Submitted:
29 September 2023
Posted:
30 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Governing equations
2. Modeling
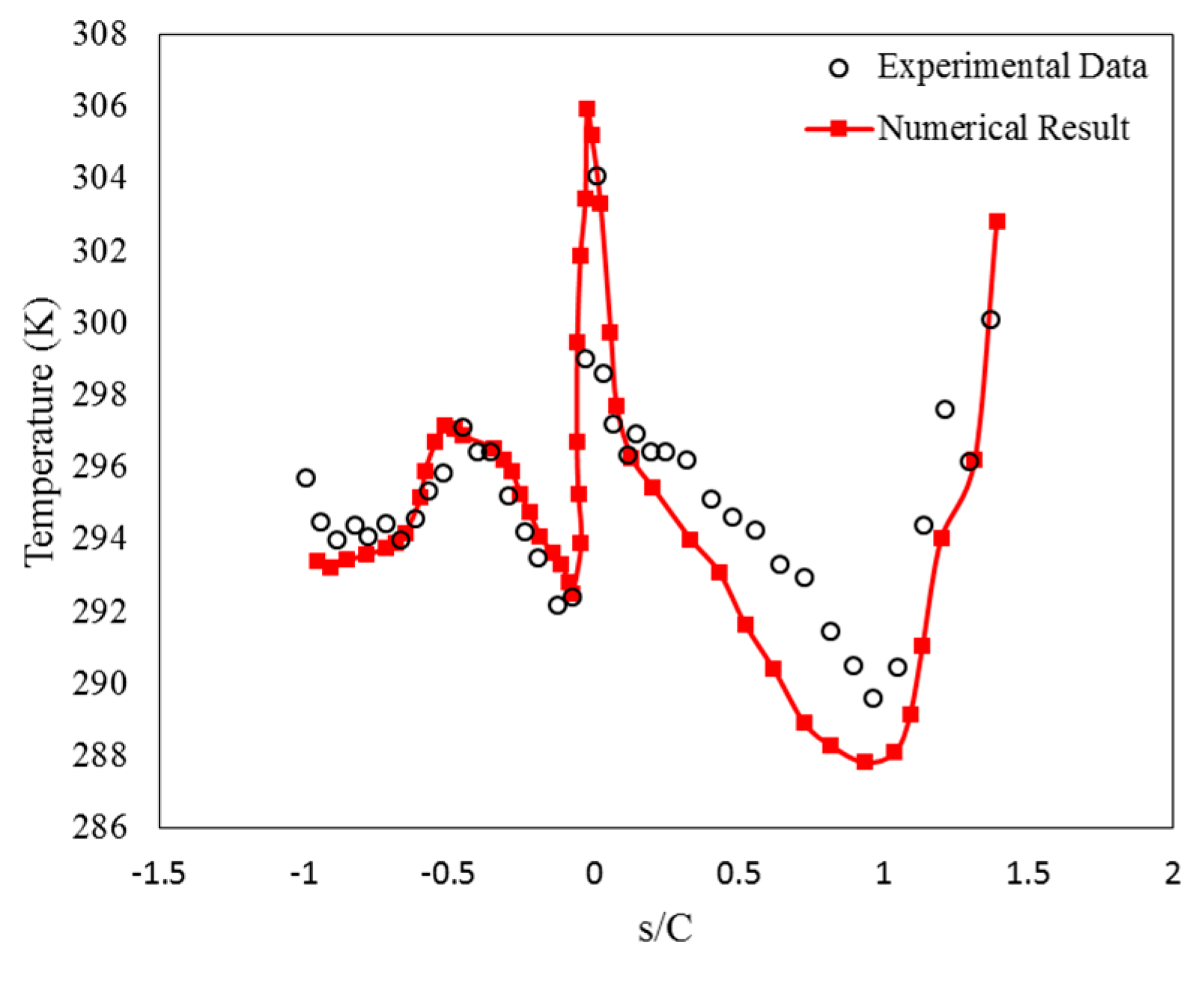
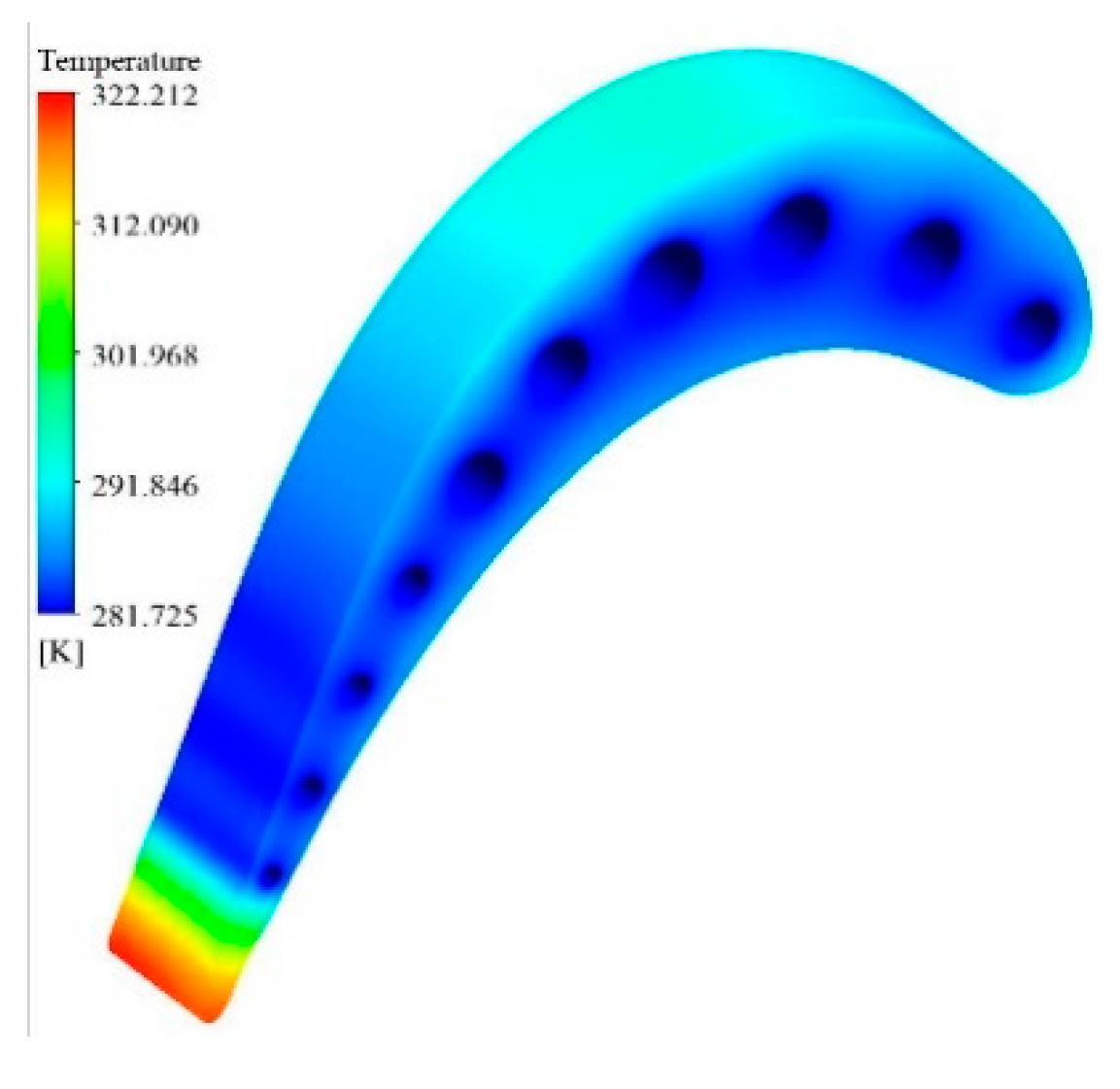
3. Validation
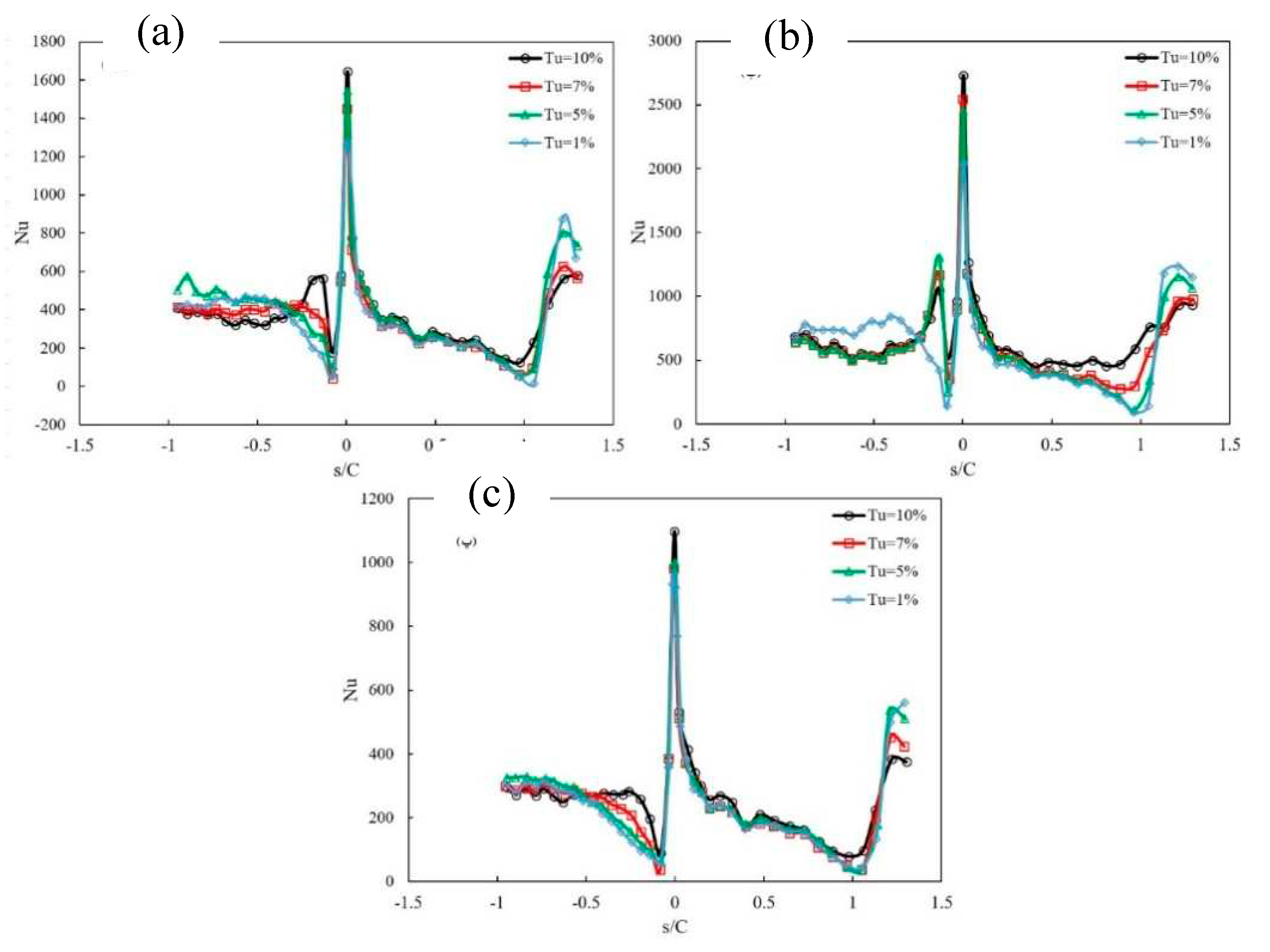
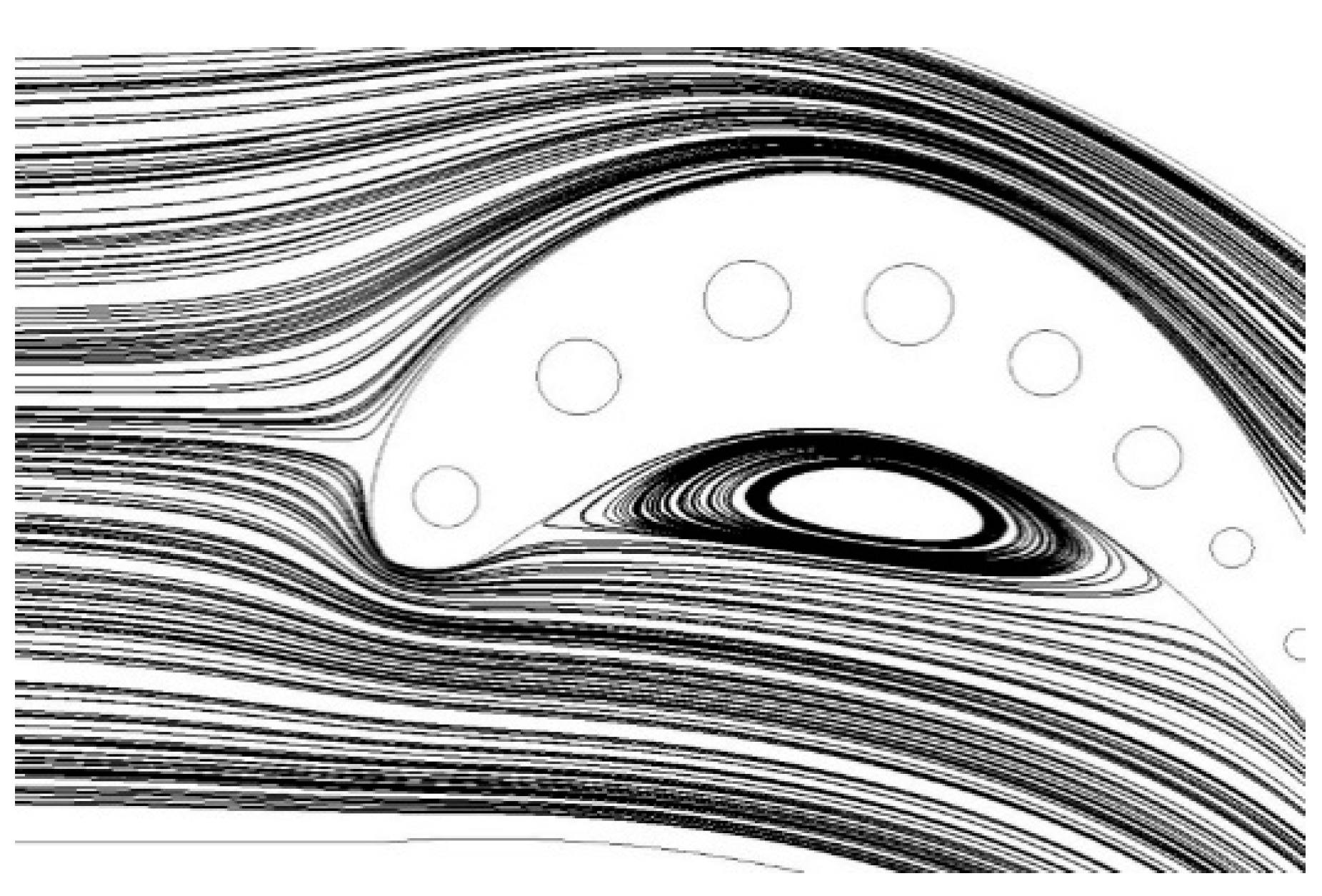
4. Investigation of Reynolds effect and turbulence intensity
5. Conclusion
- Increasing the intensity of turbulence improves the transition conditions and makes it happen faster and increases the turbulent area.
- The increased turbulence intensity has delayed the flow separation near the leading edge.
- The increase in turbulence intensity disturbs the calm boundary layer region and thus increases the heat transfer coefficients.
References
- S. A. Self and J. H. Whitelaw, “Laser Anemometry for Combustion Research,” Combust. Sci. Technol., vol. 13, no. 1–6, pp. 171–197, Oct. 1976. [CrossRef]
- G. J. Van Fossen and R. S. Bunker, “Augmentation of Stagnation Region Heat Transfer Due to Turbulence From a DLN Can Combustor,” J. Turbomach., vol. 123, no. 1, pp. 140–146, Jan. 2001. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Hosseini and A. Keshmiri, “Experimental and numerical investigation of different geometrical parameters in a centrifugal blood pump,” Res. Biomed. Eng., vol. 38, no. 5, pp. 423–437, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Shojaeefard, S. E. Hosseini, and J. Zare, “Numerical simulation and multi-objective optimization of the centrifugal pump inducer,” Modares Mech. Eng., vol. 17, no. 7, pp. 205–216, 2018.
- H. Consigny and B. E. Richards, “Short Duration Measurements of Heat-Transfer Rate to a Gas Turbine Rotor Blade,” J. Eng. Power, vol. 104, no. 3, pp. 542–550, Jul. 1982. [CrossRef]
- T. Arts, J. M. Duboue, and G. Rollin, “Aerothermal Performance Measurements and Analysis of a Two-Dimensional High Turning Rotor Blade,” J. Turbomach., vol. 120, no. 3, pp. 494–499, Jul. 1998. [CrossRef]
- P. W. Giel, R. J. Boyle, and R. S. Bunker, “Measurements and Predictions of Heat Transfer on Rotor Blades in a Transonic Turbine Cascade,” Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. Int. Gas Turbine Institute, Turbo Expo IGTI, vol. 5 A, pp. 623–638, Feb. 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Blair, “Influence of Free-Stream Turbulence on Turbulent Boundary Layer Heat Transfer and Mean Profile Development, Part I—Experimental Data,” J. Heat Transfer, vol. 105, no. 1, pp. 33–40, Feb. 1983. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Shojaeefard, S. E. Hosseini, and J. Zare, “CFD simulation and Pareto-based multi-objective shape optimization of the centrifugal pump inducer applying GMDH neural network, modified NSGA-II, and TOPSIS,” Struct. Multidiscip. Optim., vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 1509–1525, 19. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- W. K. Anderson and D. L. Bonhaus, “An implicit upwind algorithm for computing turbulent flows on unstructured grids,” Comput. Fluids, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 1–21, Jan. 1994. [CrossRef]
- F. BONETTO, J. L. LEBOWITZ, and L. REY-BELLET, “FOURIER’S LAW: A CHALLENGE TO THEORISTS,” Math. Phys. 2000, pp. 128–150, May 2000. [CrossRef]
- J. Zare, S. E. Hosseini, and M. R. Rastan, “Airborne dust-induced performance degradation in NREL phase VI wind turbine: a numerical study,” Int. J. Green Energy, pp. 1–20, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Zare, S. E. Hosseini, and M. R. Rastan, “NREL Phase VI wind turbine in the dusty environment,” arXiv Prepr. arXiv2304.06285, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Hosseini, O. Karimi, and M. A. AsemanBakhsh, “Multi-objective Optimization of Savonius Wind Turbine,” arXiv:2308.14648, Aug. 2023. arXiv:2308.14648, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- O. Karimi, M. K. Koopaee, A. reza Tavakolpour-Saleh, and S. E. Hosseini, “Investigating Overlap Ratio Effect on Performance of a Modified Savonius Wind Turbine: An Experimental Study,” Preprints, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. E. Hosseini, O. Karimi, and M. A. AsemanBakhsh, “Experimental Investigation and Multi-objective Optimization of Savonius Wind Turbine Based on modified Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II,” Preprints, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- F. Duchaine, N. Maheu, V. Moureau, G. Balarac, and S. Moreau, “Large-Eddy simulation and conjugate heat transfer around a low-mach turbine blade,” J. Turbomach., vol. 136, no. 5, Oct. 2013. [CrossRef]
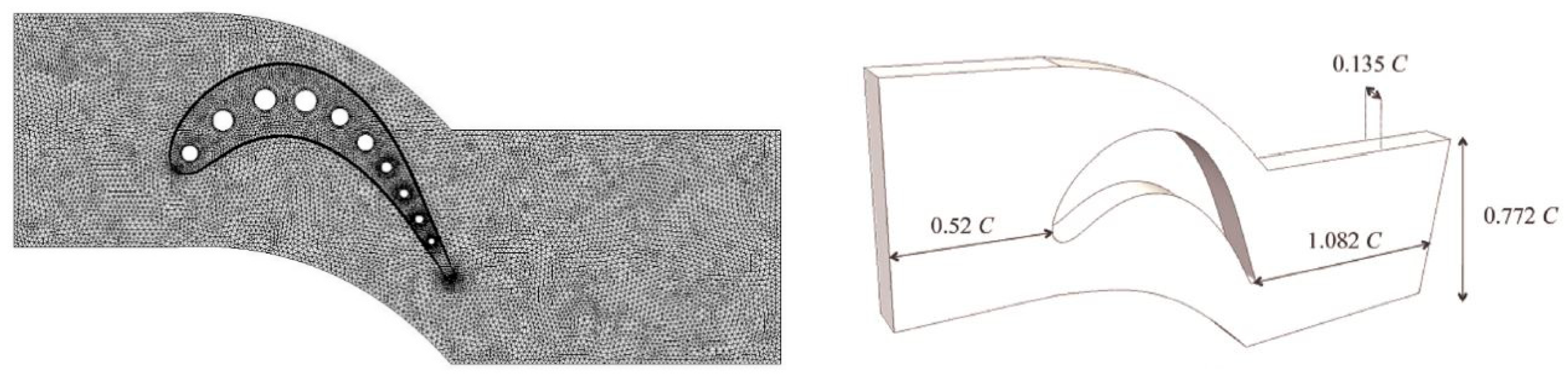
| Cord length | 73.9 mm |
| Axial cord length | 67 mm |
| blade height | 100 mm |
| Cord/blade spacing | 0.772 |
| inlet angle | 127° |
| Vane installation angle | 63.5° |
| Inlet Mach number | 0.068 |
| Outlet Mach number | 0.116 |
| Reynolds input | 93101 |
| Reynolds output | 158088 |
| total inlet pressure | 102274.8 Pa |
| Total inlet temperature | 348.06 K |
| Outlet static pressure | 101315.9 Pa |
| Cord length | 73.9 mm |
| Axial cord length | 67 mm |
| blade height | 100 mm |
| Cord/blade spacing | 0.772 |
| inlet angle | 127° |
| Vane installation angle | 63.5° |
| Inlet Mach number | 0.068 |
| Outlet Mach number | 0.116 |
| Reynolds input | 93101 |
| Reynolds output | 158088 |
| total inlet pressure | 102274.8 Pa |
| Total inlet temperature | 348.06 K |
| Outlet static pressure | 101315.9 Pa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




