Submitted:
06 October 2023
Posted:
09 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wide-energy range gamma-ray imaging
2.2. Materials and Monte Carlo simulation
2.3. The principle prototype and data acquisition
3. Results
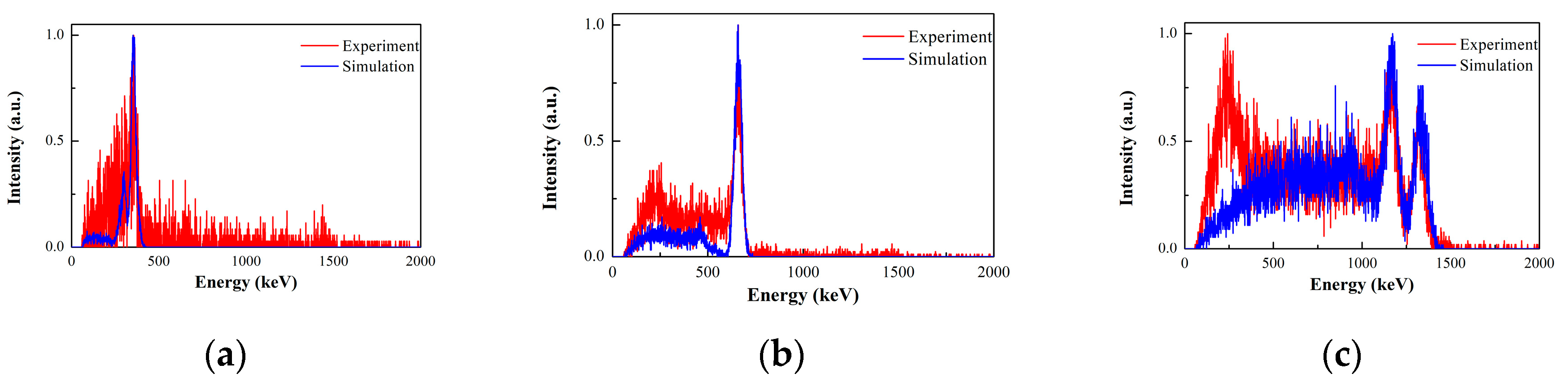
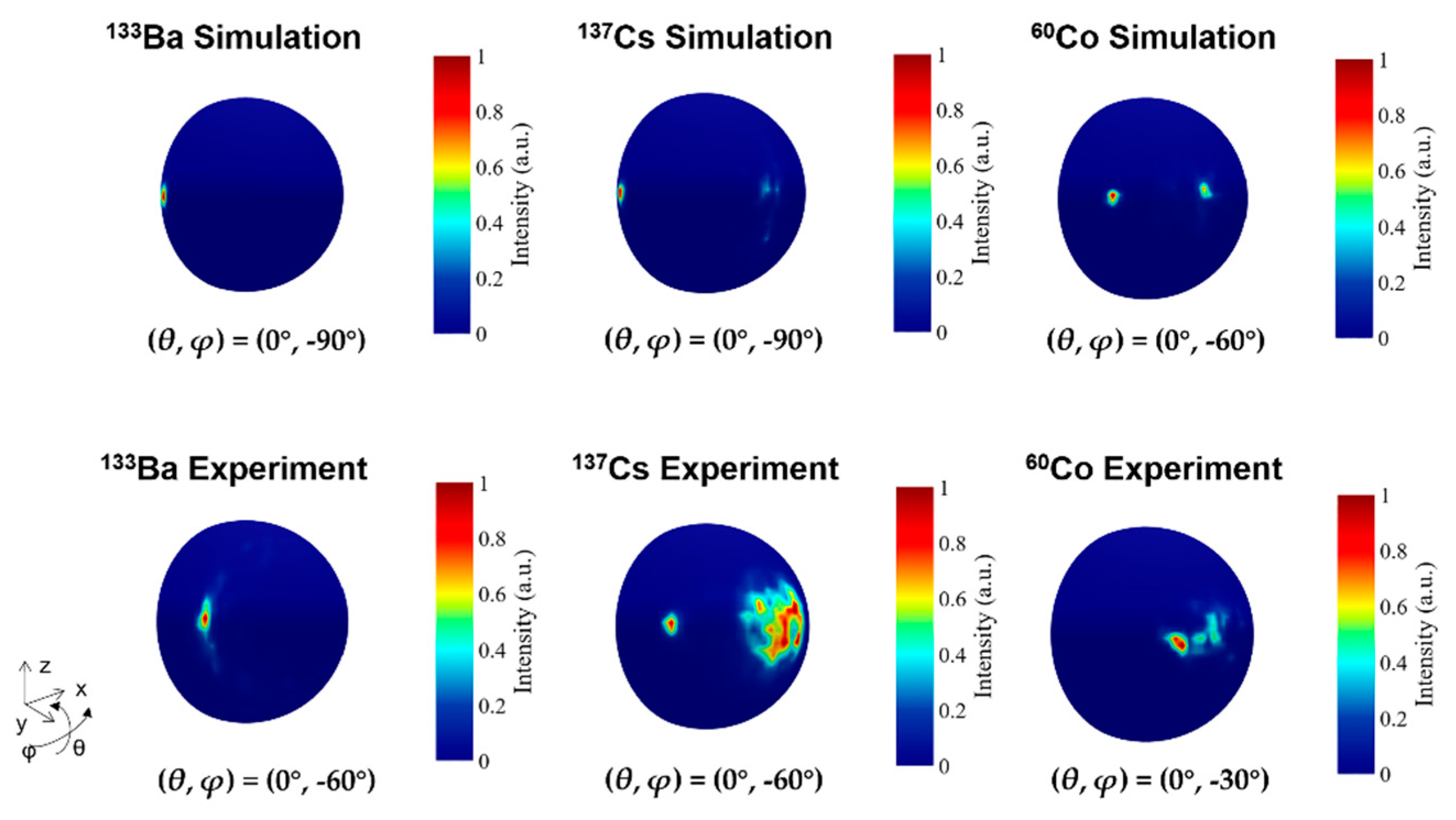
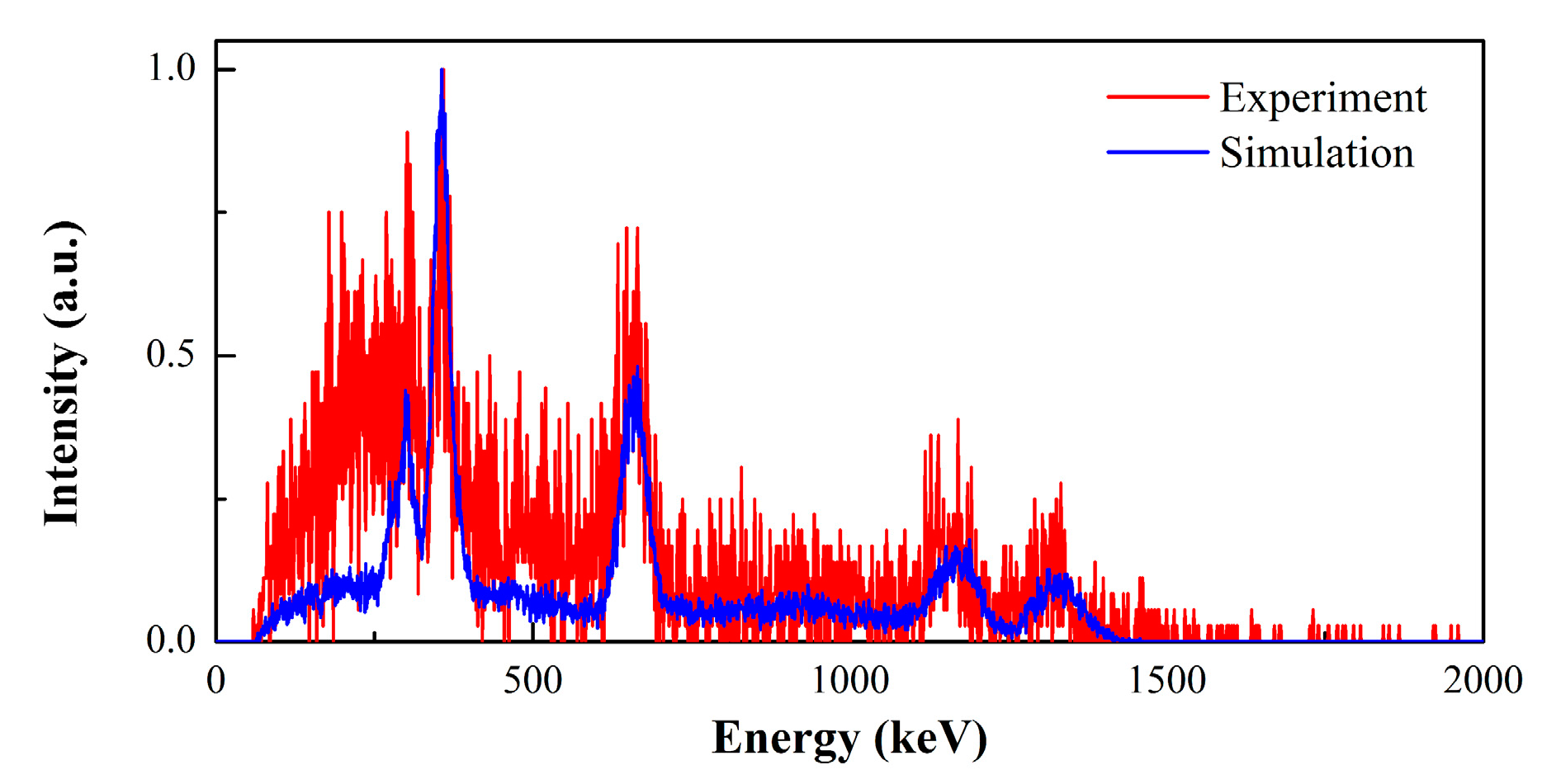
3.1. Single source imaging and performance evaluation
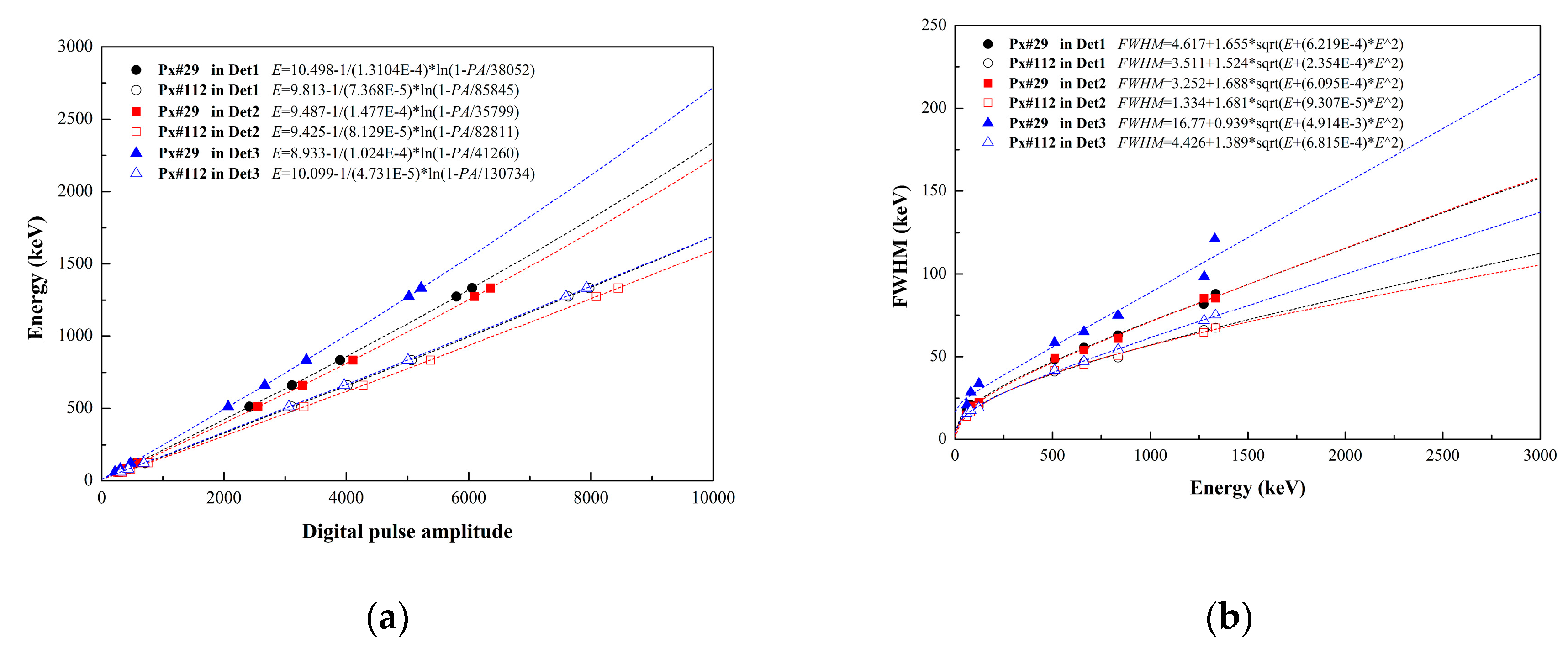
3.1.1. Detection efficiency and image resolution
3.1.2. Field of view
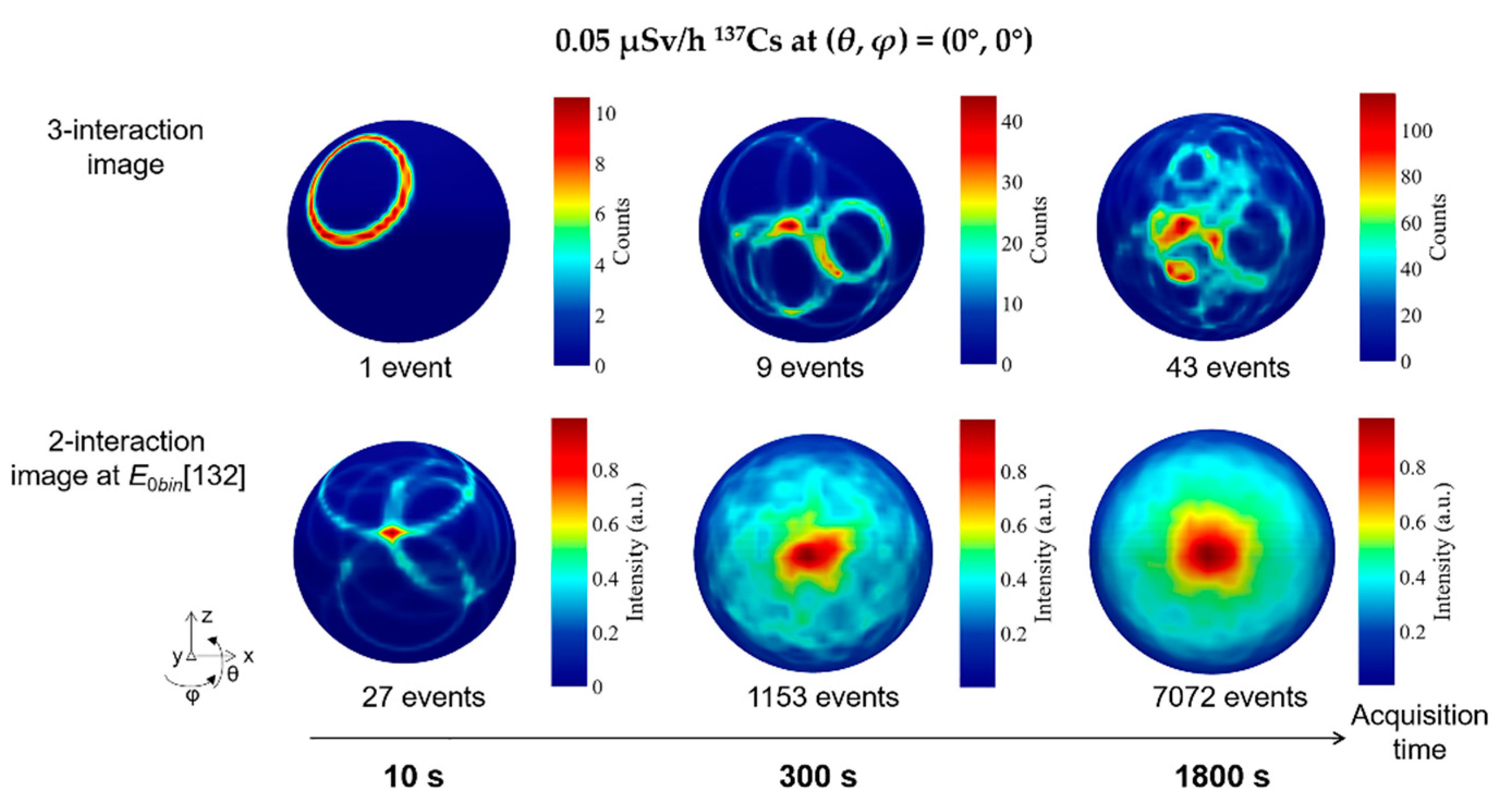
3.1.3. Imaging sensitivity
3.2. Multiple point-like source imaging
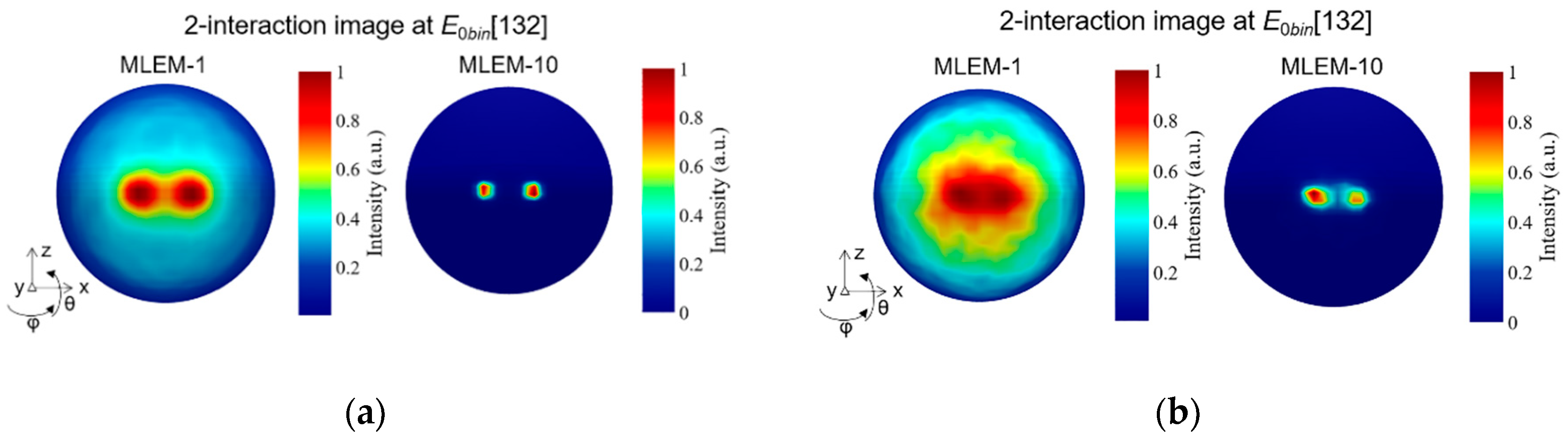
3.2.1. Angular resolution
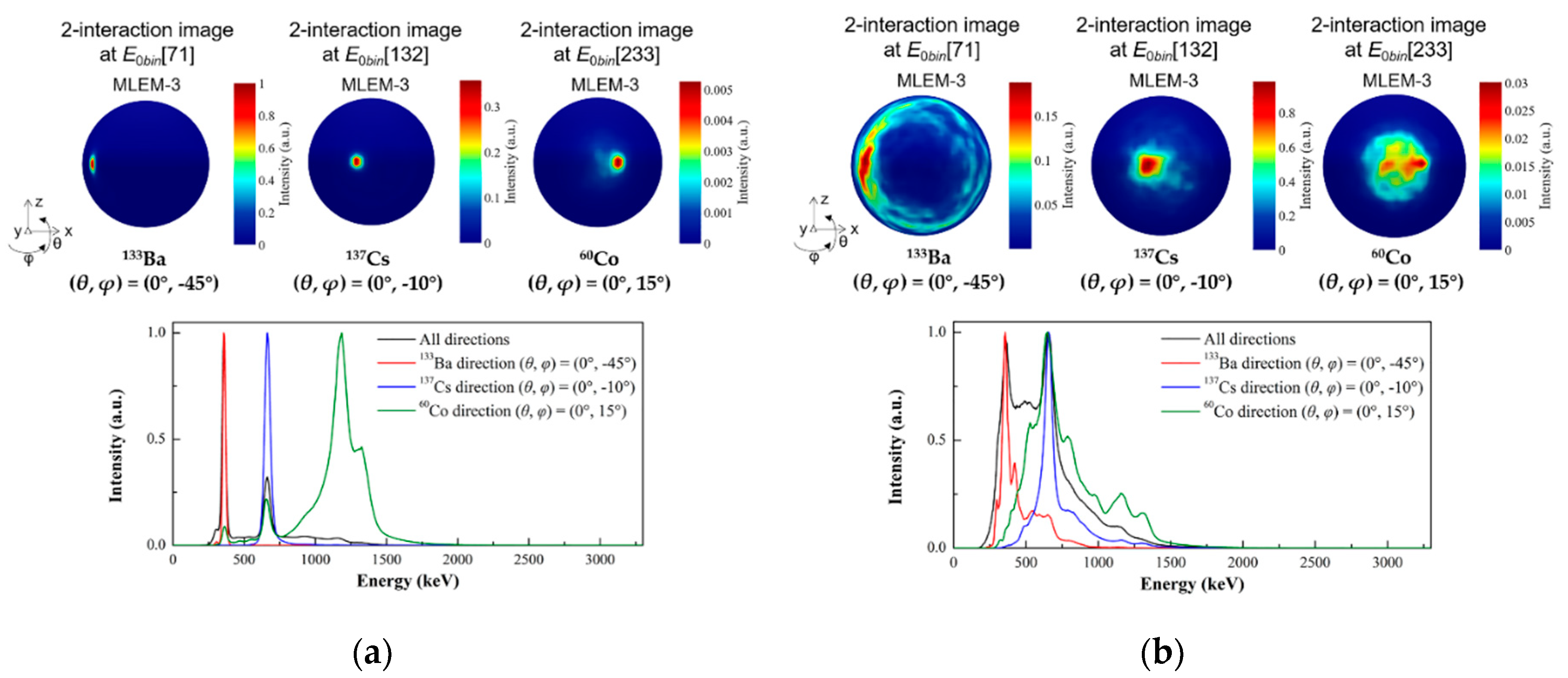
3.2.2. Simultaneous imaging of three point-like sources
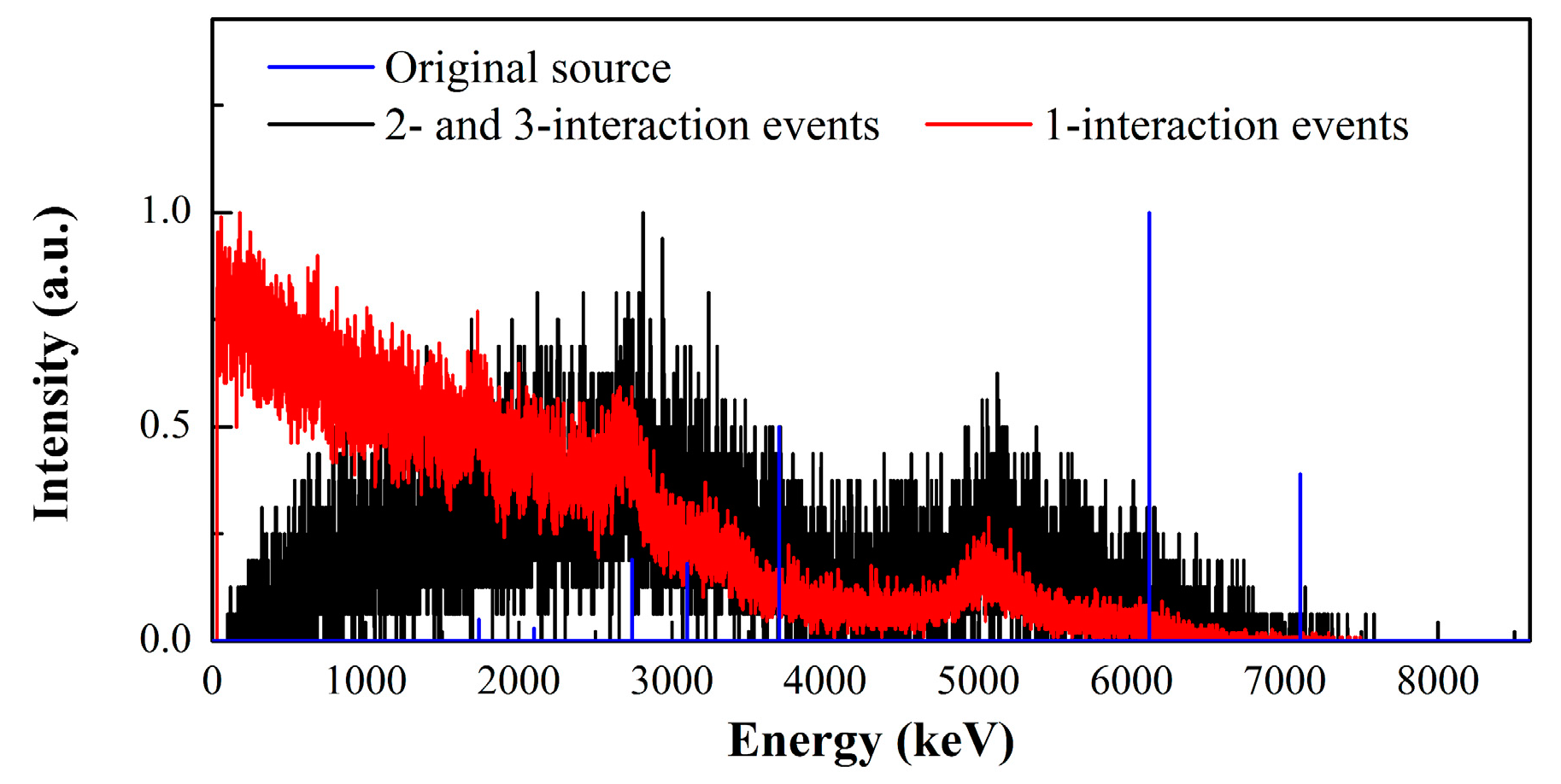
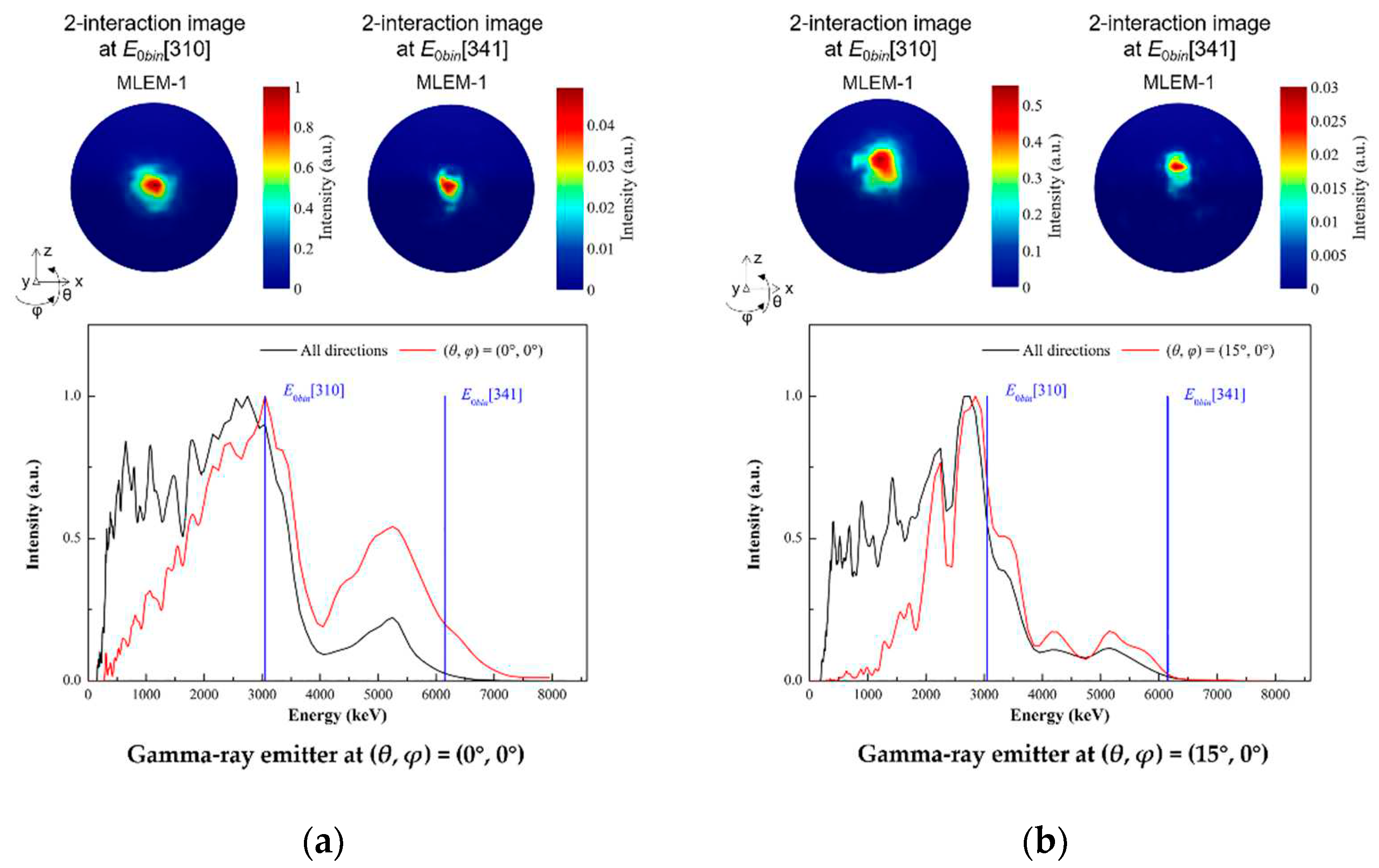
3.3. High energy gamma-rays imaging evaluation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parajuli, R.K.; Sakai, M.; Parajuli, R.; Tashiro, M. Development and Applications of Compton Camera—A Review. Sens. 2022, 22, 7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, A.; Tatischeff, V.; Argan, A.; Brandt, S.; Bulgarelli, A.; Bykov, A.; Costantini, E.; Curadoda Silva, R.; A. Grenier, I.; Hanlon, L.; et al. Gamma-ray astrophysics in the MeV range: The ASTROGAM concept and beyond. Exp. Astron. 2021, 51, 1225–1254.
- Kishimoto, A.; Kataoka, J.; Taya, T.; Tagawa, L.; Mochizuki, S.; Ohsuka, S.; Nagao, Y.; Kurita, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kawachi, N.; et al. First demonstration of multi-color 3-D in vivo imaging using ultra-compact Compton camera. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, S.; Kataoka, J.; Koide, A.; Fujieda, K.; Maruhashi, T.; Kurihara, T.; Sueoka, K.; Tagawa, L.; Yoneyama, M.; Inaniwa, T. High-precision compton imaging of 4.4 MeV prompt gamma-ray toward an on-line monitor for proton therapy. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers, Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2018, 936, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, M.; Ley, J.L.; Dauvergne, D.; Freud, N.; Krimmer, J.; Létang, J.M.; Maxim, V.; Richard, M.-H.; Rinaldi, I.; Testa, É. Monitoring ion beam therapy with a Compton camera: Simulation studies of the clinical feasibility. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2020, 4, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lee, W. Multiple scattering Compton camera with neutron activation for material inspection. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers, Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2015, 784, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshikawa, N.; Omata, A.; Masubuchi, M.; Kataoka, J.; Kadonaga, Y.; Tokoi, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Imada, A.; Toyoshima, A.; Matsunaga, K.; et al. Activation imaging: New concept of visualizing drug distribution with wide-band X-ray and gamma-ray imager. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers, Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2023, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikaze, Y.; Nishizawa, Y.; Sanada, Y.; Torii, T.; Jiang, J.; Shimazoe, K.; Takahashi, H.; Yoshino, M.; Ito, S.; Endo, T.; Tsutsumi, K.; Kato, S.; Sato, H.; Usuki, Y.; Kurosawa, S.; Kamada, K.; Yoshikawa, A. Field test around Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant site using improved Ce:Gd3(Al,Ga)5O12 scintillator Compton camera mounted on an unmanned helicopter. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Terasaka, Y.; Utsugi, W.; Kikuchi, H.; Kiyooka, H.; Torii, T. Radiation imaging using a compact Compton camera mounted on a crawler robot inside reactor buildings of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shy, D.; Xia, J.; He, Z. Artifacts in High-Energy Compton Imaging With 3-D Position-Sensitive CdZnTe. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2020, 67, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runkle, R.C.; Chichester, D.L.; Thompson, S.J. Rattling nucleons: New developments in active interrogation of special nuclear material. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers, Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2012, 663, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudac, D.; Pavlovic, M.; Obhodas, J.; Nad, K.; Orlic, Z.; Uroic, M.; M. Korolija; Rendic, D.; Meric, I.; Pettersen, H.; et al. Detection of Chemical Warfare (CW) agents and the other hazardous substances by using fast 14 MeV neutrons. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers, Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2020, 971, 164066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, J.M.; Riley, K.; Bortfeld, T.; Seco, J. Energy- and time-resolved detection of prompt gamma-rays for proton range verification. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, L37–L49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffrey, A.; Harkness-Brennan, L.; Alshammari, H.; Boston, A.; Boston, H.; Griffiths, O.; Judson, D.; Kalantan, S.; Le Crom, B.; Nolan, P.; et al. Gamma-ray imaging performance of the GRI+ Compton camera. J. Instrum. 2021, 16, P09015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, R.; Johnson, W.; Kurfess, J.; Phlips, B.; Wulf, E. Three-Compton telescope: theory, simulations, and performance. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2002, 49, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.; Barrio, J.; Etxebeste, A.; Ortega, P.G.; Lacasta, C.; Oliver, J.F.; Solaz, C.; Llosá, G. Performance evaluation of MACACO: a multilayer Compton camera. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 7321–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, A.R.; Barrio, J.; Etxebeste, A.; López, J.G.; Jiménez-Ramos, M.C.; Lacasta, C.; Muñoz, E.; Oliver, J.F.; Roser, J.; Llosá, G. MACACO II test-beam with high energy photons. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 245027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, L.; Borja-Lloret, M.; Casaña, J.; Hueso-González, F.; Ros, A.; Roser, J.; Senra, C.; Solaz, C.; Viegas, R.; Llosá, G. System characterization and performance studies with MACACO III Compton camera. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 208, 110922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanowska, J.; Swiderski, L.; Szczesniak, T.; Sibczynski, P.; Moszynski, M.; Grodzicka, M.; Kamada, K.; Tsutsumi, K.; Usuki, Y.; Yanagida, T.; et al. Performance of cerium-doped Gd3Al2Ga3O12 (GAGG:Ce) scintillator in gamma-ray spectrometry. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers, Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2013, 712, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.S. Prototypes of SiPM-GAGG Scintillator Compton Cameras. Adv. X-Ray Radiat. Detect.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 239–258. [Google Scholar]
- Omata, A.; Masubuchi, M.; Koshikawa, N.; Kataoka, J.; Kato, H.; Toyoshima, A.; Teramoto, T.; Ooe, K.; Liu, Y.; Matsunaga, K.; et al. Multi-modal 3D imaging of radionuclides using multiple hybrid Compton cameras. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZHANG, J.; MA, X.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, X.; LI, J.; LEI, W.; Zhao, W.; AI, X. Simulation design and performance evaluation of the wide-energy range gamma-ray imaging detectors. Sci. Sin. Technol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilderman, S.J.; Clinthorne, N.H.; Fessler, J.A.; Rogers, W.L. List-mode maximum likelihood reconstruction of Compton scatter camera images in nuclear medicine. In Proceedings of the 1998, https://doiEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Rec.ord, ON, ssmicanada, 8–14 November.1998, Torog/10.1109/nto; pp. 17738716–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; He, Z. Gamma-ray energy-imaging integrated spectral deconvolution. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A: Accel. Spectrometers, Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2007, 574, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, E.; Barrientos, L.; Bernabéu, J.; Borja-Lloret, M.; Llosá, G.; Ros, A.; Roser, J.; Oliver, J.F. A spectral reconstruction algorithm for two-plane Compton cameras. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinelli, S.; Allison, J.; Amako, K.; Apostolakis, J.; Araujo, H.; Arce, P.; Asai, M.; Axen, D.; Banerjee, S.; Barrand, G.; et al. GEANT4—a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A. 2003, 506, 250–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Yi, M.; Lee, J.S. Silicon photomultiplier signal readout and multiplexing techniques for positron emission tomography: a review. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2022, 12, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Liang, X.Z.; Cai, J.L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.C.; Li, D.W.; Xiao, X.; Pang, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Wei, L.; Shuai, L. Prototype of an array SiPM-based scintillator Compton camera for radioactive materials detection. Radiat. Detect. Technol. Methods 2019, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, W.; Robson, J.; Malcolm, R. Scattered neutrons and gamma rays from the 16O(n, n′γ)16O reaction at En=14.1 MeV. Nucl. Phys. 1966, 75, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
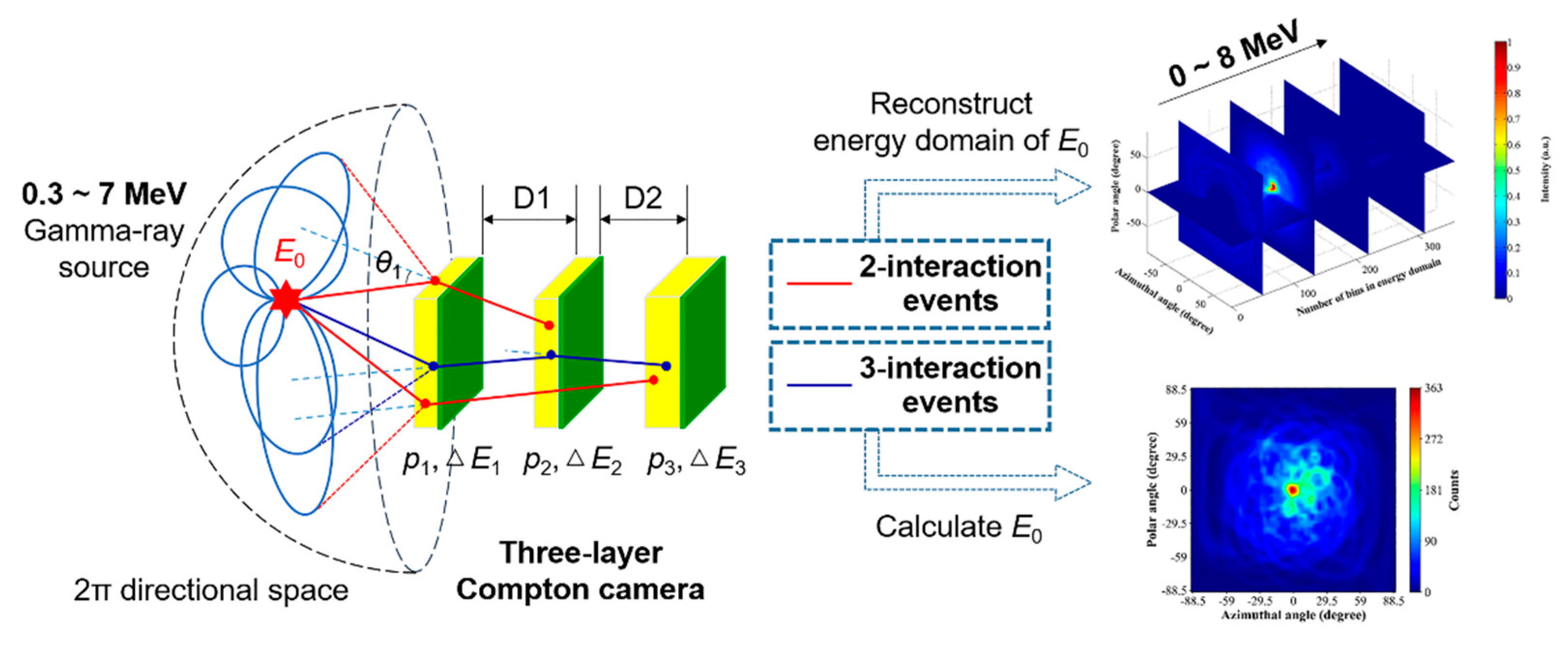
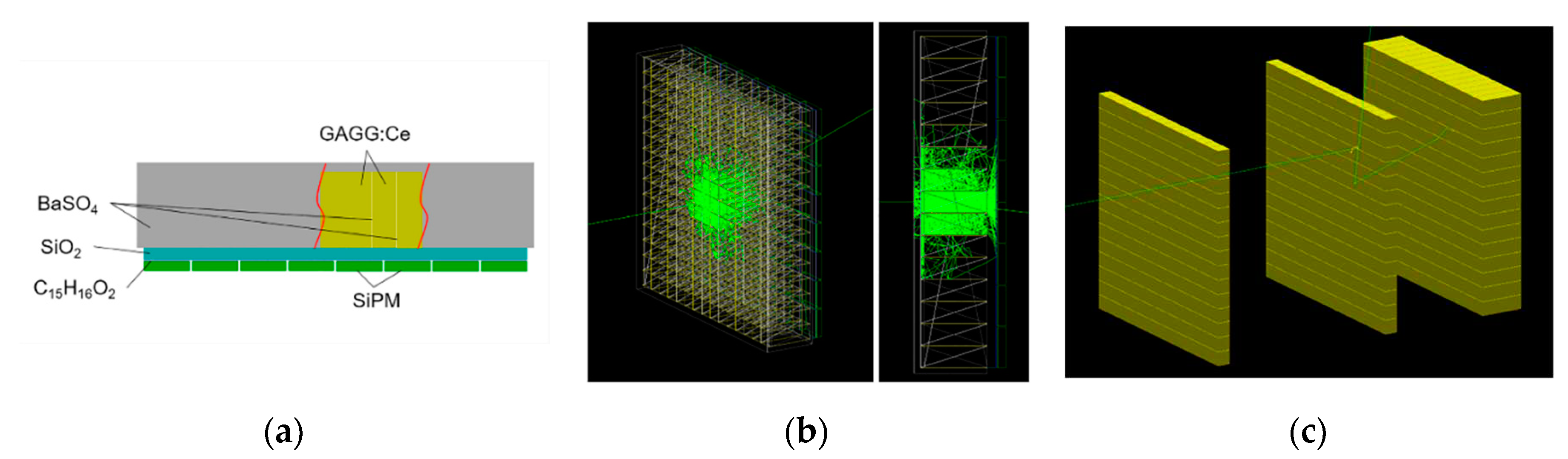
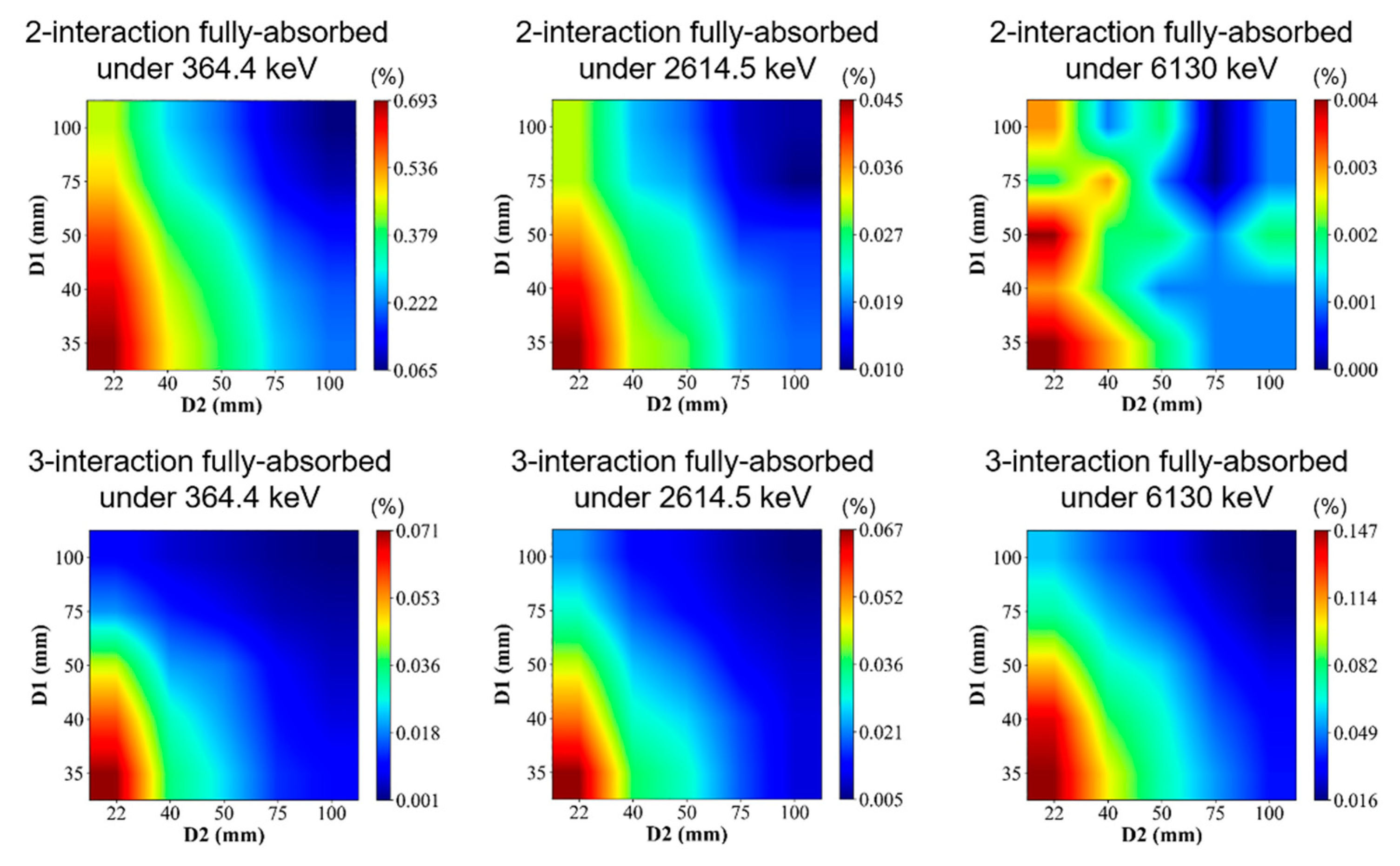
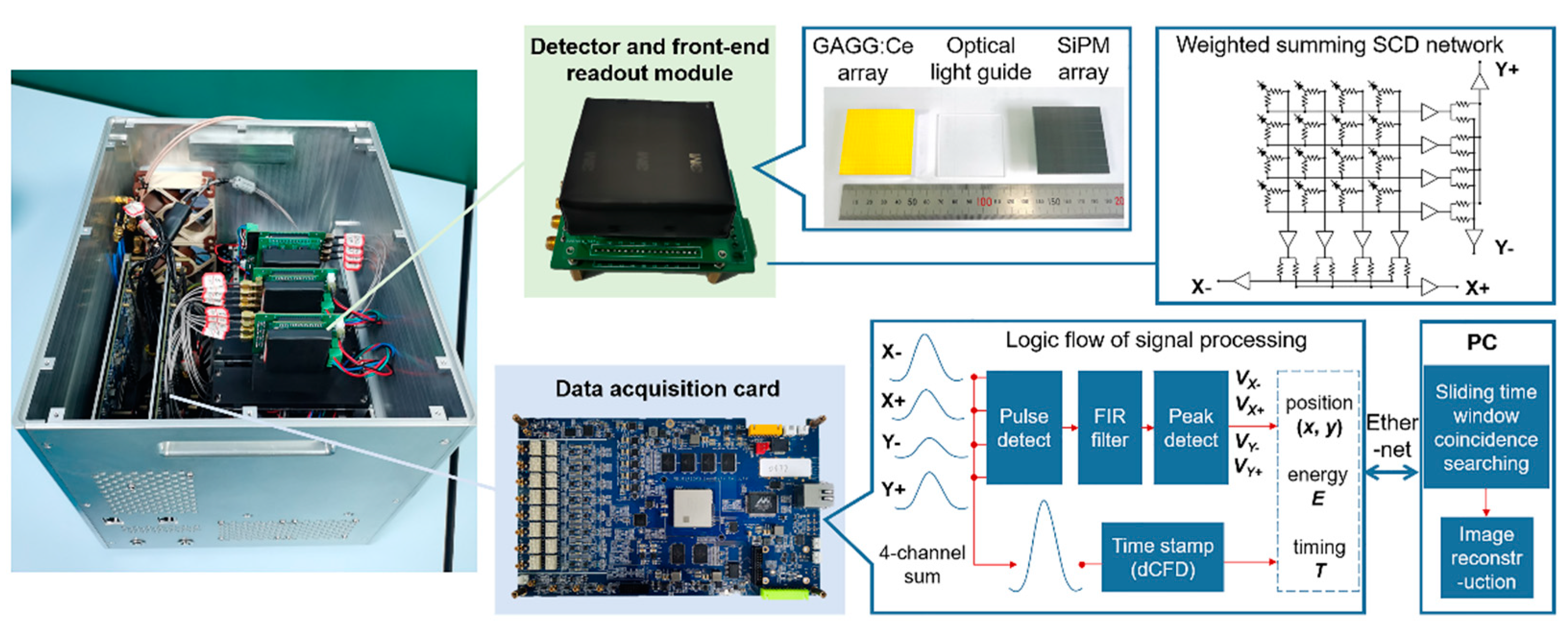

| Settings of gamma emission$conditions | Nuclide | Representative$energy (keV) | Total count from source | Count of 2-interaction events | Count of 3-interaction events | Proportion of effective events (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation$(N gammas emit within Ω=0.031 sr at d=1 m, N is equal to the sum of the emission probability of each energy branch multiplied by the base number 107) | N = 13418000 | 133Ba | 356 | 760871 | 11266 | 65 | 1.49 |
| N = 8499000 | 137Cs | 661.7 | 317619 | 10029 | 129 | 3.20 | |
| N = 19983260 | 60Co | 1173.2/1332.5 | 585709 | 13415 | 141 | 2.31 | |
| Experiment$(Point-like source with radioactivity A, distance d and acquisition time t) | A = 0.262 MBq$d = 0.25 m$t = 3600 s | 133Ba | 356 | 376788 | 8253 | 43 | 2.20 |
| A = 1.88 MBq$d = 1 m$t = 1800 s | 137Cs | 661.7 | 628321 | 13186 | 87 | 2.11 | |
| A = 1.92 MBq$d = 1 m$ t = 1800 s | 60Co | 1173.2/1332.5 | 1129416 | 20176 | 148 | 1.80 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





