Submitted:
12 October 2023
Posted:
16 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and discussion
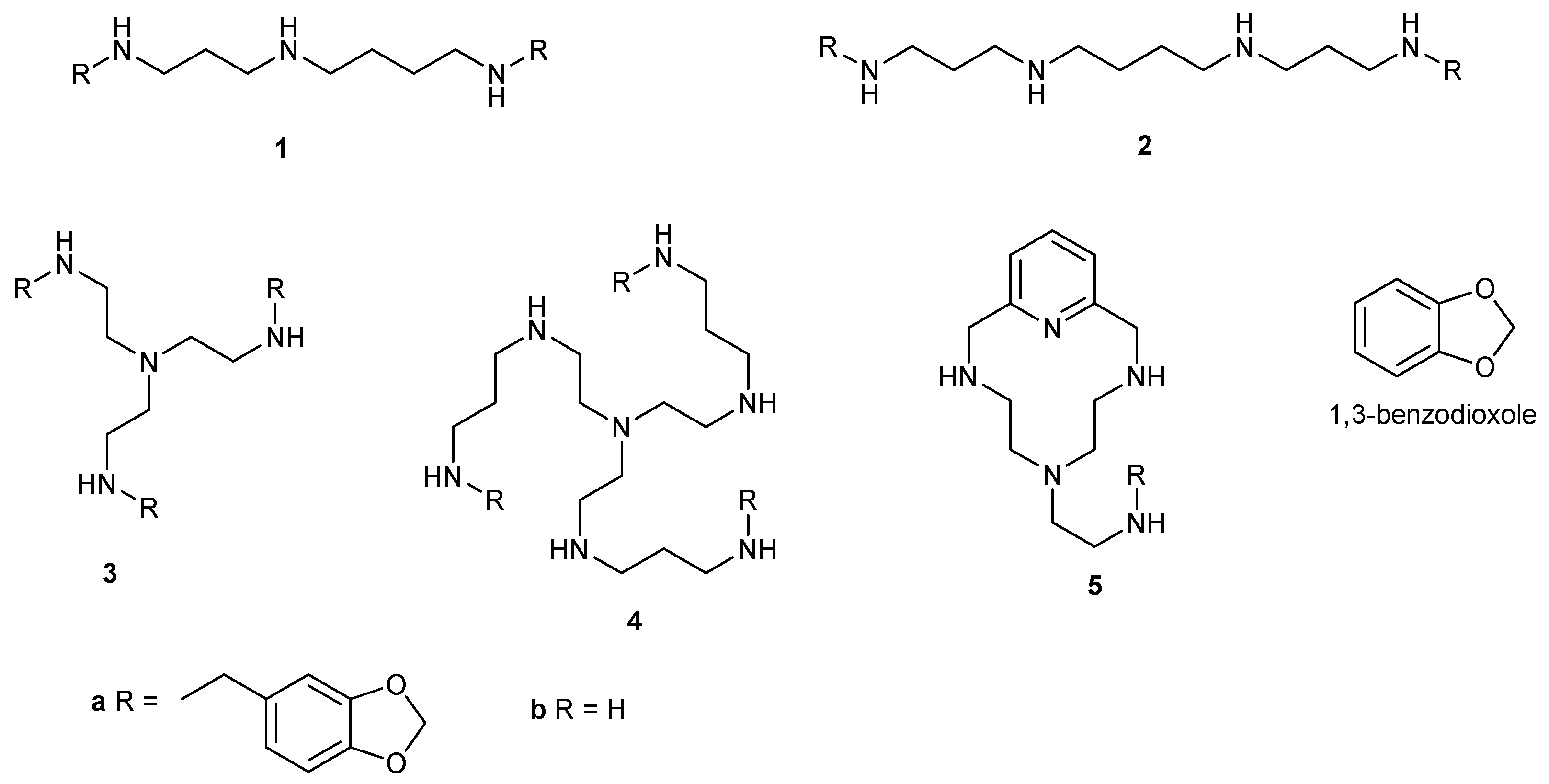
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Basicity of the receptors
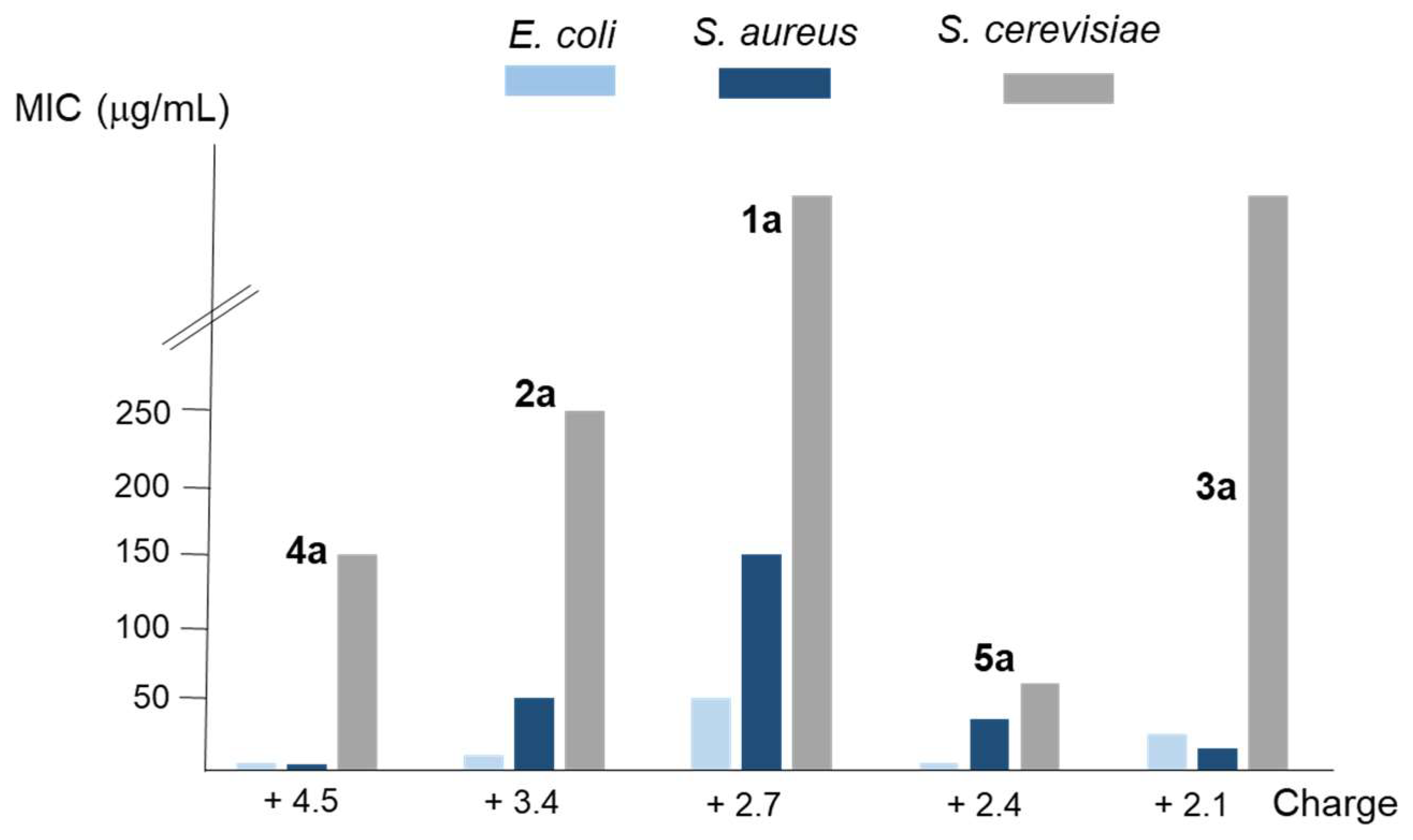
2.3. Determination of the antimicrobial activity
2.3.1. Determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
2.3.1. Determination of the minimal microbicidal (bactericidal/fungicidal) concentration (MBC or MFC)
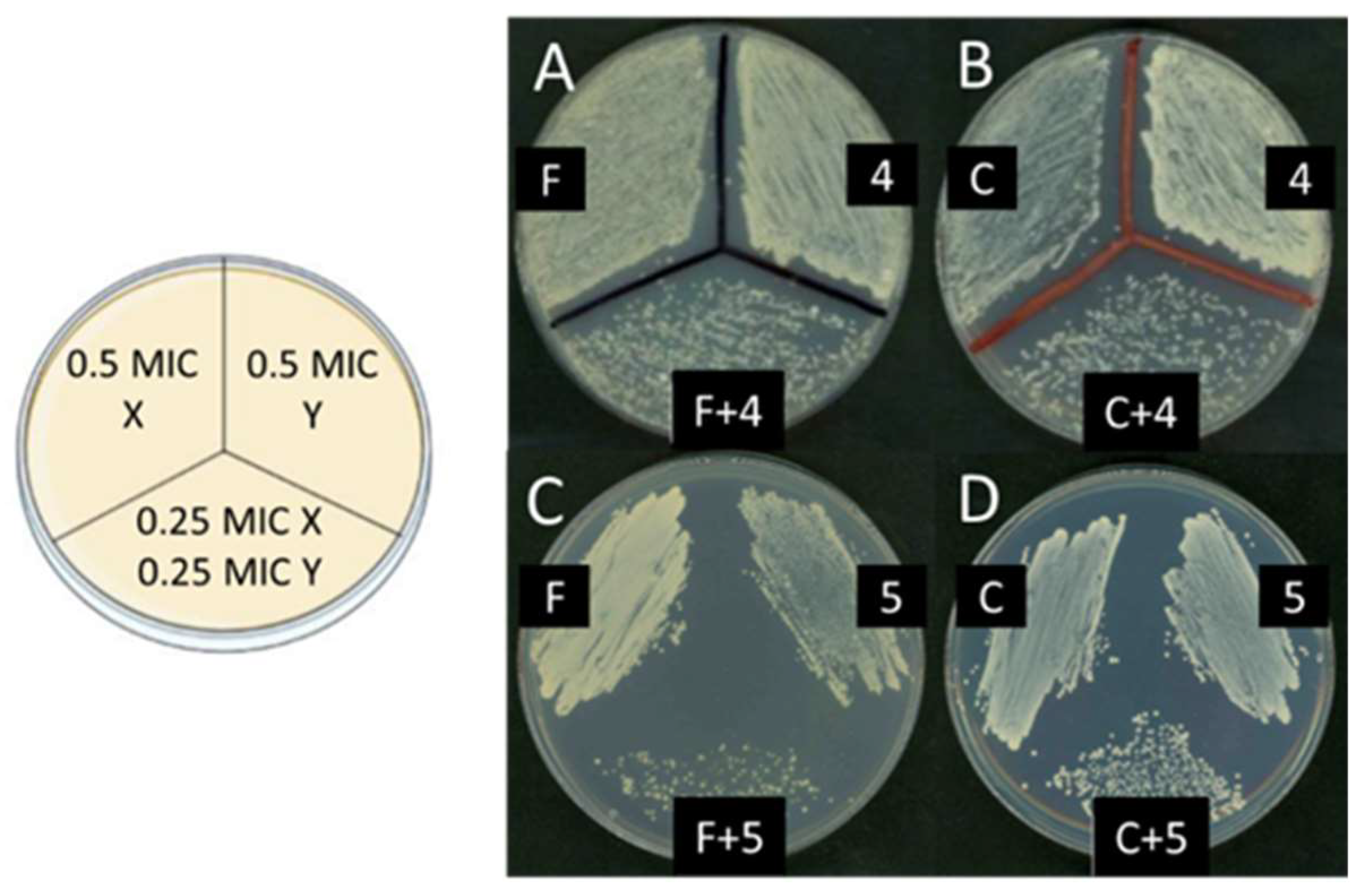
2.3.3. Determination of the synergies between compounds and control antifungal and antibacterial substances by the checkerboard titration approach
2.5. Compound cytotoxicity on human cells
2.6. Antimicrobial potential of other derived compounds from polyamine 5b
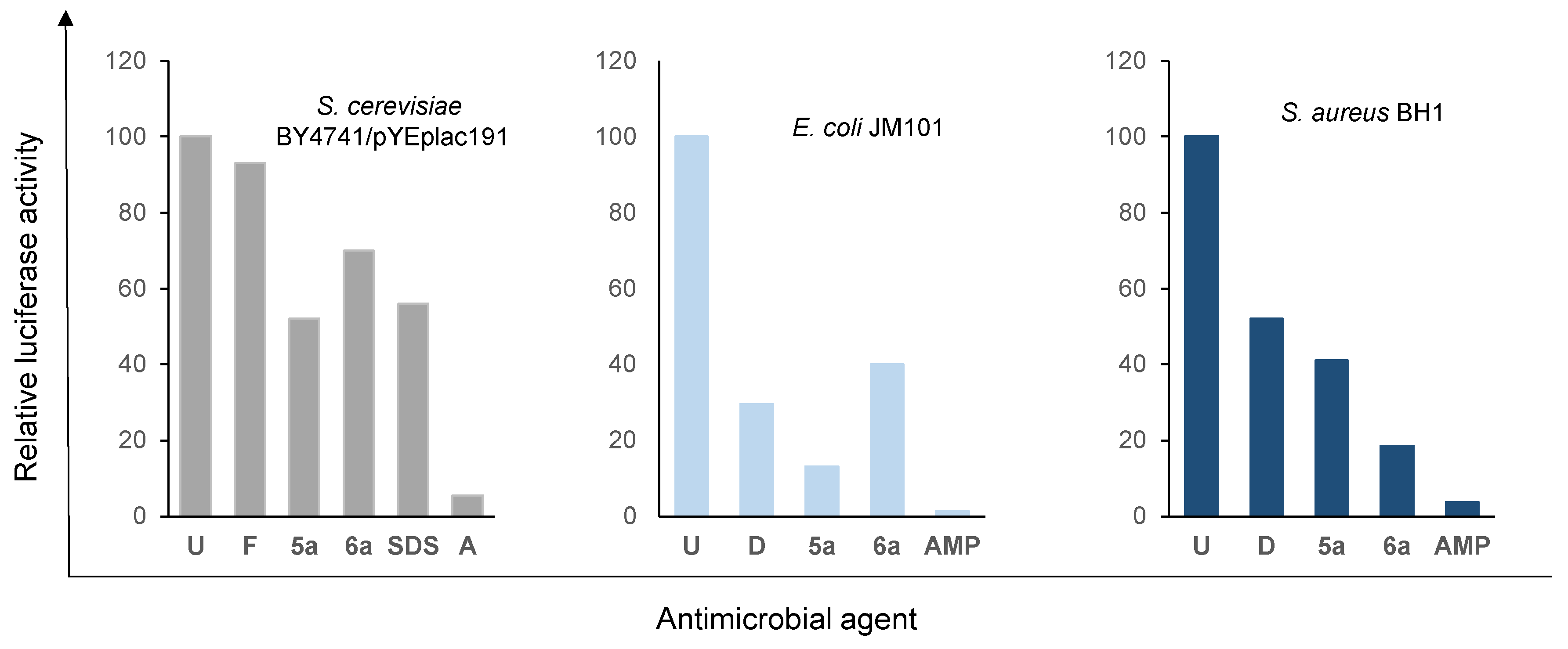
2.7. Intracellular ATP concentrations and microbiolytic activity.
2.7.1. Analysis of the intracellular ATP concentration in cells treated with the most active compounds considered in this work.
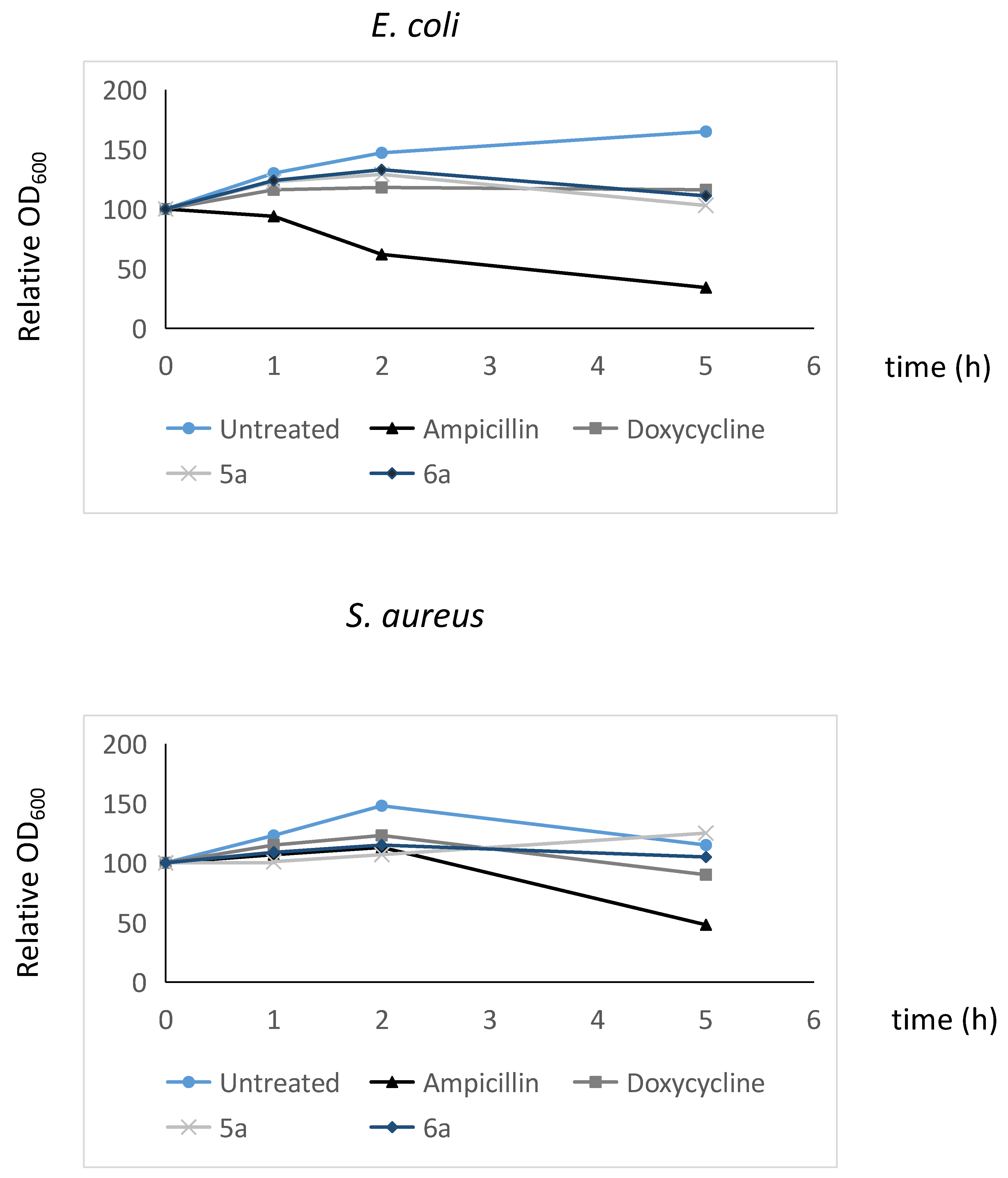
2.7.2. Determination of microbiolytic activity of the microbicidal compounds considered in this work using Time-Kill kinetics.
3. Materials and Methods
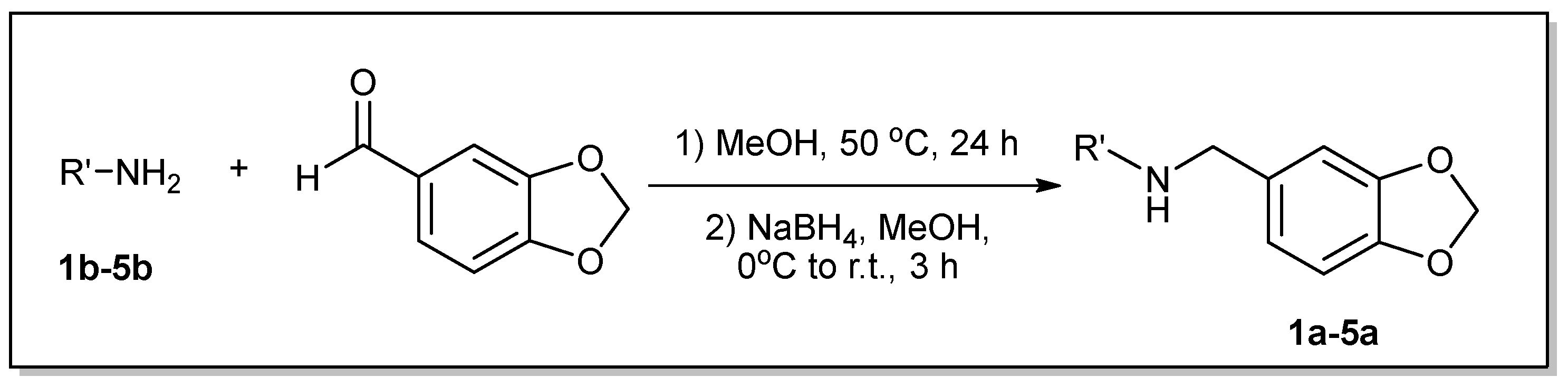
3.1. Synthesis
3.2. Potentiometric titrations
3.3. Antimicrobial activity
3.3.1. Bacterial and yeast strains and growth conditions
3.3.2. Preparation of stock solutions of test and control compounds
3.3.3. Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
3.3.4. Determination of the Minimum Microbicidal Concentration (MMC)
3.3.5. Determination of the synergies between the polyamines and control antifungal and antibacterial substances by the checkerboard titration approach.
3.3.6. Analysis of the intracellular ATP concentration in bacterial and yeast cultures treated with the tested compounds.
3.3.7. Analysis of the lytic activity of microbicidal compounds.
3.4. Determination of compound cytotoxicity on human cells.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- O. ’Neill, J. Tackling drug-resistant infections globally: Final report and recommendations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistance; Wellcome Trust and the UK Department of Health: London, 2016, 80 pp. Wellcome Trust and the UK Department of Health: London.
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; Johnson, S.C.; Browne, A.J.; Chipeta, M.G.; Fell, F.; Hackett, S.; Haines-Woodhouse, G.; Kashef Hamadani, B.H.; Kumaran, E.A.P.; McManigal, B.; Naghavi, M. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet. 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2020 Antibacterial agents in clinical and preclinical development: an overview and analysis; Geneva: World Health Organization: Geneva, 2021. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- Melchiorre, C.; Bolognesi, M.L.; Minarini, A.; Rosini, M.; Tumiatti, V. Polyamines in drug discovery: From the universal template approach to the multitarget-directed ligand design strategy. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5906–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorre, C.; Angeli, P.; Brasili, L.; Giardina, D.; Pigini, M.; Quaglia, W. Polyamines: a possible “passe-partout” for receptor characterization. Actual. Chim. Ther. 1988, 149–168. [Google Scholar]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Minarini, A.; Budriesi, R.; Cacciaguerra, S.; Chiarini, A.; Spampinato, S.; Tumiatti, V.; Melchiorre, C. Universal template approach to drug design: polyamines as selective muscarinic receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 4150–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottcher, T.; Kolodkin-Gal, I.; Kolter, R.; Losick, R.; Clardy, J. Synthesis and activity of biomimetic biofilm disruptors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2927–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goytia, M.; Dhulipala, V.L.; Shafer, W.M. Spermine impairs biofilm formation by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 343, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, R.; Wood, S.J.; Nguyen, T.B.; Miller, K.A.; Suresh Kumar, E.V.; Datta, A.; David, S.A. Structural correlates of antibacterial and membrane-permeabilizing activities in acylpolyamines. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhzem, A.H.; Shuxian, S.; Wonfor, T.; Woodman, T.J.; Laabei, M.; Blagbrough, I.S. Practical synthesis of antimicrobial long linear polyamine succinamides. ACS Bio. & Med. Chem. Au. 2022, 2, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Négrel, S.; Brunel, J.M. Synthesis and biological activities of naturally functionalized polyamines: An overview. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 3406–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djouhri-Bouktab, L.; Vidal, N.; Rolain, J.M.; Brunel, J.M. Synthesis of new 3,20-bispolyaminosteroid squalamine analogues and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 7417–7421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djouhri-Bouktab, L.; Alhanout, K.; Andrieu, V.; Raoult, D.; Rolain, J.M.; Brunel, J.M. Squalamine ointment for Staphylococcus aureus skin decolonization in a mouse model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1306–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, C.; Loncle, C.; Vidal, N.; Letourneux, Y.; Brunel, J.M. New stereoselective titanium reductive amination synthesis of 3-amino and polyaminosterol derivatives possessing antimicrobial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khusnutdinova, E.F.; Sinou, V.; Babkov, D.A.; Kazakova, O.; Brunel, J.M. Development of new antimicrobial oleanonic acid polyamine conjugates. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Pachaiyappan, B.; Gruber, J.D.; Schmidt, M.G.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Woster, P.M. Antibacterial diamines targeting bacterial membranes. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3140–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappori, A.A.; Haura, E.; Rodriguez, F.A.; Boulware, D.; Kapoor, R.; Neuger, A.M.; et al. Phase I/II study of atrasentan, an endothelin A receptor antagonist, in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curreli, F.; Belov, D.S.; Ahmed, S.; Ramesh, R.R.; Kurkin, A.V.; Altieri, A.; Debnath, A.K. Synthesis, antiviral activity, and structure-activity relationship of 1,3-benzodioxolyl pyrrole-based entry inhibitors targeting the Phe43 Cavity in HIV-1 gp120. ChemMedChem. 2018, 13, 2332–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millan, M.J.; Cussac, D.; Milligan, G.; Carr, C.; Audinot, V.; Gobert, A.; Lejeune, F.; Rivet, J.M.; Brocco, M.; Duqueyroix, D.; Nicolas, J.P.; Boutin, J.A.; Newman-Tancredi, A. Antiparkinsonian agent piribedil displays antagonist properties at native, rat, and cloned, human alpha(2)-adrenoceptors: cellular and functional characterization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 297, 876–887. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El Razik, H.A.; Badr, M.H.; Atta, A.H.; Mouneir, S.M.; Abu-Serie, M.M. Benzodioxole-pyrazole hybrids as anti-inflammatory and analgesic agents with COX-1,2/5-LOX inhibition and antioxidant potential. Arch. Pharm. (Weinheim). 2017, 350, 1700026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenian, P.; Vo, K.T.; Barr-Walker, J.; Lynch, K.L. Fentanyl, fentanyl analogs and novel synthetic opioids: A comprehensive review. Neuropharmacology 2017, 134, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickels, K.C.; Wirrell, E.C. Stiripentol in the management of epilepsy. CNS Drugs 2017, 31, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, F.K.; Case, D.E. Activity of the natural algicide, cyanobacterin, on angiosperms. Plant Physiol. 1986, 80, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudenmann, R.W.; Öxler, F.; Bernschneider-Reif, S. The origin of MDMA (ecstasy) revisited: the true story reconstructed from the original documents. Addiction 2006, 101, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalant, H. The pharmacology and toxicology of "ecstasy" (MDMA) and related drugs. CMAJ. 2001, 165, 917–928. [Google Scholar]
- Mibu, N.; Yokomizo, K.; Murakami, K.; Ono, Y.; Ishimaru, M.; Otsubo, M.; Inao, H.; Ono, Y.; Zhou, J.R.; Sumoto, K. Antiviral activity and molecular geometry of some new symmetrical tris(aminoalkyl)amine derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.C.L.; Peixoto Da Silva, K.; De Souza, I.A.; Magali De Araújo, J.; Brondani, D.J. Synthesis, antitumour and antimicrobial activities of new peptidyl derivatives containing the 1,3-benzodioxole system. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 39, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Ke, S. Discovery of γ-lactam derivatives containing 1,3-benzodioxole unit as potential anti-phytopathogenic fungus agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 126826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabli, R.I.; Al-Ghamdi, A.R.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Al-Agamy, M.H.; Attia, M.I. Synthesis, structure elucidation, and antifungal potential of certain new benzodioxole–imidazole molecular hybrids bearing ester functionalities. Drug. Des. Devel. Thery. 2019, 13, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Li, Z.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Qin, T.; Liu, J.; Du, H.; Ye, H. 4-Aminoquinolines bearing a 1,3-benzodioxole moiety: Synthesis and biological evaluation as potential antifungal agents. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomadze, N.; Schneider, H.-J.; Albelda, M.T.; García-España, E.; Verdejo, B. Dramatic selectivity differences in the association of DNA and RNA models with new ethylene- and propylene diamine derivatives and their copper complexes. Org. Biomol. Chem, 2006, 9, 1755–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albelda, M.T.; García-España, E.; Jiménez, H.R.; Llinares, J.-M.; Soriano, C.; Sornosa Ten, A.; Verdejo, B. Cu2+ and AMP complexation of enlarged tripodal polyamines. Dalton Trans. 2006, 37, 4474–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sornosa Ten, A.; Humbert, N.; Verdejo, B.; Llinares, J.M.; Elhabiri, M.; Jezierska, J.; Soriano, C.; Kozlowski, H.; Albrecht-Gary, A.-M.; García-España, E. Cu2+ Coordination properties of a 2-pyridine heptaamine tripod: Characterization and binding mechanism. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 8985–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, B.; Ferrer, A.; Blasco, S.; Castillo, C.E.; González, J.; Latorre, J.; Máñez, M.A.; Basallote, M.G.; Soriano, C.; García-España, E. Hydrogen and copper ion-induced molecular reorganizations in scorpionand-like ligands. A potentiometric, mechanistic, and solid-state study. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 5707–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencini, A.; Bianchi, A.; García- España, E.; Micheloni, M.; Ramírez, J.A. Proton coordination by polyamine compounds in aqueous solution. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1999, 188, 97–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swagatika, S.; Tomar, R.S. ABC transporter Pdr5 is required for cantharidin resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 553, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.H.; Lu, C.D. Polyamine effects on antibiotic susceptibility in bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowski, M.; van der Rest, M.; Cybularz-Kolaczkowska, A.; Soumillion, J.P.; Konings, W.N.; Goffeau, A. Anticancer drugs, ionophoric peptides, and steroids as substrates of the yeast multidrug transporter Pdr5p. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 31543–31548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sucher, NJ. Searching for synergy in silico, in vitro and in vivo. Synergy 2014, 1, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Fuente, A.; Vázquez, F.; Viéitez, J.M.; et al. CISNE: An accurate description of dose-effect and synergism in combination therapies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loewe, S. The problem of synergism and antagonism of combined drugs. Arzneimittelforschung 1953, 3, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Meletiadis, J.; Pournaras, S.; Roilides, E.; Walsh, T.J. Defining fractional inhibitory concentration index cutoffs for additive interactions based on self-drug additive combinations, monte carlo simulation analysis, and in vitro-in vivo correlation data for antifungal drug combinations against Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, E. Metabolic Interactions of Pesticides. In Pesticide Biotransformation and Disposition; Hodgson, E., Ed.; Academic Press, Cambridge, U.S.A., 2012; Chapter 7, pp. 149–178. [CrossRef]
- Verdejo, B.; Inclán, M.; Blasco, S.; Ballesteros-Garrido, R.; Savastano, M.; Bianchi, A.; García-España, E. Selective recognition of neurotransmitters in aqueous solution by hydroxyphenyl aza-scorpiand ligands. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 5424–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtinen, J.; Järvinen, S.; Virta, M.; Lilius, E.M. Real-time monitoring of antimicrobial activity with the multiparameter microplate assay. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2006, 66, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, D.; Andreu, C.; del Olmo, M.; Varea, T.; Diaz, D.; Asensio, G. The introduction of fluorine atoms or trifluoromethyl groups in short cationic peptides enhances their antimicrobial activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 6971–6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, Z.; Yousefi, N.; Sadeghi, D.; Ghasemian, A. Synergistic bactericidal activity of a naturally isolated phage and ampicillin against urinary tract infecting Escherichia coli O157. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, I.; Roberts, M. Tetracycline antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology of bacterial resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2001, 65, 232–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albelda, M.T.; García-España, E.; Jiménez, H.R.; Llinares, J.M.; Soriano, C.; Sornosa-Ten, A.; Verdejo, B. Cu2+ and AMP complexation of enlarged tripodal polyamines. Dalton Trans. 2006, 37, 4474–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-España, E.; Ballester, M.-J.; Lloret, F.; Moratal, J.M.; Faus, J.; Bianchi, A. Low-spin six-co-ordinate cobalt(II) complexes. A solution study of tris(violurato)cobaltate(II) ions. Dalton Trans. 1988, 1, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanelli, M.; Micheloni, M. Proceedings of the I Spanish-Italian Congress on Thermodynamics of Metal Complexes, Peñíscola, Castellón, 1990. Program for the automatic control of the microburette and the acquisition of the electromotive force readings.
- Gran, G. Determination of the equivalence point in potentiometric titrations. Part II. Analyst 1952, 77, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossotti, F.J.; Rossotti, H. Potentiometric titrations using Gran plots: A textbook omission. J. Chem. Educ. 1965, 42, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, P.; Sabatini, A.; Vacca, A. Investigation of equilibria in solution. Determination of equilibrium constants with the HYPERQUAD suite of programs. Talanta, 1996, 43, 1739–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushnie, T.P.T.; Cushnie, B.; Echeverría, J.; Fowsantear, W.; Thammawat, S.; Dodgson, J.L.A.; Law, S.; Clow, S.M. Bioprospecting for antibacterial drugs: a multidisciplinary perspective on natural product source material, bioassay selection and avoidable pitfalls. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkova, M.S.; Orlov, D.S.; Golubeva, O.Y.; Chakchir, O.B.; Eliseev, I.E.; Grinchuk, T.M.; Shamova, O.V. Application of Antimicrobial Peptides of the Innate Immune System in Combination With Conventional Antibiotics—A Novel Way to Combat Antibiotic Resistance? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankey, G.A.; Sabath, L.D. Clinical relevance of bacteriostatic versus bactericidal mechanisms of action in the treatment of Gram-Positive bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carton Herrán, J.D. Actividad antifúngica de la combinación de fluconazol con otros fármacos: Un enfoque terapéutico alternativo de las candidiasis. PhD Thesis, Facultad de Medicina y Enfermería, Universidad del País Vasco, Leioa (Vizcaya), 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reis De Sá, L.F.; Toledo, F.T.; De Sousa, B.A.; Gonçalves, A.C.; Tessis, A.C.; Wendler, E.P.; Comasseto, J.V.; Dos Santos, A.A.; Ferreira-Pereira, A. Synthetic organotelluride compounds induce the reversal of Pdr5p mediated fluconazole resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleeman, R.; LaVoi, T.M.; Santos, R.G.; Morales, A.; Nefzi, A.; Welmaker, G.S.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Houghten, R.A.; Shaw, L.N. Combinatorial libraries as a tool for the discovery of novel, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents targeting the ESKAPE pathogens. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 3340–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clothier, R.; Gómez-Lechón, M.; Kinsner-Ovaskainen, A.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; O’Connor, J.E.; Prieto, P.; Stanzel, S. Comparative analysis of eight cytotoxicity assays evaluated within the ACuteTox Project. Toxicology in vitro 2013, 27, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reaction(b) | 1a | 2a | 3a | 4a | 5a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L + H ⇄ HL | 10.433(2) | 10.81(3) | 9.12(2) | 10.95(1) | 10.48(1) |
| LH + H ⇄ H2L | 8.964(2) | 9.481(8) | 8.35(3) | 9.63(1) | 8.78(1) |
| H2L + H ⇄ H3L | 7.699(2) | 8.245(7) | 6.93(3) | 9.12(1) | 7.30(1) |
| H3L + H ⇄ H4L | 7.41(1) | 8.07(1) | |||
| H4L + H ⇄ H5L | 7.48(1) | ||||
| H5L + H ⇄ H6L | 6.35(2) | ||||
| log β (c) | 27.09 | 35.94 | 24.29 | 51.60 | 26.56 |
| n(d) | 2.7 | 3.4 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 2.4 |
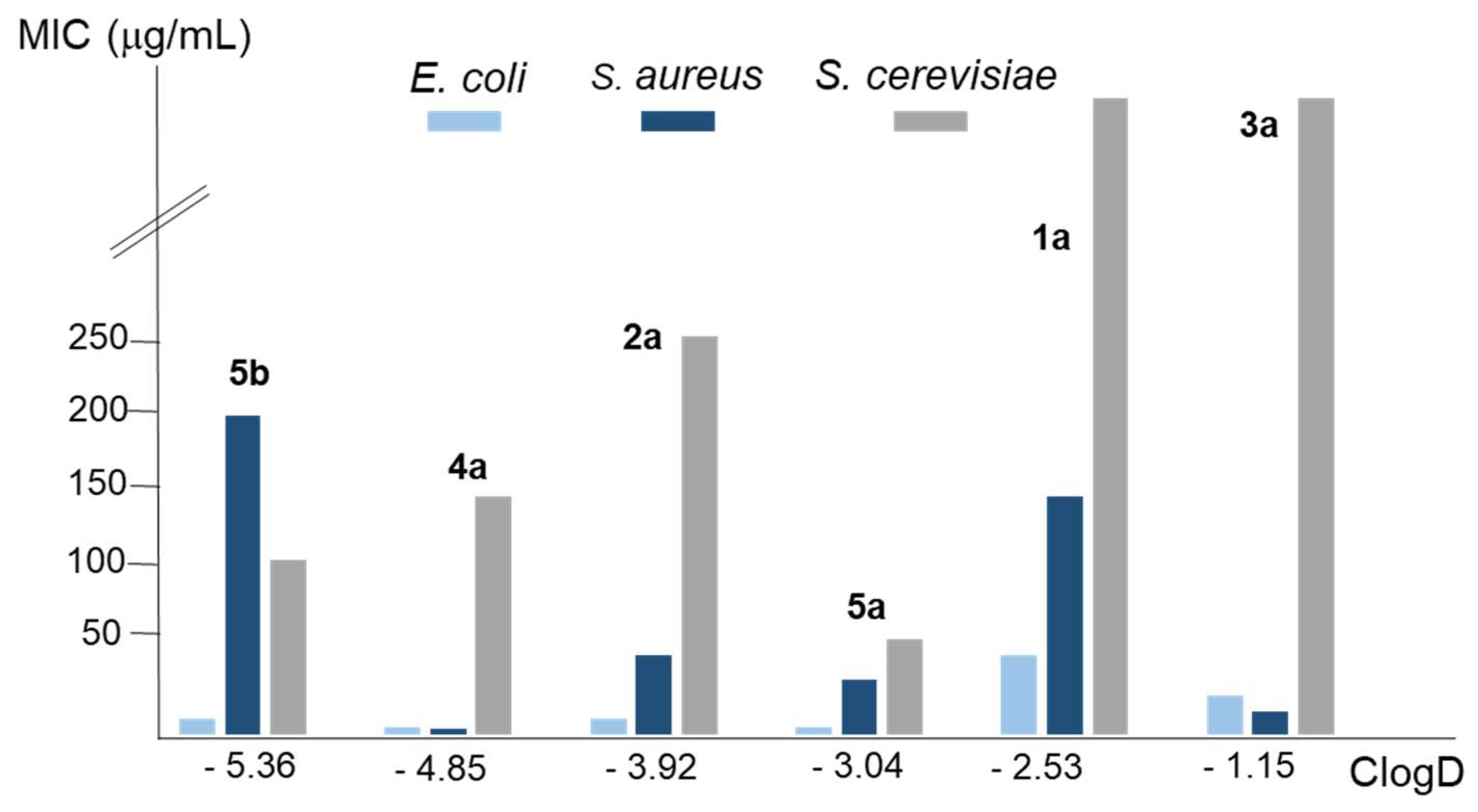
| Compound | MIC (µg/mL), yeasta | MIC (µg/mL), bacteriaa | ClogDb | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BY4741/YEplac195 | BY4741/PDR5 | E. coli JM101 | S. aureus BHI | pH 7.4 | |
| 1a | > 400 | > 400 | 50 | 150 | -2.53 |
| 1b | > 400 | > 400 | 400 | > 400 | -7.33 |
| 2a | 250 | 250 | 10 | 50 | -3.92 |
| 2b | > 400 | > 400 | 100 | 400 | -8.74 |
| 3a | > 400 | > 400 | 25 | 15 | -1.15 |
| 3b | > 400 | > 400 | 250 | 400 | -8.02 |
| 4a | 150 | 150 | 5 | 4 | -4.85 |
| 4b | > 400 | > 400 | 400 | 250 | -12.72 |
| 5a | 60 | 60 | 5 | 35 | -3.04 |
| 5b | 110 | 110 | 10 | 200 | -5.36 |
| 1,3-benzodioxole | >500 | >500 | >500 | >500 | +1.6 |
| Fluconazole | 10 | 60 | - | - | |
| Cycloheximide | 0.5 | 0.5 | - | - | |
| Amphotericin B | 1 | 1 | |||
| Doxycycline | - | - | 1 | 0.25 | |
| Ampicillin | - | - | 2 | 0.14 | |
| Gentamicin | - | - | 0.02 | 0.04 | |
| Ciprofloxacin | - | - | 0.04 | 0.1 | |
| Compound | S. cerevisiae strains | E. coli JM101 | S. aureus BHI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | n.d.a | 100b | n.d.a |
| 2a | n.d.a | 20b | 100b |
| 3a | n.d.a | 50b | 30b |
| 4a | Fungistatic | 10b | 8b |
| 5a | Fungistatic | 10b | 70b |
| 5b | Fungistatic | 20 b | n.d.a |
| BY4741/YEplac195 | 4a | 5a | 5b |
| Fluconazole | + | + | + |
| Cycloheximide | + | + | + |
| Amphotericin B | + | + | - |
| BY4741/PDR5 | |||
| Fluconazole | n.d.a | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Cycloheximide | + | + | + |
| Amphotericin B | + | + | - |
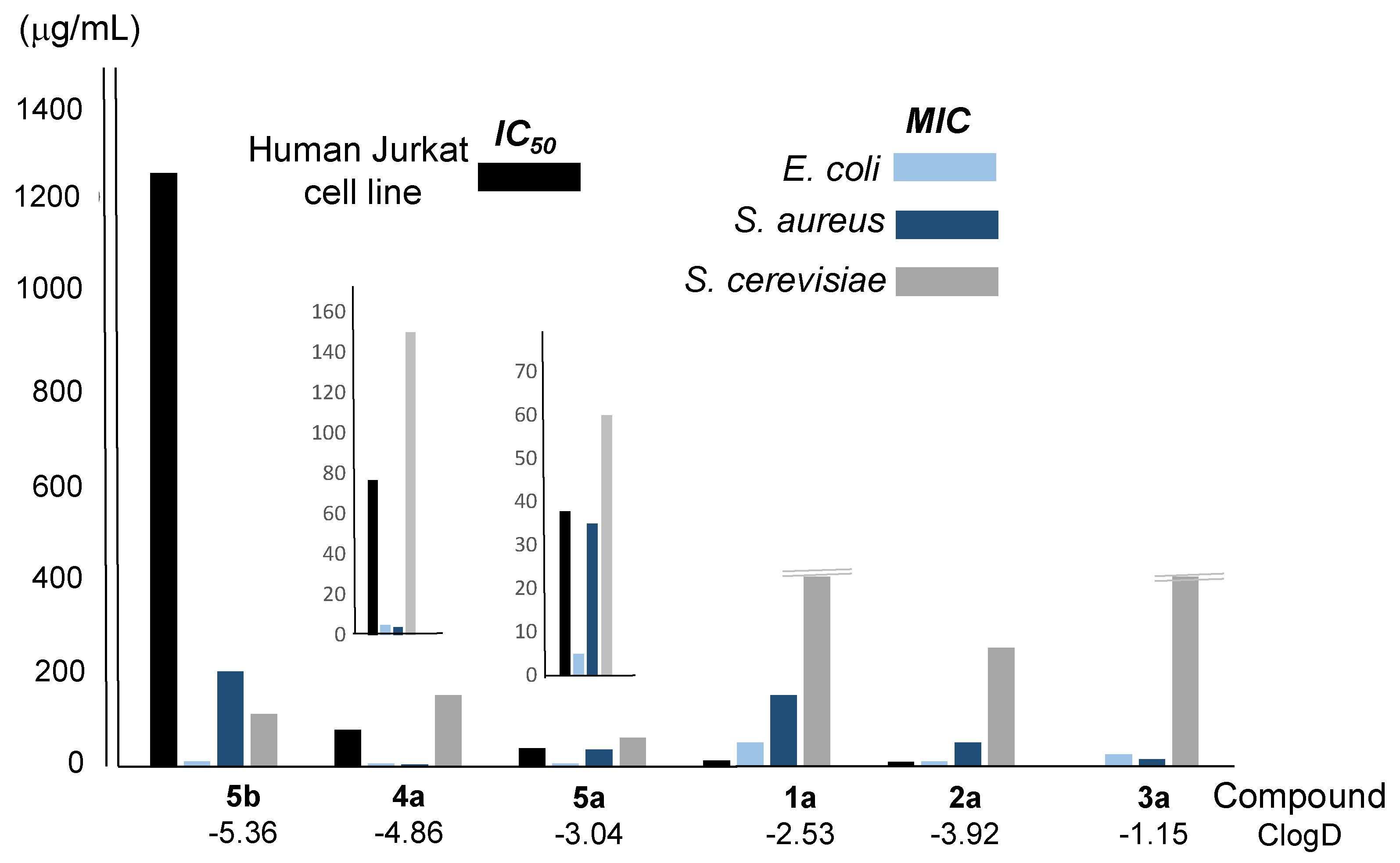
| Compound/ClogD | IC50 (μg/mL)a |
MIC E. coli (μg/mL) |
MIC S. aureus (μg/mL) |
MIC yeast (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a/-2.53 | 11.41 | 50 | 150 | >400 |
| 2a/-3.92 | 8.80 | 10 | 50 | 250 |
| 3a/-1.15 | 1.86 | 25 | 15 | >400 |
| 4a/-4.85 | 76.86 | 5 | 4 | 150 |
| 5a/-3.04 | 37.84 | 5 | 35 | 60 |
| 5b/-5.36 | 1252 | 10 | 200 | 110 |
| Reaction(b) | 6a | 7a | 8a |
|---|---|---|---|
| L + H ⇄ HL | 9.93(1) | 10.153(9) | 9.943(3) |
| LH + H ⇄ H2L | 9.11(1) | 9.473(9) | 8.736(3) |
| H2L + H ⇄ H3L | 7.92(1) | 8.516(8) | 7.296(4) |
| H3L + H ⇄ H4L | 6.67(2) | 7.341(9) | |
| log β (c) | 33.72 | 35.48 | 26.17 |
| n(d) | 1.91 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Compound | MIC (µg/mL), yeasta | MIC (µg/mL), bacteriaa | CLogDb | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BY4741/YEplac195 | BY4741/PDR5 | E. coli JM101 | S. aureus BHI | pH 7.4 | |
| 5a | 60 | 60 | 5 | 35 | -3.04 |
| 5b | 110 | 110 | 10 | 200 | -5.36 |
| 6a | 45 | 45 | 2.5 | 40 | -3.36 |
| 7a | 295 | 295 | 13 | 135 | -3.12 |
| 8a | 400 | 400 | 15 | 100 | -3.01 |
| Compound | S. cerevisiae strains | E. coli JM101 | S. aureus BHI |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6a | Fungistatic | 10b | 160b |
| 7a | n.d.a | Bacteriostatic | n.d.a |
| 8a | n.d.a | 60b | 400b |
| 6a | 7a | 8a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BY4741/YEplac195 | |||
| Fluconazole | - | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Cycloheximide | + | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Amphotericin | + | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| BY4741/PDR5 | |||
| Fluconazole | n.d.a | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Cycloheximide | + | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Amphotericin | + | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| E. coli | |||
| Ampicillin | - | - | + |
| Ciprofloxacin | - | - | - |
| Doxycycline | - | - | + |
| Gentamicin | - | + | + |
| S. aureus | |||
| Ampicillin | - | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Ciprofloxacin | - | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Doxycycline | - | n.d.a | n.d.a |
| Gentamicin | - | n.d.a | n.d.a |
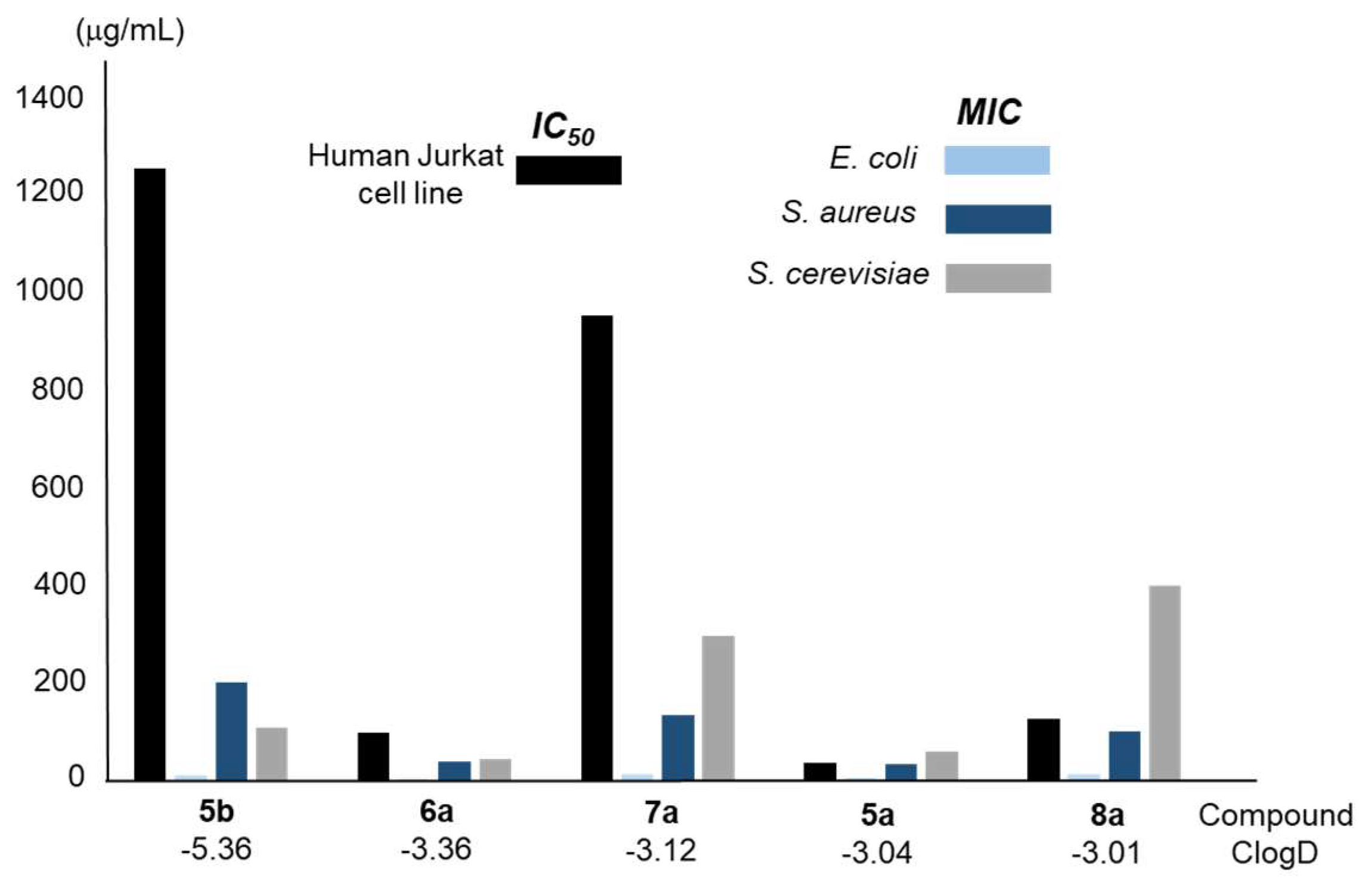
| Compound/ClogD | IC50 (μg/mL)a |
MIC E. coli (μg/mL) |
MIC S. aureus (μg/mL) |
MIC yeast (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a/-3.04 | 37.84 | 5 | 35 | 60 |
| 5b/-5.36 | 1252 | 10 | 200 | 110 |
| 6a/-3.36 | 97.95 | 2.5 | 40 | 45 |
| 7a/-3.12 | 950.61 | 13 | 135 | 295 |
| 8a/-3.01 | 127.95 | 15 | 100 | 400 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





