Submitted:
25 September 2023
Posted:
28 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
3. Materials and Methods
3. Results
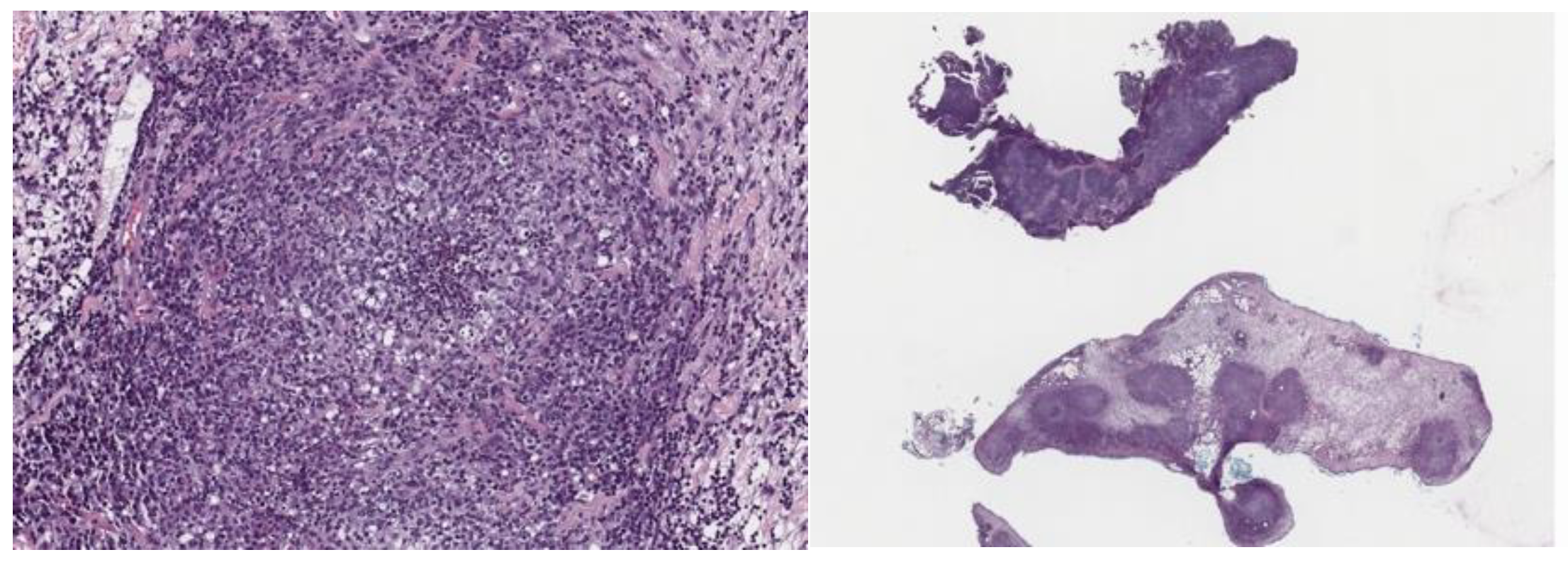
3.1. Case 1
3.1.1. Subsubsection
3.2. Case 2
3.3. Case 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez, J.; Reinacher, M.; Perpiñán, D.; Ramis, A. Identification of group 1 coronavirus antigen in multisystemic granulomatous lesions in ferrets (Mustela putorius furo). J. Comp. Pathol. 2008, 138, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Ramis, A.J.; Reinacher, M.; Perpiñán, D. Detection of feline infectious peritonitis virus-like antigen in ferrets. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, M.M.; Ramsell, K.; Morera, N.; Juan-Sallés, C.; Jiménez, J.; Ardiaca, M.; Montesinos, A.; Teifke, J.P.; Löhr, C.V.; Evermann, J.F.; et al. Clinicopathologic Features of a Systemic Coronavirus-Associated Disease Resembling Feline Infectious Peritonitis in the Domestic Ferret (Mustela putorius). Vet. Pathol. 2008, 45, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.H.; Kiupel, M.; West, K.H.; Raymond, J.T.; Grant, C.K.; Glickman, L.T. Coronavirus-associated epizootic catarrhal enteritis in ferrets. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2000, 217, 4–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, A.G.; Kiupel, M.; Maes, R.K. Molecular characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with epizootic catarrhal enteritis (ECE) in ferrets. Virol. 2006, 349, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, A.G. , Kiupel, M.; Garner, M.M.; Clark, A.K.; Maes, R.K. Comparative sequence analysis of the distal one-third of the genomes of a systemic and an enteric ferret coronavirus. Virus Res. 2010, 149, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autieri, C.R. , Miller, C.L.; Scott, K.E.; Kilgore, A.; Papscoe, V.A.; Garner, M.M.; Haupt, J.L.; Bakthavatchalu, V.; Muthupalani, S.; Fox, J.G. Systemic coronaviral disease in 5 ferrets. Comp. Med. 2015, 64, 6–508. [Google Scholar]
- Gnirs, K.; Quinton, J.F.; Dally, C.; Nicolier, A.; Ruel, Y. Cerebral pyogranuloma associated with systemic coronavirus infection in a ferret. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2016, 57, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescano, J.; Quevedo, M.; Gonzales-Viera, O.; Luna, L.; Keel, M.K.; Gregory, F. First case of systemic coronavirus infection in a domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo) in Peru. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindemann, D.M.; Eshar, D.; Schumacher, L.L.; Almes, K.M.; Rankin, A.J. Pyogranulomatous panophthalmitis with systemic coronavirus disease in a domestic ferret (Mustela putorius furo). Vet. Ophthalmol. 2016, 19, 2–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michimae, Y. , Mikami, S.; Okimoto, K.; Toyosawa, K.; Matsumoto, I; Kouchi, M.; Koujitani, T.; Inoue, T.; Seki, T. The first case of feline infectious peritonitis-like pyogranuloma in a ferret infected by coronavirus in Japan. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 23, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigemoto, J.; Muraoka, Y.; Wise, A.G.; Kiupel, M.; Maes, R.K.; Torisu, S. Two cases of systemic coronavirus-associated disease resembling feline infectious peritonitis in domestic ferrets in Japan. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2014, 23, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarbert, D.K.; Bolin, L.L.; Stout, A.E.; Schaefer, D.M.W.; Ruby, R.E.; Fernandez, J. R-R.; Duhamel, G.E.; Whittaker, G.R.; de Matos, R. Persistent infection and pancytopenia associated with ferret systemic coronaviral disease in a domestic ferret. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2020, 32, 4–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, S.E. , Beaufrère, H.H.; Brisson,B. A.; Fraser, R.S.; Smith, D.A. Pancreatitis and systemic coronavirus infection in a ferret (Mustela putorius furo). Comp. Med. 2018, 68, 3–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.; Kiupel, M.; Maes, R.K. Ferret coronavirus-associated diseases. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2010, 13, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C. A review of feline infectious peritonitis virus infection: 1963–2008. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2009, 11, 225–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haake, C.; Sarah Cook, S.; Pusterla, N.; Murphy, B. Coronavirus Infections in Companion Animals: Virology, Epidemiology, Clinical and Pathologic Features. Viruses 2020, 12(9), 1023–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, E.; Lamm, C.; Denk, D.; Stidworthy, M.- F.; Carrasco, D.C.; Kubiak, M. Systemic coronavirus-associated disease resembling feline infectious peritonitis in ferrets in the UK. Vet Rec. 2012, 171, 8–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, Y.; Ritz, S.; Weber, K.; Sauter-Louis, C.; Hartmann, K. Randomized, placebo-controlled study of the effect of propentofylline on survival time and quality of life of cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, S.; Egberink, H.; Hartmann, K. Effect of Feline Interferon-Omega on the survival time and quality of life of cats with Feline Infectious Peritonitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.M.; Wolf, J.D.; Lieber, C.M.; Sourimant, J.; Lin, M.J.; Babusis, D.; DuPont, V.; Chan, J.; Barrett, K.T.; Lye, D.; et al. Oral prodrug of remdesivir parent GS-441524 is efficacious against SARS-CoV-2 in ferrets. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6415–6426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.M.; Wolf, J.D.; Plemper, R.K. Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.E.; Vogel, H.; Castillo, D.; Olsen, M.; Pedersen, N.; Murphy, B. Investigation of monotherapy and combined anticoronaviral therapies against feline coronavirus serotype II in vitro. J. Fel. Med. Surg. 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Kim, Y.; Liu, H.; Galasiti Kankanamalage, A.C.; Eckstrand, C.; Groutas, W.C.; Bannasch, M.; Meadows, J.M.; Chang, K-O. Efficacy of a 3C-like protease inhibitor in treating various forms of acquired feline infectious peritonitis. J. Feline. Med. Surg. 2018, 20, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, K.D.; Galasiti Kankanamalage, A.C.; Rathnayake, A.D.; Honeyfield, A.; Groutas, W.; Chang, K.-O.; Kim, Y. Protease inhibitors broadly effective against feline, ferret and mink coronaviruses. Antiviral Res. 2018, 160, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.; Novicoff, W.; Nadeau, J.; Evans, S. Unlicensed GS-441524-Like Antiviral Therapy Can Be Effective for at-Home Treatment of Feline Infectious Peritonitis. Animals. 2021, 11, 2257–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, N.C.; Perron, M.; Bannasch, M.; Montgomery, E.; Murakami, E.; Liepnieks, M.; Liu, H. Efficacy and safety of the nucleoside analog GS-441524 for treatment of cats with naturally occurring feline infectious peritonitis J. Feline. Med. Surg. 2019, 21, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Tests (ref. range) Unit | Diagnosis1 | Week 31 | Week 141 | 1 month post treatment 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (6.5-11.0) M/μL | 7.9 | 12.9 H | 11.3 H | 10.2 |
| HCT (43-55) % | 37 L | 63 H | 57 H | 55 |
| HGB (15.0-19.0) g/dL | 12 L | 20.5 H | 19.5 H | 17.1 |
| WBC (2.5-8.0) K/μL Neutrophils (1.37-4.74) K/μL |
4.3 2.75 (64%) |
8.5 H 2.13 (25%) |
6.8 1.97 (29%) |
4.5 1.62 (36%) |
| Lymphocytes (0.87-3.36) K/μL | 1.3 (31%) | 5.70 (67%) H | 4.42 (65%) H | 2.43 (54%) |
| Total protein (5.5-7.6) g/dL | 4.6 L | 8.8 H | 7.0 | 6.3 |
| Albumin (2.4-4.5) g/dL | 1.5 L | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| Globulin (2.9-4.9) g/dL | 3.1 | 5.1 H | 3.2 | 2.7 L |
| A/G ratio (0.8-2) | 0.5 L | 0.7 | 1.2 | 1.3 |
| ALT (10-280) IU//L | 51 | 170 | 288 H | 186 |
| ALP (15-45) IU/L TBIL (0.0-1.0) mg/dL |
86 H 0.1 |
16 0.1 |
20 0.1 |
21 0.2 |
| Creatinine (0.2-0.8) mg/dL BUN (10-33) mg/dL |
0.3 11 |
1.0 H 38 H |
1.0 H 38 H |
1.3 H 42 H |
| Tests (ref. range) Unit | Diagnosis1 | Week 21 | Week 121 | Week 171 | 7 months after treatment1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (6.35-11.20) M/μL | 7.18 | 8.26 | 7.79 | 9.40 | 9.75 |
| HCT (37-55) % | 32.8 L | 40.7 | 36.2 L | 41.8 | 44.6 |
| HGB (11.0-17.0) g/dL | 11.5 | 13 | 12.5 | 14.7 | 15.5 |
| WBC (2.0-10.0) K/μL Neutrophils (0.62-3.30) K/μL |
8.7 3.82 (43.7%) |
16.7 H 10.72 (64.2%) H |
6.5 2.15 (33.2%) |
6.4 2.32 (36.4%) |
5.5 3.28 (59.7%) |
| Lymphocytes (1.00-8.00) K/μL | 3.73 (42.7%) | 4.88 (29.3%) | 3.59 (55.5%) | 3.30 (51.8%) | 1.79 (32.6%) |
| Total protein (5.2-7.3) g/dL | 8.2 H | 7.5 H | 6.8 | 6.9 | 5.7 |
| Albumin (2.6-3.8) g/dL | 2.7 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 2.5 L |
| Globulin (1.8-3.1) g/dL | 5.5 H | 4.8 H | 3.7 H | 3.7 H | 3.3 H |
| A/G ratio | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| ALT (82-289) U//L | 135 | 68 | 63 L | 75 L | 102 |
| ALP (9-84) U/L TBIL (0.1-1.0) mg/dL |
<10 0.3 |
32 0.3 |
29 0.2 |
21 0.4 |
20 0.2 |
| Creatinine (0.4-0.9) mg/dL BUN (10-45) mg/dL |
0.3 17 |
0.3 16 |
0.6 36 |
0.6 33 |
0.6 29 |
| Tests (ref. range2) Unit | Diagnosis (ref. range)1 | Week 42 | Week 92 | Week 122 | 3 months after treatment2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBC (6.5-11.0) M/μL | 11.45 H (6.35-11.20) | NA | 12.7 H | NA | NA |
| HCT (43-55) % | 40.2 (37.0-55.0) | 51 | 62 H | 58 H | 53 |
| HGB (15.0-19.0) g/dL | 14.3 (11.0-17.0) | NA | 17.1 | NA | NA |
| WBC (2.5-8.0) K/μL Neutrophils (1.37-4.74) K/μL |
12.8 (2-10) H 5.46 (0.62-3.30)(42.6%) H |
13.8 H 4.28 (31%) |
9.8 H 1.27 (13%) L |
7.5 1.87 (24%) |
3.6 0.83 (23%) |
| Lymphocytes (0.87-3.36) K/μL | 5.91 (1.00-8.00)(46.1%) | 8.69 (63%) | 7.74 (79%) H | 5.93 (76%) H | 2.66 (74%) |
| Total protein (5.2-7.3) g/dL | 10.9 (5.2-7.3) H | 9.0 H | 7.1 | 7.4 | 6.8 |
| Albumin (2.4-4.5) g/dL | 2.6 (2.6-3.8) | 2.5 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 3.5 |
| Globulin (2.9-4.9) g/dL | 8.3 (1.8-3.1) H | 6.5 H | 3.7 | 3.2 | 3.3 |
| A/G ratio | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.1 |
| ALT (10-280) U//L | 65 (82-289) L | 60 | 50 | 88 | 63 |
| ALP (15-45) U/L TBIL (0.0-1.0) mg/dL |
43 (9-84) 0.4 |
45 0.0 |
40 0.1 |
33 0.1 |
29 0.1 |
| Creatinine (0.2-0.8) mg/dL BUN (10-33) mg/dL |
0.6 (0.4-0.9) 13 (10-45) |
NA 35 H |
0.8 32 |
0.8 40 H |
NA 35 H |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




