1. Introduction
Enteric viruses, the major cause of acute gastroenteritis and enteric hepatitis worldwide, are among the most important waterborne pathogens [
1]. Despite their divergence in pathogenesis and life cycle, they are all transmitted by the fecal-oral route, through both food and water contamination. They spread in the environment mostly as non-enveloped particles, making them resistant to unfavorable conditions and persisting for extended periods. Their infectious dose is low [
2] and, combined with their extremely high excretion of up to 10
8-10
11 genome copies/gr of feces [
3], enteric viruses are capable to produce large outbreaks. The most important viruses in this group can be divided in enterotropic and hepatotropic viruses, being norovirus (NoV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV) the best known and characterized of each category [
4].
NoV are the causal agent of approximately 20% of all gastroenteritis, infecting 685 million people every year and causing 200,000 deaths per year, making them the leading cause of gastroenteritis in many regions [
5,
6]. Genus
Norovirus, within the
Caliciviridae family has high diversity and all known NoV are classified into 10 different genogroups (GI to GX), but only NoV GI, GII, GIV, GVIII and GIX are capable to infect humans, with GI and GII being the most common. NoV GI is less commonly found in patients with acute gastroenteritis across the globe than NoV GII [
7,
8,
9]. Genotype GII.17 emerged in Asia and was responsible for gastroenteritis linked with NoV in the year 2014 and has subsequently been documented worldwide [
10,
11]. Across the world, NoV have been detected in different water bodies, including rivers, sewage, municipal water, groundwater and recreational water [
12,
13]. NoV can cause both sporadic cases and outbreaks during all the year, with a significant seasonality, having a peak of incidence in cold seasons [
14].
HAV is a member of the
Hepatovirus genus, belonging to the family
Picornaviridae, and a cause of acute viral hepatitis. Based on the capsid nucleotide variability, three genotypes (I, II and III) and six subgenotypes (IA, IB, IIA, IIB, IIIA and IIIB) of HAV have been described [
15]. The primary mechanism of transmission of HAV is the faecal-oral route and direct contact with an infected person [
16]. Thus, the virus is present in different water environments and it is extremely resistant to adverse conditions: it can stay infectious about 60 days in tap water, more than 6 weeks in river water, above 8 weeks in groundwater, and about 30 weeks in seawater [
17,
18]. One and a half million people suffer from hepatitis A annually, which is an underestimation of the number of infected people due to the asymptomatic presentation of the virus [
4]. Hepatitis A outbreaks of are mainly associated with water supplies [
19], but foodborne transmission [
18,
20,
21] and infections between men having sex with man are also common [
22]. The consumption of improperly cooked or raw oysters and clams from sewage-contaminated water has led to multiple outbreaks of HAV infection [
23]. Hepatitis A can be prevented by vaccination, but the vaccine is not administered worldwide. The global distribution of hepatitis A is divided in non-endemic countries and endemic countries. Non-endemic regions are usually high-income countries with improved hygienic-sanitary conditions, whereas endemic regions typically correspond to low-income countries with poor water sanitation [
15].
In recent years, hepatitis E virus (HEV), a viral agent with zoonotic potential, has emerged. HEV causes foodborne hepatitis, sometimes with chronicity in immunocompromised individuals [
24], and complications in pregnant women that may even lead to a high mortality rate [
25]. HEV virus is a foodborne and waterborne pathogen threatening global health in developed and developing countries [
26,
27]. HEV has eight different genotypes: genotypes 1–4 and 7 are known to be the main threats to humans [
28]. Genotype 7 (HEV-7) was firstly isolated in camels [
29,
30]. Another genotype related with camels was also described (HEV-8), but it has yet to be demonstrated that it can infect humans [
31].
Riyadh city, the capital of the kingdom of Saudi Arabia has an arid environment with few rainfall and extreme temperatures in the summer months. For this reason, the water is a rare and precious commodity. The scarcity of this resource has been increased due to the explosive demographic increase in the area, moving in sixty years from 150,000 inhabitants to about 6.5 million [
32]. In addition, the government is covering the big demand of water for agriculture by the use of two conventional sources and a non-conventional one. Conventional resources include surface water and groundwater, whereas the non-conventional source is treated wastewater. Twenty-five percent of tertiary treated wastewater is used to irrigate landscapes in public parks in a number of cities and crop irrigated areas across Saudi Arabia. Wadi Hanifa lake, which is the main drainage system for the city and used for irrigation, receives treated wastewater from the Manfuha sewage treatment plant [
33].
Several enteric pathogens, including Astrovirus, Rotavirus A and Adenoviruses, have been detected in stool samples of children with gastroenteritis in Saudi Arabia and in water environments, using simple molecular detection techniques [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39]. Taking into account that Saudi Arabia is an intermediate region regarding HAV endemicity, with also high risk of HEV because of close contact with camels, the virology profile of both Wadi Hanifa lake and well water may provide valuable information on the prevalence and survival of enteric viruses in desert environments. In the present study, we have investigated for the first time the occurrence of NoV GI and GII,HAV, and HEV in water samples of Wadi Hanifa lake and the neighboring wells through RT-qPCR.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample collection
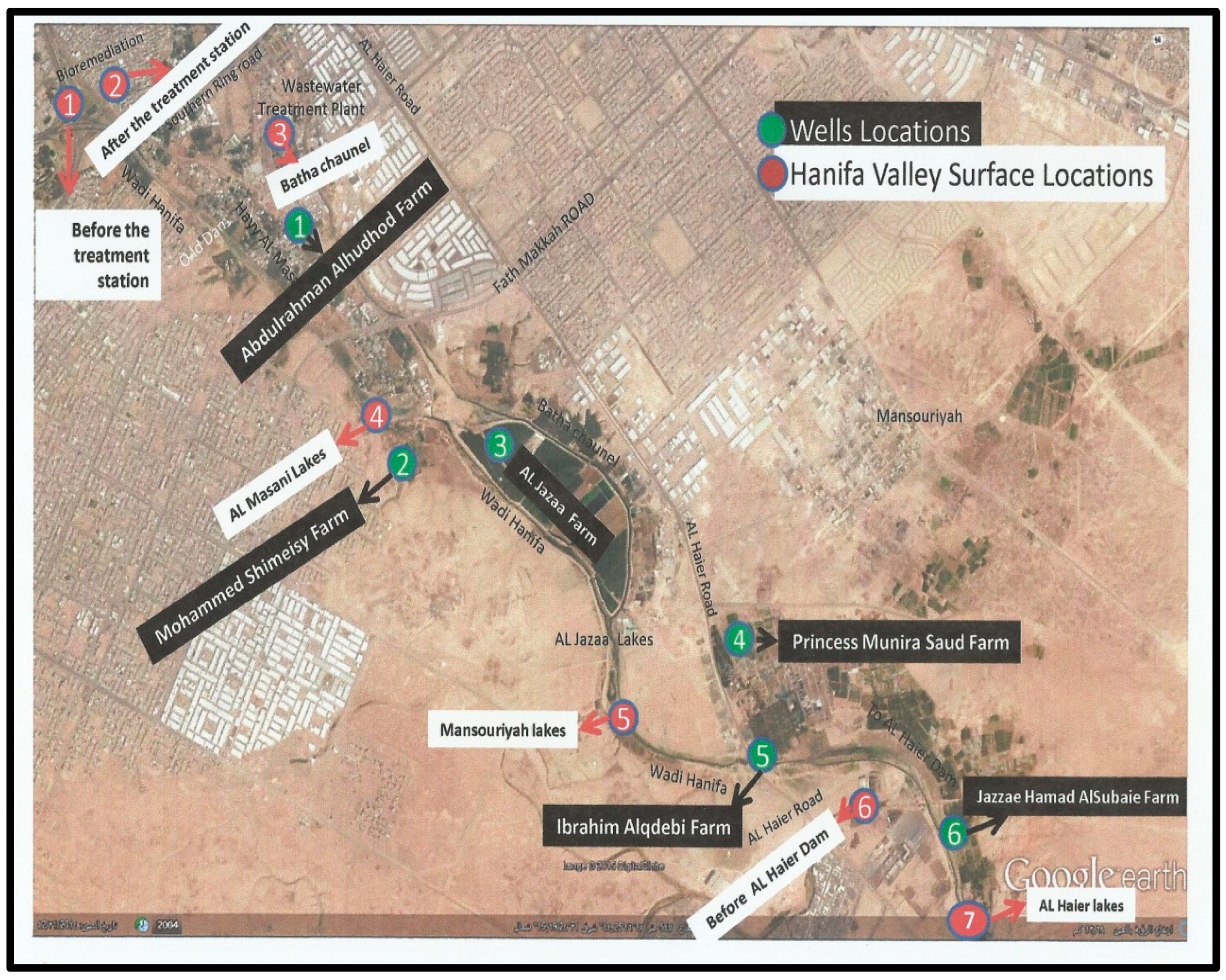
To evaluate the presence of enteric viruses in different water environments in Riyadh, samples (10 L) were collected monthly from December 2014 to November 2015 to ascertain the prevalence and seasonality of viruses. Locations S1-S7 were selected strategically to cover most of the Wadi Hanifa lake surface area, and locations W1-W6 covered the wells between Wadi Hanifa and Batha channel (
Figure 1). The location of each sampling site was as follows: S1,before the raw water treatment in the bioremediation treatment plant; S2,after the water treatment in bioremediation treatment plant; S3,Batha stream channel after leaving the Manfuha treatment plant; S4,waterway after lake factories directly; S5,waterway after Mansoriyah lake; S6, watercourse before Dam Al Haierlake; S7,watercourse after Dam Al Haier lake. The bioremediation treatment plan uses the foodchain for the treatment of urban wastewater by combining both primary producers and consumer organisms with the support of a low-tech eco-centric infrastructure that maintains the ecosystem. This treated water is used for urban functions such as a river park system and increase the water flow in Wadi Hanifa. The choice of wells was dependent on their proximity to Wadi Hanifa lake and the permission of their owners.
Figure 1.
Sampling locations in the google map (red: surface water (S1-S7); green: well water (W1-W6)).
Figure 1.
Sampling locations in the google map (red: surface water (S1-S7); green: well water (W1-W6)).
The total number of samples was 156 (84 surface water samples from Wadi Hanifa and 72 well water samples). Samples were collected in sterile containers and transported on ice to the laboratory where they were kept at 4°C until processing within 24 hours. Physicochemical and microbiological analysis were performed in all samples prior the concentration. Furthermore, temperatures were obtained and recorded at each collection day, from accuweather website.
Table 1 shows the average water temperatures of the surface water samples.
Table 1.
Average surface water temperature at the time of sample collection.
Table 1.
Average surface water temperature at the time of sample collection.
| Month |
Average T (S1-S7) ℃ |
| December |
23.85 |
| January |
21.2 |
| February |
24.50 |
| March |
25 |
| April |
27 |
| May |
29.5 |
| June |
29.5 |
| July |
30.2 |
| August |
31 |
| September |
30 |
| October |
29.1 |
| November |
25 |
2.2. Viral concentration
All water samples were concentrated using an optimized glass wool filtration method [
40] in the Department of Botany and Microbiology of the King Saud University. Briefly, each water sample passed through a positive-charged glass wool filter to detain all viruses in the sample. Then, viruses were eluted with 200 mL of glycine beef extract (GBE) buffer (glycine 0.05M, beef extract 3%) at pH 11. The buffer was recirculated through the filter for 1 hour to improve the recovery of enveloped viruses. After this elution, 20% of polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000 was added to the eluate and a secondary concentration based on flocculation-precipitation was performed. The concentrate (2 mL) was stored at -80ºC until the nucleic acid extraction.
2.3. Total nucleic acid extraction
Total RNA was extracted from 500 μl of sample using the NucliSENS® miniMAG® extraction system (Biomérieux). Nucleic acid extraction was performed according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer, obtaining a final volume of 100μl. To evaluate nucleic acid extraction efficiency, 10 μl of Mengovirus strain MC
0 were added to each sample before the lysis step [
41,
42]. Once extracted, all samples were stored at -80ºC.
2.4. Virus detection and quantification (RT-qPCR)
2.4.1. HAV, NoV GI and NoV GII
Mengovirus quantification, and HAV, NoV GI, and NoV GII screening were performed by using a multiplex Real-time RT-qPCR as previously described [
41]. Mengovirus recovery efficiencies ≥1% were considered acceptable, whereas recoveries < 1% were considered unacceptable and the nucleic acid extraction was repeated. Once acceptable efficiencies were reached for all samples, they were tested for the presence of HAV, NoV GI and NoV GII. Positive samples were then processed in a monoplex RT-qPCR for virus quantification. The monoplex RT-qPCR was selected for quantification because the multiplex assay is slightly less sensitive. Positive samples that were not detected in the monoplex or those which were below the limit of quantification were qualified as “detectable non-quantificable” samples and were arbitrarily scored as bearing <5 genome copies/reaction (rxn).
Both multiplex and monoplex RT-qPCR have the same cycling parameters: 60 minutes at 55ºC for reverse transcription and 5 minutes at 95ºC for initial denaturalization, followed by 45 cycles consisting of 15 seconds at 95ºC, 60 seconds at 60ºC and 60 seconds at 65ºCfor amplification. Fluorescence was read at every cycle after the last step [
42,
43,
44,
45].
2.4.2. HEV
HEV was detected and quantified by Real-time RT-qPCR using primers and probe previously described [
17]. The amplification program was modified as follows: 30 minutes at 50ºC for reverse transcription and 10 minutes at 95ºC for initial denaturalization, followed by 45 cycles consisting of 15 seconds at 95ºC and 60 seconds at 58º C for amplification. Fluorescence was read at every cycle. All RT-qPCR were performed using Invitrogen® Ultrasense One Step RT-qPCR System kit and Stratagene® Mx3000p thermocycler. All sets of primers and probes are shown in
Table 2.
Table 2.
Primers and probes employed for virus detection and quantification.
Table 2.
Primers and probes employed for virus detection and quantification.
| Virus |
Primers |
| Mengovirus |
Fw: 5’-GCGGGTCCTGCCGAAAGT-3’ |
| Rv: 5’-TGCACGCCATCTTCATTCACA-3’ |
| Probe (Multiplex): 5’-[VIC]-AGCACGTGGGAGGGCGATCG-[MGB]-3’ |
| Probe (Monoplex): 5’-[6FAM]-AGCACGTGGGAGGGCGATCG-[MGB]-3’ |
| Hepatitis A virus |
Fw: 5’-TCACCGCCGTTTGCCTAG-3’ |
| Rv: 5’-GAGCCCTGGAAGAAAG-3’ |
| Probe (Multiplex): 5’-[6FAM]-CCTGAACCTGCAGGAATTAA-[MGB]-3’ |
| Probe (Monoplex): 5’-[6FAM]-CCTGAACCTGCAGGAATTAA-[MGB]-3’ |
| Norovirus GI |
Fw:5’-CGCTGGATGCGNTTCCAT-3’ |
| Rv:5’-CCTTAGACGCCATCATCATTTAC-3’ |
| Probe (Multiplex): 5’-[TxRED]-TGGACAGGAGAYCGCRATCT-[IBRQ]-3’ |
| Probe (Monoplex): 5’-[6FAM]-TGGACAGGAGAYCGCRATCT-[TAMRA]-3’ |
| Norovirus GII |
Fw: 5’-ATGTTCAGRTGGATGAGRTTCTCWGA-3’ |
| Rv: 5’-TCGACGCCATCTTCATTCACA-3’ |
| Probe (Multiplex): 5’-[ATTO]-AGCACGTGGGAGGGCGATCG-[BHQ]-3’ |
| Probe (Monoplex):5’-[6FAM]-AGCACGTGGGAGGGCGATCG-[TAMRA]-3’ |
| Hepatitis E virus |
Fw: 5’-GGTGGTTTCTGGGGTGAC-3’ |
| Rv: 5’-AGGGGTTGGTTGGATGAA-3’ |
| Probe: 5’-[6FAM]-TGATTCTCAGCCCTTCGC-[BHQ]-3’ |
2.5. Statistical analysis
Neither prevalence nor quantification date were normally distributed, differences in positivity and comparison between mean viral loads were performed using the Mann Whitney test. P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All tests were performed using SigmaPlot 11.0.
3. Results
3.1. Seasonal distribution of enteric viruses in surface water
3.1.1. Prevalence of Hepatitis viruses
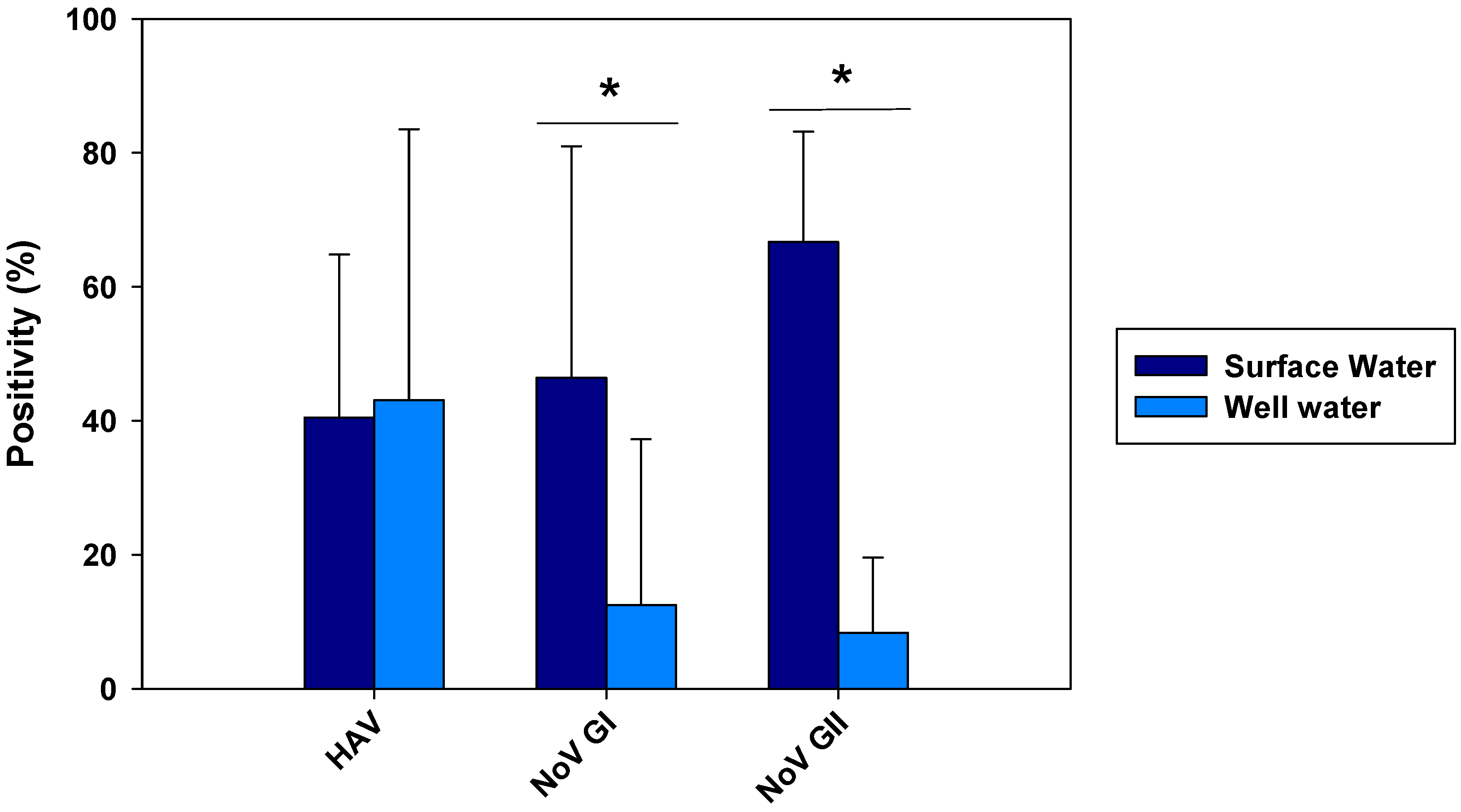
From all 84 samples analyzed from Wadi Hanifa surface water, 34 (40.48%) were positive for HAV (
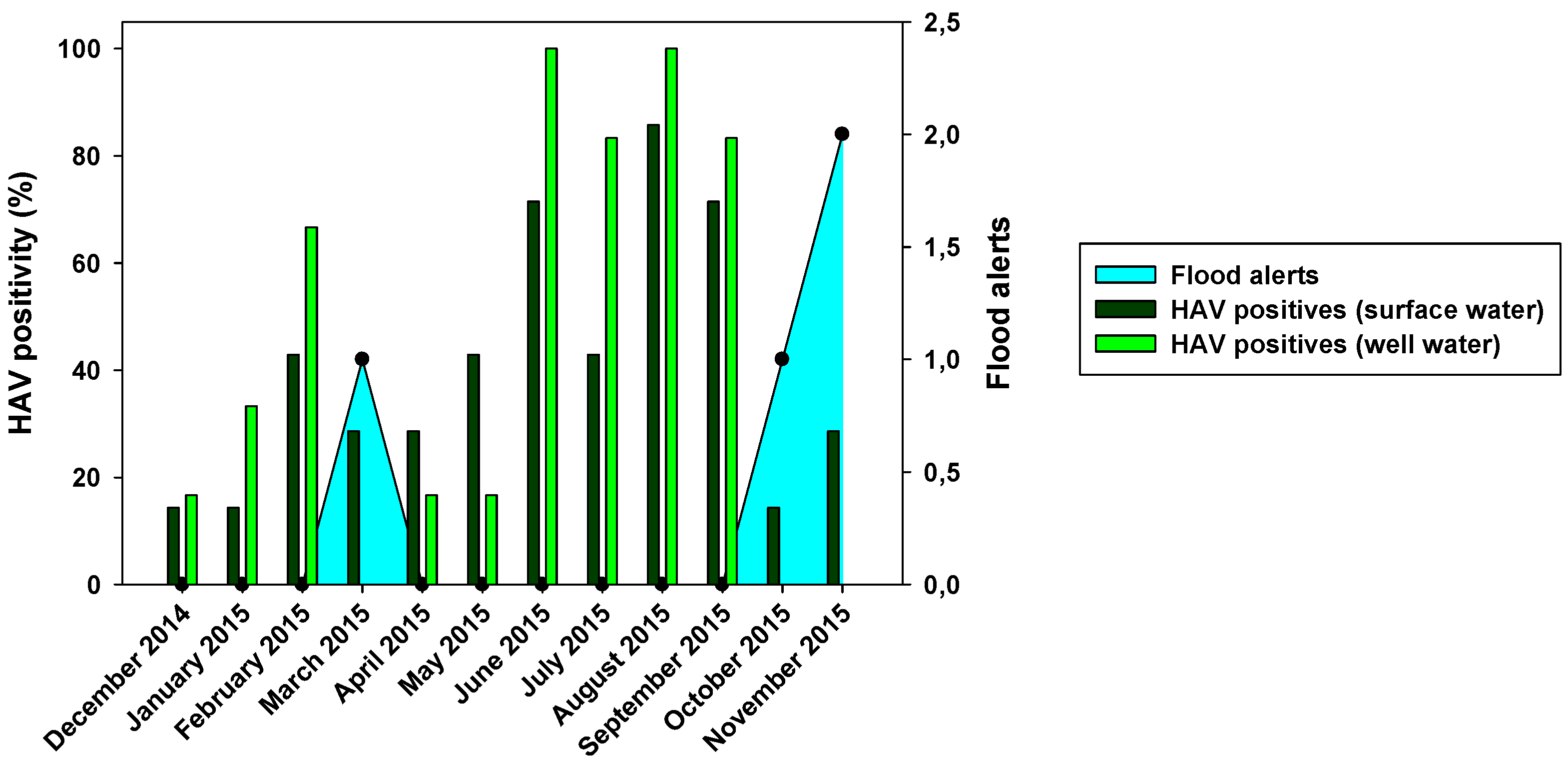
Figure 2). HEV was not detected in any surface water sample. Regarding the seasonality of HAV, the result of this study revealed that it was present in the surface water of Wadi Hanifa Lake all year round. The highest HAV prevalence (or positivity) was found during summertime (June-September) being August the month with the highest prevalence (83.3%), whereas the lowest prevalence (15%) was observed in the winter season (December-January), (
Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Prevalence of HAV, NoV GI, and NoV GII in surface and well water samples. The data shown are mean and SD of monthly positivity percentages. Differences between surface and well water samples were assessed with the t-test (*p<0.05).
Figure 2.
Prevalence of HAV, NoV GI, and NoV GII in surface and well water samples. The data shown are mean and SD of monthly positivity percentages. Differences between surface and well water samples were assessed with the t-test (*p<0.05).
Figure 3.
Monthly HAV positivity for both surface and well water compared with flood alerts.
Figure 3.
Monthly HAV positivity for both surface and well water compared with flood alerts.
3.1.2. Prevalence of NoVGI and GII
The prevalence of NoV was also very high. In fact, from 84 samples analyzed for NoV GI and GII, 39 (46.43%) were positive for NoV GI and 56 (66.67%) were positive for NoV GII (
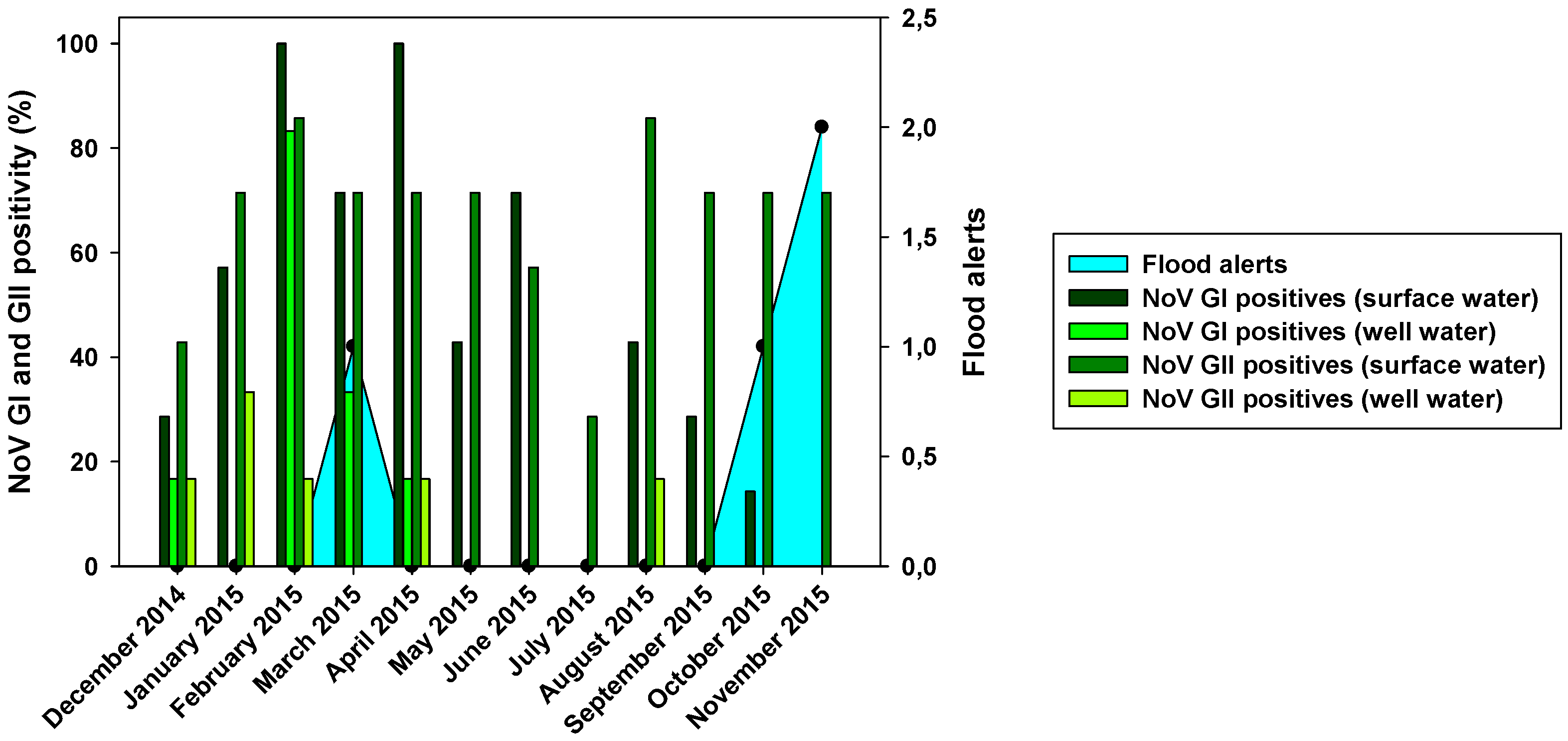
Figure 2). NoV GI was present all the year round with the exception of two months: July and November (
Figure 4). NoV GI prevalence was high from February to June, having their highest in February and April. On the other hand, the NoV GII prevalence was mostly stable through all the year round, varying between 30 to 85%.
Figure 4.
Monthly NoV GI and GII positivity for surface and well water related with flood alerts.
Figure 4.
Monthly NoV GI and GII positivity for surface and well water related with flood alerts.
3.2. Seasonal distribution of enteric viruses in wells
3.2.1. Prevalence of Hepatitis viruses
A total of 72 samples were analyzed from neighboring wells of Wadi Hanifa lake for HAV and HEV;31 samples (43.06%) were positive for HAV, whereas only two (2.77%) were positive for HEV. One of them was collected in May in the fourth well water sample location (W4), and the other in November, in the first well water sample location (W1).
HAV was present mostly all the year round, but it was extremely prevalent in summer season (95%), while the lowest presence was observed in the cold season (0-15%) (
Figure 3). These results are in line with those found in surface water. We can observe a relationship between the abundance of HAV in Wadi Hanifa lake and its high prevalence in wells.
3.2.2. Prevalence of NoV GI and GII
Out of 72 well water samples tested for NoV, 9 (12.5%) were positive for NoV GI and 6 (8.33%) for NoV GII (
Figure 2). The highest virus prevalence was in the wet season, which includes the winter and spring months, with and additional finding of GII in August (
Figure 4). Despite a reduction in viral loads, probably due to the viral loss in water filtration from surface water to wells, we could observe that the months with the highest NoV prevalence in surface water were also the ones with the highest positivity in well water.
3.3. Differences between sampling areas
Two of the most interesting sampling areas in this study were S1 and S2 locations. S1 is located before the bioremediation station that uses the biological trophic chain in nature to increase Wadi Hanifa’s water quality [
46]; S2 is located in an area that receives treated water from this bioremediation station. Sampling areas S3 to S7 are located further away from the Manfuha wastewater treatment plant (
Figure 1).
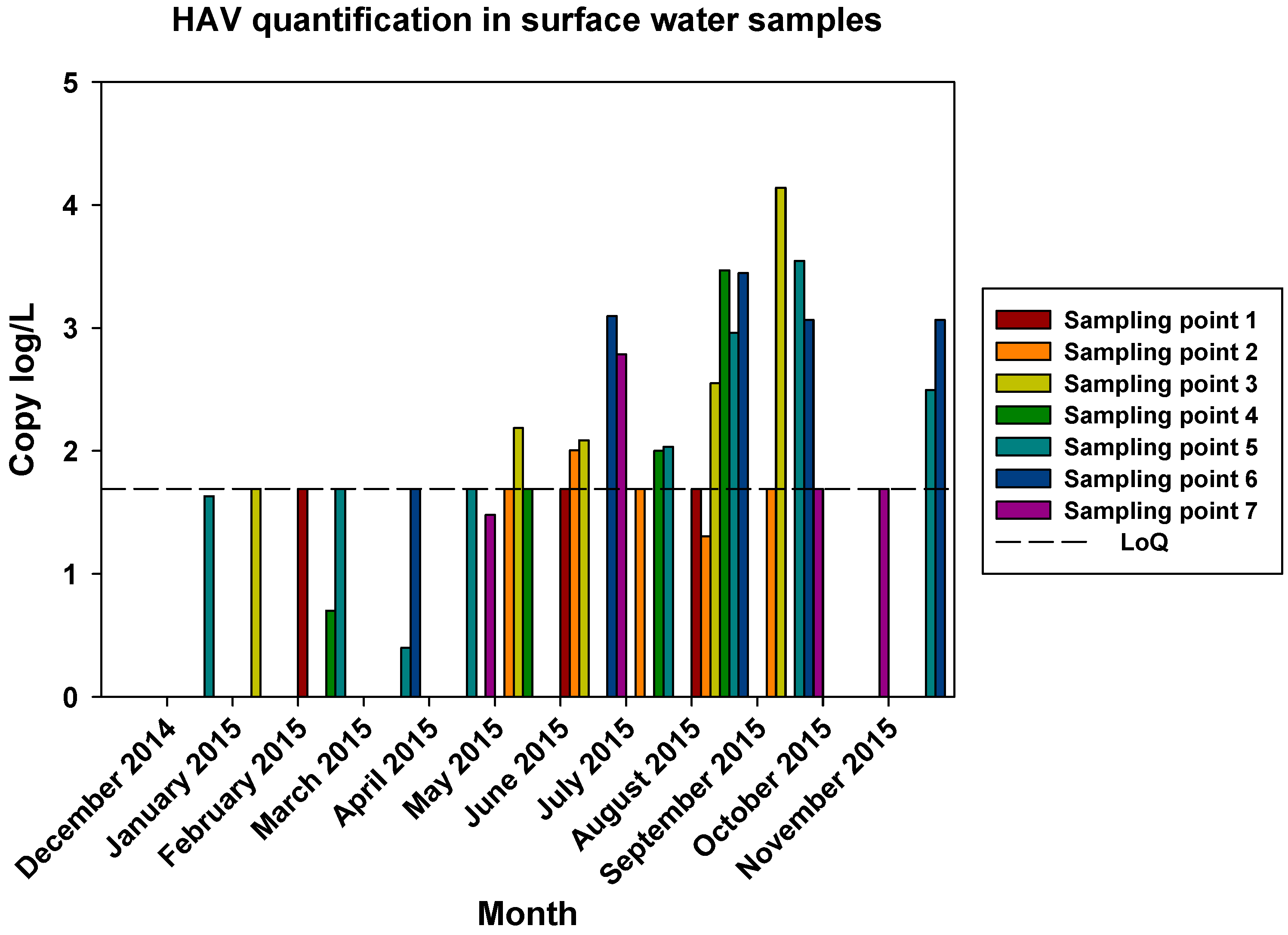
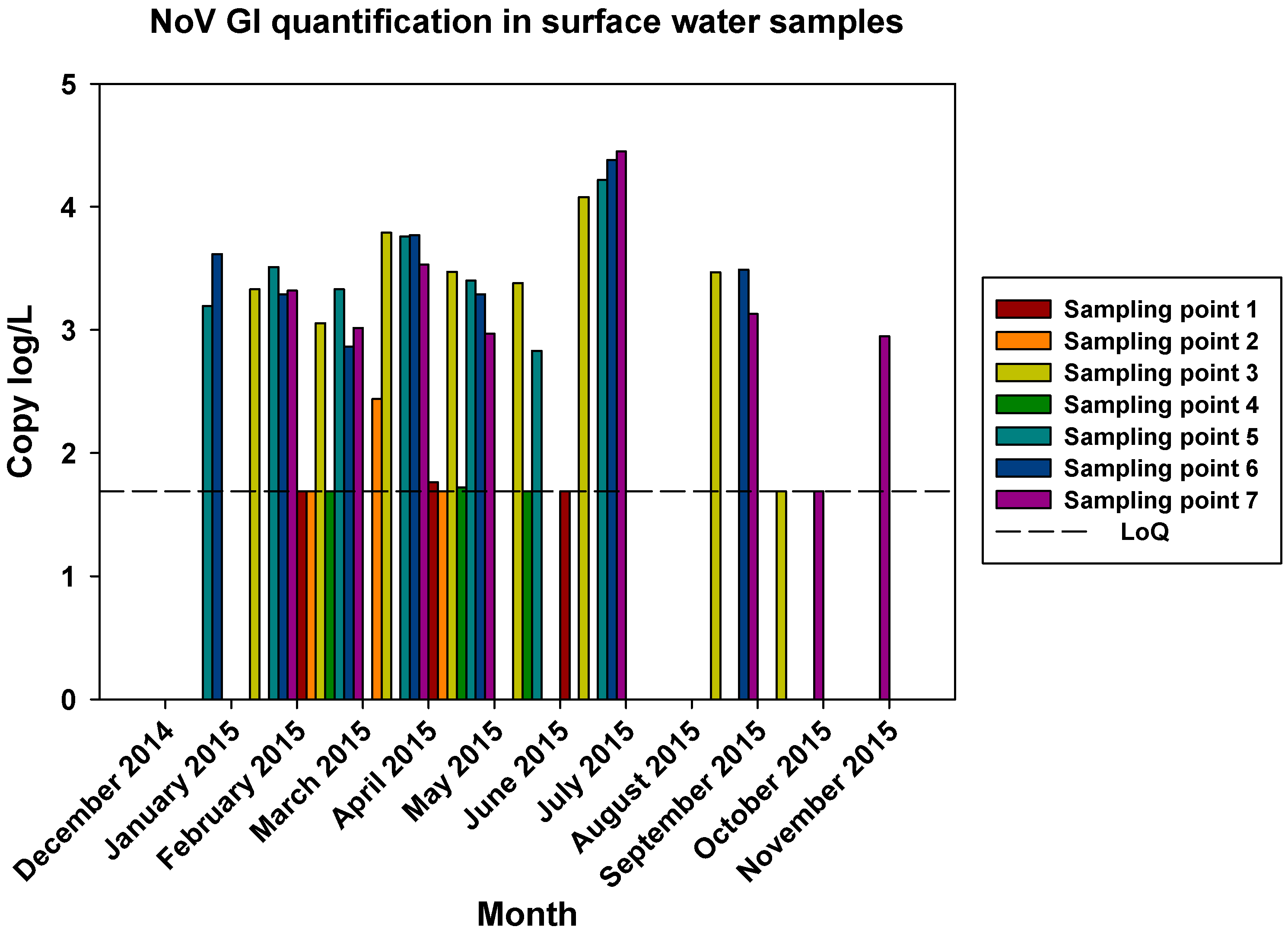
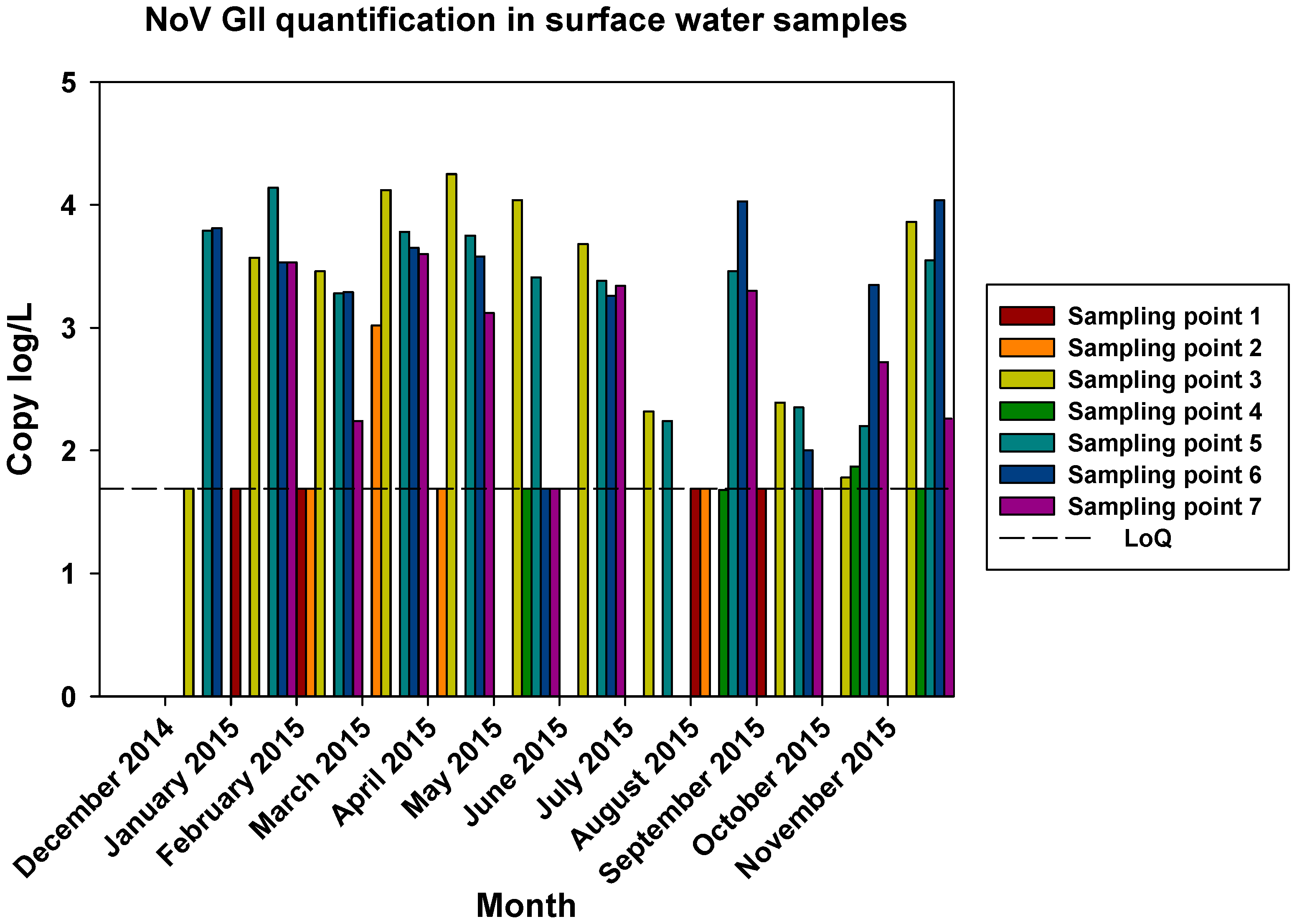
The comparisons of the viral loads of all three viruses at the different sampling points over time are represented in
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7. By comparing the viral loads between S1 and S2 samples, we observed that Wadi Hanifa’s bioremediation station could neither eliminate nor significantly reduce the presence of enteric viruses in water. In some months, HAV, NoV GI or NoV GII were detected in both S1 and S2 samples (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6). We could also detect HAV more frequently in the S2 sampling location than in the S1 location (
Figure 5).
Figure 5.
Monthly viral load of HAV detected in all seven surface water sampling points.
Figure 5.
Monthly viral load of HAV detected in all seven surface water sampling points.
Figure 6.
Monthly NoV GI viral load in all seven surface water sampling locations.
Figure 6.
Monthly NoV GI viral load in all seven surface water sampling locations.
Figure 7.
Monthly NoV GII viral load in all seven surface water sampling locations.
Figure 7.
Monthly NoV GII viral load in all seven surface water sampling locations.
The prevalence of all three viruses tended to increase as samples were taken further away from the Manfuha wastewater treatment plant. In S5, S6 and S7 locations, we could detect the maximum number of positive samples (50% to 100% positivity depending on the virus), and we could also detect the higher concentration of genomic copies in these samples. We detected the maximum prevalence in S5 location for HAV and NoV GII, and in S7 for NoV GI. S6 location had the highest mean viral load for all three viruses: 2.68 log of genome copies/L (log gc/L) for HAV, 3.55 log gc/L for NoV GI and 3.35 log gc/L for NoV GII.
S3 sampling location had a significantly high prevalence for NoV GI (with the same prevalence as S7) and NoV GII comparing to S1 and S2 locations, but not for HAV. This latter one was an interesting sampling location because we could also detect one of the highest concentrations for all three viruses despite it was located immediately after the treatment plant. The mean viral load of positive samples collected in this location were 2.53, 3.28 and 3.23 log gc/L for HAV, NoV GI and NoV GII, respectively.
3.4. Comparison of viral load in Wadi Hanifa lake and the neighboring wells
The positivity of Wadi Hanifa lake samples and well water samples were recorded and compared in
Figure 2. The results obtained showed clearly that the prevalence of both groups of NoV was significantly higher in the lake than in the wells (p<0.05). Regarding HAV, there was no significant difference between surface water and well water. Considering separately the samples in each season (May-Sept for dry season and Oct-March for wet season), no significant differences were observed between surface and well water samples for HAV in any season (
Table 3). In contrast, significant differences in the viral loads of NoV GI and NoV GII were detected between surface and well water during the dry season. Concerning HEV which was found only in two different wells, the viral load was 2.96 log gc/L and 2.71 log gc/L in May and November, respectively.
Table 3.
Monthly HAV, NoV GI and NoV GII viral loads in surface and well water samples. NA means that none of the samples were positive for that virus.
Table 3.
Monthly HAV, NoV GI and NoV GII viral loads in surface and well water samples. NA means that none of the samples were positive for that virus.
| |
Viral load (Log10 Mean ± SD) |
| Month |
Surface water |
Well water |
| HAV |
NoV GI |
NoV GII |
HAV |
NoV GI |
NoV GII |
| December 2014 |
1.63 ± 0.00 |
3.40 ± 0.21 |
3.10 ± 0.99 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
| January 2015 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
3.36 ± 0.09 |
3.29 ± 0.83 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
NA |
1.75 ± 0.05 |
| February 2015 |
1.20 ± 0.50 |
3.06 ± 0.17 |
2.60 ± 0.75 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
1.94 ± 0.39 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
| March 2015 |
1.04 ± 0.65 |
3.45 ± 0.52 |
3.63 ± 0.36 |
NA |
1.78 ± 0.08 |
NA |
| April 2015 |
1.58 ± 0.11 |
2.46 ± 0.78 |
3.27 ± 0.87 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
| May 2015 |
1.86 ± 0.23 |
2.63 ± 0.70 |
2.50 ± 1.01 |
<1.69 ± 0.00 |
NA |
NA |
| June 2015 |
2.33 ± 0.52 |
3.76 ± 1.04 |
3.41 ± 0.16 |
2.15 ± 0.34 |
NA |
NA |
| July 2015 |
1.91 ± 0.15 |
NA |
1.96 ± 0.27 |
1.66 ± 0.34 |
NA |
NA |
| August 2015 |
2.57 ± 0.83 |
3.36 ± 0.17 |
3.02 ± 0.97 |
2.72 ± 0.47 |
NA |
1.68 ± 0.00 |
| September 2015 |
2.83 ± 0.98 |
1.69 ± 0.00 |
2.02 ± 0.30 |
1.90 ± 0.17 |
NA |
NA |
| October 2015 |
1.69 ± 0.00 |
2.94 ± 0.00 |
2.37 ± 0.58 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
| November 2015 |
2.78 ± 0.29 |
NA |
3.08 ± 0.93 |
NA |
NA |
NA |
When quantifying positive samples, the mean log gc/L ranged between 1.04 to 2.83 for HAV in Wadi Hanifa lake, and between 1.66 to 2.72 in wells. The highest mean values were observed in September, whereas the lowest mean values were in March. According to these data, we can confirm that HAV levels in wells increased in the hot season (
Table 3). Regarding NoV, the mean log of gc/L ranged between 1.69 to 3.76 for NoV GI and 1.96 to 3.63 for NoV GII in surface water of Wadi Hanifa lake. The highest mean values were observed in June and March for NoV GI and NoV GII, respectively. The lowest mean values were in September and July for NoV GI and NoV GII, respectively.
4. Discussion
Wadi Hanifa lake runs through the city of Riyadh and around 70% of the city is located within its catchment area. The term “Wadi” usually refers to a dry riverbed that contains water only after heavy rain episodes, and this is the natural condition of Wadi Hanifa. However, the sampling area covered in the present study, in the south of Wadi Hanifa, bears a continuous flow of water resulting from the effluents of the Manfuha sewage treatment plant, drained Riyadh groundwater and storm water channels draining different sectors of the city [
47]. It also represents a convenient system for disposing Riyadh wastewater.
Temperatures in summer reach an average of 42.9 °C (109.2 ºF) and precipitation averages only 60 millimeters (2.4 in) per year in the driest places. Rain falls with great intensity for short periods between October and April, causing flash floods. Usually April is the rainiest month, but 2015 had atypical heavy rains with floods in October and November, affecting the results. The nature of the dry, warm climate leads to a high percentage of the scarce rainfall being instantly evaporated. The remaining water mostly ends up as groundwater. While abundant, the levels of the water table are being tested by the rapid growth the city of Riyadh has seen in the past fifty years, from a population of 150,000 in 1960 to an estimated 6.5 million todays. For that, Wadi Hanifa surface and well water have a particular interest because of their potential to contain high titers of enteric viruses.
Prevalence of NoV GI and NoV GII as summarized in
Figure 2 showed differences in positivity between surface and well water samples, which was probably due to processes of water filtration. The similar HAV positivity for both types of samples and lower NoV prevalence in well water samples would mean that HAV is more resistant to water filtration than NoV. The higher HAV prevalence in both well water and surface water was detected in the driest months (June-August). That could point that groundwater protects viruses from temperature, sunlight, and drought. For NoV, most of the positive samples were detected in December-April and then prevalence decreases for NoV GI, with minimum prevalence in the first two months of the wet season. HAV shows a similar behavior than NoV GI but its higher prevalence was detected in June-September. For well water samples, all three viruses were absent in rainy months. Heavy rain and floods could dilute viruses in water, causing that NoV GI and HAV in surface water and all three viruses in well water were harder to detect. Prevalence of NoV GII seems to be not affected by rain since its positivity was about the same before and after the rainy period. There was also a negative correlation between rainfall and HAV and NoV GI prevalence. For these two viruses, all three months with floods registered (March, October, and November) showed significant decreases in prevalence in surface and well water (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). Despite of that, the mean viral load of HAV in November was one of the highest found in the study. Previous studies showed that since the vaccination program started in 2008, the seasonality of HAV begun to shift, from detecting most of the hepatitis A cases in summer to being able to detect hepatitis A cases in autumn [
32]. Our data corroborates this seasonality shift since the highest viral loads are detected not only in November, but also in the second half of the summer months (August and September). No correlation between NoV GII and rainfall was observed. Nevertheless, in March 2015, NoV GII was not detected in well water samples (
Figure 4).
Surface water presents a certain HAV-NoV duality when comparing viral loads. HAV has its highest titer in August and September 2015 for well water and surface water, respectively. In these months, NoV GI had its minimum viral load in surface water samples and NoV GII quantification was lowest in surface water and minimum in well water too. Additionally, lower HAV viral loads correlated with higher viral load periods for NoV (January-March 2015). Similar results were found in well water samples but only for NoV GI and HAV, since NoV GII was mostly undetectable.
In Saudi Arabia, there is little published evidence on HAV incidence unlike its seroprevalence. In 2021 the seroprevalence of HAV oscillated between 8% to 100%, with the highest incidence reported in the Eastern region compared to Central and Western regions [
30]. In this study, a sustained shift in Hepatitis A endemicity compared with what was recorded before the implementation of the vaccine was observed. In our study, we found a high prevalence of HAV (approximately 40%) between December 2014 and November 2015. This result was completely unexpected, considering the fact that Saudi Arabia implemented childhood HAV vaccination program in 2008, and Badur et al. in 2021 reported that the total number of new hepatitis cases has declined by about 90% after 2008 [
32]. The same study points to a significant increase in hepatitis A incidence in the years 2016 to 2018. The surprisingly high viral load in November 2015 could indicate the beginning of that episode of higher HAV incidence.
HEV was detected in two well water samples, hence it seems that there is no significant shedding of this virus in the environment. Few data were found regarding the prevalence of HEV in Saudi Arabia in humans. Arif et al., reported that the seroprevalence of HEV in Riyadh was 8.4% [
34]. More recently, Al Dossary et al. in 2021 reported that the seroprevalence of HEV in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia was low (3.2%) [
48]. However, recent serological studies in camels showed a prevalence of 23.1% in local camels in Jeddah province [
49]. This high prevalence in camels highlighted the role of camels as a zoonotic reservoir for HEV infection to humans. Further investigations are needed to know the actual prevalence of HEV in humans in Riyadh and in the overall Saudi Arabia. On the other hand, the absence of HEV positive samples could be due to the employed RT-qPCR assay that only detects the major HEV genotypes (HEV-1 to HEV-4) and not camel HEV genotypes. In fact, a novel HEV genotype, named Dromedary camel HEV which was first detected in 2014 in camels in the Middle East, was reported to be the main cause of acute hepatitis in a transplant patient in the United Arab Emirates who regularly consumed camel milk and meat [
50]. In Saudi Arabia, more precisely in Jeddah province, the prevalence of HEV was low (1.77%) in domestic camels [
51]. The absence of data in Riyadh prevented us from drawing definite conclusions.
Regarding NoVin Saudi Arabia, so far there is no information at all on its prevalence, except for one report in the literature [
34]. In this study, 1000 stool samples were collected and screened for many enteric viruses. The prevalence of NoV was determined by ELISA, and it was 3.5%. Our data in this study, showed that the prevalence of NoV GI and GII in surface water of Wadi Hanifa lake, was between 45% and 65%, which is higher than what was reported in the study of Tayeb et al. The use of a quantitative molecular technique such as the Real-time RT-qPCR provided more precise data in our work. We conclude that the incidence of NoVin Saudi Arabia is so far underestimated. We hope that our results will provide the authorities with useful information to focus on these viruses and take appropriate measures. Improving the treatment of wastewater in several treatment plants in Riyadh could be efficient to reduce the transmission of such viruses through lakes which are used for irrigation and agricultural purposes.
In any case, this study has the limitation of covering only one year, and further research is needed to confirm our data.
5. Conclusions
Water-based epidemiology through the detection and quantification of the various human viruses in environmental waters is critical for the adoption of public health measures for the prevention of diseases as well as for the implementation of mitigation measures in response to outbreaks. Hence, conducting regular viral monitoring of treated wastewater discharged into the environment is important for the prevention of diseases associated with exposure to virus contaminated water. Meanwhile, the detection of viral genome copies in water and wastewater does not necessarily mean that the detected particles are infectious. However, genome copies are indicative of potential infections and health risk associated with the virus contaminated matrices.
Since the information on the presence of enteric viruses in water in Saudi Arabia is scarce, it is hard to establish comparisons with other data which represents a limitation of the present study. Nevertheless, we can confirm the higher prevalence of HAV and NoV in surface water than in well water samples. Quantitative data showed that both NoV GI and GII are present in higher viral levels in Wadi Hanifa than in the surrounding wells, although this is not the case of HAV, showing similar titers in well and surface waters.
Our data also point to strong rainfall events that negatively correlate with HAV/NoV GI prevalence in surface water, although only with HAV in well water. We could also observe opposite patterns between the viral loads of HAV and both NoV GI and GII.
The sporadic detection of HEV points to the low prevalence of the major genotypes of this pathogen in Saudi Arabia’s environment. However, the assessment of the zoonotic potential of HEV-7 and the recent description of HEV-8, both having camels as their natural reservoir, in which they show a high seropositivity, make HEV screening a major priority in Saudi Arabia.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, ABo and RMP; methodology, IA, ABl, NAO; formal analysis, SG; investigation, IA, ABl; resources, ABo, RMP, SG, MIC; data curation, SG, MIC; writing—original draft preparation, IA, ABl; writing—review and editing, Abo, RMP, SG, MIC; supervision, ABo, RMP; funding acquisition, RMP, IA, ABo. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia for funding this research work through the project no. (IFKSUOR3–270-1). This work was also supported in part by the XRB-Biotechnology Reference Network (Generalitat de Catalunya).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ganesh, A.; Lin, J. Waterborne human pathogenic viruses of public health concern. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2013, 23, 544–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Estes, M.K.; Crawford, S.E.; Neill, F.H.; Ramani, S.; Hill, H.; Ferreira, J.; Graham, D.Y. Determination of the 50% Human Infectious Dose for Norwalk Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, A.; Pintó, R. M.; Guix, S. Foodborne viruses. Curr. Opinion In Food Sc. 2016, 8, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanrewaju, A.A.; Enitan-Folami, A.M.; Sabiu, S.; Edokpayi, J.N.; Swalaha, F.M. Global public health implications of human exposure to viral contaminated water. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 981896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global Prevalence of Norovirus in Cases of Gastroenteritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lan. Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartey, B. L.; Quaye, O.; Damanka, S.A.; Agbemabiese, C.A.; Armachie, J.; Dennis, F.E.; Enweronu-Laryea, C.; Armah, G.E. Understanding pediatric norovirus epidemiology: a decade of study among Ghanaian Children. Viruses. 2020, 12, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinjé, J. Advances in laboratory methods for detection and typing of norovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.A. Evolution of norovirus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laconi, A.; Cavicchio, L.; Tassoni, L.; Cunial, G.; Milani, A.; Ustulin, M.; Di Martino, G.; Forzan, M.; Campalto, M.; Monne, I.; Beato, M. S. Identification of two divergent swine Noroviruses detected at the slaughterhouse in North East Italy. Por. Health Manag. 2020, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, S.; Alansari, K.; K. Smatti, M.; Zaraket, H.; Al Thani, A.A.; Yassine, H.M. Epidemiological, molecular, and clinical features of norovirus infections among pediatric patients in Qatar. Viruses. 2019, 11, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zheng, L.; Chen, C.; Luo, S.; Guo, P.; Kong, J.; Song, Y.; Huo, Y. Genomic and biological characterization of a pandemic norovirus variant GII. 4 Sydney 2012. Virus genes. 2020, 56, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, G.; Pourshaban, M.; Iaconelli, M.; Muscillo, M. Quantitative real-time PCR of enteric viruses in influent and effluent samples from wastewater treatment plants in Italy. Annalidell’Istitutosuperiore di sanita. 2010, 46, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, T.; Gima, A.; Akiba, M. Detection of Norovirus and Rotavirus present in suspended and dissolved forms in drinking water sources. Food Environ. Virol. 2019, 11, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounts, A.W.; Ando, T.; Koopmans, M.; Bresee, J.S.; Noel, J.; Glass, R.I. Cold weather seasonality of gastroenteritis associated with Norwalk-like viruses. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181 (Supplement_2), S284-S287.–content. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, P., Pintó, R.M., Feng, Z., Cui, F., Gentile, A., Shouval, A. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2023 (in press).
- Pintó, R.M., Pérez-Rodríguez, F.J., Costafreda, M.I., Chavarría-Miró, G., Guix, S., Ribes, E., Bosch, A. Pathogenicity and virulenceof hepatitis A virus. Virulence 2021, 12(1), 1174–1185.
- Rodríguez-Lázaro, D.; Cook, N.; Ruggeri, F.M.; Sellwood, J.; Nasser, A.; Nascimento, M.S.J.; Van der Poel, W.H. Virus hazards from food, water and other contaminated environments. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2012, 36, 786–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, N., Bertrand, I., Gantzer, C., Pintó, R.M., Bosch, A. Persistence of Hepatitis A Virus in Fresh Produce and Production Environments, and the Effect of Disinfection Procedures: A Review. Food Environ. Virol. 2018, 10(3), 253–262. [CrossRef]
- Jothikumar, N.; Cromeans, T.L.; Robertson, B.H.; Meng, X.J.; Hill, V.R. A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. Met. 2006, 131, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N.G.; Revillion, M.; Roque-Afonso, A.M.; Dussaix, E.; Giraud, M.; Liberpre, C.; Astagneau, E.D. A food-borne outbreak of hepatitis A virus (HAV) infection in a secondary school in Upper Normandy, France, in November 2006. Eurosurveillance. 2008, 13, 18885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purpari, G.; Macaluso, G.; Di Bella, S.; Gucciardi, F.; Mira, F.; Di Marco, P.; Guercio, A. Molecular characterization of human enteric viruses in food, water samples, and surface swabs in Sicily. Inter. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 80, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Kishi, T.; Ishihara, A.; Watanabe, D.; Uehira, T.; Ishida, H.; Mita, E. Outbreak of hepatitis A linked to European outbreaks among men who have sex with men in Osaka, Japan, from March to July 2018. Hepa. Res. 2019, 49, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbashir, S.; Parveen, S.; Schwarz, J.; Rippen, T.; Jahncke, M.; DePaola, A. Seafood Pathogens and Information on Antimicrobial Resistance: A review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 70, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Ali, I.A.; Ghazal, H.; Fazili, J.; Nusrat, S. Mystery of Hepatitis E Virus: Recent Advances in Its Diagnosis and Management. Int. J. Hepatol. 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneethan, U.; Al Mohajer, M.; Shata, M.T. Hepatitis E and pregnancy: understanding the pathogenesis. Liver international. 2008, 28, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, Y.E.; Toung, O.P.; Taib, N.M.; Sekawi, Z.B. Hepatitis E Virus: An emerging enigmatic and underestimated pathogen. Saudi J. Biol. Sc. 2022, 29, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, M.A.; Harrison, T.J.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Smith, D.B.; Consortium, I. R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upfold, N.S.; Luke, G.A.; Knox, C. Occurrence of human enteric viruses in water sources and shellfish: A focus on Africa. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.Y.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.K.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; Purdy, M.A.; Teo, C.G. Chronic infection with camelid hepatitis E virus in a liver transplant recipient who regularly consumes camel meat and milk. Gastroenterol. 2016, 150, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Simmonds, P.; International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses Hepeviridae Study Group, Jameel, S.; Emerson, S.U.; Harrison, T.J.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Purdy, M.A. Consensus proposals for classification of the family Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 2223–2232.
- Sander, A.L.; Corman, V.M.; Lukashev, A.N.; Drexler, J.F. Evolutionary origins of enteric hepatitis viruses. Cold Spring HarbPerspect Med. 2018: 1690.
- Badur, S.; Öztürk, S.; Ozakay, A.; Khalaf, M.; Saha, D.; Van Damme, P.A. Review of the Experience of Childhood Hepatitis A Vaccination in Saudi Arabia and Turkey: Implications for hepatitis A Control and Prevention in the Middle East and North African Region. Hum. Vacc. Immuno. 2021, 17, 3710–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, I.; Hanif, A.; Alanazi, I.O.; Al-Ashkar, I.; Alhetheel, A.; Eifan, S. Novel insights of waterborne human rotavirus A in Riyadh (Saudi Arabia) involving G2 predominance and Emergence of a Thermotolerant sequence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.; Qattan, I.; Al-Faleh, F.; Ramia, S. Epidemiology of Hepatitis E virus (HEV) Infection in Saudi Arabia. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1994, 88, 163–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheyami, A. M. Rotavirus gastroenteritis and strain diversity in Saudi Arabia. Current status and future prospects. Saudi Med. J. 2010, 31, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tayeb, H.T.; Dela Cruz, D.M.; Al-Qahtani, A.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; Carter, M.J. Enteric viruses in pediatric diarrhea in Saudi Arabia. J. Med.Virol. 2008, 80, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ayeb, H.T., Al-Ahdal, M.N., Cartear, M.J., Al-Qahtani, A.A., Cruz, D.M. Dela, 2010. Molecular epidemiology of human astrovirus infections in Saudi Arabia pediatric patients. J. Med. Virol. 82, 2038–2042.
- Nour, I.; Hanif, A.; Zakri, A.M.; Al-Ashkar, I.; Alhetheel, A.; Eifan, S. Human adenovirus molecular characterization in various water environments and seasonal impacts in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Inter. J. Environ. Res. Pub. Health. 2021, 18, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, I.; Hanif, A.; Alanazi, F.; Zakri, A.M.; Al-Ashkar, I.; Alhetheel, A.; Eifan, S. Evaluation of three different concentration and extraction methods for recovery efficiency of human adenovirus and human rotavirus virus A. J. Virol. Met. 2021, 295, 114212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; Abid, I.; Al-Otaibi, N.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F.J.; Fuentes, C.; Guix, S.; Pintó, R.M.; Bosch, A.; 2019. Glass Wool Concentration Optimization for the Detection of Enveloped and Non-enveloped Waterborne Viruses. Food Environ. Virol. 2019, 11, 184–192.
- Fuentes, C.; Guix, S.; Pérez-Rodriguez, F.J.; Fuster, N.; Carol, M.; Pintó, R.M.; Bosch, A. Standardized Multiplex one-step qRT-PCR for Hepatitis A virus, Norovirus GI and GII Quantification in bivalve Mollusks and Water. Food Microbiol. 2014, 40, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costafreda, M.I.; Bosch, A.; Pintó, R. M. (2006). Development, evaluation, and standardization of a real-time TaqMan Reverse Transcription-PCR Assay for Quantification of Hepatitis A Virus in Clinical and Shellfish Samples. App.Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3846–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A. K.; Le Saux, J.C.; Parnaudeau, S.; Pommepuy, M.; Elimelech, M.; Le Guyader, F.S. (2007). Evaluation of Removal of Noroviruses during Wastewater Treatment, Using Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR: Different Behaviors of Genogroups I and II. App. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7891–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loisy, F.; Atmar, R.L.; Guillon, P.; Le Cann, P.; Pommepuy, M.; Le Guyader, F.S. Real-time RT-PCR for Norovirus screening in Shellfish. J. Virol. Met. 2005, 123, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, R.M.; Costafreda, M.I.; Bosch, A. Risk assessment in shellfish-borne outbreaks of hepatitis A. App. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7350–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, S.; Makhzoumi, J.; Grose, M. Landscape practice in the Middle East between local and global aspirations. Land. Res. 2016, 41, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamid, A.A.; Alfayzi, S.A.; Hamadto, M.A. A Sustainable Water Resources Management Plan for Wadi Hanifa in Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Uni. 2007, 19, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dossary, R.A.; Alnafie, A.N.; Aljaroodi, S.A.; Rahman, J.U.; Hunasemarada, B.C.; Alkharsah, K.R. Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus Infection Among Blood Donors in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. J. Multi. Health. 2021, 27, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Hassan, A.M.; El-Daly, M.M.; Qadri, I.; Tolah, A.M.; Al-Subhi, T.L.; Alzahrani, A.A.; Alsaaidi, G.A.; Al-Abdullah, N.; Kaki, R.M.; Li, T.C.; Azhar, E.I. Seroprevalence of Dromedary Camel HEV in Domestic and Imported Camels from Saudi Arabia. Viruses. 2020, 12, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, A.K.; Joseph, M.; Wong, E.Y.; Tang, Y.; Sivakumar, S.; Xie, J.; Bai, R.; Wernery, R.; Wernery, U.; Yuen, K.Y. New hepatitis E virus genotype in camels, the Middle East. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kafrawy, S.A.; Hassan, A.M.; El-Daly, M M.; Al-Hajri, M.; Farag, E.; Elnour, F.A.; Khan A.; Tolah, A.M.; Alandijany, T.A.; Othman, N.A.; Memish, Z.A.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C.; Zumla, A.; Azhar, E.I. Genetic Diversity of Hepatitis E virus (HEV) in Imported and Domestic Camels in Saudi Arabia. Sc. Rep. 2022, 12, 7005.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).