Introduction:
Muscle and bone tissues share a common somitic mesodermal origin and constitute musculoskeletal functional units for movement. In addition, they may function in calcium reservoirs, protect the internal organs, and maintain glucose homeostasis, possibly with a common molecular network 1, 2. Mechanostat theory suggests mechanical loading impacts bone mass and geometry, while evidence suggests that muscle force can drive bone adaptivity responses 3. Previous evidence suggests a positive correlation between muscle mass and bone mineral density (BMD), indicating that an increase in muscle mass is linked to higher BMD. Conversely, the loss of muscle mass associated with aging could contribute to bone loss 2, 3. Furthermore, pathological states such as vitamin D deficiency and glucocorticoid imbalance can exacerbate bone and muscle loss. Consequently, it is essential to understand the reciprocal phenomenon between bone mass, geometry, and muscle mass to characterize functional units for movement and enhance physical health in humans 4, 5.
Many overlapping signaling pathways, including Wnt, Hedgehog, Growth Hormone (GH), Interleukine-6 (IL-6), Irisin, Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and receptor activator of NF-kB ligand (RANKL) serve as a fundamental mechanism for understanding muscle and bone metabolism 6, 7. It has been accepted that Wnt signaling regulates bone metabolism with its activation leading to bone formation, while its inhibition via sclerostin and Dickopff-1 (DKK-1) downregulates bone formation. On the other hand, the activation of RANKL and proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) further enhances bone loss through resorption. RANKL is also expressed in skeletal muscle and inhibits myogenic differentiation, leading to muscle loss 9. The relationship between sclerostin and inflammatory cytokines and exercise has not been explored extensively 8.
Furthermore, muscle metabolism is primarily regulated by irisin, a pro-myogenic factor derived from the fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 (FNDC5), attributed to skeletal muscle hypertrophy and increased protein synthesis via AKT/mTOR pathway 9. Several studies reported an association between low circulating irisin levels and low muscle and bone mass; however, its relationship with fat and lean body mass remains uncertain10, 11. These various signaling pathways ultimately exert autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine effects on bone and muscle.
Although the concept of "inflammageing" was introduced a while ago, there is still a lack of research addressing this complex molecular network of bone, muscle, and inflammatory markers 12. Evidence suggests that aging is associated with concomitant muscle and bone mass loss, resulting in sarcopenia and osteoporosis. In fact, evidence from animal and human studies supports the reciprocity in understanding these conditions and shares common patterns of cellular dysregulation, including decreased estrogen hormone, increased inflammatory cytokine signaling (IL-6 and TNF-α), suppression of Wnt gene, and increased RANKL level. Age-related muscle loss, sarcopenia, is characterized by muscle mass and strength loss. Various factors influence sarcopenia, such as nutrition, physical activity/mechanical loading, and genetic components 13.
The benefits of physical activity throughout the lifespan have been well-accepted within the scientific community. However, only a few studies have explored the interaction of bone, muscle and inflammatory markers simultaneously. Previous work reported that competitive physical activity is associated with serum levels of irisin and RANKL but not with bone markers and vitamin D levels, suggesting that myokines levels are related to the degree of muscle strength and volume of the physical activity compared to the control group 14. Another study reported the inverse association between Wnt inhibitors sclerostin, expressed in higher levels in sarcopenic women with low skeletal muscle mass, suggesting the important linkage between muscle and bone via physical force 15. Similarly, the cross-sectional study reported that serum IL-6 was inversely associated with skeletal muscle and bone parameters in women between 20-89 years, suggesting the importance of understanding the concept of inflammageing. However, this study did not examine other bone, muscle, or inflammatory marker parameters 16.
Although studies support the idea that mechanical signal/physical activity plays a tremendous role in muscle and bone health, the precise mechanisms for bone-muscle crosstalk are still not apparent. These observations led us to hypothesize that RANKL, Irisin, IL-6, sclerostin, and DKK-1 could negatively affect muscle mass and strength in response to physical activity. This study aims to evaluate and compare bone and inflammatory markers between young men and women, as well as examine their relationship with muscle performance, to enhance understanding of the bone-muscle crosstalk mechanism. Therefore, recognizing the significance of these bone, muscle, and inflammatory markers aids in the development of novel screening methods for predicting adverse health events in clinical and sports performance populations. Additionally, these markers can potentially be utilized to establish links with training regimens and monitor healthcare outcomes.
Methods:
In this non-randomized cross-sectional study, a total of 40 college-aged students aged 18-25 years were screened for their eligibility. Two participants were lost in follow-up and were excluded; therefore, 38 healthy young men (n=18) and women(n=20) of diverse ethnicities (Caucasian, African American, and Asian) completed the protocols. All the participants were healthy and recreationally active, without cardiovascular and metabolic diseases or physical disabilities, and not taking any medications that affect muscle metabolism. Only nine female participants reported the use of contraceptives. All the participants were provided with the study protocol details outlining the risks and benefits of the study. Participants provided the written informed consent form before participating. All the protocols were approved by the Lander University Institutional Review Board.
Protocol
This study utilized a non-randomized, cross-sectional design with sex as an independent variable. We performed G*Power 3.1 analysis to estimate the sample sizes needed for 80% power based on α =0.05 and effect sizes (Cohen's d s) for sex differences in sclerostin and IL-6 16, 17. We found a large effect size for gender (1.13, 1.42), requiring 20 sample sizes per group. Participants completed two visits to the Human Performance Laboratory. During the first visit, participants completed written consent, a health history questionnaire, a menstrual history questionnaire, an international physical activity questionnaire (IPAQ), a bone-specific physical activity questionnaire (BPAQ) 18, and familiarization with the testing protocol. The validated long-form IPAQ was used to measure physical activity scores based on the metabolic equivalents (MET) of self-reported physical activities for seven days 19, 20. Participants also completed the calcium intake questionnaire consisting of daily calcium intake information based on certain foods consumed daily or weekly 21. Further, lower and upper body strength were assessed by vertical jump test and handgrip dynamometry, respectively. During the second visit, a blood sample was drawn to quantify the levels of sclerostin, DKK-1, irisin, IL-6, RANKL, TNF-α, and vitamin D.
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS 27.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). Unless otherwise stated, all descriptive statistics were reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD). All the dependent variables were tested for normality using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Sex differences comparisons for non-normally distributed dependent variables (Sclerostin and DKK-1) were performed using the Mann-Whitney U test. Independent t-tests were used to compare the physical characteristics of the two groups. Independent t-tests were used to compare serum levels of irisin, IL-6, RANKL, TNF-α and vitamin D, and muscle performance variables. One-way ANCOVA adjusting for height and weight was used to determine those markers and muscle performance. Bonferroni adjusted p values were used for the independent t-tests to avoid inflated type I error. Pearson Product Moment Correlation coefficients (r) were computed to determine the relationships between bone and inflammatory markers and muscle performance variables for all 38 participants. Correlations between non-normally distributed variables were computed using Spearman's Rho (rs). We also included independent variables such as sex, age, BMI, IPAQ, BPAQ, CI, Time in air, Jump height, velocity, power, relative power, and grip strength variables in the stepwise regression models in determining if any of those independent variables predict bone, muscle, and inflammatory markers. The levels of significance were set at p ≤ 0.05.
Results
Table 1 showed physical characteristics, body mass index, total bone physical activity questionnaire score, dietary calcium intake, and total physical activity scores. Male and female participants had a significant difference in height, weight, and tBPAQ score.
Figure 1. and
Figure 2. showed serum sclerostin and DKK-1levels were significantly higher in male compared to female participants (p<0.05). Data on bone, muscle, and inflammatory markers are presented in
Table 2. Male participants showed higher serum irisin (p<0.05 Hedges’ g = .66, 95% C.I. [.015, 1.30]) and vitamin D (p<0.05 Hedges’ g = .65 95% C.I. [.005, 1.29]) than female participants. We found no significant difference in serum levels of IL-6, RANKL, and TNF-α (p>0.05). Participants' upper and lower body muscle performance was reported in
Table 3. A significant difference was found in lower-body muscle performance between male and female participants, which was significantly higher in male participants. (p<0.01). We found no significant difference in right and left-hand grip strength between the two groups. For the entire cohort
Table 4. we found a significant positive correlation between BMI and IL-6 (p<0.05). Vitamin D is positively associated with time in the air, jump height, and velocity, whereas negatively associated with relative power (p<0.05). TNF-α was negatively associated with time in the air, jump height, and power (p<0.05). We also found a significant positive relationship between RANKL and upper body strength (p<0.05). We did not find any relationship between irisin and muscle performance.
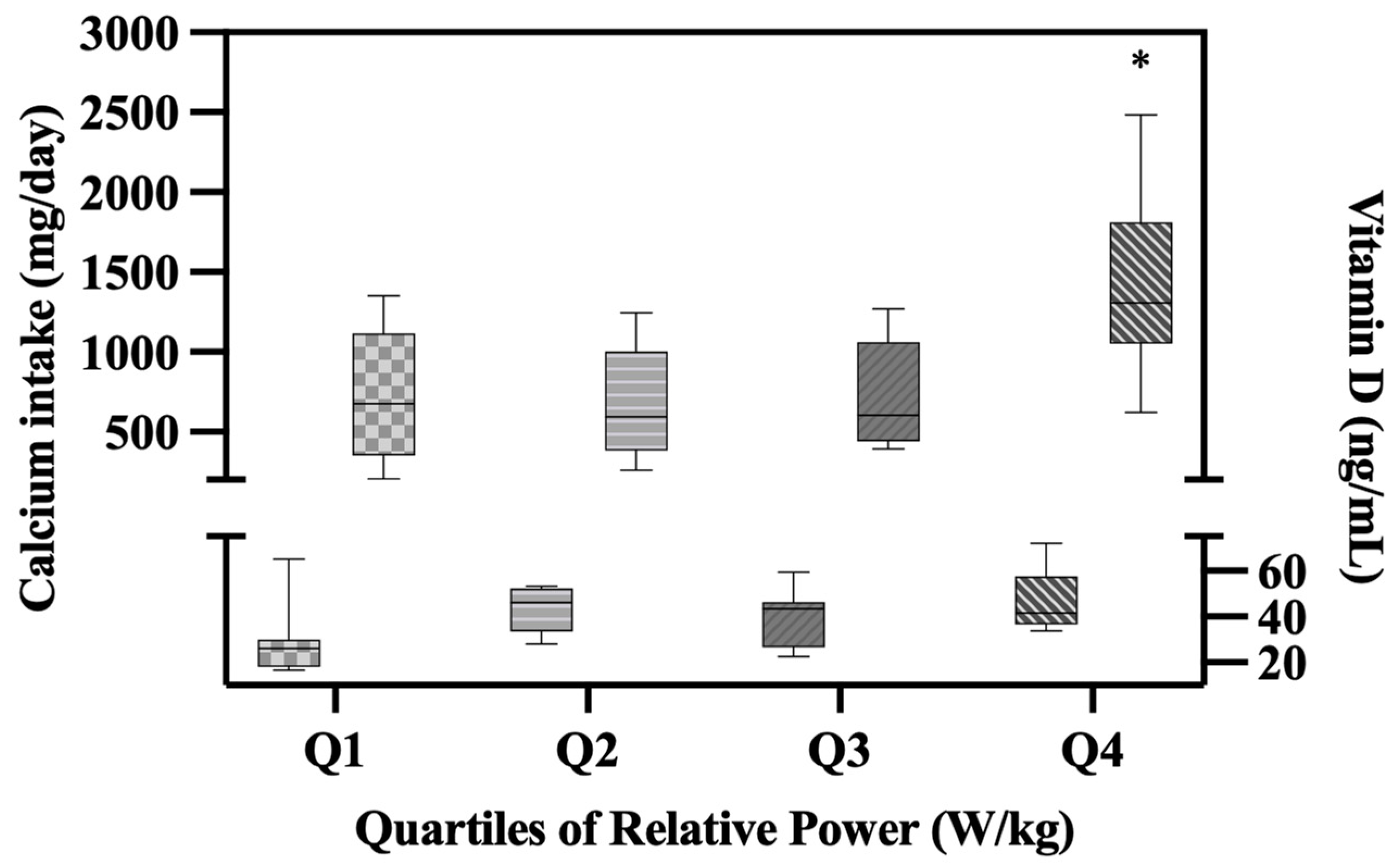
We also found significant relationships between dietary calcium intake and lower body muscle performance variables, including velocity (r= 0.42; p = .01), power (r=0.42; p = .009), and relative power (r = 0.47; p = .003). Due to this association between muscle performance variables, dietary calcium intake, and vitamin D, yet no significant associations between vitamin D and calcium intake, we conducted a gradient analysis on calcium intake and vitamin D across quartiles of relative power. We chose quartiles (Q) of relative power as the predictor variable due to having the strongest association with both calcium intake and vitamin D. One-way ANOVA revealed significant differences in calcium intake (p = .001) and vitamin D (p = .02) levels between quartiles of relative power. Calcium intakes were significantly higher in Q4 (1,410.37 mg/day; SD = 566.82;) compared to the other quartiles (Q1 = 711.17 mg/day, SD = 409.53 p= 0.06; Q2 = 674.01 mg/day, SD = 333.70; p= 0.03; Q3 = 732.27 mg/day, SD = 330.48; p= 0.08). Additionally, vitamin D levels were significantly higher in Q4 (46.71 ng/mL; SD 13.71;) compared to Q1 (27.80 ng/mL, SD 14.99; p=0.01) (
Figure 5).
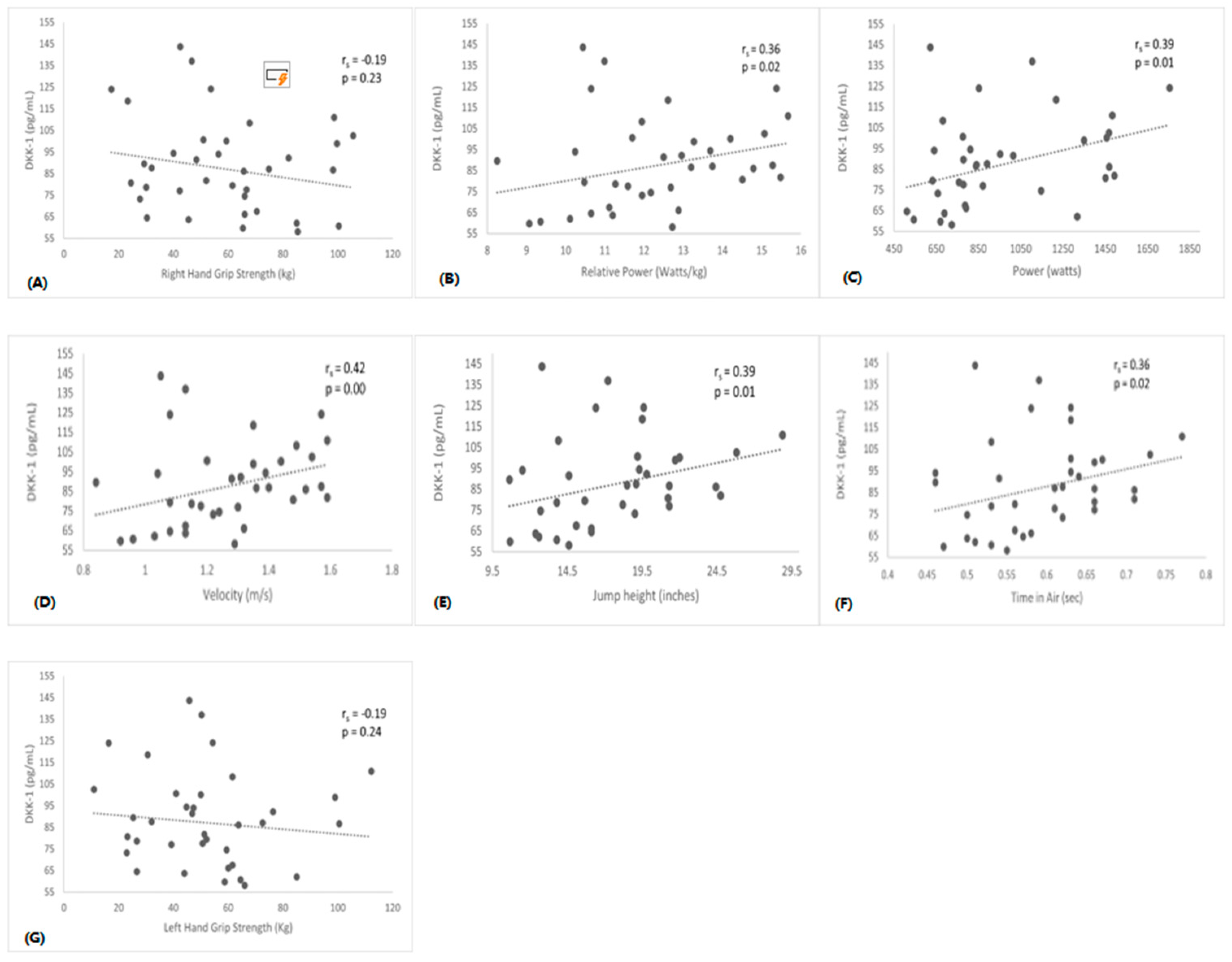
Further, spearman rho correlation analysis showed that sclerostin and DKK-1 were positively associated with lower body muscle performance
Figure 3 and
Figure 4. We did not find significant correlations between serum sclerostin and DKK-1 with upper-body muscle performance.
Figure 3.
Correlations between serum Sclerostin vs Time in Air (Panel A), Jump Height (Panel B), Velocity (Panel C), Power (Panel D), Relative Power (Panel E), Right Hand Grip (Panel F), and, Left Hand Grip (Panel G).
Figure 3.
Correlations between serum Sclerostin vs Time in Air (Panel A), Jump Height (Panel B), Velocity (Panel C), Power (Panel D), Relative Power (Panel E), Right Hand Grip (Panel F), and, Left Hand Grip (Panel G).
Figure 4.
Correlations between serum DKK-1 vs Time in Air (Panel A), Jump Height (Panel B), Velocity (Panel C), Power (Panel D), Relative Power (Panel E), Right Hand Grip (Panel F), and, Left Hand Grip (Panel G).
Figure 4.
Correlations between serum DKK-1 vs Time in Air (Panel A), Jump Height (Panel B), Velocity (Panel C), Power (Panel D), Relative Power (Panel E), Right Hand Grip (Panel F), and, Left Hand Grip (Panel G).
Figure 5.
Boxplot showing Calcium Intake and Vitamin D levels across quartiles of Relative Power. *p<0.05 significant. Effect sizes: calcium intake μ2 = 0.37 (95% C.I. [0.08, 0.53]); vitamin D μ2 = 0.25 (95% C.I. [.005, .417]).
Figure 5.
Boxplot showing Calcium Intake and Vitamin D levels across quartiles of Relative Power. *p<0.05 significant. Effect sizes: calcium intake μ2 = 0.37 (95% C.I. [0.08, 0.53]); vitamin D μ2 = 0.25 (95% C.I. [.005, .417]).
Table 5. showed Stepwise regression analysis performed using sex, BMI, calcium intake, tBPAQ, cBPAQ, total PA levels, jump height, velocity, power, relative power, and right and left handgrip to predict bone and inflammatory markers. We found that BMI is a 16% predictor of serum IL-6. Sex and calcium intake account for 34%-43% of serum sclerostin. Sex and tBAPQ account for 18% and 37% of serum DKK-, respectively. cBPAQ accounted for 14% of serum levels of irisin. Relative power, right-hand grip, and calcium intake predict 20%, 32%, and 40% of serum levels of vitamin D, respectively. Further, the right-hand grip predicted serum RANKL by 27%. Time in air accounted for 10% serum of TNF-α.
Discussion
The main findings from this study indicate that serum sclerostin, DKK-1, irisin, and vitamin D levels are significantly different between male and female participants. Also, a significant difference was found only in lower body muscle performance between the two groups. A positive relationship was found between sclerostin and DKK-1 with lower body muscle performance. Further, low to moderate relationships were found between RANKL, TNF-α, and Vitamin D with muscle performance variables.
Our findings of higher sclerostin levels in male participants aligned with the previous studies 17, 23, where serum sclerostin levels were higher in male participants. We expected that sclerostin levels would be higher in males, although the precise underlying mechanism remained unclear. One plausible explanation could be that a larger skeletal mass in men could primarily increase sclerostin secretion in the bloodstream by osteocytes, assuming that circulating sclerostin levels indicate the overall skeletal mass. However, it is important to note that this study did not assess the participant's bone mineral density to account for the skeletal mass variations. In contrast to a previous study, our study reported a significant variation in serum DKK-1 levels, with higher levels observed in male participants 24. This gender difference in DKK-1 levels potentially holds significance in relation to skeletal mass, health status, genetic factors, and hormonal variations, all of which can impact the outcomes. Further investigation is warranted to delve into these findings. It is worth noting that while the previous study encompassed 24 a comparison between older and younger populations, our study solely focused on a cohort of healthy young individuals.
In Spearman’s correlation analysis, we found a significant moderate relationship between sclerostin, DKK-1, and lower body muscle performance, which contrasts with the previous study15. The significance of circulating sclerostin and DKK-1 in relation to skeletal mass remains unclear. The association between sclerostin and muscle mass might be influenced by the interplay between bone mineral density and muscle mass rather than a direct link. Given the crosstalk of muscle, bone, and body fat, the correlation between sclerostin, DKK-1 and muscle mass could be affected by body composition. Also, our study comprised of the healthy population compared to the sarcopenic population in the previous study 15. We did not find significant differences between hand grip strength, sclerostin, or DKK-1.
In contrast, a previous study reported that sclerostin levels are negatively associated with grip strength, possibly due to mechanical forces caused by gravity 25. The inverse relationship could suggest that changes in sclerostin levels could influence muscle activity, which could possibly increase serum sclerostin levels during muscle atrophy or disuse. Also based on animal models, Wnt7a signaling stimulated the growth of skeletal muscles and enhanced muscle strength through the non-canonical pathway involving the activation of JNK or AKT-mTOR. These findings suggest the possibility of a similar implication in human studies in relation to muscle performance 26.
A growing body of evidence indicates that sarcopenia may impact on metabolic abnormalities involving detrimental myokines and hormonal substances, such as Vitamin D, irisin, IL-6, RANKL, and TNF-α 27. In contrast to the previous study, we found that female participants had lower irisin levels than males 28. While a definitive explanation for this inconsistency is lacking, variations in population characteristics, such as age, body composition, and health status, could account for it. One hypothesis proposes that under normal metabolic conditions, skeletal muscle is the primary source of circulating irisin, while in obese individuals, adipose tissue may produce and thus exert some influence on irisin levels. In this study, we did not find significant differences in BMI between male and female participants 33. Although BPAQ scores were widely reported as a predictor for bone mineral density 29, surprisingly, in this study, we found that the current BPAQ score is the predictor of serum irisin levels accounting for 14% of the variance. Also, tBPAQ was negatively associated with right-hand grip strength (0.34), which might be related to upper-body muscle performance. There was also no correlation between irisin and muscle performance variables, contrasting the previous studies 15, 30. These intriguing findings warrant further investigation. Several studies reported that exercise induces changes in the irisin levels 28, 30. However, based on IPAQ scores, we found no correlation between physical activity and circulating irisin levels. While finding a long-term association between physical activity and irisin levels is not anticipated, it is important to acknowledge the questionnaire that may have influenced these findings although the participants were physically active. It is important to note that while irisin's involvement in the browning of white fat cells and its impact on energy expenditure have been well studied, additional research is needed to identify its specific connections and interactions with bone and muscle.
We found significant differences in the serum vitamin D levels between men and women in this study, although both groups showed sufficient vitamin D levels, which agrees with the previous study 31. Many factors affect vitamin D status; however, in this study, we collected blood samples in the late Fall season. We also reported participants dietary calcium intake analysis and found that female participants have lower calcium intake compared to male counterparts although the levels were not significant. Only a few studies have reported the relationship between vitamin D levels and muscle performance. Interestingly we found a significant correlation between vitamin D serum levels and lower body muscle performance, in contrast to the previous studies 31, 32. Newer findings indicate that low vitamin D levels are associated with decreased muscle mass in older adults; however, in our study, all the participants were young and physically active based on the IPAQ score. We also found calcium intake, right-hand grip strength, and relative power as a predictor of vitamin D levels.
Previous studies reported that elevated levels of circulating inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, IL-6, and RANKL, can contribute to muscle catabolism, ultimately reducing the mass and strength 34. TNF-α has been shown to stimulate the production of additional catabolic cytokines, including IL-6, thereby triggering a subsequent cycle of inflammation. Contrary to the findings of previous studies 16, 35, 38, we did not observe significant gender differences in IL-6 and TNF-α levels. However, it should be noted that the participants in those studies were older compared to our study population. Interestingly, we found a significant relationship between IL-6 and BMI, aligning with one study 38, suggesting that the pro-inflammatory cytokines regulate adipose and skeletal muscle, which could be a way to differentiate between inflammation related to underlying disease and muscle recovery. A meta-analysis study reported that higher IL-6 is negatively associated with grip strength, which this study did not corroborate 42. However, the population sample was among the older population compared to our study. Furthermore, we observed a negative relationship between TNF-α and lower body muscle performance, which aligns with the previous study 38. This suggests that cytokine levels could potentially influence muscle strength, which can have various effects on the body, even at a young age.
Additionally, we did not find a significant sex difference in serum levels of RANKL. Animal models suggest that overexpression of RANKL causes decreased muscle function, emphasizing its role in bone and muscle metabolism 37. Additionally, anti-RANKL treatment has been reported to improve muscle inflammation and loss 39. While limited research has explored the relationship between RANKL, muscle performance, and exercise performance in humans, our study identified a positive association between RANKL and hand grip strength, contrasting the findings from another study 40, which showed no significant relationship between hand grip strength and RANKL levels in healthy individuals and patients with heart failure. Also, acute training exercise showed no changes in the serum RANKL level in college women, which aligns with the current study as all the participants are active based on the IPAQ score. The precise mechanism underlying this relationship remains unexplored; however, it is possible to hypothesize that RANKL initiates a signaling cascade and induces osteoclasts differentiation in bone and muscle, inhibiting myogenic differentiation via NF-κB activation resulting in muscle loss 41. Further, animal studies suggested RANKL also contributes to decreased glucose uptake in the skeletal muscle and lowers the contractile properties of muscle function 43.
This study has certain limitations that should be taken into account. Our findings need to be interpreted within the context of the research design, which was cross-sectional in nature, as well as the comparisons made regarding physical activity and the relatively smaller sample size. This study reported correlations between biomarkers and muscle performance variables and did not establish causality. Notably, we did not measure bone mineral density or muscle cross-sectional area, which could have provided additional insights and expanded the scope of the results. Furthermore, the assessment of physical activity levels relied on self-reported questionnaires, which may introduce some subjectivity. It is worth considering the possibility of exploring exercise interventions in relation to the current variables in the future studies to enhance our understanding of this area further.
Conclusion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate bone, muscle, and inflammatory markers in young healthy population. We found sex disparities for sclerostin, DKK-1, irisin, and Vitamin D levels. Further, we also found an association between muscle performance and bone, muscle, and inflammation markers. Extensive literature exists regarding the interaction between bone and muscle; however, several crucial aspects remain to be addressed. Most of the studies predominantly focused on one-way communication between bone and muscle. In contrast, in our study we delineate the difference between sex and muscle performance, aiming to identify common bone and inflammatory markers; comprehending bone and muscle crosstalk as a complex endeavor and numerous unexplored areas necessitate further investigation. Additionally, this study provides insights into the concepts of "Exerkines" and "Inflammageing," and their counterregulatory roles in inflammation, bone, and muscle metabolism. Exploring these potential biomarkers allows us to assess individual fitness levels and disease prognosis more effectively at a young age.
Authors Contributions
PSG designed this study and collected the data. PSG conducted all the biochemical assays. AE ran statistical analyses. PSG, AE, IKA, and JS drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All procedures performed in studies, including human participants, were per the ethical standards and approved by Lander University Institutional Review Board (approval number 1/2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Written Informed consent was obtained from all the participants included in this study.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all the study participants who participated in this study. This study was funded by the President’s Grant awarded at Lander University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- Mikolajewicz N, Sehayek S, Wiseman PW, et al. Transmission of mechanical information by purinergic signaling. Biophysical journal. 2019;116(10):2009-2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2019.04.012. [CrossRef]
- DiGirolamo DJ, Clemens TL, Kousteni S. The skeleton as an endocrine organ. Nature Reviews Rheumatology. 2012; 8(11):674-683. doi:10.1028/nrrheum.2012.157. [CrossRef]
- Frost HM. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff's Law for clinicians. The Angle Orthodontist. 2004;74(1):3-15. https://doi.org/10.1043/00033219(2004)074<0003:AUOBPA>2.0.CO;2. [CrossRef]
- Herrmann M, Engelke K, Ebert R, et al. Interactions between muscle and bone—where physics meets biology. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030432. [CrossRef]
- Nassari S, Duprez D, Fournier-Thibault C. Non-myogenic contribution to muscle development and homeostasis: the role of connective tissues. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2017;5:22. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2017.00022. [CrossRef]
- DiGirolamo DJ, Kiel DP, Esser KA. Bone and skeletal muscle: neighbors with close ties. Journal of bone and mineral research. 2013;28(7):1509-1518. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1969. [CrossRef]
- Kirk B, Feehan J, Lombardi G, et al. Muscle, bone, and fat crosstalk: the biological role of myokines, osteokines, and adipokines. Current Osteoporosis Reports. 2020; 18(4):388-400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-020-00599-y. [CrossRef]
- Kouvelioti R, Kurgan N, Falk B, et al. Cytokine and Sclerostin Response to High-Intensity Interval Running versus Cycling. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2019;51(12): 2458-2464. 10.1249/mss.0000000000002076.
- Bonnet N, Bourgoin L, Biver E, et al. RANKL inhibition improves muscle strength and insulin sensitivity and restores bone mass. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2019; 129(8):3214-3223. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI125915. [CrossRef]
- Liang H, Qi W, Jiajue R, et al. Serum Irisin level is associated with fall risk, muscle strength, and cortical porosity in postmenopausal women. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2023;14:1096950. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1096950. [CrossRef]
- Park HS, Kim HC, Zhang D, et al. The novel myokine irisin: clinical implications and potential role as a biomarker for sarcopenia in postmenopausal women. Endocrine. 2019; 64:341-348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1814-y. [CrossRef]
- Franceschi C, Bonafè M, Valensin S, et al. Inflamm-aging: an evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Annals of the new York Academy of Sciences. 2000;908(1):244-254. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06651.x. [CrossRef]
- He C, He W, Hou J, et al. Bone and muscle crosstalk in aging. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2020;8:585644. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.585644. [CrossRef]
- Gaudio A, Rapisarda R, Xourafa A, et al. Effects of competitive physical activity on serum irisin levels and bone turnover markers. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation. 2021:1-7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01529-0. [CrossRef]
- Kim JA, Roh E, Hong SH, et al. Association of serum sclerostin levels with low skeletal muscle mass: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Bone. 2019;128:115053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2019.115053. [CrossRef]
- Miller RM, Freitas ED, Heishman AD, et al. Associations of serum IL-6 with muscle, bone, and adipose tissue in women. Cytokine. 2022;151:155787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155787. [CrossRef]
- Amrein K, Amrein S, Drexler C, et al. Sclerostin and its association with physical activity, age, gender, body composition, and bone mineral content in healthy adults. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2012;97(1):148-154. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-2152. [CrossRef]
- Weeks BK, Beck BR. The BPAQ: a bone-specific physical activity assessment instrument. Osteoporosis International. 2008;19:1567-1577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-008-0606-2. [CrossRef]
- Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2003;35(8):1381-95. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB. [CrossRef]
- Hagströmer M, Oja P, Sjöström M. The International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ): a study of concurrent and construct validity. Public Health Nutrition. 2006;9(6):755-762. https://doi.org/10.1079/PHN2005898. [CrossRef]
- Musgrave KO, Liane Giambalvo MS RD, Leclerc HL, et al. Validation of a quantitative food frequency questionnaire for rapid assessment of dietary calcium intake. Journal of the American Dietetic Association. 1989;89(10):1484-1485 https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-8223(21)02399-3. [CrossRef]
- Liakou CG, Mastorakos G, Makris K, et al. Changes of serum sclerostin and Dickkopf-1 levels during the menstrual cycle. A pilot study. Endocrine. 2016;(54):543-551. DOI 10.1007/s12020-016-1056-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1056-9. [CrossRef]
- Mödder UI, Hoey KA, Amin S, et al. Relation of age, gender, and bone mass to circulating sclerostin levels in women and men. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2011; 26(2):373-379. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.217. [CrossRef]
- Coulson J, Bagley L, Barnouin Y, et al. Circulating levels of dickkopf-1, osteoprotegerin and sclerostin are higher in old compared with young men and women and positively associated with whole-body bone mineral density in older adults. Osteoporosis International. 2017; (28):2683-2689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-4104-2. [CrossRef]
- Thorson S, Prasad T, Sheu Y, et al. Sclerostin and bone strength in women in their 10th decade of life. Journal of Bone Mineral and Research. 2013; 28(9): 2008-2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1929. [CrossRef]
- Bentzinger CF, von Maltzahn J, Dumont NA, et al. Wnt7a stimulates myogenic stem cell motility and engraftment, resulting in improved muscle strength. Journal of Cell Biology. 2014;205(1):97–111. J. www.jcb.org/cgi/doi/10.1083/jcb.201310035.
- Herrmann M, Engelke K, Ebert R, et al. Interactions between muscle and bone—where physics meets biology. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030432. [CrossRef]
- Kabasakalis A, Nikolaidis S, Tsalis G, Mougios V. Response of blood biomarkers to sprint interval swimming. International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance. 2020;15(10):1442-1447. https://doi.org/10.1123/ijspp.2019-0747. [CrossRef]
- Kim S, Baker BS, Sharma-Ghimire P, et al. Association between bone-specific physical activity scores and pQCT-derived measures of bone strength and geometry in healthy young and middle-aged premenopausal women. Archives of Osteoporosis. 2018;13:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-018-0495-8. [CrossRef]
- Daskalopoulou SS, Cooke AB, Gomez YH, et al. Plasma irisin levels progressively increase in response to increasing exercise workloads in young, healthy, active subjects. European Journal of Endocrinology. 2014;171(3):343-352. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-14-0204. [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi AS, Parker BA, Capizzi JA, et al. 25 (OH) vitamin D is associated with greater muscle strength in healthy men and women. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 2013;45(1):157. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31826c9a78. [CrossRef]
- Brännström A, Yu JG, Jonsson P, et al. Vitamin D in relation to bone health and muscle function in young female soccer players. European Journal of Sports Science. 2017;17(2):249-256. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2016.1225823. [CrossRef]
- Anastasilakis AD, Polyzos SA, Saridakis ZG, et al. Circulating irisin in healthy, young individuals: day-night rhythm, effects of food intake and exercise, and associations with gender, physical activity, diet, and body composition. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2014;99(9):3247-3255. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-1367. [CrossRef]
- Singh T, Newman AB. Inflammatory markers in population studies of aging. Ageing research reviews. 2011;10(3):319-329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2010.11.002. [CrossRef]
- Tiainen K, Hurme M, Hervonen A, et al. Inflammatory markers and physical performance among nonagenarians. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biomedical Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2010;65(6):658-663. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glq056. [CrossRef]
- Lukic L, Lalic NM, Rajkovic N, et al. Hypertension in obese type 2 diabetes patients is associated with increases in insulin resistance and IL-6 cytokine levels: potential targets for an efficient preventive intervention. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014;11(4):3586-3598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403586. [CrossRef]
- Bonnet N, Bourgoin L, Biver E, et al. RANKL inhibition improves muscle strength and insulin sensitivity and restores bone mass. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2019;129(8):3214-23. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI125915. [CrossRef]
- Visser M, Pahor M, Taaffe DR, et al. Relationship of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α with muscle mass and muscle strength in elderly men and women: the Health ABC Study. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2002;57(5):M326-332. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/57.5.M326. [CrossRef]
- Hamoudi D, Marcadet L, Piette Boulanger A, et al. An anti-RANKL treatment reduces muscle inflammation and dysfunction and strengthens bone in dystrophic mice. Human Molecular Genetics. 2019;28(18):3101-3112. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddz124. [CrossRef]
- Loncar G, Bozic B, Von Haehling S, et al. Association of adiponectin with peripheral muscle status in elderly patients with heart failure. European Journal of Internal Medicine. 2013;24(8):818-823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2013.09.011. [CrossRef]
- Dufresne SS, Dumont NA, Boulanger-Piette A, et al. Muscle RANK is a key regulator of Ca2+ storage, SERCA activity, and function of fast-twitch skeletal muscles. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2016;310(8):C663-672. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00285.2015. [CrossRef]
- Mikó A, Pótó L, Mátrai P, et al. Gender difference in the effects of interleukin-6 on grip strength–a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatrics. 2018;18(1):1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-018-0798-z. [CrossRef]
- Sylow L, Nielsen IL, Kleinert M, et al. Rac1 governs exercise-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle through regulation of GLUT4 translocation in mice. The Journal of Physiology. 2016;594(17):4997-5008. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP272039. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).