Introduction
A global health crisis triggered by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, necessitated rapid research and the introduction of vaccines. Among these, the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine (BNT162b2) showed significant efficacy in clinical trials, mainly undertaken in Western cohorts. There remains a significant gap in knowledge regarding the vaccine's effectiveness in Africa, particularly within Sub-Saharan Africa. Given the unique genetic diversity, endemic diseases, and specific microenvironmental conditions present in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), examining the long-term efficacy of vaccines in this region is pivotal. These distinct factors have been substantiated to impact responses to various viral vaccines, highlighting the critical need to understand vaccines' sustained performance and implications within this specific context [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. This study bridges this knowledge gap, examining the longitudinal serological response to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine within Sub-Saharan Africa and underscoring potential disparities across diverse populations [
6]. To address the pressing need for region-specific data from SSA, we conducted a 12-month analysis exploring the antibody responses to the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine within a Ugandan cohort. This study is critical in formulating vaccination strategies and discerning the trajectories of long-term immunity in the region. By examining the correlations between baseline antibody levels, breakthrough infections, and subsequent antibody responses, our study aimed to offer essential insights for developing public health strategies appropriately tailored to meet the unique challenges and contexts of the region.
Our study provides a comprehensive analysis of the one-year SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody dynamics (IgG, IgM, IgA) a region typically underrepresented in global vaccine research, illuminating seroconversion patterns and the influence of baseline serostatus on vaccine effectiveness, with broader implications for booster strategies and breakthrough infections. This research contributes pivotal insights capable of informing and refining vaccination strategies and public health policies throughout Africa by bridging a significant knowledge gap. The findings emphasize the importance of understanding diverse vaccine responses to facilitate the formulation of customized and pragmatic immunization strategies.
Study population and study design
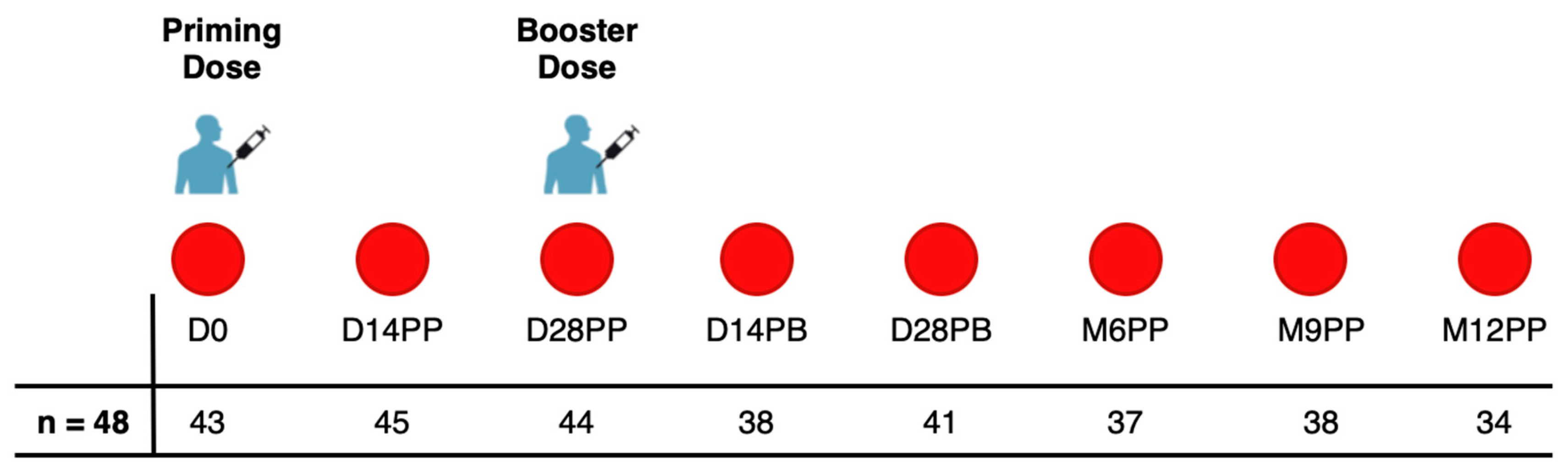
In this study, we collected 320 specimens from a cohort of 48 individuals who received two doses of the PFZ vaccine on day 0 and day 30. Participants were monitored for 12 months after their initial vaccination, with samples collected from March 21, 2021, to January 6, 2023. Of the 48 participants, 45.8% (n=22) were female and 54.2% (n=26) were male. The age ranged from 19 to 49 years, with a median of 30 years and an Interquartile Range (IQR) of 25-35.3 years. Blood samples were collected prior to the administration of both the first and second doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, BNT162b2. In addition, samples were collected on Days 14 and 28 following the initial dose. Approximately 30 days following the initial vaccination, a booster was administered, with samples subsequently collected on Days 14 and 28 and then at six, nine and twelve months after the first dose, as shown in
Figure 1.
Binding antibody ELISA to detect SARS-CoV-2-specific IgG, IgM, and IgA levels.
We used a validated enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to quantify the presence and levels of specific SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, targeting both spike and nucleoprotein antigens in the specimens, quantifying IgG, IgM, and IgA concentrations in ng/ml through detected optical densities at 450 nm. The established cut-off values for antibody positivity within this population were: S-directed IgG (0.432), IgM (0.459), and IgA (0.226); and N-directed IgG (0.454), IgM (0.229), and IgA (0.225). Further details on the ELISA protocol and cut-off criteria can be found in our previous publication [
7].
Statistical methods
We used box plots to visually represent medians, means, and quartiles for our statistical analysis. Diverging bar graphs were used to show the percentage of seroconversion at each follow-up time point. We applied the Wilcoxon test for pairwise comparisons to determine significant differences in antibody responses across time points, with a Bonferroni correction to adjust for multiple testing. Given the missing data/samples across time points, we opted for unpaired tests. A threshold of p > 0.05 was deemed non-significant (ns). Significance levels were as follows: * for p <= 0.05, ** for p < 0.01, *** for p < 0.001, and **** for p < 0.0001.
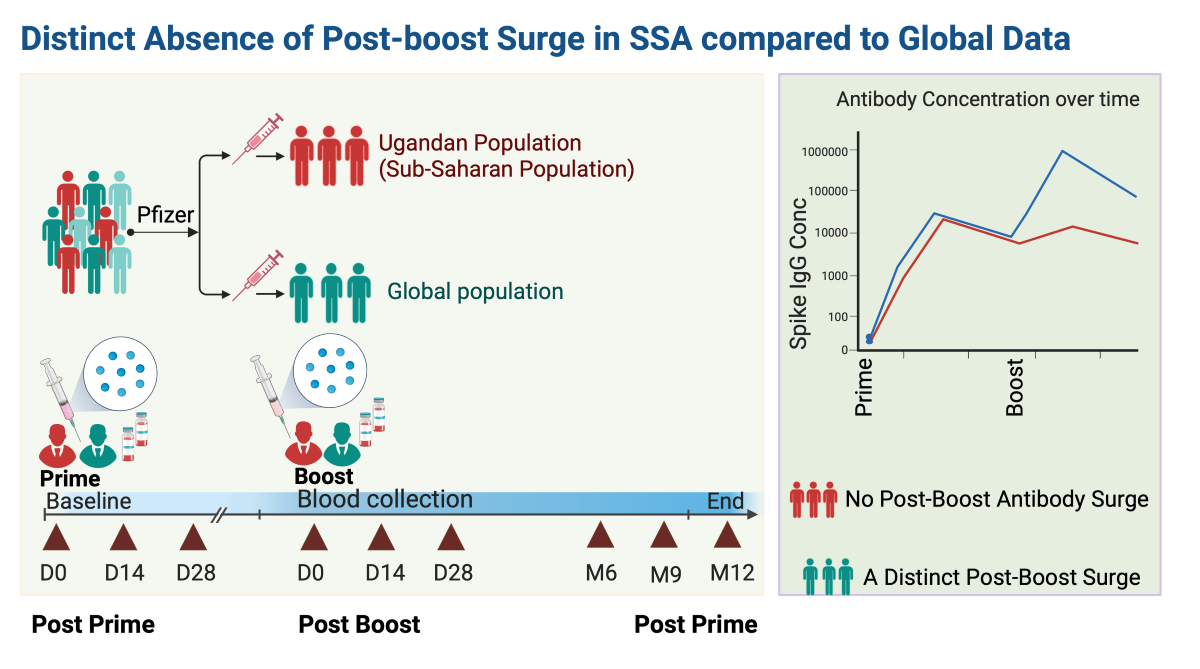
Post-vaccination Trends Showed a Robust S-IgG Response, with No significant Booster Dose Effect, Sub-optimal S-IgM, and Time-Limited S-IgA Elevation
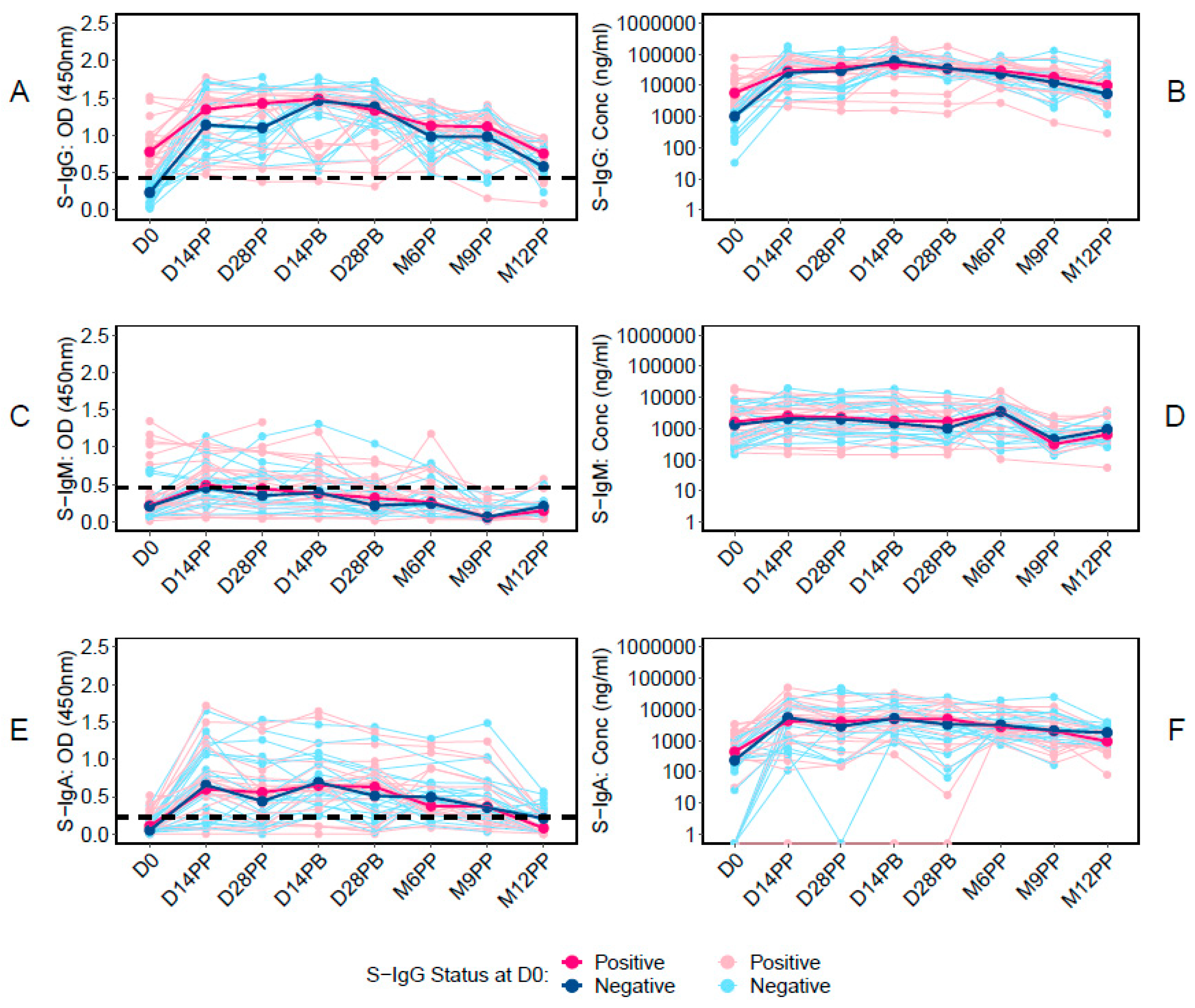
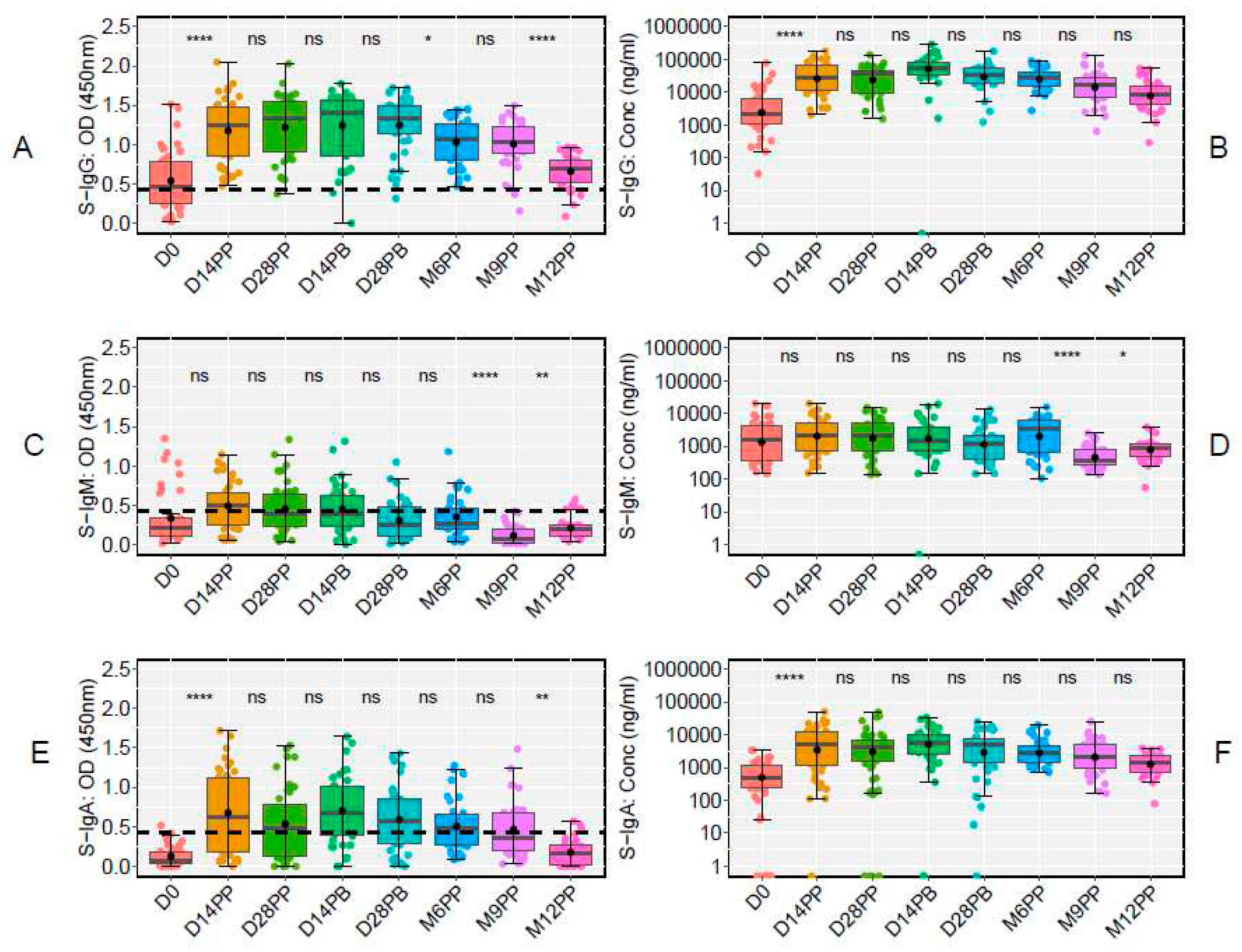
We first examined the temporal dynamics of antibodies targeting the Spike protein, starting with the baseline S-IgG antibody responses at Day 0 (D0) and then examining their median values at subsequent time points. Of the 48 participants in the study, 43 had available baseline S-IgG data. These individuals were stratified based on their S-IgG seropositivity at baseline: those with levels at or above the S-IgG cutoff were designated as S-IgG+ (shown in red), while those below the threshold were labelled as S-IgG- (represented in blue), as illustrated in
Figure 2. A marked rise in S-IgG antibody responses from day 0 (D0) to 14 days post-priming dose was evident for both S-IgG positive (S-IgG+) and negative (S-IgG-) groups, with the increase being more pronounced for the S-IgG- group (
Figure 2A and 2B). Notably, while the initial immune response at D0 differed significantly between the two groups, with S-IgG+ participants displaying higher responses, the post-vaccination S-IgG antibody distributions became indistinguishable at subsequent intervals. After 14 days post-priming, the concentrations of S-IgG antibodies remained relatively comparable between both groups. Notably, there was no discernible enhancement in immune responses after the booster dose administration.
On the other hand, S-IgM antibody responses remained low throughout, with most participants registering responses below the cutoff. No distinction was observed in S-IgM antibody levels between S-IgG+ and S-IgG- participants at any point, as depicted in
Figure 2C and 2D. In contrast, S-IgA antibodies surged exponentially within the first 14 days post-priming. This trend persisted until the sixth month post-priming before a noticeable decline, as shown in
Figure 2E and 2F. Notably, there were no significant variations in S-IgA responses between S-IgG+ and S-IgG- participants at any given time, suggesting equivalent S-IgA immune responses across the timeframes evaluated.
These data highlight a robust S-IgG response post-vaccination, a suboptimal S-IgM response, and a consistent S-IgA response that eventually declines after six months. The findings offer valuable insights into the antibody profile following vaccination and supports the importance of monitoring these responses over time.
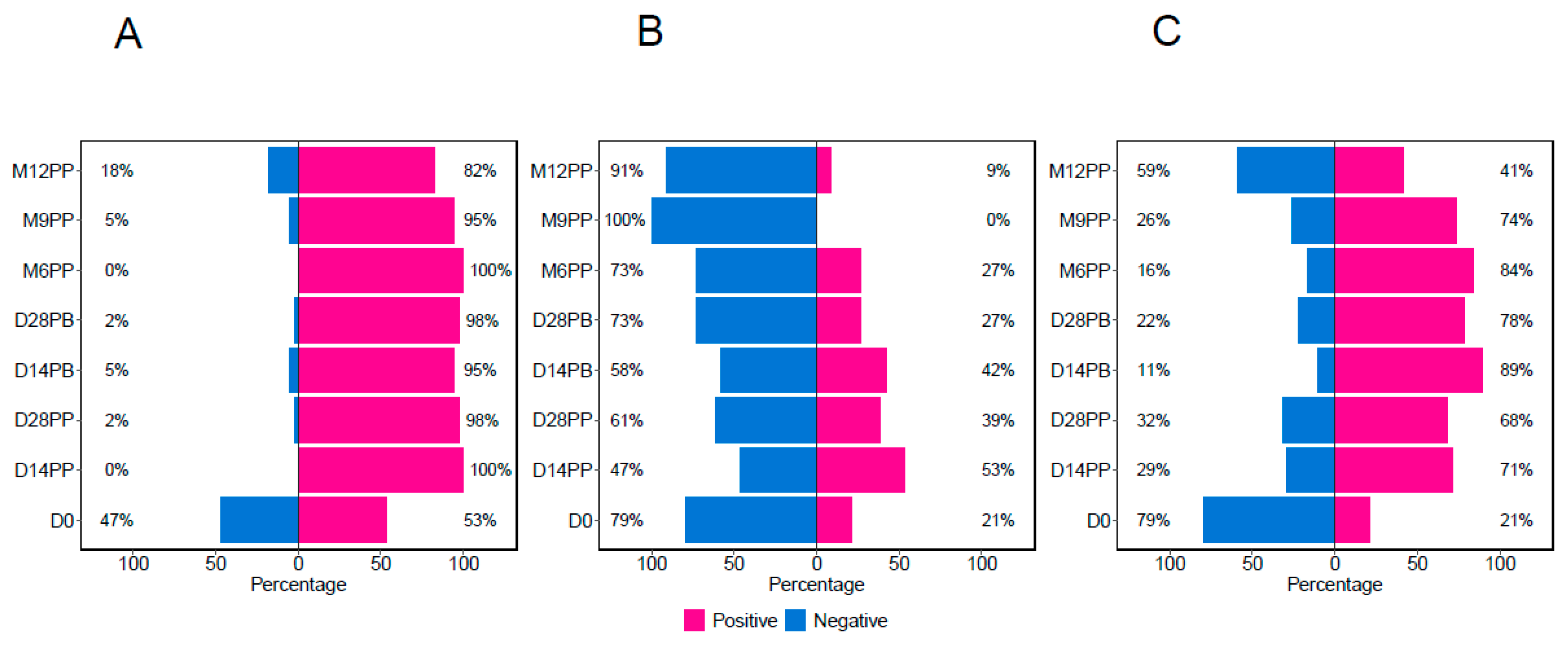
Rapid and Sustained Seroconversion of S-IgG and S-IgA Following Primary Vaccination, but Transient S-IgM Seropositivity
Using predefined cutoffs of 0.432 for S-IgG, 0.459 for S-IgM, and 0.226 for S-IgA [
7], participants were categorised based on their S-IgG positivity as positive or negative at the initial time point. This classification provided the count (and percentages) of participants exhibiting positive or negative results for any antibodies at the respective time points. All 320 samples contributed to this classification, with the sample distribution for each time point depicted in
Figure 1. At the beginning of the study (Day 0), 47% of the participants were without S-IgG antibodies. By Day 14 post-primary vaccination, all participants exhibited S-IgG positivity, which remained above 80% for the study duration,
Figure 3A. Initially (Day 0), 21% of the participants demonstrated the presence of S-IgM antibodies, which increased to 53% by D14PP. Nevertheless, as depicted in
Figure 3B, most participants experienced a decline in antibody responses after reaching a peak, dropping to 27% six months post-primary dose, and showing a total absence of S-IgM seropositivity nine months after the primary vaccination. The percentage of S-IgA-positive participants rose from 21% on Day 0 to 71% fourteen days post-prime, as illustrated in
Figure 3C. This upward trend persisted until six months post-primary vaccination, at which point it began to decline, eventually stabilising at 41% by 12 months post-primary vaccination.
The use of box plots and an unpaired Wilcoxon test highlighted significant dynamics in antibody responses to the S-antigen over time. Specifically, we observed a marked increase in S-IgG antibody OD values and concentrations from day 0 to day 14 post-prime, with high levels persisting until day 28 post-boost. On day 0, the OD values were 0.464 (IQR 0.250, 0.793), and concentrations were 40.986 BAU/ml (IQR 20.314, 113.864). By day 14 post-prime, these had increased to 1.247 (IQR 0.850, 1.474) and 534.576 BAU/ml (IQR 204.062, 1257.831). Elevated levels persisted until day 28 post-boost, with OD values at 1.330 (IQR 1.147, 1.489) and concentrations at 642.461 BAU/ml (IQR 341.770, 993.056). However, a notable decline in S-IgG OD levels was evident from six months post-prime to twelve months post-prime, summarised in Table 1. Notably, the decline in S-IgG antibody concentrations was not statistically significant, as they remained stable throughout the follow-up period,
Figure 4A and 4B. In contrast, we observed relatively modest S-IgM antibody responses, which substantially reduced after six months post-priming (
Figure 4C and 4D). Concurrently, a significant increase in S-IgA antibody levels was observed on day 14 following the initial dose, and these elevated S-IgA levels persisted until month nine post-prime, where a significant decline in S-IgA OD responses was evident (
Figure 4E and 4F). These findings offer valuable insights into the temporal dynamics of the Pfizer vaccine-induced antibody responses against the S-antigen, shedding light on potential correlates of immunity and providing guidance for future vaccination strategies.
Post-Vaccination Longitudinal Analysis Unveiled Breakthrough Infections with no Significant Difference by Baseline S-IgG Serostatus
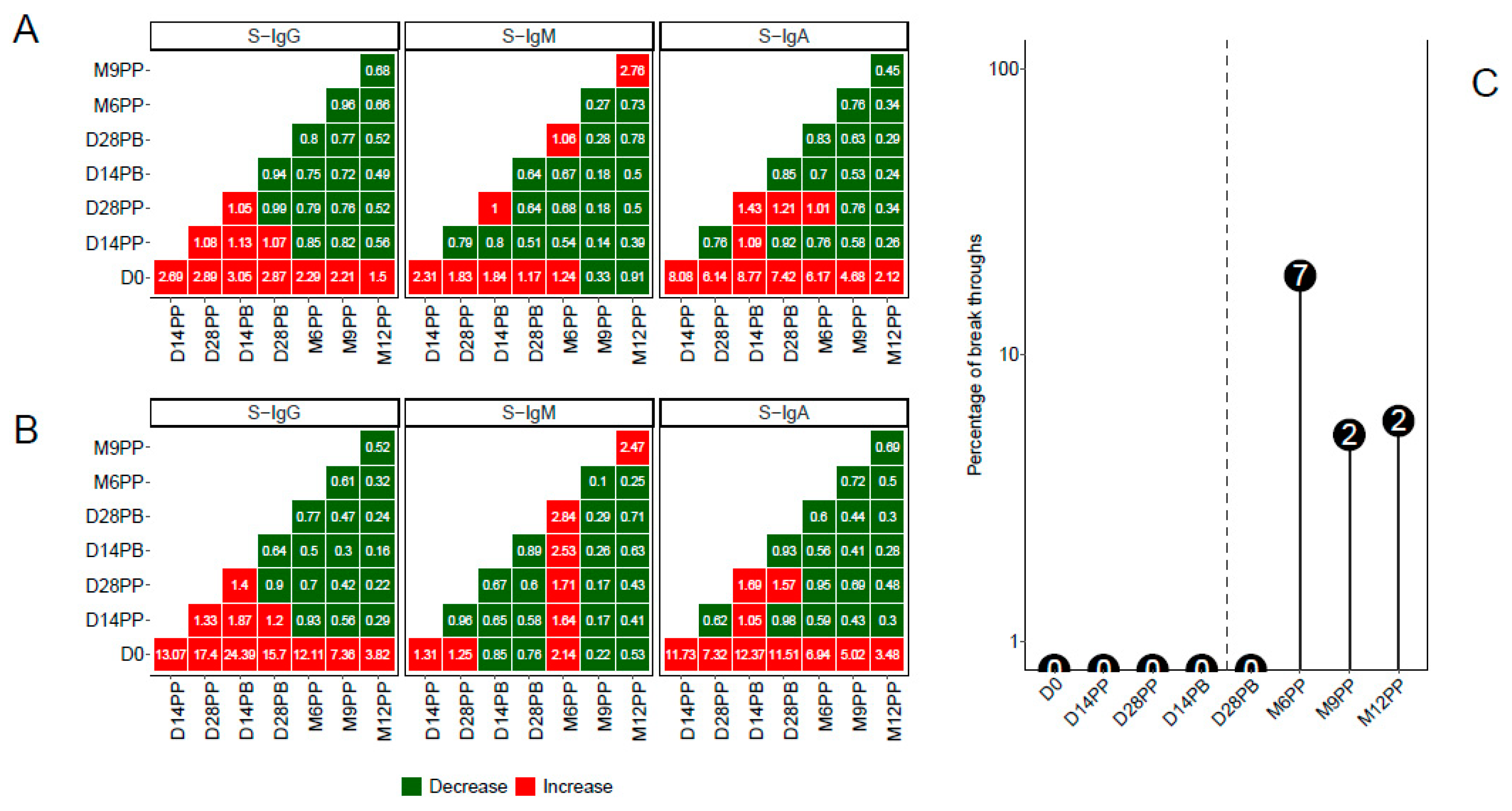
Through a pairwise analysis of antibody OD levels (
Figure 5A) and concentrations (
Figure 5B), we constructed heatmaps to represent the median fold changes in Spike antibody responses between consecutive time points. Increased responses were visually highlighted in red, while reduced responses were indicated in green. The data indicates pronounced fold increases in S-IgG and S-IgA antibody responses compared to D0, although changes between adjacent time points remained marginal. Additionally, subtle variations in S-IgM between pairwise time points were noted.
A distinct rise in N-IgG antibody levels after a completed vaccination regimen was indicative of an infection. Participants manifesting this surge, 14 days following their complete vaccine dosage, were classified as breakthrough cases. An 11-fold escalation in N-IgG levels signified a confirmed infection. Six months after full vaccination, a noticeable rise in infected participants was observed. In total, 11 individuals were identified as breakthrough: seven became infected six months post vaccination, two at nine months, and two at a year post prime. When stratified by baseline S-IgG status, five participants were previously S-IgG positive, five were S-IgG negative, and one remained unclassified due to the absence of initial S-IgG data,
Figure 5C.
The Early Rise in S-IgG Antibody Responses in Seronegative Participants Subsequently Aligned with Seropositive Counterparts Throughout the Subsequent Study Duration
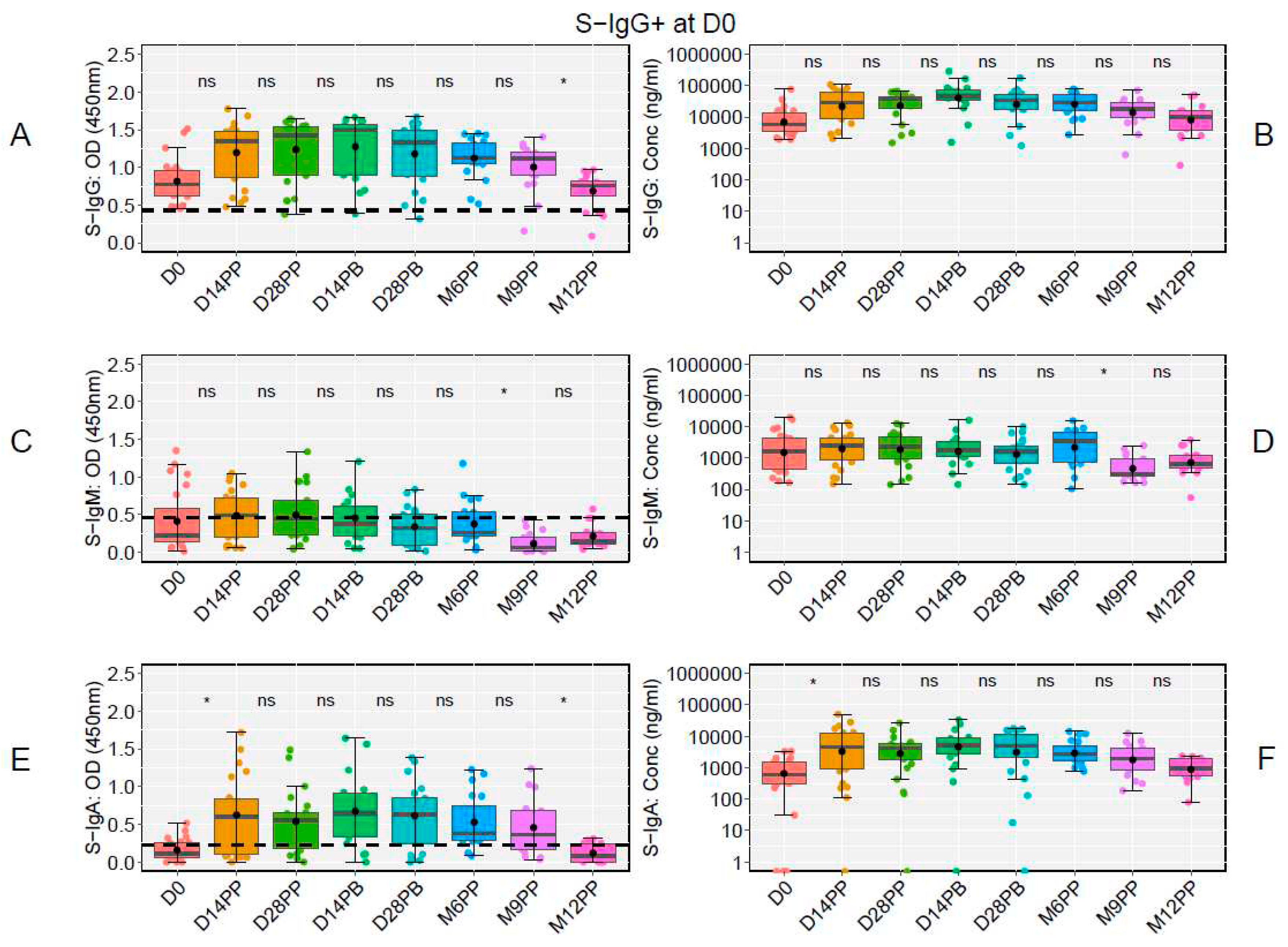
At the study's onset (D0), of the 48 participants, 23 tested positive for S-IgG, 20 tested negative, and five lacked baseline specimens. Notably, there was a significant decline in S-IgG OD antibody responses at 12 months post-prime relative to 9 months, as illustrated in
Figure 6A and 6B. Modest levels of S-IgM were observed in these participants (
Figure 6C and 6D), with a marked rise in S-IgA antibodies from D0 to D14PP, persisting until M9PP before a significant decline (
Figure 6E and 6F).
Among the 20 participants initially lacking S-IgG antibodies, we observed a significant increase in S-IgG antibodies from the day of vaccination to two weeks post-vaccination, sustained until a month after the booster, with a notable decline in OD levels by the sixth month, but consistent antibody concentrations across all study time points without any significant rise post-boost, as shown in Figure 7A and 7B. Participants with a baseline seronegative status showed reduced S-IgM antibody levels (Figure 7C and 7D). However, S-IgA responses rose from D0 to D14 after the initial vaccination and stabilized (Figure 7E and 7F). In our findings, baseline seronegative participants showed a comparable IgG antibody trajectory to their seropositive counterparts, except that the latter group did not exhibit a post-prime boost in antibody concentrations. This pattern did not change when breakthrough participants were excluded from the analysis, Supplementary Figure 3.
Limited Early Presence of N-Directed Antibody Responses but Significant Increase by 12 Months Post-Prime in Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19-Vaccinated Individuals
Within the N-directed antibody response context, participants, irrespective of their baseline S-IgG status, exhibited low N-directed IgG responses, illustrated in Supplementary Figure 1A and 1B. Initially, only a minimal proportion were N-IgG seropositive at baseline; however, this markedly increased to 62% at 12 months post-prime (M12PP), as depicted in Supplementary Figure 1C. Moreover, the presence of low levels of N-IgM was a consistent observation among both S-IgG+ and S-IgG- participants, as demonstrated in
Figure 1D and 1E. The percentage of participants testing positive for S-IgM decreased from 51% at baseline to 24% on Day 28 post-boost (D28PB) before experiencing a rise to 57% six months following the initial dose (Supplementary Figure 1F). This rise could be attributed to subsequent breakthrough infections. We consistently observed low levels of N-directed N-IgG and N-IgM antibodies throughout the study, as depicted in Supplementary Figure 2A-2D. The analysis revealed no statistically significant variations in these levels over time.
Discussion
In the global response to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine (BNT162b2) played a pivotal role, demonstrating notable efficacy in diverse populations worldwide. However, until now, there is a striking lack of data regarding its performance within the African demographic, particularly SSA. This gap is particularly significant considering the distinct and extensive genetic diversity [
8,
9,
10], environmental, and epidemiological activation microenvironment prevalent within African populations [
1,
11], that do influence vaccine-induced immune responses [
6,
12]. Our study provides critical insights into the dynamics of longitudinal antibody responses post-Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccination within the SSA demographic, presenting findings that align with and differ from international datasets. The significant and persistent S-IgG response observed within 14 days after the initial dose is consistent with global data, underscoring the vaccine's potential to induce potent immunity across a wide range of demographics [
13]. This robust response was sustained throughout, regardless of participants' baseline S-IgG serostatus. While the lack of a pronounced increase in S-IgG levels post-booster in our cohort aligns with some populations [
14], it contrasts with many others [
15,
16], highlighting differential immune dynamics that merit further investigation. Numerous factors might account for these disparities: genetic divergences, unique HLA patterns in the African populace affecting antigen processing [
8], protective advantages from earlier SARS-CoV-2 exposure [
17], and a consistently low booster response in those with prior exposure, as noted in studies on other viruses [
18]. Further research is warranted to elucidate this. The transient and subdued S-IgM response observed post-vaccination, largely falling below established thresholds, reflects its customary early emergence and subsequent decline as memory responses develop. The limited detection of this isotype post-vaccination is consistent with the induction of a mature memory response, as previously observed in natural infections in this population [
19] and others [
20,
21]. S-IgA, vital for mucosal defence against SARS-CoV-2 [
22], showed a significant trend: an initial increase followed by a decline six months after the primary vaccination, highlighting the need for ongoing surveillance to ensure lasting protective immunity. Our analysis showed a comparable frequency of breakthrough infections between participants with baseline S-IgG positive and those with baseline S-IgG negative serostatus; the differences were not statistically significant. Regardless of their baseline serostatus, all individuals experiencing breakthrough infections remained asymptomatic, highlighting the potential protective benefits of vaccination [
23]. These data also align with the concept of "hybrid immunity," suggesting that a synergistic effect of natural immunity and vaccination might enhance overall protection. In our study, we examined the longitudinal profiles of the Pfizer vaccine within the SSA context, specifically focusing on the Ugandan demographic. While many of our findings mirrored global trends, the unique antibody dynamics we identified underscore the significance of tailored, region-specific research. Such findings reinforce the necessity of understanding regional distinctions to effectively shape and implement vaccination strategies and public health policies in diverse settings.
Several critical implications emerge in our study examining the longitudinal profiles of the Pfizer vaccine in SSA. We observed a robust S-IgG antibody response post-vaccination, consistent with global trends [
14,
24], underscoring the vaccine's ability to induce potent adaptive immunity in the African cohort. Post-vaccination antibody peaks were higher than those following infection; however, the subsequent trajectory aligned with hybrid immunity, most of the time. The transient nature of the S-IgM response, mirroring findings from other populations, suggests the typical transient nature of these antibodies post-vaccination rather than vaccine inefficacy. Notably, the early surge and subsequent decline of S-IgA antibodies at six months offers insights into the temporal dynamics of mucosal immunity [
14,
25], which plays a crucial role against respiratory pathogens like SARS-CoV-2 [
26,
27]. Our analysis of breakthrough infections in participants devoid of symptoms, underscored the potential protectiveness of the elicited immunity [
28,
29].
Furthermore, the lack of a pronounced surge in S-IgG antibodies post-second dose in our cohort contrasts with other populations [
16], hinting at unique genetic or environmental determinants in SSA that might influence the vaccine's response. The limited surge in antibody response after the second dose might indicate a potentially altered prime-boost strategy for the Ugandan population. Perhaps a longer interval between doses, as shown in mice studies, might yield a different outcome [
30]. This difference necessitates deeper evaluation into genetic predispositions, especially considering the HLA diversity in Africans and its potential impact on adaptive vaccine responses.
While this study provides insights into the antibody dynamics post-Pfizer vaccination among the Ugandan subset of the SSA population, it is not without limitations. First, the participant sample size of 48 might only partially capture the diverse and heterogeneous SSA demographic [
31,
32,
33]. Furthermore, we primarily focused on binding antibody responses, omitting the evaluation of antibody functionality [
34]. The significance of T-cell-mediated immunity [
35,
36], crucial for sustained viral defense, was also not examined in our study. Furthermore, while the 12-month period provides a thorough overview, it may not capture the intricacies of long-term immune memory or potential changes in immunity that arise later. Furthermore, considering the continuous emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, a definitive assessment of the vaccine's performance against these novel strains in this setting is yet to be established. Considering our findings, we recommend comprehensive studies across varied African demographics. Given the unique genetic diversity and environmental and health challenges faced in the African setting, it is crucial to conduct region-specific studies. Such research should focus on understanding the efficacy of booster doses across various age groups and health statuses, especially in individuals with co-existing endemic infections such as malaria or HIV. Moreover, studies should also evaluate the durability of vaccine-induced immunity in the African population, considering local disease prevalence and potential interactions with other prevalent infections. Understanding these factors can offer insights into optimizing vaccination strategies tailored to the African context. There is a need to investigate T-cell responses post-vaccination for a holistic understanding of vaccine-induced immunity. The observed dynamics in both baseline seropositive and seronegative individuals suggest the potential necessity for periodic booster doses. Future studies should also consider the relationship between genetic factors, vaccine response, and breakthrough infections in this population. Evaluating the vaccine in relation to prevalent SARS-CoV-2 strains in SSA and the effects of prior natural infections could guide optimal vaccination strategies.
In conclusion, this study highlighted the antibody responses to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in SSA, a demographic previously underrepresented in global datasets. We observed a strong S-IgG response, with notable differences in S-IgM and S-IgA dynamics and responses relative to baseline S-IgG serostatus. Notably, a post-boost surge was absent, emphasizing the need for customized vaccination plans for areas with unique environmental and genetic profiles, like SSA. Region-centric studies are vital to ensure that vaccination strategies resonate with diverse serological and genetic contexts, enhancing their effectiveness.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: JSer. Laboratory investigation: JSK, JSem, GKO, IS, LK, SM, BG, and the COVID-19 Immunoprofiling team. Data curation, software, and formal statistical analysis: VA and JSer. Writing- original draft; JSer. Writing- reviewing and editing; PK, VA and GKO. Project Supervision: JSer and PK. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
The Government of Uganda supported this work through the Science, Technology, and Innovation Secretariat, Office of the President (STI-OP) under grant number MOSTI-PRESIDE-COVID-19-2020/15. Some objectives of this work were partially funded by the EDCTP2 program, backed by the European Union (grant number RIA2020EF-3008-COVAB). The research was carried out at the MRC/UVRI and LSHTM Uganda Research Unit, a collaboration between the UK Medical Research Council (MRC), an entity of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), and the UK Foreign, Commonwealth, and Development Office (FCDO) under the MRC/FCDO Concordat agreement. This unit is also affiliated with the EDCTP2 programme supported by the European Union. The Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation partly funded this work through the GIISER Uganda Grant (Investment ID INV-036306). The conclusions and findings presented are solely those of the authors and do not represent the foundation's positions or policies.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study received approval from the Uganda Virus Research Institute's Research and Ethics Committee (GC/127/833) and the Uganda National Council for Science and Technology (HS637ES). All procedures adhered to the respective ethical guidelines. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Data availability statement
This study presents all original data generated. Please contact the corresponding author for further inquiries or access to the raw data supporting the article's conclusions. The authors will provide this data without undue reservation.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank all participants whose samples contributed to this longitudinal cohort study. The reagent, Monoclonal Anti-SARS Coronavirus Recombinant Human Antibody (Clone CR3022, produced in HEK293 Cells), was procured through BEI Resources, NIAID, NIH, and produced under HHSN272201400008C. The reagent, Monoclonal Anti-SARS Coronavirus Recombinant Human IgG1 (Clone CR3022), produced in Nicotiana benthamiana, was sourced from BEI Resources, NIAID, NIH (NR-52392). The Nucleoprotein mAb CR3009 (Product No. 101011) utilized as a positive control was sourced from the Centre for AIDS Reagents, NIBSC, UK.
Conflict of Interest
The authors confirm that no commercial or financial relationships exist that could lead to a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Muyanja, E.; Ssemaganda, A.; Ngauv, P.; Cubas, R.; Perrin, H.; Srinivasan, D.; Canderan, G.; Lawson, B.; Kopycinski, J.; Graham, A.S.; et al. Immune activation alters cellular and humoral responses to yellow fever 17D vaccine. J Clin Invest 2014, 124, 3147–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasin, C.; Balelli, I.; Van Effelterre, T.; Bockstal, V.; Solforosi, L.; Prague, M.; Douoguih, M.; Thiébaut, R. Dynamics of the Humoral Immune Response to a Prime-Boost Ebola Vaccine: Quantification and Sources of Variation. J Virol 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabagenyi, J.; Natukunda, A.; Nassuuna, J.; Sanya, R.E.; Nampijja, M.; Webb, E.L.; Elliott, A.M.; Nkurunungi, G. Urban-rural differences in immune responses to mycobacterial and tetanus vaccine antigens in a tropical setting: A role for helminths? Parasitol Int 2020, 78, 102132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, R.; Metcalf, T.; Fourati, S.; Bartsch, Y.; Kyosiimire-Lugemwa, J.; Canderan, G.; Alter, G.; Muyanja, E.; Okech, B.; Namatovu, T.; et al. Schistosoma mansoni infection alters the host pre-vaccination environment resulting in blunted Hepatitis B vaccination immune responses. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2023, 17, e0011089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Factors That Influence the Immune Response to Vaccination. Clin Microbiol Rev 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.A.; Nazareth, J.; Jarkhi, A.; Pan, D.; Das, M.; Logan, N.; Scott, S.; Bryant, L.; Abeywickrama, N.; Adeoye, O.; et al. Ethnic differences in cellular and humoral immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in UK healthcare workers: a cross-sectional analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 58, 101926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluka, G.K.; Namubiru, P.; Kato, L.; Ankunda, V.; Gombe, B.; Cotten, M.; Team, C.-I.; Musenero, M.; Kaleebu, P.; Fox, J.; et al. Optimisation and Validation of a conventional ELISA and cut-offs for detecting and quantifying anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike, RBD, and Nucleoprotein IgG, IgM, and IgA antibodies in Uganda. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirugo, G.; Hennig, B.J.; Adeyemo, A.A.; Matimba, A.; Newport, M.J.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Ryckman, K.K.; Tacconelli, A.; Mariani-Costantini, R.; Novelli, G.; et al. Genetic studies of African populations: an overview on disease susceptibility and response to vaccines and therapeutics. Hum Genet 2008, 123, 557–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolday, D.; Fung, C.Y.J.; Morgan, G.; Casalino, S.; Frangione, E.; Taher, J.; Lerner-Ellis, J.P. HLA Variation and SARS-CoV-2 Specific Antibody Response. Viruses 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Hollenbach, J.A. The immunogenetics of COVID-19. Immunogenetics 2023, 75, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nono, J.K.; Kamdem, S.D.; Netongo, P.M.; Dabee, S.; Schomaker, M.; Oumarou, A.; Brombacher, F.; Moyou-Somo, R. Schistosomiasis Burden and Its Association With Lower Measles Vaccine Responses in School Children From Rural Cameroon. Front Immunol 2018, 9, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukwasibwe, S.; Mboowa, G.; Sserwadda, I.; Nankabirwa, J.I.; Arinaitwe, E.; Ssewanyana, I.; Taremwa, Y.; Tumusiime, G.; Kamya, M.R.; Jagannathan, P.; et al. Impact of high human genetic diversity in Africa on immunogenicity and efficacy of RTS,S/AS01 vaccine. Immunogenetics 2023, 75, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncunill, G.; Aguilar, R.; Ribes, M.; Ortega, N.; Rubio, R.; Salmerón, G.; Molina, M.J.; Vidal, M.; Barrios, D.; Mitchell, R.A.; et al. Determinants of early antibody responses to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in a cohort of exposed and naïve healthcare workers. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, M.J.; Lyke, K.E.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Raabe, V.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; et al. Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults. Nature 2020, 586, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Vrbicky, K.; Montefiori, D.; Huang, W.; Nestorova, B.; Chang, Y.; Carfi, A.; Edwards, D.K.; Oestreicher, J.; Legault, H.; et al. Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 after a booster of mRNA-1273: an open-label phase 2 trial. Nature Medicine 2022, 28, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasrado, N.; Barouch, D.H. SARS-CoV-2 Hybrid Immunity: The Best of Both Worlds. J Infect Dis 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovay, A.; Nassiri, S.; Maby-El Hajjami, H.; Marcos Mondéjar, P.; Akondy, R.S.; Ahmed, R.; Lawson, B.; Speiser, D.E.; Fuertes Marraco, S.A. Minimal immune response to booster vaccination against Yellow Fever associated with pre-existing antibodies. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2172–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwanga, J.; Ankunda, V.; Sembera, J.; Kato, L.; Oluka, G.K.; Baine, C.; Odoch, G.; Kayiwa, J.; Auma, B.O.; Jjuuko, M.; et al. Rapid, early, and potent Spike-directed IgG, IgM, and IgA distinguish asymptomatic from mildly symptomatic COVID-19 in Uganda, with IgG persisting for 28 months. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1152522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amellal, H.; Assaid, N.; Charoute, H.; Akarid, K.; Maaroufi, A.; Ezzikouri, S.; Sarih, M. Kinetics of specific anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM, IgA, and IgG responses during the first 12 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection: A prospective longitudinal study. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0288557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurano, M.; Morita, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Yokoyama, R.; Shimura, T.; Qian, C.; Xia, F.; He, F.; Zheng, L.; Ohmiya, H.; et al. Response kinetics of different classes of antibodies to SARS-CoV2 infection in the Japanese population: The IgA and IgG titers increased earlier than the IgM titers. Int Immunopharmacol 2022, 103, 108491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterlin, D.; Mathian, A.; Miyara, M.; Mohr, A.; Anna, F.; Claër, L.; Quentric, P.; Fadlallah, J.; Devilliers, H.; Ghillani, P.; et al. IgA dominates the early neutralizing antibody response to SARS-CoV-2. Sci Transl Med 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreano, E.; Paciello, I.; Piccini, G.; Manganaro, N.; Pileri, P.; Hyseni, I.; Leonardi, M.; Pantano, E.; Abbiento, V.; Benincasa, L.; et al. Hybrid immunity improves B cells and antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nature 2021, 600, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkowski, M.; de Jager, W.; Schiuma, M.; Covizzi, A.; Lai, A.; Gabrieli, A.; Corbellino, M.; Bergna, A.; Ventura, C.D.; Galli, M.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulin Isotypes, and Neutralization Activity Against Viral Variants, According to BNT162b2-Vaccination and Infection History. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 793191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinti, I.; Mortari, E.P.; Fernandez Salinas, A.; Milito, C.; Carsetti, R. IgA Antibodies and IgA Deficiency in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021, 11, 655896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, Y.; Omata, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Kinoshita-Iwamoto, N.; Terada, M.; Suzuki, T.; Morioka, S.; Uemura, Y.; Ohmagari, N.; Maeda, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Neutralizing Humoral IgA Response Occurs Earlier but Is Modest and Diminishes Faster than IgG Response. Microbiol Spectr 2022, 10, e0271622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, J. SIgA in various pulmonary diseases. Eur J Med Res 2023, 28, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Grubbs, G.; Lee, Y.; Huang, C.; Ravichandran, S.; Forgacs, D.; Golding, H.; Ross, T.M.; Khurana, S. Antibody affinity maturation and cross-variant activity following SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination: Impact of prior exposure and sex. EBioMedicine 2021, 74, 103748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, A.; Muecksch, F.; Schaefer-Babajew, D.; Wang, Z.; Finkin, S.; Gaebler, C.; Ramos, V.; Cipolla, M.; Mendoza, P.; Agudelo, M.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain antibody evolution after mRNA vaccination. Nature 2021, 600, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Dominguez, D.; Henry, C.; Ma, L.; Jani, H.; Amato, N.J.; Manning, T.; Freyn, A.; Davis, H.; Hsiao, C.J.; Li, M.; et al. Altering the mRNA-1273 dosing interval impacts the kinetics, quality, and magnitude of immune responses in mice. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 948335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukwasibwe, S.; Traherne, J.A.; Chazara, O.; Jayaraman, J.; Trowsdale, J.; Moffett, A.; Jiang, W.; Nankabirwa, J.I.; Rek, J.; Arinaitwe, E.; et al. Diversity of KIR genes and their HLA-C ligands in Ugandan populations with historically varied malaria transmission intensity. Malar J 2021, 20, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, A.V.; Allsopp, C.E.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Taylor, T.E.; Yates, S.N.; Anstey, N.M.; Wirima, J.J.; Brewster, D.R.; McMichael, A.J.; Molyneux, M.E.; et al. Extensive genetic diversity in the HLA class II region of Africans, with a focally predominant allele, DRB1*1304. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagkrati, I.; Duke, J.L.; Mbunwe, E.; Mosbruger, T.L.; Ferriola, D.; Wasserman, J.; Dinou, A.; Tairis, N.; Damianos, G.; Kotsopoulou, I.; et al. Genomic characterization of HLA class I and class II genes in ethnically diverse SSAn populations: A report on novel HLA alleles. Hla 2023, 102, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Chao, T.L.; Chang, T.Y.; Hsiao, C.C.; Lu, D.C.; Chiang, Y.W.; Lai, G.C.; Tsai, Y.M.; Fang, J.T.; Ieong, S.; et al. Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Infection through Blocking Membrane Fusion. Microbiol Spectr 2022, 10, e0181421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, H.; Moosmann, C.; Schober, K.; Lang, V.; Verhagen, J.; Zeun, J.; Mackensen, A.; Kremer, A.N.; Völkl, S.; Aigner, M. Identification and characterization of T-cell receptors with therapeutic potential showing conserved specificity against all SARS-CoV 2 strains. Immunobiology 2023, 228, 152720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, D.; Brglez, V.; Allouche, J.; Zorzi, K.; Fernandez, C.; Teisseyre, M.; Cremoni, M.; Benzaken, S.; Pradier, C.; Seitz-Polski, B. Both Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Are Essential to Prevent Infection: a Prospective Study in a Working Vaccinated Population from Southern France. J Clin Immunol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).