Submitted:
07 October 2023
Posted:
10 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Wood Material
- Impregnation Material (Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)2))
2.2. Methods
- Impregnation methods (Immersion Method and Vacuum Method)
- Preparation of samples
- Testings of surface and burning properties
- Surface Roughness Test
- Water Contact Angle Test
- FTIR Analysis
- TGA
- TGA Analysis
- LOI
- LOI Analysis
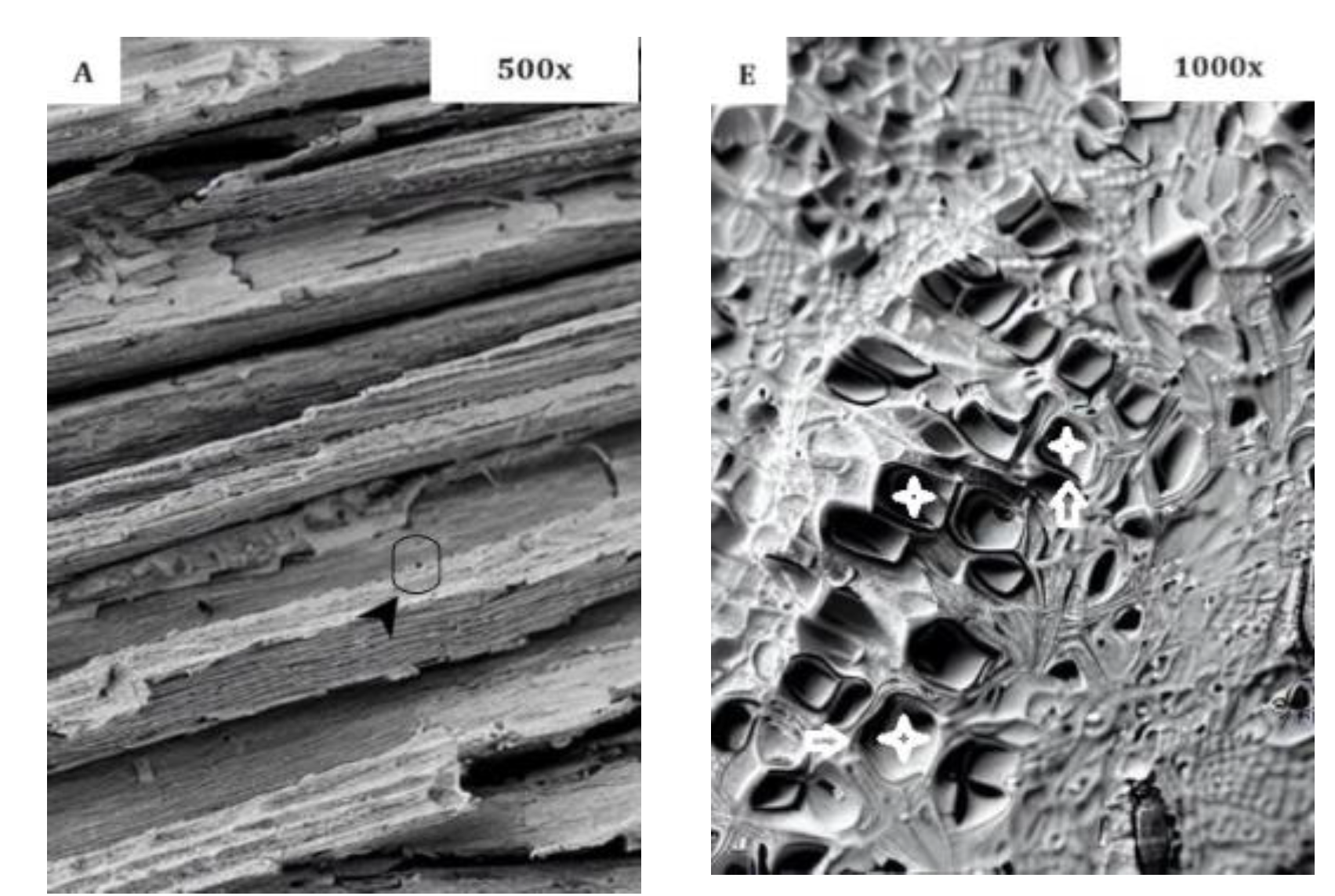
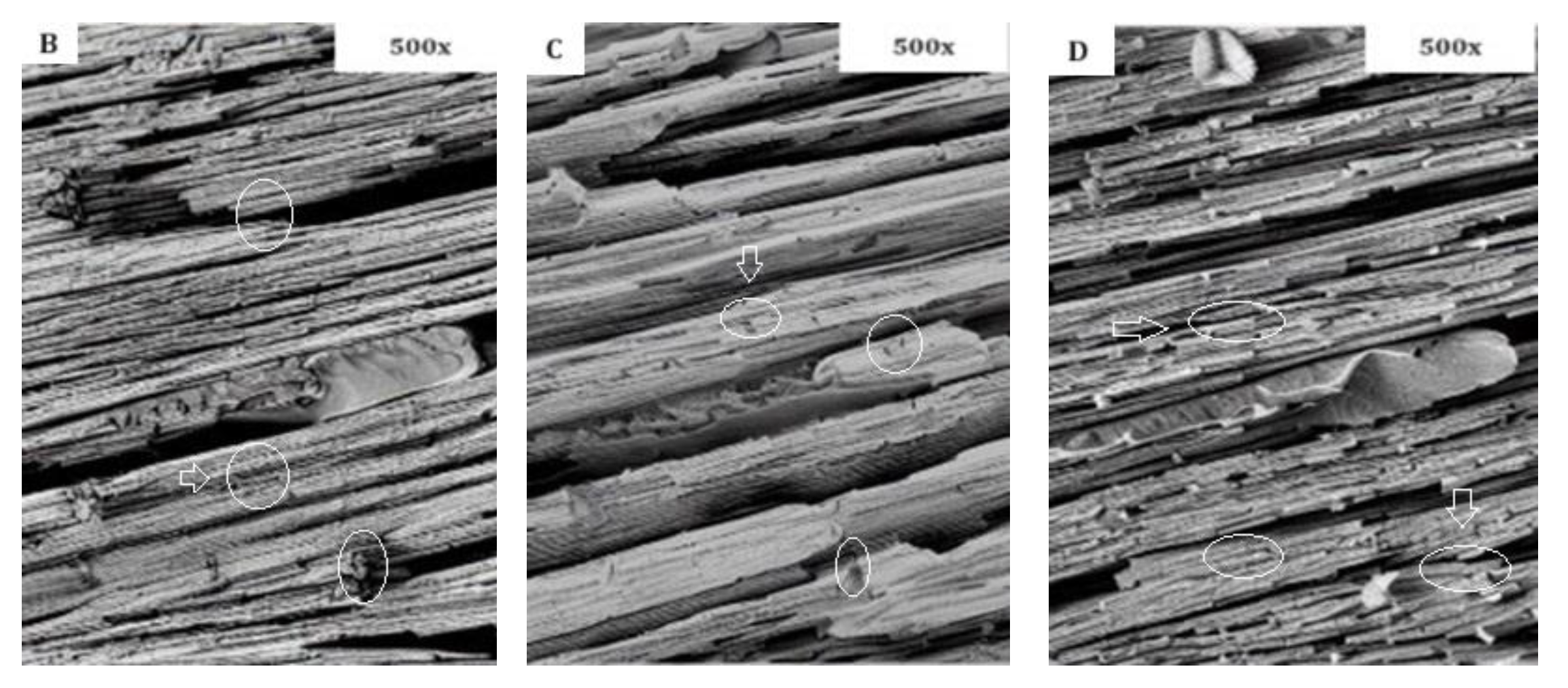
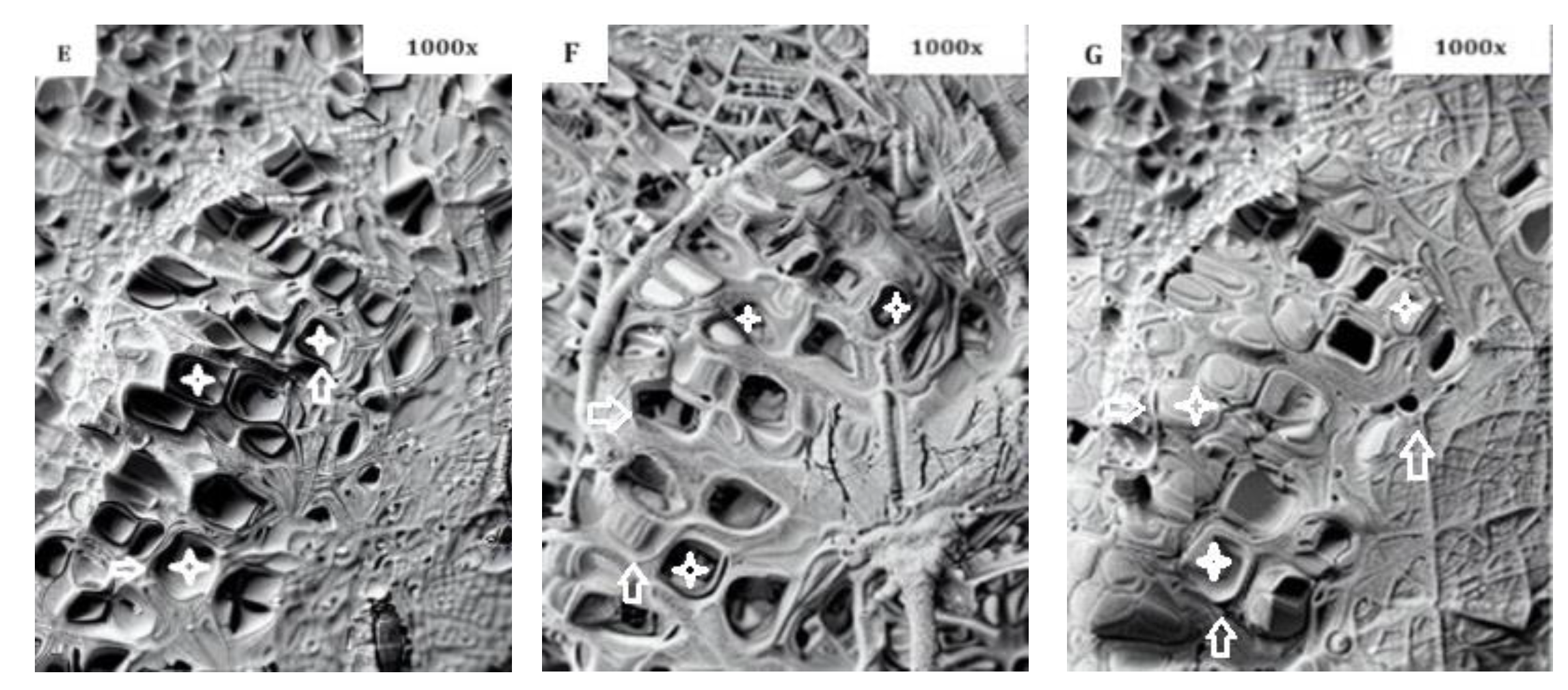
- SEM Analysis
- Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusion
References
- Asif, M. Sustainability of timber, wood and bamboo in construction. In Sustainability of Construction Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Shaxton, UK, 2009; pp. 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosillo-Calle, F.; Woods, J. The Biomass Assessment Handbook; Taylor & Francis Ltd: London, United Kingdom, 2012; ISBN 9781136554902. [Google Scholar]
- Aristri, M.A.; Lubis, M.A.R.; Yadav, S.M.; Antov, P.; Papadopoulos, A.N.; Pizzi, A.; Fatriasari, W.; Ismayati, M.; Iswanto, A.H. Recent Developments in Lignin- and Tannin-Based Non-Isocyanate Polyurethane Resins for Wood Adhesives—A Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimak, K.M.; Slimak, R.A. Enhancing the strength, moisture resistance, and fire-resistance of wood, timber, lumber, similar plant-derived construction and building materials, and other cellulosic materials. 2020, U.S. Patent No. 6,146, 766.
- Östman, B.; Voss, A.; Hughes, A.; Hovde, P.J.; Grexa, O. Durability of fire retardant treated wood products at humid and exterior conditions review of literature. Fire Mater. 2001, 25, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, A.M.; Giudice, C.A. Flame-retardant impregnants for woods based on alkaline silicates. Fire Saf. J. 2009, 44, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.-Y.; Kang, C.-W.; Park, H.-J. Impregnation and mechanical properties of three softwoods treated with a new fire retardant chemical. J. Wood Sci. 2014, 60, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Medina, L.; Li, Y.; Carosio, F.; Hajian, A.; Berglund, L.A. Nanostructured Wood Hybrids for Fire-Retardancy Prepared by Clay Impregnation into the Cell Wall. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 36154–36163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madyaratri, E.W.; Ridho, M.R.; Aristri, M.A.; Lubis, M.A.R.; Iswanto, A.H.; Nawawi, D.S.; Antov, P.; Kristak, L.; Majlingová, A.; Fatriasari, W. Recent Advances in the Development of Fire-Resistant Biocomposites—A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-L.; Ma, Z.-Y.; Yao, H.-X.; Qin, B.; Gao, Y.-C.; Xia, Z.-J.; Huang, Z.-H.; Yin, Y.-C.; Tu, H.; Ye, H.; et al. Economical Architected Foamy Aerogel Coating for Energy Conservation and Flame Resistance. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, M. Poplar Research Institute from its Establishment to the Present 1962-2014. T.R. Ministry of Forestry and Water Affairs, General Directorate of Forestry, Poplar and Fast-Growing Forest Trees Research Institute. Directorate Publication No: 270, Various Publications Series No: 25, Izmit, Türkiye, 2014.
- Marchi, M.; Bergante, S.; Ray, D.; Barbetti, R.; Facciotto, G.; Pier, M.C.; Hynynen, J.; Nervo, G. Universal reaction norms for the sustainable cultivation of hybrid poplar clones under climate change in Italy. iForest - Biogeosciences For. 2022, 15, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmaca, C. Performance of Various Poplar Clones in the Early Years. Master's thesis, Düzce University, Institute of Science and Technology, Düzce, Türkiye, 2018.
- Birler, A.S. Poplar cultivation in Türkiye: Nursery-afforestation-protection-revenue-economy-wood characteristics. Poplar and Fast-Growing Forest Trees Research Directorate of the Ministry of Environment and Forestry, Ankara, Türkiye, 2010.
- Bozkurt, Y., Erdin, N. Wood anatomy. İstanbul University, Publishing of Faculty of Forestry, Istanbul, Türkiye, 2000.
- Gaudet, M.; Jorge, V.; Paolucci, I.; Beritognolo, I.; Mugnozza, G.S.; Sabatti, M. Genetic linkage maps of Populus nigra L. including AFLPs, SSRs, SNPs, and sex trait. Tree Genet. Genomes 2007, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, B.; Yapıcı, F.; Kol, H. Ş.; Özcan, C.; Esen, R.; Korkmaz, M. Determination of thermal conductivity finished on impregnated wood material. In Proceedings of 6th International Advanced Technologies Symposium (IATS’11), Elazığ, Türkiye, 2011.
- Keskin, H.; Kesi̇k, H.I.; Temel, F.; Öztürk, Y. Bonding Strength and Surface Roughness Properties of Wood Materials Impregnated with VacsolAqua. Kastamonu Univ. J. For. Fac. 2016, 16, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, A.; Aydin, İ. Effects of Treatment with Fire Retardant Chemicals on Technologic Properties of Wood and Wooden Materials. Duzce University Faculty of Forestry Journal of Forestry 2016, 12(1), 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Göker, Y.; Ayrılmış, N. Performance characteristicsand thermal degredation of wood and wood-based products in fire. Journal of the Faculty of Forestry Istanbul University 2002, 52(2/1-2), 1-22.
- He, X.; Li, X.J.; Zhong, Z.; Mou, Q.; Yan, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, L. Effectiveness of impregnation of ammonium polyphosphate fire retardant in poplar wood using microwave heating. Fire Mater. 2015, 40, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Guan, H.; Wang, X. In Situ Polymerization of Furfuryl Alcohol with Ammonium Dihydrogen Phosphate in Poplar Wood for Improved Dimensional Stability and Flame Retardancy. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chai, Y.; Ni, L.; Lyu, W. Flame Retardant Properties and Thermal Decomposition Kinetics of Wood Treated with Boric Acid Modified Silica Sol. Materials 2020, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuai, B.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Tong, J.; Zhan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Cai, L. Development of densified wood with high strength and excellent dimensional stability by impregnating delignified poplar by sodium silicate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Lu, D.; Yue, K.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Z. Fire Resistance Improvement of Fast-Growing Poplar Wood Based on Combined Modification Using Resin Impregnation and Compression. Polymers 2022, 14, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As, N., Akbulut, T. Odunun fiziksel özelliklerini iyileştiren işlemler ve mekanik özellikler üzerine olan etkisi. Journal of the Faculty of Forestry Istanbul University 1989, 39(3), 98-112.
- LeVan, S.L.; Winandy, E.J. Effect of fire retardant treatment on wood strenght: A Rewiev. Wood and Fiber Science 1990, 22(1), 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ayrılmış, N. Effects of various fire retardants on fire and technological properties of some wood based panel products. Doctoral Thesis. Istanbul University, Institute of Science. İstanbul, Türkiye, 2006.
- Demir, A. The effects of fire retardant chemicals on thermal conductivity of plywood produced from different wood species. Master Thesis, . Karadeniz Technical University, Institute of Science. Trabzon, Türkiye, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gökmen, K. The effect of heat treatment with tall oil impregnation on the properties of wood material. Master's thesis, Bartın University, Institute of Science and Technology, Bartın, Türkiye, 2017.
- Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Effect of vacuum impregnation on mechanical properties of fast-growing poplar. Journal of Northeast Forestry University 2019, 47(6), 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Cai, J.; Wu, M.; Zhou, N.; Huang, Z.; Cai, L.; Zhang, Y. Surface properties of poplar wood after heat treatment, resin impregnation, or both modifications. BioResources 2021, 16, 7561–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gao, M.; Wang, J.; Mu, H.; Qi, D. Fast Preparation of High-Performance Wood Materials Assisted by Ultrasonic and Vacuum Impregnation. Forests 2021, 12, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, P.; Zuo, Y.; Li, P.; Bi, X.; Li, X. Preparation of highly-densified modified poplar wood by evacuating the micro-pores of wood through a gas expansion method. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2023, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Rafique, I.; Anwar, Z.; Muhammad, B. Recent Developments in Different Types of Flame Retardants and Effect on Fire Retardancy of Epoxy Composite. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 1512–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, P.; Pepin, S. Trends in Chemical Wood Surface Improvements and Modifications: A Review of the Last Five Years. Coatings 2021, 11, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalerczyk, J.; Walkiewicz, J.; Dziurka, D.; Mirski, R. Nanomaterials to improve fire properties in wood and wood-based composite panels. In Emerging Nanomaterials: Opportunities and Challenges in Forestry Sectors. ed.; Taghiyari, H., Morrell, J.J., Eds.; Husen, A. Cham: Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Şirin, M.; Baltaş, H. Ecological structure: production of organic impregnation material from mussel shell and combustion. 2022, 32. [CrossRef]
- Zumdahl, S. S.; DeCoste, D. J. Chemical principles. 7th ed.; Cengage Learning: Belmont, USA, 2012.
- Haynes, W. M. CRC handbook of chemistry and physics., 95th ed.; CRC press: New York, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- TS 2470. Methods and general properties of sampling from wood for physical and mechanical experiments, TSE, Ankara, Türkiye, 1976.
- Kılıç, Ö.; Anıl, M. The effects of limestone characteristic properties and calcination temperature to the lime quality, Asian Journal of Chemistry 2006, 18(1), 655-666.
- Ropp, R.C. Encyclopedia of the Alkaline Earth Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Duchesne, J.; Reardon, E. Measurement and prediction of portlandite solubility in alkali solutions. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D 1413-99. Standard method of testing wood preservatives by laboratory soil block cultures. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, USA, 1995.
- ASTM-D 1413-07. Standard Test Method of Testing Wood Preservatives by Laboratory Soilblock Cultures. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, USA, 2007.
- TS EN 2472. Wood-determination of density for physical and mechanical tests. Turkish Standards Institution, Ankara, Türkiye, 1972.
- TS 4084. Wood - Determination of radial and tangential swelling. Turkish Standard Institution, Ankara, Türkiye, 1983.
- TS EN 317. Particleboards and fibreboards–Determination of swelling in thickness after immersion in water, TSE. Ankara, Türkiye, 1999.
- DIN 4768. Determination of values of surface roughness parameters, Ra, Rz, Rmax, using electrical contact (Stylus) instruments. Concepts and measuring conditions, 1990.
- ASTM D 2863. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Minimum Oxygen Concentration to Support Candle-Like Combustion of Plastics (Oxygen Index),” ASTM International, West Conshohocken, USA, 2006.
- Habibzade, S.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Omidvar, A.; Roudi, H.R. Effects of impregnation with styrene and nano-zinc oxide on fire-retarding, physical, and mechanical properties of poplar wood. Cerne 2016, 22, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, W. Forming textured hydrophobic surface coatings via mixed wax emulsion impregnation and drying of poplar wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 421–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holy, S.; Temiz, A.; Demirel, G.K.; Aslan, M.; Amini, M.H.M. Physical properties, thermal and fungal resistance of Scots pine wood treated with nano-clay and several metal-oxides nanoparticles. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogutlu, C.; Dongel, N. The effect of the impregnate process of wooden material to color changes and surface roughness. Journal of Polytechnic 2009, 12(3), 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Keski̇n, H.; Bülbül, R. Impacts of impregnation with Tanalith-E on surface roughness of solid wood materials. Furnit. Wooden Mater. Res. J. 2019, 2, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aykaç, S.; Sofuoğlu, S.D. A study on the comparison of surface roughness parameters in bamboo material applied with cellulosic, synthetic, polyurethane and water-based varnishes. 2020, 3, 84–92. [CrossRef]
- Kartal, S. Wettebality, water absorption and thickness swelling of particleboard made from remediated CCA-treated wood. Journal of the Faculty of Forestry Istanbul University 2001, 51(1), 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.R.; Calderon, J.U.; Lennox, B.R. Surface Energy of Modified Nanoclays and Its Effect on Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.J.; Fadhillah, F.; Saleem, H.; Hawari, A.; Benamor, A. Organically Modified Nanoclay Filled Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes for Reverse Osmosis Application. Materials 2019, 12, 3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emampour, M.; Khademieslam, H.; Faezipour, M.M.; Talaeipour, M. Effects of coating Populus nigra wood with nanoclay. BioResources 2020, 15, 8026–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhuthali, A.; Low, I.; Dong, C. Characterisation of the water absorption, mechanical and thermal properties of recycled cellulose fibre reinforced vinyl-ester eco-nanocomposites. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2012, 43, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.; Maji, T.K. Comparative study on the properties of wood polymer composites based on different modified soybean oils. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2016, 37, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A. I. Fire performance of thermally modified wood impregnated with clay nanomaterials. Feb-Fresenius Environmental Bulletin 2022, 31(5), 5292-5296.
- Bodirlau, R.; Teaca, C. A. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and thermal analysis of lignocellulose fillers treated with organic anhydrides. Romanian Journal of Physics 2009, 54(1-2), 93-104.
- Esteves, B.; Marques, A.V.; Domingos, I.; Pereira, H. Chemical changes of heat treated pine and eucalypt wood monitored by FTIR. Maderas-Cienc Tecnol 2013, 15, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, K. A structural scheme of soil allophane. American Mineralogist 1967, 52, 690–708. [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infra-red Spectra of Complex Molecules; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Romero, M.Q.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.-Y. Intumescent multilayer hybrid coating for flame retardant cotton fabrics based on layer-by-layer assembly and sol–gel process. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 10647–10655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beram, A.; Yaşar, S. NaOH ile Modifiye Edilmiş Kızılçam (Pinus brutia Ten. ) Yongalarının Levha Üretimindeki Performansı. 2018, 9, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faix, O.; Meier, D.; Fortmann, I. Thermal degradation products of wood. A collection of electron-impact (EI) mass spectra of monomeric lignin derived products. Holz als Roh- und Werkstoff. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 1990, 48, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotilainen, R.A.; Toivanen, T.-J.; Alén, R.J. FTIR Monitoring of Chemical Changes in Softwood During Heating. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2000, 20, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windeisen, E.; Strobel, C.; Wegener, G. Chemical changes during the production of thermo-treated beech wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moser, F.; Trautz, M.; Beger, A. L.; Löwer, M.; Jacobs, G.; Hillringhaus, F.; Wormit, A.; Usadel, B.; Reimer, J. Fungal mycelium as a building material,” in: Proceedings of the Annual Symposium of the International Associationfor Shell and Spatial Structures, IASS 2017, Hamburg, Germany, 2017.
- Xu, F.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, G. Novel High-Efficiency Casein-Based P–N-Containing Flame Retardants with Multiple Reactive Groups for Cotton Fabrics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13999–14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, Z.; Matsue, N.; Henmi, T. Nanometer-scale chemical modification of nano-ball allophane. Clays Clay Miner. 2007, 55, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Hu, J.; Fan, D. Effect of nitrogen phosphorus flame retardants on thermal degradation of wood. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2633–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowden, L.A.; Hull, T.R. Flammability behaviour of wood and a review of the methods for its reduction. Fire Sci. Rev. 2013, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.; Cao, J. Montmorillonite-catalyzed furfurylated wood for flame retardancy. Fire Saf. J. 2021, 121, 103297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Siddhanta, S.K.; Chakrabarti, A. Characterization of poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) modified polyaniline prepared in stable aqueous medium. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, F.; Sun, X.; Xiao, B.; Sun, R. Physico-chemical and thermal characterization of cellulose from barley straw. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 88, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, A.; Foresti, M.L.; Cerrutti, P.; Galvagno, M. Bacterial Cellulose from Simple and Low Cost Production Media by Gluconacetobacter xylinus. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 21, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakiewicz, P.; Drożdżek, M.; Laskowska, A.; Grześkiewicz, M.; Bytner, O.; Radomski, A.; Zawadzki, J. Effects of thermal modification on selected physical properties of sapwood and heartwood of black poplar (Populus nigra L.). BioResources 2019, 14, 8391–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaşar, S.; Güler, G. Chemical characterization of black poplar (Populus nigra L.) sawdust hemicelluloses esterified with acyl chlorides. Turk. J. For. 2021, 22, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydemir, D.; Civi, B.; Alsan, M.; Can, A.; Sivrikaya, H.; Gunduz, G.; Wang, A. Mechanical, morphological and thermal properties of nano-boron nitride treated wood materials. Maderas. Ciencia y Tecnología 2016, 18, 19-32. [CrossRef]
| CAS number | 1305-78-8 |
| PubChem CID | 14778 |
| UN number | 1910 |
| Molecule formula | CaO |
| Molecular mass | 56.0774 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to yellow/brown powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 3.34 gr/cm³ |
| melting point | 2613 °C |
| Boiling point | 3850 °C (100 hPa) |
| Solubility | (in water) reacts to form calcium hydroxide |
| Acidity (pKa) | 12.8 |
| Method | Sample Type | Concentration of Solution (%) | Impregnation Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | A | - | - |
| Immersion | B | 1 | 120 |
| C | 3 | 120 | |
| D | 5 | 120 | |
| Vacuum | E | 1 | 30+30 |
| F | 3 | 30+30 | |
| G | 5 | 30+30 |
| Sample Type | D0 (g/cm3) | WA-2 h | WA-24 h | TS-2 h | TS-24 h | WPG (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.36 (0.09)1 a2 | 38.21 (3.57) a | 72.89 (5.88) a | 14.86 (2.43) a | 17.26 (3.45) a | - |
| B | 0.41 (0.13) b | 33.83 (3.26) b | 67.86 (6.11) b | 13.23 (1.31) b | 15.08 (3.04) b | 0.62 (0.09) a |
| C | 0.44 (0.09) c | 29.42 (2.61) c | 63.22 (5.67) c | 11.38 (1.14) c | 13.77 (2.14) c | 0.73 (0.21) b |
| D | 0.45 (0.11) c | 26.55 (1.93) d | 59.49 (4.93) d | 10.75 (0.81) cd | 12.13 (1.86) cd | 0.91 (0.18) b |
| E | 0.42 (0.12) b | 31.26 (2.79) c | 63.92 (4.55) c | 11.49 (1.05) c | 14.86 (2.11) b | 1.12 (0.30) c |
| F | 0.46 (0.14) c | 24.12 (2.44) d | 58.32 (5.22) d | 9.08 (1.27) d | 12.22 (1.37) cd | 1.79 (0.35) d |
| G | 0.49 (0.09) d | 22.07 (1.66) e | 54.11 (4.83) e | 8.83 (0.95) d | 11.45 (1.96) d | 2.28 (0.51) e |
| Sample Type | Surface roughness (Ra) (║) | Changes (%) | Contact Angle | Changes (%) | LOI (%) | Changes (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 2.77 (0.31)1 a2 | - | 41 (4.66) a | - | 23.16 (2.55) b | - |
| B | 3.36 (0.99) b | 21.3 | 54 (4.34) b | 31.7 | 26.75 (3.07) b | 15.5 |
| C | 3.90 (0.83) c | 40.8 | 59 (5.27) c | 43.9 | 28.44 (2.43) b | 22.8 |
| D | 4.12 (0.46) d | 48.7 | 62 (4.02) d | 51.2 | 30.08 (1.94) b | 29.8 |
| E | 3.58 (0.60) c | 29.2 | 61 (3.95) c | 48.8 | 28.27 (1.64) b | 22.0 |
| F | 4.35 (0.97) d | 57.0 | 66 (6.26) e | 60.9 | 30.62 (2.44) b | 32.2 |
| G | 5.22 (0.44) e | 88.4 | 68 (6.31) e | 65.8 | 31.23 (2.74) b | 34.8 |
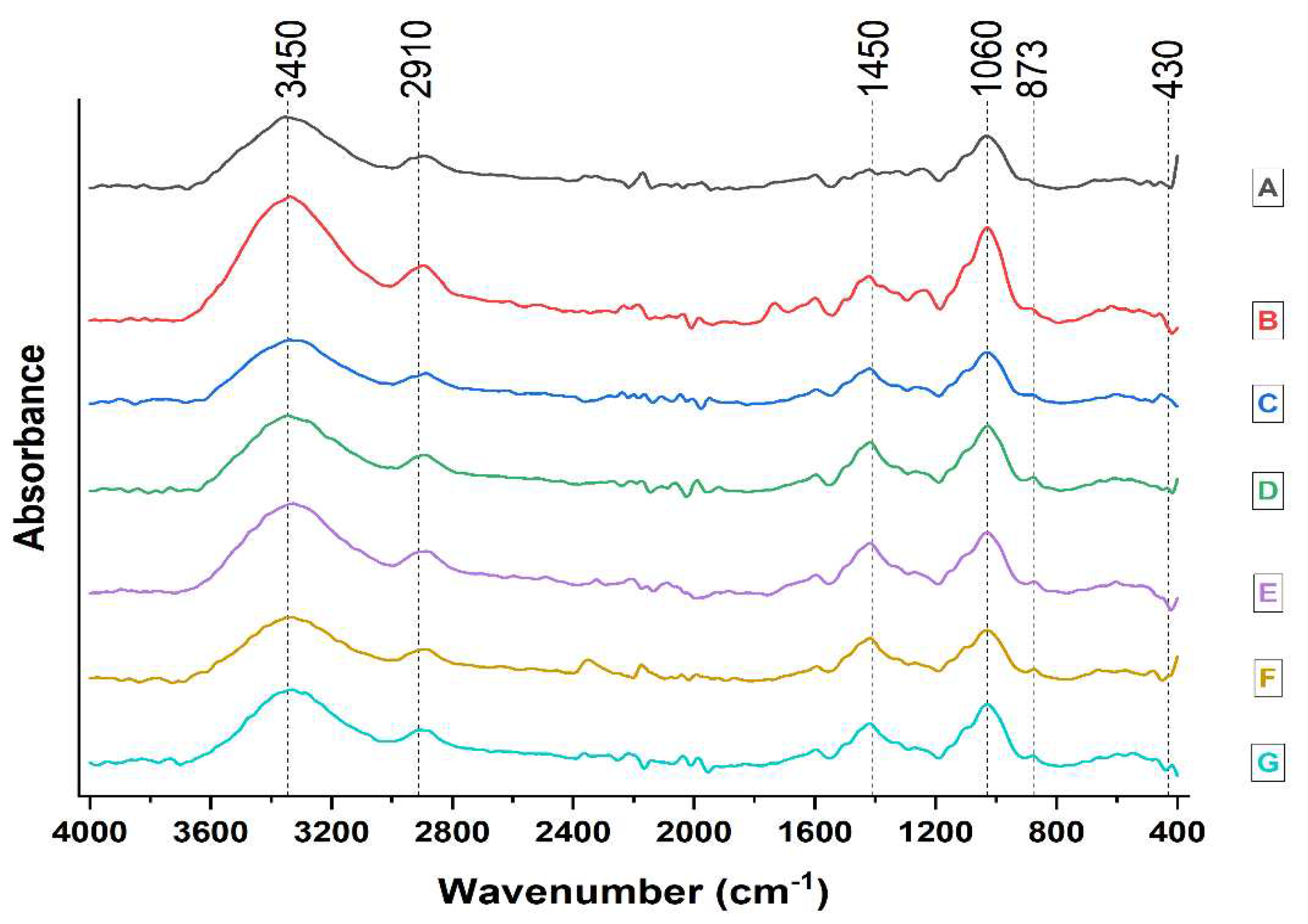
| Spectrum band position, cm-1 | Active wood mass group | Type of vibration |
|---|---|---|
| 3450 - 3400 | O-H of alcohols, phenols and acids | O-H stretching |
| 2970 - 2850 | CH2, CH- and CH3 | C-H stretching |
| 1462 - 1425 | CH2 cellulose, lignin | C-H deformations |
| 1060 - 1025 | C-O-C | Deformation |
| 876 | Anti-symmetric out-of-phase stretching in pyranose ring | Stretching in pyranose ring |
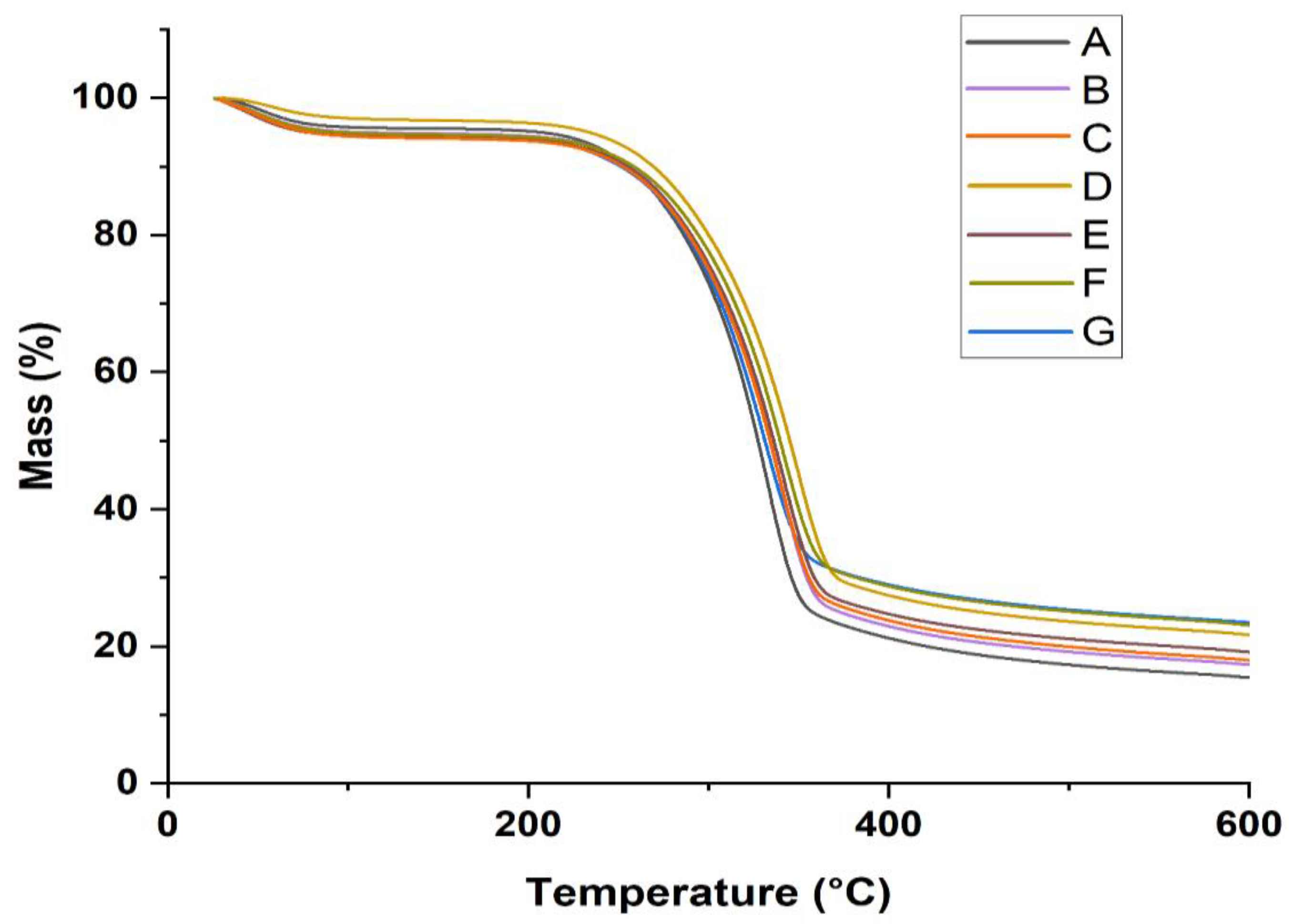
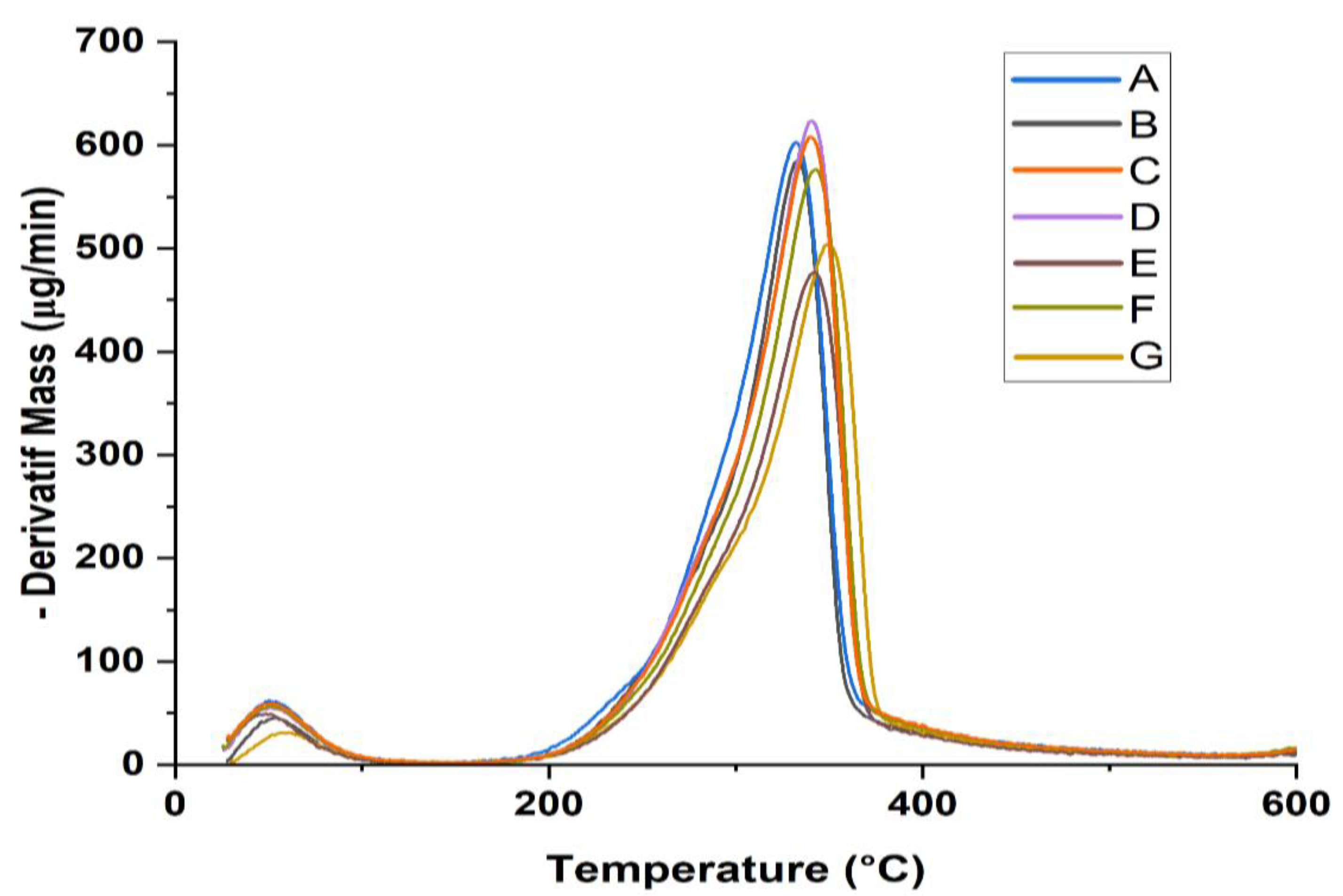
| Sample type | T0 (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Tf (°C) | RW at 600 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 140 | 329 | 476 | 16.2 |
| B | 140 | 332 | 494 | 18.3 |
| C | 140 | 337 | 503 | 18.5 |
| D | 140 | 338 | 531 | 22.3 |
| E | 140 | 339 | 532 | 19.8 |
| F | 140 | 342 | 576 | 24.4 |
| G | 140 | 347 | 584 | 24.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





