Submitted:
27 September 2023
Posted:
28 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
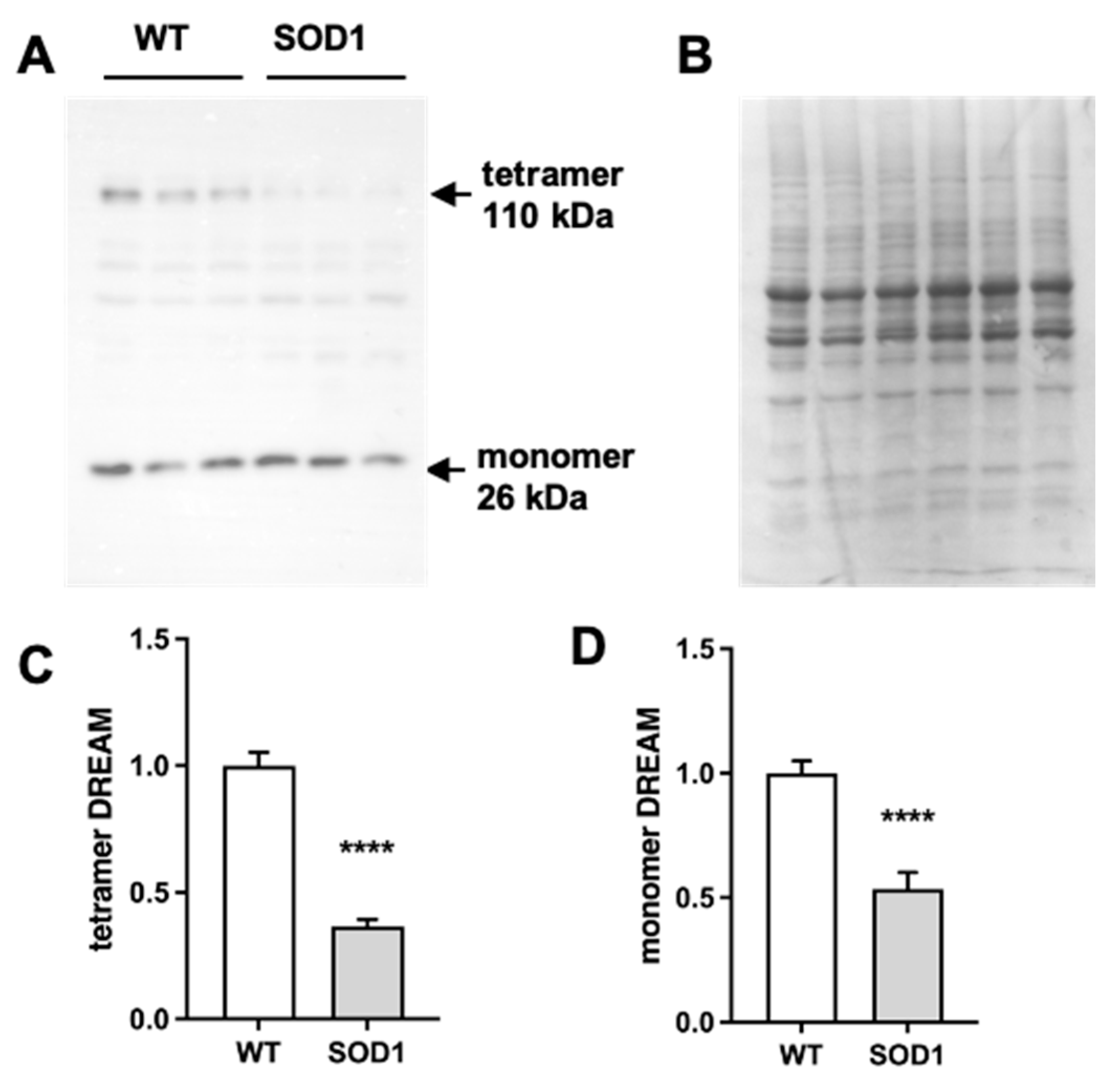
2.1. Expression of DREAM is significantly reduced in the lumbar spinal cord of SOD1G93A mice.
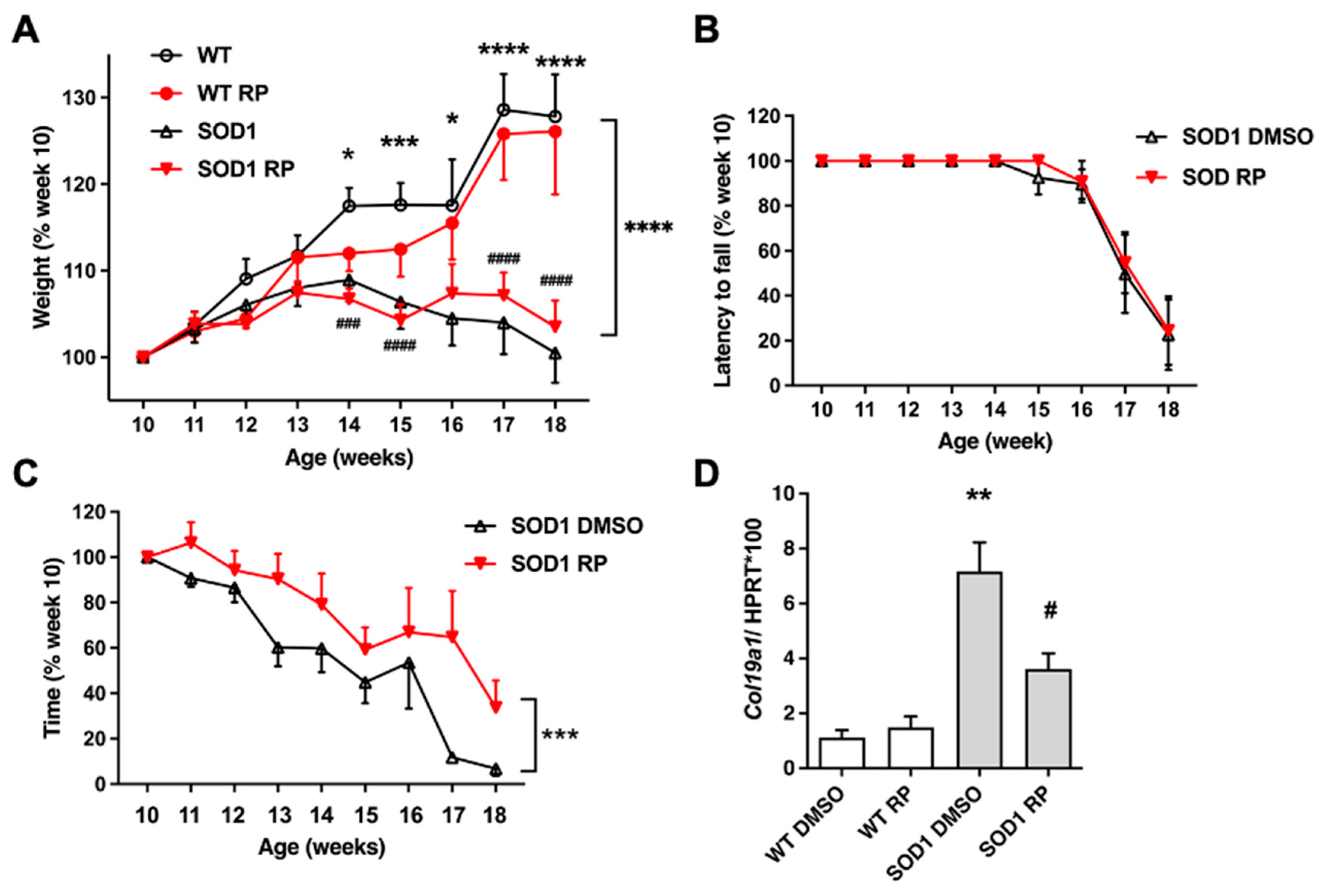
2.2. Repaglinide treatment delayed the loss of motor strength in SOD1G93A mice.
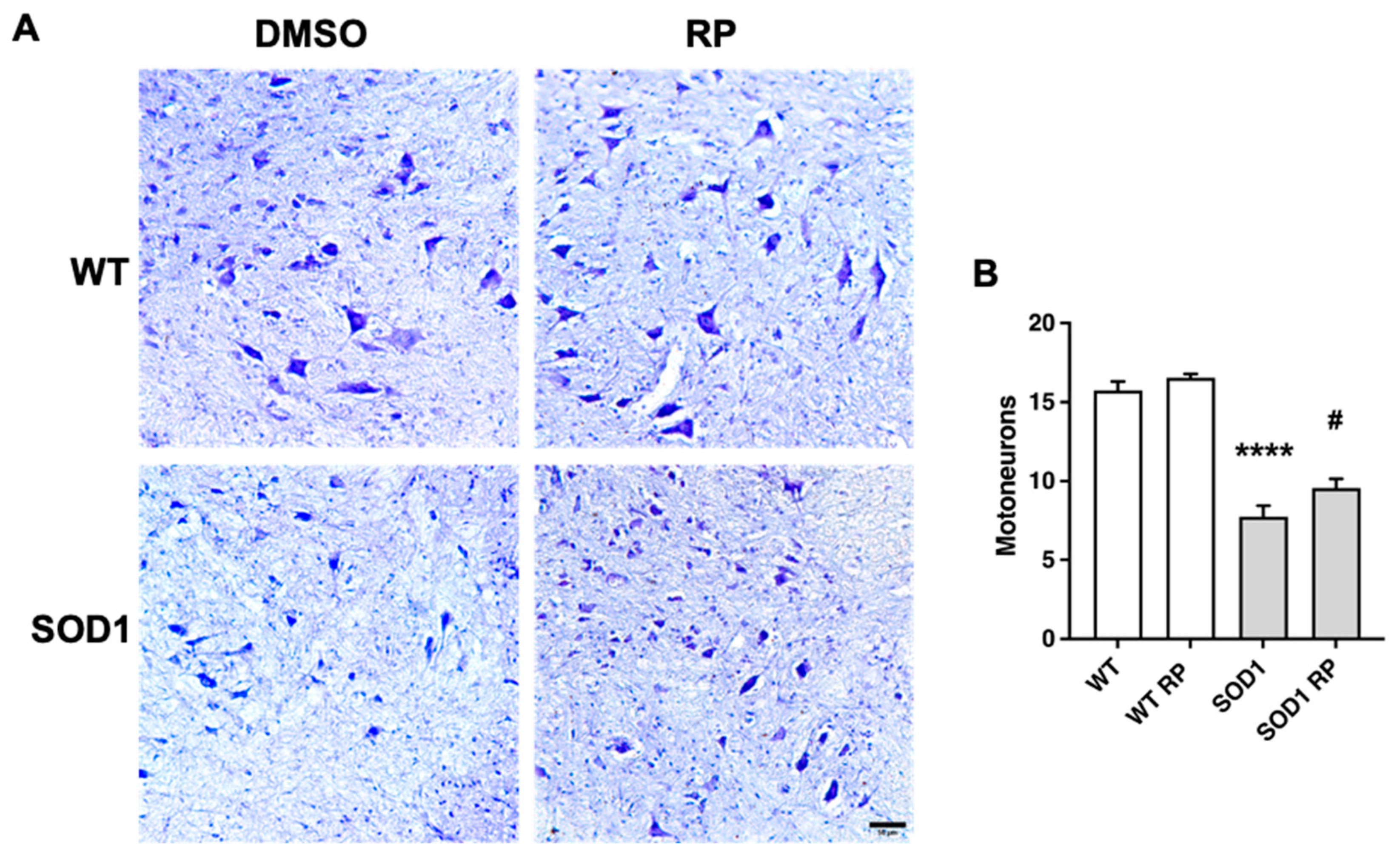
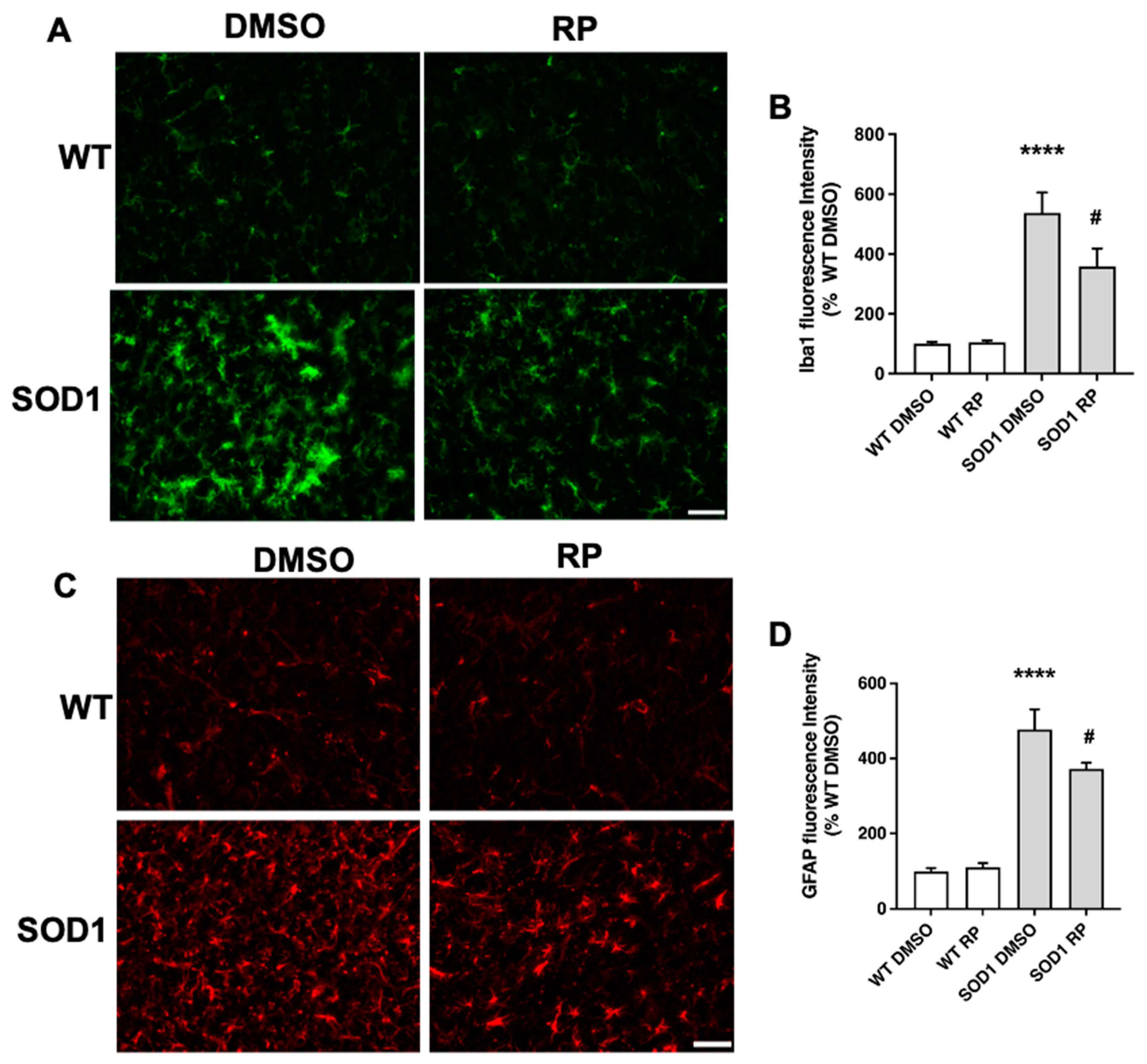
2.3. Treatment with RP reduces motoneuron loss and improves gliosis in the ventral horn of SOD1G93A spinal cord.
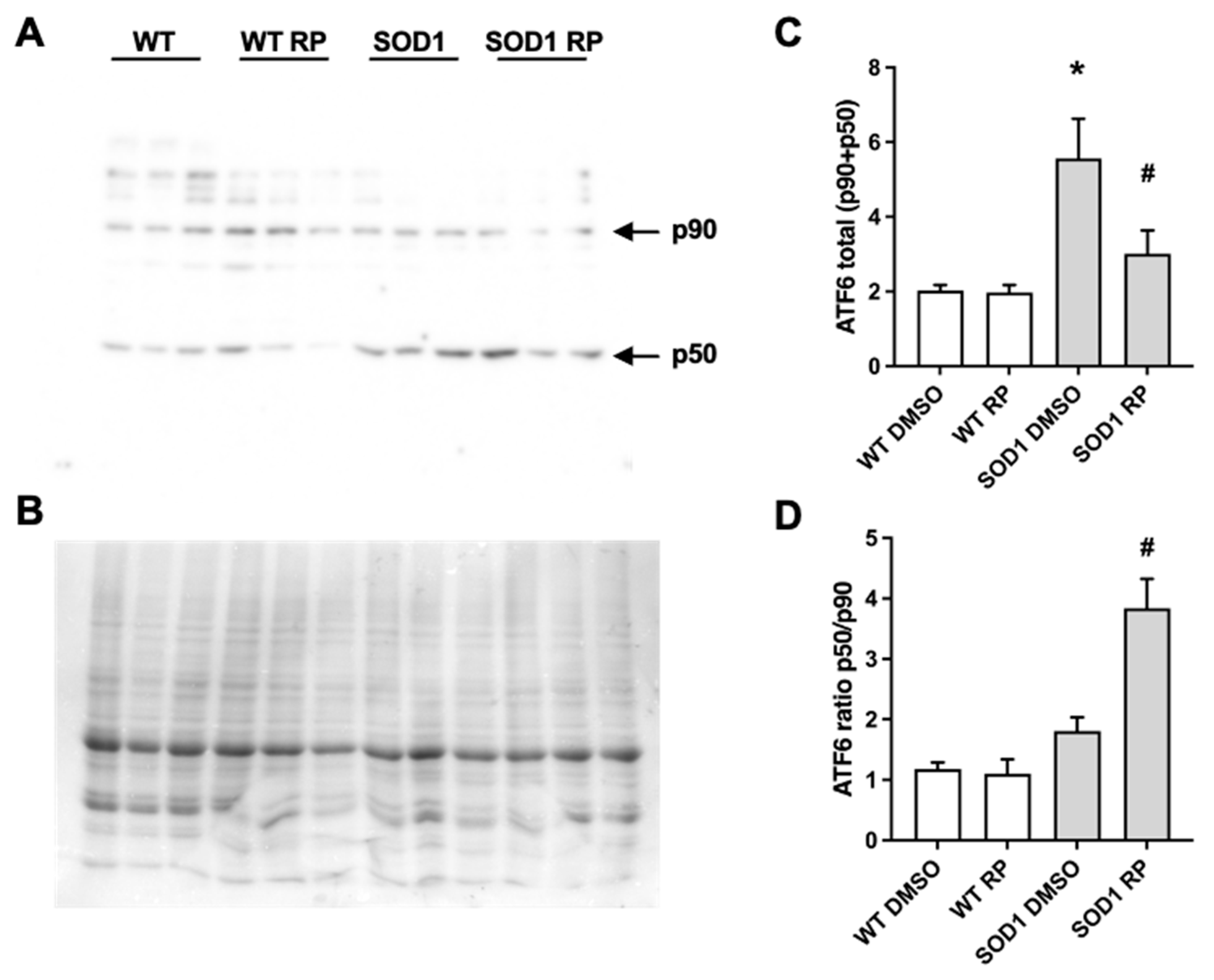
2.5. RP administration stimulates ATF6 processing in the spinal cord of SOD1G93A mice.
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and treatments.
4.1.1. Animals
4.1.2. Treatments
4.2. Weight control and behavioral tests
4.3. Western blot
4.4. Real-time qPCR.
4.5. Histology
4.5.1. Tissue Processing
4.5.2. Immunofluorescence, Nissl staining and Image Analysis.
4.6. Statistical analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- An, W.F.; Bowlby, M.R.; Betty, M.; Cao, J.; Ling, H.P.; Mendoza, G.; Hinson, J.W.; Mattsson, K.I.; Strassle, B.W.; Trimmer, J.S., et al. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature 2000, 403, 553-556. [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, J.D.; Choi, E.K.; Luo, Y.; Lilliehook, C.; Crowley, A.C.; Merriam, D.E.; Wasco, W. Calsenilin: a calcium-binding protein that interacts with the presenilins and regulates the levels of a presenilin fragment. Nat Med 1998, 4, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrion, A.M.; Link, W.A.; Ledo, F.; Mellstrom, B.; Naranjo, J.R. DREAM is a Ca2+-regulated transcriptional repressor. Nature 1999, 398, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Kovacs, I.; Zhang, Z. Differential distribution of KChIPs mRNAs in adult mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 2004, 128, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantero-Recasens, G.; Butnaru, C.M.; Valverde, M.A.; Naranjo, J.R.; Brouwers, N.; Malhotra, V. KChIP3 coupled to Ca(2+) oscillations exerts a tonic brake on baseline mucin release in the colon. Elife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerng, H.H.; Pfaffinger, P.J. Modulatory mechanisms and multiple functions of somatodendritic A-type K (+) channel auxiliary subunits. Front Cell Neurosci 2014, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venn, N.; Haynes, L.P.; Burgoyne, R.D. Specific effects of KChIP3/calsenilin/DREAM, but not KChIPs 1, 2 and 4, on calcium signalling and regulated secretion in PC12 cells. Biochem J 2008, 413, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinaro, P.; Sanguigno, L.; Casamassa, A.; Valsecchi, V.; Sirabella, R.; Pignataro, G.; Annunziato, L.; Formisano, L. Emerging Role of DREAM in Healthy Brain and Neurological Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.Y.; Song, Y.J.; Zhang, C.L.; Liu, J. K(V) Channel-Interacting Proteins in the Neurological and Cardiovascular Systems: An Updated Review. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, M.; Villar, D.; Gonzalez, P.; Dopazo, X.M.; Mellstrom, B.; Naranjo, J.R. Building the DREAM interactome. Sci China Life Sci 2011, 54, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, M.H.; Cao, J.; Knoppers, M.H.; Jurman, M.E.; Distefano, P.S.; Rhodes, K.J.; Xie, Y.; An, W.F. Kinetic modulation of Kv4-mediated A-current by arachidonic acid is dependent on potassium channel interacting proteins. J Neurosci 2001, 21, 4154–4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Takezawa, D.; Tachibanaki, S.; Kawamura, S.; Tokumitsu, H.; Kobayashi, R. Neuronal calcium sensor proteins are direct targets of the insulinotropic agent repaglinide. Biochem J 2003, 375, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowlby, M.R.; Chanda, P.; Edris, W.; Hinson, J.; Jow, F.; Katz, A.H.; Kennedy, J.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Pitts, K.; Ryan, K., et al. Identification and characterization of small molecule modulators of KChIP/Kv4 function. Bioorg Med Chem 2005, 13, 6112-6119. [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, J.R.; Zhang, H.; Villar, D.; Gonzalez, P.; Dopazo, X.M.; Moron-Oset, J.; Higueras, E.; Oliveros, J.C.; Arrabal, M.D.; Prieto, A., et al. Activating transcription factor 6 derepression mediates neuroprotection in Huntington disease. J Clin Invest 2016, 126, 627-638. [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, A.W.; Varner, J.D. A review of the mammalian unfolded protein response. Biotechnol Bioeng 2011, 108, 2777–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardiman, O.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Chio, A.; Corr, E.M.; Logroscino, G.; Robberecht, W.; Shaw, P.J.; Simmons, Z.; van den Berg, L.H. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017, 3, 17085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurney, M.E.; Pu, H.; Chiu, A.Y.; Dal Canto, M.C.; Polchow, C.Y.; Alexander, D.D.; Caliendo, J.; Hentati, A.; Kwon, Y.W.; Deng, H.X., et al. Motor neuron degeneration in mice that express a human Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase mutation. Science 1994, 264, 1772-1775. [CrossRef]
- Larrode, P.; Calvo, A.C.; Moreno-Martinez, L.; de la Torre, M.; Moreno-Garcia, L.; Molina, N.; Castiella, T.; Iniguez, C.; Pascual, L.F.; Mena, F.J.M., et al. DREAM-Dependent Activation of Astrocytes in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol 2018, 55, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Savignac, M.; Mellstrom, B.; Bebin, A.G.; Oliveros, J.C.; Delpy, L.; Pinaud, E.; Naranjo, J.R. Increased B cell proliferation and reduced Ig production in DREAM transgenic mice. J Immunol 2010, 185, 7527–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, A.C.; Manzano, R.; Atencia-Cibreiro, G.; Olivan, S.; Munoz, M.J.; Zaragoza, P.; Cordero-Vazquez, P.; Esteban-Perez, J.; Garcia-Redondo, A.; Osta, R. Genetic biomarkers for ALS disease in transgenic SOD1(G93A) mice. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, N.; Barhum, Y.; Lotan, I.; Steiner, I.; Offen, D. DJ-1 knockout augments disease severity and shortens survival in a mouse model of ALS. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0117190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.E.; Rasmussen, A.L.; Bennett, W.; King, A.; West, A.K.; Chung, R.S.; Chuah, M.I. Microglia and motor neurons during disease progression in the SOD1G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: changes in arginase1 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. J Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rando, A.; de la Torre, M.; Martinez-Muriana, A.; Zaragoza, P.; Musaro, A.; Hernandez, S.; Navarro, X.; Toivonen, J.M.; Osta, R. Chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil increases survival of SOD1 mouse model of ALS. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0210752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, H.; Polymenidou, M.; Cleveland, D.W. Non-cell autonomous toxicity in neurodegenerative disorders: ALS and beyond. J Cell Biol 2009, 187, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatrava-Ferreras, L.; Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Herranz, A.S.; Reimers, D.; Montero Vega, T.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Richart Lopez, L.A.; Bazan, E. Effects of intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood stem cells in 3-acetylpyridine-lesioned rats. Stem Cells Int 2012, 2012, 135187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Perucho, J.; Vallejo-Munoz, M.; Casarejos, M.J.; Reimers, D.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Gomez, A.; Ulzurrun de Asanza, G.M.; Bazan, E. Liver Growth Factor "LGF" as a Therapeutic Agent for Alzheimer's Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, A.; Cozzolino, M.; Crosio, C.; Nencini, M.; Casciati, A.; Gralla, E.B.; Rotilio, G.; Valentine, J.S.; Carri, M.T. Familial ALS-superoxide dismutases associate with mitochondria and shift their redox potentials. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 13860–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igoudjil, A.; Magrane, J.; Fischer, L.R.; Kim, H.J.; Hervias, I.; Dumont, M.; Cortez, C.; Glass, J.D.; Starkov, A.A.; Manfredi, G. In vivo pathogenic role of mutant SOD1 localized in the mitochondrial intermembrane space. J Neurosci 2011, 31, 15826–15837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamata, H.; Manfredi, G. Different regulation of wild-type and mutant Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase localization in mammalian mitochondria. Hum Mol Genet 2008, 17, 3303–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayvergiya, C.; Beal, M.F.; Buck, J.; Manfredi, G. Mutant superoxide dismutase 1 forms aggregates in the brain mitochondrial matrix of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. J Neurosci 2005, 25, 2463–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitoh, H.; Kadowaki, H.; Nagai, A.; Maruyama, T.; Yokota, T.; Fukutomi, H.; Noguchi, T.; Matsuzawa, A.; Takeda, K.; Ichijo, H. ALS-linked mutant SOD1 induces ER stress- and ASK1-dependent motor neuron death by targeting Derlin-1. Genes Dev 2008, 22, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filezac de L'Etang, A.; Maharjan, N.; Cordeiro Brana, M.; Ruegsegger, C.; Rehmann, R.; Goswami, A.; Roos, A.; Troost, D.; Schneider, B.L.; Weis, J., et al. Marinesco-Sjogren syndrome protein SIL1 regulates motor neuron subtype-selective ER stress in ALS. Nat Neurosci 2015, 18, 227-238. [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Cabuy, E.; Caroni, P. A role for motoneuron subtype-selective ER stress in disease manifestations of FALS mice. Nat Neurosci 2009, 12, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.K.; Shin, K.S.; Yuan, J.; Kang, S.J. Superoxide dismutase 1 mutants related to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis induce endoplasmic stress in neuro2a cells. J Neurochem 2008, 104, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Thielen, P.; Matus, S.; Nassif, M.; Court, F.; Kiffin, R.; Martinez, G.; Cuervo, A.M.; Brown, R.H.; Glimcher, L.H. XBP-1 deficiency in the nervous system protects against amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by increasing autophagy. Genes Dev 2009, 23, 2294–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, E.V.; Ayala, V.; Jove, M.; Dalfo, E.; Cacabelos, D.; Povedano, M.; Bellmunt, M.J.; Ferrer, I.; Pamplona, R.; Portero-Otin, M. Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress interplay in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 2007, 130, 3111–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, H.; Almer, G.; Yamashita, S.; Guegan, C.; Nagai, M.; Xu, Z.; Sosunov, A.A.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd; Przedborski, S. Spinal cord endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with a microsomal accumulation of mutant superoxide dismutase-1 in an ALS model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 6025–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montibeller, L.; de Belleroche, J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) are characterised by differential activation of ER stress pathways: focus on UPR target genes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2018, 23, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in motor neurons of the spinal cord in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2010, 69, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiskinis, E.; Sandoe, J.; Williams, L.A.; Boulting, G.L.; Moccia, R.; Wainger, B.J.; Han, S.; Peng, T.; Thams, S.; Mikkilineni, S., et al. Pathways disrupted in human ALS motor neurons identified through genetic correction of mutant SOD1. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 781-795. [CrossRef]
- Matus, S.; Lopez, E.; Valenzuela, V.; Nassif, M.; Hetz, C. Functional contribution of the transcription factor ATF4 to the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e66672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzhashiashvili, Y.; Monckton, C.P.; Shah, H.S.; Kunjamma, R.B.; Popko, B. The UPR-PERK pathway is not a promising therapeutic target for mutant SOD1-induced ALS. Neurobiol Dis 2019, 127, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charif, S.E.; Vassallu, M.F.; Salvanal, L.; Igaz, L.M. Protein synthesis modulation as a therapeutic approach for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Neural Regen Res 2022, 17, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C.; Axten, J.M.; Patterson, J.B. Pharmacological targeting of the unfolded protein response for disease intervention. Nat Chem Biol 2019, 15, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medinas, D.B.; Gonzalez, J.V.; Falcon, P.; Hetz, C. Fine-Tuning ER Stress Signal Transducers to Treat Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front Mol Neurosci 2017, 10, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liao, Y.; Rahaman, A.; Kumar, V. Towards Understanding the Relationship Between ER Stress and Unfolded Protein Response in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 892518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, M.; Radford, H.; Sekine, Y.; Moreno, J.; Verity, N.; le Quesne, J.; Ortori, C.A.; Barrett, D.A.; Fromont, C.; Fischer, P.M., et al. Partial restoration of protein synthesis rates by the small molecule ISRIB prevents neurodegeneration without pancreatic toxicity. Cell Death Dis 2015, 6, e1672. [CrossRef]
- Mercado, G.; Castillo, V.; Soto, P.; Lopez, N.; Axten, J.M.; Sardi, S.P.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Hetz, C. Targeting PERK signaling with the small molecule GSK2606414 prevents neurodegeneration in a model of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2018, 112, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugallo, R.; Marlin, E.; Baltanas, A.; Toledo, E.; Ferrero, R.; Vinueza-Gavilanes, R.; Larrea, L.; Arrasate, M.; Aragon, T. Fine tuning of the unfolded protein response by ISRIB improves neuronal survival in a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, M.; Radford, H.; Zents, K.A.M.; Molloy, C.; Moreno, J.A.; Verity, N.C.; Smith, E.; Ortori, C.A.; Barrett, D.A.; Bushell, M., et al. Repurposed drugs targeting eIF2α-P-mediated translational repression prevent neurodegeneration in mice. Brain 2017, 140, 1768-1783. [CrossRef]
- Sidrauski, C.; McGeachy, A.M.; Ingolia, N.T.; Walter, P. The small molecule ISRIB reverses the effects of eIF2alpha phosphorylation on translation and stress granule assembly. Elife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidrauski, C.; Tsai, J.C.; Kampmann, M.; Hearn, B.R.; Vedantham, P.; Jaishankar, P.; Sokabe, M.; Mendez, A.S.; Newton, B.W.; Tang, E.L., et al. Pharmacological dimerization and activation of the exchange factor eIF2B antagonizes the integrated stress response. Elife 2015, 4, e07314. [CrossRef]
- Boyce, M.; Bryant, K.F.; Jousse, C.; Long, K.; Harding, H.P.; Scheuner, D.; Kaufman, R.J.; Ma, D.; Coen, D.M.; Ron, D., et al. A selective inhibitor of eIF2alpha dephosphorylation protects cells from ER stress. Science 2005, 307, 935-939. [CrossRef]
- Dalla Bella, E.; Bersano, E.; Antonini, G.; Borghero, G.; Capasso, M.; Caponnetto, C.; Chio, A.; Corbo, M.; Filosto, M.; Giannini, F., et al. The unfolded protein response in amyotrophic later sclerosis: results of a phase 2 trial. Brain 2021, 144, 2635-2647. [CrossRef]
- Das, I.; Krzyzosiak, A.; Schneider, K.; Wrabetz, L.; D'Antonio, M.; Barry, N.; Sigurdardottir, A.; Bertolotti, A. Preventing proteostasis diseases by selective inhibition of a phosphatase regulatory subunit. Science 2015, 348, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaytler, P.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D.; Bertolotti, A. Selective inhibition of a regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 1 restores proteostasis. Science 2011, 332, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Popko, B.; Tixier, E.; Roos, R.P. Guanabenz, which enhances the unfolded protein response, ameliorates mutant SOD1-induced amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 2014, 71, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, B.C.; Bond, P.J.; Sadowski, P.G.; Jha, B.K.; Zak, J.; Goodman, J.M.; Silverman, R.H.; Neubert, T.A.; Baxendale, I.R.; Ron, D., et al. The molecular basis for selective inhibition of unconventional mRNA splicing by an IRE1-binding small molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012, 109, E869-878. [CrossRef]
- Kriss, C.L.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.A.; Mailloux, A.W.; Powers, J.J.; Tang, C.H.; Kang, C.W.; Zanesi, N.; Epling-Burnette, P.K.; Sotomayor, E.M.; Croce, C.M., et al. Overexpression of TCL1 activates the endoplasmic reticulum stress response: a novel mechanism of leukemic progression in mice. Blood 2012, 120, 1027-1038. [CrossRef]
- Mimura, N.; Fulciniti, M.; Gorgun, G.; Tai, Y.T.; Cirstea, D.; Santo, L.; Hu, Y.; Fabre, C.; Minami, J.; Ohguchi, H., et al. Blockade of XBP1 splicing by inhibition of IRE1alpha is a promising therapeutic option in multiple myeloma. Blood 2012, 119, 5772-5781. [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, I.; Denko, N.C.; Olson, M.; Van Melckebeke, H.; Lust, S.; Tam, A.; Solow-Cordero, D.E.; Bouley, D.M.; Offner, F.; Niwa, M., et al. Identification of an Ire1alpha endonuclease specific inhibitor with cytotoxic activity against human multiple myeloma. Blood 2011, 117, 1311-1314. [CrossRef]
- Ri, M.; Tashiro, E.; Oikawa, D.; Shinjo, S.; Tokuda, M.; Yokouchi, Y.; Narita, T.; Masaki, A.; Ito, A.; Ding, J., et al. Identification of Toyocamycin, an agent cytotoxic for multiple myeloma cells, as a potent inhibitor of ER stress-induced XBP1 mRNA splicing. Blood Cancer J 2012, 2, e79. [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, K.; Lucas, J.L.; Vuga, D.; Wang, X.; Brumm, D.; Stiles, C.; Kriebel, D.; Der-Sarkissian, A.; Krishnan, K.; Schweitzer, C., et al. Potent and selective inhibitors of the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 endoribonuclease. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 12743-12755. [CrossRef]
- Fribley, A.M.; Cruz, P.G.; Miller, J.R.; Callaghan, M.U.; Cai, P.; Narula, N.; Neubig, R.R.; Showalter, H.D.; Larsen, S.D.; Kirchhoff, P.D., et al. Complementary cell-based high-throughput screens identify novel modulators of the unfolded protein response. J Biomol Screen 2011, 16, 825-835. [CrossRef]
- Maher, P. The Potential of Flavonoids for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiseman, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, K.P.; Harding, H.P.; Haynes, C.M.; Price, J.; Sicheri, F.; Ron, D. Flavonol activation defines an unanticipated ligand-binding site in the kinase-RNase domain of IRE1. Mol Cell 2010, 38, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canosa, A.; Calvo, A.; Barberis, M.; Brunetti, M.; Restagno, G.; Cammarosano, S.; Ilardi, A.; Vigliani, M.C.; Chio, A.; Moglia, C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis onset after prolonged treatment with a VEGF receptors inhibitor. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 2015, 16, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Liu, F.; Shen, P.; Tao, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H. Salvianolic acid B, a new type I IRE1 kinase inhibitor, abrogates AngII-induced angiogenesis by interacting with IRE1 in its active conformation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2023, 50, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, H.C.; Vidadala, V.N.; Potter, Z.E.; Papa, F.R.; Backes, B.J.; Maly, D.J. Development of a Chemical Toolset for Studying the Paralog-Specific Function of IRE1. ACS Chem Biol 2019, 14, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, E.S.; Perera, B.G.; Igbaria, A.; Morita, S.; Prado, K.; Thamsen, M.; Caswell, D.; Macias, H., et al. Allosteric inhibition of the IRE1alpha RNase preserves cell viability and function during endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell 2014, 158, 534-548. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, G.; Luo, D.; Cao, Y.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Liu, B. Baicalein induces apoptosis and autophagy via endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 732516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.S.; Yen, J.H.; Kou, M.C.; Wu, M.J. Luteolin and Apigenin Attenuate 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal-Mediated Cell Death through Modulation of UPR, Nrf2-ARE and MAPK Pathways in PC12 Cells. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0130599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.X.; Conn, P.M. Pharmacoperones as Novel Therapeutics for Diverse Protein Conformational Diseases. Physiol Rev 2018, 98, 697–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieran, D.; Kalmar, B.; Dick, J.R.; Riddoch-Contreras, J.; Burnstock, G.; Greensmith, L. Treatment with arimoclomol, a coinducer of heat shock proteins, delays disease progression in ALS mice. Nat Med 2004, 10, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, F.; Yermalovich, A.; Nguyen, T.; Hummasti, S.; Fu, W.; Eizirik, D.L.; Mathis, D.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Restoration of the unfolded protein response in pancreatic beta cells protects mice against type 1 diabetes. Sci Transl Med 2013, 5, 211ra156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, U.; Yilmaz, E.; Ozcan, L.; Furuhashi, M.; Vaillancourt, E.; Smith, R.O.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science 2006, 313, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batulan, Z.; Taylor, D.M.; Aarons, R.J.; Minotti, S.; Doroudchi, M.M.; Nalbantoglu, J.; Durham, H.D. Induction of multiple heat shock proteins and neuroprotection in a primary culture model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis 2006, 24, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittler, A.; Lurz, R.; Lueder, G.; Priller, J.; Lehrach, H.; Hayer-Hartl, M.K.; Hartl, F.U.; Wanker, E.E. Geldanamycin activates a heat shock response and inhibits huntingtin aggregation in a cell culture model of Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet 2001, 10, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrialls.gov ID: NCT04516096. A Compassionate Use Protocol of AMX0035 for Treatment of Patients With Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04516096?term=Amylyx%20AMX0035&rank=1 (accessed on 13/09/2023).
- Martinus, R.D.; Garth, G.P.; Webster, T.L.; Cartwright, P.; Naylor, D.J.; Hoj, P.B.; Hoogenraad, N.J. Selective induction of mitochondrial chaperones in response to loss of the mitochondrial genome. Eur J Biochem 1996, 240, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Levichkin, I.V.; Stasinopoulos, S.; Ryan, M.T.; Hoogenraad, N.J. A mitochondrial specific stress response in mammalian cells. EMBO J 2002, 21, 4411–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharaoh, G.; Sataranatarajan, K.; Street, K.; Hill, S.; Gregston, J.; Ahn, B.; Kinter, C.; Kinter, M.; Van Remmen, H. Metabolic and Stress Response Changes Precede Disease Onset in the Spinal Cord of Mutant SOD1 ALS Mice. Front Neurosci 2019, 13, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riar, A.K.; Burstein, S.R.; Palomo, G.M.; Arreguin, A.; Manfredi, G.; Germain, D. Sex specific activation of the ERalpha axis of the mitochondrial UPR (UPRmt) in the G93A-SOD1 mouse model of familial ALS. Hum Mol Genet 2017, 26, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilleros-Holgado, P.; Gomez-Fernandez, D.; Pinero-Perez, R.; Reche-Lopez, D.; Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Suarez-Carrillo, A.; Romero-Gonzalez, A., et al. mtUPR Modulation as a Therapeutic Target for Primary and Secondary Mitochondrial Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, M.W.; Nargund, A.M.; Haynes, C.M. Signaling the mitochondrial unfolded protein response. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013, 1833, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegelin, M.D.; Dohi, T.; Raskett, C.M.; Orlowski, G.M.; Powers, C.M.; Gilbert, C.A.; Ross, A.H.; Plescia, J.; Altieri, D.C. Exploiting the mitochondrial unfolded protein response for cancer therapy in mice and human cells. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Rivero, J.M.; Pastor-Maldonado, C.J.; Povea-Cabello, S.; Alvarez-Cordoba, M.; Villalon-Garcia, I.; Talaveron-Rey, M.; Suarez-Carrillo, A.; Munuera-Cabeza, M.; Reche-Lopez, D.; Cilleros-Holgado, P., et al. Activation of the Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response: A New Therapeutic Target? Biomedicines 2022, 10. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Hurtado, A.; Burgos, D.F.; Gonzalez, P.; Dopazo, X.M.; Gonzalez, V.; Rabano, A.; Mellstrom, B.; Naranjo, J.R. Inhibition of DREAM-ATF6 interaction delays onset of cognition deficit in a mouse model of Huntington's disease. Mol Brain 2018, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Hurtado, A.; Peraza, D.A.; Cercos, P.; Lagartera, L.; Gonzalez, P.; Dopazo, X.M.; Herranz, R.; Gonzalez, T.; Martin-Martinez, M.; Mellstrom, B., et al. Targeting the neuronal calcium sensor DREAM with small-molecules for Huntington's disease treatment. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 7260. [CrossRef]
- Peraza, D.A.; Cercos, P.; Miaja, P.; Merinero, Y.G.; Lagartera, L.; Socuellamos, P.G.; Izquierdo Garcia, C.; Sanchez, S.A.; Lopez-Hurtado, A.; Martin-Martinez, M., et al. Identification of IQM-266, a Novel DREAM Ligand That Modulates K(V)4 Currents. Front Mol Neurosci 2019, 12, 11. [CrossRef]
- Socuellamos, P.G.; Olivos-Ore, L.A.; Barahona, M.V.; Cercos, P.; Perez Pascual, M.; Arribas-Blazquez, M.; Naranjo, J.R.; Valenzuela, C.; Gutierrez-Rodriguez, M.; Artalejo, A.R. IQM-PC332, a Novel DREAM Ligand with Antinociceptive Effect on Peripheral Nerve Injury-Induced Pain. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivan, S.; Calvo, A.C.; Rando, A.; Munoz, M.J.; Zaragoza, P.; Osta, R. Comparative study of behavioural tests in the SOD1G93A mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Anim 2015, 64, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellstrom, B.; Kastanauskaite, A.; Knafo, S.; Gonzalez, P.; Dopazo, X.M.; Ruiz-Nuno, A.; Jefferys, J.G.; Zhuo, M.; Bliss, T.V.; Naranjo, J.R., et al. Specific cytoarchitectureal changes in hippocampal subareas in daDREAM mice. Mol Brain 2016, 9, 22. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




