Submitted:
10 October 2023
Posted:
11 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The role of low and high-affinity IgE in food allergy
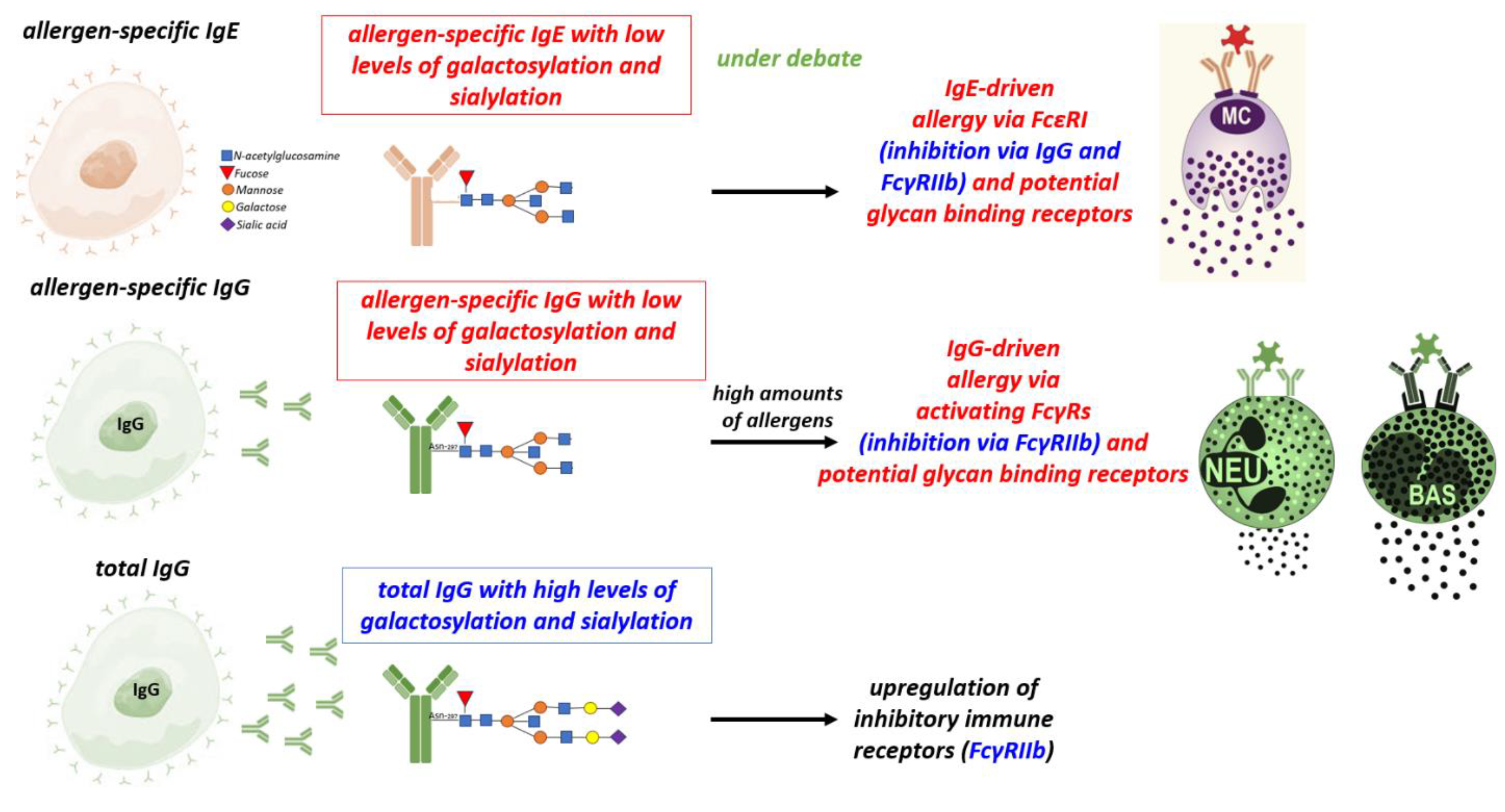
3. The role of antibody isotypes, subclasses and of antibody Fc glycosylation subclasses
3.1. IgG
3.2. Mucosal IgA
4. Antibody Ig-Fc glycosylation
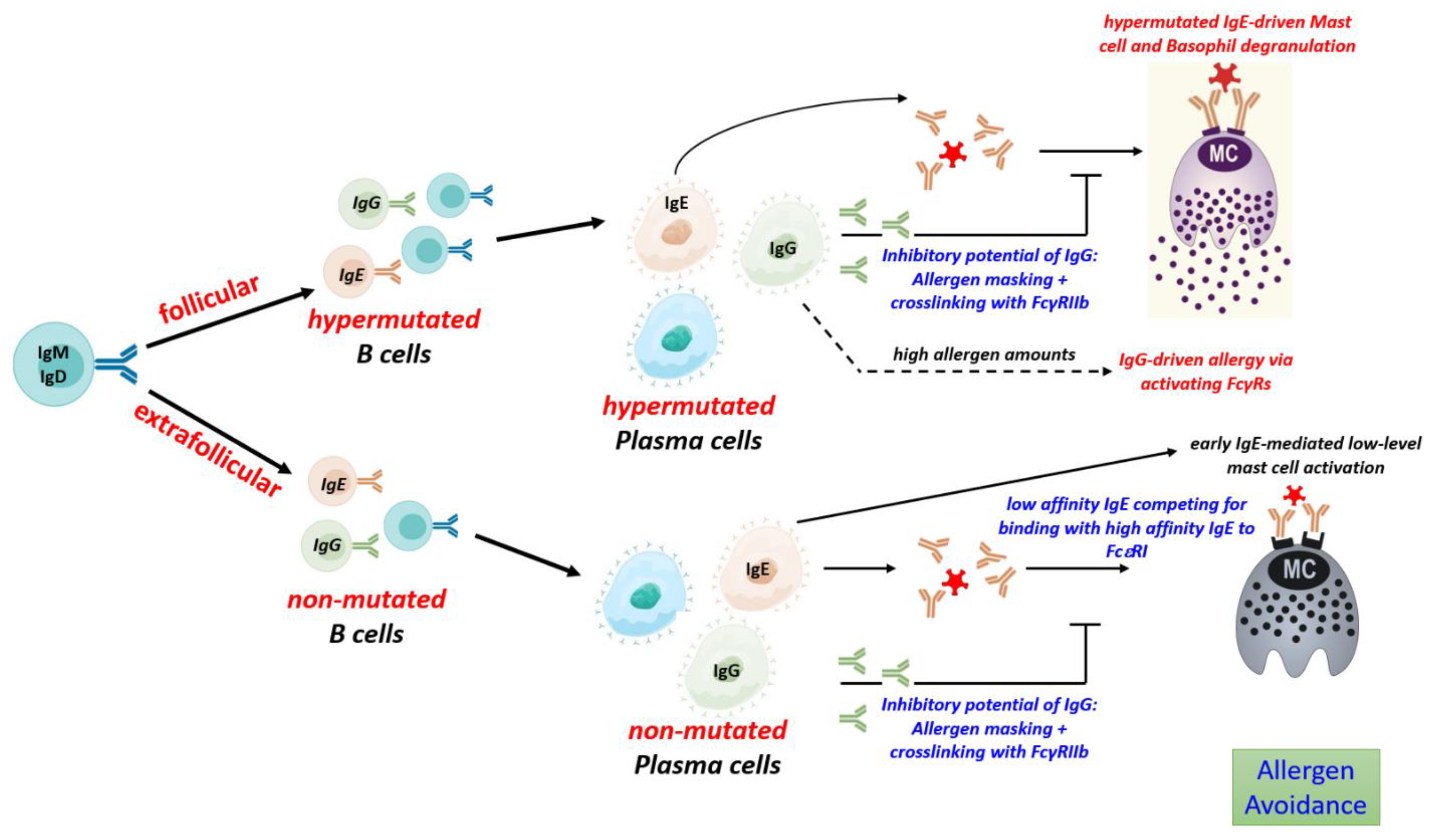
5. Development of antibodies in food allergy
5.1. Allergen-specific to T cell activation
5.2. Production of unmutated, low affinity IgE
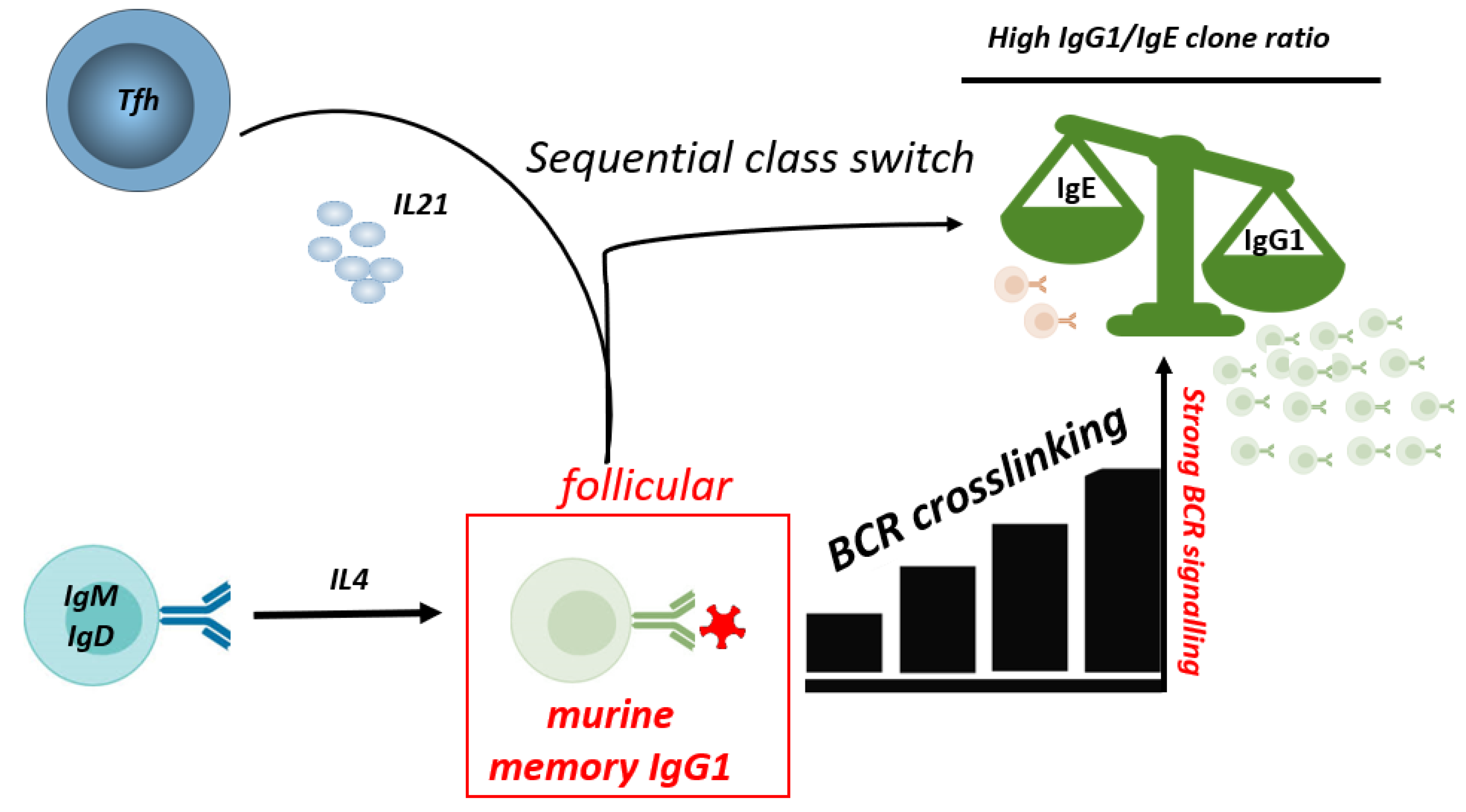
5.3. Production of mutated, high affinity IgE
5.4. Regulation of IgG to IgE ratios
6. Development of differentially glycosylated antibodies
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jackson, K. D.; Howie, L. D.; Akinbami, O. J. Trends in Allergic Conditions among Children: United States, 1997-2011; US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and …, 2013.
- Simons, F. E. R.; Ardusso, L. R. F.; Bilo, M. B.; Dimov, V.; Ebisawa, M.; El-Gamal, Y. M.; Ledford, D. K.; Lockey, R. F.; Ring, J.; Sanchez-Borges, M. 2012 Update: World Allergy Organization Guidelines for the Assessment and Management of Anaphylaxis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, D.; Poowutikul, P.; Pansare, M.; Kamat, D. Food Allergy: A Review. Pediatr. Ann. 2020, 49, e50–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, A. T.; Meize-Grochowski, R. Epinephrine Auto-Injectors for Anaphylaxis Treatment in the School Setting: A Discussion Paper. SAGE Open Nurs. 2019, 5, 2377960819845246. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R. S.; Springston, E. E.; Warrier, M. R.; Smith, B.; Kumar, R.; Pongracic, J.; Holl, J. L. The Prevalence, Severity, and Distribution of Childhood Food Allergy in the United States. Pediatrics 2011, 128, e9–e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R. S.; Warren, C. M.; Smith, B. M.; Blumenstock, J. A.; Jiang, J.; Davis, M. M.; Nadeau, K. C. The Public Health Impact of Parent-Reported Childhood Food Allergies in the United States. Pediatrics 2018, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R. S.; Warren, C. M.; Smith, B. M.; Jiang, J.; Blumenstock, J. A.; Davis, M. M.; Schleimer, R. P.; Nadeau, K. C. Prevalence and Severity of Food Allergies among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e185630–e185630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurukulaaratchy, R. J.; Karmaus, W.; Arshad, S. H. Gender and Atopy Influences on the Natural History of Rhinitis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S. C. A.; Roskin, K. M.; Jackson, K. J. L.; Joshi, S. A.; Nejad, P.; Lee, J.-Y.; Wagar, L. E.; Pham, T. D.; Hoh, R. A.; Nguyen, K. D. Shaping of Infant B Cell Receptor Repertoires by Environmental Factors and Infectious Disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaat2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (10) Younoszai, M. K.; Lynch, A. In Vivo D-Glucose Absorption in the Developing Rat Small Intestine. Pediatr. Res. 1975, 9, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdowski, L. A.; Clandinin, T.; Thomson, A. B. R. Ontogeny, Growth and Development of the Small Intestine: Understanding Pediatric Gastroenterology. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2010, 16, 787. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, N. O.; Hausman, A. M.; Ifkovits, C. A.; Buse, J. B.; Gould, G. W.; Burant, C. F.; Bell, G. I. Human Intestinal Glucose Transporter Expression and Localization of GLUT5. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1992, 262, C795–C800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.; Haverson, K.; Inman, C.; Harris, C.; Jones, P.; Corfield, G.; Miller, B.; Stokes, C. The Development of the Mucosal Immune System Pre-and Post-Weaning: Balancing Regulatory and Effector Function. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ierodiakonou, D.; Garcia-Larsen, V.; Logan, A.; Groome, A.; Cunha, S.; Chivinge, J.; Robinson, Z.; Geoghegan, N.; Jarrold, K.; Reeves, T. Timing of Allergenic Food Introduction to the Infant Diet and Risk of Allergic or Autoimmune Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Jama 2016, 316, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, K.; Barman, M.; Brekke, H. K.; Hesselmar, B.; Johansen, S.; Sandberg, A.-S.; Wold, A. Late Introduction of Fish and Eggs Is Associated with Increased Risk of Allergy Development–Results from the FARMFLORA Birth Cohort. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 61, 1393306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, J.; Sicherer, S.; Wood, R. The Natural History of Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicherer, S. H.; Urisu, A. Natural History and Prevention of Food Allergy. Food Allergy E-Book Expert Consult Basic 2011, 251. [Google Scholar]
- Chatchatee, P.; Järvinen, K.-M.; Bardina, L.; Beyer, K.; Sampson, H. A. Identification of IgE-and IgG-Binding Epitopes on As1-Casein: Differences in Patients with Persistent and Transient Cow’s Milk Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, K.-M.; Beyer, K.; Vila, L.; Bardina, L.; Mishoe, M.; Sampson, H. A. Specificity of IgE Antibodies to Sequential Epitopes of Hen’s Egg Ovomucoid as a Marker for Persistence of Egg Allergy. Allergy 2007, 62, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, L.; Beyer, K.; Järvinen, K.-M.; Chatchatee, P.; Bardina, L.; Sampson, H. A. Role of Conformational and Linear Epitopes in the Achievement of Tolerance in Cow’s Milk Allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2001, 31, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicherer, S. H.; Wood, R. A.; Vickery, B. P.; Jones, S. M.; Liu, A. H.; Fleischer, D. M.; Dawson, P.; Mayer, L.; Burks, A. W.; Grishin, A. The Natural History of Egg Allergy in an Observational Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostara, M.; Chondrou, V.; Sgourou, A.; Douros, K.; Tsabouri, S. HLA Polymorphisms and Food Allergy Predisposition. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2020, 9, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grotenboer, N. S.; Ketelaar, M. E.; Koppelman, G. H.; Nawijn, M. C. Decoding Asthma: Translating Genetic Variation in IL33 and IL1RL1 into Disease Pathophysiology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berin, M. C. Mechanisms That Define Transient versus Persistent Food Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbein, A. B.; Qamar, N.; Erickson, K. A.; Kwasny, M. J.; Cai, M.; Szychlinski, C.; Singh, A. M.; Fuleihan, R. L. Cytokine Responses to Egg Protein in Previously Allergic Children Who Developed Tolerance Naturally. Ann. Allergy. Asthma. Immunol. 2014, 113, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frischmeyer-Guerrerio, P. A.; Guerrerio, A. L.; Chichester, K. L.; Bieneman, A. P.; Hamilton, R. A.; Wood, R. A.; Schroeder, J. T. Dendritic Cell and T Cell Responses in Children with Food Allergy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2011, 41, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, D. P.; Haynes, L.; Sayles, P. C.; Duso, D. K.; Eaton, S. M.; Lepak, N. M.; Johnson, L. L.; Swain, S. L.; Lund, F. E. Reciprocal Regulation of Polarized Cytokine Production by Effector B and T Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yuan, W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Kuchroo, V. K.; Mohib, K.; Rothstein, D. M. B Cell IL-4 Drives Th2 Responses in Vivo, Ameliorates Allograft Rejection, and Promotes Allergic Airway Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 762390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurdayal, R.; Ndlovu, H. H.; Revaz-Breton, M.; Parihar, S. P.; Nono, J. K.; Govender, M.; Brombacher, F. IL-4–Producing B Cells Regulate T Helper Cell Dichotomy in Type 1-and Type 2-Controlled Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, E8430–E8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, H.; Plantinga, M.; Deswarte, K.; Pouliot, P.; Willart, M. A. M.; Kool, M.; Muskens, F.; Lambrecht, B. N. Inflammatory Dendritic Cells—Not Basophils—Are Necessary and Sufficient for Induction of Th2 Immunity to Inhaled House Dust Mite Allergen. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2097–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looney, T. J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Roskin, K. M.; Hoh, R. A.; King, J.; Glanville, J.; Liu, Y.; Pham, T. D.; Dekker, C. L.; Davis, M. M. Human B-Cell Isotype Switching Origins of IgE. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-S.; Narayanan, S.; Subramaniam, S.; Ho, W. Q.; Lafaille, J. J.; Lafaille, M. A. C. de. Biology of IgE Production: IgE Cell Differentiation and the Memory of IgE Responses. IgE Antibodies Gener. Funct. 2015, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Udoye, C. C.; Rau, C. N.; Freye, S. M.; Almeida, L. N.; Vera-Cruz, S.; Othmer, K.; Korkmaz, R. Ü.; Clauder, A.-K.; Lindemann, T.; Niebuhr, M. B-Cell Receptor Physical Properties Affect Relative IgG1 and IgE Responses in Mouse Egg Allergy. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 1375–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-S.; Subramaniam, S.; Narang, V.; Srinivasan, K.; Saunders, S. P.; Carbajo, D.; Wen-Shan, T.; Hidayah Hamadee, N.; Lum, J.; Lee, A. IgG1 Memory B Cells Keep the Memory of IgE Responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takhar, P.; Smurthwaite, L.; Coker, H. A.; Fear, D. J.; Banfield, G. K.; Carr, V. A.; Durham, S. R.; Gould, H. J. Allergen Drives Class Switching to IgE in the Nasal Mucosa in Allergic Rhinitis. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5024–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoh, R. A.; Joshi, S. A.; Lee, J.-Y.; Martin, B. A.; Varma, S.; Kwok, S.; Nielsen, S. C. A.; Nejad, P.; Haraguchi, E.; Dixit, P. S. Origins and Clonal Convergence of Gastrointestinal IgE+ B Cells in Human Peanut Allergy. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaay4209–eaay4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, R. A.; Hauser, A. E.; Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A. Maintenance of Serum Antibody Levels. Annu Rev Immunol 2005, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geha, R. S.; Jabara, H. H.; Brodeur, S. R. The Regulation of Immunoglobulin E Class-Switch Recombination. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Robinson, M. J.; Chen, X.; Smith, G. A.; Taunton, J.; Liu, W.; Allen, C. D. C. Regulation of B Cell Fate by Chronic Activity of the IgE B Cell Receptor. Elife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croote, D.; Darmanis, S.; Nadeau, K. C.; Quake, S. R. High-Affinity Allergen-Specific Human Antibodies Cloned from Single IgE B Cell Transcriptomes. Science 2018, 362, 1306–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffleur, B.; Duchez, S.; Tarte, K.; Denis-Lagache, N.; Péron, S.; Carrion, C.; Denizot, Y.; Cogné, M. Self-Restrained B Cells Arise Following Membrane IgE Expression. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jr, D. M. IgE Receptor and Signal Transduction in Mast Cells and Basophils. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 717–723. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, H. The Receptor with High Affinity for IgE. Immunol. Rev. 1992, 125, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, S. J.; Tsai, M. IgE and Mast Cells in Allergic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, H.; Yasueda, H.; Akiyama, K. Affinity of IgE Antibody to Antigen Influences Allergen-induced Histamine Release. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Leach, S.; Liu, W.; Ralston, E.; Scheffel, J.; Zhang, W.; Lowell, C. A.; Rivera, J. Molecular Editing of Cellular Responses by the High-Affinity Receptor for IgE. Science 2014, 343, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X. Low-Affinity but High-Avidity Interactions May Offer an Explanation for IgE-Mediated Allergen Cross-Reactivity. Allergy 2021, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Dolpady, J.; Wabl, M.; Curotto de Lafaille, M. A.; Lafaille, J. J. Sequential Class Switching Is Required for the Generation of High Affinity IgE Antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher, M. M.; Phillips, R.; Brown, S. J.; Cro, S.; Cornelius, V.; Carlsen, K. C. L.; Skjerven, H. O.; Rehbinder, E. M.; Lowe, A. J.; Dissanayake, E. Skin Care Interventions in Infants for Preventing Eczema and Food Allergy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gowthaman, U.; Chen, J. S.; Zhang, B.; Flynn, W. F.; Lu, Y.; Song, W.; Joseph, J.; Gertie, J. A.; Xu, L.; Collet, M. A. Identification of a T Follicular Helper Cell Subset That Drives Anaphylactic IgE. Science 2019, 365, eaaw6433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, B.; Martinez, F. D.; Halonen, M.; Barbee, R. A.; Cline, M. G. Association of Asthma with Serum IgE Levels and Skin-Test Reactivity to Allergens. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzsimmons, C. M.; Falcone, F. H.; Dunne, D. W. Helminth Allergens, Parasite-Specific IgE, and Its Protective Role in Human Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plum, T.; Binzberger, R.; Thiele, R.; Shang, F.; Postrach, D.; Fung, C.; Fortea, M.; Stakenborg, N.; Wang, Z.; Tappe-Theodor, A. Mast Cells Link Immune Sensing to Antigen-Avoidance Behaviour. Nature 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florsheim, E. B.; Bachtel, N. D.; Cullen, J.; Lima, B. G. C.; Godazgar, M.; Carvalho, F.; Chatain, C. P.; Zimmer, M. R.; Zhang, C.; Gautier, G. Immune Sensing of Food Allergens Promotes Avoidance Behaviour. Nature 2023, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udoye, C. C.; Manz, R. A. IgE-Mast Cell Mediated Allergy a Sensor of Food Quality. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Karsten, C. M.; Pandey, M. K.; Figge, J.; Kilchenstein, R.; Taylor, P. R.; Rosas, M.; McDonald, J. U.; Orr, S. J.; Berger, M.; Petzold, D. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of IgG1 Mediated by Fc Galactosylation and Association of FcγRIIB and Dectin-1. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1401–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuk, Z. Y. Induction and Suppression of Allergic Diarrhea and Systemic Anaphylaxis in a Murine Model of Food Allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petry, J.; Rahmöller, J.; Dühring, L.; Lilienthal, G.-M.; Lehrian, S.; Buhre, J. S.; Bartsch, Y. C.; Epp, A.; Lunding, H. B.; Moremen, K. W. Enriched Blood IgG Sialylation Attenuates IgG-Mediated and IgG-Controlled-IgE-Mediated Allergic Reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, R. T.; Posgai, M. T.; Mahler, A.; Barasa, N.; Jacob, C. O.; Köhl, J.; Ehlers, M.; Stringer, K.; Shanmukhappa, S. K.; Witte, D. IgG1 Protects against Renal Disease in a Mouse Model of Cryoglobulinaemia. Nature 2015, 517, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, K.; Hundt, J. E.; Yu, X.; Ehlers, M.; Petersen, F.; Karsten, C. M.; Köhl, J.; Kridin, K.; Kalies, K.; Kasprick, A. Autoimmune Pre-Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 103236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Winkler, A.; Lorenz, A. K.; Holecska, V.; Blanchard, V.; Eiglmeier, S.; Schoen, A.-L.; Bitterling, J.; Stoehr, A. D.; Petzold, D. T Cell–Independent B Cell Activation Induces Immunosuppressive Sialylated IgG Antibodies. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 3788–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, P.; Kerstein, A.; Klapa, S.; Schinke, S.; Karsten, C. M.; Yu, X.; Ehlers, M.; Epplen, J. T.; Holl-Ulrich, K.; Wiech, T. Pathogenetic and Clinical Aspects of Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Associated Vasculitides. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Marques, O.; Riemekasten, G. Functional Autoantibodies Directed against Cell Surface Receptors in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodoun, M. V.; Kucuk, Z. Y.; Strait, R. T.; Krishnamurthy, D.; Janek, K.; Clay, C. D.; Morris, S. C.; Finkelman, F. D. Rapid Desensitization of Mice with Anti-FcγRIIb/FcγRIII MAb Safely Prevents IgG-Mediated Anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beutier, H.; Gillis, C. M.; Iannascoli, B.; Godon, O.; England, P.; Sibilano, R.; Reber, L. L.; Galli, S. J.; Cragg, M. S.; Rooijen, N. V. IgG Subclasses Determine Pathways of Anaphylaxis in Mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strait, R. T.; Morris, S. C.; Yang, M.; Qu, X.-W.; Finkelman, F. D. Pathways of Anaphylaxis in the Mouse. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagaratham, C.; Ansari, Y. S. E.; Lewis, O. L.; Oettgen, H. C. IgE and IgG Antibodies as Regulators of Mast Cell and Basophil Functions in Food Allergy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A. F.; James, L. K.; Bahnson, H. T.; Shamji, M. H.; Couto-Francisco, N. C.; Islam, S.; Houghton, S.; Clark, A. T.; Stephens, A.; Turcanu, V. IgG4 Inhibits Peanut-Induced Basophil and Mast Cell Activation in Peanut-Tolerant Children Sensitized to Peanut Major Allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, C. A.; Akdis, M. Mechanisms of Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Immune Tolerance to Allergens. World Allergy Organ. J. 2015, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamji, M. H.; Valenta, R.; Jardetzky, T.; Verhasselt, V.; Durham, S. R.; Würtzen, P. A.; van Neerven, R. J. J. The Role of Allergen-specific IgE, IgG and IgA in Allergic Disease. Allergy 2021, 76, 3627–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, Y. S. E.; Kanagaratham, C.; Burton, O. T.; Santos, J. V.; Hollister, B.-M. A.; Lewis, O. L.; Renz, H.; Oettgen, H. C. Allergen-Specific IgA Antibodies Block IgE-Mediated Activation of Mast Cells and Basophils. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 881655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, R. T.; Morris, S. C.; Finkelman, F. D. IgG-Blocking Antibodies Inhibit IgE-Mediated Anaphylaxis in Vivo through Both Antigen Interception and FcγRIIb Cross-Linking. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickery, B. P.; Lin, J.; Kulis, M.; Fu, Z.; Steele, P. H.; Jones, S. M.; Scurlock, A. M.; Gimenez, G.; Bardina, L.; Sampson, H. A. Peanut Oral Immunotherapy Modifies IgE and IgG4 Responses to Major Peanut Allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchini, R.; Karagiannis, S. N.; Jordakieva, G.; Jensen-Jarolim, E. The Role of IgG4 in the Fine Tuning of Tolerance in IgE-Mediated Allergy and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilienthal, G.-M.; Rahmöller, J.; Petry, J.; Bartsch, Y. C.; Leliavski, A.; Ehlers, M. Potential of Murine IgG1 and Human IgG4 to Inhibit the Classical Complement and Fcγ Receptor Activation Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, H. A.; Durham, S. R.; Gould, H. J. Local Somatic Hypermutation and Class Switch Recombination in the Nasal Mucosa of Allergic Rhinitis Patients. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 5602–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strait, R. T.; Mahler, A.; Hogan, S.; Khodoun, M.; Shibuya, A.; Finkelman, F. D. Ingested Allergens Must Be Absorbed Systemically to Induce Systemic Anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; DiLillo, D. J.; Bournazos, S.; Giddens, J. P.; Ravetch, J. V.; Wang, L.-X. Modulating IgG Effector Function by Fc Glycan Engineering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, 3485–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S. C.; Cheung, C. K.; Barratt, J. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of IgA Nephropathy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, A.; Hobusch, J.; Bartsch, Y. C.; Petry, J.; Lilienthal, G.-M.; Koeleman, C. A. M.; Eschweiler, S.; Möbs, C.; Hall, A.; Morris, S. C. Sialylation of IgG Antibodies Inhibits IgG-Mediated Allergic Reactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J. V. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Immunoglobulin G Resulting from Fc Sialylation. science 2006, 313, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhre, J. S.; Becker, M.; Ehlers, M. IgG Subclass and Fc Glycosylation Shifts Are Linked to the Transition from Pre-to Inflammatory Autoimmune Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1006939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeling, M.; Pöhnl, M.; Kara, S.; Horstmann, N.; Riemer, C.; Wöhner, M.; Liang, C.; Brückner, C.; Eiring, P.; Werner, A. Immunoglobulin G-Dependent Inhibition of Inflammatory Bone Remodeling Requires Pattern Recognition Receptor Dectin-1. Immunity 2023, 56, 1046–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plomp, R.; Hensbergen, P. J.; Rombouts, Y.; Zauner, G.; Dragan, I.; Koeleman, C. A. M.; Deelder, A. M.; Wuhrer, M. Site-Specific N-Glycosylation Analysis of Human Immunoglobulin e. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, K.-T. C.; Platzer, B.; Washburn, N.; Mani, V.; Bartsch, Y. C.; Conroy, M.; Pagan, J. D.; Bosques, C.; Mempel, T. R.; Fiebiger, E. A Single Glycan on IgE Is Indispensable for Initiation of Anaphylaxis. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeling, M.; Brückner, C.; Nimmerjahn, F. Differential Antibody Glycosylation in Autoimmunity: Sweet Biomarker or Modulator of Disease Activity? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shade, K.-T. C.; Conroy, M. E.; Washburn, N.; Kitaoka, M.; Huynh, D. J.; Laprise, E.; Patil, S. U.; Shreffler, W. G.; Anthony, R. M. Sialylation of Immunoglobulin E Is a Determinant of Allergic Pathogenicity. Nature 2020, 582, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dühring, L.; Petry, J.; Lilienthal, G.-M.; Bartsch, Y. C.; Kubiak, M.; Pfeufer, C.; Lehrian, S.; Buhre, J. S.; Lunding, H. B.; Kern, C. Sialylation of IgE Reduces FcεRIα Interaction and Mast Cell and Basophil Activation in Vitro and Increases IgE Half-life in Vivo. Allergy 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Simpson, J. L.; Zhang, J.; Gibson, P. G. Galectin-3: Its Role in Asthma and Potential as an Anti-Inflammatory Target. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Koziol-White, C. J.; Jester, W. F.; Smith, S. A.; Nycholat, C. M.; Macauley, M. S.; Panettieri, R. A.; Paulson, J. C. CD33 Recruitment Inhibits IgE-Mediated Anaphylaxis and Desensitizes Mast Cells to Allergen. J. Clin. Invest. 2021, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, L. N.; Jiang, W.; Bhamidipati, K.; Millican, M.; Macaubas, C.; Hung, S.; Mellins, E. D. The Other Function: Class II-Restricted Antigen Presentation by B Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, N.; Luu, M.; Ong, P. Y.; Tam, J. S. The Role of Skin Barrier in the Pathogenesis of Food Allergy. Children 2015, 2, 382–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakwerth, C. A.; Ordovas-Montanes, J.; Blank, S.; Schmidt-Weber, C. B.; Zissler, U. M. Role of Respiratory Epithelial Cells in Allergic Diseases. Cells 2022, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Splunter, M. van; Liu, L.; Neerven, R. J. J. van; Wichers, H. J.; Hettinga, K. A.; Jong, N. W. D. Mechanisms Underlying the Skin-Gut Cross Talk in the Development of IgE-Mediated Food Allergy. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asero, R.; Antonicelli, L. Does Sensitization to Foods in Adults Occur Always in the Gut? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 154, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodoun, M. V.; Tomar, S.; Tocker, J. E.; Wang, Y. H.; Finkelman, F. D. Prevention of Food Allergy Development and Suppression of Established Food Allergy by Neutralization of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin, IL-25, and IL-33. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divekar, R.; Kita, H. Recent Advances in Epithelium-Derived Cytokines (IL-33, IL-25 and TSLP) and Allergic Inflammation. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whetstone, C. E.; Ranjbar, M.; Omer, H.; Cusack, R. P.; Gauvreau, G. M. The Role of Airway Epithelial Cell Alarmins in Asthma. Cells 2022, 11, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, I. C. M.; Toellner, K.-M.; Cunningham, A. F.; Serre, K.; Sze, D. M.-Y.; Zúñiga, E.; Cook, M. C.; Vinuesa, C. G. Extrafollicular Antibody Responses. Immunol. Rev. 2003, 194, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, R. A.; Shlomchik, M. J. Germinal Center and Extrafollicular B Cell Responses in Vaccination, Immunity, and Autoimmunity. Immunity 2020, 53, 1136–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, F.; Figgett, W. A.; Saulep, D.; Lepage, M.; Hibbs, M. L. B-cell Stage and Context-dependent Requirements for Survival Signals from BAFF and the B-cell Receptor. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, J.; Yeh, C.-H.; Kelsoe, G.; Kuraoka, M. Germinal Center Responses to Complex Antigens. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 284, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlomchik, M. J.; Weisel, F. Germinal Center Selection and the Development of Memory B and Plasma Cells. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 247, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgueta, R.; Benson, M. J.; Vries, V. C. D.; Wasiuk, A.; Guo, Y.; Noelle, R. J. Molecular Mechanism and Function of CD40/CD40L Engagement in the Immune System. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotty, S. Follicular Helper CD4 T Cells (Tfh). Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berin, M. C. Targeting Type 2 Immunity and the Future of Food Allergy Treatment. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20221104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, L. M.; Tarlinton, D. M. Regulation of Germinal Center Responses, Memory B Cells and Plasma Cell Formation—an Update. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 39, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, A. S.; Ansari, M. J. Heterogeneity of Memory B Cells. Am. J. Transplant. 2018, 18, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade-Vallance, A. K.; Allen, C. D. C. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Regulation of IgE B Cell Responses. Curr Opin Immunol 2021, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M. E. R. The B-Cell Antigen Receptor of IgE-Switched Plasma Cells Regulates Memory IgE Responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2020, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, R.; Tolar, P. Chronic Calcium Signaling in IgE+ B Cells Limits Plasma Cell Differentiation and Survival. Immunity 2021, 54, 2756–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrat, S.; Kaur, N.; Liu, X.; Ben, L.-H.; Kajimura, D.; Murphy, A. J.; Sleeman, M. A.; Limnander, A.; Orengo, J. M. Chronic Allergen Exposure Drives Accumulation of Long-Lived IgE Plasma Cells in the Bone Marrow, Giving Rise to Serological Memory. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaav8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luger, E. O. Induction of Long-Lived Allergen-Specific Plasma Cells by Mucosal Allergen Challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L. C.; Scheerens, H. Targeting IgE Production in Mice and Humans. Curr Opin Immunol 2014, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, A.; Panetta, V.; Cappella, A.; Hofmaier, S.; Hatzler, L.; Rohrbach, A.; Tsilochristou, O.; Bauer, C.-P.; Hoffmann, U.; Forster, J. IgG and IgG4 to 91 Allergenic Molecules in Early Childhood by Route of Exposure and Current and Future IgE Sensitization: Results from the Multicentre Allergy Study Birth Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellusova, J. Metabolic Control of B Cell Immune Responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 63, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmi, Y.; Ise, W.; Harazono, A.; Takakura, D.; Fukuyama, H.; Baba, Y.; Narazaki, M.; Shoda, H.; Takahashi, N.; Ohkawa, Y. Sialylation Converts Arthritogenic IgG into Inhibitors of Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, Y. C.; Eschweiler, S.; Leliavski, A.; Lunding, H. B.; Wagt, S.; Petry, J.; Lilienthal, G.-M.; Rahmöller, J.; Haan, N. de; Hölscher, A. IgG Fc Sialylation Is Regulated during the Germinal Center Reaction Following Immunization with Different Adjuvants. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhre, J. S.; Pongracz, T.; Künsting, I.; Lixenfeld, A. S.; Wang, W.; Nouta, J.; Lehrian, S.; Schmelter, F.; Lunding, H. B.; Dühring, L. MRNA Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 Induce Comparably Low Long-Term IgG Fc Galactosylation and Sialylation Levels but Increasing Long-Term IgG4 Responses Compared to an Adenovirus-Based Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Guan, C.; Ji, T.; Cao, C.; Jiang, J.; Liu, M.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, P.; Gong, F. Increased Circulating T Follicular Helper 13 Subset Correlates with High IgE Levels in Pediatric Allergic Asthma. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 2010–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifle, R.; Rothe, T.; Ipseiz, N.; Scherer, H. U.; Culemann, S.; Harre, U.; Ackermann, J. A.; Seefried, M.; Kleyer, A.; Uderhardt, S. Regulation of Autoantibody Activity by the IL-23–TH17 Axis Determines the Onset of Autoimmune Disease. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




