Submitted:
02 October 2023
Posted:
03 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
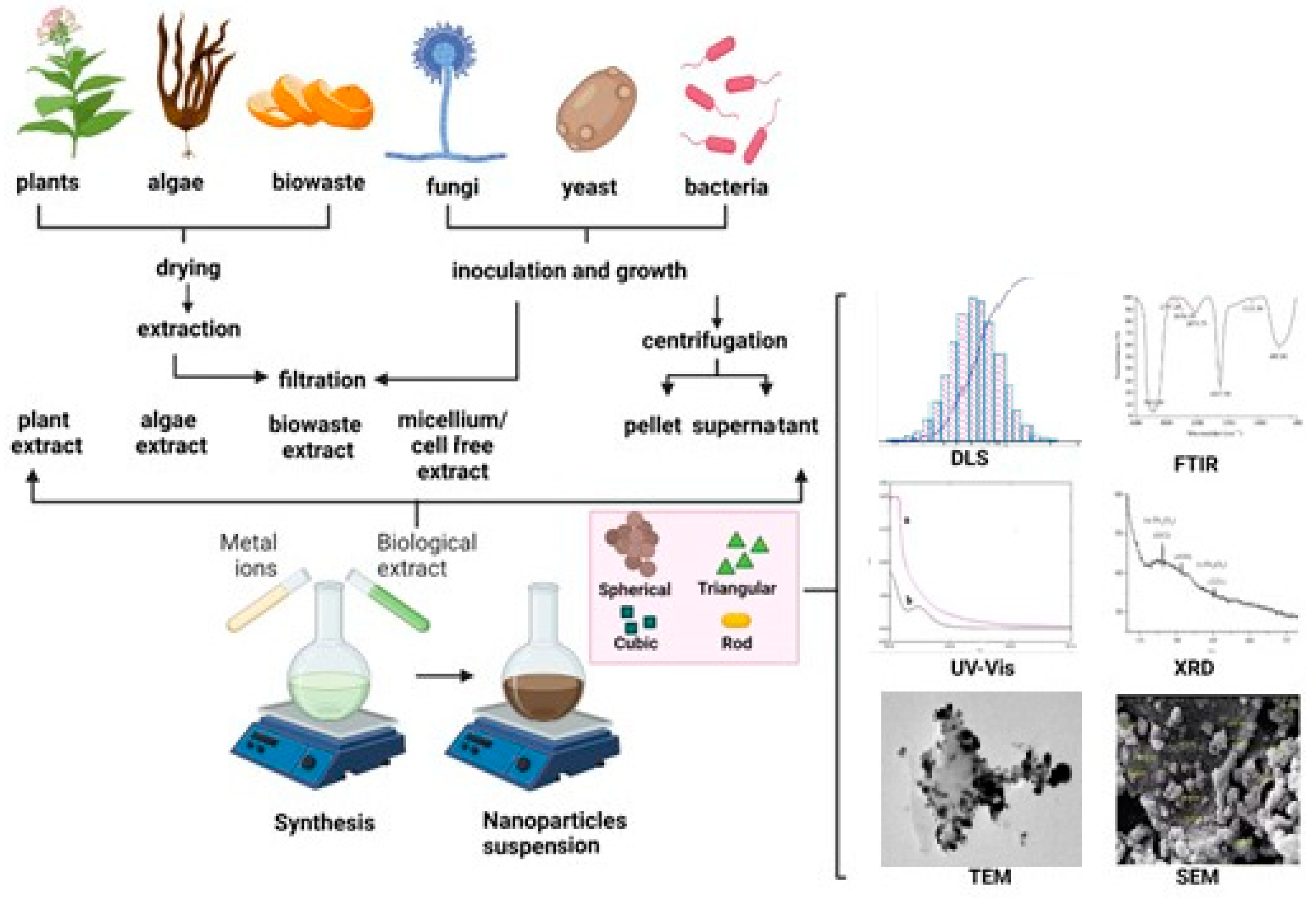
1. Introduction
2. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles
2.1. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using microorganisms
2.2. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using bacteria
2.3. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using fungi
2.4. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using algae
2.5. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using plants
2.6. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using from biological waste products
3. Characterization methods
3.1. UV–VIS spectroscopy
3.2. TEM and HRTEM
3.3. SEM
3.4. EDX
3.5. XRD
3.6. DLS
4. Antimicrobial properties of green-mediated synthesis iron oxide nanoparticles
4.1. Antibacterial activity.
4.1.1. Mechanisms of Antibacterial IONPs Activity.
4.1.2. Membrane disruption
4.1.3. Protein and DNA damage
4.1.4. Antibiofilm activities
4.2. Antifungal activity
4.3. Antiparasitic activity
4.4. Antiviral activity
5. Conclusions and future prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aisida, S.O.; Madubuonu, N.; Alnasir, M.H.; Ahmad, I.; Botha, S.; Maaza, M.; Ezema, F.I. Biogenic synthesis of iron oxide nanorods using Moringa oleifera leaf extract for antibacterial applications. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Singh, N.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.C. Green synthesis of nanoparticles and its potential application. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamzad, M.; Kamari Bidkorpeh, M. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by the aqueous extract of Laurus nobilis L. leaves and evaluation of the antimicrobial activity. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2020, 10, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Kamarasu, P.; McClements, D.J.; Moore, M.D. Metal and metal oxide-based antiviral nanoparticles: Properties, mechanisms of action, and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 306, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Fan, K.; Yan, X. Iron oxide nanozyme: A multifunctional enzyme mimetic for biomedical applications. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3207–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.H.; Miah, M.Y.; Paul, S.C.; Aka, T.D.; Saha, O.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sharif, M.J.I.; Habiba, O.; Ashaduzzaman, M. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticle using Carica papaya leaf extract: application for photocatalytic degradation of remazol yellow RR dye and antibacterial activity. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Ur Rahman, A.; Tajuddin; Husen, A. Biogenic fabrication of iron/iron oxide nanoparticles and their application. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zafar, H.; Zia, M.; Ul Haq, I.; Phull, A.R.; Ali, J.S.; Hussain, A. Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.-C. Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya; Naveen; Kaur, K. ; Sidhu, A.K. Green Synthesis: An Eco-friendly Route for the Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, D.; Nag, M.; Sheikh, H.I.; Sarkar, T.; Edinur, H.A.; Pati, S.; Ray, R.R. Microbiologically-Synthesized Nanoparticles and Their Role in Silencing the Biofilm Signaling Cascade. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 636588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, M.; Mollania, N.; Momeni-Moghaddam, M.; Sadeghifar, F. Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by Bacillus cereus strain HMH1: Characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity analysis on MCF-7 and 3T3 cell lines. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 270, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, M.; Khan, R.; Shah, N.; Bangash, I.R.; Abbasi, B.H.; Hano, C.; Liu, C.; Ullah, S.; Hashmi, S.S.; Nadhman, A.; Celli, J. A review of microbial mediated iron nanoparticles (ionps) and its biomedical applications. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, F.; Fozia, F.; Aslam, M.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, S.; Ullah, R.; Almutairi, M.H.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Characterization, Antiplasmodial and Cytotoxic Activities of Green Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Nephrolepis exaltata Aqueous Extract. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Greener synthesis of lignin nanoparticles and their applications. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 612–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, M.; Ghandehari, F.; Rezaee, M. Biosynthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by Cytoplasmic Extract of Bacteria Lactobacillus Fermentum. Journal of Medicinal and Chemical Sciences 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram, P.A.; Augustine, R.; Kannan, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by Bacillus subtilis strains isolated from rhizosphere soil. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2012, 17, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torabian, P.; Ghandehari, F.; Fatemi, M. Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by cytoplasmic extracts of bacteria lactobacillus casei. Asian Journal of Green Chemistry 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dlamini, N.G.; Basson, A.K.; Pullabhotla, R.V. Wastewater Treatment by a Polymeric Bioflocculant and Iron Nanoparticles Synthesized from a Bioflocculant. Polymers (Basel) 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharde, A.A.; Parikh, R.Y.; Baidakova, M.; Jouen, S.; Hannoyer, B.; Enoki, T.; Prasad, B.L.V.; Shouche, Y.S.; Ogale, S.; Sastry, M. Bacteria-mediated precursor-dependent biosynthesis of superparamagnetic iron oxide and iron sulfide nanoparticles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 5787–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharde, A.; Wani, A.; Shouche, Y.; Joy, P.A.; Prasad, B.L.V.; Sastry, M. Bacterial aerobic synthesis of nanocrystalline magnetite. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9326–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, R.K.; Kumar, P.; Burman, U.; Joshi, P.; Agrawal, A.; Raliya, R.; Tarafdar, J.C. Magnesium and iron nanoparticles production using microorganisms and various salts. Mater Sci-Pol 2012, 30, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, M.; Hosseini, M.R. From the iron boring scraps to superparamagnetic nanoparticles through an aerobic biological route. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.R.; Kerkar, S. Biosynthesis of iron nanoparticles by sulphate reducing bacteria and its application in remediating chromium from water. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, K.A.; Baronetti, J.L.; Quinteros, M.A.; Páez, P.L.; Paraje, M.G. Intra- and Extracellular Biosynthesis and Characterization of Iron Nanoparticles from Prokaryotic Microorganisms with Anticoagulant Activity. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, J.M.; Telling, N.D.; Coker, V.S.; Pattrick, R.A.D.; van der Laan, G.; Arenholz, E.; Tuna, F.; Lloyd, J.R. Control of nanoparticle size, reactivity and magnetic properties during the bioproduction of magnetite by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 455709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, S.L.; Shetty, A.R.; Senpan, A.; Echeverry-Rendón, M.; Reece, L.M.; Allain, J.P. Fabrication of a Functionalized Magnetic Bacterial Nanocellulose with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Vis. Exp. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raĭkher, Yu.L.; Stepanov, V.I.; Stolyar, S.V.; Ladygina, V.P.; Balaev, D.A.; Ishchenko, L.A.; Balasoiu, M. Magnetic properties of biomineral particles produced by bacteria Klebsiella oxytoca. Phys. Solid State 2010, 52, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Yokoyama, S.; Asaoka, H.; Kusano, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Seno, M.; Takada, J.; Fujii, T.; Nakanishi, M.; Murakami, R. Characteristics of hollow microtubes consisting of amorphous iron oxide nanoparticles produced by iron oxidizing bacteria, Leptothrix ochracea. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2405–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayemi, J.D.; Dozie-Nwachukwu, S.; Danyuo, Y.; Odusanya, O.S.; Anuku, N.; Malatesta, K.; Soboyejo, W.O. Biosynthesis and the conjugation of magnetite nanoparticles with luteinizing hormone releasing hormone (LHRH). Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2015, 46, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeldt, S.; Mickoleit, F.; Jörke, C.; Clement, J.H.; Markert, S.; Jérôme, V.; Schwarzinger, S.; Freitag, R.; Schüler, D.; Uebe, R.; Schenk, A.S. Towards standardized purification of bacterial magnetic nanoparticles for future in vivo applications. Acta Biomater. 2021, 120, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P. Stenotrophomonas and microbacterium: mediated biogenesis of copper, silver and iron nanoparticles—proteomic insights and antibacterial properties versus biofilm formation. J. Clust. Sci. 2017, 28, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Menguy, N.; Gatel, C.; Boureau, V.; Snoeck, E.; Patriarche, G.; Leroy, E.; Pan, Y. Crystal growth of bullet-shaped magnetite in magnetotactic bacteria of the Nitrospirae phylum. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, M.P.; Pawar, K.D. Immobilization of cellulase on iron tolerant Pseudomonas stutzeri biosynthesized photocatalytically active magnetic nanoparticles for increased thermal stability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 106, 110169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de França Bettencourt, G.M.; Degenhardt, J.; Zevallos Torres, L.A.; de Andrade Tanobe, V.O.; Soccol, C.R. Green biosynthesis of single and bimetallic nanoparticles of iron and manganese using bacterial auxin complex to act as plant bio-fertilizer. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 101822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, S.A.; Eltarahony, M.M.; Abd-El-Haleem, D.A. Disinfection of water and wastewater by biosynthesized magnetite and zerovalent iron nanoparticles via NAP-NAR enzymes of Proteus mirabilis 10B. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 23661–23678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Hochella, M.F.; Gorby, Y.A.; Kennedy, D.W.; McCready, D.E.; Madden, A.S.; Lower, B.H. Bioreduction of hematite nanoparticles by the dissimilatory iron reducing bacterium Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haikarainen, T.; Paturi, P.; Lindén, J.; Haataja, S.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Finne, J.; Papageorgiou, A.C. Magnetic properties and structural characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles formed by Streptococcus suis Dpr and four mutants. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 16, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-W.; Rawn, C.J.; Rondinone, A.J.; Love, L.J.; Roh, Y.; Everett, S.M.; Lauf, R.J.; Phelps, T.J. Large-scale production of magnetic nanoparticles using bacterial fermentation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcey; Kuruvilla, A.; Thomas, D. Synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles from optimized iron reducing bacteria isolated from iron ore mining sites. undefined, 2014.
- Chatterjee, S.; Mahanty, S.; Das, P.; Chaudhuri, P.; Das, S. Biofabrication of iron oxide nanoparticles using manglicolous fungus Aspergillus niger BSC-1 and removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 385, 123790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharde, A.; Rautaray, D.; Bansal, V.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, I.; Yusuf, S.M.; Sanyal, M.; Sastry, M. Extracellular biosynthesis of magnetite using fungi. Small 2006, 2, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, H.; Venkat Kumar, S.; Rajeshkumar, S. A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles – An eco-friendly approach. Resource-Efficient Technologies 2017, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghuthaymi, M.A.; Almoammar, H.; Rai, M.; Said-Galiev, E.; Abd-Elsalam, K.A. Myconanoparticles: synthesis and their role in phytopathogens management. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakariya, N.A.; Majeed, S.; Jusof, W.H.W. Investigation of antioxidant and antibacterial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPS) synthesized from the aqueous extract of Penicillium spp. Sensors International 2022, 3, 100164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, C.-L.; Chen, X.-F. Recent advances on biosorption by aerobic granular sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.P.; Reis, I.G.; Bonatto, C.C. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles by plants: current trends and challenges. In Green processes for nanotechnology; Basiuk, V. A., Basiuk, E. V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2015; pp. 259–275; ISBN 978-3-319-15460-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, A.; Jain, N.; Barathi L., M. ; Akhtar, Mohd.S.; Yun, Y.-S., Panwar, J. Synthesis, characterization and mechanistic insights of mycogenic iron oxide nanoparticles. In Nanotechnology for sustainable development, Diallo, M. S., Fromer, N. A., Jhon, M. S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2014; pp. 337–348; ISBN 978-3-319-05040-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mahanty, S.; Bakshi, M.; Ghosh, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Das, P.; Das, S.; Chaudhuri, P. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mediated by Filamentous Fungi Isolated from Sundarban Mangrove Ecosystem, India. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccile, N.; Noiville, R.; Stievano, L.; Van Bogaert, I. Sophorolipids-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, J.; Mollick, M.M.R.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Acharya, K. An eco-friendly route of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles formation and investigation of the mechanical properties of the HPMC-γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposites. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, M.; Sabry, S.; Ghozlan, H.; El-Gendy, A.A.; Carpenter, E.E. Microbial-Physical Synthesis of Fe and Fe3 O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles UsingAspergillus niger YESM1 and Supercritical Condition of Ethanol. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Ahmad, R.; Sardar, M. Biosynthesized iron oxide nanoparticles mimicking peroxidase activity: application for biocatalysis and biosensing. J Nanoengng Nanomfg 2015, 5, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainshtein, M.; Belova, N.; Kulakovskaya, T.; Suzina, N.; Sorokin, V. Synthesis of magneto-sensitive iron-containing nanoparticles by yeasts. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Gadd, G.M. Iron coral: Novel fungal biomineralization of nanoscale zerovalent iron composites for treatment of chlorinated pollutants. Chemical Engineering Journal 2020, 402, 126263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, D.; Verduin, J.J.; Shah, M.; Sharma, S.B.; Poinern, G.E.J. A Review of Current Research into the Biogenic Synthesis of Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles via Marine Algae and Seagrasses. Journal of Nanoscience 2017, 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, M.G.; Vaz, B. da S.; de Morais, E.G.; Costa, J.A.V. Biologically active metabolites synthesized by microalgae. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 835761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Namvar, F.; Ahmad, M.B.; Mohamad, R. Green biosynthesis and characterization of magnetic iron oxide (Fe₃O₄) nanoparticles using seaweed (Sargassum muticum) aqueous extract. Molecules 2013, 18, 5954–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, R.S.; Sundaramanickam, A.; Srinath, R.; Ramesh, T.; Saranya, K.; Meena, M.; Surya, P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by bloom forming marine microalgae Trichodesmium erythraeum and its applications in antioxidant, drug-resistant bacteria, and cytotoxicity activity. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society 2019, 23, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyam, V.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Ganeshkumar, V.; Thavamani, P.; Chen, Z.; Naidu, R.; Megharaj, M. Cultivation of Chlorella on brewery wastewater and nano-particle biosynthesis by its biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, D.M.S.A.; Ismail, M.M.; Aly-Eldeen, M.A. Biogenic synthesis and antimicrobial potency of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using algae harvested from the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research 2019, 45, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, J.; Kalaiselvam, S. Biogenic synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using inedible borassus flabellifer seed coat: characterization, antimicrobial, antioxidant activity and in vitro cytotoxicity analysis. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, C.; Brayner, R.; Margueritat, J.; Hémadi, M.; Couté, A.; Yéprémian, C.; Djediat, C.; Aubard, J.; Fiévet, F.; Livage, J.; Coradin, T. Nano-gold biosynthesis by silica-encapsulated micro-algae: a “living” bio-hybrid material. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siji, S.; Njana, J.; AmritaP, J.; Vishnudasan, D. Biogenic Synthesis of Iron oxide Nanoparticles from Marine Algae. 2018.
- Win, T.T.; Khan, S.; Bo, B.; Zada, S.; Fu, P. Green synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Chlorella-K01 extract for potential enhancement of plant growth stimulating and antifungal activity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; El-Kassas, H.Y.; Shams El-Din, N.G.; Eissa, D.I.; El-Sherbiny, B.A. Green synthesis, characterization applications of iron oxide nanoparticles for antialgal and wastewater bioremediation using three brown algae. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 1538–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, Y.P.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Kuwano, N.; Bt Ahmad Khairudin, N.B.; Bt Mohamad, S.E.; Lee, K.X. Green Synthesis of Magnetite (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Using Seaweed (Kappaphycus alvarezii) Extract. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arularasu, M.V.; Devakumar, J.; Rajendran, T.V. An innovative approach for green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: Characterization and its photocatalytic activity. Polyhedron 2018, 156, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kassas, H.Y.; Aly-Eldeen, M.A.; Gharib, S.M. Green synthesis of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles using two selected brown seaweeds: Characterization and application for lead bioremediation. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, S.M.; Madkour, F.F.; El-Kassas, H.Y.; Mohamed, A.A.; Elgarahy, A.M. Green synthesis of recyclable iron oxide nanoparticles using Spirulina platensis microalgae for adsorptive removal of cationic and anionic dyes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 65549–65572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, I.; Nazar, N.; Ata, S.; Sultan, M.; Ali, A.; Abbas, A.; Jilani, K.; Kamal, S.; Sarim, F.M.; Khan, M.I.; Jalal, F.; Iqbal, M. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using pomegranate seeds extract and photocatalytic activity evaluation for the degradation of textile dye. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2019, 8, 6115–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, S.; Tahir, A.; Chen, Y. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their environmental applications and implications. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolade, O.P.; Williams, A.B.; Benson, N.U. Green synthesis of iron-based nanomaterials for environmental remediation: A review. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management 2020, 13, 100279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, V.V.; Makarova, S.S.; Love, A.J.; Sinitsyna, O.V.; Dudnik, A.O.; Yaminsky, I.V.; Taliansky, M.E.; Kalinina, N.O. Biosynthesis of stable iron oxide nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Hordeum vulgare and Rumex acetosa plants. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5982–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunakaran, S.; Ramanujam, S.; Gurunathan, B. Green synthesised iron and iron-based nanoparticle in environmental and biomedical application: - a review. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.K.; Senapati, K.K.; Sarma, K.C. Synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles coated with green tea polyphenols and their use for removal of dye pollutant from aqueous solution. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2017, 5, 2214–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.S. Iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by controlled bio-precipitation using leaf extract of Garlic Vine (Mansoa alliacea). Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 53, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Becerra, R.; Zorrilla, C.; Ascencio, J.A. Production of iron oxide nanoparticles by a biosynthesis method: an environmentally friendly route. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16147–16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwer, Z.; Jamali, A.R.; Khan, W.; Bhatti, J.; Akhter, F.; Batool, M. Green synthesis of active Fe2O3 nanoparticles using Aloe barbadensis and Camellia sinensis for efficient degradation of malachite green and Congo red dye. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.B.; Han, S.S. One-Pot Green Synthesis of Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles by Ultrasonic Irradiation and Their In Vitro Cytotoxicity on Human Keratinocytes CRL-2310. J. Clust. Sci. 2016, 27, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moacă, E.-A.; Watz, C.G.; Flondor Ionescu, D.; Păcurariu, C.; Tudoran, L.B.; Ianoș, R.; Socoliuc, V.; Drăghici, G.-A.; Iftode, A.; Liga, S.; Dragoș, D.; Dehelean, C.A. Biosynthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Physico-Chemical Characterization and Their In Vitro Cytotoxicity on Healthy and Tumorigenic Cell Lines. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpagavinayagam, P.; Vedhi, C. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Avicennia marina flower extract. Vacuum 2019, 160, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambri, N.D.S.; Taib, N.I.; Abdul Latif, F.; Mohamed, Z. Utilization of neem leaf extract on biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirdeshpande, K.D.; Sridhar, A.; Cholkar, K.M.; Selvaraj, R. Structural characterization of mesoporous magnetite nanoparticles synthesized using the leaf extract of Calliandra haematocephala and their photocatalytic degradation of malachite green dye. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Chopra, D.S.; Singh, D.; Singh, N. Optimization and ecofriendly synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles as potential antioxidant. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13, 9034–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Karak, N. One-step approach to prepare magnetic iron oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid for efficient organic and inorganic pollutants removal. Mater. Chem. Phys 2014, 144, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groiss, S.; Selvaraj, R.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Vinayagam, R. Structural characterization, antibacterial and catalytic effect of iron oxide nanoparticles synthesised using the leaf extract of Cynometra ramiflora. J. Mol. Struct 2017, 1128, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, Á. de J.; Reyes-López, S.Y.; Mondragón-Sánchez, M. de L.; Robles-Cortés, A.I.; Pérez, R. Eco-friendly synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Evaluation of their catalytic activity in methylene blue degradation by kinetic adsorption models. Results in Physics 2019, 12, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshtkhoo, N.; Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Savardashtaki, A.; Amani, A.M.; Taghizadeh, S. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by aqueous leaf extract of Daphne mezereum as a novel dye removing material. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Tsang, E.P. Biosynthesized iron nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Eichhornia crassipes and its mechanism in the hexavalent chromium removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 399, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, M.; Saravanan, S.; Soga, T. Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by using eucalyptus globulus plant extract. e-J. Surf. Sci. Nanotech. 2014, 12, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Zavaleta, K.; Chacon-Laiza, Y.; Asmat-Campos, D.; Raquel-Checca, N. Green Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus globulus Extract and Their Application in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Agricultural Soil. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atarod, M.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Sajadi, S.M. Green synthesis of a Cu/reduced graphene oxide/Fe3 O4 nanocomposite using Euphorbia wallichii leaf extract and its application as a recyclable and heterogeneous catalyst for the reduction of 4-nitrophenol and rhodamine B. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 91532–91543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Kumar Jaiswal, K.; Amjad, M. Euphorbia herita leaf extract as a reducing agent in a facile green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles and antimicrobial activity evaluation. Inorganic and Nano-Metal Chemistry, 2020, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Karade, V.C.; Parit, S.B.; Dawkar, V.V.; Devan, R.S.; Choudhary, R.J.; Kedge, V.V.; Pawar, N.V.; Kim, J.H.; Chougale, A.D. A green approach for the synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles from Gardenia resinifera plant and it’s In vitro hyperthermia application. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Sathy, B.N.; Mony, U.; Koyakutty, M.; Nair, S.V.; Menon, D. Biocompatible magnetite/gold nanohybrid contrast agents via green chemistry for MRI and CT bioimaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plachtová, P.; Medříková, Z.; Zbořil, R.; Tuček, J.; Varma, R.S.; Maršálek, B. Iron and iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized using green tea extract: improved ecotoxicological profile and ability to degrade malachite green. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8679–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razack, S.A.; Suresh, A.; Sriram, S.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Sadanandham, S.; Veerasamy, M.; Nagalamadaka, R.B.; Sahadevan, R. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Hibiscus rosa-sinensis for fortifying wheat biscuits. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.T.; Ovais, M.; Ullah, I.; Ali, M.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Maaza, M. Biosynthesis of iron oxide (Fe2 O3 ) nanoparticles via aqueous extracts ofSageretia thea (Osbeck.) and their pharmacognostic properties. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews 2017, 10, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagasubbulakshmi, S.; Kadirvelu, K. Green synthesis of Iron oxide nanoparticles using Lagenaria siceraria and evaluation of its Antimicrobial activity. Def. Life. Sc. Jl. 2017, 2, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, K.; Sathish, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Ramachandran, T. Fast kinetics and high adsorption capacity of green extract capped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the adsorption of Ni(II) ions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2018, 59, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Upadhyay, L.S.B. Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using plant derivatives of Lawsonia inermis (Henna) and its surface modification for biomedical application. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2019, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, M.; Nayak, P.L. Ecofriendly green synthesis of iron nanoparticles from various plants and spices extract. International Journal of Plant, Animal and Environmental Sciences, 2013.
- Lohrasbi, S.; Kouhbanani, M.A.J.; Beheshtkhoo, N.; Ghasemi, Y.; Amani, A.M.; Taghizadeh, S. Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles Using Plantago major Leaf Extract and Their Application as a Catalyst for the Decolorization of Azo Dye. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, H.S.; Boda, M.A.; Shah, M.A.; Parveen, S.; Wani, A.H. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Platanus orientalis leaf extract for antifungal activity. Green Processing and Synthesis 2019, 8, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madubuonu, N.; Aisida, S.O.; Ahmad, I.; Botha, S.; Zhao, T.; Maaza, M.; Ezema, F.I. Bio-inspired iron oxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava aqueous extract for antibacterial activity. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasantharaj, S.; Sathiyavimal, S.; Senthilkumar, P.; LewisOscar, F.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Ruellia tuberosa: Antimicrobial properties and their applications in photocatalytic degradation. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2019, 192, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, S.P.; Sengodan, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Sesbania grandiflora Leaf Extract as Reducing Agent. Journal of Nanoscience 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xie, A.; Li, S.; Wang, X. Green synthesis of soya bean sprouts-mediated superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 2938–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, W.; Khan, A.U.; Shams, S.; Qin, L.; Yuan, Q.; Ahmad, A.; Wei, Y.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Ullah, S.; Rahman, A.U. Eco-benign approach to synthesize spherical iron oxide nanoparticles: A new insight in photocatalytic and biomedical applications. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2020, 205, 111821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, S.M.H.; Mohammad, F.; Ahmad, S. Terminalia belerica Mediated Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles of Copper, Iron and Zinc Metal Oxides as the Alternate Antibacterial Agents Against some Common Pathogens. Bionanoscience 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EBSCOhost | 88941904 | Biogenic synthesis of fe3o4 nanoparticles using tridax procumbens leaf extract and its antibacterial activity on pseudomonas aeruginosa. Available online: https://web.p.ebscohost.com/abstract?direct=true&profile=ehost&scope=site&authtype=crawler&jrnl=18423582&asa=Y&AN=88941904&h=NhJp6M8b1WHqokbPkvy5F0nS964DyVei%2fYOlyPXMzZ%2blxWEL%2bup4DlP5C6UyJ0YZzT9E2pRtdXzXFwEIzdyKMQ%3d%3d&crl=c&resultNs=AdminWebAuth&resultLocal=ErrCrlNotAuth&crlhashurl=login.aspx%3fdirect%3dtrue%26profile%3dehost%26scope%3dsite%26authtype%3dcrawler%26jrnl%3d18423582%26asa%3dY%26AN%3d88941904 (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Manquián-Cerda, K.; Cruces, E.; Angélica Rubio, M.; Reyes, C.; Arancibia-Miranda, N. Preparation of nanoscale iron (oxide, oxyhydroxides and zero-valent) particles derived from blueberries: Reactivity, characterization and removal mechanism of arsenate. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lateef, A.; Oloke, J.K.; Gueguim Kana, E.B.; Oyeniyi, S.O.; Onifade, O.R.; Oyeleye, A.O.; Oladosu, O.C.; Oyelami, A.O. Improving the quality of agro-wastes by solid-state fermentation: enhanced antioxidant activities and nutritional qualities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelere, I.A.; Lateef, A. A novel approach to the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles: the use of agro-wastes, enzymes, and pigments. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.G.; Garzón-Romero, C.; Salazar, M.A.; Lagos, K.J.; Campaña, K.O.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K.; Rivera, M.R.; Niebieskikwiat, D.; Benitez, M.J.; Romero, M.P. Bioinspired Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles Based on Iron Oxides Using Orange Waste and Their Application as Photo-Activated Antibacterial Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpomie, K.G.; Ghosh, S.; Gryzenhout, M.; Conradie, J. Ananas comosus peel–mediated green synthesized magnetite nanoparticles and their antifungal activity against four filamentous fungal strains. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periakaruppan, R.; Chen, X.; Thangaraj, K.; Jeyaraj, A.; Nguyen, H.H.; Yu, Y.; Hu, S.; Lu, L.; Li, X. Utilization of tea resources with the production of superparamagnetic biogenic iron oxide nanoparticles and an assessment of their antioxidant activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo-Villarreal, N.; Verástegui-Domínguez, L.; Rodríguez-Batista, R.; Gándara-Martínez, E.; Alcorta-García, A.; Martínez-Delgado, D.; Rodríguez-Castellanos, E.A.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, F.; Gómez-Rodríguez, C. Green Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles of Iron Oxide Using Aqueous Extracts of Lemon Peel Waste and Its Application in Anti-Corrosive Coatings. Materials (Basel) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Y.; Mangrich, A.S.; Schultz, J.; Grasel, F.S.; Mattoso, N.; Mosca, D.H. Green chemistry preparation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles containing Fe3O4 cores in biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 116, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, A.; Nangia, A.; Prasad, M.N.V. A green synthetic route to phenolics fabricated magnetite nanoparticles from coconut husk extract: Implications to treat metal contaminated water and heavy metal stress in Oryza sativa L. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Murthy, T.P.; Gowrishankar, B.S.; Krishna, R.H.; Chandraprabha, M.N.; Mathew, B.B. Magnetic modification of coffee husk hydrochar for adsorptive removal of methylene blue: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology 2020, 2, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, S.; Kumar, A.; Selvaraj, R. Facile synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using inedible Cynometra ramiflora fruit extract waste and their photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Mater. Res. Bull. 2018, 97, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadiyan, Z.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Hara, H.; Mohamad, S.E.B.; Kalantari, K.; Taib, S.H.M.; Rasouli, E. Cytotoxicity assay of plant-mediated synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles using Juglans regia green husk extract. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Nazir, S.; Nazir, A.; Munir, S.; Mahmood, T.; Afzal, M.; Ansari, F.L.; Mazhar, K. Microwave-assisted green synthesis of superparamagnetic nanoparticles using fruit peel extracts: surface engineering, T 2 relaxometry, and photodynamic treatment potential. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 3833–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, S.; Rao, Y.S.; Balaji, T.; Prathima, B.; Jyothi, N.V.V. Biogenic synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using plantain peel extract. Mater. Lett. 2013, 100, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusefi, M.; Shameli, K.; Ali, R.R.; Pang, S.-W.; Teow, S.-Y. Evaluating Anticancer Activity of Plant-Mediated Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Punica Granatum Fruit Peel Extract. J. Mol. Struct 2020, 1204, 127539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvakkumar, R.; Hong, S.I. Green synthesis of spinel magnetite iron oxide nanoparticles. AMR 2014, 1051, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areeshi, M.Y. Rice straw mediated green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles and its application to improve thermal stability of endoglucanase enzyme. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 374, 109722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrampoush, M.H.; Miria, M.; Salmani, M.H.; Mahvi, A.H. Cadmium removal from aqueous solution by green synthesis iron oxide nanoparticles with tangerine peel extract. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, Ch.; Gangadhara, S.; Venkateswarlu, P. Bio-inspired green synthesis of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles using watermelon rinds and their catalytic activity. Appl. Nanosci. 2016, 6, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buarki, F.; AbuHassan, H.; Al Hannan, F.; Henari, F.Z. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Hibiscus rosa sinensis Flowers and Their Antibacterial Activity. J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 2022, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirezen, D.A.; Yılmaz, Ş.; Yılmaz, D.D.; Yıldız, Y.Ş. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Ceratonia Siliqua L. Aqueous Extract: Optimization, Characterization, Stabilization and Evaluation of Its Antibacterial Activity Against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Res. Sq. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Mourdikoudis, S.; Pallares, R.M.; Thanh, N.T.K. Characterization techniques for nanoparticles: comparison and complementarity upon studying nanoparticle properties. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12871–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dixit, C.K. Methods for characterization of nanoparticles. In Advances in nanomedicine for the delivery of therapeutic nucleic acids; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 43–58. ISBN 9780081005576.
- Mohammed, L.; Gomaa, H.G.; Ragab, D.; Zhu, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: A review. Particuology 2017, 30, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shah, T.; Ullah, R.; Zhou, P.; Guo, M.; Ovais, M.; Tan, Z.; Rui, Y. Review on recent progress in magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and diverse applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 629054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, A.H.; Wilson, M.J.; Schiffer, P.; Williams, M.E. TEM-induced structural evolution in amorphous Fe oxide nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12632–12633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Ledwani, L.; Mehrotra, T.; Kumar, N.; Pervaiz, N.; Kumar, R. Biosynthesis of hematite nanoparticles using Rheum emodi and their antimicrobial and anticancerous effects in vitro. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2020, 206, 111841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Singh, N.B.; Agarwal, A. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Amla seed for methylene blue dye removal from water. Materials Today: Proceedings 2023, 72, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón Bedoya, P.A.; Botta, P.M.; Bercoff, P.G.; Fanovich, M.A. Influence of the milling materials on the mechanochemical synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Alloys Compd 2023, 939, 168720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindaba, G.T.; Demsash, H.D.; Jayakumar, M. Green synthesis, characterization, and application of metal oxide nanoparticles for mercury removal from aqueous solution. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 195, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasani, M.; Fataei, E.; Safari, R.; Nasehi, F.; Mosayyebi, M. Antimicrobial Potentials of Iron Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles Green-Synthesized in Fusarium solani. Journal of Chemical Health Risks 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, S.; Khan, M.S. Phyto-interactive impact of green synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles and Rhizobium pusense on morpho-physiological and yield components of greengram. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 194, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, K.; Singh, J.; Dhaliwal, A.S. Green synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic nanocomposite based on reduced graphene oxide/Fe3 O4 prepared using leaf extract of Azadirachta indica. Inorganic and Nano-Metal Chemistry 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, A.; Warrier, V.G.; Devasia, J.; Ganganagappa, N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles immobilized on microporous molecular sieves as efficient porous catalyst for photodegradation, transesterification and esterification reactions. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrouz, M.; Ahmadi-Nouraldinvand, F.; Elias, S.G.; Alebrahim, M.T.; Tseng, T.M.; Zahedian, H. Green synthesis of spermine coated iron nanoparticles and its effect on biochemical properties of Rosmarinus officinalis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using Coriandrum sativum L. leaf extract. IJBB 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, M.; Bhatia, T.; Gupta, R. Green & sustainable synthetic route of obtaining iron oxide nanoparticles using Hylocereus undantus (pitaya or dragon fruit). Materials Today: Proceedings 2022, 50, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.H.; Latif, S.; Abdulaziz, F.; Shah, N.S.; Imran, M.; Muhammad, N.; Iqbal, J.; Shahid, M.; Salam, M.A.; Khasim, S.; Khan, H.U. Photocatalytic response in water pollutants with addition of biomedical and anti-leishmanial study of iron oxide nanoparticles. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2022, 234, 112544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- K, V.; G, P.; S, M.; G, R.; S, S. Echinochloa frumentacea grains extract mediated synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles: A greener nano drug for potential biomedical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.I.; Umar, M.B.; Tijani, O.J.; Muhammad, R. Antidiabetic potentials of green-synthesized alpha iron oxide nanoparticles using stem extract of Securidaca longipedunculata. Int. Nano Lett. 2022, 12, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javad, S.; Maqsood, S.; Shah, A.A.; Singh, A.; Noor Shah, A.; Nawaz, M.; Bashir, M.A.; M. El Nashar, E.; A. Alghamdi, M.; F.El-kott, A.; Mosa, W.F.A. Iron nanoparticles mitigates cadmium toxicity in Triticum aestivum; Modulation of antioxidative defense system and physiochemical characteristics. Journal of King Saud University - Science 2023, 35, 102498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, P.; Rao, M.; Murugesan, G.; Narasimhan, M.K.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Vinayagam, R.; Lan Chi, N.T.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Selvaraj, R. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of the green-synthesized hematite nanoparticles. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by using ficus carica leaf extract and its antioxidant activity. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 12, 2108–2116. [CrossRef]
- (2) (PDF) Green Synthesis-Mediated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles using. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/371416474_Green_Synthesis-Mediated_Iron_Oxide_Nanoparticles_using (accessed on 19 September 2023).
- Hazel, D.; Gobi, N. One-Pot Facile Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Stem Extract of Amaranthus Campestris and Comparison of its Characteristics with Chemically Synthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwumulo, H.F.; Muwonge, H.; Ibingira, C.; Lubwama, M.; Kirabira, J.B.; Ssekitoleko, R.T. Green synthesis and characterization of iron-oxide nanoparticles using Moringa oleifera: a potential protocol for use in low and middle income countries. BMC Res. Notes 2022, 15, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthi, S.; Kavitha, M.; Kumar, E.R.; Balamurugan, A.; Al-Douri, Y.; Alzahrani, H.K.; Keshk, A.A.; Habeebullah, T.M.; Abdel-Hafez, S.H.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Natural tannic acid (green tea) mediated synthesis of ethanol sensor based Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Investigation of structural, morphological, optical properties and colloidal stability for gas sensor application. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 352, 131071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad AlGarni, T.; Ali, M.H.H.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M. Green biosynthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Chlorella vulgaris extract for enhancing degradation of 2,4 dinitrophenol. Journal of King Saud University - Science 2023, 35, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahwan, T.; Abu Sirriah, S.; Nairat, M.; Boyacı, E.; Eroğlu, A.E.; Scott, T.B.; Hallam, K.R. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their application as a Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of aqueous cationic and anionic dyes. Chemical Engineering Journal 2011, 172, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiak, B.; Rangam, N.; Jiricek, P.; Gordeev, I.; Tóth, J.; Kövér, L.; Mohai, M.; Borowicz, P. Surface study of fe3o4 nanoparticles functionalized with biocompatible adsorbed molecules. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, A.; Chhetri, K.; Acharya, D.; Pant, B.; Adhikari, A. Green Synthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Psidium guajava L. Leaves Extract for Degradation of Organic Dyes and Anti-microbial Applications. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundekkad, D.; Alex, A.V. Analysis of structural and biomimetic characteristics of the green-synthesized Fe3O4 nanozyme from the fruit peel extract of Punica granatum. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 3863–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birusanti, A.B.; Espenti, C.S.; Mala, S. Plant-Extract-Assisted Eco-friendly synthesis of Iron oxide nanoparticles using cape gooseberry Extract and their Antibacterial study. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, P.; Golubeva, A.; Dąbek, P.; Pryshchepa, O.; Sagandykova, G.; Pomastowski, P.; Gloc, M.; Dobrucka, R.; Kurzydłowski, K.; Buszewski, B.; Witkowski, A. Study on Biogenic Spindle-Shaped Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles by Pseudostaurosira trainorii in Field of Laser Desorption/Ionization Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsov, A.V.; Tsybulya, S.V. Influence of nanoparticles size on XRD patterns for small monodisperse nanoparticles of cu0 and tio2 anatase. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weirich, T.E.; Zou, X.; Ramlau, R.; Simon, A.; Cascarano, G.L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Hovmöller, S. Structures of nanometre-size crystals determined from selected-area electron diffraction data. Acta Crystallogr, A, Found Crystallogr 2000, 56, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, G.; Hühn, D.; Perrier, A.; Cordier, L.; Pickett, C.J.; Nann, T.; Parak, W.J. On the use of pH titration to quantitatively characterize colloidal nanoparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 15141–15149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu Demirezen, D.; Yılmaz, Ş.; Demirezen Yılmaz, D.; Yıldız, Y.Ş. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Ceratonia siliqua L. aqueous extract: improvement of colloidal stability by optimizing synthesis parameters, and evaluation of antibacterial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. IJMR 2022, 113, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Ebrahimzadeh Sepasgozar, S.; Mohseni, S.; Feyzizadeh, B.; Morsali, A. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Achillea Nobilis Extract and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant and Antibacterial properties. Journal of Food Biosciences and Technology 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Portney, N.G.; Cui, D.; Budak, G.; Ozbay, E.; Ozkan, M.; Ozkan, C.S. Zeta potential: a surface electrical characteristic to probe the interaction of nanoparticles with normal and cancer human breast epithelial cells. Biomed. Microdevices 2008, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwegmann, H.; Feitz, A.J.; Frimmel, F.H. Influence of the zeta potential on the sorption and toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles on S. cerevisiae and E. coli. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 347, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakulkhu, U.; Mahmoudi, M.; Maurizi, L.; Salaklang, J.; Hofmann, H. Protein corona composition of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with various physico-chemical properties and coatings. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Senthilkumar, P.; Rashmitha, S.; Veera, P.; Sahithya, C.S. Azadirachta indica influenced biosynthesis of super-paramagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles and their applications in tannery water treatment and X-ray imaging. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2018, 8, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wypij, M.; Czarnecka, J.; Świecimska, M.; Dahm, H.; Rai, M.; Golinska, P. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of biogenic silver nanoparticles synthesized from Streptomyces xinghaiensis OF1 strain. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamipoor, S.; Fayyazi, F.; Bahadorikhalili, S. Phytochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles using anthemis nobilis extract and its antibacterial activity. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie 2020, 234, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Zhou, X.; Parsaee, Z. Ultrasound-assisted biosynthesis of CuO-NPs using brown alga Cystoseira trinodis: Characterization, photocatalytic AOP, DPPH scavenging and antibacterial investigations. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesner, M.R.; Lowry, G.V.; Casman, E.; Bertsch, P.M.; Matson, C.W.; Di Giulio, R.T.; Liu, J.; Hochella, M.F. Meditations on the ubiquity and mutability of nano-sized materials in the environment. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8466–8470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinise, N.; Fuku, X.G.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Mayedwa, N.; Maaza, M. ZnO nanoparticles via Moringa oleifera green synthesis: Physical properties & mechanism of formation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 406, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titus, D.; James Jebaseelan Samuel, E.; Roopan, S.M. Nanoparticle characterization techniques. In Green synthesis, characterization and applications of nanoparticles; Elsevier, 2019; pp. 303–319 ISBN 9780081025796.
- Niraimathee, V.A.; Subha, V.; Ravindran, R.S.E.; Renganathan, S. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles from Mimosa pudica root extract. IJESD 2016, 15, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouafia, A.; Laouini, S.E. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by aqueous leaves extract of Mentha Pulegium L.: Effect of ferric chloride concentration on the type of product. Mater. Lett. 2020, 265, 127364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, W.J.; Abid, M.A.; Kadhim, D.A.; Mejbel, M.K. Synthesis of iron oxide (β-fe2 o3 ) nanoparticles from Iraqi grapes extract and its biomedical application. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 881, 012099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Firestein, K.L.; Fernando, J.F.S.; Siriwardena, D.; von Treifeldt, J.E.; Golberg, D. Recent progress of in situ transmission electron microscopy for energy materials. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1904094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inkson, B.J. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for materials characterization. In Materials characterization using nondestructive evaluation (NDE) methods; Elsevier, 2016; pp. 17–43 ISBN 9780081000403.
- Zheng, H.; Meng, Y.S.; Zhu, Y. Frontiers of in situ electron microscopy. MRS Bull. 2015, 40, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawer, U.; Raghavendra, V.B.; Ningaraju, S.; Krishna, K.L.; Ghosh, A.R.; Melappa, G.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biofabrication of gold nanoparticles mediated by the endophytic Cladosporium species: Photodegradation, in vitro anticancer activity and in vivo antitumor studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamdagni, P.; Khatri, P.; Rana, J.S. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using flower extract of Nyctanthes arbor-tristis and their antifungal activity. Journal of King Saud University - Science 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Delmas, C.; Zhu, T.; Winter, M.; Wang, M.-S.; Huang, J. Understanding all solid-state lithium batteries through in situ transmission electron microscopy. Materials Today 2021, 42, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Ashokkumar, T. Plant-mediated biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles: A review of literature, factors affecting synthesis, characterization techniques and applications. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2017, 5, 4866–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patravale, V.; Dandekar, P.; Jain, R. Characterization techniques for nanoparticulate carriers. In Nanoparticulate Drug Delivery; Elsevier, 2012; pp. 87–121 ISBN 9781907568985.
- Yadav, V.K.; Fulekar, M.H. Biogenic synthesis of maghemite nanoparticles (γ-Fe2O3) using Tridax leaf extract and its application for removal of fly ash heavy metals (Pb, Cd). Materials Today: Proceedings 2018, 5, 20704–20710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladi-Fard, R.; Aali, R.; Mohammadi-Aghdam, S.; Mortazavi-derazkola, S. The surface modification of spherical ZnO with Ag nanoparticles: A novel agent, biogenic synthesis, catalytic and antibacterial activities. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2022, 15, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, K.; Moorthy Babu, S.; Bhagavannarayana, G. Study of the influence of dopants on the crystalline perfection of ferroelectric glycine phosphite single crystals using high-resolution X-ray diffraction analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinov, S.; Sha, W.; Guo, Z.; Tang, C.C.; Long, A.E. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction study of the phase transformations in titanium alloys. Materials Characterization 2002, 48, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monshi, A.; Foroughi, M.R.; Monshi, M.R. Modified Scherrer Equation to Estimate More Accurately Nano-Crystallite Size Using XRD. WJNSE 2012, 02, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S. DLS and zeta potential - What they are and what they are not? J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: a practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszuba, M.; McKnight, D.; Connah, M.T.; McNeil-Watson, F.K.; Nobbmann, U. Measuring sub nanometre sizes using dynamic light scattering. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, J.C.; Sarkar, M.; Fiuza, T.; Cousin, F.; Depeyrot, J.; Dubois, E.; Mériguet, G.; Perzynski, R.; Peyre, V. Design of concentrated colloidal dispersions of iron oxide nanoparticles in ionic liquids: Structure and thermal stability from 25 to 200 °C. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 607, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, Y.N.; Asnis, J.; Häfeli, U.O.; Bach, H. Metal nanoparticles: understanding the mechanisms behind antibacterial activity. J. Nanobiotechnology 2017, 15, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihem, L.; Hanine, D.; Faiza, B. Antibacterial Activity of α-Fe2O3 and α-Fe2O3@Ag Nanoparticles Prepared by Urtica Leaf Extract. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2020, 15, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shen, M.; Xia, J.; Shi, X. Recent developments of cancer nanomedicines based on ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles and nanoclusters. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2021, 16, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMatar, M.; Makky, E.A.; Var, I.; Koksal, F. The Role of Nanoparticles in the Inhibition of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria and Biofilms. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, W.I.; Nelson, K.L.; Yoon, J.; Sedlak, D.L. Bactericidal effect of zero-valent iron nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4927–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisida, S.O.; Batool, A.; Khan, F.M.; Rahman, L.; Mahmood, A.; Ahmad, I.; Zhao, T.; Maaza, M.; Ezema, F.I. Calcination induced PEG-Ni-ZnO nanorod composite and its biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Phys 2020, 255, 123603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touati, D. Iron and oxidative stress in bacteria. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 373, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathy, N.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles-an antimicrobial study. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2008, 9, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, S.A. The influence of PEG 20,000 concentration on the size control and magnetic properties of functionalized bio-compatible magnetic nanoparticles | Abstract. Der Pharma Chemica 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Armijo, L.M.; Wawrzyniec, S.J.; Kopciuch, M.; Brandt, Y.I.; Rivera, A.C.; Withers, N.J.; Cook, N.C.; Huber, D.L.; Monson, T.C.; Smyth, H.D.C.; Osiński, M. Antibacterial activity of iron oxide, iron nitride, and tobramycin conjugated nanoparticles against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. J. Nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Xue, B.; Yang, L.; Shen, Z.; Jin, M.; Wang, J.; Qiu, Z. The Detailed Bactericidal Process of Ferric Oxide Nanoparticles on E. coli. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielyan, L.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Gevorgyan, V.; Ananyan, M.; Trchounian, A. Antibacterial effects of iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles: distinguishing concentration-dependent effects with different bacterial cells growth and membrane-associated mechanisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 2773–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Jin, J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, M. Synthesis, characterization, antimicrobial activity and mechanism of a novel hydroxyapatite whisker/nano zinc oxide biomaterial. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 10, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohanski, M.A.; DePristo, M.A.; Collins, J.J. Sublethal antibiotic treatment leads to multidrug resistance via radical-induced mutagenesis. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guittat, L.; Alberti, P.; Rosu, F.; Van Miert, S.; Thetiot, E.; Pieters, L.; Gabelica, V.; De Pauw, E.; Ottaviani, A.; Riou, J.-F.; Mergny, J.-L. Interactions of cryptolepine and neocryptolepine with unusual DNA structures. Biochimie 2003, 85, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nel, A.E.; Mädler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, T.; Laurent, S.; Stanicki, D.; Wilkinson, K.J. Relating the Surface Properties of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs) to Their Bactericidal Effect towards a Biofilm of Streptococcus mutans. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shabib, N.A.; Husain, F.M.; Ahmed, F.; Khan, R.A.; Khan, M.S.; Ansari, F.A.; Alam, M.Z.; Ahmed, M.A.; Khan, M.S.; Baig, M.H.; Khan, J.M.; Shahzad, S.A.; Arshad, M.; Alyousef, A.; Ahmad, I. Low Temperature Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles and Their ROS Mediated Inhibition of Biofilm Formed by Food-Associated Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolen’ko, Y.V.; Bañobre-López, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, C.; Carbó-Argibay, E.; Sailsman, A.; Piñeiro-Redondo, Y.; Cerqueira, M.F.; Petrovykh, D.Y.; Kovnir, K.; Lebedev, O.I.; Rivas, J. Large-Scale Synthesis of Colloidal Fe3 O4 Nanoparticles Exhibiting High Heating Efficiency in Magnetic Hyperthermia. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 8691–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, W.; Wu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, H. The antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of mesoporous hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticles in an alternating magnetic field. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4492–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madubuonu, N.; Aisida, S.O.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, I.; Zhao, T.-K.; Botha, S.; Maaza, M.; Ezema, F.I. Biosynthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles via a composite of Psidium guavaja-Moringa oleifera and their antibacterial and photocatalytic study. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2019, 199, 111601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, J.K.; Ali, M.S.; Oh, I.-G.; Baek, K.-H. Proteasome inhibitory, antioxidant, and synergistic antibacterial and anticandidal activity of green biosynthesized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles using the aqueous extract of corn (Zea mays L.) ear leaves. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 45, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Zare, M.; Kiyanpour, S.; Berenjian, A.; Niknezhad, S.V.; Ghasemi, Y. Biosynthesis of xanthangum-coated INPs by using Xanthomonas campestris. IET nanobiotechnol. 2018, 12, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Abdullah, M.S. bin; Nanda, A.; Ansari, M.T. In vitro study of the antibacterial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Penicillium brevicompactum (MTCC-1999). Journal of Taibah University for Science 2016, 10, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, G.; Logeshwaran, V.; Sarathbabu, S.; Jha, P.K.; Jeyaraj, M.; Rajkuberan, C.; Senthilkumar, N.; Sivaramakrishnan, S. Green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles using Couroupita guianensis Aubl. fruit extract for their antibacterial and cytotoxicity activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoonus, J.; Resmi, R.; Beena, B. Evaluation of antibacterial and anticancer activity of green synthesized iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 46, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karagoly, H.; Rhyaf, A.; Naji, H.; Albukhaty, S.; AlMalki, F.A.; Alyamani, A.A.; Albaqami, J.; Aloufi, S. Green synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity, and antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles using Nigella sativa seed extract. Green Processing and Synthesis 2022, 11, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.U.; Kareem, A.; Nami, S.A.A.; Khan, M.S.; Rehman, S.; Bhat, S.A.; Mohammad, A.; Nishat, N. Biogenic synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Agrewia optiva and Prunus persica phyto species: Characterization, antibacterial and antioxidant activity. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2018, 185, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, W.; Khan, M.A.; Nazir, M.; Siddiquah, A.; Mushtaq, S.; Hashmi, S.S.; Abbasi, B.H. Papaver somniferum L. mediated novel bioinspired lead oxide (PbO) and iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles: In-vitro biological applications, biocompatibility and their potential towards HepG2 cell line. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 103, 109740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.; Zafar, A.; Saif, M.S.; Ali, Z.; Nazar, M.; Waqas, M.; Haq, A.U.; Tariq, T.; Hassan, S.G.; Iqbal, F.; Shu, X.-G.; Hasan, M. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanorods using Withania coagulans extract improved photocatalytic degradation and antimicrobial activity. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2020, 204, 111784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Ahmed, B.; Khan, M.S.; Musarrat, J. Differential surface contact killing of pristine and low EPS Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Aloe vera capped hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2018, 188, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasu, M.V.; Arokiyaraj, S.; Viayaraghavan, P.; Kumar, T.S.J.; Duraipandiyan, V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Kaviyarasu, K. One step green synthesis of larvicidal, and azo dye degrading antibacterial nanoparticles by response surface methodology. J Photochem Photobiol B, Biol 2019, 190, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachheti, R.K.; Konwarh, R.; Gupta, V.; Husen, A.; Joshi, A. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: cutting edge technology and multifaceted applications. In Nanomaterials and plant potential; Husen, A., Iqbal, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; ISBN 978-3-030-05568-4. [Google Scholar]
- Parveen, S.; Wani, A.H.; Shah, M.A.; Devi, H.S.; Bhat, M.Y.; Koka, J.A. Preparation, characterization and antifungal activity of iron oxide nanoparticles. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 115, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.A.; Zahir, E.; Shahid, S.M.; Khan, M.N.; Asghar, M.A.; Iqbal, J.; Walker, G. Iron, copper and silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis using green and black tea leaves extracts and evaluation of antibacterial, antifungal and aflatoxin B 1 adsorption activity. LWT 2018, 90, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henam, S.D.; Ahmad, F.; Shah, M.A.; Parveen, S.; Wani, A.H. Microwave synthesis of nanoparticles and their antifungal activities. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 213, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, P.; Chauhan, R.P.; Garg, N.; Verma, K. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of chitosan coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 75, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, G.M. Nanoparticles as safe and effective delivery systems of antifungal agents: Achievements and challenges. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 523, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorostkar, R.; Ghalavand, M.; Nazarizadeh, A.; Tat, M.; Hashemzadeh, M.S. Anthelmintic effects of zinc oxide and iron oxide nanoparticles against Toxocara vitulorum. Int. Nano Lett. 2017, 7, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- hassan, ahmed; Ramdan, M. ; S.F. A, O.; Elkabawy, L. In vitro anthelmintic effects of iron oxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles against Fasciola Spp. in Dakhla Oasis, Egypt. Benha Veterinary Medical Journal 2021, 41, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, D.; Yadav, N.; Ahmad, S.; Namdev, P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Lochab, B.; Singh, S. Pre-clinical study of iron oxide nanoparticles fortified artesunate for efficient targeting of malarial parasite. EBioMedicine 2019, 45, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Rafiei, A.; Jelowdar, A.; Salimi, A.; Asfaram, A.; Ostovan, A. Magnetic solid lipid nanoparticles co-loaded with albendazole as an anti-parasitic drug: Sonochemical preparation, characterization, and in vitro drug release. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 268, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, Q. ul; Islam, A.; Nadhman, A.; Yasinzai, M. Comparative analysis of chemically and biologically synthesized iron oxide nanoparticles against Leishmania tropica. BioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.E.A.; Afridi, S.; Khalil, A.T.; Ali, M.; Zohra, T.; Salman, M.; Ikram, A.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Maaza, M. Bio-redox potential of Hyphaene thebaica in bio-fabrication of ultrafine maghemite phase iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3 NPs) for therapeutic applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2020, 112, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, M.; Vora, A. Nanotechnology-based antiviral therapeutics. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 748–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, C.; Carnamucio, F.; Giuffrè, O.; Foti, C. Metal-Based Compounds in Antiviral Therapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdiero, S.; Falanga, A.; Vitiello, M.; Cantisani, M.; Marra, V.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antiviral agents. Molecules 2011, 16, 8894–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahabadi, N.; Khorshidi, A.; Zhaleh, H.; Kashanian, S. Synthesis, characterization, cytotoxicity and DNA binding studies of Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 nanoparticles coated by an antiviral drug lamivudine. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sahoo, G.C.; Chawla-Sarkar, M.; Nayak, M.K.; Trivedi, K.; Rana, S.; Pandey, K.; Das, V.; Topno, R.; Das, P. Antiviral effect of Glycine coated Iron oxide nanoparticles iron against H1N1 influenza A virus. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 45, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Nayak, M.; Sahoo, G.C.; Pandey, K.; Sarkar, M.C.; Ansari, Y.; Das, V.N.R.; Topno, R.K.; Bhawna; Madhukar, M. ; Das, P. Iron oxide nanoparticles based antiviral activity of H1N1 influenza A virus. J. Infect. Chemother. 2019, 25, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gour, A.; Jain, N.K. Advances in green synthesis of nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bacterial strain | Type of nanoparticle | Mechanism of synthesis | Size of nanoparticle (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcaligens faecalis | Fe2O3 | Extracellular | 12.3 | Irregular spherical | [19] |
| Actinobacter spp. | ɣ-Fe2O3 | Extracellular | 10–50 | Crystal | [20] |
| Actinobacter spp. | FeO-NPs | Intracellular | 10–40 | Quasi-spherical | [21] |
| Bacillus cereus | Fe3O4 | Extracellular | 29.3 | Spherical | [12] |
| Bacillus coagulans | FeO-NPs | Extracellular | - | - | [22] |
| Bacillus subtilis | Fe3O4 | Extracellular | 60–80 | Spherical | [17] |
|
Bacillus subtilis Bacillus pasteurii Bacillus licheniformis |
Fe3O4 | Extracellular | 37–97 | Rhombohedral | [23] |
| Desulfotomacculum acetoxidans | Fe3O4 | - | 21 | - | [24] |
| Desulfovibrio, strain LS4 | Fe2O3 | Extracellular | 19 | Round shaped | [24] |
| Escherichia coli | Fe3O4 | Extracellular | 23 ± 1 | Spherical | [25] |
| Geobacter sulfurreducens | Fe3O4 | Extracellular | 10–50 | - | [26] |
| Gluconacetobacter xylinus | Fe3O4 | Intracellular | 50 | - | [27] |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | Ferrihydrite nanoparticles | - | 2–5 | - | [28] |
| Lactobacillus casei | Fe3O4 | Intracellular | 10–15 | Spherical | [18] |
| Lactobacillus fermentum | Fe3O4 | Intracellular | 10–15 | Spherical | [16] |
| Leptothrix ochracea | - | Extracellular | 100 | Hollow tube | [29] |
| Magnetospirillum magneticum | Fe3O4 | Intracellular | 10–60 | Cuboidal, rectangular, and spherical NPs | [30] |
| Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense | Fe3O4 | Extracellular/ Intracellular | 25–55 | Polydisperse | [31] |
| Microbacterium marinilacus | FeO-NPs | Extracellular | 25–88 | Irregular | [32] |
| Nitrospirae (MYR-1) | Fe2O3 | Intracellular | 40 | Bullet-shaped | [33] |
| Pseudomonas stutzeri | Fe2O3 | - | 10-20 | - | [34] |
| Paenibacillus polymyxa | FeO-NPs | - | 26.65 | Spherical | [35] |
| Proteus mirabilis | Fe3O4 | Intracellular | 1.44–1.92 | Spherical | [36] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Fe3O4 | Extracellular | 23 | Spherical | [25] |
| Shewanella oneidensis | Fe2O3 | Intracellular | 30–43 | Pseudo hexagonal shape | [37] |
| Streptococcus suis | Fe3O4 | - | - | - | [38] |
| Thermoanaerobacter sp | Fe3O4 | Extracellular | ~13.0 | Spherical | [39] |
| Thiobacillus thioparus | Fe3O4 | Intracellular | - | - | [40] |
| Fungi | Location of synthesis | Type of nanoparticle | Size of nanoparticle (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria alternate | Cell-free filtrate | γ-Fe2O3 | 75–650 | Cubic | [51] |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | Fungal biomass | Fe2O3 | 42.4 | Irregular spherical | [22] |
| Aspergillus japonicus | Fungal biomass | Fe3O4 | 60–70 | Cubic | [48] |
| Aspergillus niger YESM 1 | Fungal homogenate | Fe3O4 | 18-50 | Spherical | [52] |
| Aspergillus niger BSC-1 | Cell-free filtrate | Fe3O4 | 20–40 | Orthorhombic | [41] |
| Aspergillus wentii | Fungal biomass | Fe2O3 | 46 | - | [22] |
| Baker’syeast | Fungal biomass | Fe2O3 | 2–10 | - | [53] |
| Candida bombicola | Fungal biomass | Fe3O4 | 8.5–4.5 | - | [50] |
| Chaetomium globosum | Fungal biomass | Fe2O3 | 25.3 | Irregular spherical | [22] |
| Cryptococcus humicola | - | Fe3O4 | 8-9 | Spherical | [54] |
| Curvularia lunata | Fungal biomass | Fe2O3 | 20.8 | Irregular spherical | [22] |
| Fusarium incarnatum | Fungal cell filtrate | Fe3O4 | 30.56 ± 8.68 | Spherical | [49] |
| Fusarium oxysporum | Fungal biomass | Fe3O4 | 10-40 | Cube | [42] |
| Neurospora crassa | Fungal biomass | Fe3O4 | 50 | Coralline appearance | [55] |
| Phialemoniopsis ocularis | Fungal cell filtrate | Fe3O4 | 13.13 ± 4.32 | Spherical | [49] |
| Pochonia chlamydosporium | Fungal biomass | Fe2O3 | ~12-50 | Spherical | [22] |
| Thichoderma asperellum | Fungal cell filtrate | Fe3O4 | 25 ± 3.94 | Spherical | [49] |
| Verticillium sp. | Fungal biomass | Fe3O4 | 100–400 | Cubo-octahedrally | [42] |
| Algae | Location of synthesis | Type of nanoparticle | Size of nanoparticle (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chaetomorpha antennina | Cell-free extract | Fe3O4 | 9–10 | - | [64] |
| Chlorella K01 | Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 76.5 | Spherical | [65] |
| Colpomenia sinuosa | Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 11.24–33.71 | Spherical | [61] |
| Colpomenia sinuosa | Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 17.78 | Cubic | [66] |
| Kappaphycus alvarezzi | Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 14.7 | Spherical | [67,68] |
| Padina pavonica | Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 31.41 | Spherical | [66] |
| Padina pavonica | Freeze-dried powder | Fe3O4 | 10–19.5 | Spherical | [69] |
| Petalonia fascia | Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 9.42, | Spherical | [66] |
| Pterocladia capillacea | Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 16.85–22.47 | Spherical | [61] |
| Sargassum acinarium | Freeze-dried powder | Fe3O4 | 21.6–27.4 | Spherical | [69] |
| Sargassum muticum | Freeze-dried powder | Fe3O4 | 18 | Cubic | [58] |
|
Spirulina platensis |
Dried powder | Fe3O4 | 10 | - | [70] |
| Turbinaria turbinata | Cell-free extract | Fe3O4 | 8–14 | - | [64] |
| Plant species | Part of the plant | Type of nanoparticle | Size of nanoparticle (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medicago sativa | Leaves | Fe2O3/Fe3O4 | 3.1 | Spherical | [78] |
| Aloe barbadensis | Leaves | Fe2O3 | 80–100 | Spherical | [79] |
| Amla | Seeds | Fe2O3 | 2-5 | Spherical | [140] |
| Arisaema amurense | Root | Fe2O3 | 24.55 ± 6.9 | Nearly spherical | [80] |
| Artemisia annua | Leaves | Fe2O3/Fe3O4 | 4.7 ± 0.8 | Spherical | [81] |
| Avecinnia marina | Flowers | FeO-NPs | 10–40 | Non-uniform | [82] |
| Azadirachta indica | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 9-12 | Irregular | [83] |
| Calliandra haematocephala | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 85.4–87.9 | Bead-like spherical | [84] |
| Carica papaya | Leaves | α-Fe2O3 | 2.15 | Spherical to agglomerate | [6] |
| Coriandrum sativum | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 20–90 | Spherical | [85] |
| Colocasia esculenta | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 15 | Spherical | [86] |
| Cynometra ramiflora | Leaves | FeO-NPs | - | Agglomerated | [87] |
| Cynara cardunculus | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 13.5 | Semi-spherical | [88] |
| Daphne mezereum | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 6.5–14.9 | Spherical | [89] |
| Eichhornia crassipes | Leaves | FeO-NPs | >100 | Rod-shaped | [90] |
| Eucalyptus globulus | Leaves | β-Fe2O3 | 100 | Spherical | [91] |
| Eucalyptus globulus | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 2.34 ± 0.53 | Spherical | [92] |
| Euphorbia wallichii | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 10–15 | Spherical | [93] |
| Euphorbia herita | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 25–80 | Spherical | [94] |
| Gardenia resinifera | Leaves | α-Fe2O3 | 3–8 | Spherical | [95] |
| Grapes | Seeds | Fe3O4 | 35 | Spherical | [96] |
| Green tea | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 5.7 ± 4.1 | Spherical | [97] |
| Hibiscus rosasinensis | Flower | FeO-NPs | 65 | Spinel | [98] |
| Sageretia thea | Leaves | Fe2O3 | 29 | Tetragonal crystalline | [99] |
| Lagenaria siceraria | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 30–100 | Cube | [100] |
| Lantana camara | Leaves | FeO-NPs | - | Crystalline nanorods | [101] |
| Laurus nobilis L | Leaves | α-Fe2O3 | 8.03 ± 8.99 | Spherical | [3] |
| Lawsonia inermis | Plant | FeO-NPs | 150–200 | Spherical | [102] |
| Mangifera indica L | Leaves | FeO-NPs | - | Polycrystalline nanorod | [103] |
| Mansoa alliacea | Leaves | β-Fe2O3 | 18.22 | Spherical nanoparticles | [77] |
| Moringa oleifera | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 15.01 ± 6.03 | Rods | [1] |
| Plantago major | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 4.6–30.6 | Spherical | [104] |
| Platanus orientalis | Leaves | α-Fe2O3 and γ-Fe2O3 | 38 | Spherical | [105] |
| Psidium guajava | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 1–5 | Spherical | [106] |
| Punica granatum | Seeds | Fe2O3 | 25–55 | Semi spherical | [71] |
| Rheum emodi | Roots | α-Fe2O3 | 12 | Spherical | [139] |
| Ruellia tuberose | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 20–80 | Hexagonal rods | [107] |
| Rumex acetosa | Plant | FeO-NPs | 40 | Amorphous | [74] |
| Sesbania grandiflora | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 25–60 | Agglomerated non-spherical | [108] |
| Soya bean | Sprouts | Fe3O4 | 8 | Spherical | [109] |
| Tamarix aphylla | Leaves | Fe2O3 | 5–100 | Oval | [110] |
| Terminalia belerica | Fruits | FeO-NPs | 15–23 | Spherical | [111] |
| Tridax procumbens | Leaves | Fe3O4 | 80–100 | Irregular spherical | [112] |
| Vaccinium corymbosum | Leaves | FeO-NPs | 52.4 | Irregular shape non agglomerated | [113] |
| Biological source | Type of waste | Size of nanoparticle (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ananas comosus | Fruit peel | 10–16 | Spherical | [117] |
| Acacia mearnsii | Biochar | 18–35 | - | [120] |
| Camellia sinensis | Tea waste | 28.5 | Spherical | [118] |
| Citrus Aurantifolia | Fruit peel | 3–10 | - | [119] |
| Cocos nucifera L | Fruit peel | 10–100 | Clustered | [121] |
| Coffee | Waste hydrochar | 10–40 | Spherical | [122] |
| Cynometra ramiflora | Fruit peel | 10–25 | Agglomerated | [123] |
| Juglans regia | Dried green husk | 12.6 | Cubic | [124] |
| Lemon | Fruit peel | 3 and 10 | Orthorhombic | [119] |
|
Malus domestica Citrus limon |
Fruit peel | 17–25 | Spherical | [125] |
| Orange | Fruit peel | 50 | Quasi spherical | [116] |
| Plantain | Fruit peel | 30–50 | Spherical | [126] |
| Punica Granatum | Fruit peel | 40 | Rod shaped | [127] |
| Rambutan | Fruit peel | 100–200 | Agglomerated spinel | [128] |
| Rice | Straw | 9.9 ± 2.4 | Aggregated spherical | [129] |
| Tangerine | Fruit peel | 50 | Spherical | [130] |
| Watermelon | Rinds | 2–20 | Spherical | [131] |
| Property | Characterization techniques |
|---|---|
| Size | TEM, XRD, DLS, NTA, SAXS, HRTEM, SEM, AFM, EXAFS, FMR, DCS, ICP-MS, UV-Vis, MALDI, NMR, TRPS, EPLS, magnetic susceptibility |
| Shape | TEM, HRTEM, SEM, AFM, STEM, EPLS, FMR, 3D-tomography |
| Chemical composition | XRD, XPS, ICP-MS, ICP-OES, SEM-EDX, NMR, MFM, LEIS, EELS |
| Crystal structure | XRD, EXAFS, HRTEM, electron diffraction, STEM |
| Surface Charge | Zeta potential, EPM |
| Magnetic properties | SQUID, VSM, Mössbauer, MFM, FMR, XMCD, magnetic susceptibility |
| Treated Bacterial Strain | Biological source for IONP generation | Antibacterial assay | Size of nanoparticle (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Escherichia coli |
Moringa M. oleifera | WDM | 15.01 ± 6.03 | Rod-like morphology | [1] |
| composite of Psidium guavaja-Moringa oleifera | WDM | 82 ± 7.0 | Spherical | [223] | |
| Zea mays L.) ear leaves | WDM | 37.86 | Spherical | [224] | |
| Xanthomonas campestris | WDM | 20–80 | Polymorphous, spherical, oval and hexagonal. | [225] | |
| Penicillium sp. | DDM | 11.3 | Spherical | [45] | |
| Penicillium brevicompactum | DDM | 30–50 | Spherical | [226] | |
| Glycosmis mauritiana; Rutaceae/Leaves | DDM | ≤100 | Spherical | [133] | |
| Couroupita guianensis,Lecythidaceae/fruit extract | DDM | 17 | Spherical | [227] | |
| Nigella sativa seed extract | DDM | 31.45 | Spherical | [228] | |
| Piper betel leaves extract | WDM | 25.17 | Cubic | [229] | |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Penicillium sp. | DDM | 11.6 | Spherical | [45] |
| Zea mays L.) ear leaves | WDM | 37.86 | Spherical | [224] | |
| Agrewia optiva (Dhaman or Biul) and Prunus persica (Peach) leaf extract | WDM | 15–60 (AO) 13–70 (PP) |
Spherical, granular | [230] | |
| Papaver somniferum | WDM | 38 ± 13 | Elliptical or Spherical | [231] | |
| Glycosmis mauritiana; Rutaceae/Leaves | DDM | ≤100 nm | Spherical | [133] | |
| Couroupita guianensis,Lecythidaceae/fruit extract | DDM | 17 | Spherical | [227] | |
| Pseudomona aeuruginosa | Penicillium sp. | DDM | 11.6 | Spherical | [45] |
| Moringa M. oleifera | WDM | 15.01 ± 6.03 | Rod-like morphology | [230] | |
| Agrewia optiva (Dhaman or Biul) and Prunus persica (Peach) leaf extract | WDM | 15-60 (AO) 13-70 (PP) |
Spherical, granular | [230] | |
| Papaver somniferum | WDM | 38 ± 13 | Elliptical or Spherical | [231] | |
| Withania coagulans/Berries | DDM | 15–20 | Nanorods | [232] | |
| Aloe vera/leaf extract | cellular damage assessed by SEM | 8.26 | Cubical, Rhomboidal, Spherical | [233] | |
| Acorus calamus/rhizome | WDM | 20–30 | Spherical | [234] | |
| Piper betel leaves extract | WDM | 25.17 | Cubic | [228] | |
| Salmonella sp | composite of Psidium guavaja-Moringa oleifera | WDM | 82 ± 7.0 | Spherical | [223] |
| Moringa M. oleifera | WDM | 15.01 ± 6.03 | Rod-like morphology | [230] | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | Penicillium sp. | DDM | 12 | Spherical | [45] |
| Composite of Psidium guavaja-Moringa oleifera | WDM | 82 ± 7.0 | Spherical | [106] | |
| Moringa M. oleifera | WDM | 15.01 ± 6.03 | Rod-like morphology | [106] | |
| Agrewia optiva (Dhaman or Biul) and Prunus persica (Peach) leaf extract | WDM | 15–60 (AO) 13–70 (PP) |
Spherical, granular | [230] | |
| Penicillium brevicompactum | DDM | 30–50 | Spherical | [226] | |
| Glycosmis mauritiana; Rutaceae/Leaves | WDM | ≤100 | Spherical | [133] | |
| Withania coagulans/Berries | WDM | 15–20 | Nanorods | [232] | |
|
Couroupita guianensis, Lecythidaceae/fruit extract |
WDM | 17 | Spherical | [227] | |
| Nigella sativa seed extract | WDM | 31.45 | Spherical | [229] | |
| Piper betel leaves extract | WDM | 25.17 | Cubic | [228] | |
| Streptococcus pyogenes | Zea mays L.) ear leaves | WDM | 37.86 | Spherical | [224] |
| Agrewia optiva (Dhaman or Biul) and Prunus persica (Peach) leaf extract | WDM | 15–60 (AO) 13–70 (PP) |
Spherical | [230] | |
| Piper betel leaves extract | WDM | 25.17 | Cubic | [228] |
| Treated fungal strain | Biological source for IONP generation | Approach | Size (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Inhibition zone (mm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alternaria alternata | - | Tannic acid | 10–30 | quasi circular |
21.33 ± 3.83 | [236] |
| Arthogrophis cuboida | Euphorbia hirta | Leaf extract | 25 – 80 |
Cavity like structures | 25.33 ± 0.5 | [94] |
| Aspergillus flavus | Laurus nobilis L. | Leaf extract | 8.03 ± 8.99 | crystalline, spherical; partly hexagonal | 13 | [3] |
| Green Tea (GT) or black Tea (BT) | Leaf extract | 42–60 | agglomerated & spherical | Aflatoxin reduction [%]:GT: 43.5 ± 1.5BT: 39.2 ± 0.9 | [237] | |
| Aspergillus fumigatus | Euphorbia hirta | Leaf extract | 25 – 80 | Cavity like structures | 21.67 ± 1.5 | [94] |
| Aspergillus niger | - | Tannic acid | 10–30 | circular | 26.33 ± 1.15 | [236] |
| Platanus orientalis | Leaf extract | 38 | spherical | 16 | [105] | |
| Euphorbia hirta | Leaf extract | 25 – 80 | Cavity like structures | 18.67 ± 0.5 | [94] | |
| Aspergillus parasiticus | Green Tea (GT) or Black Tea (BT) | Leaf extract | 42–60 | agglomerated & spherical | Aflatoxin reduction [%]:GT: 51.6 ± 1.6BT: 47.1 ± 3.1 | [237] |
| Cladosporium herbarum | - | Tannic acid | 10–30 | circular | 18.00 ± 1.00 | [236] |
| Euphorbia helioscopia | Leaf extract | 7 – 10 | spherical | 38.33 | [238] | |
| Mucor piriformis | Platanus orientalis | Leaf extract | 38 | spherical | 26 | [105] |
| Penicillium chrysogenum | - | Tannic acid | 10–30 | circular | 28.67 ± 1.53 | [236] |
| Penicillium spinulosum | Laurus nobilis L. | Leaf extract | 8.03 ± 8.99 | crystalline, spherical; partly hexagonal | 14 | [3] |
| Trichothecium roseum | - | Tannic acid | 10–30 | circular | 22.67 ± 2.52 | [236] |
| Treated microorganism | Biological source for IONP generation | Approach | Size (nm) |
Nanoparticle morphology | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasites | |||||
| Plasmodium | Nephrolepis exaltata | IONPs alone | 16 | Roughly spherical | [14] |
| Leishmania tropica KWH23 | Trigonella foenum-graecum | Synergistic effects of IONPs and LED light together | - | - | [245] |
| Virus | |||||
| Poliovirus (Type 1 and 3) | Hyphaene thebaica | IONPs alone | 10 | Quasi-spherical and cuboidal | [246] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





