Submitted:
28 September 2023
Posted:
30 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature review on dynamic energy losses of buildings
3. Research hypothesis
3.1. Research gap identification
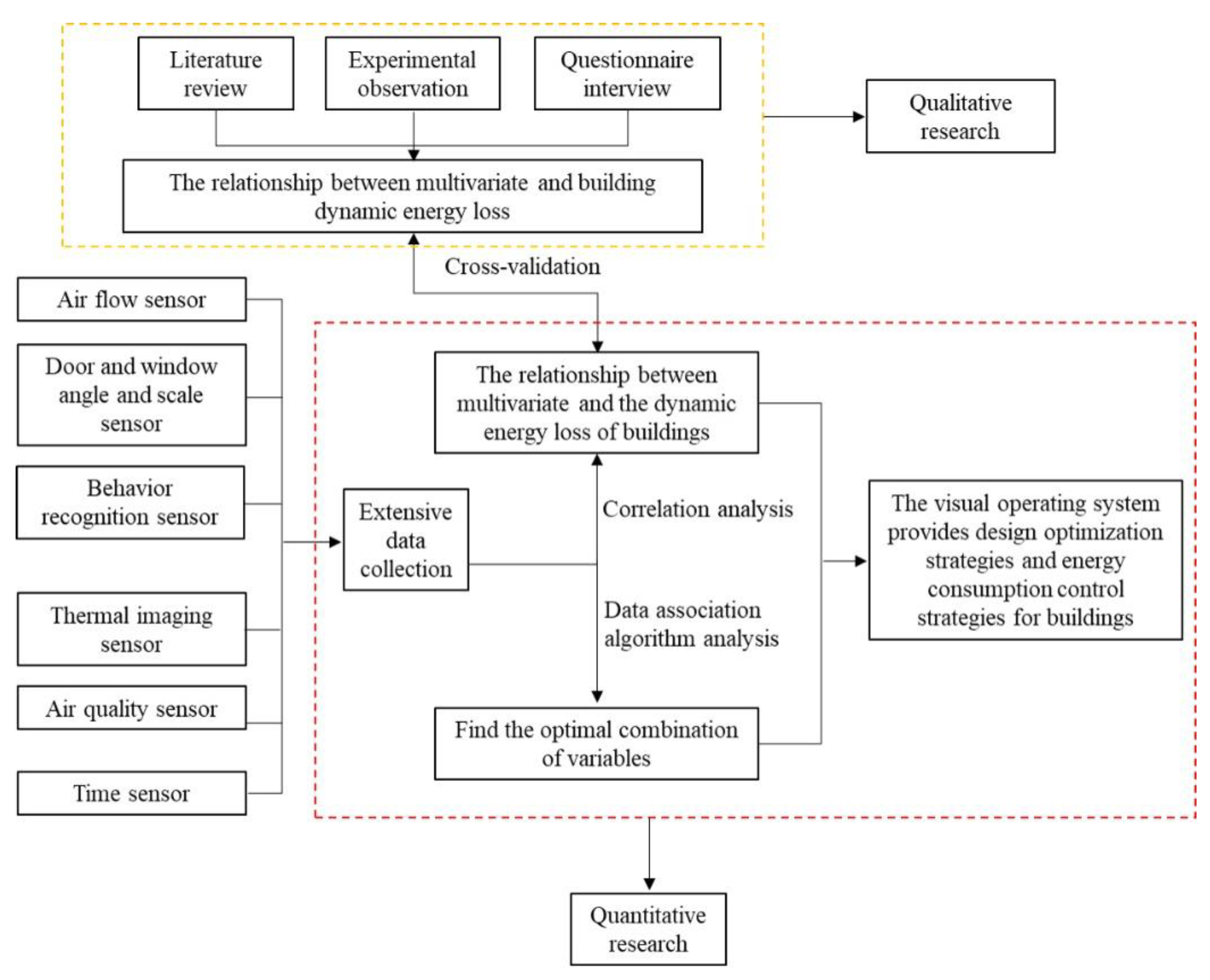
3.2. Technical support and workflow of the dynamic monitoring system
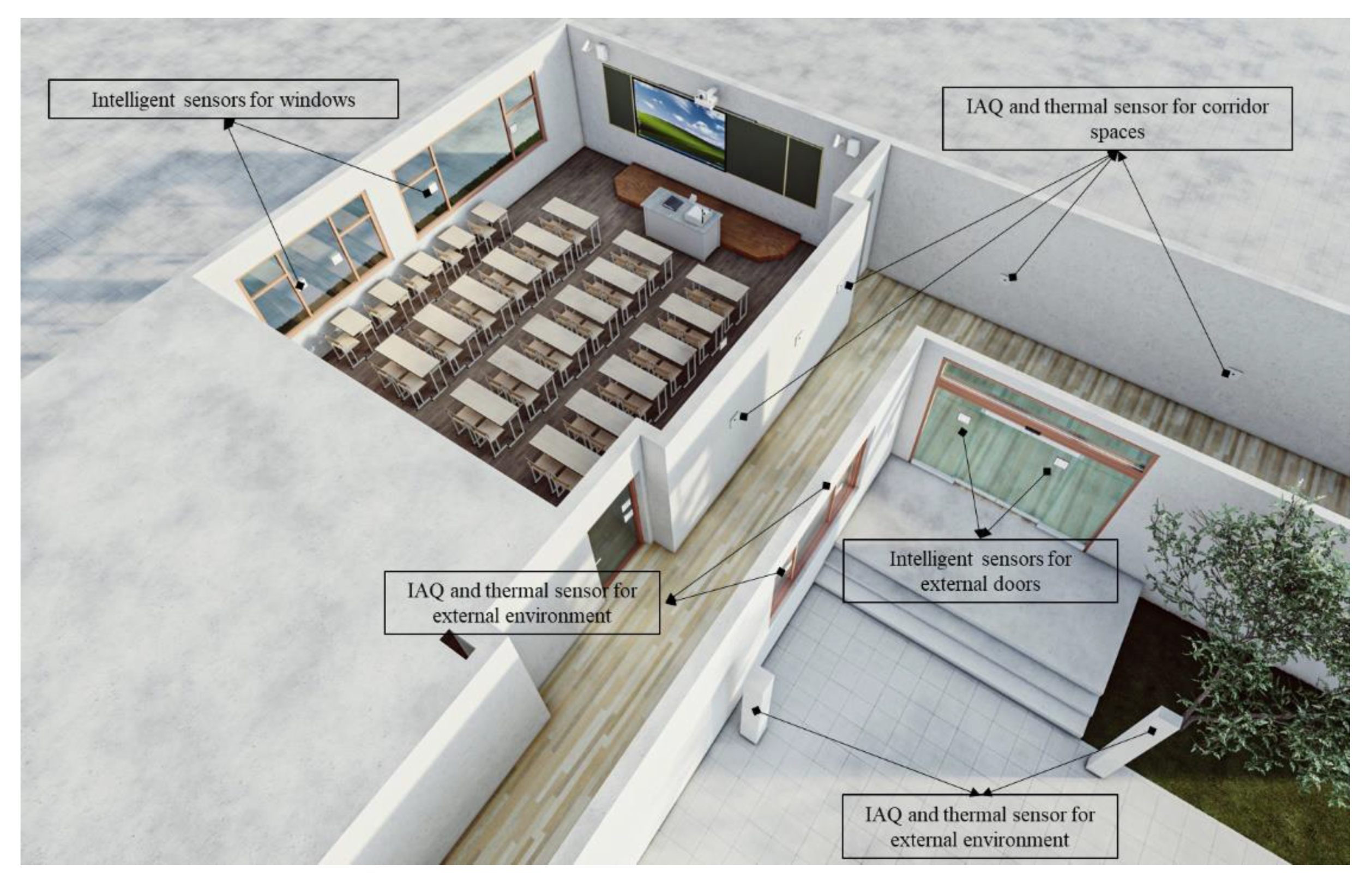
3.3. Data capture based on smart sensors
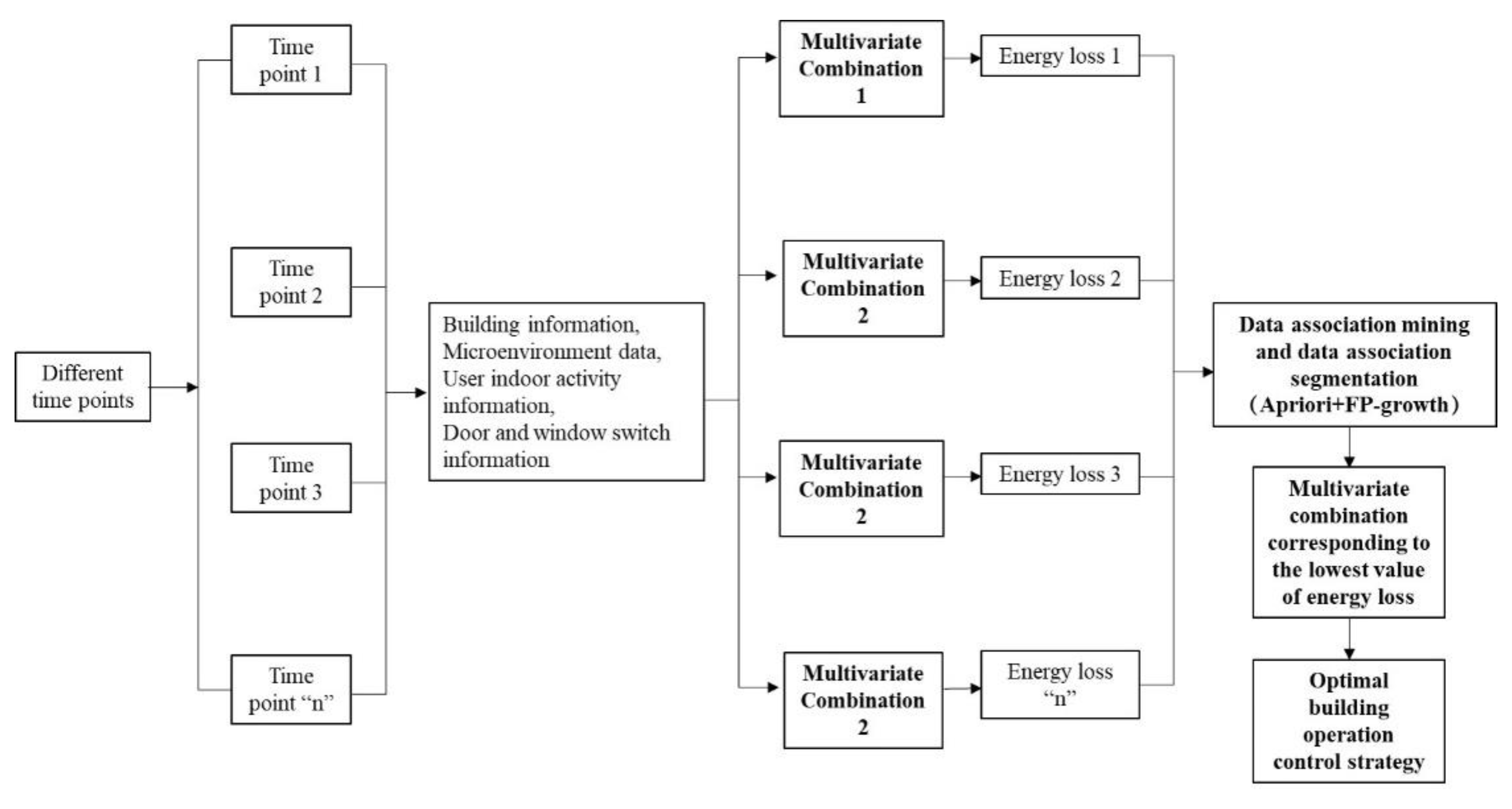
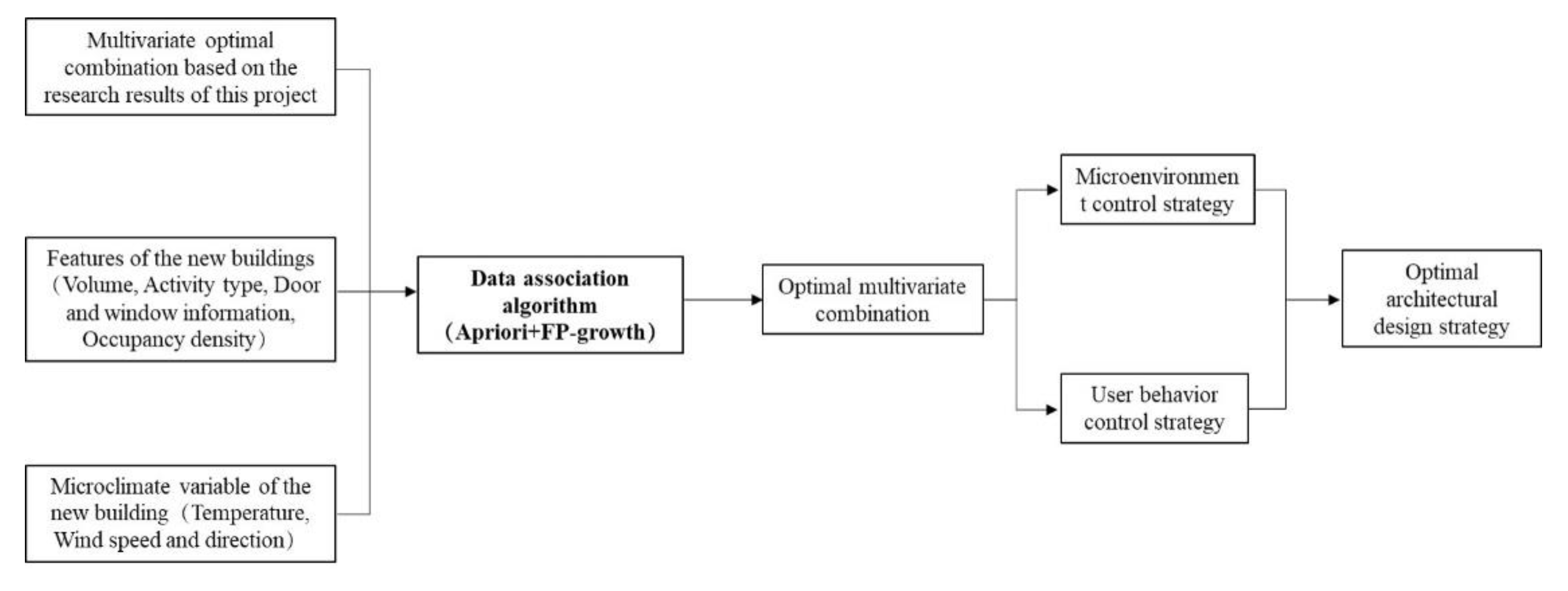
3.4. Reverse and positive thinking for existing and future school buildings, respectively
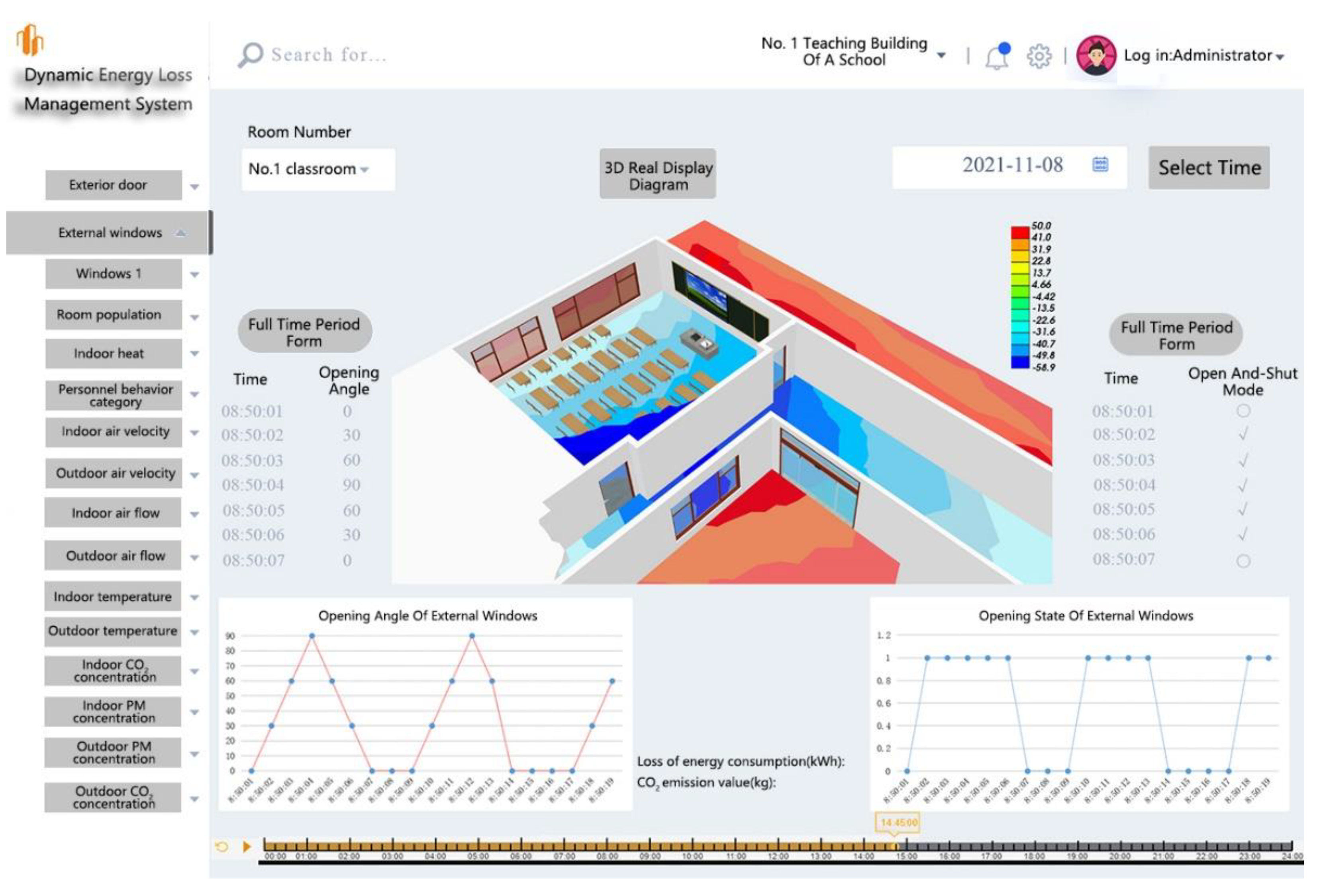
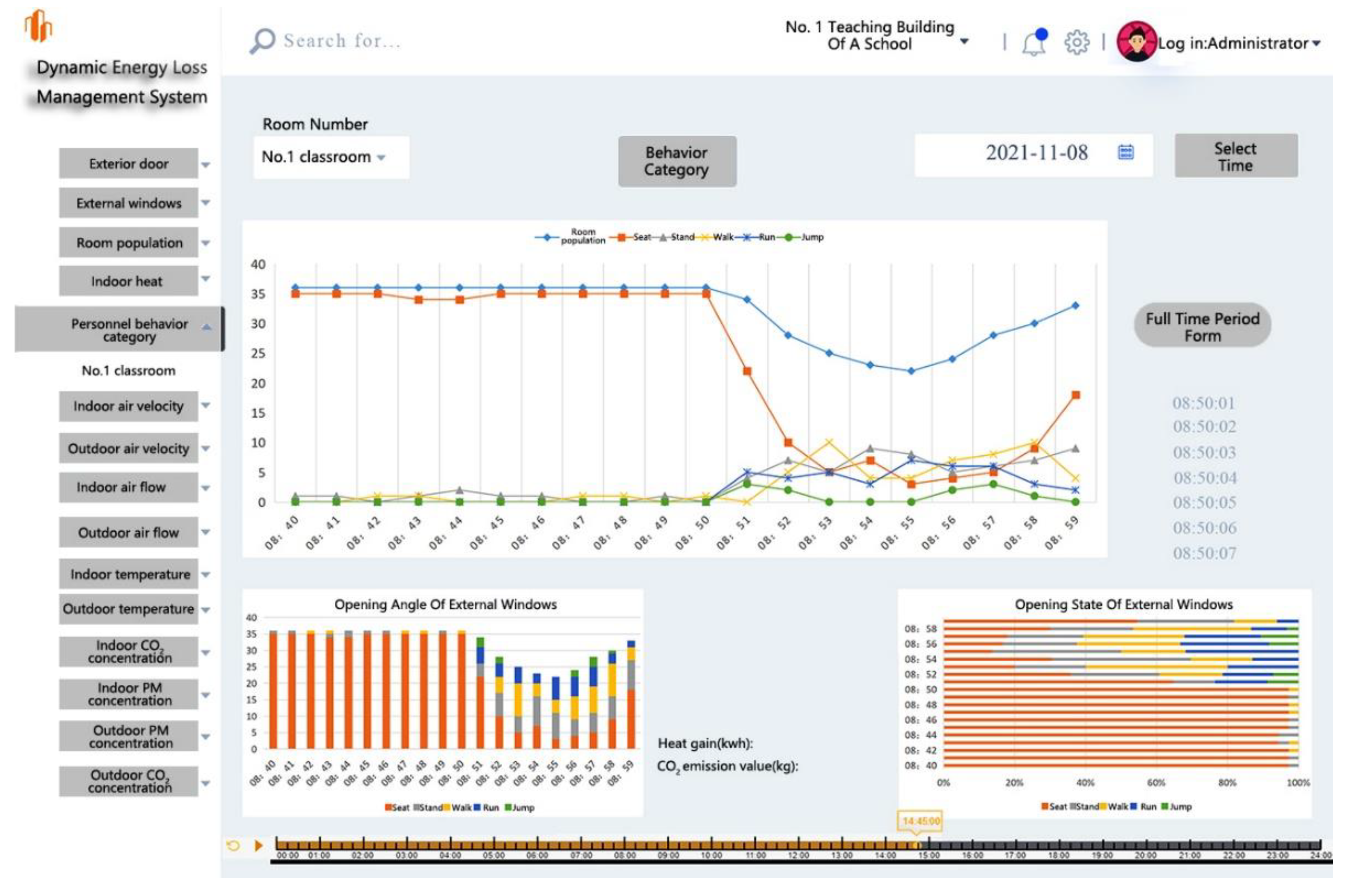
3.5. Expected visual operation interface
4. Conclusions and future work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, X., Ma, X., Chen, B., Shang, Y., & Song, M. (2022). Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: Strategies and countermeasures. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 176, 105959. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. (Ed.). (2020). (rep.). Annual Development Research Report on Building Energy Efficiency in China 2019 (pp. 1–420). Beijing: China Construction Industry Press.
- Pérez-Lombard, L., Ortiz, J., & Pout, C. (2008). A review on buildings energy consumption information. Energy and buildings, 40(3), 394-398. [CrossRef]
- Chen, S., Li, N., Guan, J., Xie, Y., Sun, F., & Ni, J. (2008). A statistical method to investigate national energy consumption in the residential building sector of China. Energy and Buildings, 40(4), 654-665. [CrossRef]
- Juan, X., & Weijun, G. (2018). Analysis on energy consumption of rural building based on survey in northern China. Energy for sustainable development, 47, 34-38. [CrossRef]
- Hong, T. (2009). A close look at the China design standard for energy efficiency of public buildings. Energy and Buildings, 41(4), 426-435. [CrossRef]
- Saroglou, T., Meir, I. A., & Theodosiou, T. (2017). Quantifying energy consumption in skyscrapers of various heights. Procedia environmental sciences, 38, 314-321. [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, P., Trabucco, D., & Wood, A. (2009). Five energy generations of tall buildings: an historical analysis of energy consumption in high-rise buildings. The Journal of Architecture, 14(5), 591-613. [CrossRef]
- Lotfabadi, P. (2014). High-rise buildings and environmental factors. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 38, 285-295. [CrossRef]
- Delzendeh, E., Wu, S., Lee, A., & Zhou, Y. (2017). The impact of occupants’ behaviours on building energy analysis: A research review. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews, 80, 1061-1071. [CrossRef]
- Masoso, O. T., & Grobler, L. J. (2010). The dark side of occupants’ behaviour on building energy use. Energy and buildings, 42(2), 173-177. [CrossRef]
- Kang, H., Lee, M., Hong, T., & Choi, J. K. (2018). Determining the optimal occupancy density for reducing the energy consumption of public office buildings: A statistical approach. Building and Environment, 127, 173-186. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. (Ed.). (2022). (rep.). Annual Development Research Report on Public Building Energy Efficiency in China 2022 (pp. 160–170). Beijing: China Construction Industry Press.
- Ministry of Education of China. (2021). Statistical Bulletin on the Development of National Education in 2020. Retrieved March 16, 2023, from http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_sjzl/sjzl_fztjgb/202108/t20210827_555004.html.
- Pereira, L. D., Raimondo, D., Corgnati, S. P., & Da Silva, M. G. (2014). Energy consumption in schools–A review paper. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 40, 911-922.
- Alam, M., & Devjani, M. R. (2021). Analyzing energy consumption patterns of an educational building through data mining. Journal of Building Engineering, 44, 103385. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z., Ruan, Y., Sun, K., Huang, J., & Liu, H. (2020). Study on energy consumption of public buildings in Qingdao based on statistical date. Architecture Technology, 51(06), 662-665.
- Wu, W., Xu, Q., Feng, J., Xu, w., & Zhi, J. (2021). Analysis of 2020 annual energy consumption date in Shanghai public buildings energy monitoring system. Shanghai Energy Conservation, 2021(07), 673-678.
- Yu, F., Wu, F., & Cao, F. (2020). Analysis on Energy Consumption Status of Existing Public Buildings in Hangzhou. Zhejiang Construction, 37(03), 53-56.
- Qiu, Z & Ni, W. (2020). Statistical Analysis of Energy Consumption of Public Buildings in Wuxi City. Building Energy Efficiency, 48(06), 84-88.
- Xing, J., Chen, J., & Ling, J. (2015). Energy consumption of 270 schools in Tianjin, China. Frontiers in Energy, 9, 217-230. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Yang, B., Li, C., Li, H & Li, H. (2016). Investigation and analysis of energy consumption of office buildings and commercial buildings in Tianjin. Building Technology, 14, 94-96.
- Jiang, J., Wang, D., Liu, Y., Xu, Y & Liu, J. (2019). Experimental study on relationship between indoor temperature and learning efficiency of primary and middle school students in winter. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 49(05), 99-105+85.
- Berardi, U., Tronchin, L., Manfren, M., & Nastasi, B. (2018). On the effects of variation of thermal conductivity in buildings in the Italian construction sector. Energies, 11(4), 872. [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, L. S. (2013). Heat transmission coefficient measurements in buildings utilizing a heat loss measuring device. Sustainability, 5(8), 3601-3614. [CrossRef]
- Kempton, L., Daly, D., Kokogiannakis, G., & Dewsbury, M. (2022). A rapid review of the impact of increasing airtightness on indoor air quality. Journal of Building Engineering, 57, 104798. [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M., Ghaddar, N., & Ghali, K. (2012). Optimal location and thickness of insulation layers for minimizing building energy consumption. Journal of Building Performance Simulation, 5(6), 384-398. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mumin, A., Khattab, O., & Sridhar, G. (2003). Occupants’ behavior and activity patterns influencing the energy consumption in the Kuwaiti residences. Energy and buildings, 35(6), 549-559. [CrossRef]
- Wood, G., & Newborough, M. (2003). Dynamic energy-consumption indicators for domestic appliances: environment, behaviour and design. Energy and buildings, 35(8), 821-841. [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, A., Mohammadi, A., Kabir, E., & Lambeva, L. (2008). Occupants’ operation of lighting and shading systems in office buildings. Journal of building performance simulation, 1(1), 57-65. [CrossRef]
- Masoso, O. T., & Grobler, L. J. (2010). The dark side of occupants’ behaviour on building energy use. Energy and buildings, 42(2), 173-177. [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P. C., Leal, V., & Andersen, M. (2013). Occupants’ interaction with electric lighting and shading systems in real single-occupied offices: Results from a monitoring campaign. Building and Environment, 64, 152-168. [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N. S. M., Wilkinson, S., & Fassman, E. (2015). Do occupants in green buildings practice better energy saving behaviour in computer usage than occupants in conventional buildings? Journal of Green Building, 10(4), 178-193.
- Almeida, L., Tam, V. W., Le, K. N., & She, Y. (2020). Effects of occupant behaviour on energy performance in buildings: a green and non-green building comparison. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 27(8), 1939-1962. [CrossRef]
- Rijal, H. B., Tuohy, P., Nicol, F., Humphreys, M. A., Samuel, A., & Clarke, J. (2008). Development of an adaptive window-opening algorithm to predict the thermal comfort, energy use and overheating in buildings. Journal of Building Performance Simulation, 1(1), 17-30. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W., Ding, Y., Bai, L., & Sun, Y. (2020). Research on occupants’ window opening behavior in residential buildings based on the survival model. Sustainable Cities and Society, 60, 102217. [CrossRef]
- Nicol, J. F. (2001). Characterizing occupant behavior in buildings. Towards a stochastic model of occupant use of windows, light, blinds, heater and fans. In Proceedings of building simulation 01, an IBPSA Conference.
- Santin, O. G., Itard, L., & Visscher, H. (2009). The effect of occupancy and building characteristics on energy use for space and water heating in Dutch residential stock. Energy and buildings, 41(11), 1223-1232. [CrossRef]
- Herkel, S., Knapp, U., & Pfafferott, J. (2008). Towards a model of user behaviour regarding the manual control of windows in office buildings. Building and environment, 43(4), 588-600. [CrossRef]
- Schweiker, M., & Shukuya, M. (2009). Comparison of theoretical and statistical models of air-conditioning-unit usage behaviour in a residential setting under Japanese climatic conditions. Building and Environment, 44(10), 2137-2149. [CrossRef]
- Hong, T., Taylor-Lange, S. C., D’Oca, S., Yan, D., & Corgnati, S. P. (2016). Advances in research and applications of energy-related occupant behavior in buildings. Energy and buildings, 116, 694-702. [CrossRef]
- Heebøll, A., Wargocki, P., & Toftum, J. (2018). Window and door opening behavior, carbon dioxide concentration, temperature, and energy use during the heating season in classrooms with different ventilation retrofits—ASHRAE RP1624. Science and Technology for the Built Environment, 24(6), 626-637.
- Jones, R. V., Fuertes, A., Gregori, E., & Giretti, A. (2017). Stochastic behavioural models of occupants’ main bedroom window operation for UK residential buildings. Building and Environment, 118, 144-158. [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, J., & Gosselin, L. (2020). Probabilistic window opening model considering occupant behavior diversity: A data-driven case study of Canadian residential buildings. Energy, 195, 116981.
- Andersen, R., Fabi, V., Toftum, J., Corgnati, S. P., & Olesen, B. W. (2013). Window opening behaviour modelled from measurements in Danish dwellings. Building and environment, 69, 101-113. [CrossRef]
- Fabi, V., Andersen, R. K., & Corgnati, S. (2015). Verification of stochastic behavioural models of occupants’ interactions with windows in residential buildings. Building and Environment, 94, 371-383. [CrossRef]
- Barthelmes, V. M., Becchio, C., Fabi, V., & Corgnati, S. P. (2017). Occupant behaviour lifestyles and effects on building energy use: Investigation on high and low performing building features. Energy Procedia, 140, 93-101. [CrossRef]
- Peng, C., Yan, D., Wu, R., Wang, C., Zhou, X., & Jiang, Y. (2012, June). Quantitative description and simulation of human behavior in residential buildings. In Building simulation (Vol. 5, pp. 85-94). Tsinghua Press. [CrossRef]
- Hetherington, J., Roetzel, A., & Fuller, R. (2015). The impact of occupant behaviour on residential greenhouse gas emissions reduction. Journal of Green Building, 10(4), 127-140. [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, I., Hoes, P. J., & Hensen, J. L. (2016). Occupant behavior in building energy simulation: Towards a fit-for-purpose modeling strategy. Energy and Buildings, 121, 188-204. [CrossRef]
- Yan, D., Hong, T., Dong, B., Mahdavi, A., D’ Oca, S., Gaetani, I., & Feng, X. (2017). IEA EBC Annex 66: Definition and simulation of occupant behavior in buildings. Energy and Buildings, 156, 258-270. [CrossRef]
- Shi, S., & Zhao, B. (2016, April). Occupants’ interactions with windows in 8 residential apartments in Beijing and Nanjing, China. In Building Simulation (Vol. 9, pp. 221-231). Tsinghua University Press. [CrossRef]
- Yao, M., & Zhao, B. (2017). Window opening behavior of occupants in residential buildings in Beijing. Building and Environment, 124, 441-449. [CrossRef]
- Mo, H., Sun, H., Liu, J., & Wei, S. (2019). Developing window behavior models for residential buildings using XGBoost algorithm. Energy and Buildings, 205, 109564. [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B., Jeong, J. W., & Park, J. S. (2016). Occupant behavior regarding the manual control of windows in residential buildings. Energy and buildings, 127, 206-216. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., & Greenberg, S. (2015). Window operation and impacts on building energy consumption. Energy and Buildings, 92, 313-321. [CrossRef]
- Cedeno Laurent, J. G., Samuelson, H. W., & Chen, Y. (2017, December). The impact of window opening and other occupant behavior on simulated energy performance in residence halls. In Building Simulation (Vol. 10, pp. 963-976). Tsinghua University Press. [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, F., Gholipour, Y., & Yan, W. (2017). A study of the impact of occupant behaviors on energy performance of building envelopes using occupants’ data. Energy and Buildings, 148, 182-198. [CrossRef]
- Pan, S., Han, Y., Wei, S., Wei, Y., Xia, L., Xie, L., ... & Yu, W. (2019). A model based on Gauss Distribution for predicting window behavior in building. Building and Environment, 149, 210-219. [CrossRef]
- Daniel, L., Soebarto, V., & Williamson, T. (2015). House energy rating schemes and low energy dwellings: The impact of occupant behaviours in Australia. Energy and Buildings, 88, 34-44. [CrossRef]
- Mori, H., Kubota, T., Antaryama, I. G. N., & Ekasiwi, S. N. N. (2020). Analysis of window-opening patterns and air conditioning usage of urban residences in tropical southeast Asia. Sustainability, 12(24), 10650. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B., Niu, R., & Wei, S. (2017). An Analysis of the Use of Air Conditioners in Summer in Beijing. Architectural Journal, 000(003), 114-117.
- Ren, J., Zhou, X., An, J., Yan, D., Shi, X., Jin, X., ... & Tang, L. (2020). A Comparative Analysis of Window Operating Behavior in Three Different Open-plan Offices in Nanjing. Architectural Journal, 36(12), 54-61. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G., Zhang, X., & Yan, D. (2006). Effects of Operation Mode of Air Conditioning on Energy Consumption of Heating and Air Conditioning in Residential Buildings. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University, 05, 119-121.
- Zhao, Q., Lin, J., Huang, Z., & Duan, M. (2017). Impacts of Occupant Behavior Pattern on Air-Condtioning Energy Consumption of Rural Residential Buildings in Chongqing. Refrigeration & Air Conditioning, 31(06), 627-635.
- Zhou, X., Yan, D., An, J., & Hong, T. (2014). Comparison and Analysis of Energy Consumption of Four Office Buildings in China and the United States. Building Science, 30(06), 55-65.
- Luo, T., Yan, D., Jiang, Y., & Zhao, J. (2017). Study on Lighting Energy Simulation Method for Office Buildings (Part I). Building Science, 33(04), 101-109.
- Luo, T., Yan, D., Jiang, Y., & Zhao, J. (2017). Study on Lighting Energy Simulation Method for Office Buildings (Part II). Building Science, 33(06), 123-129.
- Yan, D., Feng, X., Wang, C., Hong, T., William O’ Brien., H.Burak Gunay., ... & Ardeshir Mahdavi. (2015). Current State and Future Perspective of Occupant Behavior Simulation in Buildings. Building Science, 31(10), 178-187.
- He, D., Huang, Y., & Ding, Y. (2014). Systematically Analysis and Study on Technical Measures of Energy Savings for Typical Public Buildings in Chongqing. Journal of Chongqing Jianzhu University, 16(04), 112-116.
- Qiu, S., Li, A., & Zhang, X. (2008). Behavioural energy efficiency: Analysis of the opening rate of naturally ventilated residential windows in Xian. Proceedings of the Annual Railway HVAC Academic Conference, 117-120.
- Zhang, J. (2011). Study on the Influence of Building Height and Orientation on Natural Ventilation Behavior of Users in Offices. Huazhong Architecture, 29(08), 50-53.
- Chen, W., & Li, S. (2011). The Investigation of Thermal Comfort and the Occupant Behaviour Models of Window Control during Summer Season of Hot Summer/ Cold Winter Region. Refrigeration, 30(02), 76-81.
- Jian, Y., Li, Q., Bai, Z., & Kong, X. (2011). Study on Influences of Usage Behavior of Residential Air Handling Unit on Energy Consumption in Summer. Building Science, 27(12), 16-19+86. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X., Liu, T., Shi, X., & Jin, X. (2018). Case study of window operating behavior patterns in an open-plan office in the summer. Energy and Buildings, 165, 15-24.
- Chen, S., Zhang, H., & Ge, J. (2018). Feature Analysis of Use Behavior of Air Conditioners in the University Research Building. Architecture & Culture, 000(009), 170-172.
- Li, J., Fu, L., & Di, H. (2008). Test and analysis of heat loss through open windows in heated residential rooms. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 38(003), 111-113.
- Chen, B., Qin, Y., Yang, Y., & Zhu, C. (2018). Test analysis of window opening and closing behaviour in heated residential rooms and building energy consumption. West Leather, 40(08), 28.
- Li, J., Fu, L., & Di, H. (2020). Research on personnel window opening behavior based on Logistic regression and average Bayesian network models. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 50(09), 135-140+121.
- Pan, S., Xu, C., Wei, S., Tarek MHassan., Xie, L., Xiong, Y., & Pieterde Wilde. (2015). Research on the Occupant Window Opening Behaviour in an Office Building in Beijing. Building Science, 31(10), 212-217.
- Ma, H., Shao, X., Liang, C., Wang, H., Wu, C., LI, X., & Ma, Y. (2016). Feasibility analysis on combination strategies of window ventilation and air cleaners in residential buildings under haze weather. Heating Ventilating & Air Conditioning, 46(02), 18-23.
- Yan, D., Feng, X., Wang, C., Hong, T., William O’Brien., H. Burak Gunay., ... & Ardeshir Mahdavi. (2015). Current State and Future Perspective of Occupant Behavior Simulation in Buildings. Building Science, 31(10), 178-187.
- Zhou, T., & Fu, Y. (2020). A machine learning-based method for predicting window opening and closing behaviour during the transition season. China City Press, 205-210.
- Fabi, V., Andersen, R. V., Corgnati, S. P., & Olesen, B. W. (2013). A methodology for modelling energy-related human behavior: Application to window opening behavior in residential buildings. Building Simulation, Vol. 6, pp. 415-427.
- Liu, Y., Wang, X., Cui, Y., Wei, S., & Pan, S. (2021). Measurement and Modelling of Occupants’ Window Opening Behavior in Residential Buildings in the Hot Summer and Cold Winter Regions in Summer. Journal of human settlements in West China, 36(05), 15-23.
- Yao, X. (2019). Simulation and Contrastive Analysis of Indoor Wind Environment in Two Different Windows in Hot Summer and Cold Winter Areas. Architecture & Culture, 01, 37-38.
- Han, X., Wang, C., Pan, S., Qin, M., Zhang, H., Liu, Y., & Wang, T. (2021). Field measurement and analysis of window opening behavior of residential buildings in severe cold region in winter. Journal of Jilin Jianzhu University, 38(02), 41-47.
- Piao, Y., Wang, C., Pan, S., Cui, T., Zhao, M., & Qi, J. (2020). Study on the window opening behavior of office buildings in the transition season of severe cold area. Journal of Jilin Jianzhu University, 37(02), 43-49.
- Gu, Y., Cui, T., Liu, Y., Pan, S., Liu, K., Yang, F., & Piao, Y. (2020). Theoretical and Field Measurement of Occupants’ Window Opening Behavior in an Office Building of Xian in a Season of Transition. Building Science, 36(12), 62-73.
- 90. Zhang, Shuai & Liu, Yan & Yang, Liu & Liu, Jiang & Hou, Liqiang. (2019). The difference between steady-state calculation and dynamic simulation for energy efficiency of residential buildings with different storeys in severe cold and cold zones. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science.
- Van der Veken, J., Saelens, D., Verbeeck, G., & Hens, H. (2004). Comparison of steady-state and dynamic building energy simulation programs. In Proceedings of the international Buildings IX ASHREA conference on the performance of exterior envelopes of whole buildings, Clearwater Beach, Florida 2004.
- Dalla Mora, T., Teso, L., Carnieletto, L., Zarrella, A., & Romagnoni, P. (2021). Comparative Analysis between Dynamic and Quasi-Steady-State Methods at an Urban Scale on a Social-Housing District in Venice. Energies, 14(16), 5164. [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, D. F. M., & Zareipour, H. (2013). Data association mining for identifying lighting energy waste patterns in educational institutes. Energy and Buildings, 62, 210-216. [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, M., Haghighat, F., Fung, B. C., Lazrak, A., & Yoshino, H. (2018). Development of building energy saving advisory: A data mining approach. Energy and Buildings, 172, 139-151. [CrossRef]
- Li, G., Hu, Y., Chen, H., Li, H., Hu, M., Guo, Y., ... & Sun, M. (2017). Data partitioning and association mining for identifying VRF energy consumption patterns under various part loads and refrigerant charge conditions. Applied energy, 185, 846-861. [CrossRef]
- Costa, A., Keane, M. M., Torrens, J. I., & Corry, E. (2013). Building operation and energy performance: Monitoring, analysis and optimisation toolkit. Applied energy, 101, 310-316. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L. G. B., Pegalajar, M. C., Molina-Solana, M., & Guo, Y. K. (2020). A case study on understanding energy consumption through prediction and visualization (VIMOEN). Journal of Building Engineering, 30, 101315. [CrossRef]
- Ellegård, K., & Palm, J. (2011). Visualizing energy consumption activities as a tool for making everyday life more sustainable. Applied Energy, 88(5), 1920-1926. [CrossRef]
- Mattinen, M. K., Heljo, J., Vihola, J., Kurvinen, A., Lehtoranta, S., & Nissinen, A. (2014). Modeling and visualization of residential sector energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Journal of cleaner production, 81, 70-80. [CrossRef]
- Truong, H., Francisco, A., Khosrowpour, A., Taylor, J. E., & Mohammadi, N. (2017). Method for visualizing energy use in building information models. Energy Procedia, 142, 2541-2546. [CrossRef]
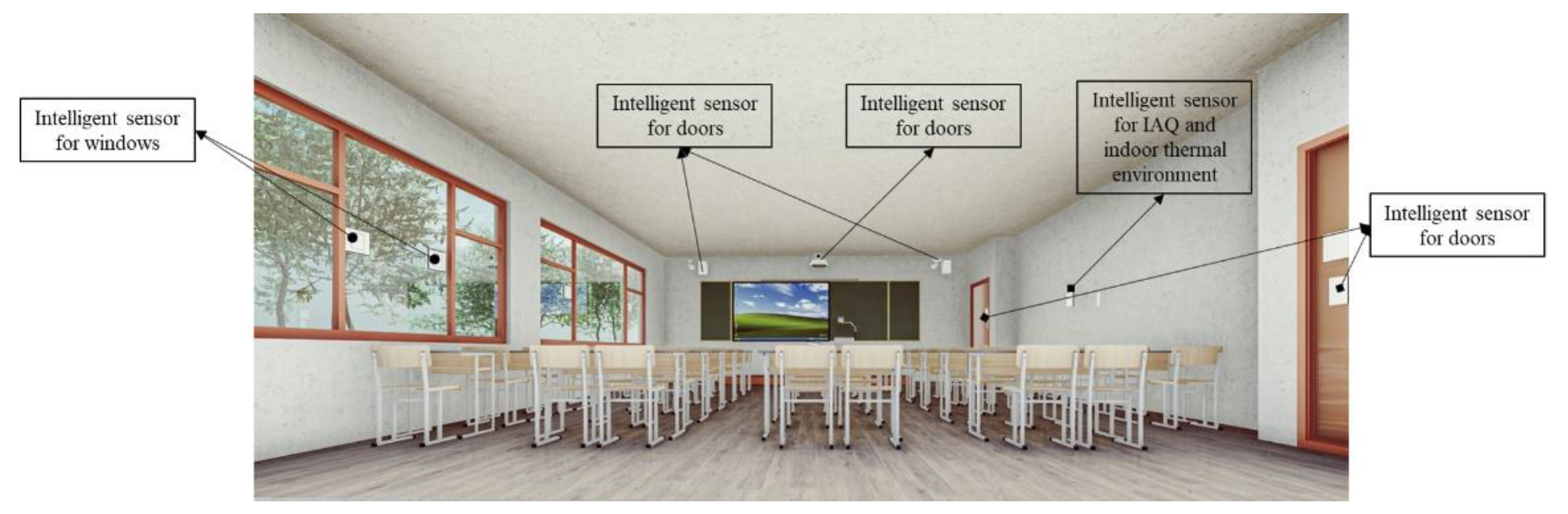
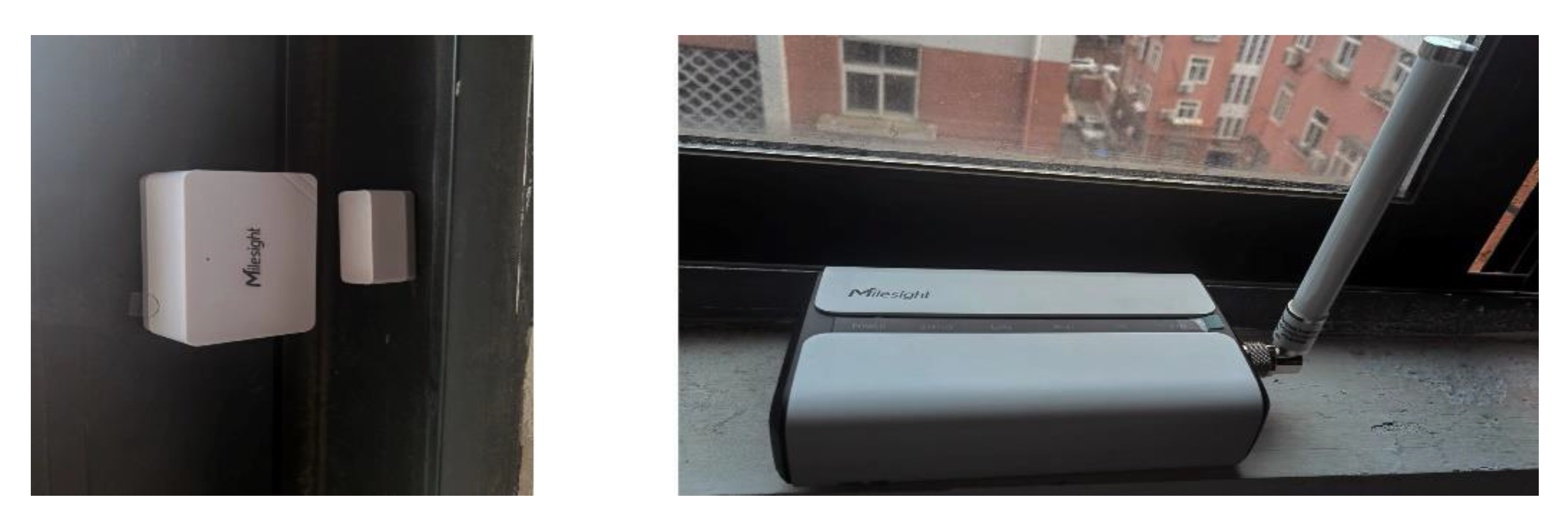



| Types | References | Main content | Main outcomes |
| 1 | [28,29,30,31,32,33,34] | Investigates the relationship between energy-using terminals and energy consumption in unoccupied buildings | • Public buildings consume more energy during non-occupied periods than occupied periods because people leave computers and lights on when not working. • Modifying user behavior with household appliances can reduce energy consumption in residential buildings. |
| 2 | [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] | Focuses on user behavior related to building fabrics such as windows, shading devices, and ventilation louvers | • The indoor comfort environment is the main driving force behind occupants’ behavior, with parameters such as CO2 concentration, indoor temperature, and humidity being the most relevant. • People may adjust the indoor environment by opening windows even when the air conditioner is on. |
| 3 | [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61] | Focuses mainly on the establishment of simulation models through the collection of user behavior data and implementation of mathematical calculations | • There is a need to find a reliable and cost-friendly method of collecting large amounts of data. • The accuracy of behavior prediction models needs to be improved. |
| Types | References | Main content | Main outcomes |
| 1 | [71,72,73,74,75,76,77] | Analyse the factors that influence occupants’ behaviour. | • Occupants’ comfort tolerance temperature and thermal comfort preference are significant factors in their behavior, such as opening windows. |
| 2 | [78,79,80,81] | Quantified the energy losses associated with occupants’ behaviour. | • The quantification methods employed mainly consisted of surveys, behavioral records, and measurements of energy-using terminals (e.g., electricity meters). Many dynamic factors were not considered; thus, the accuracy of their results is low. |
| 3 | [82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89] | Focuses on collecting occupants’ behavior data and developing behavior prediction models for simulation software. | • The accuracy of user behavior prediction models is low. Thus, it cannot accurately quantify the energy losses associated with user behavior. |
| Type of data | Type of sensor | Examples of data formats | |
| External doors | Duration of the opening | Magnetic suction angle sensors | Data format of magnetic suction angle sensors (for swing doors): 08:01:57-08:02:00,open,3s; 08:02:01-08:02:03,close,2s; Data format of magnetic suction scale sensors (for sliding doors): 08:01:57,angle-0°; 08:01:58,angle-30°; |
| Magnitude of the Opening | Magnetic suction angle sensors(swing doors); Magnetic suction scale sensors(sliding doors) | ||
| The airflow speed when the doors open and air is entering | Air movement sensor | m/s | |
| External windows | Duration of the opening | Magnetic suction angle sensors | The same as the data format for external doors |
| Magnitude of the Opening | Magnetic suction angle sensors(swing doors); Magnetic suction scale sensors(sliding doors) | ||
| The airflow speed when the windows open and air is entering | Air movement sensor | m/s | |
| Air | Airflow speed | Wind speed sensor | m/s |
| Airflow direction | Wind direction sensor | N, S, W, E, SW | |
| Indoor and outdoor air temperature | Temperature sensor | ℃, | |
| Air pollutants | Air quality sensor | PMs(μg/m3)、CO2(PPM) | |
| Occupants | Number of occupants inside | Face capture sensors | No. |
| Type of activities | Siting, walking, running, jumping, talking | S-siting; W-walking; R-running; J-jumping; T-talking | |
| Infrared imaging sensor | W/p |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





