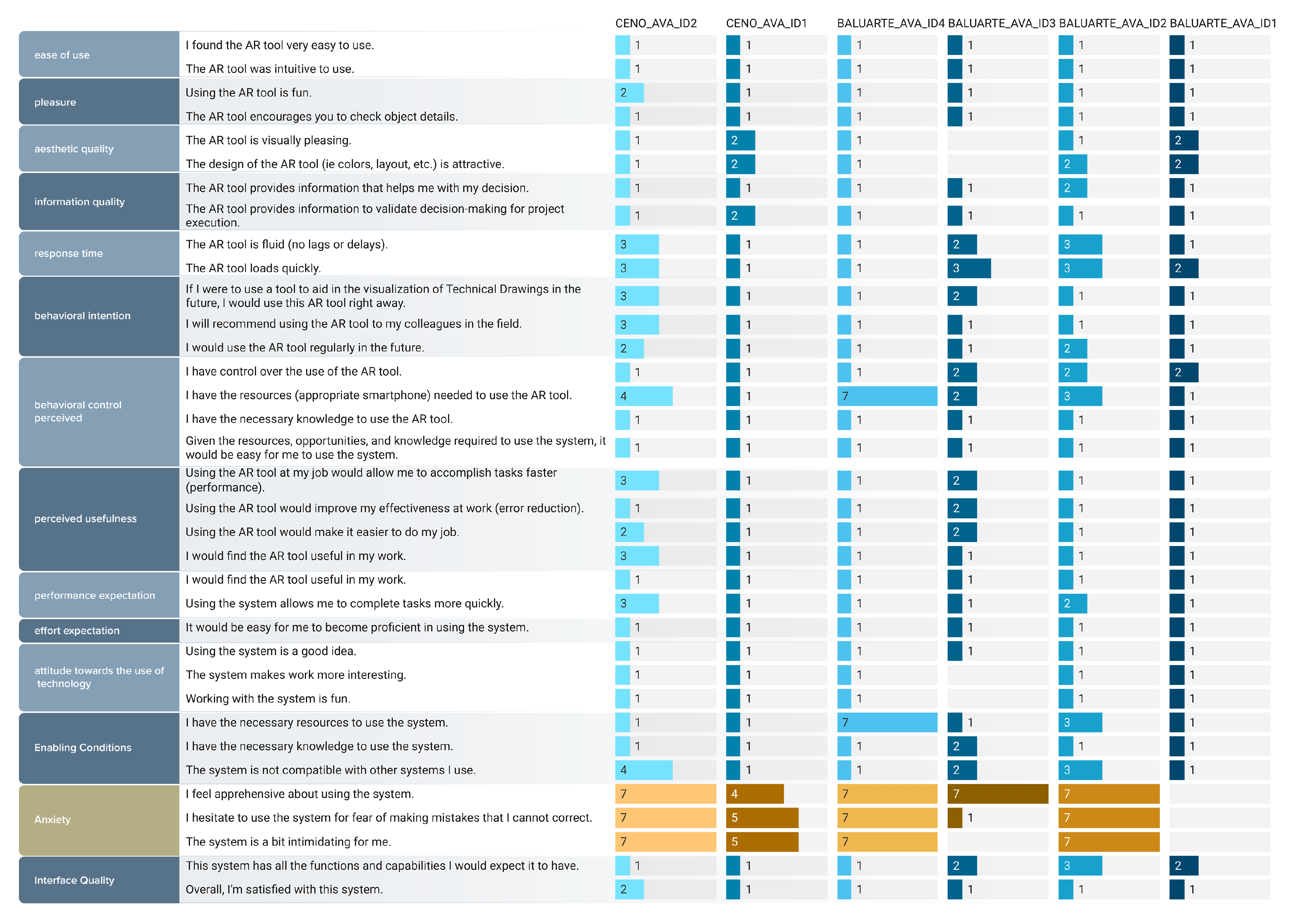
Figure 12 presents the compilation of results - the Technology Acceptance, Intention, and Use Questionnaire: the graph shows the agreement scale for each participant, with their data compared column-wise.
Overall, participants favored the Augmented TD over the conventional TD. Almost unanimously, participants appreciated the ease of use, enjoyment, aesthetic and informational quality, perceived usefulness, and overall interface quality provided by the mediation tool. However, constructs of perceived behavioral control and facilitating conditions diverged among some participants - these were associated with the resources (adequate devices) for using the Augmented TD.
The main criticism that the Augmented TD received was regarding its compatibility with devices. The versions of devices used by the workers and the available model of the set design result in a poor experience when a large number of textures are loaded, for example, in Augmented TD Sheet 1. However, Baluarte expressed interest in replacing the devices so that the technique could be immediately implemented into the workflow (in the short term).
In positive analyses, participants found it intuitive and very easy to use. The Augmented TD offered them a clear, smooth, and faster interaction experience to understand the project. Additionally, some participants mentioned excellent perceived behavioral control, both when they already had the knowledge to use it and when provided with the necessary resources, opportunities, and knowledge to use the platform. The tool also received good emotional evaluations - concerning the constructs of anxiety, intention, and attitude toward the use and control of the platform. Throughout the research, the instructions given in the first minute of interaction with each of the 4 sheets allowed participants to instantly grasp the technique. In light of this, some participants noted that manipulating the object virtually directly with their hands is ergonomically more pleasant than manipulating it directly on the screen.
6. Discussion
One of the main aspects to highlight was the adopted methodology, which decisively contributed to the conduction of this research and the attainment of results. DSR provided reliable development, suggesting the organization and sequencing of the necessary steps to solve the problem.
Typically, the results of DSR are communicated to the research and technical/practice communities, that is, stakeholders in the research, such as in this case, scenography companies, which may include technology-oriented and management-oriented audiences. The results of this method may also be of broad interest, making it worthwhile to communicate them to the general public [
14].
The software tools used in this research, such as CitNetExplorer and Vos Viewer, were crucial for visualizing and analyzing citation networks of scientific publications, constructing and visualizing bibliometric networks, analyzing the development of the research field over time, identifying relevant literature on the research topic, and creating bibliometric analysis networks to build the theoretical foundation.
The present research aimed to solve a problem related to understanding Design Thinking in scenographic production in the creative industry, which encompasses TM projects. The prescribed artifact, called Augmented TD, is a mediation tool focused on the cognitive activity of reading TDs, designed for the aforementioned contexts. Its configuration was built as the interface between its internal environment (with characteristics that shaped the mediator artifact itself, as observed from the theoretical basis) and the external environment (the conditions in which this artifact operates) to fulfill its purpose, meeting the requirements elucidated throughout the method. However, it is not expected that the implementation of a single artifact, such as the proposed one, can completely transform a reality. However, as observed from the theoretical basis, advances in this field are achieved through interactions that collectively help generate and disseminate new ideas and best practices.
One of the main aspects to highlight was the adopted methodology, which decisively contributed to the conduction of this research and the obtaining of results. DSR provided a reliable development approach, suggesting the organization and sequencing of the necessary steps to solve the problem.
The software tools used in this research, such as CitNetExplorer and Vos Viewer, were crucial for visualizing and analyzing citation networks of scientific publications, constructing and visualizing bibliometric networks, analyzing the development of the research field over time, identifying the literature related to the research topic, and creating bibliometric analysis networks to build the theoretical foundation.
This research aimed to solve a problem related to understanding Augmented Reality (AR) in the scenographic production of the creative industry, which encompasses Technical Drawings (TD) projects. The prescribed artifact, called Augmented TD (DT) in this research, is a mediation tool focused on the cognitive activity of reading TDs, designed for the aforementioned contexts. Its configuration was built as the interface between its internal environment (with characteristics that shaped the mediator artifact itself, as observed from the theoretical foundation) and the external environment (the conditions in which this artifact operates) to fulfill its purpose according to the requirements elucidated throughout the method. However, it is not expected that the implementation of such an artifact, as proposed, can completely change the reality. Nonetheless, as observed from the theoretical foundation, advances in this area are achieved through interactions that, collectively, help generate and disseminate new ideas and best practices.
The analysis of functionalities and features of similar tools obtained from the literature review, focused on projects in similar usage contexts (reading TDs with AR technologies), showed a limited variety of approaches, especially in those published in the same usage context (assembly line, business environment, or operational industries). In most of them, there is a clear search for a system that assists college students (in engineering) in visualization tasks to promote the development of their spatial skills. The artifact in this research utilizes Web-based Augmented Reality (Web AR), justified by its ability to mediate spatial cognitive processes with a system characterized by the use of embodied cognition (cognitive activities distributed by the individual and the situation they interact with) and situated cognition (practice in real contexts, increasing focus, performance, and learning), as well as its ease of use and implementation within existing processes in these usage scenarios.
Based on the data collected from the literature review and the results obtained in the empirical study, it is considered that the artifact proved to be acceptable, although it is not possible to provide an absolute answer to this research question. Participants found the Augmented TD to be very easy to use (ease of use), visually pleasing (aesthetic quality), and overall enjoyable to use (hedonic motivation). Participants expressed a willingness to use it "immediately" for visualizing project TDs (behavioral intention) and suggested that using the system would be a good idea (attitude towards technology use). These and other aspects, extracted from the acceptance, intention, and technology use questionnaire, lead to the conclusion that the artifact has the potential to be accepted by professionals in the field. However, some limitations of the prototype became evident, such as the perceived response time of the artifact, which received higher ratings on the evaluation scale for fluidity perception (lags and platform loading). Furthermore, even the devices capable of using Web AR systems still experienced lags due to hardware limitations. Additionally, most of the devices used by the participants were not suitable for platform use due to their version being lower than the requirement for running ARCore and ARKit.
Overall, participants are in favor of adopting Augmented TD or Mobile AR technology because its application in the scenography context does not require much time or specific technical knowledge (training requirement). Furthermore, the management of one of the scenography projects showed great interest in the tested solution, suggesting the development of internal training for qualified professionals to use Mobile AR, focusing on its implementation in the product lifecycle (facilitating the understanding of models and crucial technical decision-making processes such as machining, welding, cutting, electrical installation, etc.) and in the product assembly line (aiming to improve the quality line and the accuracy of design interpretation). Based on these aspects, it is possible to affirm that the proposition of Augmented TD would have broad acceptance within the scenography sector, being an artifact with low impact on its process.
It is also recognized that Augmented TD is a proposed method to be applied in TM projects within scenographic environments, rather than a finished product that can be installed and accompanied by a manual and technical support. Additionally, despite the relatively low implementation cost, its replication still requires technical qualifications regarding the processes of modeling in 3D animation software and visual effects, which involve modeling, UV mesh construction, texturing, and lighting in order to execute (upload to Web AR platforms) various types of models compatible with mobile devices. These processes need to be implemented for each new TD. This also highlights one of the limitations in its replication, as it requires designers with 3D modeling and animation hard skills. However, this task can be considered of low to medium complexity and can be carried out by qualified professionals, making the process feasible within the market. These are the nuances regarding its replication in the usual context and within the scope of scenographic production.
The final important question to address is about data awareness. A significant number of participants expressed concerns about exposing their image or submitting to research evaluations, such as undergoing extensive HE tests or the NASA-TLX, questioning whether these evaluations would be performance-related to their role in the company. Despite the support from management, this made it difficult to obtain a larger number of professional participants (both in the awareness and final evaluation stages) since their participation was explicitly voluntary. However, for those who participated in the research, their comfort and surprise with the final proposal of Mobile AR technology, the Augmented TD, were emphasized. At the end of the artifact evaluations, they questioned whether it would be implemented in the company.
7. Conclusion
AR technologies represent very useful tools for visualizing and interacting with 3D models, with Web AR being a new effective and fast way to create high-quality, accessible, and cross-platform AR content. The projection of the 3D model into the real environment provided users with the possibility of a realistic and dynamic perception of traditional physical TDs. A method was presented to implement 3D models into TDs using Web AR platforms. The advantage of the proposed system is the reduction of cognitive effort required for users to understand TM project TDs. This approach proved to be a powerful tool that improved user efficiency compared to traditional methods.
Thus, this research suggested that the use of AR could contribute to improving the reading and understanding of TDs in scenographic production, through its application by workers in their real work context, such as scenography workshops. To achieve this solution, the general objective was to propose a digital artifact with these characteristics for the design of this mediation tool, subsequently referred to as Augmented TD.
In this perspective, the artifact was designed to: enable its use in the scenography environment as a cognitive mediator for reading DTs (Design Technicals); have both physical interfaces (printed cards, direct interaction board) and digital interfaces (AR); run on Web AR platforms; provide access to AR through QR codes; offer marker-based and markerless AR tracking. This will contribute to tangential interactions and exploratory navigations, encoding egocentric project visualizations and allocentric model visualizations; utilize third-party computational methods; allow for recording or capturing images for sharing ideas and insights; enable the development of associative activities (direct hand interaction); use virtual labeling schemes; explore structural and functional prototyping; provide access to TD files in the cloud (on mobile devices).
The results obtained from the development of the artifact indicated that the method was successful, in accordance with the requirements identified in the research, with the exception of the combination of visualizations, network efficiency, and computational efficiency. The combination of visualizations was considered "partially met." In this case, the artifact did not virtually combine different types of visualizations, but through the AR interface, it was possible to visualize the model interacting with distinct visual content present in the physical world (e.g., labeling information on card 3 combined with an animated exploded view of the model in AR). Network efficiency achieved partial validation due to high loading times observed for cards 1 and 3, which were caused by the use of textures (even limited to 1024px) to meet the graphical requirements for model vividness in the system. This overload of data download also impacted computational efficiency in some device models, resulting in occasional lags when bringing the camera closer to the 3D model projected on the screen by the platform in the real world.
This study also demonstrated, through workload comparison indexes, that participants’ self-assessed workload is a reliable indicator of their actual workload costs. This was corroborated by the scale indexes obtained from the questionnaire assessing the behavioral intention to use Augmented TD. The NASA-TLX allowed participants to record their estimated mental workload for both TD reading conditions, for each display condition (with and without the use of Web AR), in both experiments (standard TD reading and with the use of Augmented TD). It was found that participants estimated the cognitive workload associated with significant improvement (overall weighted average reduction of 53.9%, among recurring participants, related to traditional TD reading activity).
The findings have interesting implications for the design and use of Web AR. This study showed that while the use of Web AR has the potential to enhance user performance in cognitive tasks for TD reading, certain considerations should be taken into account. Firstly, it is important to identify the users’ individual cognitive abilities. Secondly, the design of display characteristics (including tracking techniques, realism, and interaction) should be planned consistently with these abilities, ensuring efficient use and effectively reducing the spatial cognitive overload identified in the user group.
The study has some limitations. The field experiment, conducted through researcher access, was carried out with specific companies and projects, as previously described. Therefore, future research could be conducted with companies and projects of different natures and varying levels of market participation. Additionally, the experiment was conducted in scenography production environments, which limits the generalization of results and conclusions to other types of production, manufacturing, or industries.
Several future works can stem from this study. These include conducting a new evaluation of Augmented TD, considering a larger sample of people and a simplified process for collecting HE data through validation instruments. Gathering suggestions for improvements in procedures from workers and designers to further increase satisfaction and the level of learning achieved. Addressing the weaknesses of the project by implementing routines and/or procedures in scenography production environments to achieve higher quality levels. For example, identifying methods or platforms to convert universal 3D file formats such as .fbx and CAD to .usdz and .glTF, which are necessary for compatibility with Web AR systems, generally based on the ARKit and ARCore libraries.
The development of Augmented TD has revealed that these data and other aspects can be further investigated to contribute to research related to the design of new interactions using Web AR. Introducing the technology to facilitate HE also highlights the importance of understanding the work that users will perform with the tool. After all, interaction design indirectly includes the interactivity between the user and the chosen digital system for learning. The lack of Web AR systems capable of specifically mediating the understanding of TD systems is a significant gap in the field. Further research on systems using Web AR is needed to advance the use of such systems.
References
- Johnson Edu, F.K.D. SCENOGRAPHY: EXAMINING A NEW MARKETING STRATEGY FOR CORPORATE PROMOTION AND DEVELOPMENT. International Journal of Arts and Humanities 2017, 01, 477–488. [Google Scholar]
- Maklan, S.; Knox, S. Competing on Value: Bridging the gap between brand and customer value; Financial Times, 1998.
- de Avila, D.; de Morais Júnior, A.R.; Schaefer, E. A importância do Detalhamento e Organização de Desenhos Técnicos para o Gerenciamento de Projetos.
- Bergamaschi, M.P.; Silveira, I.F. Enhancing the understanding of 3D objects for engineering students: A mixed methodology of AR application and traditional educational materials. 2014 XVI Symposium on Virtual and Augmented Reality. IEEE, 2014, pp. 127–130.
- Freddi, M.; Frizziero, L. Design for disassembly and augmented reality applied to a tailstock. Actuators. MDPI, 2020, Vol. 9, p. 102.
- Roca-González, C.; Martín Gutiérrez, J.; García-Dominguez, M.; Mato Carrodeguas, M.d.C. Virtual technologies to develop visual-spatial ability in engineering students. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education 2017.
- Martín-Gutiérrez, J.; Saorín, J.L.; Contero, M.; Alcañiz, M.; Pérez-López, D.C.; Ortega, M. Design and validation of an augmented book for spatial abilities development in engineering students. Computers & Graphics 2010, 34, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino, M.; Monno, G.; Uva, A. Tangible digital master for product lifecycle management in augmented reality. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing (IJIDeM) 2009, 3, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Arita, K. Iterative design of seamless collaboration media. Communications of the ACM 1994, 37, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, D.; Vanderdonckt, J.; Macq, B. Analyzing interaction in augmented reality systems. International Workshop on Immersive Telepresence 2002, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Cockburn, A.; Karlson, A.; Bederson, B.B. A review of overview+ detail, zooming, and focus+ context interfaces. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2009, 41, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, A.; Prophet, J. The state of immersive technology research: A literature analysis. Computers in Human Behavior 2018, 86, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsch, C.; Felix, R.; Rauschnabel, P.A. Nostalgia beats the wow-effect: Inspiration, awe and meaningful associations in augmented reality marketing. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 2020, 53, 101987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannesson, P.; Perjons, E. An introduction to design science; Vol. 10, Springer, 2014.
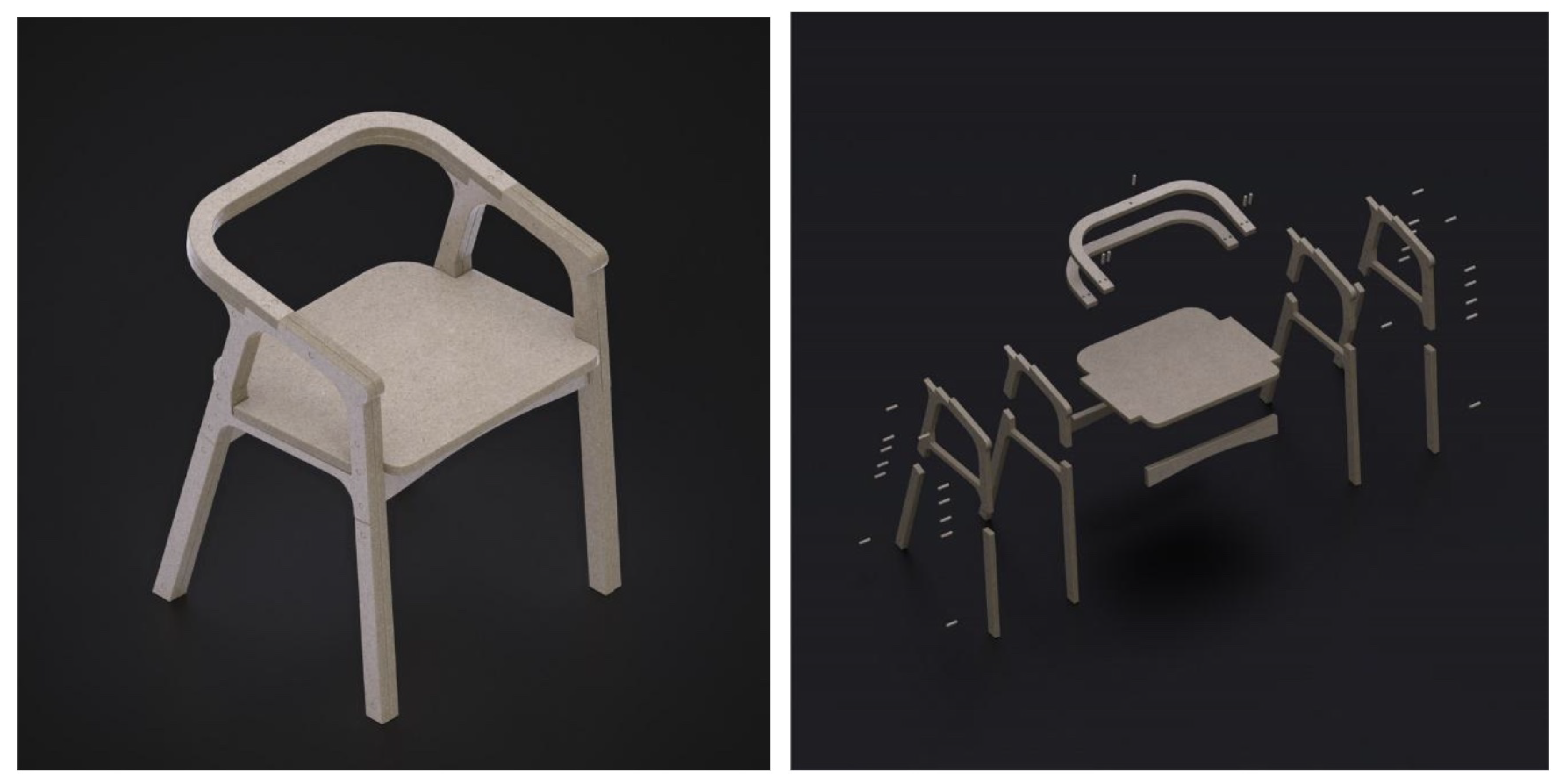
Figure 1.
Final proposed modeling for use in the Web AR mediating tool. Left: visualization of the plywood chair. Right: exploded view of the 3D model.
Figure 1.
Final proposed modeling for use in the Web AR mediating tool. Left: visualization of the plywood chair. Right: exploded view of the 3D model.
Figure 2.
Example of Augmented TD Sheet (Sheet 3) of the instantiated artifact in its first interaction.
Figure 2.
Example of Augmented TD Sheet (Sheet 3) of the instantiated artifact in its first interaction.
Figure 3.
Tests of the Tangible Board - Sheets 3 and 4.
Figure 3.
Tests of the Tangible Board - Sheets 3 and 4.
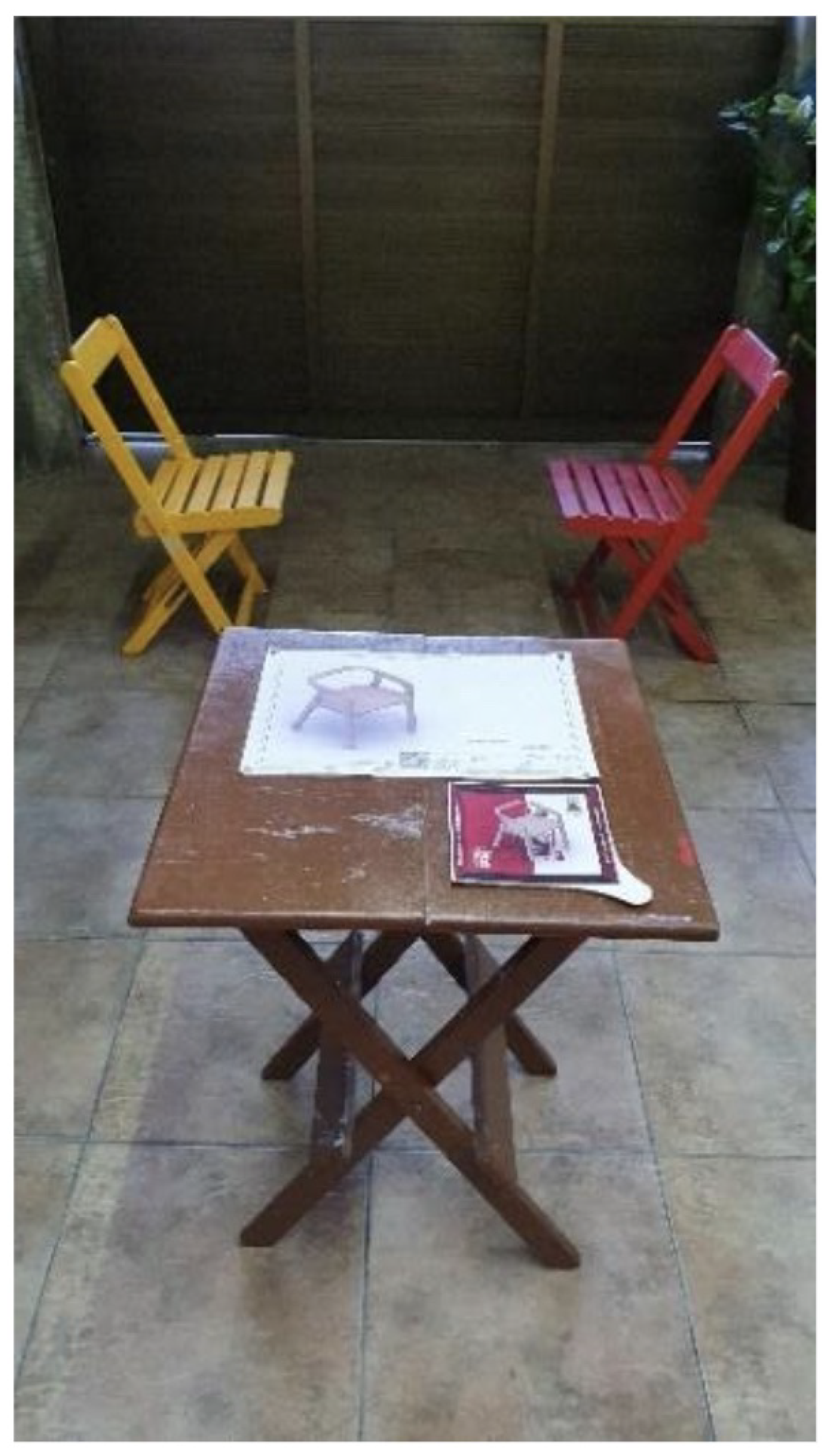
Figure 4.
Setup of the controlled environment for the experiment.
Figure 4.
Setup of the controlled environment for the experiment.
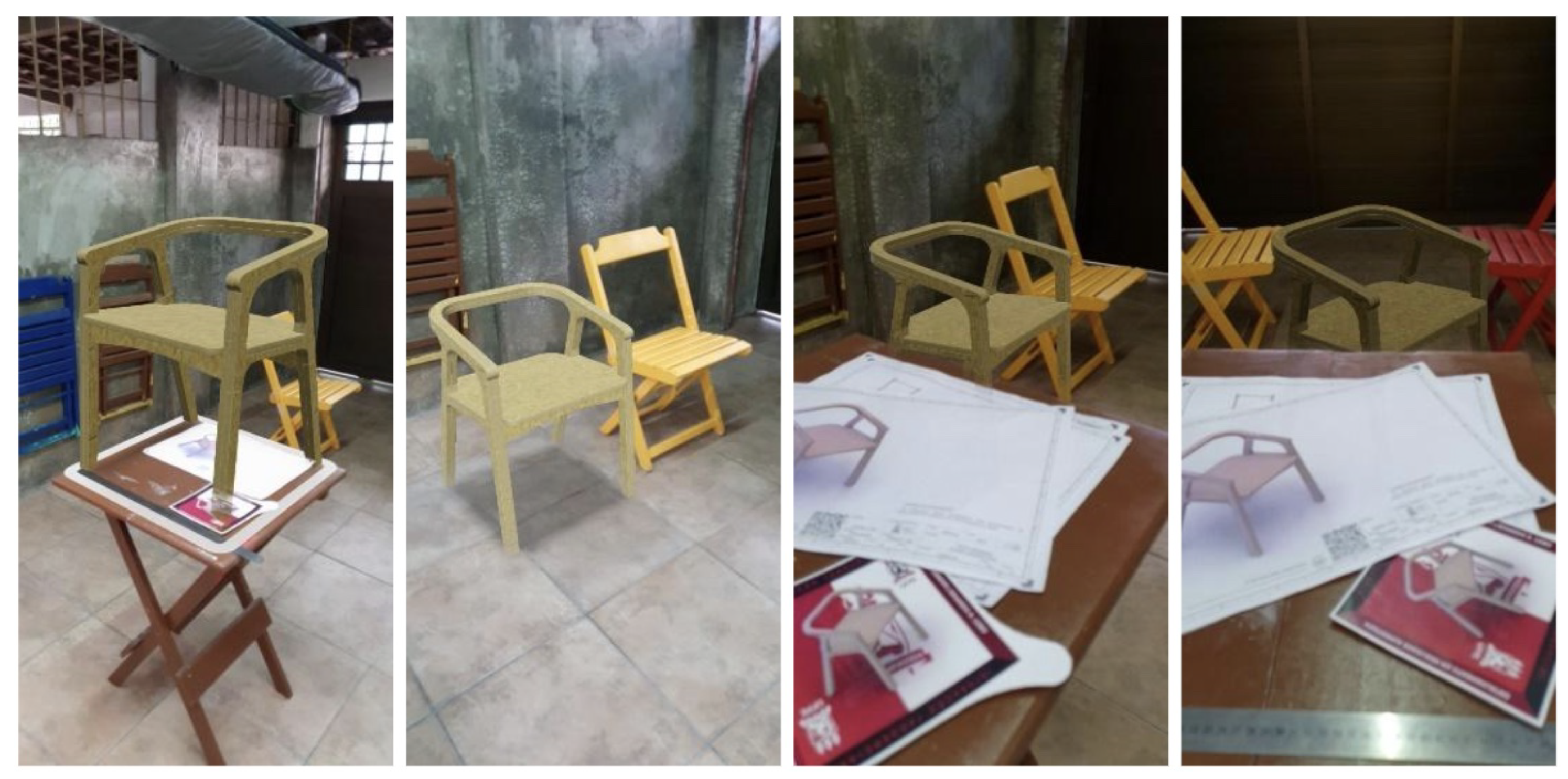
Figure 5.
Demonstration of Sheet 1 - Introduction to the Model. Overall analysis of the product and purpose. Inference of real scale and occlusion of objects in the foreground.
Figure 5.
Demonstration of Sheet 1 - Introduction to the Model. Overall analysis of the product and purpose. Inference of real scale and occlusion of objects in the foreground.
Figure 6.
Demonstration 2, Sheet 1 - Model with ergonomic reference.
Figure 6.
Demonstration 2, Sheet 1 - Model with ergonomic reference.
Figure 7.
Demonstration 3, Sheet 2. Static and Dynamic Primitive Interaction.
Figure 7.
Demonstration 3, Sheet 2. Static and Dynamic Primitive Interaction.
Figure 8.
Sheet 3 - Exploded View. Positioning and usage simulations (functional and cognitive integration).
Figure 8.
Sheet 3 - Exploded View. Positioning and usage simulations (functional and cognitive integration).
Figure 9.
Demonstration of Tangible Manipulation. UI for starting, executing, and occluding the tracking image, respectively.
Figure 9.
Demonstration of Tangible Manipulation. UI for starting, executing, and occluding the tracking image, respectively.
Figure 10.
Tangible board demonstration - Sheet 3.
Figure 10.
Tangible board demonstration - Sheet 3.
Figure 11.
NASA-TLX (PRE-EXPERIMENT), Ceno Mais and Baluarte; NASA-TLX POST-EXPERIMENT (Ceno Mais and Baluarte), respectively.
Figure 11.
NASA-TLX (PRE-EXPERIMENT), Ceno Mais and Baluarte; NASA-TLX POST-EXPERIMENT (Ceno Mais and Baluarte), respectively.
Figure 12.
Technology Acceptance, Intention, and Use Questionnaire: the graph displays the agreement scale for each participant, segmented by column. Low scores are better than high scores due to the anchor points used (completely agree / completely disagree), except for the Anxiety construct (negative statements).
Figure 12.
Technology Acceptance, Intention, and Use Questionnaire: the graph displays the agreement scale for each participant, segmented by column. Low scores are better than high scores due to the anchor points used (completely agree / completely disagree), except for the Anxiety construct (negative statements).
Table 1.
Evaluation of NASA-TLX workload (POST-EXPERIMENT) in leaders and employees of Scenographies.
Table 1.
Evaluation of NASA-TLX workload (POST-EXPERIMENT) in leaders and employees of Scenographies.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).