Submitted:
12 October 2023
Posted:
13 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. From the RNA World to the Appearance of RNA Binding Proteins through Ribozymes with Peptidyl Transferase Activity
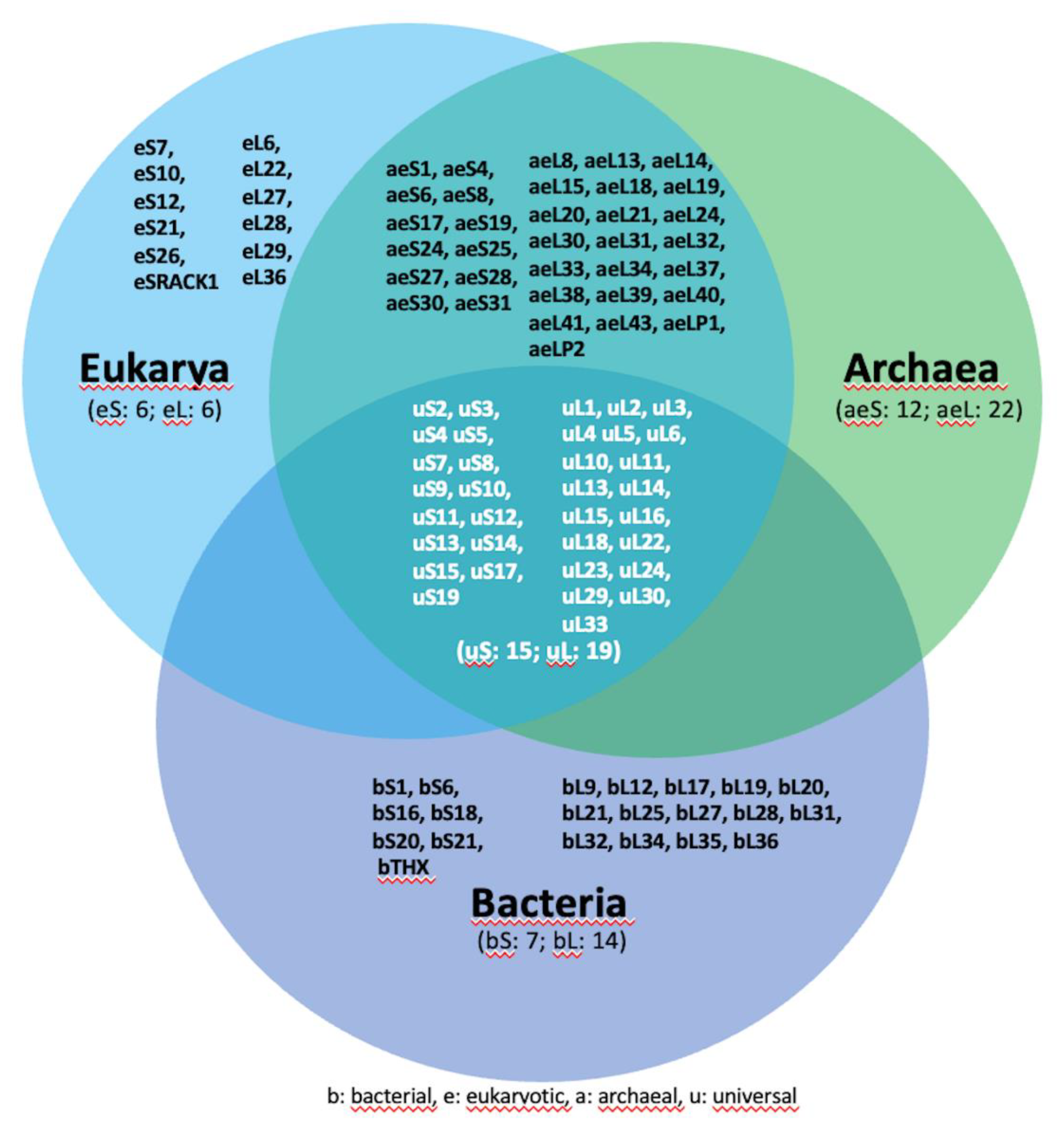
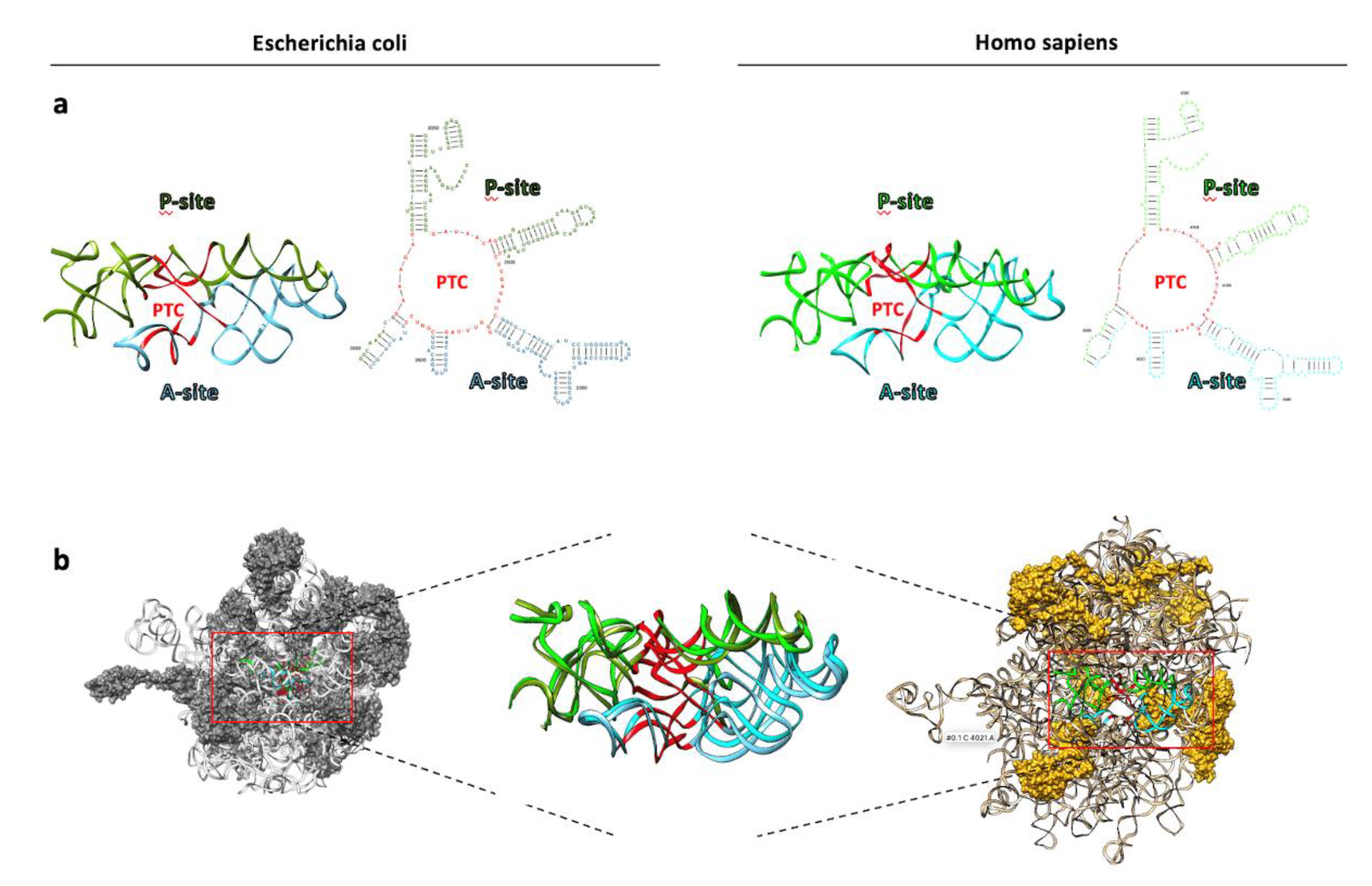
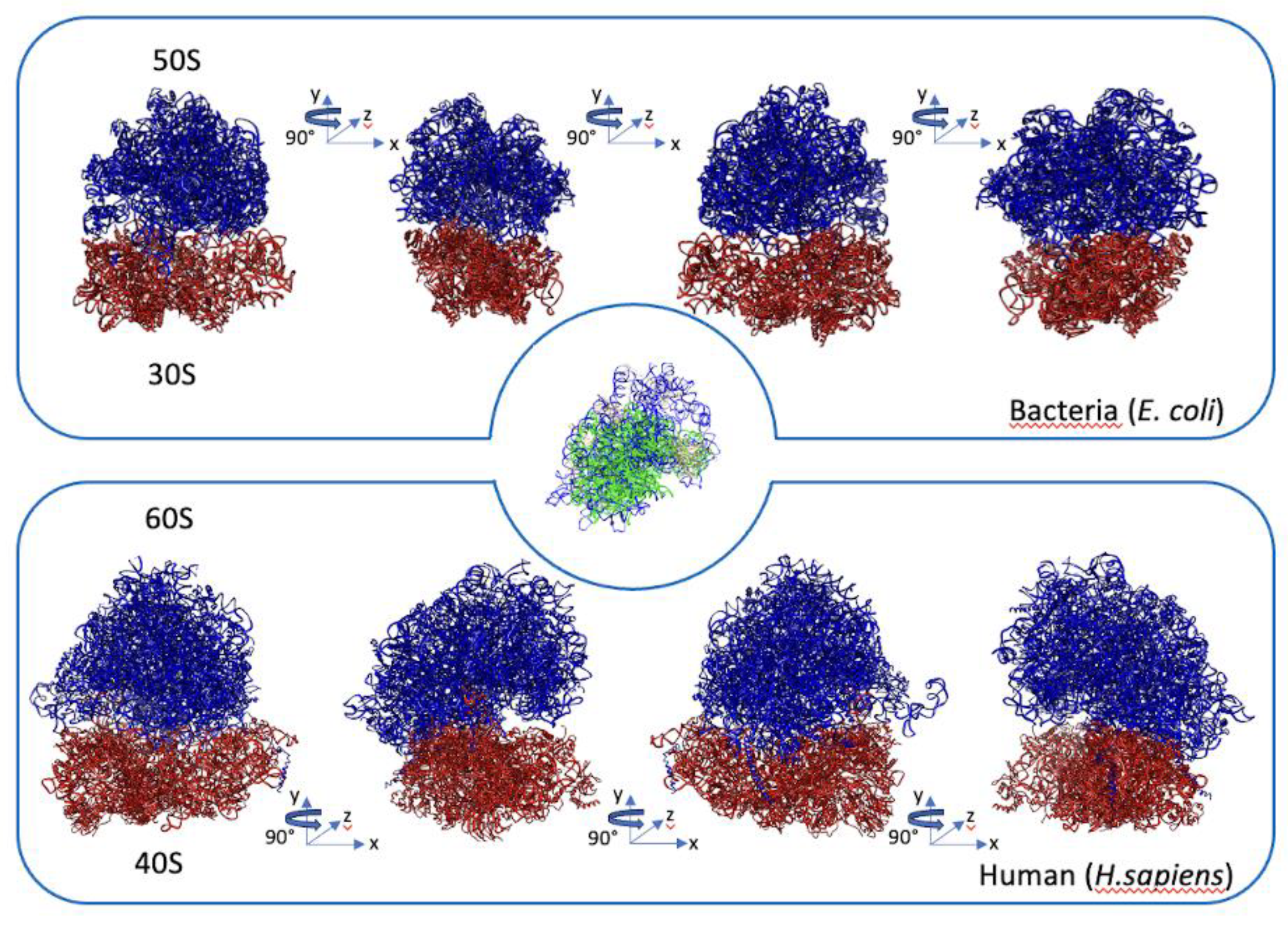
3. Overview of Ribosome and Ribosome Biogenesis
4. Ribosomopathies Cause Impaired RNA Binding Activity of RPs and RBFs
4.1. Impairment of Ribosomal Function for Rps19 Protein in Diamond-Blackfan Anemia
4.2. Impairment of Ribosomal Function for SBDS Protein in Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Y. Neelamraju, S. Hashemikhabir, e S. C. Janga, «The human RBPome: From genes and proteins to human disease», J. Proteomics, vol. 127, pp. 61–70, set. 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. Gerstberger, M. Hafner, e T. Tuschl, «A census of human RNA-binding proteins», Nat. Rev. Genet., vol. 15, fasc. 12, Art. fasc. 12, dic. 2014. [CrossRef]
- E. L. Van Nostrand et al., «A large-scale binding and functional map of human RNA-binding proteins», Nature, vol. 583, fasc. 7818, Art. fasc. 7818, lug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. E. Lukong, K. Chang, E. W. Khandjian, e S. Richard, «RNA-binding proteins in human genetic disease», Trends Genet., vol. 24, fasc. 8, pp. 416–425, ago. 2008. [CrossRef]
- H.-G. Wendel et al., «Dissecting eIF4E action in tumorigenesis», Genes Dev., vol. 21, fasc. 24, pp. 3232–3237, dic. 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. J. Kolb, D. J. Battle, e G. Dreyfuss, «Molecular functions of the SMN complex», J. Child Neurol., vol. 22, fasc. 8, pp. 990–994, ago. 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Darnell et al., «Kissing complex RNAs mediate interaction between the Fragile-X mental retardation protein KH2 domain and brain polyribosomes», Genes Dev., vol. 19, fasc. 8, pp. 903–918, apr. 2005. [CrossRef]
- N. Draptchinskaia et al., «The gene encoding ribosomal protein S19 is mutated in Diamond-Blackfan anaemia», Nat. Genet., vol. 21, fasc. 2, Art. fasc. 2, feb. 1999. [CrossRef]
- K. Bokov e S. V. Steinberg, «A hierarchical model for evolution of 23S ribosomal RNA», Nature, vol. 457, fasc. 7232, pp. 977–980, feb. 2009. [CrossRef]
- C. Hsiao, S. Mohan, B. K. Kalahar, e L. D. Williams, «Peeling the onion: ribosomes are ancient molecular fossils», Mol. Biol. Evol., vol. 26, fasc. 11, pp. 2415–2425, nov. 2009. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Mears, J. J. Cannone, S. M. Stagg, R. R. Gutell, R. K. Agrawal, e S. C. Harvey, «Modeling a minimal ribosome based on comparative sequence analysis», J. Mol. Biol., vol. 321, fasc. 2, pp. 215–234, ago. 2002. [CrossRef]
- G. E. Fox, «Origin and Evolution of the Ribosome», Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., vol. 2, fasc. 9, p. a003483, set. 2010. [CrossRef]
- N. Ban, P. Nissen, J. Hansen, P. B. Moore, e T. A. Steitz, «The Complete Atomic Structure of the Large Ribosomal Subunit at 2.4 Å Resolution», vol. 289, 2000.
- J.-P. Armache et al., «Cryo-EM structure and rRNA model of a translating eukaryotic 80S ribosome at 5.5-Å resolution», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 107, fasc. 46, pp. 19748–19753, nov. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shem, N. Garreau de Loubresse, S. Melnikov, L. Jenner, G. Yusupova, e M. Yusupov, «The Structure of the Eukaryotic Ribosome at 3.0 Å Resolution», Science, vol. 334, fasc. 6062, pp. 1524–1529, dic. 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. Khatter, A. G. Myasnikov, S. K. Natchiar, e B. P. Klaholz, «Structure of the human 80S ribosome», Nature, vol. 520, fasc. 7549, Art. fasc. 7549, apr. 2015. [CrossRef]
- E. R. Dabbs, «Mutant Studies on the Prokaryotic Ribosome», in Structure, Function, and Genetics of Ribosomes, B. Hardesty e G. Kramer, A c. di, in Springer Series in Molecular Biology. New York, NY: Springer, 1986, pp. 733–748. [CrossRef]
- M. Nomura, S. Mizushima, M. Ozaki, P. Traub, e C. V. Lowry, «Structure and function of ribosomes and their molecular components», Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol., vol. 34, pp. 49–61, 1969. [CrossRef]
- C. M. Bowman, J. E. Dahlberg, T. Ikemura, J. Konisky, e M. Nomura, «Specific Inactivation of 16S Ribosomal RNA Induced by Colicin E3 In Vivo», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., vol. 68, fasc. 5, p. 964, mag. 1971. [CrossRef]
- B. W. Senior e I. B. Holland, «Effect of Colicin E3 upon the 30S Ribosomal Subunit of Escherichia coli», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., vol. 68, fasc. 5, pp. 959–963, mag. 1971.
- Y. Endo e I. G. Wool, «The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid», J. Biol. Chem., vol. 257, fasc. 15, pp. 9054–9060, ago. 1982.
- C. R. Woese, «On the evolution of the genetic code.», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 54, fasc. 6, Art. fasc. 6, dic. 1965. [CrossRef]
- F. H. Crick, «The origin of the genetic code», J. Mol. Biol., vol. 38, fasc. 3, Art. fasc. 3, dic. 1968. [CrossRef]
- L. E. Orgel, «Evolution of the genetic apparatus», J. Mol. Biol., vol. 38, fasc. 3, Art. fasc. 3, dic. 1968. [CrossRef]
- W. Gilbert, «Origin of life: The RNA world», Nature, vol. 319, fasc. 6055, Art. fasc. 6055, feb. 1986. [CrossRef]
- M. Zuker, «On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule», Science, vol. 244, fasc. 4900, pp. 48–52, apr. 1989. [CrossRef]
- K. L. Buchmueller e K. M. Weeks, «Near native structure in an RNA collapsed state», Biochemistry, vol. 42, fasc. 47, pp. 13869–13878, dic. 2003. [CrossRef]
- R. R. Breaker, «Riboswitches and Translation Control», Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., vol. 10, fasc. 11, p. a032797, nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Semrad, R. Green, e R. Schroeder, «RNA chaperone activity of large ribosomal subunit proteins from Escherichia coli», RNA N. Y. N, vol. 10, fasc. 12, pp. 1855–1860, dic. 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. de la Cruz, K. Karbstein, e J. John L. Woolford, «Functions of Ribosomal Proteins in Assembly of Eukaryotic Ribosomes In Vivo», Annu. Rev. Biochem., vol. 84, p. 93, 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. E. Draper e L. P. Reynaldo, «RNA binding strategies of ribosomal proteins», Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 27, fasc. 2, pp. 381–388, gen. 1999. [CrossRef]
- Y. Timsit, G. Sergeant-Perthuis, e D. Bennequin, «Evolution of ribosomal protein network architectures», Sci. Rep., vol. 11, fasc. 1, Art. fasc. 1, gen. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. T. Parker et al., «Primordial synthesis of amines and amino acids in a 1958 Miller H2S-rich spark discharge experiment», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., vol. 108, fasc. 14, pp. 5526–5531, apr. 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. Zepik et al., «Chiral Amplification of Oligopeptides in Two-Dimensional Crystalline Self-Assemblies on Water», Science, vol. 295, fasc. 5558, pp. 1266–1269, feb. 2002. [CrossRef]
- Y. Suwannachot e B. M. Rode, «Mutual Amino Acid Catalysis in Salt-Induced Peptide Formation Supports this Mechanism’s Role in Prebiotic Peptide Evolution», Orig. Life Evol. Biosph., vol. 29, fasc. 5, pp. 463–471, ott. 1999. [CrossRef]
- L. J. Leman, Z.-Z. Huang, e M. R. Ghadiri, «Peptide Bond Formation in Water Mediated by Carbon Disulfide», Astrobiology, vol. 15, fasc. 9, pp. 709–716, set. 2015. [CrossRef]
- L. Leman, L. Orgel, e M. R. Ghadiri, «Carbonyl Sulfide-Mediated Prebiotic Formation of Peptides», Science, vol. 306, fasc. 5694, pp. 283–286, ott. 2004. [CrossRef]
- N. Kitadai e S. Maruyama, «Origins of building blocks of life: A review», Geosci. Front., vol. 9, fasc. 4, pp. 1117–1153, lug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Frenkel-Pinter, M. Samanta, G. Ashkenasy, e L. J. Leman, «Prebiotic Peptides: Molecular Hubs in the Origin of Life», Chem. Rev., vol. 120, fasc. 11, pp. 4707–4765, giu. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. R. Woese, «On the evolution of the genetic code.», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 54, fasc. 6, pp. 1546–1552, dic. 1965. [CrossRef]
- B. T. Wimberly et al., «Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit», Nature, vol. 407, fasc. 6802, pp. 327–339, set. 2000. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Yusupov et al., «Crystal structure of the ribosome at 5.5 A resolution», Science, vol. 292, fasc. 5518, pp. 883–896, mag. 2001. [CrossRef]
- S. Stern, R. C. Wilson, e H. F. Noller, «Localization of the binding site for protein S4 on 16 S ribosomal RNA by chemical and enzymatic probing and primer extension», J. Mol. Biol., vol. 192, fasc. 1, pp. 101–110, nov. 1986. [CrossRef]
- A. Malygin, D. D. Yanshina, e G. G. Karpova, «Interactions of human ribosomal proteins S16 and S5 with an 18S rRNA fragment containing their binding sites», Biochimie, vol. 91, fasc. 9, pp. 1180–1186, set. 2009. [CrossRef]
- D. Agarwal, D. Kamath, S. T. Gregory, e M. O’Connor, «Modulation of decoding fidelity by ribosomal proteins S4 and S5», J. Bacteriol., vol. 197, fasc. 6, pp. 1017–1025, mar. 2015. [CrossRef]
- K. Bokov e S. V. Steinberg, «A hierarchical model for evolution of 23S ribosomal RNA», Nature, vol. 457, fasc. 7232, pp. 977–980, feb. 2009. [CrossRef]
- S. Petrov et al., «Evolution of the ribosome at atomic resolution», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 111, fasc. 28, pp. 10251–10256, lug. 2014. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Kovacs, A. S. Petrov, K. A. Lanier, e L. D. Williams, «Frozen in Time: The History of Proteins», Mol. Biol. Evol., vol. 34, fasc. 5, pp. 1252–1260, mag. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Petrov et al., «History of the ribosome and the origin of translation», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., vol. 112, fasc. 50, pp. 15396–15401, dic. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Barandun, M. Hunziker, C. R. Vossbrinck, e S. Klinge, «Evolutionary compaction and adaptation visualized by the structure of the dormant microsporidian ribosome», Nat. Microbiol., vol. 4, fasc. 11, pp. 1798–1804, nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Z et al., «A creature with a hundred waggly tails: intrinsically disordered proteins in the ribosome», Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS, vol. 71, fasc. 8, apr. 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Melnikov, A. Ben-Shem, N. Garreau de Loubresse, L. Jenner, G. Yusupova, e M. Yusupov, «One core, two shells: bacterial and eukaryotic ribosomes», Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., vol. 19, fasc. 6, pp. 560–567, giu. 2012. [CrossRef]
- E. Cockman, P. Anderson, e P. Ivanov, «TOP mRNPs: Molecular Mechanisms and Principles of Regulation», Biomolecules, vol. 10, fasc. 7, Art. fasc. 7, lug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Peña, E. Hurt, e V. G. Panse, «Eukaryotic ribosome assembly, transport and quality control», Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., vol. 24, fasc. 9, Art. fasc. 9, set. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Klinge e J. L. Woolford, «Ribosome assembly coming into focus», Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., vol. 20, fasc. 2, Art. fasc. 2, feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- K. Dörner, C. Ruggeri, I. Zemp, e U. Kutay, «Ribosome biogenesis factors—from names to functions», EMBO J., vol. 42, fasc. 7, p. e112699, apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. E. Sloan, S. Mattijssen, S. Lebaron, D. Tollervey, G. J. M. Pruijn, e N. J. Watkins, «Both endonucleolytic and exonucleolytic cleavage mediate ITS1 removal during human ribosomal RNA processing», J. Cell Biol., vol. 200, fasc. 5, Art. fasc. 5, feb. 2013. [CrossRef]
- C. Montellese, N. Montel-Lehry, A. K. Henras, U. Kutay, P.-E. Gleizes, e M.-F. O’Donohue, «Poly(A)-specific ribonuclease is a nuclear ribosome biogenesis factor involved in human 18S rRNA maturation», Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 45, fasc. 11, pp. 6822–6836, giu. 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. J. Watkins e M. T. Bohnsack, «The box C/D and H/ACA snoRNPs: key players in the modification, processing and the dynamic folding of ribosomal RNA», WIREs RNA, vol. 3, fasc. 3, pp. 397–414, 2012. [CrossRef]
- K. E. Sloan, A. S. Warda, S. Sharma, K.-D. Entian, D. L. J. Lafontaine, e M. T. Bohnsack, «Tuning the ribosome: The influence of rRNA modification on eukaryotic ribosome biogenesis and function», RNA Biol., vol. 14, fasc. 9, pp. 1138–1152, set. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Taoka et al., «Landscape of the complete RNA chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome», Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 46, fasc. 18, pp. 9289–9298, ott. 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. Piekna-Przybylska, W. A. Decatur, e M. J. Fournier, «The 3D rRNA modification maps database: with interactive tools for ribosome analysis», Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 36, fasc. suppl_1, pp. D178–D183, gen. 2008. [CrossRef]
- S. Sharma e D. L. J. Lafontaine, «‘View From A Bridge’: A New Perspective on Eukaryotic rRNA Base Modification», Trends Biochem. Sci., vol. 40, fasc. 10, pp. 560–575, ott. 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. K. Natchiar, A. G. Myasnikov, H. Kratzat, I. Hazemann, e B. P. Klaholz, «Visualization of chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome structure», Nature, vol. 551, fasc. 7681, Art. fasc. 7681, nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Boccaletto et al., «MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. 2021 update», Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 50, fasc. D1, pp. D231–D235, gen. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Green e H. F. Noller, «In vitro complementation analysis localizes 23S rRNA posttranscriptional modifications that are required for Escherichia coli 50S ribosomal subunit assembly and function.», RNA, vol. 2, fasc. 10, Art. fasc. 10, gen. 1996.
- J. L. Baxter-Roshek, A. N. Petrov, e J. D. Dinman, «Optimization of Ribosome Structure and Function by rRNA Base Modification», PLOS ONE, vol. 2, fasc. 1, Art. fasc. 1, gen. 2007. [CrossRef]
- K. Jack et al., «rRNA Pseudouridylation Defects Affect Ribosomal Ligand Binding and Translational Fidelity from Yeast to Human Cells», Mol. Cell, vol. 44, fasc. 4, pp. 660–666, nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- S. Khoshnevis, R. E. Dreggors-Walker, V. Marchand, Y. Motorin, e H. Ghalei, «Ribosomal RNA 2’-O-methylations regulate translation by impacting ribosome dynamics», Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., vol. 119, fasc. 12, p. e2117334119, mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. R. Warner, «The economics of ribosome biosynthesis in yeast», Trends Biochem. Sci., vol. 24, fasc. 11, pp. 437–440, nov. 1999. [CrossRef]
- V. Y. Stefanovsky, G. Pelletier, R. Hannan, T. Gagnon-Kugler, L. I. Rothblum, e T. Moss, «An Immediate Response of Ribosomal Transcription to Growth Factor Stimulation in Mammals Is Mediated by ERK Phosphorylation of UBF», Mol. Cell, vol. 8, fasc. 5, pp. 1063–1073, nov. 2001. [CrossRef]
- V. Iadevaia, R. Liu, e C. G. Proud, «mTORC1 signaling controls multiple steps in ribosome biogenesis», Semin. Cell Dev. Biol., vol. 36, pp. 113–120, dic. 2014. [CrossRef]
- C. Mayer e I. Grummt, «Ribosome biogenesis and cell growth: mTOR coordinates transcription by all three classes of nuclear RNA polymerases», Oncogene, vol. 25, fasc. 48, Art. fasc. 48, ott. 2006. [CrossRef]
- J. van Riggelen, A. Yetil, e D. W. Felsher, «MYC as a regulator of ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis», Nat. Rev. Cancer, vol. 10, fasc. 4, pp. 301–309, apr. 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. Derenzini, L. Montanaro, e D. Trerè, «Ribosome biogenesis and cancer», Acta Histochem., vol. 119, fasc. 3, pp. 190–197, apr. 2017. [CrossRef]
- G. Thomas, «An encore for ribosome biogenesis in the control of cell proliferation», Nat. Cell Biol., vol. 2, fasc. 5, pp. E71-72, mag. 2000. [CrossRef]
- C. P. Rubbi e J. Milner, «Disruption of the nucleolus mediates stabilization of p53 in response to DNA damage and other stresses», EMBO J., vol. 22, fasc. 22, pp. 6068–6077, nov. 2003. [CrossRef]
- M. S. Lindström, J. Bartek, e A. Maya-Mendoza, «p53 at the crossroad of DNA replication and ribosome biogenesis stress pathways», Cell Death Differ., vol. 29, fasc. 5, pp. 972–982, mag. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Fumagalli et al., «Absence of nucleolar disruption after impairment of 40S ribosome biogenesis reveals an rpL11-translation-dependent mechanism of p53 induction», Nat. Cell Biol., vol. 11, fasc. 4, Art. fasc. 4, apr. 2009. [CrossRef]
- K. Burger et al., «Chemotherapeutic Drugs Inhibit Ribosome Biogenesis at Various Levels*», J. Biol. Chem., vol. 285, fasc. 16, pp. 12416–12425, apr. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Grummt, «The nucleolus—guardian of cellular homeostasis and genome integrity», Chromosoma, vol. 122, fasc. 6, pp. 487–497, dic. 2013. [CrossRef]
- C. J. Sherr, «Divorcing ARF and p53: an unsettled case», Nat. Rev. Cancer, vol. 6, fasc. 9, Art. fasc. 9, set. 2006. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhang, L. C. Zhang, L. Comai, e D. L. Johnson, «PTEN Represses RNA Polymerase I Transcription by Disrupting the SL1 Complex», Mol. Cell. Biol., vol. 25, fasc. 16, pp. 6899–6911, ago. 2005. [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, G. Thomas, e S. Volarević, «Ribosome biogenesis in cancer: new players and therapeutic avenues», Nat. Rev. Cancer, vol. 18, fasc. 1, pp. 51–63, gen. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, G. Thomas, e S. Volarević, «Ribosome biogenesis in cancer: new players and therapeutic avenues», Nat. Rev. Cancer, vol. 18, fasc. 1, pp. 51–63, gen. 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. R. Bustelo e M. Dosil, «Ribosome biogenesis and cancer: basic and translational challenges», Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., vol. 48, pp. 22–29, feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Lazaris-Karatzas, K. S. Montine, e N. Sonenberg, «Malignant transformation by a eukaryotic initiation factor subunit that binds to mRNA 5’ cap», Nature, vol. 345, fasc. 6275, pp. 544–547, giu. 1990. [CrossRef]
- D. Ruggero et al., «The translation factor eIF-4E promotes tumor formation and cooperates with c-Myc in lymphomagenesis», Nat. Med., vol. 10, fasc. 5, pp. 484–486, mag. 2004. [CrossRef]
- S. O. Sulima, K. R. Kampen, e K. De Keersmaecker, «Cancer Biogenesis in Ribosomopathies», Cells, vol. 8, fasc. 3, p. 229, mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- G. E. Palade, «A small particulate component of the cytoplasm», J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol., vol. 1, fasc. 1, pp. 59–68, gen. 1955. [CrossRef]
- Z. Shi e M. Barna, «Translating the genome in time and space: specialized ribosomes, RNA regulons, and RNA-binding proteins», Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., vol. 31, pp. 31–54, 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. D. Dinman, «Pathways to specialized ribosomes: The Brussels Lecture», J. Mol. Biol., vol. 428, fasc. 10 Pt B, pp. 2186–2194, mag. 2016. [CrossRef]
- N. R. Genuth e M. Barna, «The discovery of ribosome heterogeneity and its implications for gene regulation and organismal life», Mol. Cell, vol. 71, fasc. 3, pp. 364–374, ago. 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Kondrashov et al., «Ribosome-mediated specificity in Hox mRNA translation and vertebrate tissue patterning», Cell, vol. 145, fasc. 3, pp. 383–397, apr. 2011. [CrossRef]
- N. Krogh et al., «Profiling of 2’-O-Me in human rRNA reveals a subset of fractionally modified positions and provides evidence for ribosome heterogeneity», Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 44, fasc. 16, pp. 7884–7895, set. 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. Locati et al., «Expression of distinct maternal and somatic 5.8S, 18S, and 28S rRNA types during zebrafish development», RNA, vol. 23, fasc. 8, pp. 1188–1199, ago. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Parks et al., «Variant ribosomal RNA alleles are conserved and exhibit tissue-specific expression», Sci. Adv., vol. 4, fasc. 2, p. eaao0665, feb. 2018. [CrossRef]
- D. Simsek et al., «The Mammalian Ribo-interactome Reveals Ribosome Functional Diversity and Heterogeneity», Cell, vol. 169, fasc. 6, pp. 1051-1065.e18, giu. 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Samir et al., «Identification of Changing Ribosome Protein Compositions using Mass Spectrometry», Proteomics, vol. 18, fasc. 20, p. e1800217, ott. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Segev e J., E. Gerst, «Specialized ribosomes and specific ribosomal protein paralogs control translation of mitochondrial proteins», J. Cell Biol., vol. 217, fasc. 1, pp. 117–126, gen. 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Mukhopadhyay, P. S. Ray, A. Arif, A. K. Brady, M. Kinter, e P. L. Fox, «DAPK-ZIPK-L13a Axis Constitutes a Negative-Feedback Module Regulating Inflammatory Gene Expression», Mol. Cell, vol. 32, fasc. 3, pp. 371–382, nov. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Z. A. Knight et al., «Molecular Profiling of Activated Neurons by Phosphorylated Ribosome Capture», Cell, vol. 151, fasc. 5, pp. 1126–1137, nov. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Meyuhas, «Chapter Two - Ribosomal Protein S6 Phosphorylation: Four Decades of Research», in International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, vol. 320, K. W. Jeon, A c. di, Academic Press, 2015, pp. 41–73. [CrossRef]
- D. Simsek e M. Barna, «An emerging role for the ribosome as a nexus for post-translational modifications», Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., vol. 45, pp. 92–101, apr. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. K. Thompson, M. F. Rojas-Duran, P. Gangaramani, e W. V. Gilbert, «The ribosomal protein Asc1/RACK1 is required for efficient translation of short mRNAs», eLife, vol. 5, p. e11154, apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Gallo et al., «RACK1 Specifically Regulates Translation through Its Binding to Ribosomes», Mol. Cell. Biol., vol. 38, fasc. 23, pp. e00230-18, dic. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Vesper et al., «Selective translation of leaderless mRNAs by specialized ribosomes generated by MazF in Escherichia coli», Cell, vol. 147, fasc. 1, pp. 147–157, set. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Z. Shi et al., «Heterogeneous Ribosomes Preferentially Translate Distinct Subpools of mRNAs Genome-wide», Mol. Cell, vol. 67, fasc. 1, pp. 71-83.e7, lug. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Segev e J., E. Gerst, «Specialized ribosomes and specific ribosomal protein paralogs control translation of mitochondrial proteins», J. Cell Biol., vol. 217, fasc. 1, pp. 117–126, gen. 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Draptchinskaia et al., «The gene encoding ribosomal protein S19 is mutated in Diamond-Blackfan anaemia», Nat. Genet., vol. 21, fasc. 2, pp. 169–175, feb. 1999. [CrossRef]
- B. L. Ebert et al., «Identification of RPS14 as a 5q- syndrome gene by RNA interference screen», Nature, vol. 451, fasc. 7176, pp. 335–339, gen. 2008. [CrossRef]
- C. Bellodi et al., «Loss of function of the tumor suppressor DKC1 perturbs p27 translation control and contributes to pituitary tumorigenesis», Cancer Res., vol. 70, fasc. 14, pp. 6026–6035, lug. 2010. [CrossRef]
- J. Finch et al., «Uncoupling of GTP hydrolysis from eIF6 release on the ribosome causes Shwachman-Diamond syndrome», Genes Dev., vol. 25, fasc. 9, pp. 917–929, mag. 2011. [CrossRef]
- J. Armistead e B. Triggs-Raine, «Diverse diseases from a ubiquitous process: The ribosomopathy paradox», FEBS Lett., vol. 588, fasc. 9, pp. 1491–1500, mag. 2014. [CrossRef]
- N. C. Jones et al., «Prevention of the neurocristopathy Treacher Collins syndrome through inhibition of p53 function», Nat. Med., vol. 14, fasc. 2, pp. 125–133, feb. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Jaako et al., «Disruption of the 5S RNP-Mdm2 interaction significantly improves the erythroid defect in a mouse model for Diamond-Blackfan anemia», Leukemia, vol. 29, fasc. 11, pp. 2221–2229, nov. 2015. [CrossRef]
- G. C. Tiu et al., «A p53-dependent translational program directs tissue-selective phenotypes in a model of ribosomopathies», Dev. Cell, vol. 56, fasc. 14, pp. 2089-2102.e11, lug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. R. Oliver, T. L. Saunders, S. A. Tarlé, e T. Glaser, «Ribosomal protein L24 defect in belly spot and tail (Bst), a mouse Minute», Dev. Camb. Engl., vol. 131, fasc. 16, pp. 3907–3920, ago. 2004. [CrossRef]
- J. Cmejlova, L. Dolezalova, D. Pospisilova, K. Petrtylova, J. Petrak, e R. Cmejla, «Translational efficiency in patients with Diamond-Blackfan anemia», Haematologica, vol. 91, fasc. 11, pp. 1456–1464, nov. 2006.
- A. J. Signer, J. A. Magee, A. Salic, e S. J. Morrison, «Haematopoietic stem cells require a highly regulated protein synthesis rate», Nature, vol. 509, fasc. 7498, pp. 49–54, mag. 2014. [CrossRef]
- H. Ma et al., «N6-Methyladenosine methyltransferase ZCCHC4 mediates ribosomal RNA methylation», Nat. Chem. Biol., vol. 15, fasc. 1, pp. 88–94, gen. 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. F. Lodish, «Model for the regulation of mRNA translation applied to haemoglobin synthesis», Nature, vol. 251, fasc. 5474, pp. 385–388, ott. 1974. [CrossRef]
- E. W. Mills e R. Green, «Ribosomopathies: There’s strength in numbers», Science, vol. 358, fasc. 6363, p. eaan2755, nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- K. Khajuria et al., «Ribosome Levels Selectively Regulate Translation and Lineage Commitment in Human Hematopoiesis», Cell, vol. 173, fasc. 1, pp. 90-103.e19, mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. W. Gripp et al., «Diamond-Blackfan anemia with mandibulofacial dystostosis is heterogeneous, including the novel DBA genes TSR2 and RPS28», Am. J. Med. Genet. A., vol. 164A, fasc. 9, pp. 2240–2249, set. 2014. [CrossRef]
- L. Mirabello et al., «Novel and known ribosomal causes of Diamond-Blackfan anaemia identified through comprehensive genomic characterisation», J. Med. Genet., vol. 54, fasc. 6, pp. 417–425, giu. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Flygare et al., «Human RPS19, the gene mutated in Diamond-Blackfan anemia, encodes a ribosomal protein required for the maturation of 40S ribosomal subunits», Blood, vol. 109, fasc. 3, pp. 980–986, set. 2006. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Ulirsch et al., «The Genetic Landscape of Diamond-Blackfan Anemia», Am. J. Hum. Genet., vol. 104, fasc. 2, p. 356, feb. 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Graifer e G. Karpova, «Eukaryotic protein uS19: a component of the decoding site of ribosomes and a player in human diseases», Biochem. J., vol. 478, fasc. 5, pp. 997–1008, mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. An et al., «Computational Studies of the Structural Basis of Human RPS19 Mutations Associated With Diamond-Blackfan Anemia», Front. Genet., vol. 12, p. 650897, 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Juli et al., «Depletion of ribosomal protein S19 causes a reduction of rRNA synthesis», Sci. Rep., vol. 6, fasc. 1, Art. fasc. 1, ott. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Horos et al., «Ribosomal deficiencies in Diamond-Blackfan anemia impair translation of transcripts essential for differentiation of murine and human erythroblasts», Blood, vol. 119, fasc. 1, pp. 262–272, gen. 2012. [CrossRef]
- L. S. Ludwig et al., «Altered translation of GATA1 in Diamond-Blackfan anemia», Nat. Med., vol. 20, fasc. 7, Art. fasc. 7, lug. 2014. [CrossRef]
- R. K. Khajuria et al., «Ribosome Levels Selectively Regulate Translation and Lineage Commitment in Human Hematopoiesis», Cell, vol. 173, fasc. 1, pp. 90-103.e19, mar. 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. I. Papagiannopoulos et al., «Invariable Ribosome Stoichiometry During Murine Erythroid Differentiation: Implications for Understanding Ribosomopathies», Front. Mol. Biosci., vol. 9, 2022, Consultato: 19 settembre 2023. [Online]. Disponibile su: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2022. 8055.
- G. R. B. Boocock et al., «Mutations in SBDS are associated with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome», Nat. Genet., vol. 33, fasc. 1, pp. 97–101, gen. 2003. [CrossRef]
- M. Cipolli, «Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: clinical phenotypes», Pancreatol. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Pancreatol. IAP Al, vol. 1, fasc. 5, pp. 543–548, 2001. [CrossRef]
- F. Menne et al., «The Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome protein mediates translational activation of ribosomes in yeast», Nat. Genet., vol. 39, fasc. 4, pp. 486–495, apr. 2007. [CrossRef]
- K.-Y. Lo, Z. Li, C. Bussiere, S. Bresson, E. M. Marcotte, e A. W. Johnson, «Defining the pathway of cytoplasmic maturation of the 60S ribosomal subunit», Mol. Cell, vol. 39, fasc. 2, pp. 196–208, lug. 2010. [CrossRef]
- J. B. Moore, J. E. Farrar, R. J. Arceci, J. M. Liu, e S. R. Ellis, «Distinct ribosome maturation defects in yeast models of Diamond-Blackfan anemia and Shwachman-Diamond syndrome», Haematologica, vol. 95, fasc. 1, pp. 57–64, gen. 2010. [CrossRef]
- N. Burwick, S. A. Coats, T. Nakamura, e A. Shimamura, «Impaired ribosomal subunit association in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome», Blood, vol. 120, fasc. 26, pp. 5143–5152, dic. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Gartmann, M. Blau, J.-P. Armache, T. Mielke, M. Topf, e R. Beckmann, «Mechanism of eIF6-mediated inhibition of ribosomal subunit joining», J. Biol. Chem., vol. 285, fasc. 20, pp. 14848–14851, mag. 2010. [CrossRef]
- S. Klinge, F. Voigts-Hoffmann, M. Leibundgut, S. Arpagaus, e N. Ban, «Crystal structure of the eukaryotic 60S ribosomal subunit in complex with initiation factor 6», Science, vol. 334, fasc. 6058, pp. 941–948, nov. 2011. [CrossRef]
- F. Weis et al., «Mechanism of eIF6 release from the nascent 60S ribosomal subunit», Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., vol. 22, fasc. 11, pp. 914–919, nov. 2015. [CrossRef]
- P. Jaako, C. C. Wong, D. Adams, e A. J. Warren, «Attenuated Protein Synthesis Drives the Hematopoietic Defects in Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome», Blood, vol. 130, fasc. Supplement 1, p. 876, dic. 2017. [CrossRef]
- K. In, M. A. Zaini, C. Müller, A. J. Warren, M. von Lindern, e C. F. Calkhoven, «Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome (SBDS) protein deficiency impairs translation re-initiation from C/EBPα and C/EBPβ mRNAs», Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 44, fasc. 9, pp. 4134–4146, mag. 2016. [CrossRef]
- P. Jaako et al., «eIF6 rebinding dynamically couples ribosome maturation and translation», Nat. Commun., vol. 13, fasc. 1, Art. fasc. 1, mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Ruland et al., «Nuclear export of the pre-60S ribosomal subunit through single nuclear pores observed in real time», Nat. Commun., vol. 12, fasc. 1, Art. fasc. 1, ott. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Xue et al., «Visualizing translation dynamics at atomic detail inside a bacterial cell», Nature, vol. 610, fasc. 7930, pp. 205–211, ott. 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. S. Erdmann et al., «In situ cryo-electron tomography reveals gradient organization of ribosome biogenesis in intact nucleoli», Nat. Commun., vol. 12, fasc. 1, Art. fasc. 1, set. 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Ban et al., «A new system for naming ribosomal proteins», Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., vol. 24, pp. 165–169, feb. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Jun, Guido Novati, Joshua Pan, Clare Bycroft, Akvilė Žemgulytė, Taylor Applebaum, Alexander Pritzel, et al. 2023. «Accurate Proteome-Wide Missense Variant Effect Prediction with AlphaMissense». Science 381 (6664): eadg7492. [CrossRef]
- E. F. Pettersen et al., «UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis», J. Comput. Chem., vol. 25, fasc. 13, pp. 1605–1612, ott. 2004. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




