Submitted:
30 September 2023
Posted:
02 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
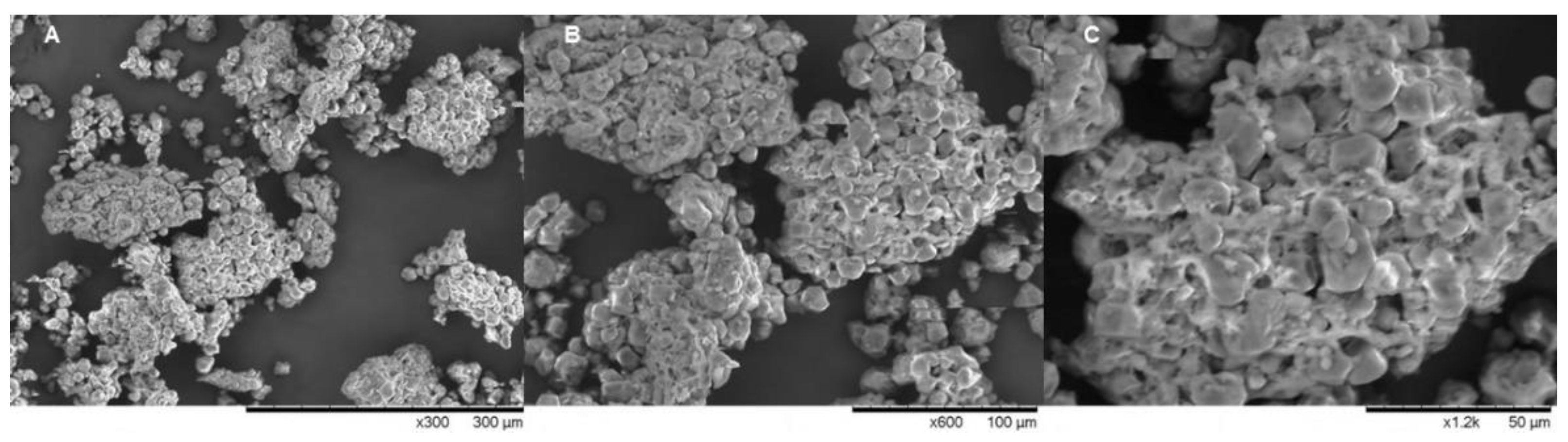
2.1. Product Obtention and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.2. Phytochemical Analysis
2.2.1. Anthocyanins
- A
- = (A 520nm -A700nm) pH1.0 - (A520nm - A700nm) pH 4.5;
- A
- ε = cyanidin-3-O-glucoside extinction coefficient;
- A
- MM = cyanidin-3-O-glucoside molecular mass;
- A
- DF = dilution factor;
- V
- = solution volume;
- m
- = mass of the extract.
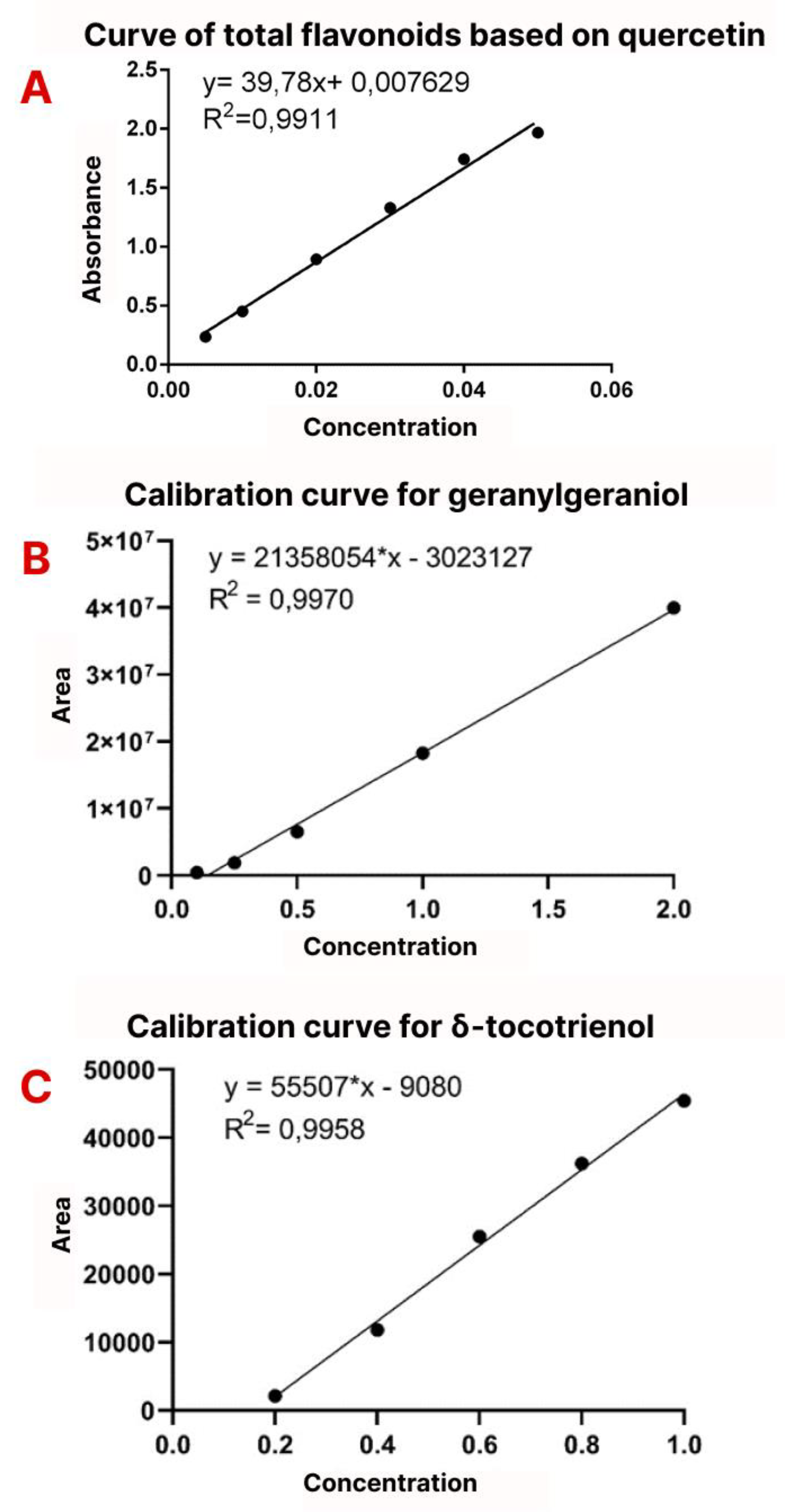
2.2.2. Total Flavonoids
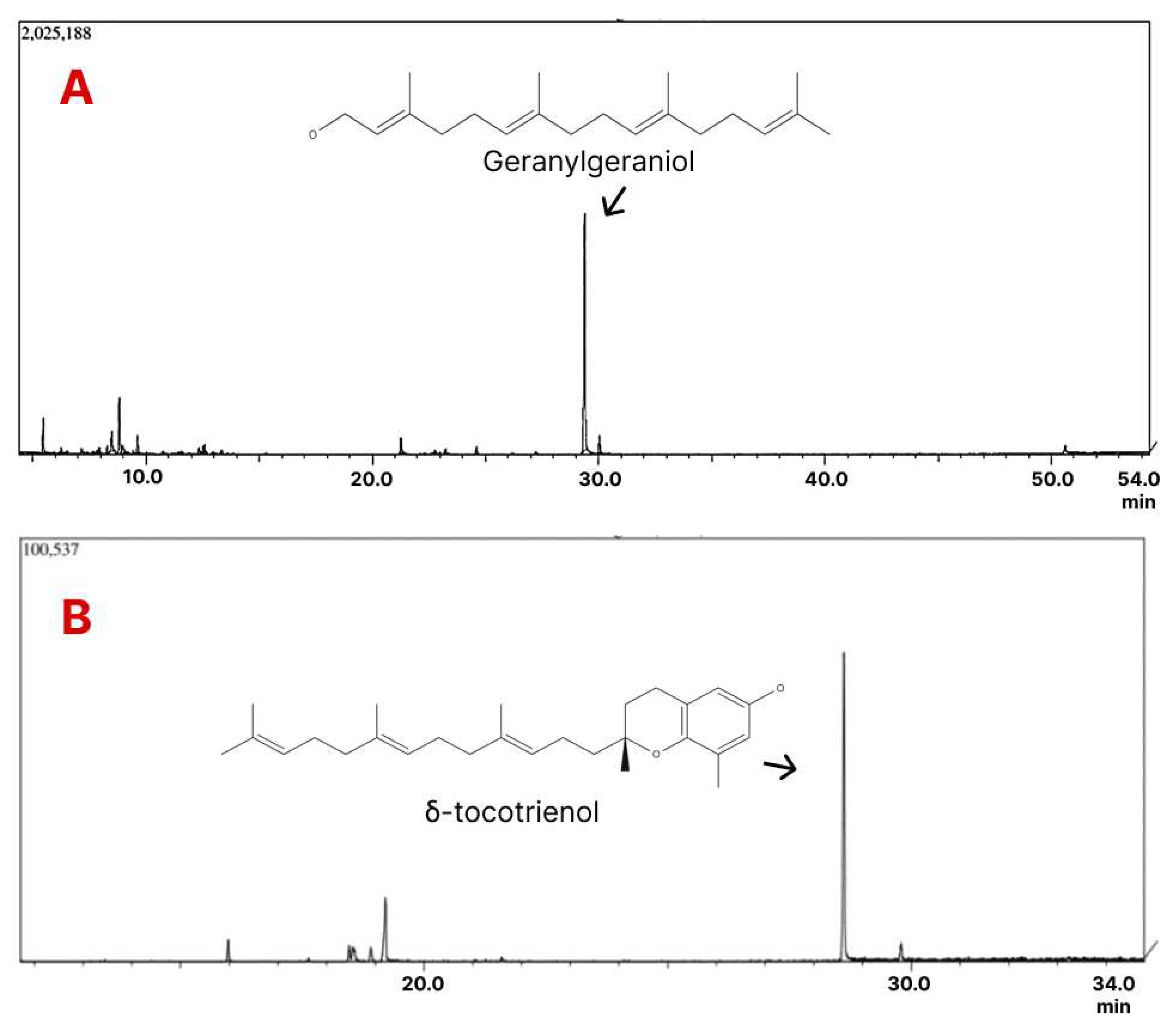
2.2.3. Geranylgeraniol
2.2.4. Δ-tocotrienol
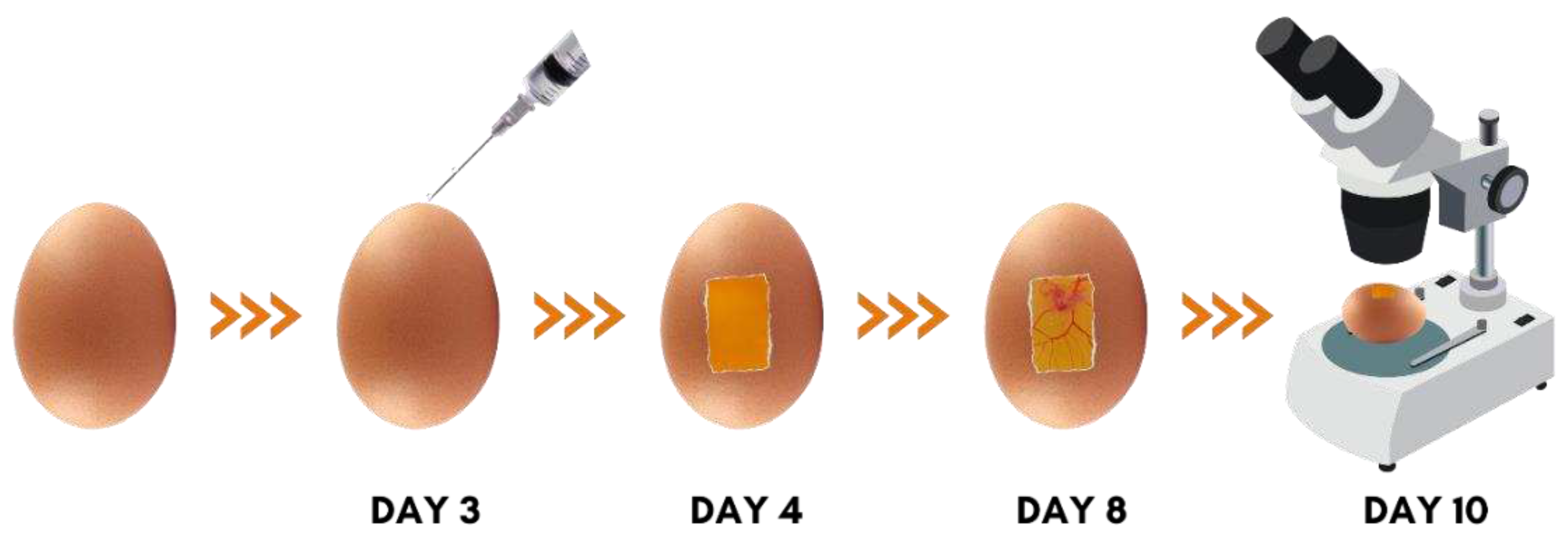
2.3. In Vivo Anti-Angiogenic CAM Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Granules Analysis
3.2. Phytochemical Analysis
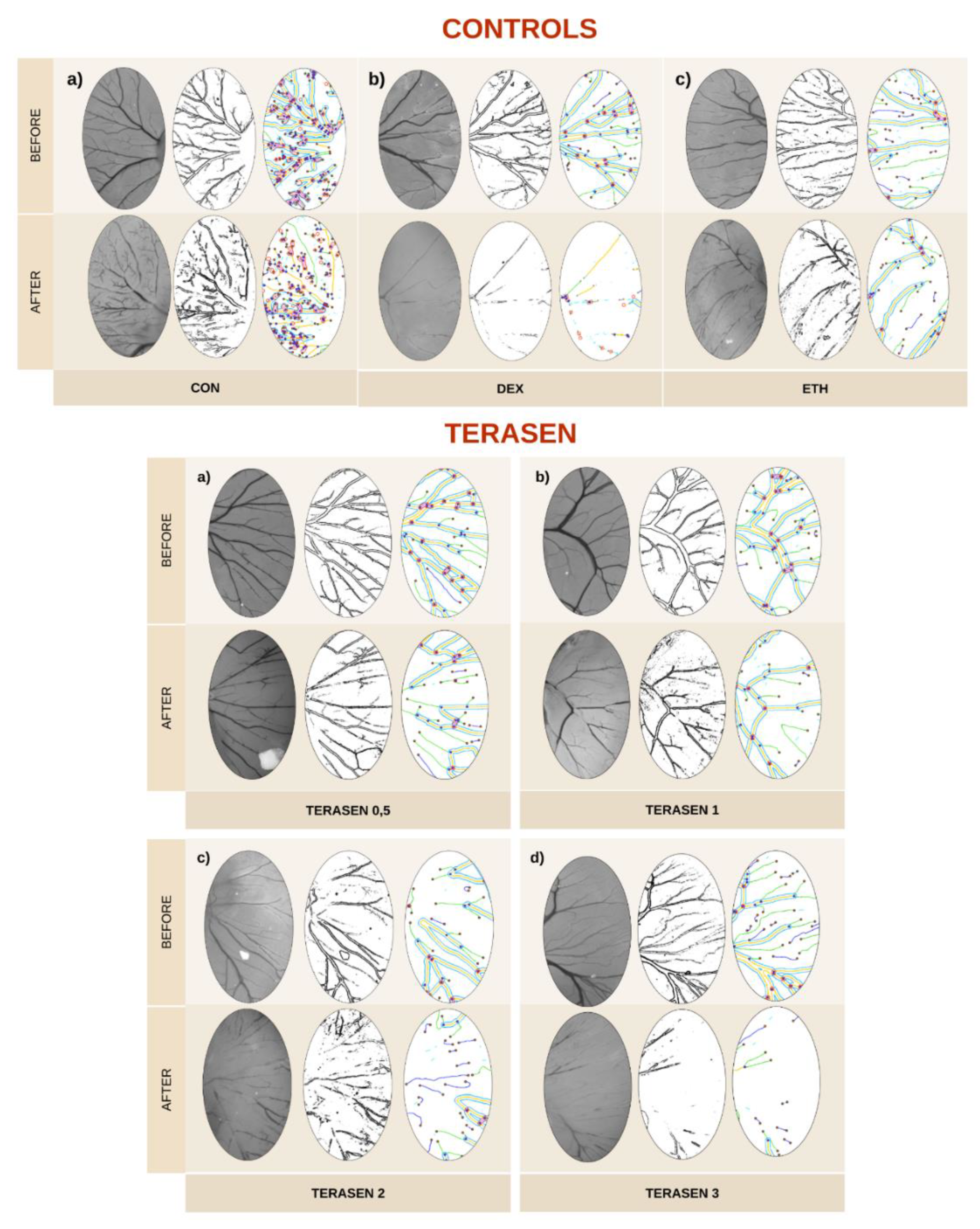
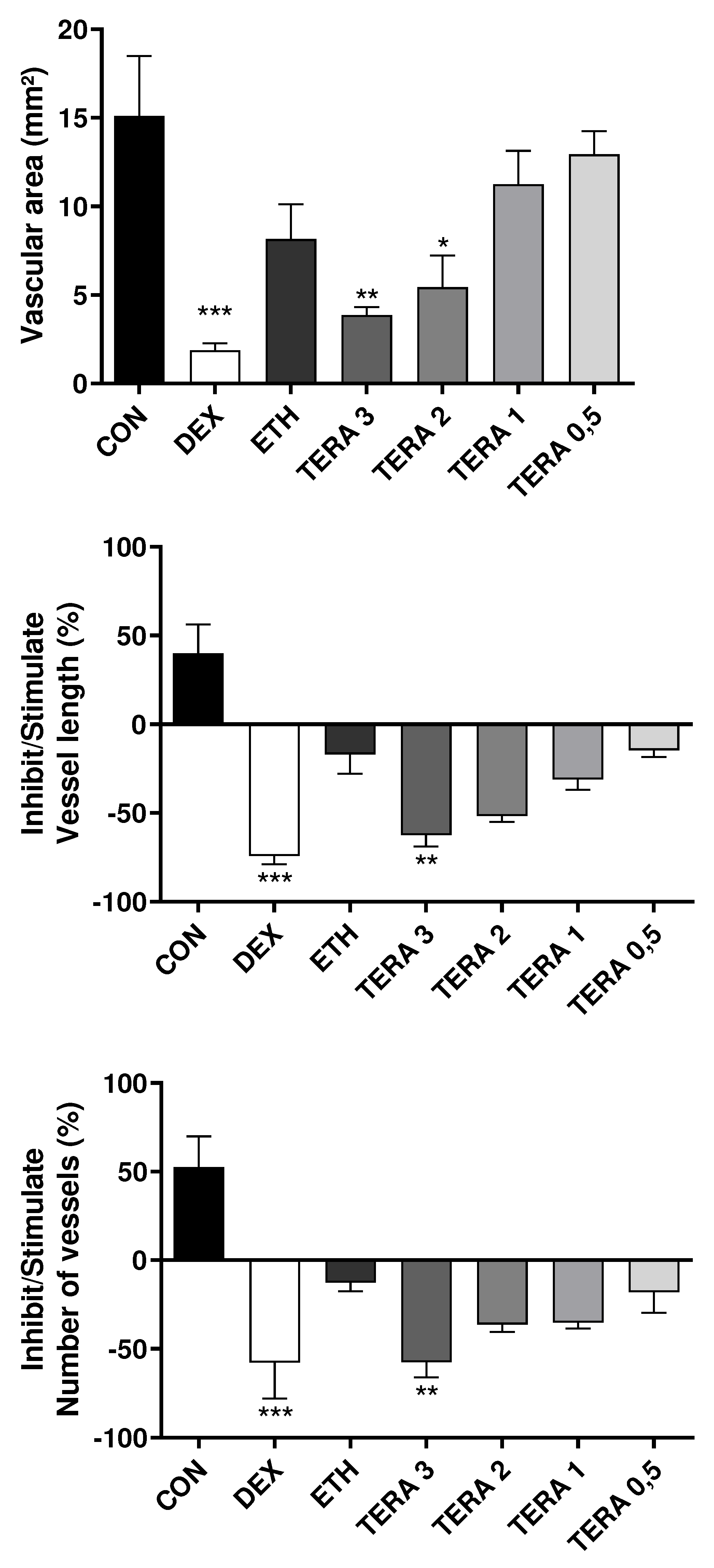
3.3. Effect of Terasen® on Angiogenesis
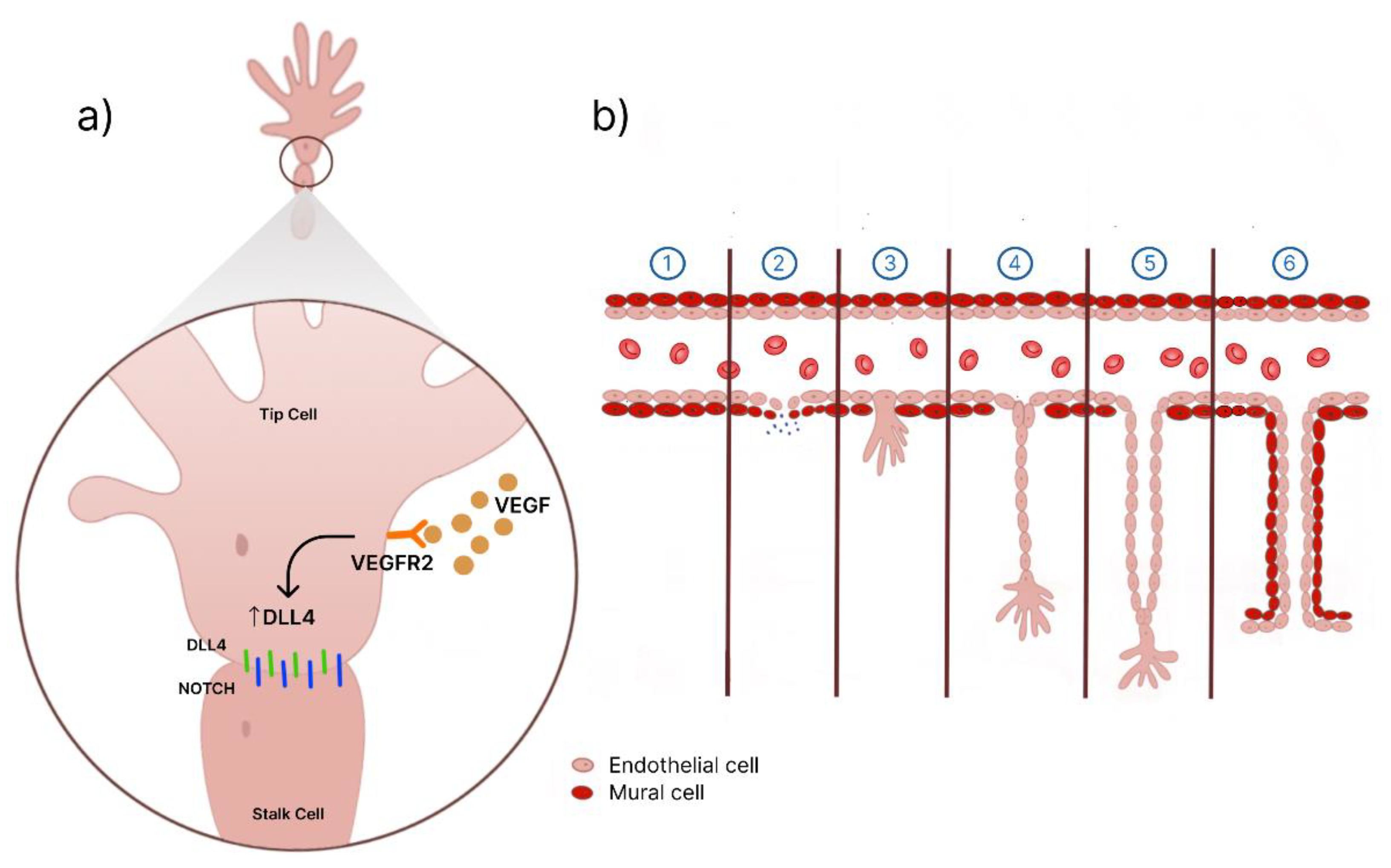
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, X.; Cui, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, Q.; Song, H.; Wang, R. Endogenous Opioid Peptides, Endomorphin-1 and -2 and Deltorphin I, Stimulate Angiogenesis in the CAM Assay. Eur J Pharmacol 2008, 579, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, A.; Belinha, J.; Mangir, N.; MacNeil, S.; Natal Jorge, R. Simulation of the Process of Angiogenesis: Quantification and Assessment of Vascular Patterning in the Chicken Chorioallantoic Membrane. Comput Biol Med 2021, 136, 104647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L. Sequential Delivery of VEGF, FGF-2 and PDGF from the Polymeric System Enhance HUVECs Angiogenesis in Vitro and CAM Angiogenesis. Cell Immunol 2018, 323, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Deng, R. Angiogenesis as a Potential Treatment Strategy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol 2021, 910, 174500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatne, D.P.; Mungekar, S.; Addepalli, V.; Mohanraj, K.; Ghone, S.A.; Rege, N.N. Development of Collateral Vessels: A New Paradigm in CAM Angiogenesis Model. Microvasc Res 2016, 103, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D. Two New Applications in the Study of Angiogenesis the CAM Assay: Acellular Scaffolds and Organoids. Microvasc Res 2022, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watchararot, T.; Prasongchean, W.; Thongnuek, P. Angiogenic Property of Silk Fibroin Scaffolds with Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane. R Soc Open Sci 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulla, S.; Reddy, V.C.; Araveti, P.B.; Lomada, D.; Srivastava, A.; Reddy, M.C.; Reddy, K.R. Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes (TNT) Conjugated with Quercetin and Its in Vivo Antitumor Activity against Skin Cancer. J Mol Struct 2022, 1249, 131556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Shibata, A.; Yamashita, S.; Tsuzuki, T.; Kariya, J.; Oikawa, S.; Miyazawa, T. In Vivo Angiogenesis Is Suppressed by Unsaturated Vitamin E, Tocotrienol. J Nutr 2007, 137, 1938–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Kim, O.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.A.; Kim, M.R.; Choi, H.S.; Shim, J.H.; Kang, K.W.; Kim, Y.C. Inhibition of Angiogenesis by Quercetin in Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Food Chem Toxicol 2010, 48, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siveen, K.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Ong, T.H.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Li, F.; Yap, W.N.; Kumar, A.P.; Fong, C.W.; Tergaonkar, V.; Hui, K.M.; et al. Y-Tocotrienol Inhibits Angiogenesis-Dependent Growth of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Abrogation of AKT/MTOR Pathway in an Orthotopic Mouse Model. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeriglio, A.; Denaro, M.; Barreca, D.; D’Angelo, V.; Germanò, M.P.; Trombetta, D. Polyphenolic Profile and Biological Activities of Black Carrot Crude Extract (Daucus Carota L. Ssp. Sativus Var. Atrorubens Alef.). Fitoterapia 2018, 124, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.S.; Stoner, G.D. Anthocyanins and Their Role in Cancer Prevention. Cancer Lett 2008, 269, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, R.; Bezerra, I.; Ferreira, M.; Soares, L. Spectrophotometric Quantification of Flavonoids in Herbal Material, Crude Extract, and Fractions from Leaves of Eugenia Uniflora Linn. Pharmacognosy Res 2017, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, D.C.; Thompson, W.D.; Sells, P.G.; Burbridge, M.F. Angiogenesis Assays Using Chick Chorioallantoic Membrane. Angiogenesis Protocols 2001, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias Pereira, A.C.; de Oliveira Carvalho, H.; Gonçalves, D.E.S.; Picanço, K.R.T.; de Lima Teixeira dos Santos, A.V.T.; da Silva, H.R.; Braga, F.S.; Bezerra, R.M.; de Sousa Nunes, A.; Nazima, M.T.S.T.; et al. Co-treatment of Purified Annatto Oil (Bixa Orellana l.) and Its Granules (Chronic®) Improves the Blood Lipid Profile and Bone Protective Effects of Testosterone in the Orchiectomy-induced Osteoporosis in Wistar Rats. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, M. de M. Fisiologia; 5. ed.; Guanabara Koogan: Rio de Janeiro, 2018.
- Šalandová, M.; Hengel, I.A.J.; Apachitei, I.; Zadpoor, A.A.; Eerden, B.C.J.; Fratila-Apachitei, L.E. Inorganic Agents for Enhanced Angiogenesis of Orthopedic Biomaterials. Adv Healthc Mater 2021, 10, 2002254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, D.E. Princípios de Farmacologia - A Base Fisiopatológica Da Farmacoterapia ; 2. ed.; Guanabara Koogan, 2009.
- Cha, S.; Kim, H.-G.; Jang, H.; Lee, J.; Chao, T.; Baek, N.-I.; Song, I.-S.; Lee, Y.M. Steppogenin Suppresses Tumor Growth and Sprouting Angiogenesis through Inhibition of HIF-1α in Tumors and DLL4 Activity in the Endothelium. Phytomedicine 2023, 108, 154513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Xie, W.; Wang, L.; Jin, X.; Meng, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Notoginsenoside R1 Activates the NAMPT-NAD+-SIRT1 Cascade to Promote Postischemic Angiogenesis by Modulating Notch Signaling. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 140, 111693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, V.; Valenta, C.; Matsko, N.B. Electron Microscopy of Pharmaceutical Systems. Micron 2013, 44, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, K.; Lenart, A. Surface Modification of Dairy Powders: Effects of Fluid-Bed Agglomeration and Coating. Int Dairy J 2013, 33, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Scharf, D.; Graule, T.; Clemens, F.J. Granulation Processing Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of Diatomite-Based Porous Granulates. Powder Technol 2014, 263, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharb, V.; Saharan, V.A.; Kharb, V.; Jadhav, H.; Purohit, S. Formulation and Evaluation of Lipid Based Taste Masked Granules of Ondansetron HCl. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2014, 62, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bot, F.; Cossuta, D.; O’Mahony, J.A. Inter-Relationships between Composition, Physicochemical Properties and Functionality of Lecithin Ingredients. Trends Food Sci Technol 2021, 111, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nieuwenhuyzen, W.; Tomás, M.C. Update on Vegetable Lecithin and Phospholipid Technologies. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2008, 110, 472–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueschelberger, H.-G. Lecithins. Emulsifiers in Food Technology 2007, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Luo, X.; Deng, Y. A Review on Phospholipids and Their Main Applications in Drug Delivery Systems. Asian J Pharm Sci 2015, 10, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, C.R.; Oliveira, M. do S.P. de; Chisté, R.C.; Carvalho, A.V. Compostos Bioativos e Potencial Antioxidante de Diferentes Acessos de Euterpe Oleracea e Euterpe Precatoria Do Banco Ativo de Germoplasma de Açaí. Research, Society and Development 2022, 11, e428111234824. [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Azevedo, D.; Barata, P.; Soares, R.; Guido, L.F.; Carvalho, D.O. Antiangiogenic and Antioxidant In Vitro Properties of Hydroethanolic Extract from Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea) Dietary Powder Supplement. Molecules 2021, 26, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Xie, C.; Li, Z.; Nagarajan, S.; Schauss, A.G.; Wu, T.; Wu, X. Flavonoids from Acai (Euterpe Oleracea Mart.) Pulp and Their Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Food Chem 2011, 128, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidelis, M.; Santos, J.S.; Escher, G.B.; Vieira do Carmo, M.; Azevedo, L.; Cristina da Silva, M.; Putnik, P.; Granato, D. In Vitro Antioxidant and Antihypertensive Compounds from Camu-Camu (Myrciaria Dubia McVaugh, Myrtaceae) Seed Coat: A Multivariate Structure-Activity Study. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2018, 120, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, A.; Oliveira, T.; Mattietto, R.; Nascimento, W.; Lopes, A. Bioactive Compounds in the Peel of Camu Camu Genotypes from Embrapa’s Active Germplasm Bank. Food Science and Technology (Brazil) 2018, 38, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frega, N.; Mozzon, M.; Bocci, F. Identification and Estimation of Tocotrienols in the Annatto Lipid Fraction by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. JAOCS, Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society 1998, 75, 1723–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.K.; Silva, C.B.; Lordello, A.L.L.; Zanin, S.M.W.; Dias, J.F.G.; Miguel, M.D.; Miguel, O.G. Identificação de δ Tocotrienol e de Ácidos Graxos No Óleo Fixo de Urucum (Bixa Orellana Linné). Revista Brasileira de Plantas Medicinais 2013, 15, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Carvalho, H.; Sauma, A.L.R.; do Nascimento, A.L.; de Lima Teixeira, A.V.T.; Gonçalves, D.E.S.; Gomes, L.; da Costa Furtado, G.; da Silva, H.R.; de Souza, G.C.; Pereira, A.C.M.; et al. Intramuscular Compatibility of an Injectable Anti-Inflammatory Nanodispersion from a Standardized Bixa Orellana Oil (Chronic®): A Toxicological Study in Wistar Rats. Inflammopharmacology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanega, R.; Nogueira, G.C.; Nascimento, C.D.O.; Faria-Machado, A.F.; Meireles, M.A.A. Selective Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Annatto Seeds by Sequential Supercritical CO2 Process. J Supercrit Fluids 2019, 150, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Rui, L.; Wilson, R.S.; Wu, X.; Liu, X. An Improved In Vivo Angiogenesis Model of Chicken Chorioallantoic Membranes in Surrogate Shells Revealed the Pro-Angiogenesis Effects of Chylomicrons. Vasc Cell 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, D.H.; Hosoya, T.; Kumazawa, S.; Jun, M.; Kim, O.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Ahn, M.R. In Vitro and In Vivo Antiangiogenic Activity of Crowberry (Empetrum Nigrum Var. Japonicum). 2016, 11, 503–506. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, H.; Wu, K.; Zheng, X.; Cai, Y.; Katakowski, M.; Chopp, M.; To, S.-S.T. Gallic Acid Suppresses Cell Viability, Proliferation, Invasion and Angiogenesis in Human Glioma Cells. Eur J Pharmacol 2010, 641, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Tao, Y.; Tao, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Shi, Z.; Tao, H. Gallic Acid Induces the Apoptosis of Human Osteosarcoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo via the Regulation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2012, 27, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrecque, L.; Lamy, S.; Chapus, A.; Mihoubi, S.; Durocher, Y.; Cass, B.; Bojanowski, M.W.; Gingras, D.; Béliveau, R. Combined Inhibition of PDGF and VEGF Receptors by Ellagic Acid, a Dietary-Derived Phenolic Compound. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fikry, E.M.; Gad, A.M.; Eid, A.H.; Arab, H.H. Caffeic Acid and Ellagic Acid Ameliorate Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis in Rats via Targeting Inflammatory Signals, Chitinase-3-like Protein-1 and Angiogenesis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 110, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metibemu, D.S.; Akinloye, O.A.; Akamo, A.J.; Okoye, J.O.; Ojo, D.A.; Morifi, E.; Omotuyi, I.O. VEGFR-2 Kinase Domain Inhibition as a Scaffold for Anti-Angiogenesis: Validation of the Anti-Angiogenic Effects of Carotenoids from Spondias Mombin in DMBA Model of Breast Carcinoma in Wistar Rats. Toxicol Rep 2021, 8, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbidelli, L. Polyphenol-Based Nutraceuticals for the Control of Angiogenesis: Analysis of the Critical Issues for Human Use. Pharmacol Res 2016, 111, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Kim, O.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.-A.; Kim, M.R.; Choi, H.S.; Shim, J.-H.; Kang, K.W.; Kim, Y.C. Inhibition of Angiogenesis by Quercetin in Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2010, 48, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulla, S.; Reddy, V.C.; Araveti, P.B.; Lomada, D.; Srivastava, A.; Reddy, M.C.; Reddy, K.R. Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes (TNT) Conjugated with Quercetin and Its in Vivo Antitumor Activity against Skin Cancer. J Mol Struct 2022, 1249, 131556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siveen, K.S.; Ahn, K.S.; Ong, T.H.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Li, F.; Yap, W.N.; Kumar, A.P.; Fong, C.W.; Tergaonkar, V.; Hui, K.M.; et al. γ-Tocotrienol Inhibits Angiogenesis-Dependent Growth of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Abrogation of AKT/MTOR Pathway in an Orthotopic Mouse Model. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Shibata, A.; Yamashita, S.; Tsuzuki, T.; Kariya, J.; Oikawa, S.; Miyazawa, T. In Vivo Angiogenesis Is Suppressed by Unsaturated Vitamin E, Tocotrienol. J Nutr 2007, 137, 1938–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.A.; de Lima Teixeira dos Santos, A.V.T.; do Nascimento, A.L.; Moreira, L.F.; Souza, I.R.S.; da Silva, H.R.; Pereira, A.C.M.; da Silva Hage-Melim, L.I.; Carvalho, J.C.T. Potential of the Compounds from Bixa Orellana Purified Annatto Oil and Its Granules (Chronic®) against Dyslipidemia and Inflammatory Diseases: In Silico Studies with Geranylgeraniol and Tocotrienols. Molecules 2022, 27, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




