Submitted:
05 October 2023
Posted:
06 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Activated Carbons
2.3. Preparation of ZnO@AC composites
2.4. Characterization techniques
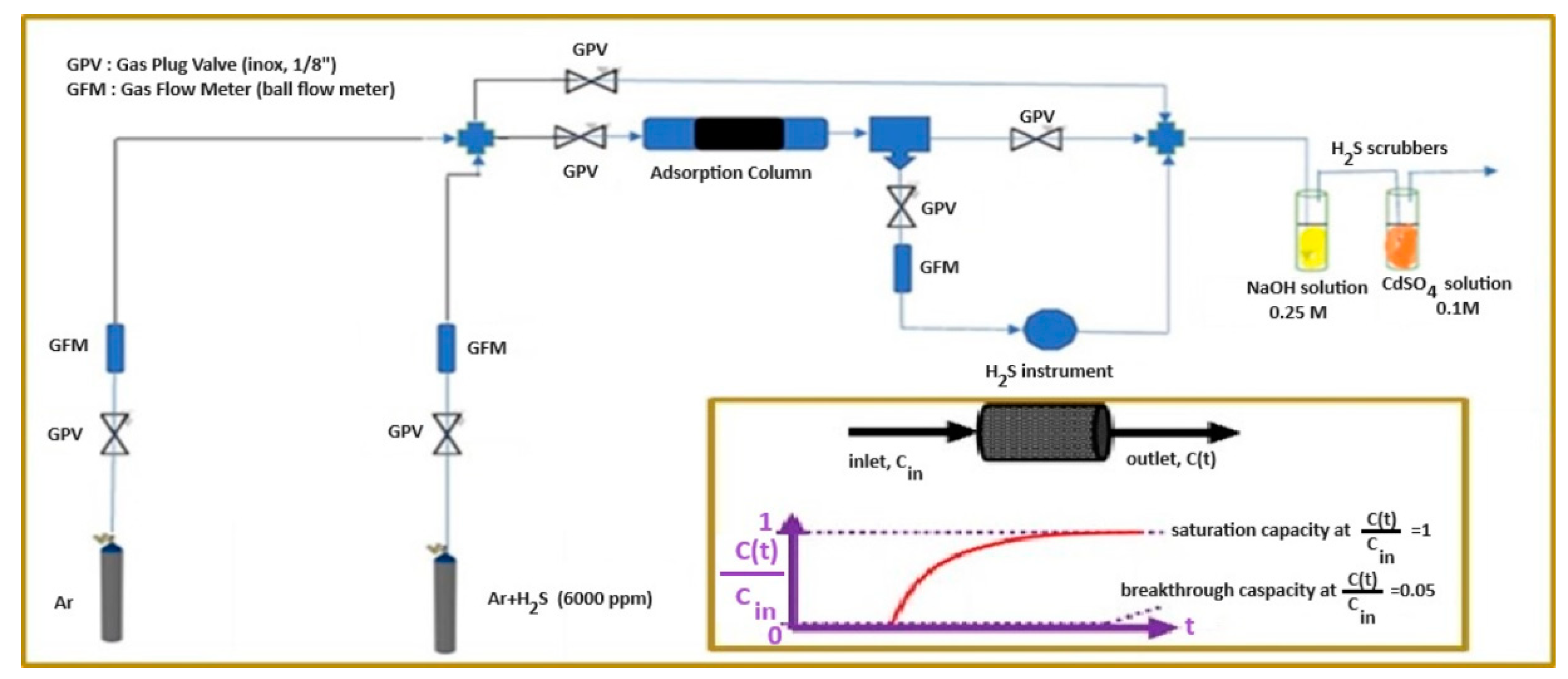
2.5. H2S sorption experimental measurements
3. Results and Discussion
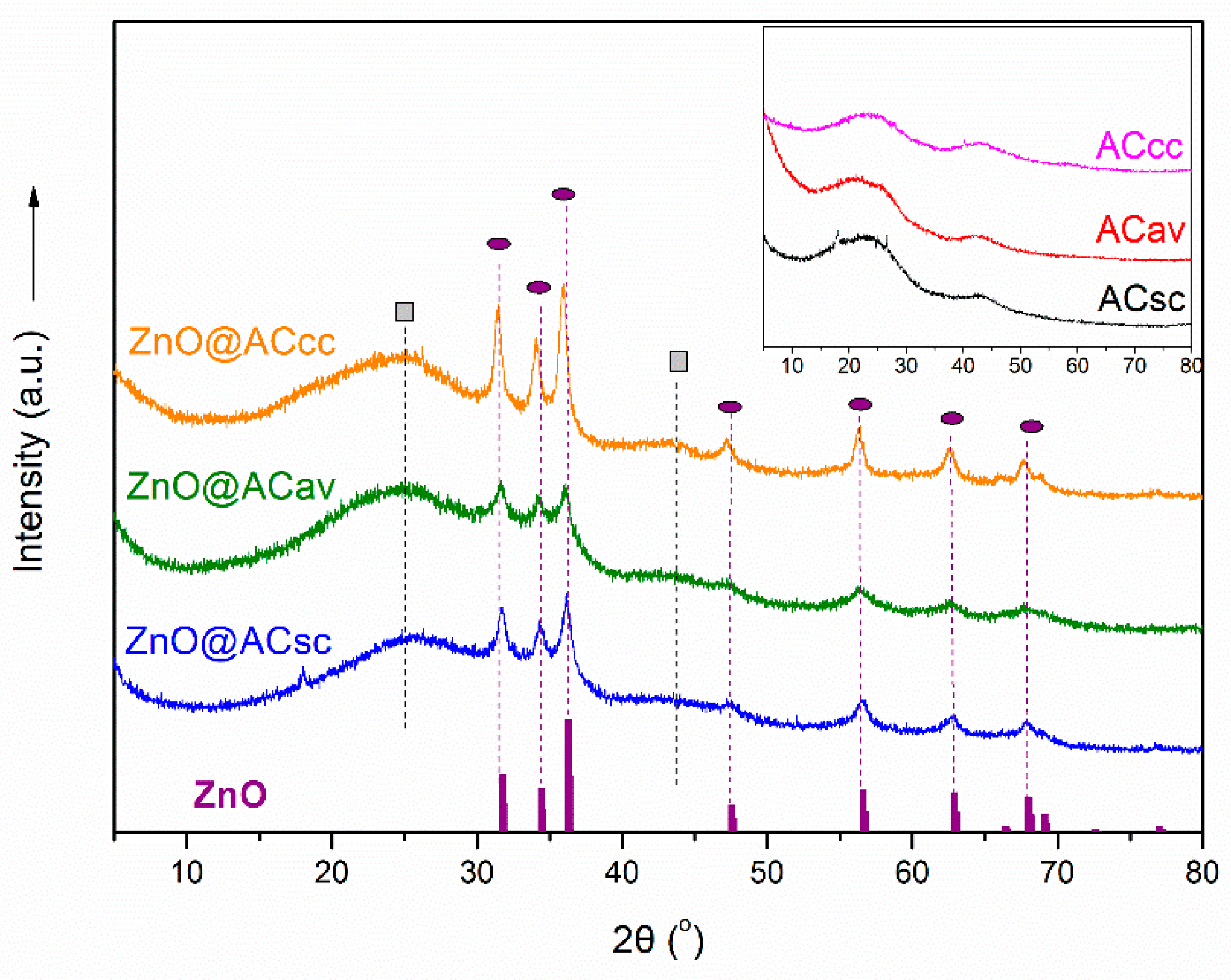
3.1. XRD Analysis of pure AC and ZnO@AC composites
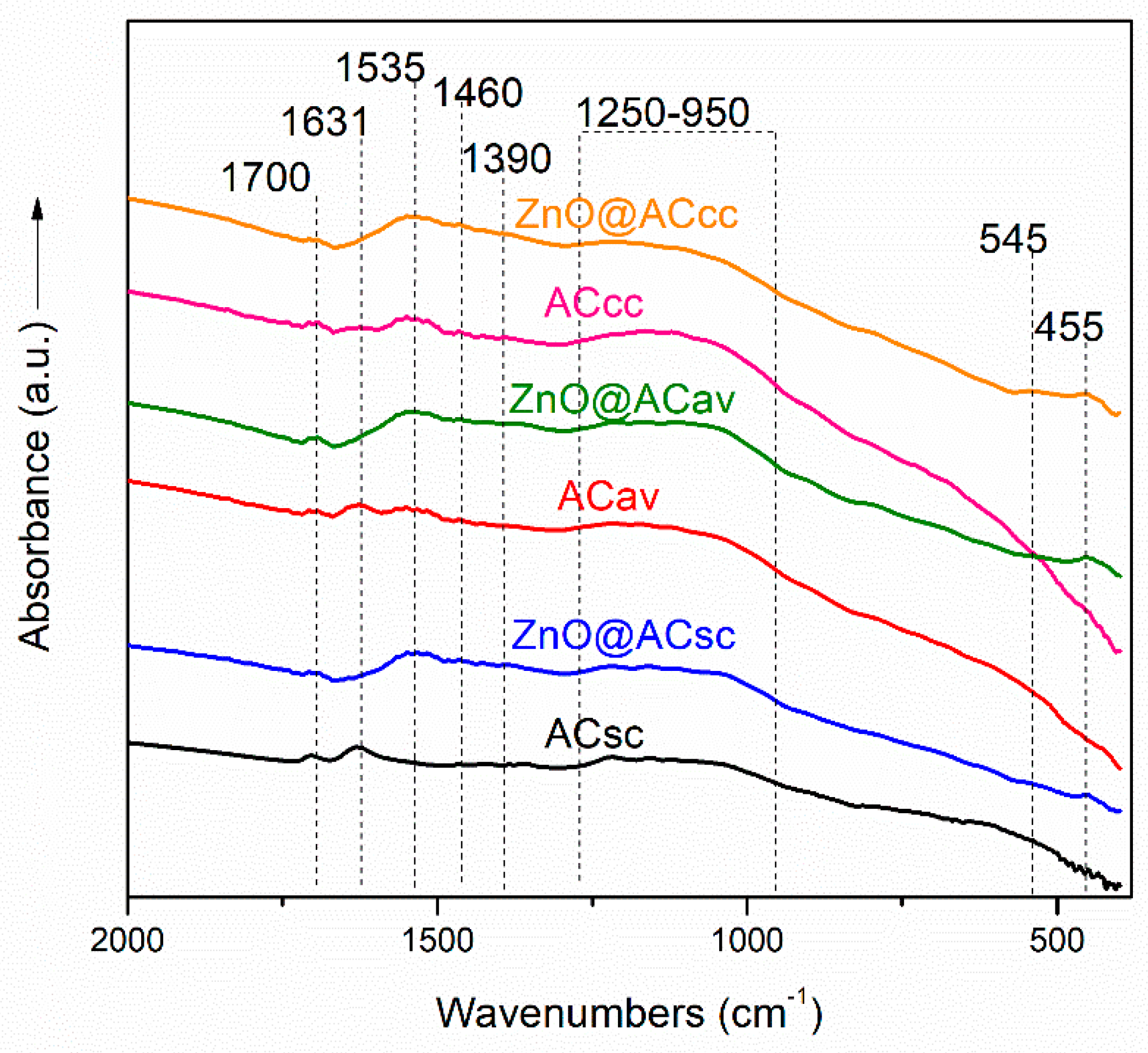
3.2. FTIR Spectroscopy of pure AC and ZnO@AC composites
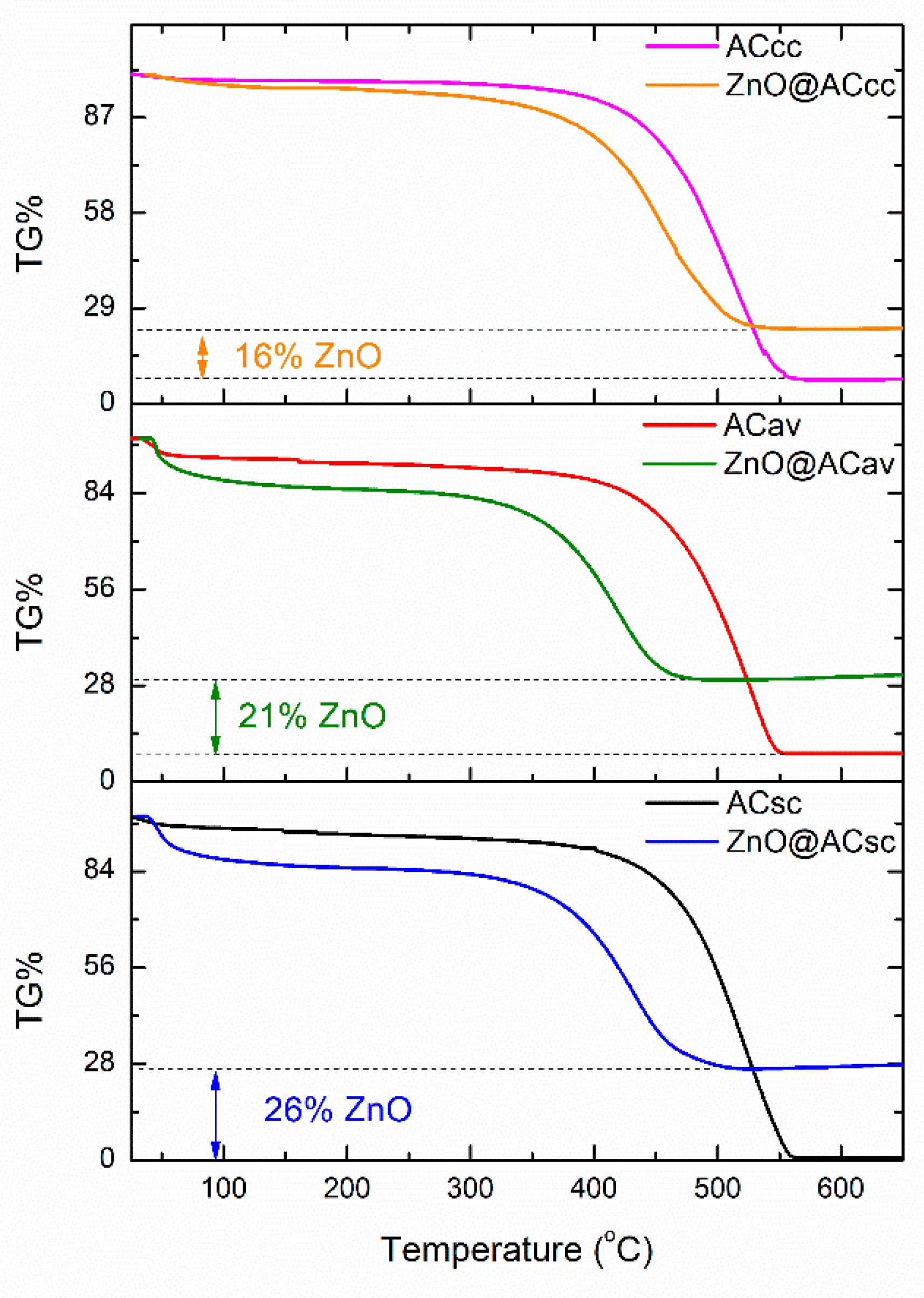
3.3. Thermogravimetric TG% analysis of pure AC and ZnO@AC composites
3.4. Nitrogen porosimetry for pore structure analysis of pure AC and ZnO@AC composites
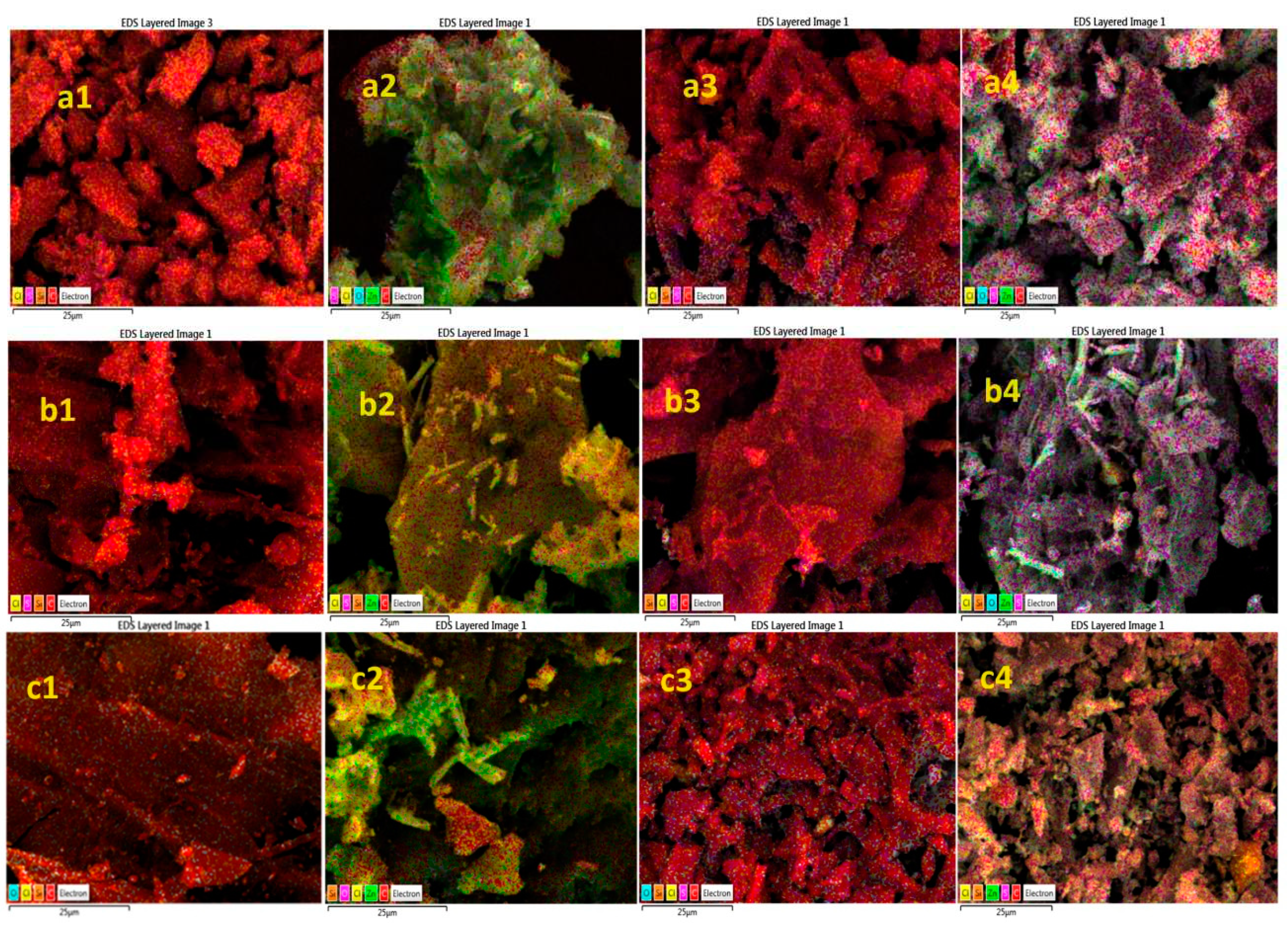
3.5. SEM-EDS images analysis of pure AC and ZnO@AC composites
3.6. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) removal experiments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomou, E.; Basina, G.; Spyrou, K.; Wahedi, Y.A.; Rudolf, P.; Gournis, D. H2S Removal by Copper Enriched Porous Carbon Cuboids. Carbon Trends 2022, 7, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Daham Wiheeb; Ili Khairunnisa Shamsudin; Mohd Azmier Ahmad; Muhamad Nazri Murat; Jinsoo Kim; Mohd Roslee Othman Present Technologies for Hydrogen Sulfide Removal from Gaseous Mixtures. Reviews in Chemical Engineering 2013, 29, 449–470. [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, A.G.; Charisiou, N.D.; Goula, M.A. Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide From Various Industrial Gases: A Review of The Most Promising Adsorbing Materials. Catalysts 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikrant, K.; Kailasa, S.K.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Lee, S.S.; Kumar, P.; Giri, B.S.; Singh, R.S.; Kim, K.-H. Biofiltration of Hydrogen Sulfide: Trends and Challenges. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 187, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Signorini, V.; Andersson, M.P.; Baschetti, M.G.; Mansouri, S.S. Hydrogen Sulfide Capture and Removal Technologies: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Developments and Emerging Trends. Separation and Purification Technology 2022, 298, 121448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabazipour, M.; Anbia, M. Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide from Gas Streams Using Porous Materials: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 22133–22164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkefli, N.N.; Noor Azam, A.M.; Masdar, M.S.; Isahak, W.N. Adsorption–Desorption Behavior of Hydrogen Sulfide Capture on a Modified Activated Carbon Surface. Materials 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashkova, S.; Baker, F.S.; Wu, X.; Armstrong, T.R.; Schwartz, V. Activated Carbon Catalyst for Selective Oxidation of Hydrogen Sulphide: On the Influence of Pore Structure, Surface Characteristics, and Catalytically-Active Nitrogen. Carbon 2007, 45, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, H.; Maghalseh, M.; Qutaina, J.; Junaidi, K.; Rene, E.R. Removal of Hydrogen Sulfide from Biogas Using Activated Carbon Synthesized from Different Locally Available Biomass Wastes - a Case Study from Palestine. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambabu, N.; Azargohar, R.; Dalai, A.K.; Adjaye, J. Evaluation and Comparison of Enrichment Efficiency of Physical/Chemical Activations and Functionalized Activated Carbons Derived from Fluid Petroleum Coke for Environmental Applications. Fuel Processing Technology 2013, 106, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, T.; Kubota, M.; Matsuda, H.; D’Elia Camacho, L.F. Adsorption Behaviors of Ammonia and Hydrogen Sulfide on Activated Carbon Prepared from Petroleum Coke by KOH Chemical Activation. Fuel Processing Technology 2016, 144, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.; Wang, S.; Jeong, H.-R. TMA and H2S Gas Removals Using Metal Loaded on Rice Husk Activated Carbon for Indoor Air Purification. Fuel 2018, 213, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierczak-Razna, J.; Gralak-Podemska, B.; Nowicki, P.; Pietrzak, R. The Use of Microwave Radiation for Obtaining Activated Carbons from Sawdust and Their Potential Application in Removal of NO2 and H2S. Chemical Engineering Journal 2015, 269, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.H.; Meneguin, J.G.; Pereira, M.V.; do Nascimento, J.F.; Arroyo, P.A. Adsorption of Hydrogen Sulfide, Carbon Dioxide, Methane, and Their Mixtures on Activated Carbon. Chemical Engineering Communications 2019, 206, 1533–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, Y.; Ke, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Qiao, W.; Ling, L. Efficient Removal of H2S with Zinc Oxide/Nitrogen-Doped Ordered Mesoporous Carbons at Room Temperature. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2022, 333, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyassi, B.; Wahedi, Y.A.; Rajabbeigi, N.; Kumar, P.; Jeong, J.S.; Zhang, X.; Kumar, P.; Balasubramanian, V.V.; Katsiotis, M.S.; Andre Mkhoyan, K.; et al. A High-Performance Adsorbent for Hydrogen Sulfide Removal. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2014, 190, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Fan, H.-L.; Shangguan, J.; Croiset, E.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Mi, J. Design of a Sorbent to Enhance Reactive Adsorption of Hydrogen Sulfide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21167–21177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvan, O.; Atakül, H. Investigation of CuO/Mesoporous SBA-15 Sorbents for Hot Gas Desulfurization. Fuel Processing Technology 2008, 89, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H. Hydrogen Sulfide Removal Technology: A Focused Review on Adsorption and Catalytic Oxidation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 674–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portela, R.; Rubio-Marcos, F.; Leret, P.; Fernández, J.F.; Bañares, M.A.; Ávila, P. Nanostructured ZnO/Sepiolite Monolithic Sorbents for H2S Removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 3, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samokhvalov, A.; Tatarchuk, B.J. Characterization of Active Sites, Determination of Mechanisms of H2S, COS and CS2 Sorption and Regeneration of ZnO Low-Temperature Sorbents: Past, Current and Perspectives. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2011, 13, 3197–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awume, B.; Tajallipour, M.; Nemati, M.; Predicala, B. Application of ZnO Nanoparticles in Control of H2S Emission from Low-Temperature Gases and Swine Manure Gas. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 2017, 228, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, S.P.; Chiappero, M.; Russo, N.; Fino, D. A Novel ZnO-Based Adsorbent for Biogas Purification in H2 Production Systems. Chemical Engineering Journal 2011, 176–177, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, S.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Shangguan, J. Tuning the ZnO-Activated Carbon Interaction through Nitrogen Modification for Enhancing the H2S Removal Capacity. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2019, 555, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Wang, L.-J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-R.; Fan, H.-L.; Huo, C. Room-Temperature Hydrogen Sulfide Removal with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle/Molecular Sieve Prepared by Melt Infiltration. Fuel Processing Technology 2019, 185, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. 1938, 60, 11. 60.
- Androutsopoulos, G.P.; Salmas, C.E. A New Model for Capillary Condensation−Evaporation Hysteresis Based on a Random Corrugated Pore Structure Concept: Prediction of Intrinsic Pore Size Distributions. 1. Model Formulation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2000, 39, 3747–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulos, G.P.; Salmas, C.E. A New Model for Capillary Condensation−Evaporation Hysteresis Based on a Random Corrugated Pore Structure Concept: Prediction of Intrinsic Pore Size Distribution. 2. Model Application. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2000, 39, 3764–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, R.J.; Hyduke, D.R.; Lastoskie, C.M. Pore Size Analysis of Activated Carbons from Argon and Nitrogen Porosimetry Using Density Functional Theory. 10.
- Salmas, C.E.; Androutsopoulos, G.P. Preparation and Characterization of Anodic Aluminum Oxide Films Exhibiting Microporosity. Chemical Engineering Communications 2008, 196, 407–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Rand, B. The Characterization of Microporous Carbons by Means of the Dubinin-Radushkevich Equation. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 1970, 33, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Nachrichten von Der Gesellschaft Der Wissenschaften Zu Göttingen. Göttinger Nachrichten Math. Phys. 1918, 2, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson, A.L. The Scherrer Formula for X-Ray Particle Size Determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffalla, S.; Mukhtar, H.; Shaharun, M. Properties of Activated Carbon Prepared from Rice Husk with Chemical Activation. Int. J. of Global Environmental Issues 2012, 12, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baikousi, M.; Georgiou, Y.; Daikopoulos, C.; Bourlinos, A.B.; Filip, J.; Zbořil, R.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Karakassides, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Robust Zero Valent Iron/Mesoporous Carbon Composites and Their Applications in Arsenic Removal. Carbon 2015, 93, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıntıg, E.; Yenigun, M.; Sarı, A.; Altundag, H.; Tuzen, M.; Saleh, T.A. Facile Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Loaded Activated Carbon as an Eco-Friendly Adsorbent for Ultra-Removal of Malachite Green from Water. Environmental Technology & Innovation 2021, 21, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Guo, H.; Shi, J.; Shi, C.; Jia, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, H.; et al. Facile One-Pot Preparation of Silver/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for Cancer Photodynamic and Photothermal Therapy. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2016, 16, 7049–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, R.; Wahyuningsih, S.; Ramelan, A.; Hanif, Q. Preparation of Nitrogen and Sulphur Co-Doped Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO-NS) Using N and S Heteroatom of Thiourea. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 2019, 509, 012119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunlan, L.; Shaoping, X.; Yixiong, G.; Shuqin, L.; Changhou, L. Effect of Pre-Carbonization of Petroleum Cokes on Chemical Activation Process with KOH. Carbon 2005, 43, 2295–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handore, K.; Bhavsar, S.; Horne, A.; Chhattise, P.; Mohite, K.; Ambekar, J.; Pande, N.; Chabukswar, V. Novel Green Route of Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles by Using Natural Biodegradable Polymer and Its Application as a Catalyst for Oxidation of Aldehydes. Journal of Macromolecular Science Part A Pure and Applied Chemistry 2014, 51, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmas, C.E. DOWNLOADS, CPSM_Nitrogen Available online: http://users.uoi.gr/ksalmas/.
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure and Applied Chemistry 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmas, C.E.; Androutsopoulos, G.P. Rigid Sphere Molecular Model Enables an Assessment of the Pore Curvature Effect upon Realistic Evaluations of Surface Areas of Mesoporous and Microporous Materials. Langmuir 2005, 21, 11146–11160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, K.; Michael, M.S. Hierarchical Porous Activated Carbon Prepared from Biowaste of Lemon Peel for Electrochemical Double Layer Capacitors. Biomass and Bioenergy 2021, 152, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Qi, J.; Hou, R.; Liu, B.; Yao, S.; Lang, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, B. Preparation of High-Performance Hierarchical Porous Activated Carbon via a Multistep Physical Activation Method for Supercapacitors. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 5456–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, H.; Li, A.; Li, H.; Cui, D.; Dong, M.; Lin, J.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Hou, H.; et al. Advanced Porous Hierarchical Activated Carbon Derived from Agricultural Wastes toward High Performance Supercapacitors. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2020, 820, 153111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Abbas, N.; Fino, D.; Russo, N. Novel Mesoporous Silica Supported ZnO Adsorbents for the Desulphurization of Biogas at Low Temperatures. Chemical Engineering Journal 2012, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
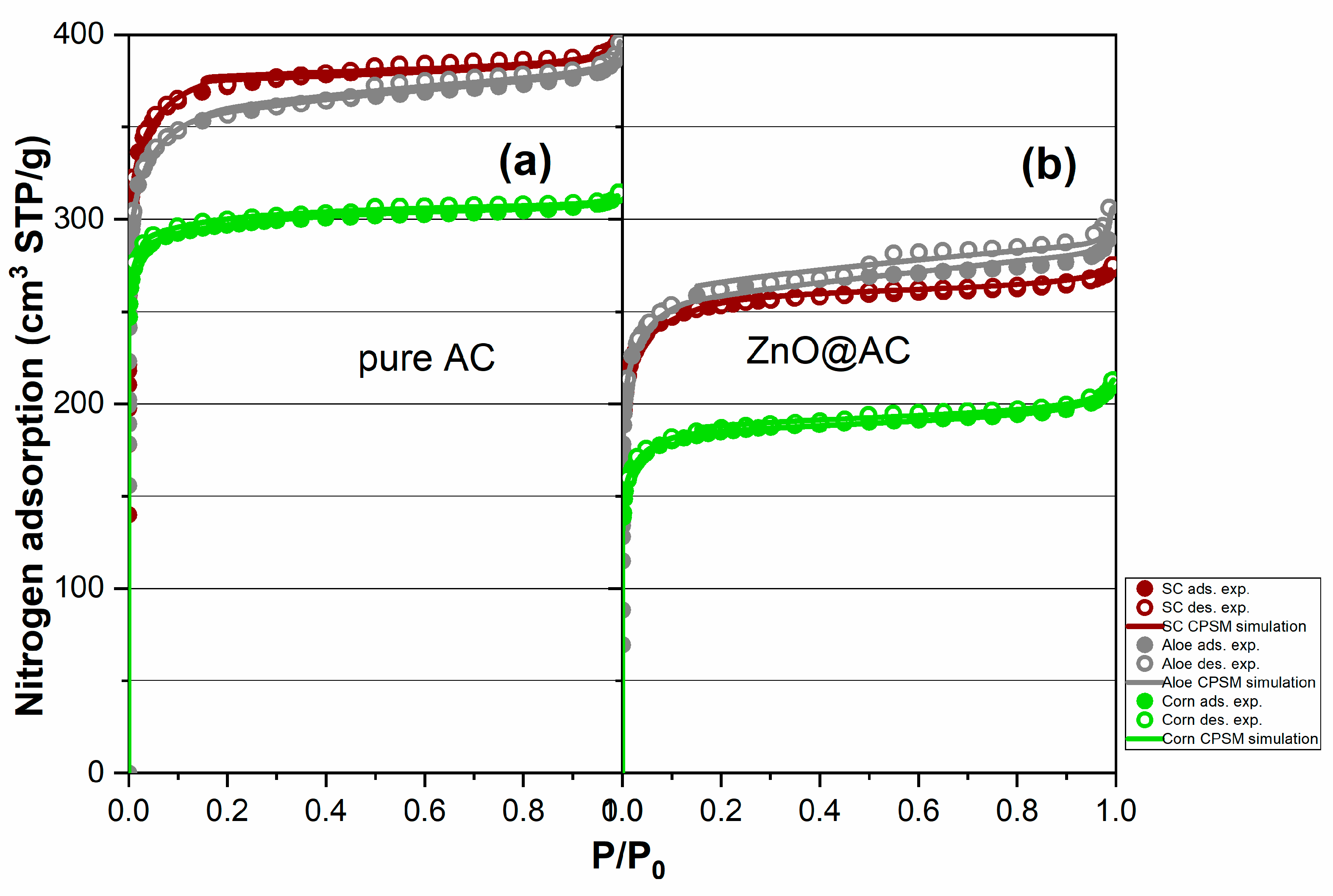
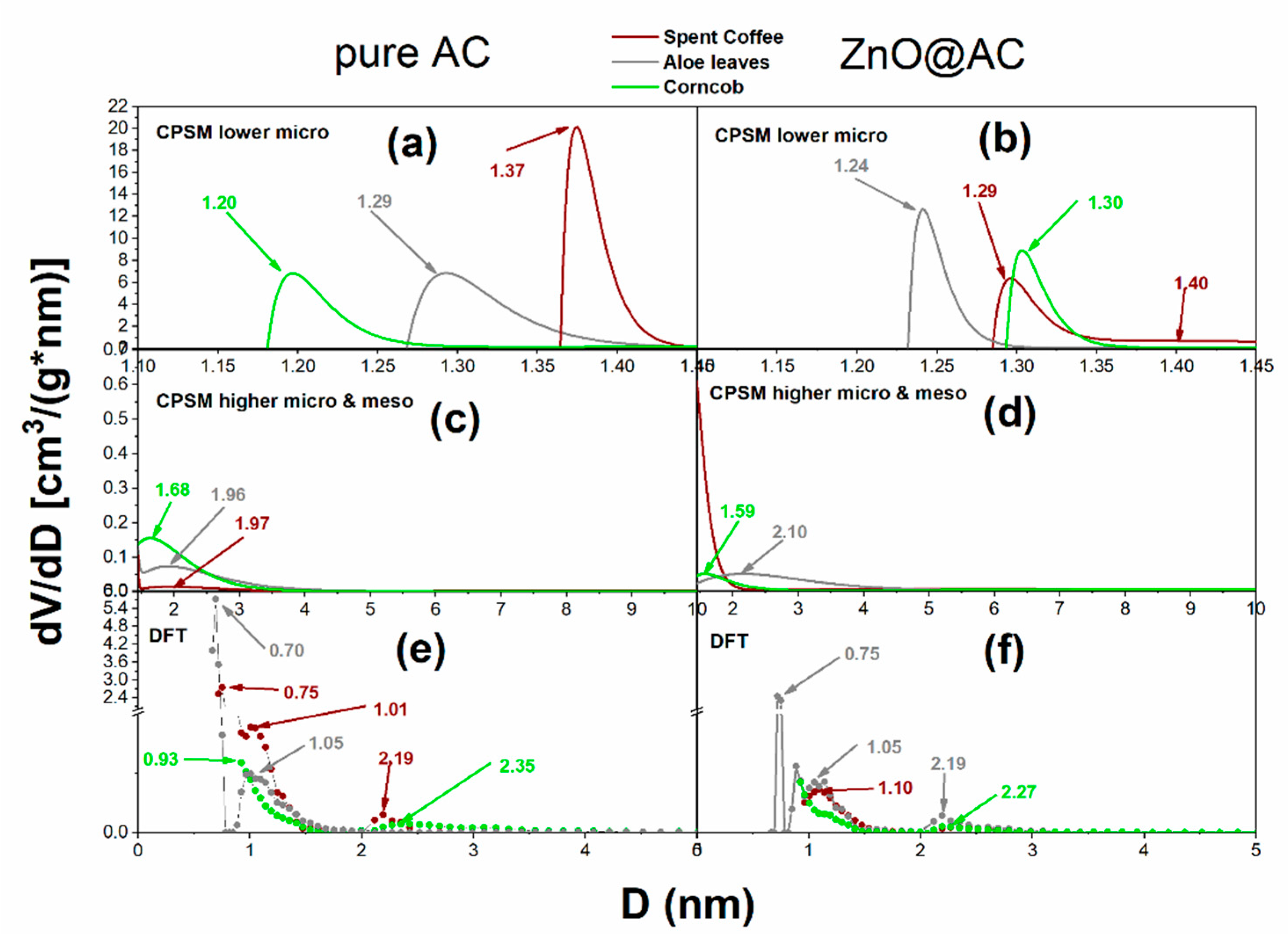
| Material code | Sg(m2/g) (BET) |
CBET | Sg(m2/g) (Lang.) |
CLang. | Sg(m2/g) (CPSM) |
decreasing ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACsc | 1195 | -65 | 1643 | 288 | 1653 | 1.5 |
| ZnO@ACsc | 818 | -64 | 1121 | 241 | 1132 | |
| ACav | 1148 | -67 | 1577 | 256 | 1594 | 1.3 |
| ZnO@ACav | 846 | -72 | 1156 | 210 | 1188 | |
| ACcc | 953 | -59 | 1300 | 506 | 1341 | 1.6 |
| ZnO@ACcc | 597 | -65 | 816 | 250 | 832 |
| Material code | Total pore volume (cm3/g) | Dmean (nm) CPSM low micro | %microp. (CPSM) |
%microp. (Dubinin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACsc | 0.615 | 1.37 | 91 | 93 |
| ZnO@ACsc | 0.422 | 1.29 | 91 | 93 |
| ACav | 0.613 | 1.29 | 80 | 90 |
| ZnO@ACav | 0.474 | 1.24 | 72 | 84 |
| ACcc | 0.484 | 1.20 | 82 | 95 |
| ZnO@ACcc | 0.329 | 1.30 | 81 | 87 |
| (SEM-EDS) S % wt. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Material code | fresh | used | increasing ratio |
| ACsc | 0.32 | 2.39 | 4.84 |
| ZnO@ACsc | 0.12 | 10.13 | |
| ACav | 0.38 | 2.31 | 5.65 |
| ZnO@ACav | 0.23 | 11.13 | |
| ACcc | 0 | 2.46 | 4.05 |
| ZnO@ACcc | 0 | 9.97 | |
| Material code | % yield | H2S flow (ml/min) |
GHSV (min-1) |
Ads. Cap. (mgH2S/gads.) |
Ads. Cap. (mmolH2S/gads.) |
times increase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACsc | 18.9 | 35.7 | 183 | 10.21 | 0.299 | 6.5 |
| ZnO@ACsc | 37.4 | 204 | 66.34 | 1.945 | ||
| ACav | 17.6 | 35.7 | 128 | 17.84 | 0.523 | 5.9 |
| ZnO@ACav | 35.7 | 136 | 106.03 | 3.109 | ||
| ACcc | 23.0 | 35.7 | 286 | 12.42 | 0.364 | 3.8 |
| ZnO@ACcc | 35.7 | 217 | 46.90 | 1.375 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





