Submitted:
29 September 2023
Posted:
05 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling sites and sampling methods
2.2. DNA extraction
2.3. Metagenomic sequencing
2.4. Data processing and operational taxonomic units (OTUs) analyses
2.5. Antagonism analyses and relative measuring
2.6. Pearson and Spearman correlation analysis
3. Results
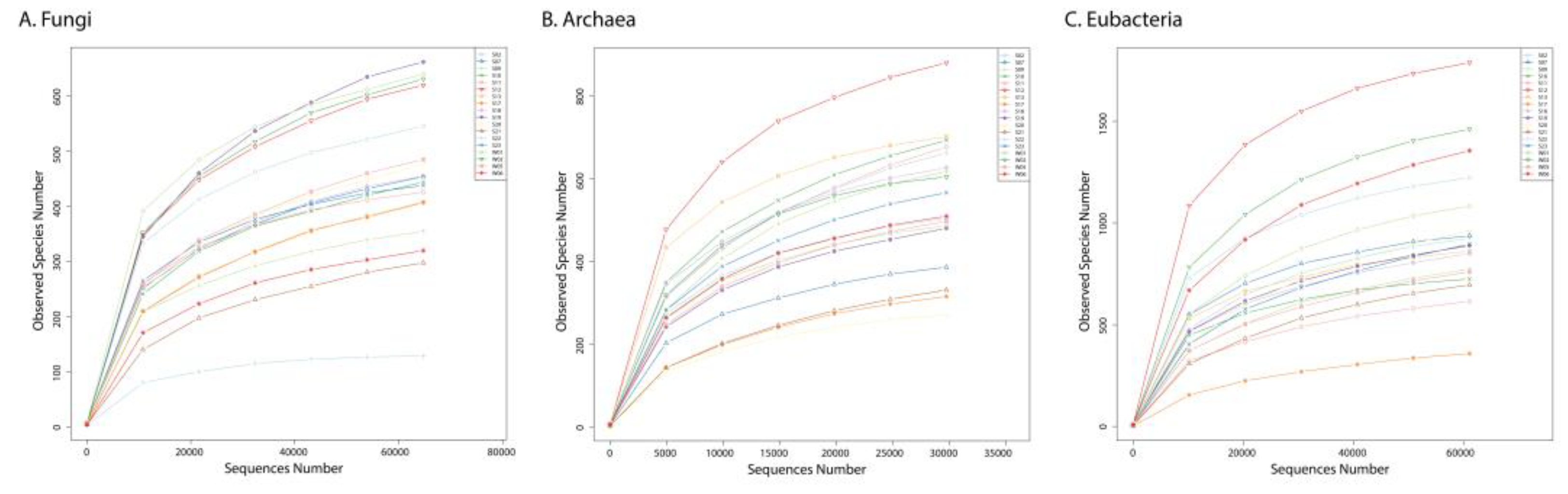
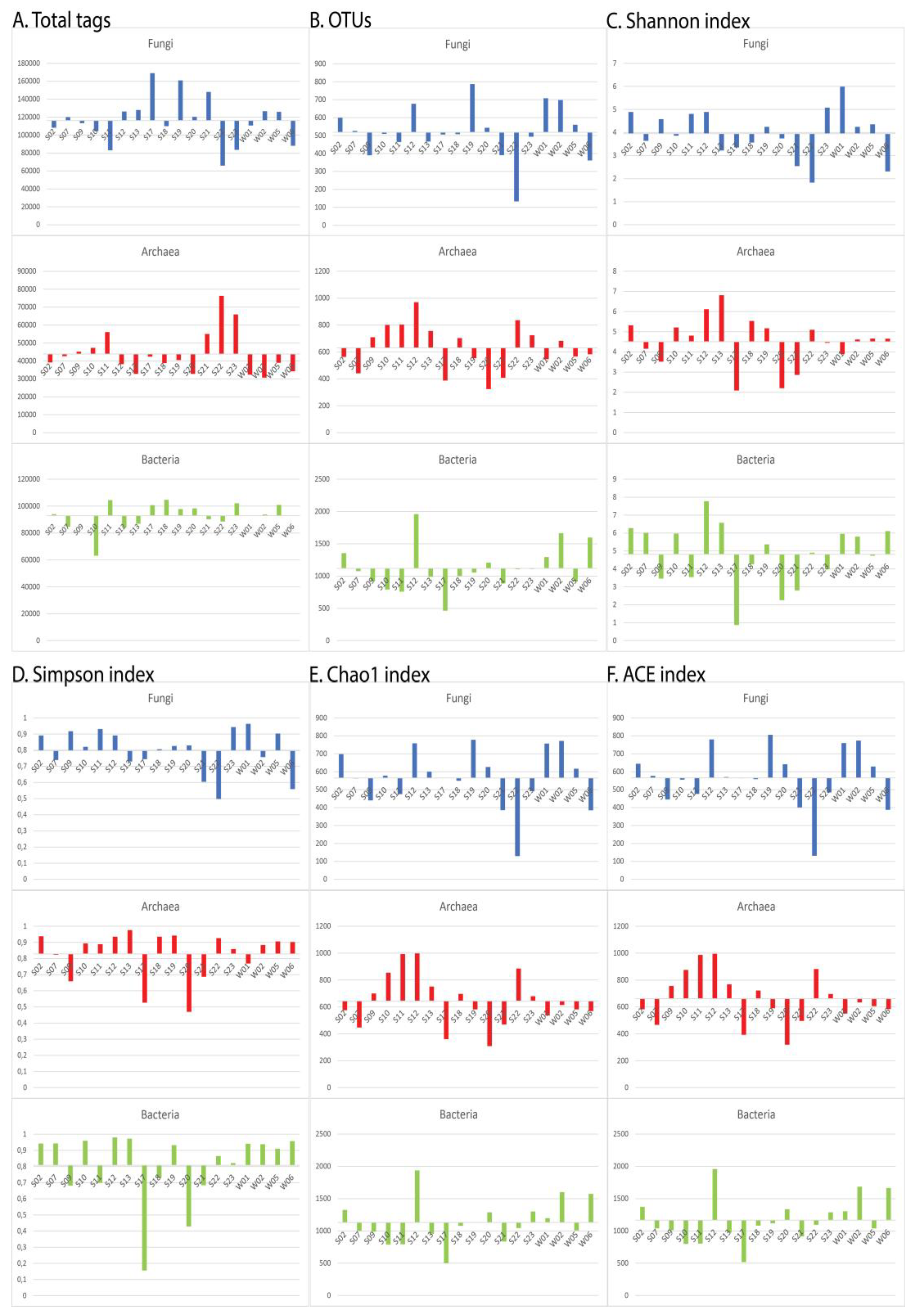
3.1. Sequencing statistics and alpha diversity indices
3.2. Antagonism study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barker, P.F.; Filippelli, G.M.; Florindo, F.; Martin, E.E.; Scher, H.D. Onset and role of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 2007, 54, 2388–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bej, A.K.; Mojib, N. Cold adaptation in Antarctic biodegradative microorganisms. Polar microbiology: the ecology, biodiversity and bioremediation potential of microorganisms in extremely cold environments 2009, 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, C.H. Cold adaptation in Arctic and Antarctic fungi. New Phytologist 2001, 151, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picazo, A.; Rochera, C.; Villaescusa, J.A.; Miralles-Lorenzo, J.; Velázquez, D.; Quesada, A.; Camacho, A. Bacterioplankton community composition along environmental gradients in lakes from Byers peninsula (Maritime Antarctica) as determined by next-generation sequencing. Frontiers in microbiology 2019, 10, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Lim, J.-H.; Jeong, J.-H.; Heo, J.-M.; Kim, I.-N. Distribution and Control of Bacterial Community Composition in Marian Cove Surface Waters, King George Island, Antarctica during the Summer of 2018. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleine, C.; Biagioli, F.; de Vera, J.P.; Onofri, S.; Selbmann, L. Endolithic microbial composition in Helliwell Hills, a newly investigated Mars-like area in Antarctica. Environmental Microbiology 2021, 23, 4002–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, G.C.; Lecomte, K.; Vignoni, P.; Rueda, E.S.; Coria, S.H.; Lirio, J.M.; Mlewski, E.C. Prokaryotic diversity and biogeochemical characteristics of benthic microbial ecosystems from James Ross Archipelago (West Antarctica). Polar Biology 2022, 45, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Garbeva, P.; Liu, X.; klein Gunnewiek, P.J.A.; Clocchiatti, A.; Hundscheid, M.P.J.; Wang, X.; de Boer, W. Volatile-mediated antagonism of soil bacterial communities against fungi. Environmental Microbiology 2020, 22, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nature Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I. , et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Gevers, D.; Earl, A.M.; Feldgarden, M.; Ward, D.V.; Giannoukos, G.; Ciulla, D.; Tabbaa, D.; Highlander, S.K.; Sodergren, E. Chimeric 16S rRNA sequence formation and detection in Sanger and 454-pyrosequenced PCR amplicons. Genome research 2011, 21, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nature Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Research 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kõljalg, U.; Nilsson, R.H.; Abarenkov, K.; Tedersoo, L.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bahram, M.; Bates, S.T.; Bruns, T.D.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Callaghan, T.M. , et al. Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Molecular Ecology 2013, 22, 5271–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A. Non-parametric estimation of the classes in a population. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A.; Lee, S.M. Estimating the Number of Classes Via Sample Coverage. J Am Stat Assoc 1992, 87, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Ma, M.C.; Yang, M.C.K. Stopping Rules and Estimation for Recapture Debugging with Unequal Failure Rates. Biometrika 1993, 80, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, L.N.; Fulthorpe, R.R.; Triplett, E.W.; Roesch, L.F.W. Rethinking microbial diversity analysis in the high throughput sequencing era. Journal of microbiological methods 2011, 86, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magurran, A. Measursuring biological diversity. In Blackwelll Publ; Company United Kingdom: New Jersey, US, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, D.S.; Yourstone, S.; Mieczkowski, P.; Jones, C.D.; Dangl, J.L. Practical innovations for high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Nature Methods 2013, 10, 999–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wuertz, S. Bacteria and archaea on Earth and their abundance in biofilms. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2019, 17, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Phillips, R.; Milo, R. The biomass distribution on Earth. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, 6506–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peay, K.G.; Kennedy, P.G.; Talbot, J.M. Dimensions of biodiversity in the Earth mycobiome. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2016, 14, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.R.; Shin, J.; Guevarra, R.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Seol, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.B.; Isaacson, R. Deciphering Diversity Indices for a Better Understanding of Microbial Communities. Journal of microbiology and biotechnology 2017, 27, 2089–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Caporaso, J.G.; Jiang, X.-T.; Sheng, H.-F.; Huse, S.M.; Rideout, J.R.; Edgar, R.C.; Kopylova, E.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R. , et al. Stability of operational taxonomic units: an important but neglected property for analyzing microbial diversity. Microbiome 2015, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccazzo, S.; Esposito, A.; Borruso, L.; Brusetti, L. Microbial communities and primary succession in high altitude mountain environments. Annals of Microbiology 2016, 66, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.; Lappan, R.; Hernández, M.; Santini, T.; Tomkins, A.G.; Greening, C. Functional basis of primary succession: Traits of the pioneer microbes. Environ Microbiol 2023, 25, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Description | Coordinates |
|---|---|---|
| Solid samples (S) | ||
| S02 | Microbial surface contamination from a rock submerged in the lagoon. | -62.641324, -60.368854 |
| S09, S10, S11, S21, S23 | Microbial surface contamination from rocks submerged in meltwater ponds close to the research base. | -62.641450, -60.356733 |
| S07, S19 | Microbial surface contamination from a rock submerged in the littoral zone of Sea Lion Tarn. | -62.647727, -60.353677 |
| S17 | Microbial surface contamination from a rock inside the area of the research base. | -62.641241, -60.361171 |
| S20 | Microbial surface contamination from algae within the littoral zone of Sea Lion Tarn. | -62.647727, -60.353677 |
| S13 | Biomass from a lithotelm in Hannah Point | -62.653262, -60.607902 |
| S22 | Biomass from a rock, submerged in an unnamed lake near the research base. | -62.640819, -60.350725 |
| S12 | Soil from underneath a patch of vegetation near the nameless lake. | -62.640819, -60.350725 |
| S18 | Sediment from the littoral zone of Sea Lion Tarn. | -62.647727, -60.353677 |
| Water samples (W) | ||
| W01 | Water from the littoral zone of the lagoon. | -62.641324, -60.368854 |
| W02 | Water from the littoral zone of Sea Lion Tarn | -62.647727, -60.353677 |
| W05 | Water from the pelagic zone of Johnson Dock | -62.659572, -60.370434 |
| W06 | Water from the littoral zone of South Bay, near the base. | -62.638681, -60.367835 |
| Sample | Total tags | OTUs | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | |
| S02 | 108303 | 39141 | 94003 | 599 | 563 | 1355 | 4,888 | 5,320 | 6,275 | 0,891 | 0,938 | 0,942 | 697,250 | 575,562 | 1325,202 | 644,266 | 582,952 | 1371,986 |
| S07 | 119964 | 42644 | 84660 | 526 | 441 | 1077 | 3,639 | 4,157 | 6,010 | 0,739 | 0,823 | 0,943 | 562,544 | 447,338 | 1003,306 | 576,516 | 466,759 | 1041,073 |
| S09 | 113287 | 45224 | 93056 | 390 | 709 | 920 | 4,579 | 3,521 | 3,455 | 0,917 | 0,659 | 0,682 | 440,429 | 700,038 | 989,007 | 445,363 | 756,005 | 1010,778 |
| S10 | 104399 | 47252 | 63121 | 509 | 801 | 792 | 3,857 | 5,213 | 5,967 | 0,821 | 0,894 | 0,959 | 578,200 | 854,182 | 789,629 | 555,830 | 875,150 | 798,890 |
| S11 | 83007 | 56071 | 104444 | 464 | 803 | 758 | 4,803 | 4,807 | 3,541 | 0,931 | 0,889 | 0,699 | 474,684 | 993,260 | 794,219 | 476,334 | 986,739 | 803,751 |
| S12 | 126350 | 38224 | 84187 | 677 | 970 | 1959 | 4,892 | 6,117 | 7,776 | 0,891 | 0,935 | 0,980 | 758,261 | 997,560 | 1936,242 | 779,822 | 994,997 | 1957,808 |
| S13 | 127940 | 32805 | 86878 | 467 | 756 | 989 | 3,218 | 6,811 | 6,573 | 0,730 | 0,976 | 0,972 | 599,820 | 751,688 | 958,425 | 570,035 | 767,540 | 975,776 |
| S17 | 169009 | 42381 | 100712 | 506 | 387 | 464 | 3,356 | 2,091 | 0,872 | 0,744 | 0,527 | 0,156 | 566,125 | 360,000 | 501,726 | 563,556 | 392,774 | 518,494 |
| S18 | 109955 | 38800 | 104705 | 508 | 703 | 999 | 3,566 | 5,533 | 4,262 | 0,806 | 0,935 | 0,729 | 549,721 | 696,966 | 1079,174 | 558,794 | 722,050 | 1083,829 |
| S19 | 160873 | 40505 | 97775 | 787 | 554 | 1055 | 4,247 | 5,170 | 5,366 | 0,826 | 0,942 | 0,932 | 778,059 | 581,346 | 1136,078 | 805,678 | 590,759 | 1119,067 |
| S20 | 120389 | 32799 | 98326 | 543 | 324 | 1209 | 3,742 | 2,203 | 2,252 | 0,829 | 0,470 | 0,428 | 626,217 | 308,983 | 1288,044 | 641,587 | 319,270 | 1336,556 |
| S21 | 148086 | 55083 | 90215 | 391 | 408 | 887 | 2,545 | 2,862 | 2,799 | 0,604 | 0,687 | 0,684 | 385,549 | 469,600 | 836,520 | 401,038 | 496,508 | 915,860 |
| S22 | 65967 | 76305 | 88563 | 133 | 836 | 1105 | 1,827 | 5,095 | 4,903 | 0,498 | 0,926 | 0,865 | 129,441 | 885,269 | 1044,691 | 131,693 | 882,408 | 1094,848 |
| S23 | 83584 | 65897 | 102063 | 494 | 724 | 1111 | 5,074 | 4,448 | 3,978 | 0,943 | 0,859 | 0,821 | 491,774 | 679,129 | 1301,684 | 484,776 | 696,083 | 1288,961 |
| W01 | 110722 | 32349 | 92749 | 708 | 546 | 1294 | 5,987 | 3,897 | 5,955 | 0,963 | 0,769 | 0,941 | 756,450 | 536,670 | 1196,763 | 759,495 | 550,773 | 1304,621 |
| W02 | 126520 | 30704 | 93799 | 698 | 682 | 1662 | 4,246 | 4,616 | 5,799 | 0,757 | 0,884 | 0,938 | 771,759 | 613,806 | 1600,936 | 773,188 | 634,555 | 1685,559 |
| W05 | 125937 | 38998 | 100912 | 560 | 567 | 915 | 4,355 | 4,660 | 4,740 | 0,903 | 0,906 | 0,910 | 616,724 | 581,394 | 1008,050 | 629,018 | 605,718 | 1040,591 |
| W06 | 88052 | 34246 | 92969 | 361 | 583 | 1597 | 2,312 | 4,655 | 6,110 | 0,559 | 0,902 | 0,957 | 384,800 | 568,860 | 1574,371 | 387,693 | 584,415 | 1665,36 |
| Average value | 116241 | 43857 | 92952 | 518 | 631 | 1119 | 3,952 | 4,510 | 4,81 | 0,797 | 0,829 | 0,808 | 564,878 | 644,536 | 1131,337 | 565,816 | 661,414 | 1167,434 |
| Sample | Total tags | OTUs | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | Fungi | Archaea | Bacteria | |
| S02 | - | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| S07 | + | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| S09 | - | + | + | - | + | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - |
| S10 | - | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| S11 | - | + | + | - | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | + | - |
| S12 | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| S13 | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| S17 | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| S18 | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | - |
| S19 | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| S20 | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| S21 | + | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| S22 | - | + | - | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | - | - | + | - |
| S23 | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + |
| W01 | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| W02 | + | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | + |
| W05 | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | - | + | - | - |
| W06 | - | - | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | + |
| Total tags | OTUs | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of cases of discrepancies | |||||||||||
| Fungi vs Archaea | 10 | 12 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | |||||
| Fungi vs Bacteria | 10 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 4 | 7 | |||||
| Archaea vs Bacteria | 10 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 10 | 11 | |||||
| Percentages of cases of discrepancies | |||||||||||
| Fungi vs Archaea | 56% | 67% | 44% | 44% | 44% | 56% | |||||
| Fungi vs Bacteria | 56% | 44% | 44% | 50% | 22% | 39% | |||||
| Archaea vs Bacteria | 56% | 56% | 22% | 17% | 56% | 61% | |||||
| Community Correlation | Effective Tags | OTUs | Shannon | Simpson | Chao1 | ACE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fungi – Archaea | -0.481 | -0.137 | 0.071 | -0.029 | -0.179 | -0.202 |
| -0.389 | -0.290 | 0.055 | -0.151 | -0.115 | -0.201 | |
| Archaea – Bacteria | -0.003 | 0.290 | 0.802 | 0.833 | 0.170 | 0.108 |
| 0.034 | 0.057 | 0.688 | 0.618 | -0.022 | -0.057 | |
| Fungi – Bacteria | 0.060 | 0.310 | 0.187 | 0.020 | 0.344 | 0.341 |
| -0.084 | 0.375 | 0.110 | -0.136 | 0.395 | 0.455 | |
| The upper shows the Pearson correlation, while the number below presents the Spearman correlation. | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





