Submitted:
12 October 2023
Posted:
13 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. SIRT1 in the regulation of trophoblast function
2.1. Effects towards placental development and differentiation
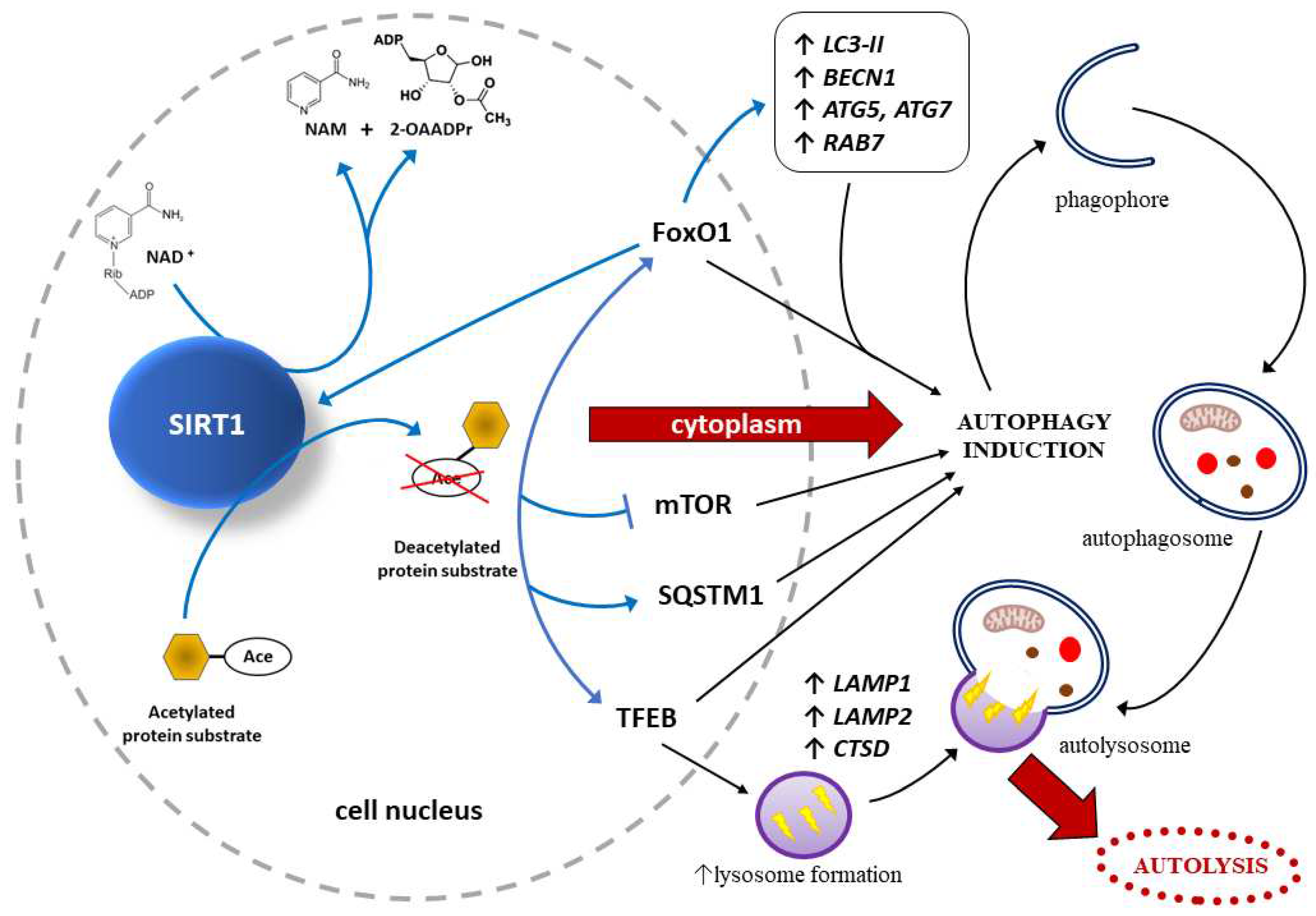
2.2. Effects of SIRT1 on autophagy within trophoblast
2.3. Effects on cell senescence phenotype occurrence within the placenta
2.4. Effects of other sirtuins towards trophoblast
3. SIRT1 and PPARγ
3.1. Role of SIRT1- and PPARγ-dependent signaling pathways in placental pathology
3.1.1. Effects of hypoxia on PPARγ activity
3.1.2. Effects of hypoxia on SIRT1 activity
3.1.3. Effects of SIRT1 and PPARγ action towards placentas exposed to oxidative stress
3.1.4. Effects of SIRT1 and PPARγ towards placentas affected by inflammatory response
3.1.5. Correlations between hyperglycemia and placental SIRT1/PPARγ activity
4. SIRT1-dependent prevention of preeclampsia
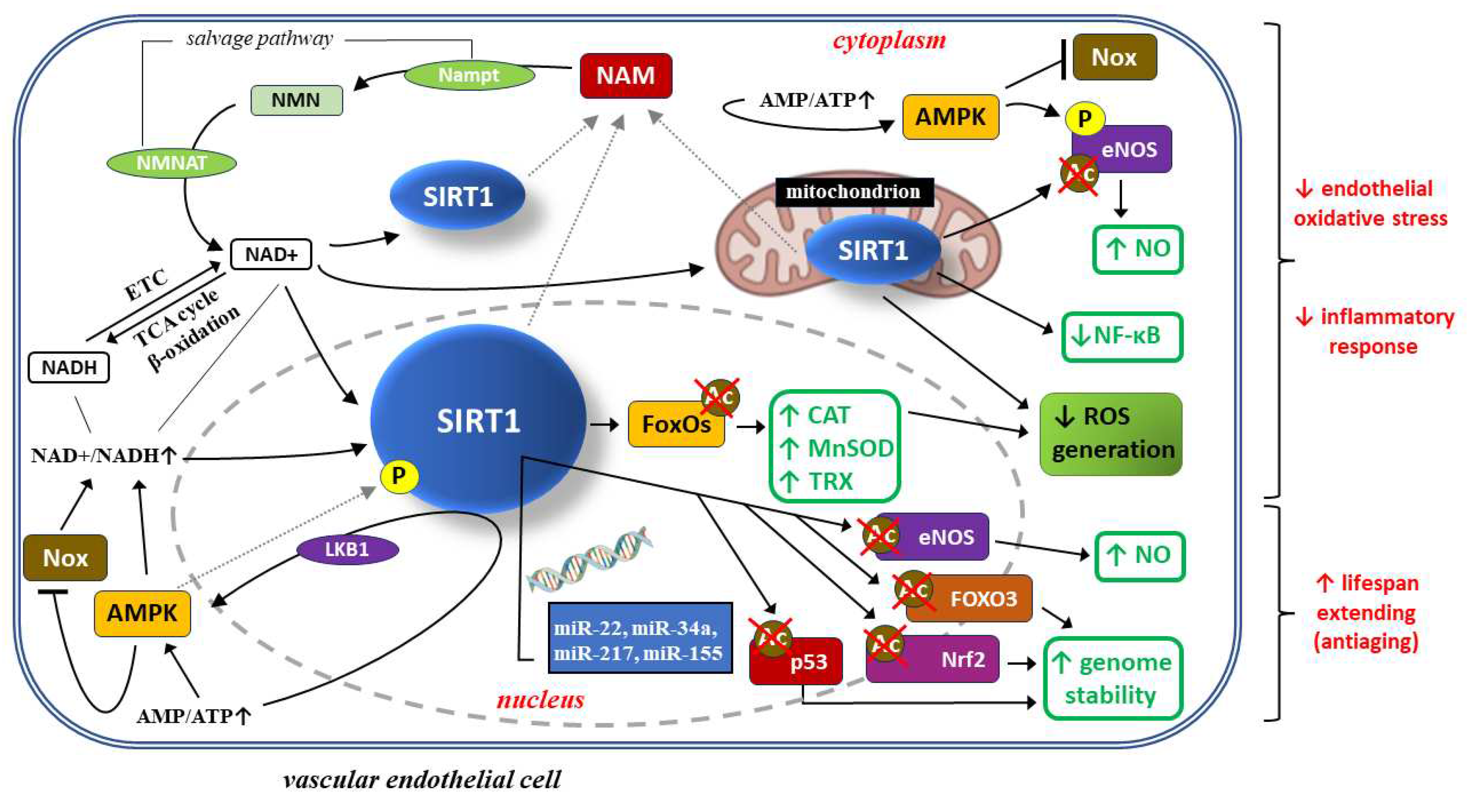
4.1. SIRT1 protective actions towards vascular endothelial cells
4.1.1. SIRT1 and the protection of endothelial cells against oxidative stress and inflammatory response
SIRT1 may protect endothelial cells through autophagy regulation
4.1.2. SIRT1 and possible protection of endothelial cells against senescence
4.2. Anti-inflammatory action of SIRT1 within the placenta in the context of preeclampsia
SIRT1 alleviates PE course on animal models of PE
SIRT1 induction alleviates PE manifestations
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-OAADPr | 2´-O-acetyl-adenosine diphosphate(ADP)-ribose. |
| AMPK | adenosine monophosphate(AMP)-activated protein kinase. |
| ARE | antioxidant response element. |
| ATG5 | ATG7, ATG8 – autophagy related-proteins 5, 7, 8. |
| Beclin-1 | the mammalian ortholog of yeast Atg6/Vps30, an essential autophagy protein that contains a Bcl-2 homology-3 domain. |
| BECN1 | Beclin-1 gene. |
| CAT | CAT – catalase gene, catalase (antioxidant enzyme), respectively. |
| CD40 | 50-kDa integral membrane protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R) family. |
| CSP | cell senescence phenotype. |
| CTSD | cathepsin D . |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition. |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase. |
| ETC | electron transport chain. |
| FEEL-1 | link domain-containing scavenger receptor-1. |
| FoxOs | forkhead O class box transcription factors. |
| FoxO1 | FoxO3 – forkhead box protein O1 and O3, respectively. |
| GCM1 | glial cells missing-1 (transcription factor). |
| GLUT1 | glucose transporter 1. |
| GOT | glutamicoxaloacetic transaminase. |
| GPT | glutamic pyruvic transaminase. |
| GPX | glutathione peroxidase. |
| GPX1 | GPX2, GPX3 – glutathione peroxidase isoforms 1, 2 and 3, respectively. |
| GSH | glutathione. |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide. |
| HIF | hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF). |
| HIF-1α | hypoxia-inducible factor 1 subunit alpha. |
| HIF-2α | hypoxia-inducible factor 2 subunit alpha. |
| HIFα | HIFβ – domains that make up the (hypoxia-inducible factor) HIF molecule domain. |
| HMGB1 | high mobility group box 1 (nonhistone nuclear protein). |
| HO-1 | heme oxygenase-1. |
| HSF1 | heat shock transcription factor 1. |
| HSP70 | 70-kDa heat shock proteins. |
| HSPs | heat shock proteins. |
| HUVEC | human umbilical vein endothelial cells. |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule 1, also known as CD54 (cluster of differentiation 54). |
| IL-1 | IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12 –interleukins: 1, 1 beta, 6, 8, 10 and 12. |
| IUFD | intrauterine fetal death. |
| IL-12p40 | interleukin-12 subunit beta (p40). |
| KO | knockout. |
| L-NAME | L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester. |
| LAMP1 | LAMP2 – lysosomal associated membrane protein 1,2. |
| LC3 | microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (MAP1LC3), a human homologue of yeast Atg8, an essential component of autophagy. |
| LC3-II | membrane-bound: lipidated form of LC3. |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase. |
| LKB1 | liver kinase B1. |
| LOX-1 | lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein-1. |
| LPL | placental lipoprotein lipase. |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide. |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. |
| mi-R217 | mi-R34a, mi-R155, mi-R22 – micro-RNA molecules. |
| MnSOD | manganese superoxide dismutase (antioxidant enzyme). |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin (an ubiquitous serine-threonine protein kinase). |
| NAD | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. |
| NAD+ | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (oxidized form). |
| NADH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form, H for hydrogen). |
| NAM | nicotinamide. |
| NCoR1 | nuclear receptor co-repressor-1. |
| NDRG1 | N-myc downstream regulated gene 1 (formerly known as Drg1, Cap43, Rit42, RTP, and PROXY-1). |
| Nampt | nicotinamide mononucleotide adenyltransferase. |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells. |
| NMN | nicotinamide mononucleotide. |
| NMNAT | nicotinamide-(mono)nucleotide adenylyltransferase. |
| NMNAT1 | NMNAT2, NMNAT3 – nicotinamide-(mono)nucleotide adenylyltransferase isoforms: 1,2, and 3. |
| NO | nitric oxide. |
| NOS | nitric oxide synthase. |
| Nox | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidases. |
| NQO1 | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-quinone oxidoreductase-1. |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. |
| p62 | ubiquitin-binding scaffold protein, also known as sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1). |
| p53 | protein encoded by the TP53 tumor suppressor gene, marker of cell senescence. |
| p21 | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21, protein marker of cell senescence. |
| PE | preeclampsia. |
| PlGF | placenta growth factor. |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. |
| PPARγ2 | an isoform of PPARγ typical for adipose tissue. |
| PPRE | PPARγ-reactive elements. |
| PRDM1 | positive regulatory (PR) domain zinc finger protein 1, a coactivator selectively activating PPARγ. |
| Prdm16 | positive regulatory domain containing 16. |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction. |
| Rab7 | a small GTPase: member of the Rab family that controls transport to late endocytic compartments such as late endosomes and lysosomes. |
| RAB7 | Rab7 gene. |
| RAGE | receptor for advanced glycation end-products . |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species. |
| RUPP | reduced uterine perfusion pressure. |
| RXR | retinoid X-receptor. |
| SASP | senescence-associated secretory phenotype. |
| sEng | soluble endoglin: the extracellular domain of membrane endoglin. |
| sFlt-1 | soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1, also known as soluble vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-1 . |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA. |
| SIRT1 | silent information regulator 2 homolog 1 or sirtuin-1. |
| SIRT1 | SIRT7 – sirtuins 1 to 7 . |
| SMAD2 | SMAD3 – small mothers against decapentaplegic proteins 2 and 3 (transcription factors). |
| SMRT | silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors. |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase. |
| SQSTM1 | sequestosome 1: also known as ubiquitin-binding scaffold protein p62. |
| SREC-1 | scavenger receptor expressed by endothelial cell-1. |
| SRT2104 | experimental drug, a selective small molecule activator of SIRT1. |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription (transcription factor). |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (transcription factor). |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or the citric acid cycle. |
| TFEB | transcription factor EB (TFEB), a member of the MiT/TFE family of basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factors, a key regulator of the autophagy/lysosomal-to-nucleus signaling pathway. |
| TLR2 | TLR4 – toll-like receptor 2 and 4. |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor alpha. |
| TRX | thioredoxin (antioxidant protein). |
| TSC | trophoblast stem cells. |
| TZD | thiazolidinediones: synthetic activators of PPARγ. |
| WT TSC | wild-type trophoblast stem cells (TSC). |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, also known as CD106 (cluster of differentiation 106). |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor. |
References
- Pham, J.; Arul Nambi Rajan, K.; Li, P.; Parast, M.M. The role of Sirtuin1-PPARγ axis in placental development and function. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018, 60, R201–R212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Jauniaux, E. What is the placenta? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015, 213(4 Suppl):S6.e1, S6-8. [CrossRef]
- James, J.L.; Carter, A.M.; Chamley, L.W. Human placentation from nidation to 5 weeks of gestation. Part I: What do we know about formative placental development following implantation? Placenta. 2012, 33, 327–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncin, F.; Natale, D.; Parast, M.M. Signaling pathways in mouse and human trophoblast differentiation: a comparative review. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015, 72, 1291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, S.J. Why is placentation abnormal in preeclampsia? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015, 213(4 Suppl):S115-22. [CrossRef]
- Thornburg, K.L.; Marshall, N. The placenta is the center of the chronic disease universe. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015, 213(4 Suppl):S14-20. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Pei, J.; Li, M.; Gu, W. SIRT1: A Novel Protective Molecule in Pre-eclampsia. Int J Med Sci. 2022, 19, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, J.; Dai, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Ono, M.; Nishi, H. Sirtuin 1 is a potential therapeutic candidate gene for fetal growth restriction via insulin-like 4. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023, 36, 2253486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, J.; Dawson, D.; Roberts, D.; Bentley-Lewis, R. A systematic review of placental pathology in maternal diabetes mellitus. Placenta. 2015, 36, 101–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak-Kim, J.; Bao, S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Gilman-Sachs, A. Immunological modes of pregnancy loss: inflammation, immune effectors, and stress. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014, 72, 129–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul Nambi Rajan, K.; Khater, M.; Soncin, F.; Pizzo, D.; Moretto-Zita, M.; Pham, J.; Stus, O.; Iyer, P.; Tache, V.; Laurent, L.C.; Parast, M.M. Sirtuin1 is required for proper trophoblast differentiation and placental development in mice. Placenta. 2018, 62:1-8. [CrossRef]
- Lappas, M.; Mitton, A.; Lim, R.; Barker, G.; Riley, C.; Permezel, M. SIRT1 is a novel regulator of key pathways of human labor. Biol Reprod. 2011, 84, 167–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, Y.; Nelson, M.C.; Ong, E.S.; Jones, Y.Z.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Chien, K.R.; Koder, A.; Evans, R.M. PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell. 1999, 4, 585–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, A.J.; Yong, H.E.; Lappas, M.; Degrelle, S.A.; Keogh, R.J.; Da Silva-Costa, F.; Fournier, T.; Abumaree, M.; Keelan, J.A.; Kalionis, B.; Murthi, P. Decreased STAT3 in human idiopathic fetal growth restriction contributes to trophoblast dysfunction. Reproduction. 2015, 149, 523–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, A.; Price, K.A.; Glimcher, L.H. Maintenance of mouse trophoblast stem cell proliferation by TGF-beta/activin. Dev Biol. 2004, 275, 158–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Huang, G.; Fan, W.; Chen, Y.; Ward, J.M.; Xu, X.; Xu, Q.; Kang, A.; McBurney, M.W.; Fargo, D.C.; Hu, G.; Baumgart-Vogt, E.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. SIRT1-mediated deacetylation of CRABPII regulates cellular retinoic acid signaling and modulates embryonic stem cell differentiation. Mol Cell. 2014, 55, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Carpino, N.; Jou, S.T.; Chao, J.R.; Tanaka, S.; Shigeyoshi, Y.; Parganas, E.; Ihle, J.N. Leukemia inhibitory factor regulates trophoblast giant cell differentiation via Janus kinase 1-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3-suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 pathway. Mol Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1673–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, F.; Xu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Gao, B.; Yu, G.; Fang, D. JAK1-mediated Sirt1 phosphorylation functions as a negative feedback of the JAK1-STAT3 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2018, 293, 11067–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tache, V.; Ciric, A.; Moretto-Zita, M.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Maltepe, E.; Milstone, D.S.; Parast, M.M. Hypoxia and trophoblast differentiation: a key role for PPARγ. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2815–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, F.; Kurtev, M.; Chung, N.; Topark-Ngarm, A.; Senawong, T.; Machado De Oliveira, R.; Leid, M.; McBurney, M.W.; Guarente, L. Sirt1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPAR-gamma. Nature. 2004, 429, 771–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Kitagishi, Y. Expression and Function of PPARs in Placenta. PPAR Res. 2013, 2013:256508. [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Chu, N.; Liu, L.; Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiang, Q.; Cheng, H.; Li, M.; Gu, W. Progesterone Attenuates SIRT1-Deficiency-Mediated Pre-Eclampsia. Biomolecules. 2022, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo, A.M.; Bergamini, E.; Brunk, U.T.; Dröge, W.; Ffrench, M.; Terman, A. Autophagy and aging: the importance of maintaining "clean" cells. Autophagy. 2005, 1, 131–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, J.; Baehrecke, E.H. Life, death and autophagy. Nat Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Levine, B.; Cuervo, A.M.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature. 2008, 451, 1069–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, Y.; Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy contributes to lysosomal storage disorders. Autophagy. 2012, 8, 715–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimori, T. Autophagy: paying Charon's toll. Cell. 2007, 128, 833–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, A.; Cheng, S.B.; Ikawa, M.; Yoshimori, T.; Huber, W.J.; Menon, R.; Huang, Z.; Fierce, J.; Padbury, J.F.; Sadovsky, Y.; Saito, S.; Sharma, S. Evidence for lysosomal biogenesis proteome defect and impaired autophagy in preeclampsia. Autophagy. 2020, 16, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Huang, C.X.; Gao, J.J.; Shi, Y.; Li, H.; Yan, H.; Yan, S.J.; Zhang, Z. Resveratrol induces SIRT1-Dependent autophagy to prevent H2O2-Induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HTR8/SVneo cells. Placenta. 2020, 91:11-18. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xia, B.; Tang, L.; Wu, W.; Tang, J.; Liang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chen, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Echinacoside protects against MPTP/MPP+-induced neurotoxicity via regulating autophagy pathway mediated by Sirt1. Metab Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Hao, R.; Wang, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, C. SIRT1/Atg5/autophagy are involved in the antiatherosclerosis effects of ursolic acid. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016, 420(1-2):171-84. [CrossRef]
- Medina, D.L.; Di Paola, S.; Peluso, I.; Armani, A.; De Stefani, D.; Venditti, R.; Montefusco, S.; Scotto-Rosato, A.; Prezioso, C.; Forrester, A.; Settembre, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, Q.; Xu, H.; Sandri, M.; Rizzuto, R.; De Matteis, M.A.; Ballabio, A. Lysosomal calcium signalling regulates autophagy through calcineurin and TFEB. Nat Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 288–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, G.; Esposito, A.; Choi, H.; Matarese, M.; Benedetti, V.; Di Malta, C.; Monfregola, J.; Medina, D.L.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Ballabio, A. mTOR-dependent phosphorylation controls TFEB nuclear export. Nat Commun. 2018, 9, 3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaishi, R.; Yamada, T.; Nakabayashi, K.; Nishihara, H.; Furuta, I.; Kojima, T.; Morikawa, M.; Yamada, T.; Fujita, N.; Minakami, H. Autophagy in the placenta of women with hypertensive disorders in pregnancy. Placenta. 2014, 35, 974–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Qi, H.B.; Kamana, K.C.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, H.; Baker, P.N. Excessive autophagy induces the failure of trophoblast invasion and vasculature: possible relevance to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. J Hypertens. 2015, 33, 106–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, K.H.; Cho, E.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Roh, C.R. Autophagy-related proteins, LC3 and Beclin-1, in placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2008, 15, 912–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Chen, M.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, S.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, L.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Tan, L.; An, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. Sirt1 deacetylates and stabilizes p62 to promote hepato-carcinogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Xu, Y.; Wan, W.; Shou, X.; Qian, J.; You, Z.; Liu, B.; Chang, C.; Zhou, T.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Liu, W. Deacetylation of nuclear LC3 drives autophagy initiation under starvation. Mol Cell. 2015, 57, 456–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, Q.Z.; Wang, X.W.; Jian, Z.L.; Chen, D.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Q.C. Melatonin Alleviates Cardiac Dysfunction Via Increasing Sirt1-Mediated Beclin-1 Deacetylation and Autophagy During Sepsis. Inflammation. 2021, 44, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Ye, X.; Chen, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, S.; Xu, P.; Yu, J.; Wen, L.; Gao, R.; Fu, Y.; Qi, H.; Kilby, M.D.; Saffery, R.; Baker, P.N.; Tong, C. Advanced Maternal Age-associated SIRT1 Deficiency Compromises Trophoblast Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through an Increase in Vimentin Acetylation. Aging Cell. 2021, 20, e13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, Z.; Maiti, K.; Dedman, L.; Smith, R. Is there a role for placental senescence in the genesis of obstetric complications and fetal growth restriction? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018, 218(2S):S762-S773. [CrossRef]
- Biron-Shental, T.; Sukenik-Halevy, R.; Sharon, Y.; Goldberg-Bittman, L.; Kidron, D.; Fejgin, M.D.; Amiel, A. Short telomeres may play a role in placental dysfunction in preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010, 202, 381.e1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasta, O.; Swiader, A.; Grazide, M.H.; Rouahi, M.; Parant, O.; Vayssière, C.; Bujold, E.; Salvayre, R.; Guerby, P.; Negre-Salvayre, A. A role for 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal in premature placental senescence in preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021, 164:303-314. [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Armstrong, C.M.; Kaeberlein, M.; Guarente, L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature. 2000, 403, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, N.J.; Beard, S.; Binder, N.K.; Onda, K.; Kaitu'u-Lino, T.J.; Chen, Q.; Tuohey, L.; De Silva, M.; Tong, S. Key players of the necroptosis pathway RIPK1 and SIRT2 are altered in placenta from preeclampsia and fetal growth restriction. Placenta. 2017, 51: 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; An, X.; Fan, D. Histone Deacetylase Sirtuin 2 Enhances Viability of Trophoblasts Through p65-Mediated MicroRNA-146a/ACKR2 Axis. Reprod Sci. 2021, 28, 1370–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Liao, L.; Wei, X.; Zhou, R. SIRT3 deficiency affects the migration, invasion, tube formation and necroptosis of trophoblast and is implicated in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Placenta. 2022, 120:1-9. [CrossRef]
- Castex, J.; Willmann, D.; Kanouni, T.; Arrigoni, L.; Li, Y.; Friedrich, M.; Schleicher, M.; Wöhrle, S.; Pearson, M.; Kraut, N.; Méret, M.; Manke, T.; Metzger, E.; Schüle, R.; Günther, T. Inactivation of Lsd1 triggers senescence in trophoblast stem cells by induction of Sirt4. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandvoß, M.; Potthast, A.B.; von Versen-Höynck, F.; Das, A.M. HELLP Syndrome. Reprod Sci. 2017, 24, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartho, L.A.; O'Callaghan, J.L.; Fisher, J.J. ; Cuffe JSM, Kaitu'u-Lino, T.J.; Hannan, N.J.; Clifton, V.L.; Perkins, A.V. Analysis of mitochondrial regulatory transcripts in publicly available datasets with validation in placentae from pre-term, post-term and fetal growth restriction pregnancies. Placenta. 2021, 112:162-171. [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W.; Halperin, D.S.; Tontonoz, P. Before they were fat: adipocyte progenitors. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 454–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppen, A.; Kalkhoven, E. Brown vs white adipocytes: the PPARgamma coregulator story. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3250–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giblin, W.; Skinner, M.E.; Lombard, D.B. Sirtuins: guardians of mammalian healthspan. Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 271–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, F.; Kurtev, M.; Chung, N.; Topark-Ngarm, A.; Senawong, T.; Machado De Oliveira, R.; Leid, M.; McBurney, M.W.; Guarente, L. Sirt1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPAR-gamma. Nature. 2004, 429, 771–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, J.R.; Milner, J. SIRT1, metabolism and cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2012, 24, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons GE Jr, Pruitt, W. M.; Pruitt, K. Diverse roles of SIRT1 in cancer biology and lipid metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2015, 16, 950–65. [CrossRef]
- Farghali, H.; Kutinová Canová, N.; Lekić, N. Resveratrol and related compounds as antioxidants with an allosteric mechanism of action in epigenetic drug targets. Physiol Res. 2013, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, L.; Wang, L.; Kon, N.; Zhao, W.; Lee, S.; Zhang, Y.; Rosenbaum, M.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, W.; Farmer, S.R.; Accili, D. Brown remodeling of white adipose tissue by SirT1-dependent deacetylation of Pparγ. Cell. 2012, 150, 620–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhou, R.; Niu, J.; McNutt, M.A.; Wang, P.; Tong, T. SIRT1 is regulated by a PPAR{γ}-SIRT1 negative feedback loop associated with senescence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7458–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Kulp, S.K.; Chen, C.S. Energy restriction as an antitumor target of thiazolidinediones. J Biol Chem. 2010, 285, 9780–9791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calleri, E.; Pochetti, G. ; Dossou KSS, Laghezza, A. ; Montanari, R.; Capelli, D.; Prada, E.; Loiodice, F.; Massolini, G.; Bernier, M.; Moaddel, R. Resveratrol and its metabolites bind to PPARs. Chembiochem. 2014, 15, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, S.J. Why is placentation abnormal in preeclampsia? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015, 213(4 Suppl):S115-22. [CrossRef]
- Racicot, K.; Kwon, J.Y.; Aldo, P.; Silasi, M.; Mor, G. Understanding the complexity of the immune system during pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014, 72, 107–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, J.; Dawson, D.; Roberts, D.; Bentley-Lewis, R. A systematic review of placental pathology in maternal diabetes mellitus. Placenta. 2015, 36, 101–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.W.; Wakeland, A.K.; Parast, M.M. Trophoblast lineage specification, differentiation and their regulation by oxygen tension. J Endocrinol. 2018, 236, R43–R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Bae, S.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med. 2004, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelman, D.M.; Gertsenstein, M.; Nagy, A.; Simon, M.C.; Maltepe, E. Placental cell fates are regulated in vivo by HIF-mediated hypoxia responses. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 3191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltepe, E.; Krampitz, G.W.; Okazaki, K.M.; Red-Horse, K.; Mak, W.; Simon, M.C.; Fisher, S.J. Hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent histone deacetylase activity determines stem cell fate in the placenta. Development. 2005, 132, 3393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeland, A.K.; Soncin, F.; Moretto-Zita, M.; Chang, C.W.; Horii, M.; Pizzo, D.; Nelson, K.K.; Laurent, L.C.; Parast, M.M. Hypoxia Directs Human Extravillous Trophoblast Differentiation in a Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Dependent Manner. Am J Pathol. 2017, 187, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Z.; Maecker, H.L.; Johnson, R.S.; Giaccia, A.J. Inhibition of PPAR gamma 2 gene expression by the HIF-1-regulated gene DEC1/Stra13: a mechanism for regulation of adipogenesis by hypoxia. Dev Cell. 2002, 2, 331–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tache, V.; Ciric, A.; Moretto-Zita, M.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Maltepe, E.; Milstone, D.S.; Parast, M.M. Hypoxia and trophoblast differentiation: a key role for PPARγ. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2815–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Ni, X. Reduced expression of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 in preeclamptic placentas is associated with decreased PPARγ but increased PPARα expression. Endocrinology. 2014, 155, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P.; Chen, C.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Su, T.H.; Chen, H. Decreased placental GCM1 (glial cells missing) gene expression in pre-eclampsia. Placenta. 2004, 25, 413–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, M.; Strick, R.; Strissel, P.L.; Vogt, N.; Parsch, H.; Beckmann, M.W.; Schild, R.L. Impaired cytotrophoblast cell-cell fusion is associated with reduced Syncytin and increased apoptosis in patients with placental dysfunction. Mol Reprod Dev. 2008, 75, 175–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baczyk, D.; Drewlo, S.; Proctor, L.; Dunk, C.; Lye, S.; Kingdom, J. Glial cell missing-1 transcription factor is required for the differentiation of the human trophoblast. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 719–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karumanchi, S.A.; Epstein, F.H. Placental ischemia and soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1: cause or consequence of preeclampsia? Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 959–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamatsu, T.; Fujii, T.; Kusumi, M.; Zou, L.; Yamashita, T.; Osuga, Y.; Momoeda, M.; Kozuma, S.; Taketani, Y. Cytotrophoblasts up-regulate soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 expression under reduced oxygen: an implication for the placental vascular development and the pathophysiology of preeclampsia. Endocrinology. 2004, 145, 4838–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lewis, D.F.; Wang, Y. Hypoxia-induced increase in soluble Flt-1 production correlates with enhanced oxidative stress in trophoblast cells from the human placenta. Placenta. 2005, 26(2-3):210-7. [CrossRef]
- Nevo, O.; Soleymanlou, N.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Kingdom, J.; Many, A.; Zamudio, S.; Caniggia, I. Increased expression of sFlt-1 in in vivo and in vitro models of human placental hypoxia is mediated by HIF-1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006, 291, R1085–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munaut, C.; Lorquet, S.; Pequeux, C.; Blacher, S.; Berndt, S.; Frankenne, F.; Foidart, J.M. Hypoxia is responsible for soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) but not for soluble endoglin induction in villous trophoblast. Hum Reprod. 2008, 23, 1407–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taché, V.; LaCoursiere, D.Y.; Saleemuddin, A.; Parast, M.M. Placental expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1/soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 correlates with severity of clinical preeclampsia and villous hypermaturity. Hum Pathol. 2011, 42, 1283–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, B.; Abe, E.; Murthi, P.; Nagamatsu, T.; Szukiewicz, D.; Salafia, C. Placental angiogenesis, maternal and fetal vessels--a workshop report. Placenta. 2007 Apr;28 Suppl A:S94-6. [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, F.P.; Drewlo, S.; English, F.A.; Kingdom, J.; Johns, E.J.; Kenny, L.C.; Walsh, S.K. Evidence implicating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Hypertension. 2011, 58, 882–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, S.A.; Minhas, A.; Whiteley, K.J.; Qu, D.; Sled, J.G.; Kingdom, J.C.; Adamson, S.L. Effects of reduced Gcm1 expression on trophoblast morphology, fetoplacental vascularity, and pregnancy outcomes in mice. Hypertension. 2012, 59, 732–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.N.; Smith, S.C.; To, K.F.; Sahota, D.S.; Baker, P.N. Increased placental apoptosis in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001, 184, 1249–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.M.; Johnson, R.D.; Smith, S.D.; Anteby, E.Y.; Sadovsky, Y. Hypoxia limits differentiation and up-regulates expression and activity of prostaglandin H synthase 2 in cultured trophoblast from term human placenta. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999, 180, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elchalal, U.; Humphrey, R.G.; Smith, S.D.; Hu, C.; Sadovsky, Y.; Nelson, D.M. Troglitazone attenuates hypoxia-induced injury in cultured term human trophoblasts. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2004, 191, 2154–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Lee, Y.M.; Chun, Y.S.; Chen, J.; Kim, J.E.; Park, J.W. Sirtuin 1 modulates cellular responses to hypoxia by deacetylating hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. Mol Cell. 2010, 38, 864–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioum, E.M.; Chen, R.; Alexander, M.S.; Zhang, Q.; Hogg, R.T.; Gerard, R.D.; Garcia, J.A. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha signaling by the stress-responsive deacetylase sirtuin 1. Science. 2009, 324, 1289–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Dioum, E.M.; Hogg, R.T.; Gerard, R.D.; Garcia, J.A. Hypoxia increases sirtuin 1 expression in a hypoxia-inducible factor-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 2011, 286, 13869–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Nelson, D.M.; Sadovsky, Y. N-myc down-regulated gene 1 modulates the response of term human trophoblasts to hypoxic injury. J Biol Chem. 2006, 281, 2764–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broady, A.J.; Loichinger, M.H.; Ahn, H.J.; Davy, P.M.; Allsopp, R.C.; Bryant-Greenwood, G.D. Protective proteins and telomere length in placentas from patients with pre-eclampsia in the last trimester of gestation. Placenta. 2017, 50:44-52. [CrossRef]
- Cudmore, M.J.; Ramma, W.; Cai, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Ahmad, S.; Al-Ani, B.; Ahmed, A. Resveratrol inhibits the release of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (sFlt-1) from human placenta. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012, 206, 253–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, N.J.; Brownfoot, F.C.; Cannon, P.; Deo, M.; Beard, S.; Nguyen, T.V.; Palmer, K.R.; Tong, S.; Kaitu'u-Lino, T.J. Resveratrol inhibits release of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase (sFlt-1) and soluble endoglin and improves vascular dysfunction - implications as a preeclampsia treatment. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Zuo, Q.; Huang, S.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zou, S.; Fan, M.; Sun, L. Resveratrol inhibits trophoblast apoptosis through oxidative stress in preeclampsia-model rats. Molecules. 2014, 19, 20570–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, G.J.; Woods, A.W.; Jauniaux, E.; Kingdom, J.C. Rheological and physiological consequences of conversion of the maternal spiral arteries for uteroplacental blood flow during human pregnancy. Placenta. 2009, 30, 473–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher, A.P.; Joshi, A.A.; Joshi, S.R. Maternal micronutrients, omega-3 fatty acids, and placental PPARγ expression. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014, 39, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Higaki, T.; Matsubara, Y.; Nawa, A. Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Int J Mol Sci. 2015, 16, 4600–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, K.R.; Tong, S.; Kaitu'u-Lino, T.J. Placental-specific sFLT-1: role in pre-eclamptic pathophysiology and its translational possibilities for clinical prediction and diagnosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 2017, 23, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccone, L.; Piragine, E.; Brogi, S.; Camodeca, C.; Fucci, R.; Calderone, V.; Nencetti, S.; Martelli, A.; Orlandini, E. Resveratrol-like Compounds as SIRT1 Activators. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 15105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokuda, K.; Ichihara, A. Preeclampsia up to date-What's going on? Hypertens Res. 2023, 46, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagel, S.; Verlohren, S. Role of placenta in development of pre-eclampsia: revisited. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020, 56, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, J.; Baker, P.N.; Tong, C. Revisiting preeclampsia: a metabolic disorder of the placenta. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 336–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, E.E.; Richardson, L.S.; Torloni, M.R.; Menon, R. Gestational tissue inflammatory biomarkers at term labor: A systematic review of literature. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018, 79, 10–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Shim, S.H.; Sung, S.R.; Lee, K.A.; Shim, J.Y.; Cha, D.H.; Lee, K.J. Gene expression analysis of the microdissected trophoblast layer of human placenta after the spontaneous onset of labor. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e77648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.J.; Davis, J.; Thompson, K.; Bryant-Greenwood, G. Visfatin/Nampt and SIRT1: Roles in Postterm Delivery in Pregnancies Associated With Obesity. Reprod Sci. 2015, 22, 1028–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, A.C.; Cornelius, D.C.; Amaral, L.M.; Faulkner, J.L. ; Cunningham MW Jr, Wallace, K. ; LaMarca, B. The role of inflammation in the pathology of preeclampsia. Clin Sci (Lond). 2016, 130, 409–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshani, A.; Konje, J.C. Placental dysfunction in obese women and antenatal surveillance. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2023, 91:102407. [CrossRef]
- Meher, A.P.; Joshi, A.A.; Joshi, S.R. Maternal micronutrients, omega-3 fatty acids, and placental PPARγ expression. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014, 39, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Q.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Yu, Z.; Fu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, D.X. Rosiglitazone pretreatment protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced fetal demise through inhibiting placental inflammation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 423:51-9. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Yu, Y.; Guan, H.B.; Qiao, C. Effect of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in a Rat Model of Preeclampsia. Reprod Sci. 2016, 23, 1058–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Garcia, S.M.; Roeder, H.A.; Nelson, K.K.; Liao, X.; Pizzo, D.P.; Laurent, L.C.; Parast, M.M.; LaCoursiere, D.Y. Maternal obesity and sex-specific differences in placental pathology. Placenta. 2016, 38:33-40. [CrossRef]
- Gillum, M.P.; Kotas, M.E.; Erion, D.M.; Kursawe, R.; Chatterjee, P.; Nead, K.T.; Muise, E.S.; Hsiao, J.J.; Frederick, D.W.; Yonemitsu, S.; Banks, A.S.; Qiang, L.; Bhanot, S.; Olefsky, J.M.; Sears, D.D.; Caprio, S.; Shulman, G.I. SirT1 regulates adipose tissue inflammation. Diabetes. 2011, 60, 3235–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Guo, Z.; Bosco, C.; Guidotti, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Parast, M.; Schaack, J. ; Hay WW Jr, Moore, T. R.; Shao, J. Maternal High-Fat Feeding Increases Placental Lipoprotein Lipase Activity by Reducing SIRT1 Expression in Mice. Diabetes. 2015, 64, 3111–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawyer, C.R.; Horvat, D.; Leonard, D.; Allen, S.R.; Jones, R.O.; Zawieja, D.C.; Kuehl, T.J.; Uddin, M.N. Hyperglycemia impairs cytotrophoblast function via stress signaling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014, 211, 541–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaki, N.; Masuyama, H.; Masumoto, A.; Takamoto, N.; Hiramatsu, Y. Expression and potential role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in the placenta of diabetic pregnancy. Placenta. 2007, 28, 315–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawerbaum, A.; Capobianco, E.; Pustovrh, C.; White, V.; Baier, M.; Salzberg, S.; Pesaresi, M.; Gonzalez, E. Influence of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activation by its endogenous ligand 15-deoxy Delta12,14 prostaglandin J2 on nitric oxide production in term placental tissues from diabetic women. Mol Hum Reprod. 2004, 10, 671–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdsworth-Carson, S.J.; Lim, R.; Mitton, A.; Whitehead, C.; Rice, G.E.; Permezel, M.; Lappas, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are altered in pathologies of the human placenta: gestational diabetes mellitus, intrauterine growth restriction and preeclampsia. Placenta. 2010, 31, 222–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knabl, J.; Hüttenbrenner, R.; Hutter, S.; Günthner-Biller, M.; Vrekoussis, T.; Karl, K.; Friese, K.; Kainer, F.; Jeschke, U. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ) is down regulated in trophoblast cells of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and in trophoblast tumour cells BeWo in vitro after stimulation with PPARγ agonists. J Perinat Med. 2014, 42, 179–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capobianco, E.; Fornes, D.; Linenberg, I.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T.; Jawerbaum, A. A novel rat model of gestational diabetes induced by intrauterine programming is associated with alterations in placental signaling and fetal overgrowth. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 422:221-232. [CrossRef]
- Viana-Mattioli, S.; Nunes, P.; Cavalli, R.; Sandrim, V. Analysis of SIRT1 Expression in Plasma and in an In Vitro Model of Preeclampsia. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020, 2020:4561083. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yua, H.; Xu, J.; Che, H. SIRT1 inhibits releases of HMGB1 and HSP70 from human umbilical vein endothelial cells caused by IL-6 and the serum from a preeclampsia patient and protects the cells from death. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017, 88:449-458. [CrossRef]
- Majeed, Y.; Halabi, N.; Madani, A.Y.; Engelke, R.; Bhagwat, A.M.; Abdesselem, H.; Agha, M.V.; Vakayil, M.; Courjaret, R.; Goswami, N.; Hamidane, H.B.; Elrayess, M.A.; Rafii, A.; Graumann, J.; Schmidt, F.; Mazloum, N.A. SIRT1 promotes lipid metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis in adipocytes and coordinates adipogenesis by targeting key enzymatic pathways. Sci Rep. 2021 ;11, 8177. [CrossRef]
- Hopp, A.K.; Grüter, P.; Hottiger, M.O. Erratum: Hopp, A. K., et al. Regulation of Glucose Metabolism by NAD+ and ADP-Ribosylation. Cells 2019, 8, 890, Erratum for: Cells. 2019, 8(8)11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, S.; Baker, J.R.; Vuppusetty, C.; Koga, T.; Colley, T.; Fenwick, P.; Donnelly, L.E.; Barnes, P.J.; Ito, K. The dynamic shuttling of SIRT1 between cytoplasm and nuclei in bronchial epithelial cells by single and repeated cigarette smoke exposure. PLoS One. 2018, 13, e0193921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, F.K. Mitochondrial Redox Metabolism: The Epicenter of Metabolism during Cancer Progression. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Sirt1 Inhibits Oxidative Stress in Vascular Endothelial Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017, 2017:7543973. [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Hausenloy, D.J.; Andreadou, I.; Horman, S.; Bertrand, L.; Beauloye, C. AMP-activated protein kinase: A remarkable contributor to preserve a healthy heart against ROS injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021, 166:238-254. [CrossRef]
- Giannakou, M.E.; Partridge, L. The interaction between FOXO and SIRT1: tipping the balance towards survival. Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 408–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Furukawa-Hibi, Y.; Chen, C.; Horio, Y.; Isobe, K.; Ikeda, K.; Motoyama, N. SIRT1 is critical regulator of FOXO-mediated transcription in response to oxidative stress. Int J Mol Med. 2005, 16, 237–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, E.; Wu, Y. Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) Enhances miR-155-Mediated Endothelial Senescence by Targeting Sirtuin1 (SIRT1). Med Sci Monit. 2019, 25:8820-8835. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Kallistatin attenuates endothelial senescence by modulating Let-7g-mediated miR-34a-SIRT1-eNOS pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2018, 22, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, G.F.; Wu, K.; Hu, K.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, J. NAMPT regulates senescence, proliferation, and migration of endothelial progenitor cells through the SIRT1 AS lncRNA/miR-22/SIRT1 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016, 478, 1382–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, D.; Zhang, N.; Yuan, T.; Tao, H. MiR-217 promotes endothelial cell senescence through the SIRT1/p53 signaling pathway. J Mol Histol. 2021, 52, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Holder, R.; Porter, C.; Shah, Z. Vitamin D3 attenuates doxorubicin-induced senescence of human aortic endothelial cells by upregulation of IL-10 via the pAMPKα/Sirt1/Foxo3a signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2021, 16, e0252816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, J.; Fu, M.; Dong, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Hu, S.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Tu, L. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition improves endothelial senescence by activating AMPK/SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020, 177:113951. [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.L.; Ruan, B.; Song, P.; Fang, Z.Q.; Yue, Z.S.; Liu, J.J.; Dou, G.R.; Han, H.; Wang, L. Shear stress-induced cellular senescence blunts liver regeneration through Notch-sirtuin 1-P21/P16 axis. Hepatology. 2022, 75, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochette, L.; Zeller, M.; Cottin, Y.; Vergely, C. Diabetes, oxidative stress and therapeutic strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014, 1840, 2709–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaludercic, N.; Di Lisa, F. Mitochondrial ROS Formation in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020, 7:12. [CrossRef]
- Keane, K.N.; Cruzat, V.F.; Carlessi, R. ; de Bittencourt PI Jr, Newsholme, P. Molecular Events Linking Oxidative Stress and Inflammation to Insulin Resistance and β-Cell Dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2015, 2015:181643. [CrossRef]
- Volpe CMO, Villar-Delfino, P. H.; Dos Anjos PMF, Nogueira-Machado, J.A. Cellular death, reactive oxygen species (ROS) and diabetic complications. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 119. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Duraisamy, A.J.; Kowluru, R.A. Sirt1: A Guardian of the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes. 2018, 67, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karbasforooshan, H.; Karimi, G. The role of SIRT1 in diabetic retinopathy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018, 97:190-194. [CrossRef]
- Kume, S.; Uzu, T.; Kashiwagi, A.; Koya, D. SIRT1, a calorie restriction mimetic, in a new therapeutic approach for type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic vascular complications. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2010, 10, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orimo, M.; Minamino, T.; Miyauchi, H.; Tateno, K.; Okada, S.; Moriya, J.; Komuro, I. Protective role of SIRT1 in diabetic vascular dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009, 29, 889–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Eto, M.; Kano, M.R.; Kahyo, T.; Setou, M.; Ogawa, S.; Iijima, K.; Akishita, M.; Ouchi, Y. Induction of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, SIRT1, and catalase by statins inhibits endothelial senescence through the Akt pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010, 30, 2205–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.B.; Sonowal, H.; Shukla, K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Ramana, K.V. Aldose reductase regulates hyperglycemia-induced HUVEC death via SIRT1/AMPK-α1/mTOR pathway. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019, 63, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, F.; Cacicedo, J.M.; Ruderman, N.; Ido, Y. SIRT1 modulation of the acetylation status, cytosolic localization, and activity of LKB1. Possible role in AMP-activated protein kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 2008, 283, 27628–27635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, G.; Niu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Sun, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, S.; Liang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cong, W.; Jin, L.; Zhu, Z. Resveratrol Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing via SIRT1-FOXO1-c-Myc Signaling Pathway-Mediated Angiogenesis. Front Pharmacol. 2019, 10:421. [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart, J. 2012, 33, 829–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, I.C.; Sun, W.; Su, M.I.; Hsu, P.H.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; DeFea, K.; Pan, S.; Tsai, M.D.; Shyy, J.Y. AMP-activated protein kinase functionally phosphorylates endothelial nitric oxide synthase Ser633. Circ Res. 2009, 104, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelius, D.C.; Wallace, K. Autophagy in preeclampsia: A new target? EBioMedicine. 2020, 57:102864. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wang, F.; Gong, G. Effect of Autophagy Regulated by Sirt1/FoxO1 Pathway on the Release of Factors Promoting Thrombosis from Vascular Endothelial Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019, 20, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daitoku, H.; Hatta, M.; Matsuzaki, H.; Aratani, S.; Ohshima, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Nakajima, T.; Fukamizu, A. Silent information regulator 2 potentiates Foxo1-mediated transcription through its deacetylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004, 101, 10042–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bi, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.X.; Chiu, J.J.; Liu, G.S.; Zhang, Y.; Bu, P.; Jiang, F. Shear stress regulates endothelial cell autophagy via redox regulation and Sirt1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchitsu, Y.; Fukuda, M. Revisiting Rab7 Functions in Mammalian Autophagy: Rab7 Knockout Studies. Cells. 2018, 7, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda-Watanabe, A.; Kitada, M.; Kanasaki, K.; Koya, D. SIRT1 inactivation induces inflammation through the dysregulation of autophagy in human THP-1 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012, 427, 191–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.N.; Jiang, X.; Tang, W.; Song, P. Influence of intermittent fasting on autophagy in the liver. Biosci Trends. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.I.; Kim, K.I.; Woo, S.K.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, K.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.S. Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 Protects Brain Vascular Endothelial Cells from Radiation-Induced Brain Damage. Cells. 2019, 8, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.L.; Li, Y. Endothelial cell senescence and age-related vascular diseases. J Genet Genomics. 2014, 41, 485–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.S.; Maeng, Y.S.; Park, Y.W.; Koos, B.J.; Kwon, Y.G.; Kim, Y.H. Increased senescence and reduced functional ability of fetal endothelial progenitor cells in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia without intrauterine growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008, 199, 259–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, J.; Mitsui-Saito, M.; Hayashi, C.; Hoshiai, T.; Senoo, M.; Chisaka, H.; Yaegashi, N.; Okamura, K. Decrease and senescence of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with preeclampsia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005, 90, 5329–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.S.; Choi, H.S.; Ham, S.A.; Yoo, T.; Lee, W.J.; Paek, K.S.; Seo, H.G. Deacetylation-mediated interaction of SIRT1-HMGB1 improves survival in a mouse model of endotoxemia. Sci Rep. 2015, 5:15971. [CrossRef]
- Holmlund, U.; Wähämaa, H.; Bachmayer, N.; Bremme, K.; Sverremark-Ekström, E.; Palmblad, K. The novel inflammatory cytokine high mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) is expressed by human term placenta. Immunology. 2007, 122, 430–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Cai, J.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Teng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Tao, M.; Xia, A.; Xue, M.; Zhou, S.; Chen, A.F. Hypoxic trophoblast HMGB1 induces endothelial cell hyperpermeability via the TRL-4/caveolin-1 pathway. J Immunol. 2014, 193, 5000–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Nie, L.; Zeng, X.; Xin, S.; Wu, M.; Yang, B.; Luo, Y.; Liu, B.; Zheng, J.; Liu, H. Enhancement of heat shock protein 70 attenuates inducible nitric oxide synthase in preeclampsia complicated with fetal growth restriction. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 35, 2555–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peraçoli, J.C.; Bannwart-Castro, C.F.; Romao, M.; Weel, I.C.; Ribeiro, V.R.; Borges, V.T.; Rudge, M.V.; Witkin, S.S.; Peraçoli, M.T. High levels of heat shock protein 70 are associated with pro-inflammatory cytokines and may differentiate early- from late-onset preeclampsia. J Reprod Immunol. 2013, 100, 129–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molvarec, A.; Szarka, A.; Walentin, S.; Beko, G.; Karádi, I.; Prohászka, Z.; Rigó J, Jr. Serum heat shock protein 70 levels in relation to circulating cytokines, chemokines, adhesion molecules and angiogenic factors in women with preeclampsia. Clin Chim Acta. 2011, 412(21-22):1957-62. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Ageta-Ishihara, N.; Nagatsu, S.; Takao, K.; Komine, O.; Endo, F.; Miyakawa, T.; Misawa, H.; Takahashi, R.; Kinoshita, M.; Yamanaka, K. SIRT1 overexpression ameliorates a mouse model of SOD1-linked amyotrophic lateral sclerosis via HSF1/HSP70i chaperone system. Mol Brain. 2014, 7:62. [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Gu, B.; Lv, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhou, X.; Qiao, W.; Mao, Z.; Zuo, G.; Li, Q.; Miao, D.; Jin, J. 1, 25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 with tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects against rheumatoid arthritis by promoting p53 acetylation-mediated apoptosis via Sirt1 in synoviocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zheng, X.D.; Li, H. Protective role of SIRT1-mediated Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway in the preeclampsia rat models. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021, 38, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACOG Practice Bulletin, No. 202: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol. 2019, 133, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Mostoslavsky, R.; Saito, S.; Manis, J.P.; Gu, Y.; Patel, P.; Bronson, R.; Appella, E.; Alt, F.W.; Chua, K.F. Developmental defects and p53 hyperacetylation in Sir2 homolog (SIRT1)-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003, 100, 10794–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBurney, M.W.; Yang, X.; Jardine, K.; Hixon, M.; Boekelheide, K.; Webb, J.R.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Lemieux, M. The mammalian SIR2alpha protein has a role in embryogenesis and gametogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Sengupta, K.; Li, C.; Kim, H.S.; Cao, L.; Xiao, C.; Kim, S.; Xu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chilton, B.; Jia, R.; Zheng, Z.M.; Appella, E.; Wang, X.W.; Ried, T.; Deng, C.X. Impaired DNA damage response, genome instability, and tumorigenesis in SIRT1 mutant mice. Cancer Cell. 2008, 14, 312–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Ye, X.; Chen, Z.; Fu, H.; Li, S.; Xu, P.; Yu, J.; Wen, L.; Gao, R.; Fu, Y.; Qi, H.; Kilby, M.D.; Saffery, R.; Baker, P.N.; Tong, C. Advanced Maternal Age-associated SIRT1 Deficiency Compromises Trophoblast Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through an Increase in Vimentin Acetylation. Aging Cell. 2021, 20, e13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhou, M.; Ge, Y.; Wang, X. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020, 187:111215. [CrossRef]
- Taskin, I.I.; Gurbuz, S.; Icen, M.S.; Derin, D.C.; Findik, F.M. Expression of sirtuin 2 and 7 in placenta accreta spectrum. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2023, 69, e20230360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.; Xu, X.; Yan, J. Placenta-derived exosomal miR-135a-5p promotes gestational diabetes mellitus pathogenesis by activating PI3K/AKT signalling pathway via SIRT1. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Zhong, L.; Huang, S.; Deng, L.; Pang, L. MiRNA-494 induces trophoblast senescence by targeting SIRT1. Hypertens Pregnancy. 2023, 42, 2219774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pei, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Luo, S.; Gu, W. CD74 deficiency reduces trophoblast invasion and proliferation mediated by SIRT1 in preeclampsia. Reproduction. 2023:REP-23-0202. [CrossRef]
- Deodati, A.; Inzaghi, E.; Cianfarani, S. Epigenetics and In Utero Acquired Predisposition to Metabolic Disease. Front Genet. 2020, 10:1270. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Kraus, W.L. SIRT1-dependent regulation of chromatin and transcription: linking NAD(+) metabolism and signaling to the control of cellular functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 ;1804, 1666-75. [CrossRef]
- Fortuny, L.; Sebastián, C. Sirtuins as Metabolic Regulators of Immune Cells Phenotype and Function. Genes (Basel). 2021, 12, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Y.; Tie, J.; Hu, D. Regulation of SIRT1 and Its Roles in Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2022, 13:831168. [CrossRef]
- Tamura, N.; Heidari, N. ; Faragher RGA, Smith RKW, Dudhia, J. Effects of resveratrol and its analogues on the cell cycle of equine mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. J Equine Sci. 2023, 34, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watroba, M.; Szukiewicz, D. Sirtuins at the Service of Healthy Longevity. Front Physiol. 2021, 12:724506. [CrossRef]
- Aksu, K.; Golal, E.; Aslan, M.A.; Ustunel, I.; Acar, N. The investigation of the role of sirtuin-1 on embryo implantation in oxidative stress-induced mice. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2021, 38, 2349–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sande, A.K.; Dalen, I.; Torkildsen, E.A.; Sande, R.K.; Morken, N.H. Pregestational maternal risk factors for preterm and term preeclampsia: A population-based cohort study. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, X.; Yuan, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H. Epidemiological trends of maternal hypertensive disorders of pregnancy at the global, regional, and national levels: a population-based study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021, 21, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




