1. Introduction
The white leg shrimp,
Litopenaeus vannamei, is a popular species worldwide in commercial farming. However, it is vulnerable to infectious threats such as bacterial and viral diseases [
1,
2,
3]. Crustaceans lack a true adaptive immune response. Thus, their defense mechanisms depend entirely on innate immune system that is activated upon recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) from various microorganisms [
4,
5]. The innate immune system plays an important role as the first line of defense, protecting hosts against infections caused by invading pathogens through mechanisms that can be activated rapidly upon recognition of a foreign threat [
6]. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are key molecules that can trigger humoral and cellular immune responses and then generate a series of removal processes of harmful molecules [
7]. They can also interact with matching PAMPs including nucleic acids, proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, and lipoproteins to induce intracellular signaling pathways through pathogen recognition [
8].
Leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) are a pivotal structure in conformational complementarity in several classes of PRRs based on protein-protein interactions. They consist of an LRR motif in the center, N-terminal (LRRNT), and C-terminal (LRRCT) to protect a hydrophobic inner core [
9,
10]. Horseshoe-shaped LRRs typically have 20-30 amino acids. They are unusually rich in hydrophobic amino acid leucine and highly conserved modules that form domains from two or more tandem LRRs to generate solenoidal curves suitable for protein-protein interactions [
9,
11,
12].
The LvLRRm is a newly reported PRR from
Litopenaeus vannamei. It is an immune related membrane protein that contains 12 LRR motifs with a hallmark sequence of 11 residues, LxxLxLxxNxL (x is any amino acid) [
7]. LvLRRm is a membrane-associated molecule involved in the antibacterial defense process by regulating antibacterial innate immune signaling pathways [
7].
Similar to other membrane proteins, LvLRRm has difficulties in producing target proteins in soluble form which can be a barrier to further research such as protein overexpression and in vitro molecular experiments. These problems can sometimes be bypassed by removing nonessential domains because many proteins have multiple domains linked by flexible loops. In addition, biological function of a protein is often dependent on domains much smaller than the full-length protein [
13,
14,
15]. Like LRR repeat protein, α-solenoid proteins have been widely investigated. Examples include ankyrin repeat proteins, HEAT repeat proteins, armadillo repeat proteins (ArmRP), and tetratricopeptide repeat proteins (TPR) [
16]. They are attractive targets for protein engineering and design for protein’s stability, specific recognition of other proteins. In particular, the ‘Hybrid LRR technique’ can be applied to LRR proteins to increase the expression and stability of origin protein. This technique can be used to fuse truncated fragments of LvLRRm with LRRCT modules from other LRRs with Variable lymphocyte receptor B (VLRB) as a hybrid partner [
17,
18]. This fusion strategy has been successfully used to design eight hybrid proteins, three of which are soluble.
Though the LvLRRm, TLR-like proteins in crustacean species are predicted to play an important role in defense against pathogens. However, the biochemical basis of ligand binding and activation of LvLRRm protein remains unclear. Here, we hypothesized that LvLRRm-hybrid proteins would show biochemical functions similar to LvLRRm and tested their affinity with flagellin, a protein that composes the bacterial flagella.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification
Suspension Sf9 cells, a clonal isolate of Spodoptera frugiperda Sf21 cells (IPLB-Sf21-AE), were cultured in a 28 °C shaking incubator in Sf900™ II SFM (Gibco) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic solution (GenDepot). Suspension High Five cells, an insect cell line that originated from ovarian cells of the cabbage looper (Trichoplusia ni), were cultured in a 28 °C shaking incubator in Express Five™ SFM (Gibco) supplemented with 9% L-Glutamine (FBS, Gibco) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic solution (GenDepot).
Hybrid proteins were cloned into BamHI and NotI sites of pAcGP67 vector (BD Biosciences) by overlap PCR using primers listed in
Table 1. The Fc domain of human IgG1 and thrombin cleavage site was designed between NotI and the BglII sites of pAcGP67. Resulting Fc-tagged LvLRRm and LvLRRm-hybrid proteins were expressed in High Five insect cells and purified by protein A Sepharose (Amicogen) affinity chromatography. After cleavage by thrombin to remove the Fc tag, hybrid proteins were further purified by Superdex
® 200 10/300 GL (GE Healthcare) size exclusion chromatography (GE AKTA Prime Plus FPLC System).
Salmonella typhimurium flagellin (stflagellin) inserted vector was received from the Institute of Membrane Proteins (IMP) in Pohang, South Korea. Then stflagellin residues F54-R451 were cloned into NcoI and XhoI sites of the pET28a vector and transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3). Cells were grown at 30 °C in Luria-Bertani (LB) and expressed in soluble fraction through optimal induction condition (Optical density (OD) 600 = 0.6 ~ 0.8) with 0.5 mM Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). The culture was allowed to grow for a period of 3 ~ 4 hour at 37 °C. Then stflagellin was purified by Ni-NTA (Bioworks) affinity chromatography. It was then further purified by ion exchange and size exclusion chromatography.
2.2. SPR (Surface Plasmon Resonance) Experiments by Single-Cycle Kinetics
Binding kinetics of LvLRRm and LvLRRm-hybrid proteins for stflagellin were determined with an iMSPR-Pro/A (icluebio, Korea) equipped with NTA-Au chip (NTA functionalized monolayer surface, icluebio, Korea). Experiments were performed using the single cycle kinetics (SCK) method. 1xHBST (HEPES 100 mM, NaCl 150 mM, Tween 20 0.005%, pH7.4) and 1xHBST containing 5 mM NiCl2 were used as reaction buffer and running buffer, respectively. The stflagellin was immobilized on the surface of a NTA-Au chip by amine coupling using 2 ug/ml 1xHBST at a flow rate of 10 ul/ml. LvLRRm and its hybrid proteins, the analyte, were applied at five different concentrations (0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 uM) for 180 s at a flow rate of 30 µl/min following the 1xHBST running buffer. Analytes bound to sensor chips were dissociated by washing with 1xHBST running buffer for 180 s. Association () and dissociation () constants were both measured over 180 s intervals. The equilibrium dissociation constant () was calculated as the ratio of off-rate to on-rate (/). Kinetic parameter sensorgrams were determined with global fitting function of Biacore Insight Evaluation Software using a 1:1-binding model.
3. Results
3.1. Design of LvLRRm-Hybrid Proteins, LhV Proteins
The open reading frame (ORF) sequence of LvLRRm encoded 576 amino acid residues (Accession number: MT180094). It contained a signal peptide (1M-95A), LRR domain (L96- C496), and transmembrane region (V511-L527). LvLRRm of LRR family proteins belongs to the ‘typical’ subfamily with 22 ~ 24 amino acids in the LRR module. It was therefore predicted to have a characteristic horseshoe-shaped structure within concave and convex: LRRNT (L96-A127), 11 LRR modules (L128-D151, L152-H175, L176-K199, L200-Q223, L224-N247, L248-D271, L272-T295, L296- S319, L321-K344, L345-R368, L369-M392) – linker (N393-E418) – 12th LRR module (L419-I442) and LRRCT (I452-C496). The parallel β sheet of concave region contains the consensus sequence of “LxxLxLxxN”, a region suitable for protein engineering.
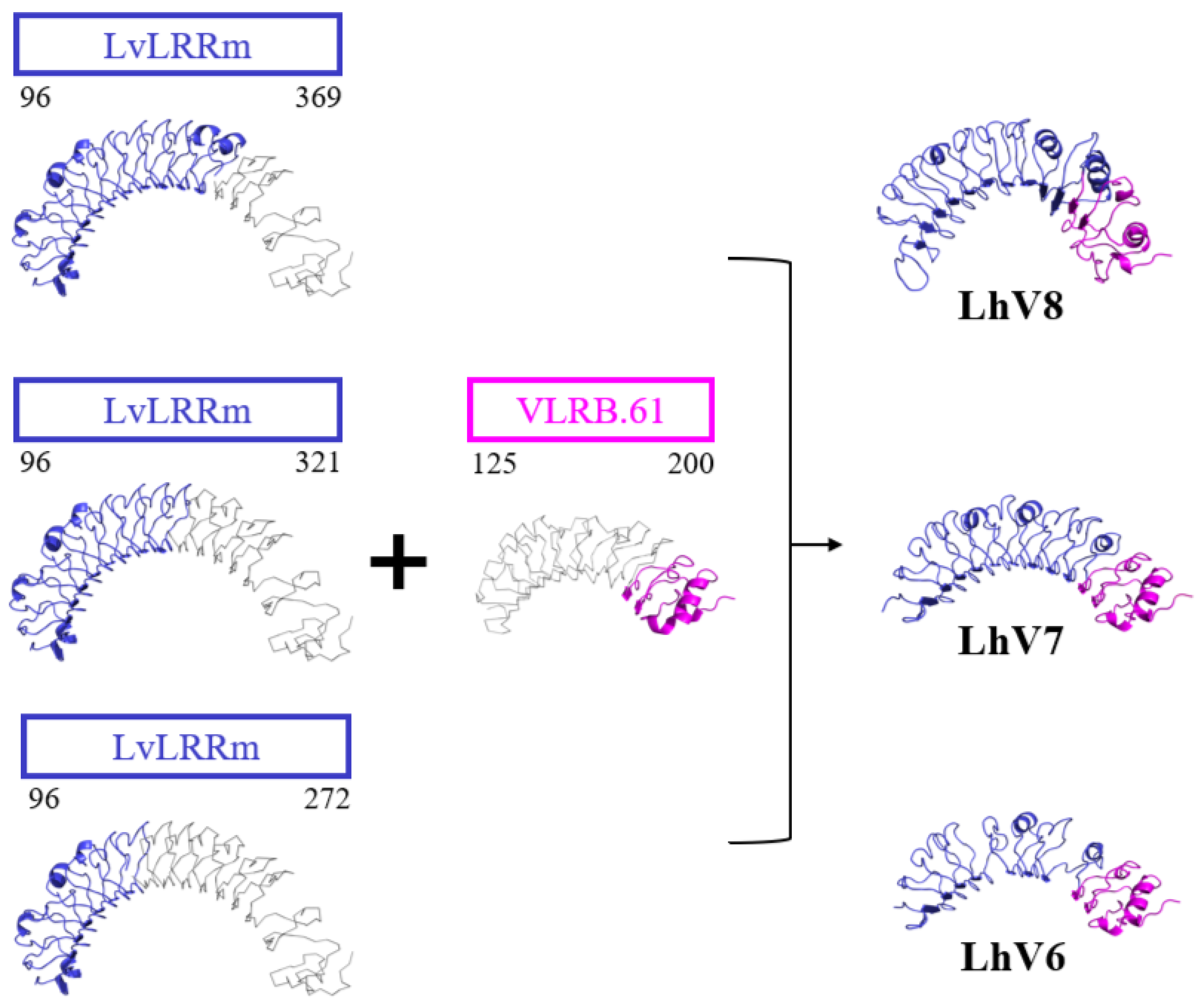
To increase stability of the protein, we applied known ‘Hybrid LRR Technique’ by removing the linker and replacing it with LRRCT from another protein. The technique generated a hybrid form of LvLRRm and a partner LRR family protein. Based on previous research, we choose a structurally compatible partner such as the Variable lymphocyte receptor B.61 (VLRB), which could mediate adaptive immune responses in jawless fish [
19,
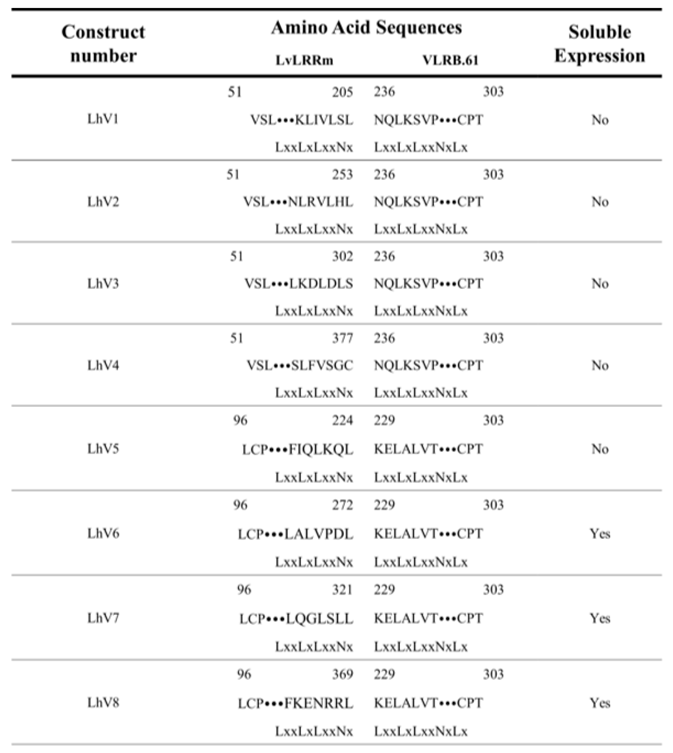
20]. We designed the hybrid form of LvLRRm-VLRB and named these proteins as ‘LhV no.’ (LvLRRm-hybrid-VLRB, no. follows designed order) (
Table 2). Sheet and loop-based hybrids were designated as LhV1-4 and LhV5-8, respectively (
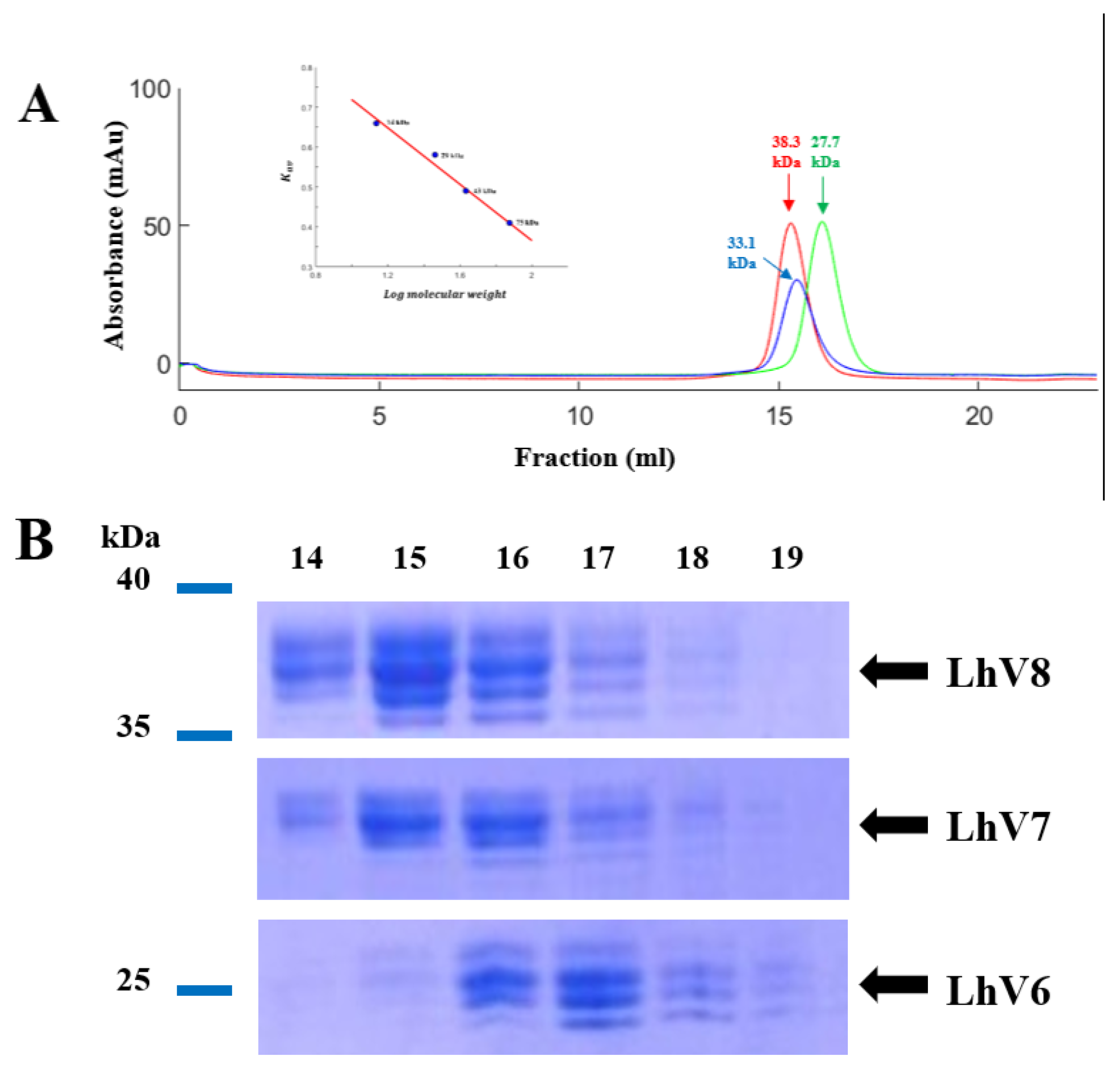
Figure 1). We fused truncated fragments of LvLRRm with the LRRCT module from other LRRs in VLRB and yielded three soluble proteins of eight designed hybrid proteins. On size exclusion chromatography, LhV6-8 eluted as suitable fractions and showed band intensities in SDS-PAGE analysis (
Figure 2AB).
3.2. Binding Kinetics Validation of LvLRRm and LhV6-8 to Stflagellin
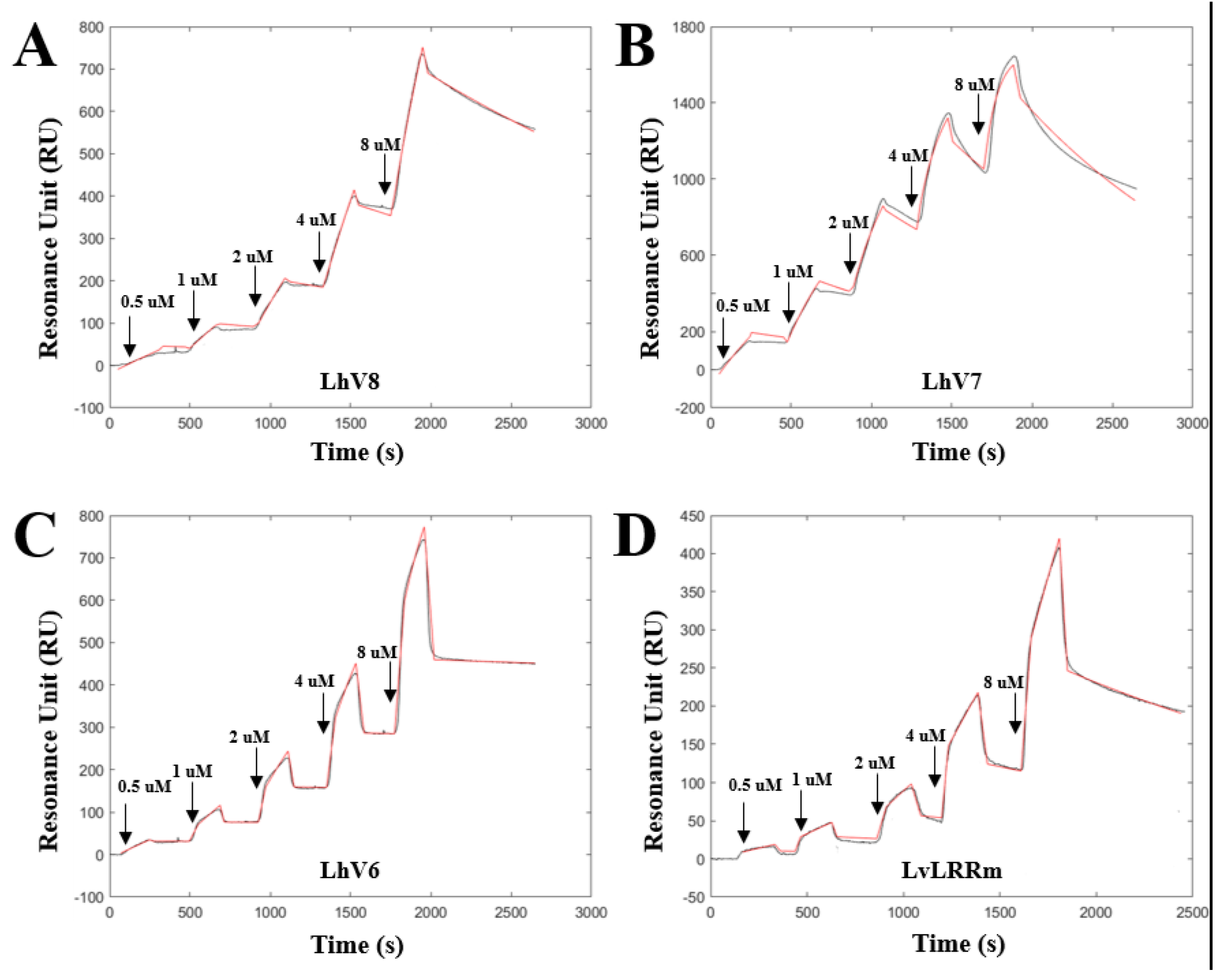
We confirmed the binding of LhV6-8 to stflagellin by SPR analysis using recombinant stflagellin immobilized NTA-Au chips. Analytes were then sequentially injected onto the target ligand in increasing concentrations (0.5 uM, 1 uM, 2 uM, 4 uM, and 8 uM) and dissociated in each trial. As expected, all hybrid proteins showed appropriate binding affinity between stflagellin and LhVs, indicating the potential for interaction as binding partner.
LhV8-stflagellin (
kon = 1.969 × 10
2 M
−1 s
−1;
koff = 3.37 × 10
−4 s
−1;
KD = 1.69 × 10
−6 M) and LhV7-stflagellin (
kon = 1.48 × 10
3 M
−1 s
−1;
koff = 6.63 × 10
−4 s
−1;
KD = 4.47 × 10
−7 M) exhibited affinity high enough affinity to recognize their partners between them, respectively (
Figure 3A,B). LhV6-
stflagellin (
kon = 4.76 × 10
2 M
−1 s
−1;
koff = 2.87 × 10
−5 s
−1;
KD = 5.99 × 10
−8 M) showed a slightly lower dissociation rate with a robust binding affinity (
Figure 3C). We also determined the binding kinetics between LvLRRm and
stflagellin, although we used a small purified amount due to unstable LvLRRm protein. SPR sensorgram revealed that LvLRRm could bind to
stflagellin with nanomolar affinity (
kon = 2.66 × 10 M
−1 s
−1;
koff = 4.36 × 10
−4 s
−1;
KD = 1.63 × 10
−5 M) (
Figure 3D).
4. Discussion
The adaptive immune system evolved about 500 million years ago and it is found mostly in vertebrates [
20,
21]. Furthermore, it is widely accepted that the innate immune response of invertebrates is sensitive and potent. However, some components and mechanisms are not pathogen specific [
22]. Knockout of the
LvLRRm gene has been shown to result in less expression of LvLRRm protein in the cell membrane, leading to decrease survival for pathogen exposure and contributing significantly to innate immune response [
7].
For most proteins, it is not easy to perform various experiments because of their partially exposed hydrophobic surfaces, non-functional loops, and lack of stability [
23,
24]. In particular, LvLRRm was not stable for soluble expression due to the linker of unknown function. To advance our research on LvLRRm, we needed a technique to induce overexpression of LvLRRm’s proteins while preserving the site responsible for recognizing external antigens in them.
We obtained LhV proteins based on VLRs using LRR-module engineering. Three of eight characterized LvLRRm-hybrid proteins were experimentally stable, folded, and successfully expressed at high levels of LhV 6-8 in an insect baculovirus expression system. Expressed LhV6-8 contains bindable loop arrangements and shape complementarity to patches of
stflagellin in predicted structures performed by I-TASSER tool (
https://zhanggroup.org/I-TASSER/) (
Figure 4). Results showed that these developed hybrid proteins could be widely used to generate target-specific molecular binders for applications in biotechnology and crustacean immunology by a rational design.
Previous studies have shown that a family of type I transmembrane glycoproteins containing LRRs in their extracellular domains can recognize conserved patterns of pathogen-derived molecules rather than the specificity of them [
25,
26,
27]. PAMPs, well-known lipopolysaccharide (LPS), peptidoglycan (PGN), glucan (GLU), and polycytidine-polycitric acid (poly IC) are known to be involved in innate immune responses by mediating protein-ligand interactions [
28]. Although PRRs can recognize a variety of molecules as ligands, flagellin was chosen in this study because its recombinant proteins could be easily engineered and produced to be suitable for SPR experiments.
Flagellin, a bacterial protein that forms flagellar filament crucial for bacterial motility, serves as a pathogen invasion signal when bacteria invade the host. It can trigger an innate immune response through recognition by Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5) [
29,
30,
31]. TLR5 is activated by a highly conserved sequence in flagellin that is essential for function. It is sequestered in the protofilament of assembled flagella [
32]. The interaction between flagellin and TLR5 appears to be direct. The binding site has been mapped to a single LRR in the receptor ectodomain [
33]. In TLR5, two surfaces (loop1-4 and loop 7-9) could form the binding between hot spot residues (R89, L93 and E114) in D0-D1 domains of
Bacillus subtilis flagellin through van der Waals interactions and a hydrogen bond [
34]. Based on the SPR analysis results and the similar arrangement of LRR loop patterns, it cannot be ruled out that LvLRRm may recognize flagellin as a PRR like TLR5. Furthermore, judging from the remaining central domain LRR loops of the LhVs without truncation, there is a possibility that the hotspot for flagellin binding may be located in that region.
Among processes used in our experiments, the single cycle kinetics (SCK) method has limitations when it comes to observing molecule-molecule interactions. SCK method involves a series of successive analyte injections at progressively higher concentrations onto the ligand surface with no regeneration occurring at each concentration point [
35]. Without regeneration, there is a possibility that while analytes continue to adhere to ligands during the association, the titer of ligand may decrease compared to the previous association step. For this reason, the ligand surface may not be stable in each cycle. In another case of a problematic issue, the analyte may form such a tight complex with the ligand surface that no regeneration condition will disrupt the interaction without denaturing the ligand. This is commonly observed for high-affinity small-molecule/protein interactions [
36]. To clarify these issues, structural studies of both LvLRRm and LvLRRm-hybrid proteins regarding potential candidates for binding are necessary.
5. Conclusion
This is the first report of hybrid proteins of LvLRRm and their kinetics validation to bacterial flagellin. LhV6-8 were well-folded. They were stable in an aqueous solution. Furthermore, in the predicted structural model by I-TASER tools, VLRB successfully replaced the extended linker region between loops 11 and 12 of the original one, maintaining its compact loop arrangement. Given the affinity of LvLRRm protein to flagellin observed in SPR analysis, we cannot rule out the possibility of interaction between them. Nonetheless, given limitations of the traditional SCK method and the lack of clear data supporting a 1:1 interaction of them, further investigation is still warranted. Hybrid LRR technology can be useful for structural studies, characterization of LvLRRm, and expression of recombinant proteins containing LRR modules.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Jie-Oh Lee in POSTECH for providing us the Salmonella typhimurium flagellin gene. This study was supported by a project entitled "Exploring the evolution of the structure and immune proteins of crustaceans in hydrothermal vents" funded by the Korean Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries (No.20170411). This work was also supported by the Technology Innovation Program (20019707, Cryo-EM based vaccine discovery and optimization technology) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea) & KEIT. This work was also partially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (No. 2015R1C1A1A01054639).
References
- López-León, P.; Luna-González, A.; Escamilla-Montes, R.; del Carmen Flores-Miranda, M.; Fierro-Coronado, J.A.; Álvarez-Ruiz, P.; Diarte-Plata, G. Isolation and characterization of infectious Vibrio parahaemolyticus, the causative agent of AHPND, from the whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Latin American Journal of Aquatic Research 2016, 44, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Ortega, C.O.; Martínez-Díaz, S.F. Phage therapy against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in the whiteleg shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) larvae. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Fan, L.; Yan, M. White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection impacts intestinal microbiota composition and function in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish & shellfish immunology 2019, 84, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, L.; Alpuche, J.; Maldonado, G.; Agundis, C.; Pereyra-Morales, A.; Zenteno, E. Review: Immunity mechanisms in crustaceans. Innate Immun 2009, 15, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Soderhall, I. Crustacean hematopoiesis and the astakine cytokines. Blood 2011, 117, 6417–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Kong, T.; Zhang, M.; Li, S. Pattern recognition receptors and their roles on the innate immune system of mud crab (Scylla paramamosain). Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2020, 102, 103469. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Xiang, J.; Li, F. Identification and functional study of an LRR domain containing membrane protein in Litopenaeus vannamei. Dev Comp Immunol 2020, 109, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, Y.J.; Zhang, Z. The involvement of crustaceans toll-like receptors in pathogen recognition. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2020, 102, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Huxley-Jones, J.; Boot-Handford, R.P.; Bishop, P.N.; Attwood, T.K.; Bella, J. LRRCE: a leucine-rich repeat cysteine capping motif unique to the chordate lineage. BMC genomics 2008, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Wildes, C.P.; Silvian, L.; Walus, L.; Mi, S.; Lee, D.H.; Meier, W.; Pepinsky, R.B. Disulfide structure of the leucine-rich repeat C-terminal cap and C-terminal stalk region of Nogo-66 receptor. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 16491–16501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajava, A.V.; Kobe, B. Assessment of the ability to model proteins with leucine-rich repeats in light of the latest structural information. Protein Sci 2002, 11, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Gao, J.; Xu, Y.H.; Xu, J.D.; Fan, Z.X.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. Novel Pattern Recognition Receptor Protects Shrimp by Preventing Bacterial Colonization and Promoting Phagocytosis. J Immunol 2017, 198, 3045–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Park, B.S.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.; Oh, S.C.; Enkhbayar, P.; Matsushima, N.; Lee, H.; Yoo, O.J.; et al. Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist eritoran. Cell 2007, 130, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.S.; Song, D.H.; Kim, H.M.; Choi, B.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.O. The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature 2009, 458, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.S.; Kim, S.E.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, M.E.; Kim, H.M.; Paik, S.G.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.O. Crystal structure of the TLR1-TLR2 heterodimer induced by binding of a tri-acylated lipopeptide. Cell 2007, 130, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speltz, E.B.; Brown, R.S.H.; Hajare, H.S.; Schlieker, C.; Regan, L. A designed repeat protein as an affinity capture reagent. Biochem Soc T 2015, 43, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Oh, S.C.; Lim, K.J.; Kasamatsu, J.; Heo, J.Y.; Park, B.S.; Lee, H.; Yoo, O.J.; Kasahara, M.; Lee, J.O. Structural diversity of the hagfish variable lymphocyte receptors. J Biol Chem 2007, 282, 6726–6732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pancer, Z.; Saha, N.R.; Kasamatsu, J.; Suzuki, T.; Amemiya, C.T.; Kasahara, M.; Cooper, M.D. Variable lymphocyte receptors in hagfish. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 9224–9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Gartland, L.; Li, J.X.; Hirano, M.; Alder, M.; Herrin, B.; Sides, J.; Kasahara, M.; Cooper, M. Characterization of adaptive immune receptors in hagfish. Journal of Immunology 2011, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, T.; Hirano, M.; Holland, S.J.; Das, S.; Schorpp, M.; Cooper, M.D. Evolution of Alternative Adaptive Immune Systems in Vertebrates. Annu Rev Immunol 2018, 36, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usharauli, D. Chronic infection and the origin of adaptive immune system. Med Hypotheses 2010, 75, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauton, C. The scope of the crustacean immune system for disease control. J Invertebr Pathol 2012, 110, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, E.P.; Beis, K.; Cameron, A.D.; Iwata, S. Overcoming the challenges of membrane protein crystallography. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2008, 18, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Bartoccioni, P.; Palacin, M. Membrane Protein Stabilization Strategies for Structural and Functional Studies. Membranes (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurnberger, T.; Brunner, F.; Kemmerling, B.; Piater, L. Innate immunity in plants and animals: striking similarities and obvious differences. Immunol Rev 2004, 198, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscia, M.R.; Giacomelli, S.; Oreste, U. Toll-like receptors: an overview from invertebrates to vertebrates. Isj-Invert Surviv J 2011, 8, 210–226. [Google Scholar]
- Bella, J.; Hindle, K.L.; McEwan, P.A.; Lovell, S.C. The leucine-rich repeat structure. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008, 65, 2307–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Bao, Z.; Wang, M. Molecular characterization of an LRR-only protein gene in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei: Sequence feature, expression pattern, and protein activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2022, 129, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.I.; Kurnasov, O.; Natarajan, V.; Hong, M.; Gudkov, A.V.; Osterman, A.L.; Wilson, I.A. Structural basis of TLR5-flagellin recognition and signaling. Science 2012, 335, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, F.; Smith, K.D.; Ozinsky, A.; Hawn, T.R.; Yi, E.C.; Goodlett, D.R.; Eng, J.K.; Akira, S.; Underhill, D.M.; Aderem, A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 2001, 410, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacchieri, S.G.; Torquato, R.; Brentani, R.R. Structural study of binding of flagellin by Toll-like receptor 5. J Bacteriol 2003, 185, 4243–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, S.G.; Gay, N.J. Structural and functional diversity in the leucine-rich repeat family of proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 1996, 65, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizel, S.B.; West, A.P.; Hantgan, R.R. Identification of a sequence in human toll-like receptor 5 required for the binding of Gram-negative flagellin. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2003, 278, 23624–23629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.S.; Jeon, Y.J.; Namgung, B.; Hong, M.; Yoon, S.I. A conserved TLR5 binding and activation hot spot on flagellin. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 40878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Bi, C.; Li, Z.; Podariu, M.; Hage, D.S. Analytical methods for kinetic studies of biological interactions: A review. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2015, 113, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, R.; Katsamba, P.S.; Nordin, H.; Pol, E.; Myszka, D.G. Analyzing a kinetic titration series using affinity biosensors. Anal Biochem 2006, 349, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).