Submitted:
08 October 2023
Posted:
08 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Biopolitical, Biogeographical, and Biological Background
2.1. Redefining Nature
2.2. The Anthropocene and Proactive Amphibian Sustainability
3. Targeting Threats to Amphibians
3.1. Biogeography, Species Richness, and Habitat Loss
3.2. Pathogens and Parasites

3.3. Data Bases for Endangerment Status
3.4. Commercialisation and Trade
4. Conservation Breeding Programs [CBPs]
4.1. Preferred terms for field conservation
| Preferred Term | Misnomers – alternatives | |
|---|---|---|
| Species Programs | ||
| Head Starting | The raising of eggs or embryos harvested from nature to advanced stages for release. | [88] |
| Repopulation | Repopulating a lost species in previously populated habitat. | Rehabilitation. Reintroduction. |
| Augmentation | The addition of individuals from captive-bred or stable, wild populations to support extant populations. | Supplementation |
| Translocation | Translocation is the transfer of a species from one location to another within their home range. | [89] |
| Relocation | Relocation is moving animals under immediate threat of extirpation from one location to another within their home range. | [89] |
| Assisted Migration | Moving populations to locations outside the historical species range, mainly in response to global heating. | [90] |
| Habitat Programs | ||
| Mitigation | Minimising damage and maximizing the eco-sustainability of environments. | [91] |
| Rehabilitation | Rehabilitation focuses on the reparation of ecosystem processes …. to repair the capacity of ecosystems to provide habitats for biota and eco-services. | [91] |
| Restoration | The aspirational target of restoring native ecosystems. | [92] |
4.2. Range, Scope, and Networking
4.3. Species Prioritisation for RBCs
4.3.1. CBP Founders and Data Bases
4.3.2. The Species Survival Triage and RBC Prioritisation
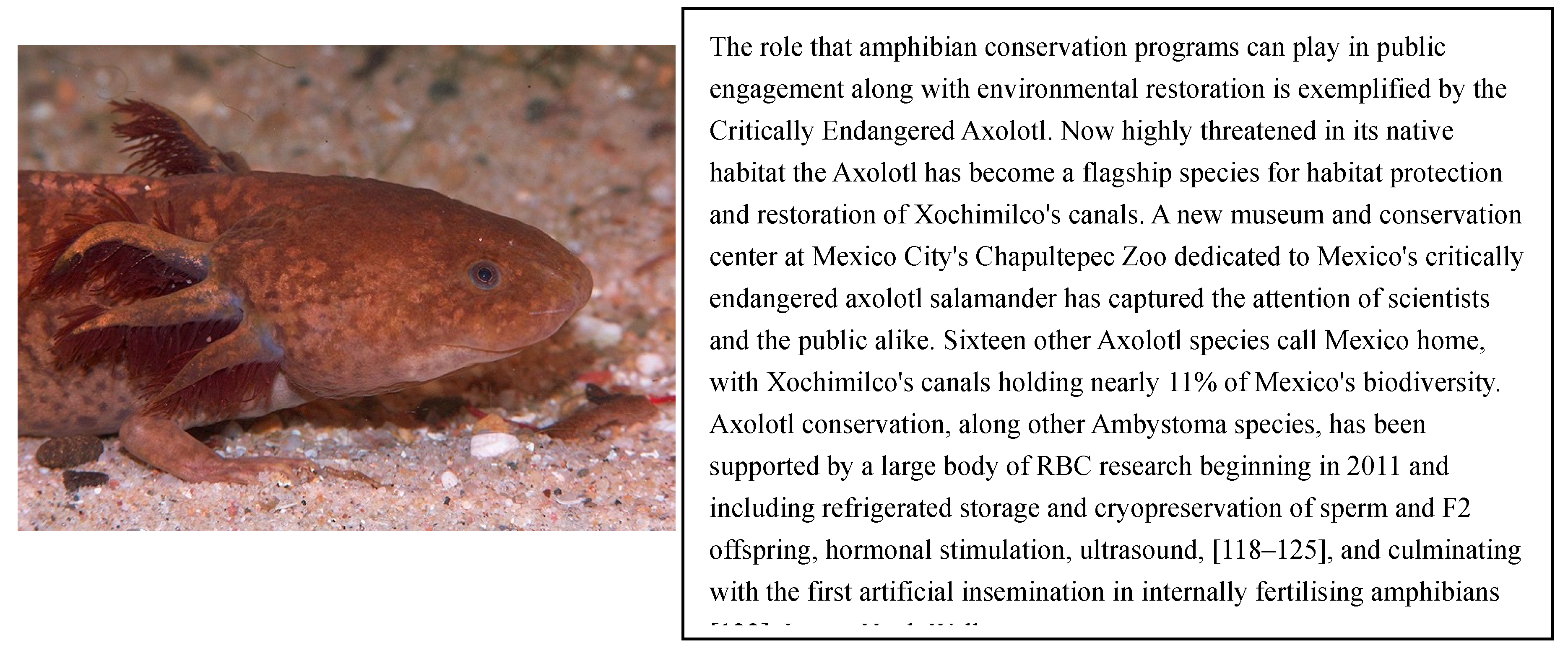
4.4. Citizen Conservation, Private Carers, and CBPs
“Ultimately, breeding space and staff is limited in zoos. With dedicated private keepers, we can expand our capacities while sharing and gaining knowledge — a win-win situation for breeding and conserving endangered species”. Anna Rauhhaus , 2023.


5.1. Genetic Management Guidelines
5.1.1. Biobanking Genetic Diversity and CBPs
5.1.2. Assisted Gene Flow
5.2. Genetically Unbiased Founders in CBPs and Biobanking
5.3. Assisted Evolution.
6. Reproduction and Biobanking Technologies
6.1. History
6.2. Ethics
6.3. Assisted Mating, Spawning, and Reproductive Maturity
6.4. Material Types and Vouchering
6.5. Life Stage and Sample Collection
6.6. Sperm Qualities - Activation, Motility, Speed, Vitality, and DNA integrity
6.7. Oocytes Collection and Storage
6.8. Sperm Collection from Testes Macerates
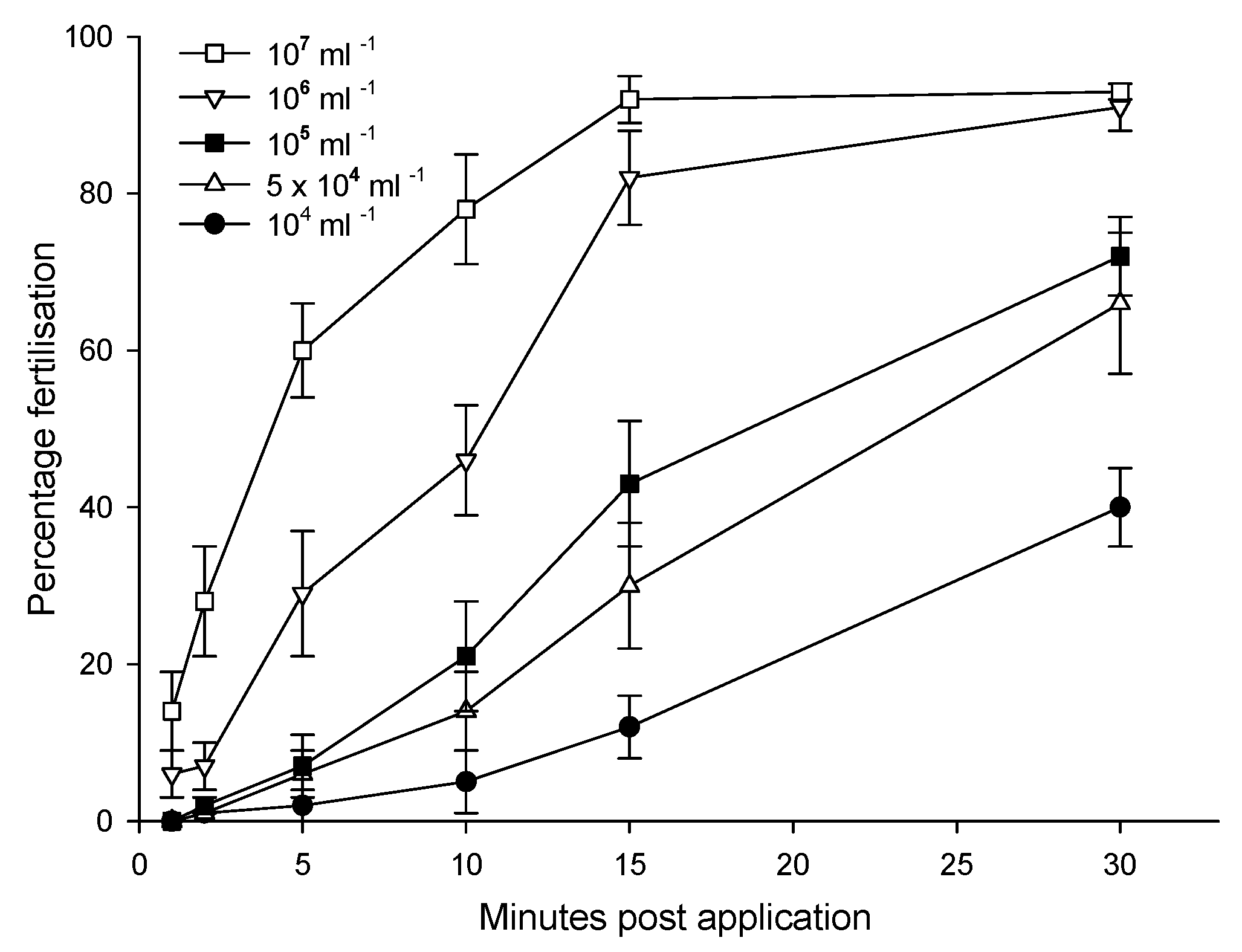
6.9. Sperm Collection through Hormonal Stimulation
6.10. Sperm Donor Stress, Trauma, and Pathogens
| Collection Method | Stress | Trauma | Sperm Yield | Donor Size | Pathogens |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testes Macerates | Low. | Low. | Very High | All Species. | Endo-parasites, virus. |
| Spermic Urine Anurans |
High, dependent on collection period and technique. | Unacceptable for very small species. | Moderate - Very Low. | Unacceptable for very small species | Endo-parasites, exo-parasites, intestinal parasites, fungus, virus, bacteria. |
| Hormonal Stimulation Salamanders |
High, dependent on collection period and technique. | Unacceptable for small to very small species. | Moderate - Very Low. | Unacceptable for small to very small species | Endo-parasites, exo-parasites, intestinal parasites, fungus, virus, bacteria. |
6.11. Refrigerated Storage of Sperm and Testes
6.12. Sperm Cryopreservation
6.13. Artificial Fertilisation
6.14. Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
6.15. Advanced Reproduction Technologies [aARTs]
| Nucleus donors | Recipients | Results | Authors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rana pipiens | R. catesbeina | Late blastula/early neurula | [220] |
| #R. brevipoda | R. nigromaculata | Died metamorphisis | [221] |
| R. pipiens | R. sylvatica | Late blastula/early neurula | [222] |
| R. nigromaculata | R. brevipoda | Adults | [223] |
| Xonopus llaevis | X. laevis | Adults | [224] |
| R. pipiens | R. palustris | Post-neurula | [225] |
| R. nigromaculata | R. brevipoda | Adults but poor reproduction | [226] |
| R. japonica | R. ornativentris | Adult frogs then F2 with female R. japonica | [227] |
| R. japonica | R. ornativentris | Adult frogs then F2 with female R. japonica | [228] |
|
R. nigromaculata R. temporaria |
R. brevipoda R. japonica |
F3. Reproductive capacity. % abnormality dependent on sex crosses. | [229] |
|
R. japonica R. temporaria |
R. temporaria R. japonica |
Adult frogs | [230] |
|
R. brevipoda R. plancyi R. brevipoda R. esculenta |
R. plancyi R. brevipoda R. esculenta R. brevipoda |
Adult frogs | [231] |
|
P. waltlii P. poireti |
P. poireti P. waltlii |
Adult salamanders | [232,234] |
7. Implementing RBCs – Economic, Political, Cultural Factors
7.1. Monetisation of Proactive Amphibian Sustainability
| Activity | Budget | % GT | Notes. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution/Systematics | 407.2 | 67.7 | Biogeography 185.2 [26.8%], Biodiversity hotspots 176.4 (29.0%), Systematics 47.3 (7.9%). |
| Generic Threats | 118.0 | 19.6 | Pollution 63.8. (10.6%), Pathogens 37.3 (6.2%), Climate catastrophe 10.7 (1.8%), Over-harvest 6.3. (1.0%). |
| Conservation status | 2.7 | 4.5 | |
| Total | 527.9 | 87.7 | |
| RBCs | |||
| Reproduction Technologies and Biobanking | 6.3 | 1.1 | Bioresource Banking 5.1 (0.9%), Genome Resource Banking 1.0 (0.2%). |
| Captive programs | 60.2 | 10.0 | 100 facilities/species over 5 years |
| Repopulation/augmentation | 5.1 | 0.9 | |
| Total | 72.0 | 12.0 | |
| Grand Total (GT) | 601.7 |
7.2. Contemporary Cost Estimates of Amphibian RBCs
7.3. Entitlement, Biopiracy, and Ownership Models
7.4. Biobanking Facilities
7.5. Biobanking Databases
“A Biobank is only as good as the quality and extent of its recorded information and database that accompanies it” Rhiannon Lloyd, 2023.
7.6. Financing Amphibian RBCs
“Finance for biodiversity and alignment of financial flows with nature to drive finances toward sustainable investments.” COP 15
7.7. Media, Public and Political Presence
7.8. Artificial Intelligence, Management, and the Future
7.9. Developing Cultural Influence
9. Conclusion and the Road Ahead
Ethics
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. The Anthropocene and Biospheric Sustainability
Appendix A.2. Oocytes Viability Period and Storage Environment
Appendix A.3. Sperm Cryopreservation
Appendix A.4. Artificial Fertilisation
Appendix A.5. Cloning
| Assessment of cell preservation in points | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMSO (%) | Sucrose (%) | |||
| 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | |
| 5 | 3 | 3 - 4 | - | - |
| 10 | - | 5 | 3 - 4 | 3 |
| 20 | - | 4 | 4 | - |
Appendix A.6.
| Year | Milestone | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| 1986 | Release of hormonally stimulated reproduction of E salamander | 337 |
| 1989 | Hormonal stimulation of reproduction of many anurans and salamanders | 338 |
| 1996 | Cryopreservation of anuran sperm in pieces of testes with fertilisation | 178,179 |
| 1998 | Cryopreservation of totipotent cells and their use in reconstruction of enucleated eggs | 18 |
| 1998 | Cryopreservation of anuran sperm suspensions with fertilisation | 180 |
| 1998 | Saccharides and anuran sperm cryopreservation | 317 |
| Refrigerated storage of anuran sperm and oocytes | 208 | |
| 2003 | Cryopreservation of Cryptobranchidae (Caudata) sperm | 194 |
| 2006 | Novel use of high concentrations of LHRH-A for gamete collection in anurans | 169 |
| 2006 | Novel use of dopamine antagonists for gamete collection in anurans | 168 |
| 2010 | Hormonal stimulation and in vitro fertilisation in Salamandridae | 118 |
| 2011 | Cryopreservation of hormonally induced anuran sperm with fertilisation | 181 |
| 2011 | Cryopreservation of hormonally induced anuran sperm with dimethyl formamide | 181 |
| 2013 | Refrigerated storage of in situ (in carcasses) anuran sperm for 7 days | 339 |
| 2016 | Generation of a reproductively mature adult from cryopreserved Salamandridae sperm | 194 |
| 2018 | Refrigerated storage of anuran oocytes in the oviducts of live females | 312 |
| 2018 | Reproductively mature anurans from cryopreserved testicular sperm | 206 |
| 2019 | Cryopreservation of anuran sperm from nature and in vitro fertilisation | 125 |
| 2020 | Seasonality in hormonally stimulated sperm | 159 |
| 2021 | Reproductively mature CE anurans from cryopreserved testicular sperm | 205 |
| 2021 | Generation of a mature adult from cryopreserved Cryptobranchoidea sperm | 194 |
| 2021 | Cryopreservation of refrigerated sperm from carcasses | 339 |
| 2022 | Assisted gene flow between in situ and ex situ anurans | 102 |
| 2022 | Gentamicin increases refrigerated sperm storage | 214 |
| 2022 | Ultrasound optimisation of Salamandridae hormonal stimulation | 124 |
| 2023 | Low saccharide concentrations of 1-5% optimal for sperm cryopreservation | 203, 205 |
| 2023 | High pressure of carbon monoxide and oxygen for anuran oocyte refrigerated storage | 313 |
References
- UNEP. UN Biodiversity Conference (COP 15). December 7-19, 2022. Available online: https://www.unep.org/un-biodiversity-conference-cop-15 (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Finn, C.; Gratarolla, F.; Pincheira-Donoso, D. More Losers than Winners: Investigating Anthropocene Defaunation through the Diversity of Population Trends. Biol. Rev. 2023, 98, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AArk. Amphibian Ark. Available online: www.amphibianark.org/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Clulow, J.; Mahony, M.; Browne, R.; Pomering, M.; Clark, A. Applications of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) to Endangered Anuran Amphibians. In Declines and disappearances of Australian frogs, Campbell, A., Ed.; Environment Australia: Canberra, Australia, 1999; pp. 219–225. ISBN 0. [Google Scholar]
- Clulow, J.; Clulow, S. Cryopreservation and Other Assisted Reproductive Technologies for the Conservation of Threatened Amphibians and Reptiles: Bringing the ARTs up to Speed. Reprod. Fert. Dev. 2016, 28, 1116–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananjeva, N.B.; Uteshev, V.K.; Orlov, N.L.; Ryabov, S.A.; Gakhova, E.N.; Kaurova, S.A. , Kramarova L.I., Shishova N.V., Browne R.K. Comparison of the Modern Reproductive Technologies for Amphibians and Reptiles. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2017, 24, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clulow, J.; Upton, R.; Trudeau, V.L.; Clulow, S. Amphibian Assisted Reproductive Technologies: Moving from Technology to Application. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1200, 413–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della-Tonga, G.; Howell, L.G.; Clulow, J.; Langhorne, C.J.; Marcec-Greaves, R.; Calatayud, N.E. Evaluating Amphibian Biobanking and Reproduction for Captive Breeding Programs According to the Amphibian Conservation Action Plan Objectives. Theriogenology 2020, 150, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, J.; Thomsen, H.; Jensen, J.B.; Marcussen, C.; Nicolajsen, T.B.; Skriver, M.B.; Søgaard, I.M.; Ezaz, T.; Purup, S.; Callesen, H.; et al. Biobanking in Amphibian and Reptilian Conservation and Management: Opportunities and Challenges. Conserv. Gen. Res. 2020, 12, 709–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, J.; Fraser, B.; Houck, M.L.; Clulow, S. Culturing and Biobanking of Amphibian Cell Lines for Conservation Applications. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians, Silla, A.J., Kouba, A.J., Heatwole, H., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 9781486313334. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, A.; Ryder, O.A.; Houck, M.L.; Staerk, J.; Conde, D.A.; Buckley, Y.M. Maximizing the Potential for Living Cell Banks to Contribute to Global Conservation Priorities. Zoo Biol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uteshev, V.K.; Gakhova, E.N.; Kramarova, L.I.; Shishova, N.V.; Kaurova, S.A.; Kidova, E.A.; Kidov, A.A.; Browne, R.K. Russian Collaborative Development of Reproduction Technologies for the Sustainable Management of Amphibian Biodiversity. Asian Herpetol. Res. 2023, 14, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, L.G.; Mawson, P.R.; Frankham, R.; Rodger, J.C.; Upton, R.M.O.; Witt, R.W.; Calatayud, N.E.; Clulow, S.; Clulow, J. Integrating Biobanking could Produce Significant Cost Benefits and Minimise Inbreeding for Australian Amphibian Captive Breeding Program. Reprod. Fert. Dev. 2021, 33, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, L.G.; Frankham, R.; Rodger, J.C.; Witt, R.R.; Clulow, S.; Upton, R.M.O.; Clulow, J. Integrating Biobanking Minimises Inbreeding and Produces Significant Cost Benefits for a Threatened Frog Captive Breeding Programs. Conserv. Lett 2021, 14, 12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.K.; Janzen, P.; Bagaturov, M.F.; van Houte, D.K. Amphibian Keeper Conservation Breeding Programs. J. Zoo. Res. 2018, 2, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.K.; Silla, A.J.; Upton, R.; Della-Togna, G.; Marcec-Greaves, R.; Shishova, N.V.; Uteshev, V.K.; Proano, B.; Perez, O.D.; Mansour, N.; et al. Sperm Collection and Storage for the Sustainable Management of Amphibian Biodiversity. Theriogenology 2019, 133, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clulow, J.; Upton, R.; Clulow, S. Cryopreservation of Amphibian Genomes: Targeting the Holy Grail, Cryopreservation of Maternal-haploid and Embryonic-diploid Genomes. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians, Silla, A.J., Kouba, A.J., Heatwole, H., Eds.; CRC Press; London, UK, 2022; pp. 147–165, ISBN 9781486313334.
- Kaurova, S.A.; Nikitina, L.A.; Uteshev, V.K.; Gakhova, E.N. Cryopreservation of Totipotent Embryo Cells and Their use in Reconstruction of Enucleated Eggs, In Proceedings of the 15th Working Meeting, Pushchino, Russian, 13–15, October 1998; pp. 206–208 (In Russian). (In Russian).
- Tapley, B.; Bradfield, B.; Michaels, C.; Bungard, M. Amphibians and Conservation Breeding Programmes: do all Threatened Amphibians Belong on the Ark? Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 2625–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenfeld, D.A.; Alberts, A.C.; Angulo, A.; Bennett, E.L.; Byers, O.; Contreras-MacBeath, T.; Drummond, G.; da Fonseca, G.A.B.; Gascon, C.; Harrison, I. Conservation Resource Allocation, Small Population Resiliency, and the Fallacy of Conservation Triage. Conserv Biol 2021, 35, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, M.C. An Introduction to Adaptive Management for Threatened and Endangered Species. J. Fish Wildl. Manage. 2011, 2011, 2, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Cartney, A.M.; Head, M.A.; Tsosie, K.S.; Sterner, B.; Glass, J.R.; Paez, S.; Geary, J.; Hudson, M. Indigenous Peoples and Local Communities as Partners in the Sequencing of Global Eukaryotic Biodiversity. npj Biodiversity 2023, 2, 8:1–8:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GEF. The Global Environment Facility (GEF). Available online: https://www.thegef.org/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Byers, O.; Lees, C.; Wilcken, J.; Schwitzer, C. The One Plan Approach: The Philosophy and Implementation of CBSG’s Approach to Integrated Species Conservation Planning. WAZA Mag. 2013, 14, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- ABS. 2014. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/abs/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Khoday, K. Decolonising the Environment: Third World Approaches to the Planetary Crisis. Indones. J. Int. Law, 2022, 19, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiddin, N.Z.; Ibrahim, I.; Abdul Aziz, S.A. Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs) and Their Part towards Sustainable Community Development. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4386:1–4386:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, W.; Mulligan, M. Decolonising Nature: Strategies for Conservation in a Developing Era. 2002. Earthscan Publications Ltd; Sterling, VA, USA, ISBN 1-85383-749-0.
- Seddon, P.J.; Griffiths, C.J.; Soorae, P.S.; Armstrong, D.P. Reversing Defaunation: Restoring Species in a Changing World. Science 2014, 345, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN/SSC. 2014. Available online: www.iucn.org/about/work/programmes/species/publications/iucn_guidelines_and__policy__statements/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Conde, D.A.; Colchero, F.; Gusset, M.; Pearce-Kelly, P.; Byers, O.; Flesness, N.; Browne, R.K.; Jones, O.R. Zoos through the Lens of the IUCN Red List: A Global Metapopulation Approach to Support Conservation Breeding Programs. PLoS One, 2013, 8, 80311:1–80311:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolly Mammoth De-extinction Project & Process | Colossal. Available online: https://colossal.com/mammoth/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Beattie, A.; Ceballos, G.; Crist, E.; Diamond, J.; Dirzo, R.; Ehrlich, A.H.; Harte, J.; Harte, M.E.; Graham, P.; et al. Underestimating the Challenges of Avoiding a Ghastly Future. Front. Conserv. Sci. 2021, 1, e615419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; Bindi, M.; Brown, S.; Camilloni, I.; Diedhiou, A.; Djalante, R.; Ebi, K.L.; Engelbrecht, F.; et al. Impacts of 1.5ºC Global Warming on Natural and Human Systems. In Global Warming of 1.5°C. An IPCC Special Report on the impacts of global warming of 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels and related global greenhouse gas emission pathways, in the context of strengthening the global response to the threat of climate change, sustainable development, and efforts to eradicate poverty; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 175–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, C.; Gratarolla, F.; Pincheira-Donoso, D. More Losers than Winners: Investigating Anthropocene Defaunation through the Diversity of Population Trends. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2023, 98, 1732–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford Dictionary. ‘Nature, n’ Available online:. Available online: https://www.oed.com/search/dictionary/?scope=Entries&q=nature (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Spencer, S. Judeo-Christian Religion's Impact on Humans' Attitudes Towards Their Environment, 2016, Swarthmore College Environmental Studies. Available online: http://fubini.swarthmore.edu/~ENVS2/sierra/Essay2.html (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Lind, A.G.; Nobre, B. Ecology as a New Foundation for Natural Theology. Religions 2021, 12, 660:1–660:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, G.S. Current Challenges and Opportunities for Space Technologies. Front. Space Technol. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.R. Biodiversity Requirements for Self-Sustaining Space Colonies. Futures 2019, 110, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakayama, S.; Ito, D.; Kamada, Y.; Shimazu, T.; Suzuki, T.; Nagamatsu, A.; Araki, R.; Ishikawa, T.; Kamimura, S.; Hirose, N.; et al. Evaluating the Long-term Effect of Space Radiation on the Reproductive Normality of Mammalian Sperm Preserved on the International Space Station. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia-Aguilar, A.; Cortés-Gómez, A.M.; Ruiz-Agudelo, C.A. Ecosystem Services Provided by Amphibians and Reptiles in Neotropical Ecosystems. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Man. 2013, 9, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.C., Dallimer, M., Irvine, K.N.; Aizlewood, S. G.; Austen, G. E.; Fish, R. D.; King, P. M.; Davies, Z. G. Human Well-being Responses to Species’ Traits. Nat. Sustain 2023. [CrossRef]
- Methorst, J.; Bonn, A.; Marselle, M.; Böhning-Gaese, K.; Rehdanz, K. Species Richness is Positively Related to Mental health – A Study for Germany. Landscape and Urban Planning 2021, 211, 104084:1–104084:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwell, P.J.; Riley, L.M.; Lemos de Figueiredo, R.; Brereton, J.E.; Mooney, A.; Rose, P.E. The Societal Value of the Modern Zoo: A Commentary on How Zoos Can Positively Impact on Human Populations Locally and Globally. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2023, 4, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, R.H.; Bouchet, P.; Fontaine, B. The Sixth Mass Extinction: fact, fiction or speculation? Biol. Reviews 2022, 97, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.; Lemos, M.F.; Astigarraga, L.; Chacón, N.; Cuvi, N.; Huggel, C.; Miranda, L.; Vale, M.M.; Ometto, J.P.; Peri, P.L.; et al. Central and South America. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Pörtner, H.O., Roberts, D.C., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E.S., Mintenbeck, K. Alegría, A. Craig, M., Langsdorf, S. Löschke, S., Möller, V., Okem, A., Rama, B., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1689–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.G.; Anderson, K.A.; Marcec-Greaves, R.; Cardoso, P.; Barton, P.S.; Birkhofer, K.; Chichorro, F.; Deacon, C.; Fartmann, T.; Fukushima, C.S.; Gaigher, R.; Habel, J.C.; Hallmann, C.A. Scientists' Warning to Humanity on Insect Extinctions. Biol. Conserv., 2020, 242, 108426:1–108426:1. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, D.L.; Grames, E.M.; Forister, M.L.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Stopak, D. Insect Decline in the Anthropocene: Death by a Thousand Cuts. Proc. Nat.l Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 118, 2023989118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenazzi, A. State of the World's Amphibians. Ann. Rev. Environ. Res. 2015, 40, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.T.J. Amphibian diversity: Decimation by Disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3011–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AmphibiaWeb. Available online: https://amphibiaweb.org (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Alroy, J. Current Extinction Rates of Reptiles and Amphibians. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 13003–13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokstad, E. Can a Dire Ecological Warning Lead to Action? Science 2019, 364, 517–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov-Danil’yan, V.I., Reyf, I.E. Foundations of Sustainability in Nature and Society. In The Biosphere and Civilization: In the Throes of a Global Crisis; Springer, Cham, ZG; 2018; pp.199-205, ISBN 978-3-319-67193-2.
- Wiens, J.J. Global Patterns of Diversification and Species Richness in Amphibians. Am. Nat. 2007, 170 (Suppl 2), 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickford, D.; Poo, S.; Posa, M.R.C.; Gower, D.; Johnson, K.; Richardson, J.; Rosen, B.; Ruber, L.; Williams, S. Southeast Asian biodiversity crisis. In Biotic evolution and environmental change in Southeast Asia; Gower, A., Johnson, K., Richardson, J., Rosen, B., Rüber, L., S. Williams, S., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: UK, 2012; pp. 434–462. ISBN 9780511735882. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Correa, M.; Baldo, D.; Candioti, F.V.; Orrico, V.; Blackburn, D.C.; Castroviejo-Fisher, S.; Onn, C.K.; Gambale, P.; Gower, D.J.; Quah, E.; et al. Amphibians in Zootaxa: 20 years Documenting the Global Diversity of Frogs, Salamanders, and Caecilians. Zootaxa 2021, 4979, 057–069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womack, M.C.; Steigerwald, E.; Blackburn, D.C.; Cannatella, D.C.; Catenazzi, A.; Che, J.; Koo, M.S.; McGuire, J.A.; Ron, S.R.; Spencer, C.L.; et al. State of the Amphibia 2020: A Review of Five Years of Amphibian Research and Existing Resources. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 2022, 110, 638–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.K.; Kaurova, S.A.; Vasudevan, K.; McGinnity, D.; Venu, G.; Gonzalez, M.; Uteshev, V.K.; Marcec-Greaves, R. Reproduction Technologies for the Sustainable Management of Caudata (salamander) and Gymnophiona (Caecilian) biodiversity. Reprod. Fert. Devel. 2022, 34, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venu, G.; Raju, N.G.; Wilkinson, M.; Browne, R.K.; Varadh, K.; Balakrishna, G.N.; Ramakrishna, S.; Venkatachalaiah, G. First records of the Long-headed Caecilian, Ichthyophis longicephalus Pillai, 1986 (Gymnophiona: Ichthyophiidae) from the States of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, India with Comments on its Conservation Status. J. Anim. Divers. 2020, 2, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, A.F.; De La Riva, I.; Guayasamin, J.M.; Chaparro, J.C.; Gagliardi-Urrutia, G.; Gutiérrez, R.C. , Brcko, I.; Vilà, C.; Castroviejo-Fisher, S. Vastly Underestimated Species Richness of Amazonian Salamanders (Plethodontidae: Bolitoglossa) and Implications about Plethodontid Diversification. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 149, 106841:1–106841:23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, R.K.; Wang, Z.; Okada, S.; McGinnity, D.; Luo, Q.; Taguchi, Y.; Kilpatrick, D.; Hardman, R.; Janzen, P.; Zhang, Z.; et al. The Sustainable Management of Giant Salamanders (Cryptobranchoidea). Review. Sustainability America, Belize, 2020.
- Gower, D. J.; Wilkinson, M. Conservation Biology of Caecilian Amphibians. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, J.; Gray, C.L.; Tapley, B.; Murray, K.A.; Gumbs, R. Poor Protection of Amphibian Evolutionary History Reveals Opportunities for Global Protected Areas. bioRxiv preprint 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Andrade, H. M.; Rodes Blanco, M.; Cisneros-Heredia, D.F.; Guerra Arévalo, N.; López de Vargas-Machuca, K.G.; Sánchez-Nivicela, J.C.; Yánez Muñoz, M. H. Red List Assessment of Amphibian Species of Ecuador: A Multidimensional Approach for their Conservation. PloSOne 2021, 16, e0251027:1–e0251027:28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, P.M.; Bower, D.S.; McDonald, P.J.; Kraus, F.; Luedtke, J.; Neam, K.; Hobin, L.; Chauvenet, A.L.M.; Allison, A.; Arida, E.; et al. Melanesia Holds the World's most Diverse and Intact Insular Amphibian Fauna. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1182:1–1182:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreone, F.; Carpenter, A.I.; Cox, N.; du Preez, L.; Freeman, K.; Furrer, S.; Garcia, G.; Glaw, F.; Glos, J.; Knox, D. The Challenge of Conserving Amphibian Megadiversity in Madagascar. PLOS Biol. 2008, 6, e118:0943–e118:0946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villacampa, J.; Whitworth, A.; Allen, L.; Malo, J.E. Altitudinal Differences in Alpha, Beta and Functional Diversity of an Amphibian Community in a Biodiversity Hotspot. Neotrop. Biodiver. 2019, 5(1), 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatiwada, J.R.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Xei, F.; Cannatella, D.C.; Jiang, J. Amphibian Community Structure along Elevation Gradients in Eastern Nepal Himalaya. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 19:1–19:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.H.; Ronnenberg, K.L.; Glidden, C.K.; Christiansen, K.R.; Blaustein, A.R. Global Patterns of the Fungal Pathogen Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis support Conservation Urgency. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 685877:1–685877:20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolby, J.E.; Daszak, P. The Emerging Amphibian Fungal Disease, Chytridiomycosis: A Key Example of the Global Phenomenon of Wildlife Emerging Infectious Diseases. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.E.; Dodd, C.K. Presence and Significance of Chytrid Fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis and other Amphibian Pathogens at Warm-water Fish Hatcheries in Southeastern North America. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 2, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- 74. Liew, N.; Mazon Moya, M.J.; Wierzbicki, C.J.; Hollinshead, M.; Dillon, M.J.; Thornton, C.R.; Ellison, A.; Cable, J.; Fisher, M.C.; Mostowy, S. Chytrid Fungus Infection in Zebrafish Demonstrates that the Pathogen can Parasitize Non-amphibian Vertebrate Hosts. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15048:1–15048:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrowes, P.A.; De la Riva, I. Detection of the Amphibian Chytrid Fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in Museum Specimens of Andean Aquatic Birds: Implications for Pathogen Dispersal. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleason, F.H.; Chambouvet, A.; Sullivan, B.K.; Lilje, O.; Jodi, J.L.; Rowley, J.J.L. Multiple Zoosporic Parasites pose a Significant Threat to Amphibian Populations. Fungal Ecol. 2014, 11, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Caballero, I.; Garcia-Longoria, L.; Gomez-Mestre, I.; Marzal, A. The Adaptive Host Manipulation Hypothesis: Parasites Modify the Behaviour, Morphology, and Physiology of Amphibians. Diversity, 2022, 14, 739:1–739:18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson, J.R.; Whitfield, S.M.; Sredl, M.J. A Recovery Engine Strategy for Amphibian Conservation in the Context of Disease. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 236, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, D.A. , Staerk, J.; Colchero, F.; Vaupel, J.W. Data Gaps and Opportunities for Comparative and Conservation Biology. Conserv. Biol. 2019, 16, 9658–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapley, B.; Michaels, C.J.; Gumbs, R.; Böhm, M.; Luedtke, J.; Pearce-Kelly, P.; Jodi, J.L.; Rowley, J.J.L. The Disparity Between Species Description and Conservation Assessment: A Case Study in Taxa with High Rates of Species Discovery. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 220, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streicher, J.W.; Sadler, R.; Loader, SP. Amphibian Taxonomy: Early 21st Century Case Studies. J. Nat. Hist. 2020, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, J.; Young, R.P.; Hilton-Taylor, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Stuart, S.N.; Milner-Gulland, E.J. A Framework for Evaluating the Impact of the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN 2023. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2022-2. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Garner, T.W.J.; Stephen, I.; Wombwell, E.; Fisher, M.C. The Amphibian Trade: Bans or Best Practice? EcoHealth 2009, 6, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, T. S. Conservation and the future of amphibians, In Kemp, T. S., Amphibians: A Very Short Introduction; online edn, Oxford Academic, Oxford, USA, 2021; pp. 117–130, ISBN 9780198842989.
- Gerson, H. International Trade in Amphibians: a Customs Perspective. Alytes 2012, 29, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer, M.A.; Hoover, C.; Dodd Jr, C.K. Challenges in Evaluating the Impact of the Trade in Amphibians and Reptiles on Wild Populations. BioScience 2005, 55, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp C., R. , A., Lemm, J., Grant, T., Jackintell, L. Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 199–209, ISBN: 9780520238541.Iguanas. In Iguanas: Biology and Conservation. Alberts, A., Lemm, J., Grant, T., Jackintell, L. Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CO, USA, 2005; University of California Press: Berkeley, CO, USA, 2005; pp. 199–209. ISBN 9780520238541. [Google Scholar]
- Langridge, J.; Sordello, R.; Reyjol, Y. Outcomes of Wildlife Translocations in Protected Areas: What is the Type and Extent of Existing Evidence? A Systematic Map Protocol. Environ. Evid. 2020, 9, 16:1–16:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDee, OA.; Handler, S.D.; Hoving, C.L.; Swanston, C.W.; Zuckerberg, B. Preparing Wildlife for Climate Change: How Far Have We Come? Journal of Wildlife Management 2021, 85, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The SER International Primer on Ecological Restoration (Version 2: October, 2004). Society for Ecological Restoration International Science & Policy Working Group, Available online: https://cdn.ymaws.com/www.ser.org/resource/resmgr/custompages/publications/ser_publications/ser_primer.pdf.
- Galatowitsch, S.; Bohnen, J. Predicting Restoration Outcomes Based on Organizational and Ecological Factors. Restoration Ecol. 2020, 28, 1201–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, O.; Lees, C.; Wilken, J.; Schwitzer, C. The One Plan approach: The Philosophy and Implementation of CBSG's Approach to Integrated Species Conservation Planning. WAZA Mag. 2013, 14, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, R.A.; Lissette Pavajeau, L. Captive Breeding, Reintroduction, and the Conservation of Amphibians. Conserv. Biol. 2008, 22, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelson III, J.R. Frogs in Glass Boxes: Responses of Zoos to Global Amphibian Extinctions. In The Ark and Beyond: The Evolution of Zoo and Aquarium Conservation; Minteer, B.A., Maienschein, J., Collins, J.P., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, Ch, USA, 2018; pp. 298–313. ISBN 9780226538464. [Google Scholar]
- Canessa, S. No Conservation without Representation? Linked Decisions and Priority Setting in Amphibian ex situ programmes. Anim. Conserv. 2017, 20, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, R.A. Which Amphibians Should Qualify for the Ark? Anim. Conserv. 2017, 20, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, B.C.; Guarino, F.; Osborne, W.; Hunter, D.A.; Skerratt, L.F.; Driscoll, D.A. Decline and Re-expansion of an Amphibian with High Prevalence of Chytrid Fungus. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, K.M.; Civitello, D.J. Ecological and Evolutionary Challenges for Wildlife Vaccination. Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballou, J.D.; Lacy, R.C.; Traylor-Holzer, K.; Bauman, K.; Ivy, J.A.; Asa, C. Strategies for Establishing and Using Genome Resource Banks to Protect Genetic Diversity in Conservation Breeding Programs. Zoo Biol. 2022, 42, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, I.; Julien, A.R.; Kouba, A.J.; Councell, K.R.; Barber, B.; Pacheco, C.; Kouba, C.K. Linking in situ and ex situ Populations of the Endangered Puerto Rican Crested Toad (Peltophryne lemur) through Genome Banking. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2021, 3, e525:1–e525:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, I.J.; Lampert, S.S.; Kouba, C.K.; Morin, D.J.; Kouba, A.J. Development of an Amphibian Sperm Biobanking Protocol for Genetic Management and Population Sustainability. Conserv. Physiol. 2022, 10, coac032:1–coac032:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, I.J.; Chen, L.; Lampert, S.S.; Kouba, C.K.; Barber, D.; Smith, D.; Cobos, C.; Kouba, A.J. Applying Sperm Collection and Cryopreservation Protocols Developed in a Model Amphibian to Three Threatened Anuran Species Targeted for Biobanking Management. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 277, 109850:1–109850:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, C.K. ; Silla, A.J., Kouba, A.J., Heatwole, H., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 188-203, ISBN 9781032372075.Banks. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians; Silla, A.J., Kouba, A.J., Heatwole, H., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 188–203. ISBN 9781032372075. [Google Scholar]
- Upton, R.; The University of Newcastle, Australia. Career Summary. Available online: https://www.newcastle.edu.au/profile/rose-upton (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Ficetola, G.F.; Rondinini, C.; Bonardi, A.; Baisero, D; Padoa-Schioppa, E. Habitat Availability for Amphibians and Extinction Threat: a Global Analysis. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger-Tal, O.; Blumstein, D.T.; Swaisgood, R.R. Conservation Translocations: a Review of Common Difficulties and Promising Directions. Anim. Conserv. 2020, 23, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G. F. , Carlo R.; Bonardi A.; Katariya V.; Schioppa E. P.; Angulo A. An Evaluation of the Robustness of Global Amphibian Range Maps. J. Biogeogr. 2014, 41, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphibian Population Management Guidelines. Created at an Amphibian Population Management Workshop; 2007 -11; San Diego, CA, USA. Schad, K., Ed.; Amphibian Ark, 2008, 31 p. Available online: https://www.amphibianark.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/AArk-Amphibian-Population-Management-Guidelines.pdf. 10 December.
- Zippel, K.; Johnson, K.; Agliardo, R.G.; Gibson, R.; McFadden, M.; Browne, R.; Martinez, C.M.; Townsend, E. The Amphibian ARK: A Global Community for Ex situ Conservation of Amphibians. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2011, 6, 340–352. [Google Scholar]
- Conservation Needs Assessments. AArk. 2023. Available online: https://www.conservationneeds.org/default.aspx (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- EDGE. Evolutionary Distinct and Globally Endangered. Zoological Society of London. Available online: https://www.edgeofexistence.org/species/ (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Gumbs, R.; Gray, C.L.; Bohm, M; Burfield, I. J.; Couchman, O.R.; Faith, D.P.; Forest, F.; Hoffmann, M.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Jetz, W. et al. The EDGE Protocol: Advancing the Prioritisation of Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered Species for Practical Conservation Action. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3001991:1–e3001991:22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, S.D.; Bickford, D.P. Amphibians Over the Edge: Silent Extinction Risk of Data Deficient Species. Divers. Distrib. 2014, 20, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betts, J.; Young, R.P.; Hilton-Taylor, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Rodríguez, J.P.; Stuart, S.N. , Milner-Gulland, E.J. A Framework for Evaluating the Impact of the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 34, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Responsible Herpetological Project. Available online: https://responsibleherpetoculture.foundation/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Mansour, N.; Lahnsteiner, F.; Patzner, R.A. Collection of Gametes from Live Axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum, and Standardization of in vitro Fertilization. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figiel, C. Cryopreservation of Sperm from the Axolotl Ambystoma mexicanum: Implications for Conservation. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 8, 748–855. [Google Scholar]
- Marcec, R.M. Development of Assisted Reproductive Technologies for Endangered North American Salamanders by Ruth Marie Marcec. Faculty of Mississippi State University, Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Animal Physiology, 2016; Mississippi, MS, USA.
- Figiel Jr., C. R. Cold Storage of Sperm from the Axolotl, Ambystoma mexicanum. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2022, 15, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
- Figiel Jr., C. R. Effects of Water Temperature on Gonads Growth in Ambystoma mexicanum Axolotl Salamanders. Animals 2023, 13, 874:1–874:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi-Sugiura, Y.; Tanaka, E.M. Artificial Insemination in Axolotl. In Salamanders. Methods in Molecular Biology; Seifert, A.W., Currie, J.D., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2023; Volume 2562, pp. 417–423. ISBN 978-1-0716-2659-7. [Google Scholar]
- Marcec-Greaves, R.M.; Kouba, C.K.; Willard, S.T.; Kouba, A.J. Ovarian Ultrasound Analysis for Developing Temporal and Spatially Explicit Hormone Regimens for Induced Ovulation and Egg deposition in the Tiger Salamander (Ambystoma tigrinum). Theriogenology Wild 2023, 2, 100038:1–100038:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, S.S.; Burger, I.J.; Julien, A.R.; Gillis, A.B.; Kouba, A.J.; Barber, D.; Kouba, C.K. Sperm Cryopreservation as a Tool for Amphibian Conservation: Production of F2 Generation Offspring from Cryo-Produced F1 Progeny. Animals 2023, 13, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankham, R. Genetics and extinction. Biol. Conserv. 2005, 126, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVISE, J. C. Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species; JSTOR: Harvard University Press, 2000; ISBN 978-0-674-26870-8. [Google Scholar]
- Frankham, R.; Ballou, J.D.; Briscoe, D.A. Introduction to Conservation Genetics; Cambridge University Press, 2002, ISBN 9780511808999.
- Onley, I.R.; Moseby, K.E.; Austin, J.J. Genomic Approaches for Conservation Management in Australia under Climate Change. Life 2021, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.E., Koepfli, K. The Role of Genomics in Conservation and Reproductive Sciences. In: Holt, W., Brown, J., Comizzoli, P. (eds) Reproductive Sciences in Animal Conservation. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 753. Springer, New York, NY. 2014.
- Ralls, K.; Ballou, J.D.; Dudash, M.R.; Eldridge, M.D.B.; Fenster, C.B.; Lacy, R.C.; Sunnucks, P.; Frankham, R. Call for a Paradigm Shift in the Genetic Management of Fragmented Populations. Conserv. Lett. 2018, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankham, R. Do Island Populations have less Genetic Variation than Mainland Populations? Heredity 1997, 78, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmands, S. Between a Rock and a Hard Place: Evaluating the Relative Risks of Inbreeding and Outbreeding for Conservation and Management. Molec. Ecol. 2007, 16, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, S.C.; Seigel, R.A. Annual Variation in the Population Ecology of the Endangered Gopher Frog, Rana sevosa Goin and Netting. Copeia 2002, 2002, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielman, D.; Brook, B. W.; Frankham, R. Most Species are not Driven to Extinction before Genetic Factors Impact Them. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U S A, 2004, 101, 15261–15264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The black-footed ferret project. Revive and Restore. Available online: https://reviverestore.org/projects/black-footed-ferret/ (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Willi, Y.; Hoffmann, A.A. Demographic Factors and Genetic Variation Influence Population Persistence under Environmental Change. J. Evol. Biol. 2009, 22, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.A.; Lacy, R.C. Genome Resource Banking for Species Conservation: Selection of Sperm Donors. Cryobiology 1995, 32, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, P.G.; Silla, A.J. Genetic Management of Threatened Amphibians: Using Artificial Fertilisation Technologies to Facilitate Genetic Rescue and Assisted Gene Flow. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians; Silla A.J., Kouba A.J., Heatwole H., Eds.; CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia, 2022; pp. 124–146, ISBN 9781032372075.
- Farquharson, K.A.; Hogg, C.J.; Grueber, C.E. A Meta-analysis of Birth-origin Effects on Reproduction in Diverse Captive Environments. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1055:1–1055:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastas, Z.M.; Byrne, P.G.; O’Brien, J.K.; Hobbs, R.J.; Upton, R.; Silla, A.J. The Increasing Role of Short-Term Sperm Storage and Cryopreservation in Conserving Threatened Amphibian Species. Animals 2023, 13, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebee, T.J.C. Conservation Genetics of Amphibians. Heredity 2005, 95, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, R.S.; Garrett, A.D.; Huber, K.E.; Hargarten, H.; Pespeni, M.H. Rare Genetic Variation and Balanced Polymorphisms are Important for Survival in Global Change Conditions. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2019, 286, 20190943:1–20190943:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnal, V.K.; Wildt, D.E.; Bird, D.M.; Monfort, S.L.; Ballou, J.D. Computer Simulations to Determine the Efficacy of Different Genome Resource Banking Strategies for Maintaining Genetic Diversity. Cryobiology 2002, 44, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahony, M.J.; Clulow, J. Appendix 2. Cryopreservation and Reconstitution Technologies: A Proposal to Establish A Genome Resource Bank For Threatened Australian Amphibians. In Guidelines for minimising disease risks associated with captive breeding, raising and restocking programs for Australian frogs; Murray, K., Skerratt, L.F., Marantelli, G., Berger, L., Hunter, D., et al., Eds.; Canberra: Australian Government, Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities, 2011, ID 1011-1151. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, A.J. Genome Resource Banks as a Tool for Amphibian Conservation. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians; Silla A.J., Kouba A.J., Heatwole H., Eds.; CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia, 2022; pp. 188–203, ISBN 9781032372075.
- Witzenberger, K.A.; Hochkirch, A. Ex situ Conservation Genetics: a Review of Molecular Studies on the Genetic Consequences of Captive Breeding Programs for Endangered Animal Species. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 1843–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A. Captive Breeding Genetics and Reintroduction Success. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 2915–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, V.; Barkha, S.; Venu, G.; Gowri, M.; Lisa, G.; Kishor. G.B. Ex-situ Management of Amphibians in Indian Zoos. Central Zoo Authority, New Delhi, 2022; pp.102.
- AArk Online Founder Calculation Tool. Available online: https://www.amphibianark.org/tools/Founder%20calculation%20tool.htm (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Frankham, R. , Ballou, J. D., Briscoe, D. A. Introduction to Conservation Genetics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, UK, 2010; p. 644. ISBN -0521702712. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, E.M.; Ferna´ndez-Beaskoetxea, S.; Godoy, J.A.; Tobler, U.; Schmidt, B.R.; Bosch, J. Genetic Management of an Amphibian Population after Chyridiomycosis Outbreak. Conserv. Genet. 2015, 16, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Benítez, S.; Morente-López, J.; Teso, M.L.R.; Lara-Romero, C.; García-Fernández, A.; Torres, E.; Iriondo, J.M. Evaluating Assisted Gene Flow in Marginal Populations of a High Mountain Species. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 638837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grummer, J.A.; Booker, T.R.; Matthey-Doret, R.; Nietlisbach, P.; Thomaz, A.T.; Whitlock, M.C. The Immediate Costs and Long-term Benefits of Assisted Gene Flow in Large Populations. Conserv. Biol. 2022, 36, 13911:1–13911:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, B.C.; Hunter, D.A.; Skerratt, L.F.; Brannelly, L.A.; Driscoll, D.A. Low Impact of Chytridiomycosis on Frog Recruitment Enables Persistence in Refuges Despite High Adult Mortality. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 182, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crates, R.; Stojanovic, D.; Heinsohn, R. The Phenotypic Costs of Captivity. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2023, 98, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, S.E.; Klop-Toker, K.; Wallace, S.; Kelly, O.; Callen, A.; Seeto, R.; Mahony, S.V.; Hayward, M.W.; Mahony, M.J. Uncovering Inbreeding, Small Populations, and Strong Genetic Isolation in an Australian Threatened Frog, Litoria littlejohni. Conserv. Genet. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penhos, J.C.; Cornfield, J.; Cordero, F. Jr. Seasonal Variation of Spermiation Produced by Chorionic Gonadotropin in the Frog. Rev. Soc. Argent. Biol. 1954, 87, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arregui, L.; Bóveda, P.; Gosálvez, J.; Kouba, A.J. Effect of Seasonality on Hormonally Induced Sperm in Epidalea calamita (Amphibia, Anura, Bufonidae) and its Refrigerated and Cryopreserved Storage. Aquaculture 2020, 529, e735677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L. F.; Waller, D. M. Inbreeding Effects in Wild Populations. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.H. , Frankham, R. Correlation Between Fitness and Genetic Diversity. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, R. Sexual Selection and Sexual Dimorphism in the Amphibia. Copeia 1979, 2, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taborsky, M.; Oliveira, R.F.; Brockmann, H.J. The Evolution of Alternative Reproductive Tactics: Concepts and Questions. In Alternative Reproductive Tactics: An Integrative Approach; Oliveira, R., Taborsky, M., Brockmann, H.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieites, D.R.; Nieto-Román, S.; Barluenga, M.; Palanca, A.; Vences, M.; Meyer, A. Post-mating Clutch Piracy in an Amphibian. Nature 2004, 431, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannelly, L.A.; Webb, R.; Skerratt, L.F.; Berger, L. Amphibians with Infectious Disease Increase their Reproductive Effort: Evidence for the Terminal Investment Hypothesis. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 150251:1–150251:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, R.K.; Li, H.; Vaughan, M. Sexually Mediated Shedding of Myxobolus fallax Spores During Spermiation of Litoria fallax (anura). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 72, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiras, J.C. An Overview on the Myxosporean Parasites in Amphibians and Reptiles. Acta Parasitol. 2005, 50, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, R. K.; Li, H., Seratt, J.; Kouba. A. Progesterone Improves the Number and Quality of Hormone Induced Fowler toad (Bufo fowleri) Oocytes. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol 2006, 4, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.K.; Seratt, J.; Vance, C.; Kouba, A. Hormonal Priming, Induction of Ovulation and In-vitro Fertilization of the Endangered Wyoming Toad (Bufo baxteri). Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol 2006, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.K. Seasonal Cycle in Anuran (Amphibia) Testis: The Endocrine and Environmental Controls. Bollettino di zoologia 1976, 43, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.K.; Tammaro, L.; Di Meglio, M.; Lela, L.; Di Matteo, L.; Chieffi, G. Circannual Testicular Rhythm in the Green Frog, Rana esculenta. Bollettino di zoologia 1981, 48, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poo, S.; Hinkson, K.M.; Stege, E. Sperm Output and Body Condition are Maintained Independently of Hibernation in an Endangered Temperate Amphibian. Reprod. Fert. Dev. 2019, 31, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poo, S.; Hinkson, K.M. Applying Cryopreservation to Anuran Conservation Biology. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2019, 1, 91:1–91:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poo, S.; Bogisich, A.; Mack, M.; Lynn, B.K.; Devan-Song, A. Post-release Comparisons of Amphibian Growth reveal Challenges with Sperm Cryopreservation as a Conservation Tool. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2022, 4, 572:1–572:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, G. 2015. Available online: https://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2015/from-corgis-to-corn-a-brief-look-at-the-long-history-of-gmo-technology/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Eskew, E.A.; Shock, B.C.; LaDouceur, E.E.B.; Keel, K.; Miller, M.R.; Foley, J.E.; Todd, B.D. Gene Expression Differs in Susceptible and Resistant Amphibians Exposed to Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 170910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amphibian Ark and the IUCN SSC ART and Biobanking Working Group webinars. Available online: https://www.amphibianark.org/art-videos/ (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Kaurova S., A.; Chekurova N., R.; Melnikova E., V.; Uteshev V., K.; Gakhova E., N. Cryopreservation of Frog Rana temporaria Sperm Without Loss of Fertilizing Capacity. In Proceedings of the 14th Working Meeting, Pushchino, 13–15 May 1996; 1996; Gakhova, E.N., Karnaukhov, V.N., Eds.; Pushchino Press: Pushchino, Russian; pp. 106–108. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Kaurova S., A.; Uteshev V., K.; Chekurova N., R.; Gakhova E., N. Cryopreservation of Testis of Frog Rana temporaria. Infusionsther Transfusionsmed 1997, 24, 379. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, R. K.; Clulow, J.; Mahony, M.; Clark, A. Successful Recovery of Motility and Fertility of Cryopreserved Cane Toad (Bufo marinus) sperm. Cryobiology 1998, 37, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishova, N. R. , Utishev, V. K., Kaurova, S. A., Browne, R. K., Gakhova, E. N. Cryopreservation of Hormonally Induced Sperm for the Conservation of Threatened Amphibians with Rana temporaria as a Model Species. Theriogenology 2011, 75, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W.M.S.; Burch, R.L. The Principles of Humane Experimental Technique; Universities Federation for Animal Welfare: Wheathampstead, UK, 1959; ISBN 0-900767-78-2. [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum, J.; Bennett, B.T. Russell and Burch's 3Rs Then and Now: The Need for Clarity in Definition and Purpose. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2015, 54, 120–132. [Google Scholar]
- NC3R. National Center for the Replacement, Reduction, and Refinement of Animals in Research. Available online: https://www.nc3rs.org.uk/who-we-are/3rs (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Ulloa, J.S.; Aubin, T.; Llusia, D.; Courtois, É.A.; Fouquet, A.; Gaucher, P.; Pavoine, S.; Sueur, J. Explosive Breeding in Tropical Anurans: Environmental Triggers, Community Composition and Acoustic Structure. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 28:1–28:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trudeau, V.L.; Raven, B.H.; Pahuja, H.K.; Narayan, E. J 2022. Chapter 4. Hormonal Control of Amphibian Reproduction. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians, Silla, A.J., Kouba, A.J., Heatwole, H., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 9781032372075. [Google Scholar]
- Zimkus, B.M.; Hassapakis, C.L.; Houck, M.L. Integrating Current Methods for the Preservation of Amphibian Genetic Resources and Viable Tissues to Achieve Best Practices for Species Conservation. Amphib. Reptile. Conserv. 2018, 12, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, R.L.; Mooney, A.; Pettit, M.T.; Bolton, A.E.; Morgan, L.; Drake, G.J.; Appeltant, R.; Walker, S.L.; Gillis, J.D.; Hvilsom, C. Resurrecting Biodiversity: Advanced Assisted Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking. Reprod. Fert. 2022, 3, R121–R146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, N.C.; Robinson, W.D. Current and forthcoming Approaches for Benchmarking Genetic and Genomic Diversity. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 622603:1–622603:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krell, F.T.; Wheeler, Q.D. Specimen Collection: Plan for the Future. Science 2014, 344, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.A.; Aleixo, A.; Allen, G.; Almeda, F.; Baldwin, C.C.; Barclay, M.V.L.; Bates, M.; Bauer, A.M.; Benzoni, F.; Berns; C.M. et al. Specimen Collection: An Essential Tool. Science 2014, 344, 814–815. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hopkins, A.J.M.; Davis, R.A. Going, Going, Gone The Diminishing Capacity of Museum Specimen Collections to Address Global Change Research: A Case Study on Urban Reptiles. Animals 2023, 13, 1078:1–1078:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Hanlon, S.J.; Rieux, A.; Farrer, R.A.; Rosa, G.M.; Waldman, B.; Bataille, A.; Kosch, T.A.; Murray, K.A.; Brankovics, B.; Fumagalli, M.; et al. Recent Asian Origin of Chytrid Fungi causing Global Amphibian Declines. Science 2018, 360, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnity, D.; Reinsch, S.R.; Schwartz, H.; Trudeau, V.; Browne, R.K. Semen and Egg Collection, Sperm Cryopreservation, and in vitro Fertilisation with Threatened North American Giant Salamanders (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis). Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2021, 34, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamer, A.J.; Mahony, M.J. 2007. Life History of an Endangered Amphibian Challenges the Declining Species Paradigm. Australian J. Zool. 2007, 55, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.Y.; Jamieson, B.G.M. The Ultrastructure of the Spermatozoa of Bufonid and Hylid Frogs (Anure, Amphibia): Implications for Phylogeny and Fertilisation Biology. Zool. Scripta 1993, 22, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltinga, D.M.; Jamieson, B.G.M. Spermatogenesis and the Mature Spermatozoon: Form, Function and Phylogenetic Implications, In Reproductive biology and phylogeny of Anura; Jamieson, G.M., Ed.; Science Publishers Inc.: NH, USA. 2013; Volume 2, pp. 119–252. ISBN 1-57808-288-9. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, T.L.; Obringer, A.R. Reproductive Research and the Worldwide Amphibian Extinction Crisis. In Reproductive sciences and integrated conservation, Holt, W.V., Pickard A.R., Rodger J.C., Wildt D.E. Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003; pp. 359–374. ISBN 0-521. [Google Scholar]
- Kouba, A.J.; Vance, C.K.; Frommeyer, M.A.; Roth, T.L. Structural and Functional Aspects of Bufo americanus Spermatozoa: Effects of Inactivation and Reactivation. J. Exp. Zool. 2003, 295, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.M.; Moore, M.G.; Willis, E.L.; Kouba, A.J.; Kouba, C.K. The Impact of Time and Environmental Factors on the Mitochondrial Vesicle and Subsequent Motility of Amphibian Sperm. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 268, 11119:1–11119:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silla, A.J.; Langhorne, C.J. Protocols for Hormonally Induced Sperm. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians, Silla, A.J., Kouba, A.J., Heatwole, H., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2022; pp. 106–123. ISBN 9781486313341. [Google Scholar]
- Herbert, D. Studies of Assisted Reproduction in the Spotted Grass Frog Limnodynastes tasmaniensis: Ovulation, Early Development and Microinjection (ICSI), Masters by Research thesis; The University of Newcastle, Australia, 2004.
- Naranjo, R.E.; Naydenova, E.; Proaño-Bolaños, C.; Vizuete, K.; Debut, A.; Arias, M.T.; Coloma, L.A. Development of Assisted Reproductive Technologies for the Conservation of Atelopus sp. (spumarius complex). Cryobiology, 2022, 105, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, R.; Clulow, S.; Calatayud, N.E.; Colyvas, K.; Seeto, R.G.Y.; Wong, L.A.M.; Mahony, M.J.; Clulow, J. Generation of Reproductively Mature Offspring from the Endangered Green and Golden Bell Frog Litoriaaurea using Cryopreserved Spermatozoa. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2021, 33, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, R.; Clulow, S.; Colyvas, K.; Mahony, M.; Clulow, J. Paradigm Shift in Frog Sperm Cryopreservation: Reduced Role for Non-penetrating Cryoprotectants. Reproduction 2023, 165, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, R.; Clulow, S.; Mahony, M.J.; Clulow, J. Generation of a Sexually Mature Individual of the Eastern Dwarf Tree Frog Litoriafallax, from Cryopreserved Testicular Macerates: Proof of Capacity of Cryopreserved Sperm Derived Offspring to Complete Development. Conserv. Physiol. 2018, 6, coy043:1–coy043:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, K.M’; Langhorne, C.J.; Vance, C.K.; Willard, S,T.; Kouba, A.J. Ultrasound imaging improves hormone therapy strategies for induction of ovulation and in vitro fertilization in the endangered dusky gopher frog (Lithobates sevosa). Conserv. Physiol. 2018, 6, coy020. [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.K.; Clulow, J.; Mahony, M. Short-term Storage of Cane Toad (Bufo marinus) Gametes. Reproduction 2001, 121, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, J.M.; Cree, A.; Molinia, F.C; Arregui, L.; Bishop, P.J. Hormone Treatment does not Reliably Induce Spermiation or Mating in Hamilton’s frog from the Archaic Leiopelmatid Lineage. Reprod. Fert. Devel. 2021, 34, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, E.L.; Gillis, A.B.; Kouba, A.J.; Barber, D.; Poole, V.; Marcec-Greaves, R.M.; Kouba, C.K. Sperm Collection and Cryopreservation for Threatened Newt Species. Cryobiology 2020, 94, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uteshev, V. K. , Kaurova, S. A., Shishova, N. V., Stolyarov, S. D., Browne, R. K., Gakhova, E. N. In vitro Fertilisation with Hormonally Induced Sperm and Eggs from Sharp-ribbed Newts Pleurodeles waltl. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2015, 22, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.G.; Marcec-Greaves, R. Topical Application of Hormone Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone (GnRH-A) Stimulates Reproduction in the Endangered Texas Blind Salamander (Eurycea rathbuni). Conser. Sci. Pract. 2022, 4, e609:1–e609:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.N.; Vagga, A. Cryopreservation: A Review Article. Cureus 2022, 14, e31564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaurova, S.A.; Browne, R.K.; Uteshev, V.K. Antibiotics for the Refrigerated Storage at 4 C of Hormonally Induced European Common Frog (Rana temporaria) Spermatozoa. Theriogenology Wild 2022, 1, 100009:1–100009:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, S.; Kroll, K.L.; Amaya, E. Generation of Transgenic Xenopus laevis: III. Sperm Nuclear Transplantation. CSH Protoc. 2007, 18, pdb.prot4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K. , Simpson, D., Gurdon, J. B. Manipulation and in vitro Maturation of Xenopus laevis Oocytes, followed by Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, to Study Embryonic Development. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 96, e52496:1–e52496:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Siqueira-Silva, D.H.; Saito, T.; dos Santos-Silva, A.P.; da Silva Costa, R.; Psenicka, M.; Yasui, G.S. Biotechnology Applied to Fish Reproduction: Tools for Conservation. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosla, K.; Kangas, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Daly, J.; Hagedorn, M.; Bischof, J. Cryopreservation and Laser Nanowarming of Zebrafish Embryos Followed by Hatching and Spawning. Adv. Biosyst. 2020, 4, e2000138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitina, L.A. Nuclear Transplantation in Fish and Amphibians. Physiol. Gen. Biol. Rev. 1997, 13, 35–72. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, R.; King, T.J. Transplantation of Living Nuclei from Blastula Cells into Enucleated Frogs’ Eggs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1952, 38, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambuichi, H. The Roles of the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm in Development. I. An Interspecific Hybrid Frog, Developed from a Combination of Rana nigromaculata nigromaculata Cytoplasm and a Diploid Nucleus of Rana nigromaculata brevipoda. J. Sci. Hiroshima-Univ., Ser. B Div. 1957, 1, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.A. Transplanation of Nuclei Between Rana pipiens and Rana sylvatica. Exp. Cell. Res. 1958, 14, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambuichi, H. The Roles of the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm in Development. III. Diploid Nucleocytoplasmic Hybrids, Derived from Rana nigromaculata brevipoda Cytoplasm and Rana nigromaculata nigromaculata Nuclei. J. Sci. Hiroshima Univ. 1961, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon, J.B. Adult Frogs Derived from the Nuclei of Single Somatic Cells. Dev. Biol. 1962, 4, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennan, S. Nucleocytoplasmic Hybrids Between Rana pipiens and Rana palustris. I. Analysis of the Developmental Properties of the Nuclei by Means of Nuclear Transplantation. Dev. Biol. 1963, 11, 243–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Nishioka, M. Reciprocal Diploid Nucleocytoplasmic Hybrids between Two Species of Japanese Pond Frogs and their Offspring. J. Sci. Hiroshima Univ., Ser. B., Div. 1, Zoology 1963, 21, 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, T.; Nishioka, M. Nucleo-cytoplasmic Hybrid Frog between Two Species of Japanese Brown Frogs and their Offspring. J. Sci. Hiroshima Univ., Ser. B., Div. 1, Zoology 1963, 21, 107–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, T.; Nishioka, M. Viability and Abnormalities of the Offspring of Nucleo-cytoplasmic Hybrids between Rana japonica and Rana ornativentris. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphibian Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1972, 1, 95–209. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, M. Abnormalities of the Offspring of Nucleo-cytoplasmic Hybrids between Rana nigromaculata and Rana brevipoda. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphibian Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1972, 1, 1–94. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, M. Nucleo-cytoplasmic Hybrids between Rana japonica and Rana temporaria temporaria. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphibian Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1, 211–243.
- Nishioka, M. Nucleo-cytoplasmic Hybrids between Rana brevipoda and Rana plancyi chosenica. Sci. Rep. Lab. Amphibian Biol. Hiroshima Univ. 1, 259–275.
- Gallien, L.; Aimar, C. A New Mode of Gemellarity, Effected by Nuclear Graft in Urodele Amphibia of the Genus Pleurodeles. C. R. Acad. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci. D. 1971, 272, 3348–3351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gallien, C.L.; Aimar, C.; Guillet, F. Nucleocytoplasmic Interactions During Ontogenesis in Individuals Obtained by Intra- and Interspecific Nuclear Transplantation in the Genus Pleurodeles (Urodale Amphibian. Dev. Biol. 1973, 33, 154–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhzherin, S.; Morozov-Leonov, S.; Nekrasova, O.; Rostovskaya, O. Geographic Peculiarities of Structure and Hemicloning Reproduction of Pelophylax esculentus Water Frog Complex (Anura, Ranidae) Populations in the East European Plain within Ukraine. Amphibia-Reptilia 2023, 44, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznick, D.; Travis, J. The Empirical Study of Adaptation in Natural Populations. Adaptation, Ch. 8 1996, 243–289.
- Rudin-Bitterli, T.S.; Evans, J.P.; Mitchell, N.J. Geographic Variation in Adult and Embryonic Desiccation Tolerance in a Terrestrial Breeding Frog. Evolution 2020, 74, 1186–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antwis, R.E.; Browne, R.K. Ultraviolet Radiation and Vitamin D3 in Amphibian Health, Behaviour, Diet and Conservation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 154, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschooren, E.; Brown, R.K.; Vercammen, F.; Pereboom, J. Ultraviolet B Radiation (UV-B) and the Growth and Skeletal Development of the Amazonian Milk Frog (Trachycephalus resinifictrix) from Metamorphosis. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. 2011, 2, 34–42. [Google Scholar]
- Baines, F.M.; Chattell, J.; Dale, J.; Garrick, D.; Gill, I.; Goetz, M.; Skelton, T.; Swatman, M. How much UVB does my reptile need? The UV-Tool, a guide to the selection of UV lighting for reptiles and amphibians in captivity. J. Zoo Aquarium Res. 2016, 4, 42–63. [Google Scholar]
- Tapley, B.; Rendle, M.; Baines, F.M.; Goetz, M.; Bradfield, K.S.; Rood, D.; Lopez, J.; Garcia, G.; Routh, A. Meeting Ultraviolet B Radiation Requirements of Amphibians in Captivity: a Case Study with Mountain Chicken Frogs (Leptodactylus fallax) and General Recommendations for Pre-release Health Screening. Zoo Biol. 2015, 34, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryder. O.A. Chapter 11. Bioresource Banking Efforts in Support of Amphibian Conservation. In Amphibian Conservation Action Plan. Gascon, C., Collins, J.P., Moore, R.D., Church, D.R., McKay, J., Mendelson JR III, E. Eds.; IUCN/SSC Amphibian Specialist Group: Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-2-8317-1008-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pukazhenthi, B.S.; Pelican, K. ; Gascon, C., Collins, J.P., Moore, R.D., Church, D.R., McKay, J., Mendelson JR III, E. Eds.; IUCN/SSC Amphibian Specialist Group: Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp.38−39, ISBN 978-2-8317-1008-2.Banking. In Amphibian Conservation Action Plan; Gascon, C., Collins, J.P., Moore, R.D., Church, D.R., McKay, J., Mendelson JR III, E., Eds.; IUCN/SSC Amphibian Specialist Group: Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK, 2007; IUCN/SSC Amphibian Specialist Group: Gland, Switzerland and Cambridge, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-2-8317-1008-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ghose, S.L.; Yap, T.A.; Byrne, A.Q.; Sulaeman, H.; Rosenblum, E.B.; Chan-Alvarado, A.; Chaukulkar, S.; Greenbaum, E.; Koo, M.S.; Kouete, M.T.; et al. Continent-wide Recent Emergence of a Global Pathogen in African Amphibians. Front. Conserv. Sci 2023, 4, 1069490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.J.; Carter, E.D.; Piovia-Scott, J.J.; Cusaac, P.W.; Peterson, A.C.; Whetstone, R.D.; Hertz, A.; Muniz-Torres, A.Y.; Bletz, M.C.; Woodhams, D.C. Broad Host Susceptibility of North American Amphibian Species to Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans Suggests High Invasion Potential and Biodiversity Risk. Nat. Commun 2023, 14, 3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, B.C.; Hollanders, M.; Hoffmann, E.P.; Newell, D.A.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; McFadden, M.; Gilbert, D.J.; Grogan, L.F. Conservation Translocations for Amphibian Species Threatened by Chytrid Fungus: A Review, Conceptual Framework, and Recommendations. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2021, 3, e524:1–e524:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, B.C.; Pasmans, F.; Skerratt, L.F.; Berger, L.; Martel, A.; Beukema, W.; Acevedo, A.A.; Burrowes, P.A.; Carvalho, T.; Catenazzi, A.; et al. Amphibian Fungal Panzootic causes Catastrophic and Ongoing Loss of Biodiversity. Science 2019, 363, 1459–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, E.H.; Amburgey, S.M.; Gratwicke, B.; Chaves, V.A.; Belasen, A.M.; Bickford, D.; Bruhl, C.A.; Calatayud, N.E.; Clemann, N.; Clulow, S. Amphibian Conservation in the Anthropocene. Biol. Conserv. 2023, 236, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taronga Conservation Society Australia. Available online: https://taronga.org.au/conservation-and-science/current-research/frog-conservation-biobanking (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Nature’s SAFE. Saving animals from extinction and halt biodiversity loss. Available online: https://www.natures-safe.com/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- United Nations Convention on Biodiversity. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/observances/biological-diversity-day/convention (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- da Cruz, R.E.; da Silva Olivera, H.G.; Salvarani, F.M. Wild Animals Biobanks: Literature Review. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e48411831268:1–e48411831268:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Society for Biological and Environmental Repositories [ISBER]. Available online: https://www.isber.org/page/BPR (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- San Diego Zoo Wildlife Alliance's Frozen Zoo. Available online: https://science.sandiegozoo.org/resources/frozen-zoo%C2%AE (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Chinese Academy of Science Kunming cell bank. Available online: http://english.kiz.cas.cn/gre/skl_Facility/ (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Hvilsom, C.; Mekarska, A; de Man, D. Play it Cool! How EAZA’s Collaborative Banking of Samples Helps Improve Population Management and Conservation. World Association of Zoos and Aquariums (WAZA) News 2022, 3, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Biodiversity Biobanks South Africa. Available online: https://bbsa.org.za/ (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Conde, D.A. , Staerk, J.; Colchero, F.; da Silva, R.; Scholey, J.; Baden, H,M.; Jouvet L.; Syed, H.; Jongejans, E.; Meiri. S.; Gaillard, J. et al. Data Gaps and Opportunities for Comparative and Conservation Biology. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 27, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, O.A. , Onuma, M. Viable Cell Culture Banking for Biodiversity Characterization and Conservation. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2018, 6, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CryoArks. Animal Biobanking for Research and Conservation. Available online: https://www.cryoarks.org/ (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- ABC, SG. IUCN Species Survival Commission, Animal Biobanking for Conservation Specialist Group. 2023. Available online: https://www.iucn.org/our-union/commissions/group/iucn-ssc-animal-biobanking-conservation-specialist-group (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Johnson, J.; A; Ruta, G; Baldos, U; Cervigni, R; Chonabayashi, S; Corong, E; Gavryliuk, O; Gerber, J; Hertel, T; Nootenboom, C. et al. 2021. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10986/35882 (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Roe, D.; Holland, E.; Nisi, N. Mitchell, T.; Tasnim, T. Loss and Damage Finance should apply to Biodiversity Loss. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 7, 1336–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework. Targets and Guidance Notes. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/gbf/targets/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Groves, C.R.; Game, E.T.; Anderson, M.G.; Cross, M.; Enquist, C.; Ferdaña, Z.; Girvetz, E.; Gondor, A.; Hall, K.R.; Higgins, J. Incorporating Climate Change into Systematic Conservation Planning. Biodivers. Conserv. 2012, 21, 1651–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GIFT, 2023. Available online: https://global-inst.com/. Why Act Now: The World in 2050. Jeffrey Sachs, Jane Goodall, Obiora Ike, Brian Wong. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KEp8XGvT8MY (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Guenot, M. Billion-dollar Startup Plans to bring the Dodo back from the Dead, and claims it can also Revive the Woolly Mammoth. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/scientists-revive-mammoth-dodo-colossal-biosciences-2023-2 (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Martinez, A.; Mammola, S. SSpecialized Terminology Reduces the Number of Citations of Scientific Papers. Proc. R. Soc. B, Biol. Sci. 2021, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvin, S.W. ,Kar, G.H. Individualism/collectivism as a Moderating Factor to the Self-image Congruity Concept. J. Vacat. Mark. 2004, 10, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fu, T.; Du, Y.; Gao, W.; Huang, K.; Liu, Z.; Chandak, P.; Liu, S.; Katwyk, P.V.; Deac, A. Scientific Discovery in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. Nature 2023, 620, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goralski, M.A; Tan, T.K. Artificial Intelligence and Sustainable Development. Inter. J. Manag. Educ., 2020, 18, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Kishore, S.; Pandey, D.K. Artificial Intelligence in Biological Sciences. Life (Basel) 2022, 12, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.M.; Meyer, T.G. , Duncan, M. 2023. By Bits and Pieces: The Contributions of Zoos and Aquariums to Science and Society via Biomaterials. J. Zool. Bot. Gard. 2023, 4, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biocentrism. Science Direct, 2023. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/social-sciences/biocentrism (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Pipere, A.; Mārtinsone, K. Metamodernism and Social Sciences: Scoping the Future. Soc. Sci. 2022, 11, 457:1–457:20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, S.M.; Pieroni, A.; Bussmann, R.W.; Abd-ElGawad, A.M.; El-Ansary, H.O. Integrating Traditional Ecological Knowledge into Habitat Restoration: Implications for Meeting Forest Restoration Challenges. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2023, 19, 33:1–33:19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C.; Biggs, R.; Norström, A.V.; Reyers, B.; Rockström, J. Social-ecological Resilience and Biosphere-based Sustainability Science. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-García, V.; Cámara-Leret, R.; Halpern, B.S.; O’Hara, C.; Renard, D.; Zafra-Calvo, N.; Sandra Díaz. Biocultural Vulnerability Exposes Threats of Culturally Important Species. PNAS 2023, 120, e2217303120. [CrossRef]
- Crutzen, P.J.; Stoemer, E.F. The “Anthropocene”. The International Geosphere–Biosphere Programme (IGBP): A Study of Global Change of the International Council for Science (ICSU) Newsletter. Global Change Newsletters 2000, 41, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, E.C.; Ramankutty, N. Putting People in the Map: Anthropogenic Biomes of the World. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C. The Great Acceleration, Anthropocene: A Very Short Introduction (Very Short Introductions); Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; p. 208. ISBN -13. [Google Scholar]
- Sobecki, S. 'New World Discovery', Oxford Handbook Topics in Literature (online edn, Oxford Academic, 16 Dec. 2013), Available online:. Available online: doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199935338.013.141 (accessed on 29 September 2023).
- Arnason, J.P. Civilisation, Culture and Power: Reflections on Norbert Elias’s Genealogy of the West. In Civilising Processes and Modernity – A Debate. Palgrave Studies on Norbert Elias; Bogner, A., Mennell, S., Eds.; Civilisations, Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, ZG, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-80378-0. [Google Scholar]
- Boon, P.I. The Environmental History of Australian Rivers: a Neglected Field of Opportunity? Mar. Freshw. 2018, 71, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turvey, S.T. Chapter 2. In the shadow of the megafauna: prehistoric mammal and bird extinctions across the Holocene. In Holocene Extinctions; Turvey, S.T., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 9780199535095. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, V.L.; Pausas, J.G. The Legacy of the Extinct Neotropical Megafauna on Plants and Biomes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 129:1–129:13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornford. R.; Spooner, F.; McRae, L.; Purvis, A.; Freeman, R. Ongoing Over-exploitation and Delayed Responses Change Highlight the Urgency for Action to Promote Vertebrate Recoveries by 2030. Proc. Biol Sci. 2023, 290, 20230464:1–20230464:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, I.; Balmford, A. Current Conservation Policies Risk Accelerating Biodiversity Loss. Nature 2023, 618, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehm, S.; Schumer, C.; 10 Big Findings from the 2023. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report on Climate Change. 2023. Available online: https://www.wri.org/insights/2023-ipcc-ar6-synthesis-report-climate-change-findings (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Barry, B. Sustainability and Intergenerational Justice. Theoria, 1997, 89, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanning, R. Youth in the Anthropocene: Questions of Intergenerational Justice and Learning in a More-Than-Human World. In Youth Cultures in a Globalized World.; Knapp, G., Krall, H. Eds.; Springer, Cham, ZG, 2021; pp 113–133, ISBN 3030651762.
- Brozović, D. Societal collapse: A literature review. Futures 2023, 145, 103075:1–103075:24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada-Román, A.; Pérez-Umaña, D. State of the Art of Geodiversity, Geoconservation, and Geotourism in Costa Rica. Geosciences 2020, 10, 211:1–211:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluniyi, O. Darwin Comes to Africa: Social Darwinism and British Imperialism in Northern Nigeria.; Discovery Institute press: Seattle, WA, USA, 2023; ISBN 978-1637120231. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.W. Anthropocene or Capitalocene? Nature, history, and the Crisis of Capitalism. In Anthropocene or Capitalocene? Nature, history, and the Crisis of Capitalism; Moore, J.W., Ed.; PM Press: Oakland, CA, 2016; pp. 1–13. ISBN 978-1629631486. [Google Scholar]
- Lidicker, W.Z. Jr. A Scientist’s Warning to Hhumanity on Human Population Growth. Global Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01232:1–e01232:19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPA. 2010. World People’s Conference on Climate Change and the Rights of Mother Earth. April 22nd, Cochabamba, Bolivia. Cochabamba People’s Agreement. 22nd April, 2010. Available online: https://pwccc.wordpress.com/2010/04/24/peoples-agreement/ (accessed on 27 September 2023).
- Saito, K. Marx in the Anthropocene: Towards the idea of degrowth communism. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; 300p., ISBN 978-1108844154.
- Sachs, J.; Goodall, J.; Ike, O.; Brian Wong, B.; GIFT. Why Act Now: The World in 2050. 2023. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KEp8XGvT8MY (accessed on 22 September, 2023).
- Graeber, D.; Wengrow, D. The Dawn of Everything: a New History of Humanity. Farrar, Straus and Giroux: New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-0374157357.
- de Lange, E.; Sze, J.S.; Allan, J.; Atkinson, S.; Booth, H.; Fletcher, R.; Khanyari, M.; Saif, O. A Global Conservation Basic Income to Safeguard Biodiversity. Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBI. Global Basic Income Foundation. 2023. Available online: https://www.globalincome.org/English/Global-Basic-Income.html (accessed on 24 September 2023).
- Domínguez, L.; Luoma, C. Decolonising Conservation Policy: How Colonial Land and Conservation Ideologies Persist and Perpetuate Indigenous Injustices at the Expense of the Environment. Land 2020, 9, 65:1–65:22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, C.; Araujo, M.B.; Jetz, W; Rahbek, C. Additive threats from pathogens, climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity. Nature 2012, 480, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich. P.R.; Barnosky, A.D.; García, A.; Pringle, R.M.; Palmer, T.M. Accelerated Modern Human–induced Species Losses: Entering the Sixth Mass Extinction. Sci. Adv 2015, 1, e140025. [CrossRef]
- Inukai, I. Terminal Colonialism and its Impact on Developing Economic Growth: a Case of Ghana. J. Afr. Stud. 1981, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Willcock, S.; Cooper, G.S.; Addy, J. Dearing, J.A. Earlier Collapse of Anthropocene Ecosystems Driven by Multiple Faster and Noisier Drivers. Nat. Sustain 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, T. Cologne Zoo Aquariums 50-year anniversary – The Road to a Conservation Center. WAZA News 2022, 3, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri, C. On the Fertilizability of the Frog Egg I. J. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Univ., Ser. VI. Zool. 1961, 14, 607–613. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, DP.; Hendrick, J.L. A Molecular Approach to Fertilisation. II. Viability and Artificial Fertilisation of Xenopus laevis Gametes. Dev. Biol. 1971, 25, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollinger, TG.; Corton, G.L. Artificial Fertilization of Gametes from the South African Clawed Frog, Xenopus laevis. Gamete Res. 1980, 3, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.L.; Mahony, M.J.; Clulow, J. Effect of Sperm Concentration, Medium Osmolality and Oocyte Storage on Artificial Fertilisation Success in a Myobatrachid Frog (Limnodynastes tasmaniensis). Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2004, 16, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uteshev, V.K.; Gakhova, E.N.; Kramarova, L.I.; Shishova, N.V.; Kaurova, S.A.; Browne, R.K. Refrigerated Storage of European Common Frog Rana temporaria Oocytes. Cryobiology 2018, 83, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagarinskiy, E.; Uteshev, V.; Fesenko, E.Jr. Prolonged hypothermic storage of oocytes of the European Common Frog Rana temporaria in a Gas Mixture of Oxygen and Carbon Monoxide. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288370:1–e0288370:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, J.H.; Chandler, D.E. Xenopus laevis Egg Jelly contains Small Proteins that are Essential to Fertilization. Dev. Biol. 1999, 210, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, S. Relative Roles of Jelly Layers in Successful Fertilization of Bufo japonicus. J. Exp. Zool. 1993, 265, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukita, M.; Itoh, T.; Watanabe, T.; Watanabe, A.; Onitake, K. Substances for the Initiation of Sperm Motility in Egg-jelly of the Japanese Newt, Cynops pyrrhogaster. Zool. Sci. 1999, 16, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.K.; Clulow, J.; Mahony, M. The effect of saccharides on the post-thaw recovery of Cane Toad (Bufo marinus) Spermatozoa. Cryo-Lett. 2002, 23, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, M.; Lin, A.; Gong, Q. Non-programmable Cryopreservation of Sperm from Industrial-farmed Murray Cod (Maccullochella p peelii). Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736811:1–736811:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, R.J.; Upton, R.; Calatayud, N.E.; Silla, A.J.; Daly, J.; McFadden, M.S.; O’Brien, J.K. Cryopreservation Cooling Rate Impacts Post-thaw Sperm Motility and Survival in Litoria booroolongensis. Animals 2023, 13, 3014:1–3014:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabagyan, N.V.; Sleptsova, L.A. Artificial insemination. In Common Frog Rana temporaria. Objects of Developmental Biology.; Detlaf, T.A., Ed.; Nauka: Moscow, RU, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Silla, A.J.; Kouba, A.J. Chapter 1. In tegrating Reproductive Technologies into the Conservation Toolbox for the Recovery of Amphibian Species. In Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians; Silla, A.J., Kouba, A.J., H Heatwole, H., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; pp. 1–9. ISBN 9781032372075. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, R.K. Book Review of ‘Reproductive Technologies and Biobanking for the Conservation of Amphibians’ by Silla, A. J., Kouba, A.J., Heatwole, H. (eds.); CSIRO Publishing: Victoria, Australia, 2022. 238 pp.; Herpetol. Rev. 2023, 54, 332–335. [Google Scholar]
- Cabada, M.O. Sperm Concentration and Fertilisation Rate in Bufo arenarum (Amphibia: Anura). J. Exp. Biol. 1975, 62, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollinger, T.G.; Corton, G.L. Artificial Fertilization of Gametes from the South African Clawed Frog, Xenopus laevis. Gamete Res. 1980, 3, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silla, A.J. Artificial Fertilisation in a Terrestrial Toadlet (Pseudophryne guentheri): Effect of Medium Osmolarity, Sperm Concentration and Gamete Storage. Reprod. Fert. Devel. 2013, 25, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, I.J.; Lampert, S.S.; Kouba, C.K.; Morin, D.J.; Kouba, A.J. Development of an Amphibian Sperm Biobanking Protocol for Genetic Management and Population Sustainability. Conserv. Physiol. 2022, 10, coac032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbinova, I. A.; Tuniyev, B.S. 1986. Keeping, captive breeding and reintroduction of northern banded newt (Triturus vittatus). In Sokolov V. E., Syroechkovskiy E. E. (Eds.), First all-Union Meeting on Problems of Zooculture, , Moscow. Moscow, Russ: Academy of Sciences of the USSR, 147–150. (In Russian). 2–4 December.
- Goncharov, B.F.; Shubravy, O.I.; Serbinova, I.A.; Uteshev, V.K. The USSR programme for breeding amphibians, including rare and endangered species. Int. Zoo Yearbook 1986, 28, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaurova S., A. , Uteshev V. K., Gapeyev A. B., Shishova N. V., Gakhova E. N., Browne R. K., Kramarova L. I. Cryopreservation of spermatozoa obtained postmortem from the European common frog Rana temporaria. Reprod. Fert. Dev., 2021, 33, 588–595. [Google Scholar]

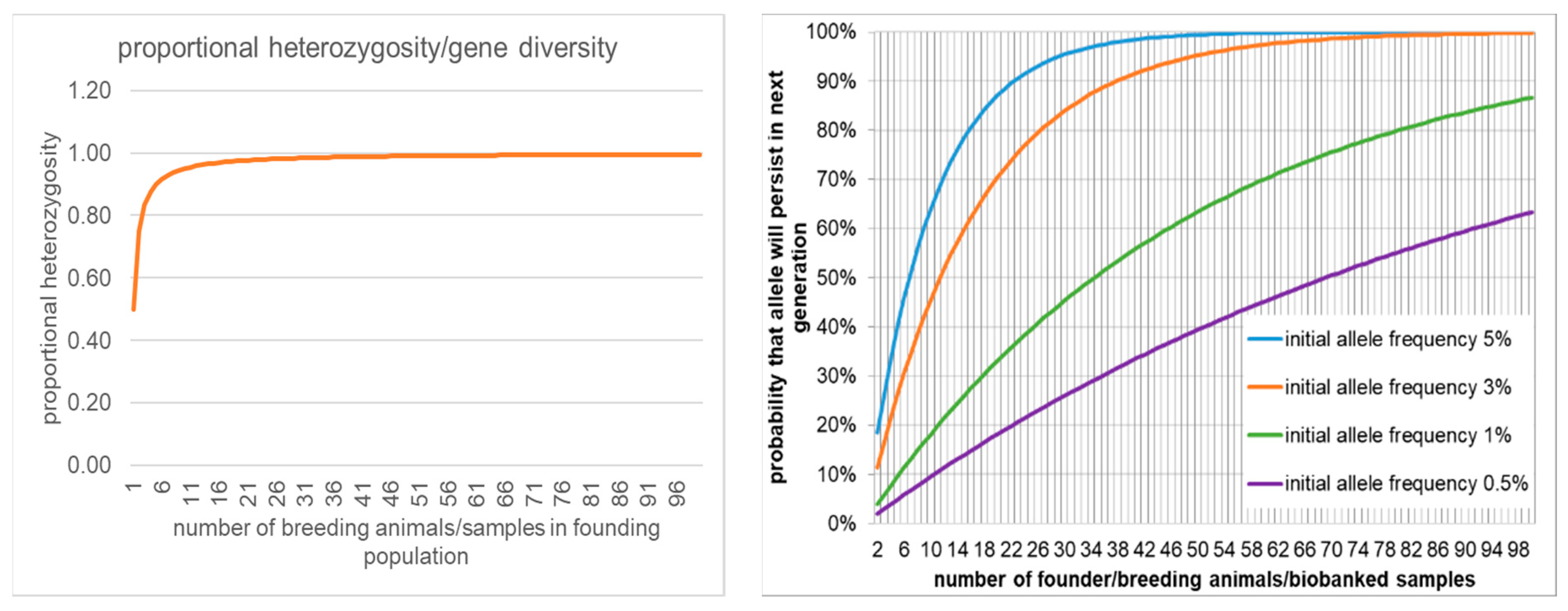
| Endangerment | CE | EN | VU | NT | LC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anurans | 9 / 8, 89% | 16 / 16, 100% | 11 / 11, 100% | 15 / 11, 100% | 21 / 11, 100% |
| Salamanders | 6 / 6, 100% | 7 / 6, 86% | 10 / 11, 100% | 13 / 12, 92% | 44 / 42, 95% |
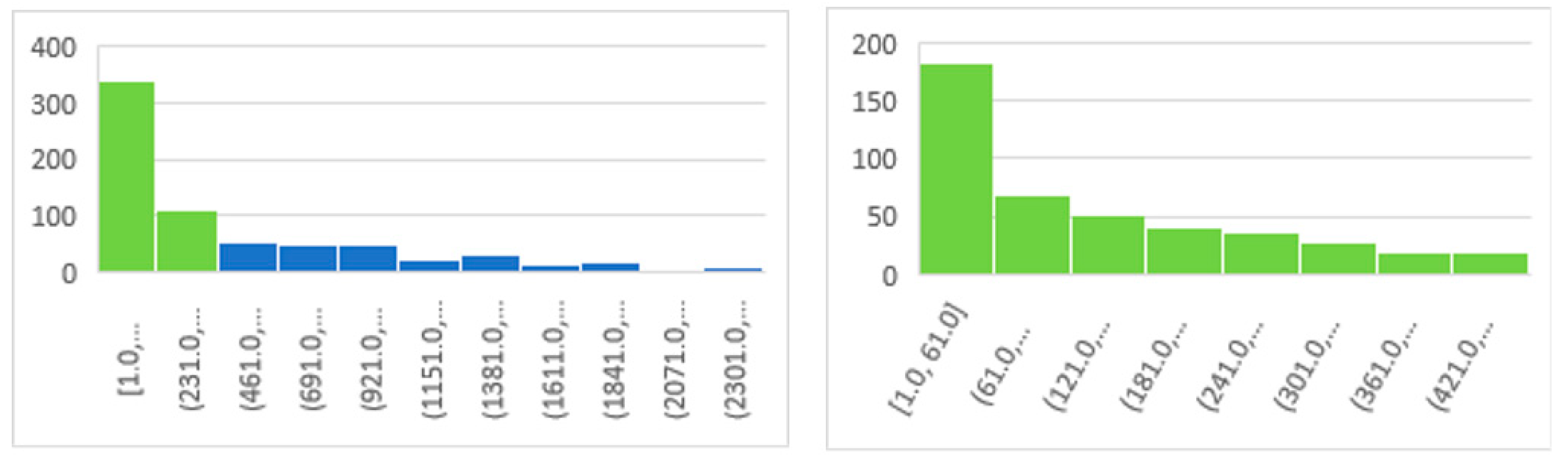


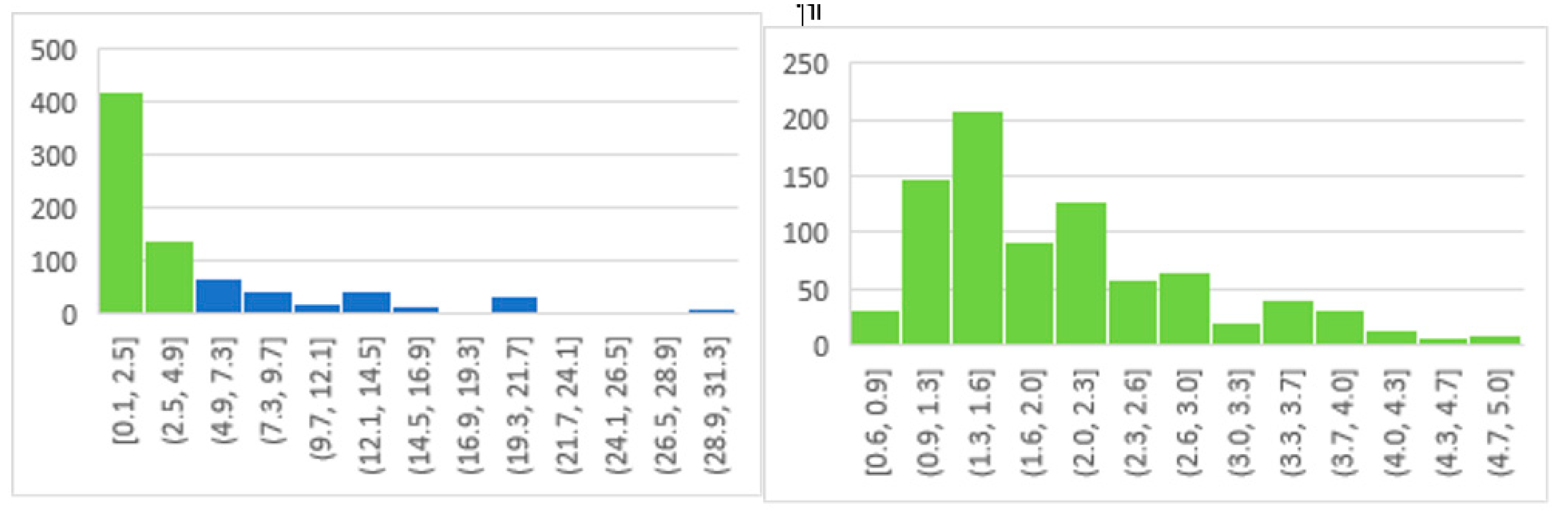
| LC | VU | EN | CE | DD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anura | 326 (3027) 10.7% | 42 (625) 6.7% | 32 (964) 3.3% | 23 (591) 4.0% | 1,000 |
| Salamanders | 13 (189) 6.9% | 17 (111) 1.5% | 17 (169) 10.1% | 8 (129) 6.2% | 48 |
| Caecilians | 0 (75) 0% | 0 (4) 0% | 0 (11) 0% | 0 (3) 0% | 97 |
| Total | 339 (3,291) 10.3% | 59 (740) 8.0% | 49 (1,144) 4.3% | 31 (723) 4.3% | 0 (1145) 0% |
| NT | LC | VU | EN | CE | DD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anura | 34 (341) | 294 (3,027) 10.7% | 42 (625) 6.7% | 64 (964) 3.3% | 217 (591) 4.0% | 209 |
| Salamanders | 0 (65) | 2 (189) 6.9% | 5 (111) 1.5% | 7 (169) 10.1% | 11 (129) 6.2% | 48 |
| Caecilians | na | 0 (75) 0% | 0 (4) 0% | 0 (11) 0% | 0 (3) 0% | 97 |
| Total | 34 (406) | 296 (3,291) 10.3% | 47 (740) 8.0% | 71 (1,144) 4.3% | 228 (723) 4.3% | na |
| Endangerment | CE | EN | VU | NT | LC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anurans | 9 / 8, 89% | 16 / 16, 100% | 11 / 11, 100% | 15 / 11, 100% | 21 / 11, 100% |
| Salamanders | 6 / 6, 100% | 7 / 6, 86% | 10 / 11, 100% | 13 / 12, 92% | 44 / 42, 95% |
| Population | Males | Females | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metapopulation? | 10 | [144] | ||
| Metapopulation | 5 | 5 | 27 Australian Threatened species. | [145] |
| Metapopulation | 20+ | 20+ | Conservation Breeding Programs | [110] |
| Fragmented/sub pop. | 10 | Every 4 years for CBPs depending on a species mean kinship | [146] | |
| Metapopulation | 15 unspecified sex | For CBP to prevent loss of genetic diversity and inbreeding depression. | [105,147,148] | |
| Metapopulation. Geographic clusters | 20 | 10 | Different geographic clusters | [149] |
| Class | VU | EN | CE | EW | EX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphibia | 2 (740) 0.2% | 4 (1,144) 0.3% | 3 (723) 0.4% | 1 (2) 50% | 0 (36/100*) 0% |
| Reptilia/Aves | 58 (1379) 4.2% | 27 (1,197) 2.3% | 32 (666) 4.8% | 3 (7) 60% | 0 (191) 0% |
| Mammalia | 80 (557) 14.4% | 66 (550) 12.0% | 34 (233) 14.6% | 2 (2) 100% | 85 (1) 1.2% |
| % species / % Biobanked | 27.6% / 1.4% | 40.7% / 4.1% | 44.5% / 4.3% | 9.0% / 10% | 34.0%*, 0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





