1. Introduction
Biofilms are commonly found in various environments, including medical devices, industrial settings, and natural ecosystems. They are of particular concern in the context of human health because biofilm forming bacteria are often more resistant to antibiotics and immune system defences than their planktonic counterparts. Biofilm formation has become an important survival mode of microbes during antimicrobial treatments (Zakaria et al. 2023). This resistance poses a significant challenge in treating biofilm-related infections. Biofilm-associated proteins (BAPs) play a significant role in the formation and stability of biofilms, which are complex communities of microorganisms encased in a protective extracellular matrix. All members of the BAP family share the following characteristics: (i) a high molecular weight; (ii) a signal sequence for extracellular secretion; and (iii) a core domain of repeats, whose number varies among different isolates (Cucarella et al. 2004).
One of the distinctive features of BAPs is their non-host homologous nature (
Table 1). This means that these proteins do not have counterparts or homologous equivalents in the host organisms or tissues with which they interact. BAPs typically have unique protein sequences that distinguish them from host proteins. These sequences may contain specific domains or motifs that enable their functions within biofilms, such as adhesion domains or matrix-binding domains. BAPs are specifically produced by microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and algae, for their biofilm-related functions. This specificity ensures that BAPs do not have functional homologs in host tissues, reducing the risk of unintended interactions. BAPs are adapted to the biofilm environment and perform specialized roles within biofilms. These roles may include mediating cell-cell interactions, participating in quorum sensing, and contributing to the maintenance of the extracellular matrix. BAPs often contain specific domains and motifs that govern their interactions with surfaces, other biofilm components, and microorganisms. Examples include fibronectin-binding domains, lectin-like domains, and carbohydrate-binding motifs (Henderson et al. 2023).
Understanding the role of BAPs is crucial in developing effective strategies to target biofilms as potential drug targets. These proteins possess various characteristics, including essential metabolic functions within biofilms and the distinction of being non-host homologous (Othman and Yahya 2019). Although many antibiotics, disinfectants, antifungals and natural products have been demonstrated to possess antibiofilm potential, their effects on expression of the BAPs remain not well investigated (Isa et al. 2022; Kamaruzzaman et al. 2022; Amran et al. 2023; Johari et al. 2023). In this mini review, we explore the multifaceted roles of BAPs in biofilm formation, their implications in infections, and their potential as targets for therapeutic intervention.
2. Biofilm Formation and the Extracellular Matrix
Biofilms are intricate structures formed by various microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and algae. The extracellular matrix of biofilms is primarily composed of polysaccharides, DNA, and proteins (Yaacob et al. 2021). Among these components, BAPs play a vital role in several key aspects of biofilm development. BAPs facilitate the initial attachment of microorganisms to surfaces. These proteins contain adhesive domains that interact with specific receptors on host tissues or abiotic surfaces. For example, in Staphylococcus aureus, the biofilm-associated protein Bap (encoded by the icaADBC cluster) is involved in adhesion to host tissues, promoting biofilm formation (Cucarella et al. 2004). BAPs contribute to the structural integrity of the extracellular matrix. They can cross-link with other matrix components, such as polysaccharides and DNA, creating a robust and protective environment for embedded microorganisms. This matrix serves as a barrier against antibiotics and immune system attacks. Once formed, biofilms require stability to persist on surfaces. BAPs also help maintaining the structural integrity of the biofilm, preventing detachment and dispersion of microorganisms. This stability enhances the resilience of biofilms against antimicrobial agents.
3. Implications in Infection
BAPs are directly linked to the pathogenicity of many bacteria (Mohamed et al. 2023). Understanding their role in infections is crucial for developing targeted therapies. Biofilm formation is often associated with chronic infections, such as those caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis patients or Staphylococcus aureus in implant-related infections. BAPs are integral to the persistence of these infections, as the biofilm matrix protects bacteria from host defences and antibiotics. Medical devices, such as catheters and prosthetic implants, can become sites of biofilm formation (Di Domenico et al. 2022). BAPs promote the colonization of these devices by pathogenic bacteria, leading to device-related infections. Targeting these proteins could help prevent such infections. BAPs is known to contribute to antibiotic resistance by physically shielding bacteria within the biofilm matrix. This resistance poses a significant challenge in treating infections associated with biofilms. Inhibiting these proteins could potentially make biofilm bacteria more susceptible to antibiotics.
4. Biofilm-Associated Proteins as Potential Drug Targets
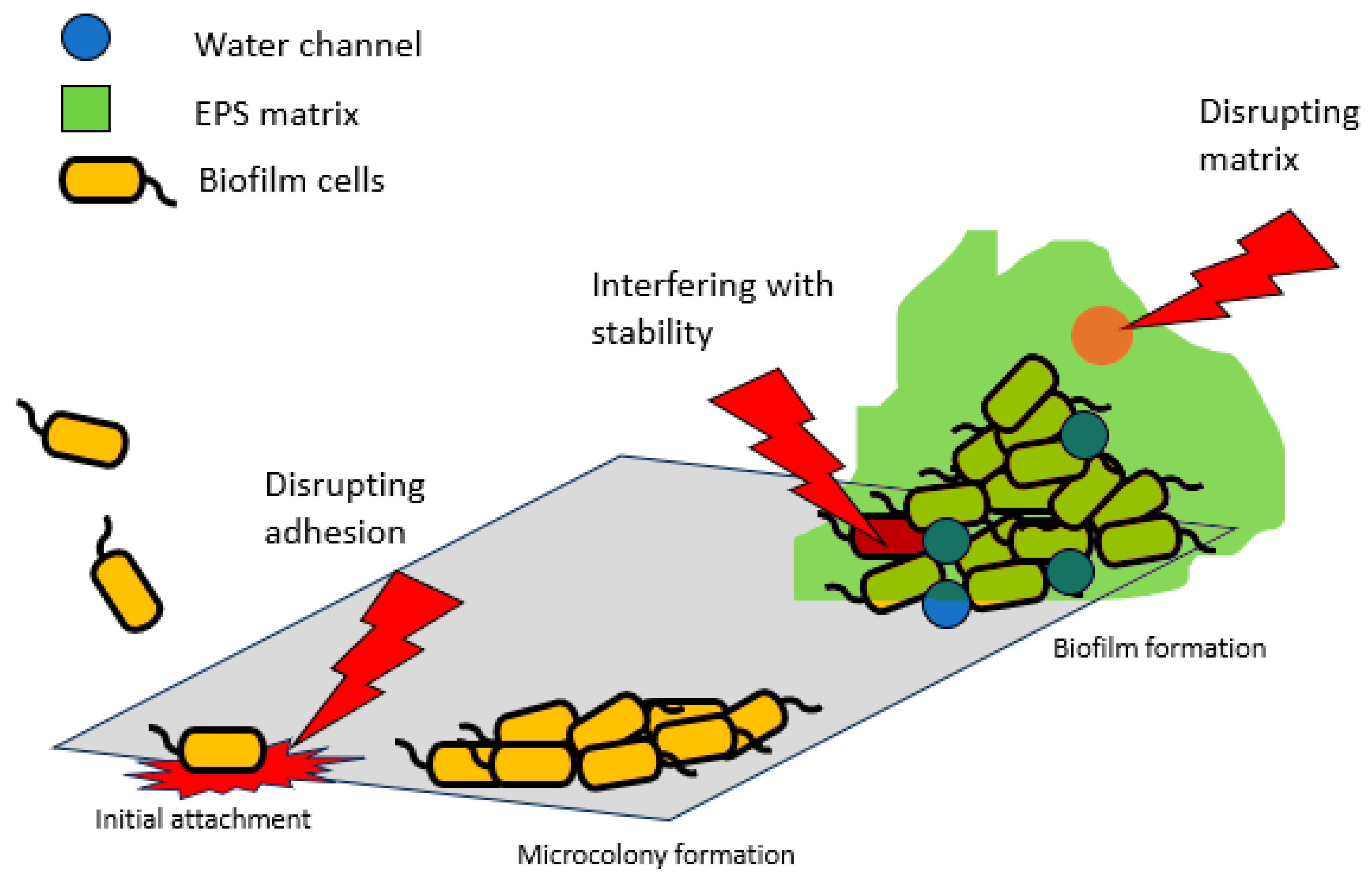
The role of BAPs in biofilm formation and infection pathogenesis makes them attractive targets for therapeutic intervention. Their essentiality is apparent in cellular adhesion, matrix formation, and biofilm stabilization (Cucarella et al. 2004).
Figure 1 summarizes how these proteins can be targeted for drug development.
Inhibiting the adhesive properties of BAPs can prevent the initial attachment of microorganisms to surfaces. This could be achieved through the development of small molecules or peptides that block the binding domains of these proteins (Parrino et al. 2019). By preventing adhesion, the formation of biofilms can be impeded, reducing the risk of infection. Targeting the interactions between biofilm-associated proteins and other matrix components can destabilize the biofilm structure. Enzymes or compounds that degrade polysaccharides, DNA, or protein components of the matrix may weaken biofilms, making them more vulnerable to treatments. Biofilm-associated proteins are essential for maintaining the stability of mature biofilms. The use of inhibitors, such as cinnamaldehyde, that disrupt the function of these proteins could lead to the detachment and dispersion of biofilm microorganisms (Topa et al. 2020). This could enhance the effectiveness of antibiotics and host immune responses against biofilm infections. Combining therapies that target BAPs with conventional antibiotics or antimicrobial agents may be a promising approach. Such combination therapies can potentially overcome the antibiotic resistance observed in biofilm infections.
5. Challenges and Future Directions
While targeting BAPs holds promise in combating biofilm-related infections, several challenges and considerations must be addressed. Developing drugs that overcome the increase in antibiotic-resistant bacteria and selectively target biofilm-associated proteins without affecting essential host proteins is a challenge (Abd Rashid et al. 2022; Elfadil et al. 2022). Specificity is crucial to minimize potential side effects. Bacteria may develop resistance to therapies that target BAPs. Continuous monitoring and adaptation of treatment strategies may be necessary. Biofilms are heterogeneous structures (Yaacob et al. 2021), and the effectiveness of therapies can vary within the same biofilm. Understanding this heterogeneity is essential for developing effective treatments. Developing efficient delivery methods for biofilm-targeting therapies, especially for biofilms in hard-to-reach areas of the body, is crucial. Translating biofilm-targeting therapies from preclinical studies to clinical trials is a complex process that requires rigorous testing for safety and efficacy.
6. Conclusion
BAPs play pivotal roles in biofilm formation and infection pathogenesis. Understanding these roles offers opportunities to develop novel strategies to combat biofilm-related infections. By targeting these proteins, researchers aim to disrupt adhesion, destabilize the biofilm matrix, and improve the effectiveness of treatments. However, addressing challenges related to specificity, resistance, and biofilm heterogeneity is essential in advancing these potential drug targets from laboratory research to clinical practice. The development of therapies targeting BAPs has the potential to revolutionize the treatment of biofilm-related infections, providing hope for better outcomes in patients affected by these challenging infections.
References
- Abd Rashid, S.A.; Yaacob, M.F.; Raihanah, N.; Anuar, T.; Johari, N.; Kamaruzzaman AN, A.; Yahya MF, Z.R. A combination of in silico subtractive and reverse vaccinology approaches reveals potential vaccine targets in Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2022, 17, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, S.S.D.; Jalil, M.T.M.; Aziz, A.A.; Yahya, M.F.Z.R. Methanolic Extract Of Swietenia macrophylla Exhibits Antibacterial And Antibiofilm Efficacy Against Gram-Positive Pathogens. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2023, 52, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucarella, C.; Tormo, M.A.; Ubeda, C.; Trotonda, M.P.; Monzón, M.; Peris, C.; Amorena, B.; Lasa, I.; Penadés, J.R. Role of Biofilm-Associated Protein Bap in the Pathogenesis of Bovine Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2177–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Oliva, A.; Guembe, M. The Current Knowledge on the Pathogenesis of Tissue and Medical Device-Related Biofilm Infections. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfadil, D.; Elkhatib, W.F.; El-Sayyad, G.S. Promising advances in nanobiotic-based formulations for drug specific targeting against multidrug-resistant microbes and biofilm-associated infections. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 170, 105721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.R.; Geoghegan, J.A. The A domain of clonal complex 1-type fibronectin binding protein B promotes adherence and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology 2023, 169, 001348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isa, S.F.M.; Hamid, U.M.A.; Yahya, M.F.Z.R. Treatment with the combined antimicrobials triggers proteomic changes in P. aeruginosa-C. albicans polyspecies biofilms. ScienceAsia 2022, 48, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, N.A.; Aazmi, M.S.; Yahya, M.F.Z.R. FTIR Spectroscopic Study Of Inhibition of Chloroxylenol-Based Disinfectant Against Salmonella enterica serovar Thyphimurium Biofilm. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2023, 52, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaruzzaman, A.N.A.; Mulok, T.E.T.Z.; Nor, N.H.M.; Yahya, M.F.Z.R. FTIR spectral changes in candida albicans biofilm following exposure to antifungals. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2022, 51, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Raafat, M.M.; Mohamed, R.S.; Ali, A.E.E. Acinetobacter baumannii biofilm and its potential therapeutic targets. Futur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, N.A.; Yahya, M.F.Z.R. In silico analysis of essential and non-homologous proteins in Salmonella typhimurium biofilm. J. Physics: Conf. Ser. 2019, 1349, 012133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, B.; Schillaci, D.; Carnevale, I.; Giovannetti, E.; Diana, P.; Cirrincione, G.; Cascioferro, S. Synthetic small molecules as anti-biofilm agents in the struggle against antibiotic resistance. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 161, 154–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigurdsson, G.; Fleming, R.M.T.; Heinken, A.; Thiele, I. A Systems Biology Approach to Drug Targets in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topa, S.H.; Palombo, E.A.; Kingshott, P.; Blackall, L.L. Activity of Cinnamaldehyde on Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Susceptibility to Antibiotics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaacob, M.F.; Murata, A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Jesse, F.F.A.; Yahya, M.F.Z.R. Biochemical composition, morphology and antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis biofilm. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2020, 33, 101225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria NF, S.; Fakharul Zaman Raja Yahya, M.; Jamil, N.M. Multiple Bacterial Strategies to Survive Antibiotic Pressure: A Review. 2023, Preprints.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).