1. Introduction
The main problem of modern materials science is the development of new materials that improve the performance characteristics of critical parts operating under extreme operating conditions (gas turbine engine parts, high-speed cutting tools, parts of aerospace friction units, etc.) [
1].
One way to improve the performance of tools and machine parts is to modify surfaces by applying thin hard coatings [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6].
Coatings based on transition metal, such as coatings based on transition metal borides, have become practically widespread due to their high hardness and wear resistance, high electrical conductivity and oxidation resistance [
7,
8].
The properties of two-component coatings are often not able to meet the user’s requirements [
9]. One of approach to improve the properties of two-component coatings is to tailor the properties by adding the third or more elements to two-element system. Studies on the effects of small amounts of elements such as C [
10,
11], N [
12,
13], Me (Al, Cu, and etc.) [
1,
14,
15], and others on the mechanical and tribological properties of molybdenum boride coatings have shown that such coatings have higher hardness and lower coefficient of friction [
9]. Carbon as a further component of the coating causes the change in morphology of the coating, but also affects the sliding behavior due to its low-friction properties. Carbon addition enables to obtain materials with reduced grain size, dense active sites and high surface area [
9,
16]. In general the introduction of carbon or nitrogen to a material based on a metal diboride has led to a decrease in grain-size and eventually an amorphisation of the material [
13,
17].
Due to introduction Al into molybdenum boride coatings, it was possible to increase hardness and heat resistance. Increased resistance to high temperature oxidation was associated with formation of a protective Al
2O
3 layer on the coating surface Such coatings may show low coefficient of friction, high wear resistance and high hardness [
1,
14].
Numerous deposition techniques were developed in this field during the past decade. Coatings in system Me-Mo-B (C or N) were produced by a multitude of methods, such as thermal spraying [
18], surface saturation by diffusion [
19], arc evaporation [
20], pulsed electrospark deposition [
21,
22], spark plasma sintering [
23,
24], magnetron sputtering [
1,
25,
26,
27], and others.
Among all the techniques, magnetron sputtering is widely recognized as one of the most promising since it keeps the geometry of substrate intact and allows one to fabricate coatings with low roughness [
1,
25,
26,
27], residual porosity and defects concentration, and high adhesion (in particular when an intense preliminary ion etching is applied) [
28].
Magnetron sputtering of mosaic multi-component cathodes (targets), or simultaneous sputtering of several cathodes (targets) simultaneously is widely recognized [
1,
25,
26,
27]. Benefits of this technique are uniform depth-wise distribution of elements even in multi-component coatings [
29,
30,
31], keep of the geometry of substrate intact, to fabricate dense coatings with low roughness, residual porosity and defects concentration [
28,
32].
For the manufacture of multi-component cathodes (targets) for magnetron sputtering, raw materials with high hardness and brittleness are mainly used. This limits the possibilities of using standard technologies: casting, hot pressure processing, cutting, etc. [
29,
33,
34]. A solution to this problem can be found by using multi-element and multi-phase cathodes produced by powder technologies, including the method of self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) [
35,
36]. However, the SHS technology also has disadvantages, such as large internal stresses in the material arising during SHS, limitations when creating complex compositions in terms of elemental composition, the inability to obtain cylindrical cathodes, problems with discharge stability, and the complexity of manufacturing mosaic cathodes with ceramic inserts [
37,
38,
39,
40].
In our previously study [
41] a metal-ceramic cylindrical composite target with a NiCr-70B
4C coating for magnetron sputtering was fabricated by a robotic complex for the detonation spraying of coatings equipped with a multi-chamber detonation accelerator. The obtained cathode target with a NiCr-70B
4C coating was used to deposit the NiB-Cr
7C
3 coating on flat specimens of 65G steel using equipment for magnetron sputtering UNICOAT 200. A dense quasi-amorphous NiB-Cr
7C
3 coating with a thickness of 2 µm was obtained. The microhardness of the NiB-Cr
7C
3 coating reached 10 GPa, and the adhesion fracture load exceeded 16 N.
Here, we report the synthesis of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating for the first time by a using magnetron sputtering of Al-Mo-B4C target produced by detonation spray coating. The microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties were investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Powder preparation
In this study, commercially available molybdenum (Mo, grade MPC, Plasmotherm, Russia), aluminum (Al grade AC, Plasmotherm, Russia), and boron carbide (B
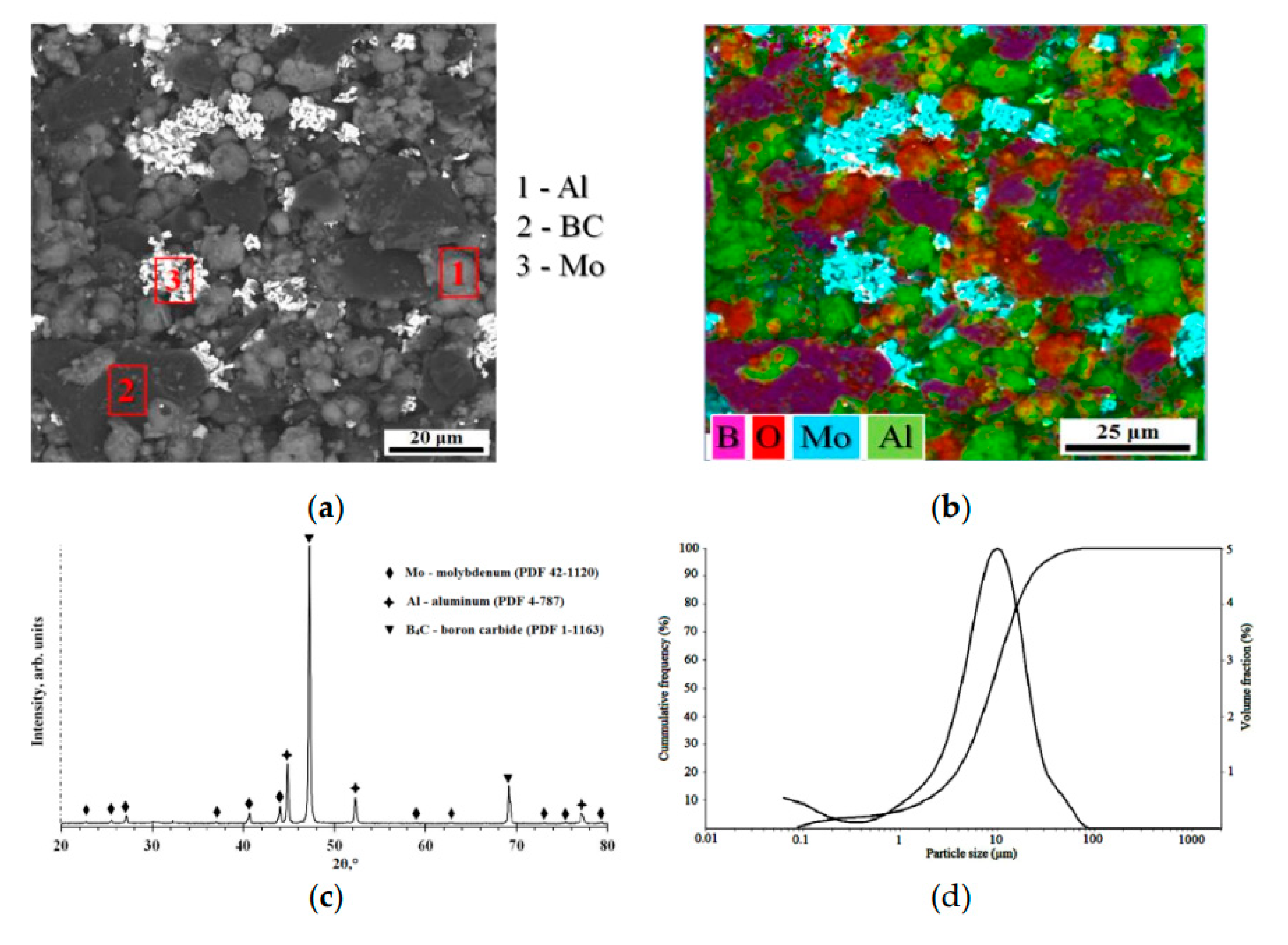
4C F600 FEPA, 78B-20C, impurities 0.2B₂O₃-0.2Si-0.2Fe-1.0N-0.2C free, Volzhsky Abrasive Plant JSC, Russia) powders were used as raw materials. The morphology and composition of the powders mixture, according to scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TESCAN MIRA 3 LMU, Czech Republic), is shown in
Figure 1a,b.
The schematic of the preparation of AlMo-30B
4C powder and coating, and Al-Mo-B(CN) coating is exhibited below in
Figure 2.
The initial powders were mixed in a ratio of 30 wt% of Al, 40 wt% of Mo and 30 wt% of B
4C (denoted as AlMo-30B
4C) in the Turbula mixer for 1 hour. The particle size distribution was measured by the laser scattering method using a particle size analyzer (Analysette 22 NanoTec Plus, Fritsch GmbH) (d(0.1): 1.81 µm, d(0.5): 8.656 µm, d(0.9): 22.44 µm) (
Figure 1d). The powder composition was dried in an electric oven at 200 ± 5°C for 60 minutes to reduce agglomeration and eliminate the possibility of sticking during the detonation spray coatings process. Diffraction pattern of the AlMo-30B
4C composite powder is displayed in
Figure 1c. The diffraction pattern is consistent with Mo (PDF: 41-1120), confirming a cubic lattice structure; with Al (PDF 4-787), confirming a cubic lattice structure; and B
4C (PDF 1-1163), confirming a rhombohedral lattice structure.
2.2. Metal-ceramic composite target and AlMo-30B4C coating preparation
Copper cathode target of equipment for magnetron sputtering UNICOAT 200 (Russia) in the form of the plate (198×78×4 mm) was made. A powder AlMo-30B
4C was sprayed on the surface of cathode targets by a robotic complex for detonation spraying of coatings (IntelMashin LLC, Russia) equipped with a multi-chamber detonation accelerator (MCDS) [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45] (
Figure 2). The parameters of the AlMo-30B
4C coating spray are listed in
Table 1. The study of the structure and distribution of elements in the AlMo-30B
4C coating material was carried out by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TESCAN MIRA 3 LMU, Czech Republic) (Figure 3).
2.3. Al-Mo-B(CN) coating preparation
The obtained cathode target with AlMo-30B4C coating were used to deposit the coating Al-Mo-B(CN) on flat specimens of steel AISI 316 (Fe–0.08C–0.75Si-2.0Mn–0.04P–0.03S–16.5Cr-11.0Ni-2.2Mo all in wt pct) (198×78×4 mm) and Si (100) (15 × 15 x 2 mm) using equipment for magnetron sputtering UNICOAT 200.
Before deposition the coating, the surfaces of the substrates were degreased and cleaned with argon ions for 10 minutes at a pressure of 8∙10−2 Pa and a voltage at an ion source of 2.2 kV. In the process of forming a coating Al-Mo-B(CN) on a steel substrate, two targets were used as the sprayed material, a standard carbon target with a purity of 99.99% and a copper target with a metal–ceramic composite coating of AlMo-30B4C.
The deposition of the AlMo-30B
4C coating was carried out using external carbon target with an excess of carbon to reduce the oxygen content in the coating. The binding of oxygen in CO and its removal during the deposition of the coating minimize the oxygen content in the final coating [
41].
The Al-Mo-B(CN) coating was deposition in the Direct Current mode (DC). Parameters of deposition process are given in
Table 2. The coating growth rate was 17 nm/min.
2.4. Coatings characterization
Structural investigation via scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) was performed on the scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TESCAN MIRA 3 LMU, Czech Republic). The specimens were transversally cut, mechanically polished and prepared by standard metallographic methods-sectioning, mounting and polishing–for sample preparation. The sample was prepared by grinding with SiC sandpapers with various specifications (200, 500, 800 and 1000#), followed by polishing with 1-μm diamond slurry according to the procedure recommended by Struers company for ceramic coatings. The specimens were cleaned with distilled water and dried at 100°C for 3 h.
Porosity of the coating was determined by metallographic method with elements of the qualitative and quantitative analyses of the geometry of the pores using an optical inverted Olympus GX51 microscope (Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) [
46]. The images were registered in an optical microscope, in bright field, magnified 500×. The image acquisition of the structure of the studied layer was done using “SIAMS Photolab” programme. At least ten arbitrarily selected typical micrographs were analyzed for each experimental point.
Phase composition of the powder and coatings was determined by the X-ray phase analysis method (diffractometer ARL 9900 WS, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Switzerland). An ARL 9900 WS X-ray powder diffractometer using Co-Kα monochromatic radiation (wavelength λ¼1.788996 Å) operating at 30 kV and 30 mA was employed to determine the X-ray diffraction patterns. XRD spectrum for phase analysis was determined by shooting the scheme θ-Θ scan focusing by Brega–Brentano in the angular range of 8–80 2Θ. Investigations were carried out in θ/2θ step scan mode at a step of 0.02 in 2θ range at a rate of 0.5/min. Crystalline phases were identified by the ICDDPDF-2 (2008) powder diffraction database.
The coating elemental concentrations and chemical states of each component were investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectrometer PHI 5000 VersaProbe (ULVAC PHI, Kanagawa, Japan). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is an indispensable tool to understand the electronic structure, bonding, magnetic properties, and origin of catalytic activities of materials in general and the binary transition metal borides in particular [
47]. Monochromatic Al-Kα X-rays (1486.6 eV) with the spot size of 200 μm was used to irradiate the sample surface. Photoelectron extraction angle was 45°. Pass energy of 23.5 eV with a step size of 0.05 eV was used to gather the high-resolution spectra. Exposure time was 50 ms/channel. MultiPak 9.0 software was used for peak fitting. From the measured intensities of spectral lines, the concentrations of all found chemical elements were calculated, taking into account the cross section for the yield of secondary electrons for a given element. Chemical bonds were determined by the magnitude of chemical shifts in the partial spectra of selected elements using the “Curve Fitting” iterative selection procedure. The spectral line width at half maximum (FWHM) during the Curve Fitting procedure was 0.9-0.6 eV. Identification of the connection was carried out based on a comparison of the measured shear energy values and those known from open libraries of international databases: “The International XPS Database of XPS Reference Spectra, Peak-fits & BE Tables”, “NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database” and “ThermoFisher Scientific”.
The topography of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating was observed by a commercial scanning electron microscope Nanoeducator II (NT-MDT Spectrum Instruments, Moscow, Russia). All of measurements were done in contact mode. Silicon ceramic tip was used as cantilever tip. The scanning area was 1000 nm. Arithmetic mean roughness (Ra) was obtained from AFM analyses.
The mechanical properties of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating, i.e., hardness and Young’s modulus, were measured by the method of “instrumental indentation” (ISO 14577-1) using a Dynamic Ultra Micro Hardness Tester DUH-211S (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) at 53 mN indenter load. The hardness of the coating was determined on three experimental samples, six tests on each. The maximum depth of penetration of the indenter into the coating is 0.25 μm. For each sample, 20 indentations were carried out. Tests were performed on the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating on a silicon substrate to ensure the accuracy of the experimental results. Young’s modulus and hardness values were obtained by the method of Oliver and Pharr [
48].
To determine the adhesion/cohesive strength, scratch resistance and the coatings destruction mechanism the scratch tester MFT-2000A (Rtec Instruments, USA) with a diamond spherical Rockwell C indenter with 120° apex angle and a radius of 200 μm was used. In all tests, the load increased linearly from 0.9 to 40 N at a scratch rate of 3.5 mm/min. The length of the scratch was 10 mm. The moment of adhesion or cohesive destruction of the coating was recorded visually after testing (using optical microscope), as well as based on changes in friction coefficient. The resulting critical loads Lc had been measured and used to assess adhesion strength for a specific reference compound coating/substrate.
The tribological evaluation of the coated substrates under dry conditions was performed using a ball on a disc tribometer MFT-2000A (Rtec Instruments, USA) according to ASTM wear testing standard G-99 [
49]. All tests were performed at 25
◦C with a relative humidity of approximately 50% by using an uncoated Ø=10 mm diameter 100Cr6 ball (ISO 683-17:2014, hardness 19 GPa). Specimens were tested under a 1 N normal load and 120 r/min sliding speed. The tests were carried out with a total sliding time of 30 min and a radius of 8 mm. During testing the friction coefficient was recorded as a function of the sliding distance. The total wear volume was calculated by measuring the track cross-sectional area with a stylus profilometer (Taylor–Hobson) at ten different locations along the wear track. The ASTM G-99 standard determines the amount of wear by measuring the appropriate linear dimensions of both specimens (ball and disk) before and after the test [
50]. Topography and wear analysis of the wear tracks on the basic parts and wear areas on the counterparts were conducted on one of the two samples after tribological testing by means of scanning electron microscopy (SEM, TESCAN MIRA 3 LMU, Czech Republic). The coating chemical composition and distribution of elements inside the wear tracks were determined using an energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) system (TESCAN MIRA 3 LMU, Brno-Kohoutovice, Czech Republic).
All of the obtained samples are characterized by almost the same microstructures, topography, phase composition, microhardness and wear resistance. Arbitrary selected data are presented in the paper.
3. Results
3.1. AlMo-30B4C coating: structure and phase composition
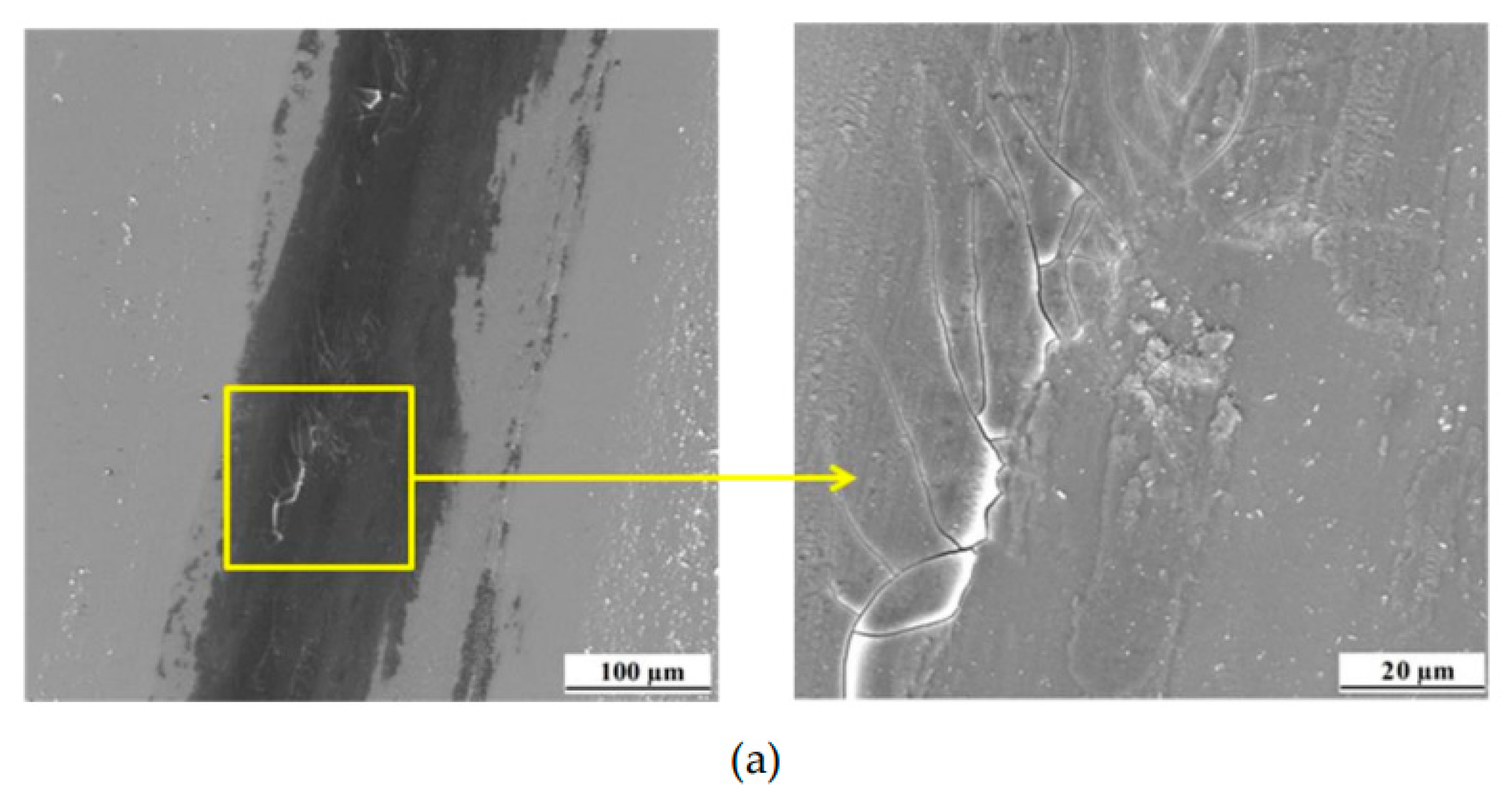
Figure 3 show the cross-sectional SEM images and X-ray diffraction pattern of the AlMo-30B
4C coating on surface of the target for magnetron sputtering. The coatings have thicknesses about 350-400 µm. The AlMo-30B
4C coating has a dense defect-free lamella-type structure with low porosity, less than 1%. It was shown that the coating structure was obtained as a result of the melting and spreading of Mo and Al metal particles. The B
4C powder particles caused no damage and showed traces of melting and were distributed throughout the entire depth of the coating (
Figure 3b,c).
The analysis of the distribution of the elements of the mixture of powders (B, C, Mo, Al) in the volume of the AlMo-30B
4C coating was study by EDX spectroscopy (
Figure 3b). Analysis of the cross section of the AlMo-30B
4C coating (
Figure 3) showed the presence of powder mixture elements (B, C, Mo, Al) in the volume of the coating. This confirms the good mixing of the components of the powder mixture in the process of preparing the mixture and in the process of detonation spraying of the coating. The elemental composition of the cross-sectional surface of the AlMo-30B
4C coating is shown in
Table 3.
X-ray diffraction analysis of the AlMo-30B
4C coating is given in
Figure 1d. The distinguished interplanar spacing calculated from reflections makes it possible to identify the following phases in the coatings: Mo (PDF: 4-804), confirming a cubic lattice structure; Al (PDF: 85-1327), confirming a cubic lattice structure; B
4C (PDF: 1-1163), confirming a rhombohedral lattice structure; which are also present in the feedstock powder, and a small amount of metal oxide phase–MoO
2 phase (PDF: 78-1073), confirming a monoclinic lattice structure. This is explained by the fact that the sprayed particles are not subject to strong oxidation during deposition. It is especially important to note that the use of the detonation spray method allows for a high rate of deposition of powder particles, which reduces the time during which the particles are in flight during coating application. This can reduce the likelihood of unwanted chemical reactions during the deposition process and improve the quality of the target coating.
3.2. Al-Mo-B(CN) coating: structure, elemental (concentrations, chemical states) and phase composition
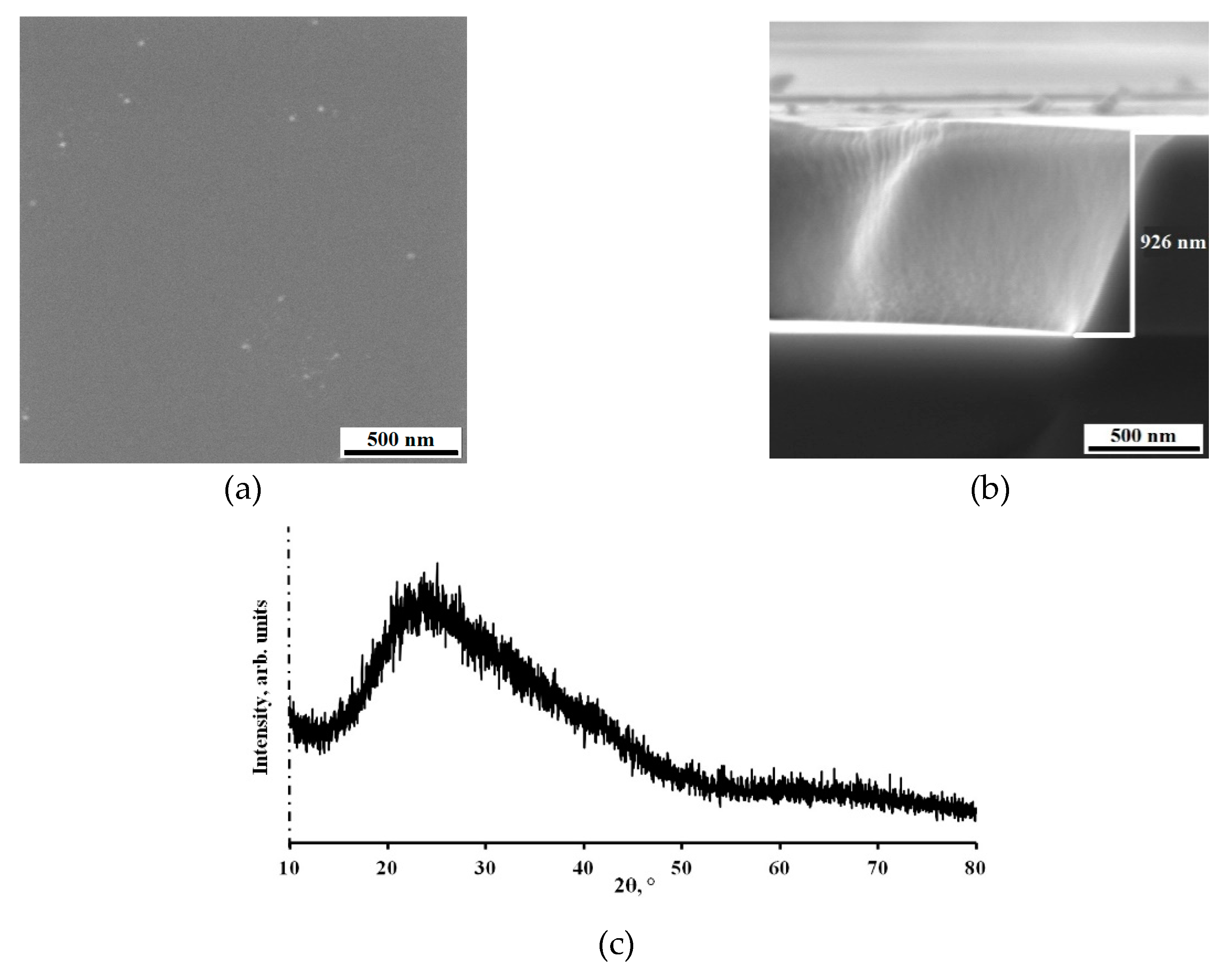
The SEM top view image, which can be seen on in Figure 4a, confirm the formation of smooth Al-Mo-B(CN) coating with slight roughness and a few scattered droplets.
Figure 4b shows characteristic image of cross-section fractures of coating deposited onto monocrystalline silicon substrate. It can be seen that the coating (thickness ~ 1 μm) is characterized by dense homogeneous with small drip inclusions structure with no columnar elements usually observed in Me-B (C or N) coatings [
15,
51,
52,
53]. It should be noted that the presence of a columnar structure, as a rule, worsens the mechanical properties of coatings due to intense diffusion of oxygen from the surface deep into the material along the boundaries of columnar grains [
1,
54,
55,
56]. The Al-Mo-B(CN) coating has a structure without typical growth defects (nodal, point, cone-shaped and open voids) for the magnetron sputtering process [
57]. Analogous morphology without any structural peculiarities was observed in Mo-Si-B-(N) [
1] and MoB(C) coatings [
17].
The results of X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD) of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coatings are given in
Figure 4c. A single broad peak dominates the pattern. A broad peak indicates an amorphous microstructure with short-range order or the presence of crystallites smaller than 2 nm, which is confirmed by previous results of other researchers [
41,
57,
58]. However, identifying the phases present in an Al-Mo-B(CN) coating is difficult because several crystalline phases can coexist in the amorphous matrix, which provides additional broadening of the diffraction peak.
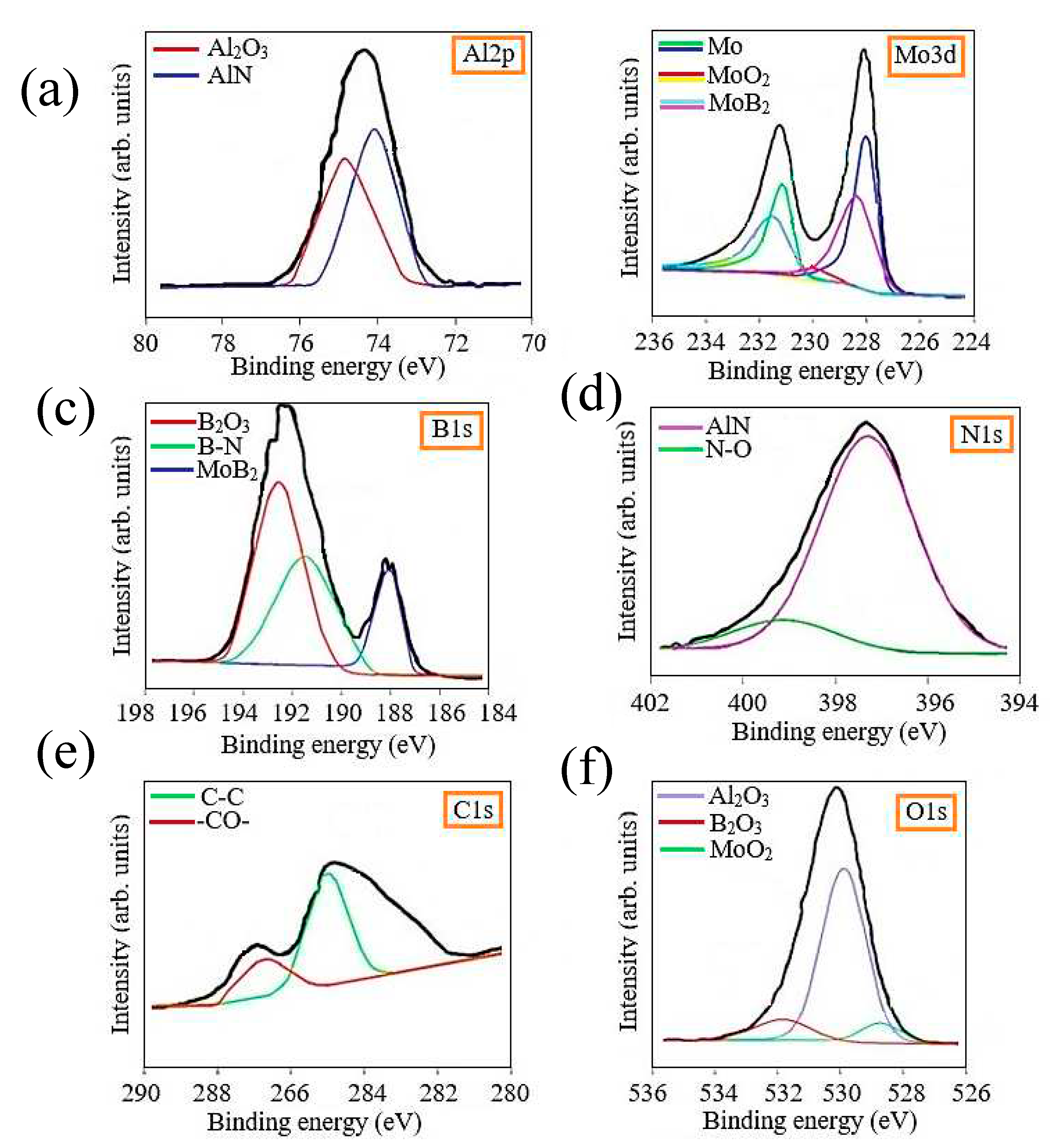
The surface of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating was analyzed by XPS in order to understand the chemical bonding state of the surface. All samples were analyzed after 30 min argon etching to remove the top contaminant layer. The Al2p, Mo 3d, B1s, N1s, C1s and O1s XPS core level spectra of Al-Mo-B(CN) coatings are presented in
Figure 5 to illustrate the chemical binding states of these elements near the surface region.
The presence of oxides in the coating is due to the presence of oxide compounds on the surface of the metal-ceramic target. From the deconvolution results of the C1s spectral peaks, it is clear that there were two different types of carbon bonds: the peak at 284.8 eV is assigned to the C-C sp2 bond, and the peak at 288.0 eV is assigned to the -CO- bond. The existence of a C-C bond indicated the existence of free carbon phases in the coating, which was also observed in other carbide coatings [
59], [
60]. As can be seen from the Mo 3d spectrum, the Mo 3d 5/2 peak centered at 227.8 eV and the Mo 3d 3/2 peak centered at 231.0 eV can be attributed to metallic Mo; the Mo 3d 5/2 peak at 230 eV and 233 eV can be attributed to MoO2, and the Mo 3d5/2 peak at 229 eV and 231.5 eV can be attributed to MoB2. The Al 2p spectra were separated into a higher intensity Al 2p3/2 peak located at 74.4 eV and a lower intensity Al 2p1/2 peak located at 75.9 eV, corresponding to Al–N and the Al-O chemical bond [
61,
62], respectively.
The Al-O bond may indicate the presence of oxygen in the form of amorphous Al2O3. For the N 1s ground level spectrum, which were deconvolved into two peaks. The first peak, located at 397.3 eV, is attributed to the Al-N bond, which proves the formation of AlN. The second peak at 399.1 eV matched well with the N-O bond that formed the Al-O-N system, an aluminum oxynitride phase. The O 1s core level spectrum consists of a peak at 531.1 eV and was assigned to the Al-O bond of amorphous Al2O3, which is consistent with the Al 2p1/2 peaks. XPS analysis confirmed the formation of the MoB2 and AlN phase with an admixture of oxygen in the form of aluminum oxide, molybdenum oxide and boron oxide.
The geometrical structure of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating was examined using an atomic force microscope (AFM). During measurement, area of 1000 x 1000 nm was scanned (Figure 6). The Al-Mo-B(CN) coating had a homogeneous surface with low roughness Ra 2.2 nm. The low roughness of coatings in the Me-B(CN) system was also noted earlier in [
9,
63,
64,
65].
The surface of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating is smooth and characterized by a granular surface morphology (
Figure 6) indicative of a fine, nanoscale grain structure which formed due to continuous renucleation during coating growth [
66]. Differences in the height and density of the protrusions indicate that the structure of the coating is polymorphic.
3.3. Mechanical properties of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating
Mechanical properties of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating, such as hardness (H), elastic modulus (E), elastic recovery (W), plasticity index (H/E), and plastic deformation resistance (H
3/E
2) are presented in
Table 4.
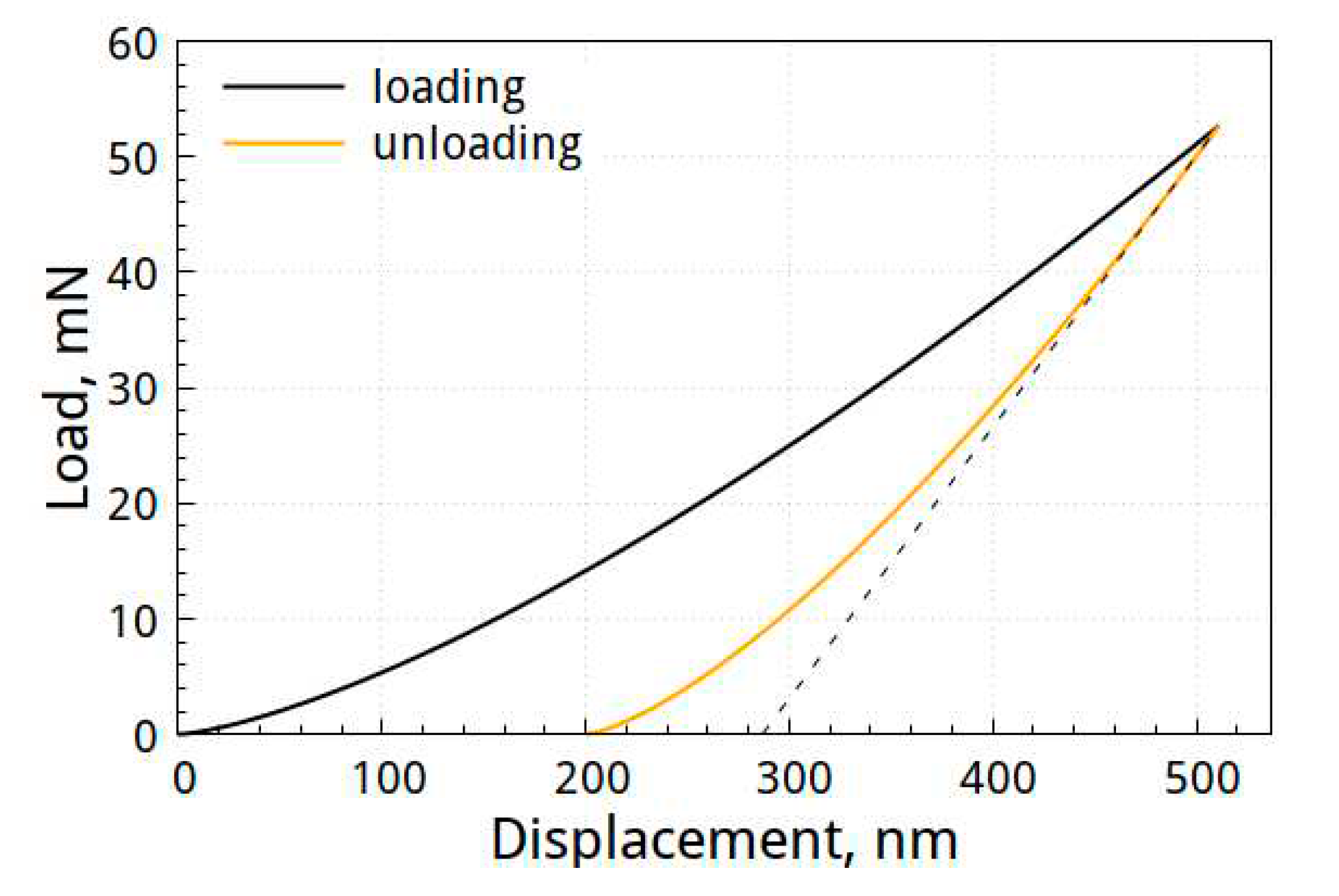
Figure 7 shows the load-displacement curve of the specimen deposited with the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
The hardness of the coatings was 13.0±3.6 GPa, the elastic modulus was 114±5.8 GPa, and the elastic recovery–45%. We should note that the mechanical properties of the obtained Al-Mo-B(CN) coating are consistent with those reported in [
67,
68,
69,
70].
Using nanoindentation data, the parameters H/E and H
3/E
2 were calculated (
Table 4), which, as was shown earlier [
71,
72], in a number of cases can serve as criteria for the wear resistance of coatings. Al-Mo-B(CN) coating has the high values of H/E = = 0.11 and H
3/E
2 = 0.17 GPa.
One of the most universal characteristic of the mechanical properties of coatings is their adhesive strength. In this paper, for its definition, the method of scratch testing was used (
Figure 8). The coating interfacial adhesive strength in scratch tests is normally indicated by critical loads Lc [
73].
At the beginning of the test (Lc1), at relatively low applied load a small number of cracks were observed without any chipping evident. In addition, Lc1 belongs to cohesive failure, which can evaluate the fracture resistance behavior of the coating [
74]. The friction force and scratch images are used as the criteria for evaluating the critical load of the coating.
The Lc1, Lc2, and Lc3 values can also be reflected from the CoF values shown in Figure 8. At the beginning of the scratch tests, the CoF increased significantly from 0 to ~0.1 due to the increasing contact area. After that, the CoF increased gradually with increasing applied load until it reached the Lc1 where the CoF jumped to ~0.15. Thereafter, the CoF remained stable until the end of the test (Figure 8).
For the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating, the initial cracking first occurred at Lc1 ~4 N (Figure 8). With increased applied load (Lc2, 8 N), first cracking within the scratched track and local spalling at the edge of the track started to occur. With increasing load the substrate is deformed and the tensile cracks become more severe on the coating’s surface progress to chipping of the coating due to the cohesive failure when the load exceeds the Lc3.
The coating did not delaminate completely up to a progressive load of 11 N, and failure of the coating was detected in a cohesive form (
Figure 8).
In the next step, tribological analyses were conducted for the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
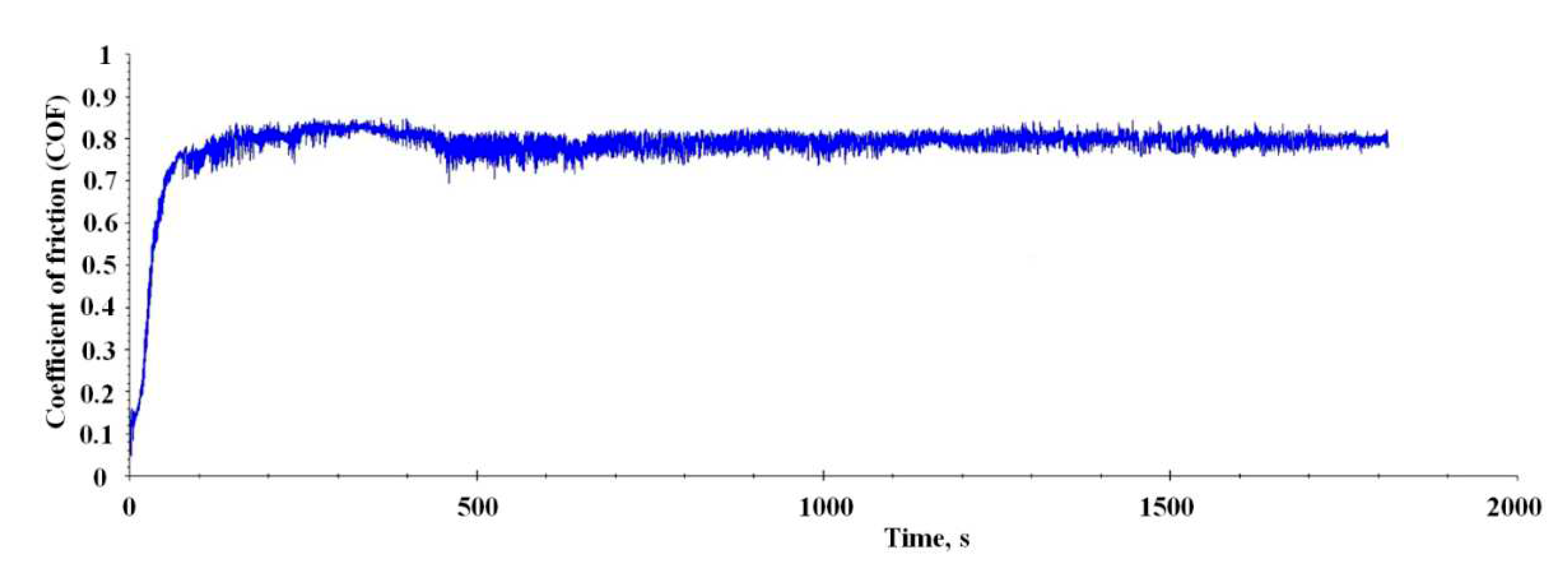
Figure 9 exhibit the friction coefficient curve of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating against steel 100Cr6 counterpart.
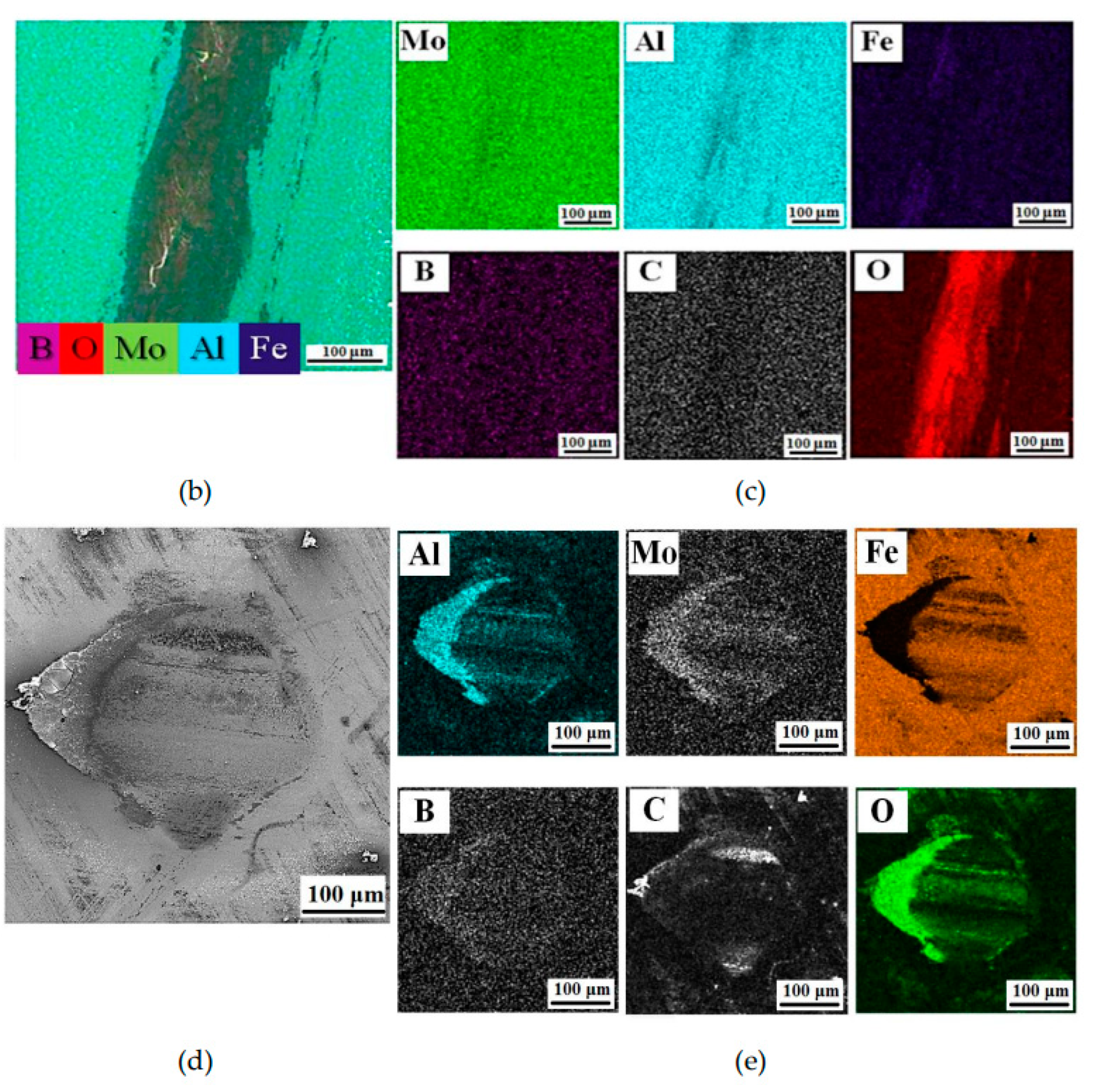
Curve shows a running-in period that extends over the about 450 second. A high and varying COF of 0.70 to 0.85 is found. After that initial period, a drop of COF towards a lower, basically constant COF of 0.75 to 0.80 is found. A detailed look into the wear scar was conducted (
Figure 10a,b). The surface of the wear track was found to be smooth, and had some delamination and fatigue cracks, and the edges of the track accumulate wear residues (
Figure 10a), which are typical signs of fatigue and abrasive wear [
75,
76]. The SEM image of wear track taken after tribological test and its EDS mapping for oxigen revealed that the surface of wear track was partly covered by oxide-based tribofilm (
Figure 10b). The corresponding elemental mapping for iron show a high concentration of iron inside the track that forms a layer parallel to the wear direction. This proves that the material of the counter body is oxygenized during the wear process, accumulates in the track and forms a discontinuous layer. The wear debris on the surface of counterpart material were observed to segregate on the edges of the tribocontact area (
Figure 10c). The layer of stuck wear products contained elements of both the coating and the counterpart material.
4. Conclusions
The composite metal-ceramic Al-Mo-B4C target manufactured by a robotic complex for detonation spraying of coatings, as well as the chemical composition, the microstructure and properties of thin Al-Mo-B(CN) coating synthesized by magnetron sputter deposition using this target have been investigated within this work.
The main results can be summarized as follows:
- copper cathode target with AlMo-30B4C coating of equipment for magnetron sputtering UNICOAT 200 (Russia) in the form of the plate (198×78×4 mm) was made;
- AlMo-30B4C coating (thickness ~ 350-400 µm) was fabricated by a robotic complex for detonation spraying;
- AlMo-30B4C coating has a dense defect-free lamella-type structure with low porosity, less than 1%;
- the XRD results revealed that the AlMo-30B4C coating consisted of the Mo, Al, B4C phases, and a small amount of metal oxide phase - MoO2 phase;
- the obtained composite metal-ceramic Al-Mo-B4C target was used to deposit the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating (DC mode) on flat specimens of AISI 316 steels and silicon using equipment for magnetron sputtering UNICOAT 200;
- a smooth Al-Mo-B(CN) coating (thickness ~ 1 μm) with little roughness (Ra 2.2 nm) and a small number of scattered droplets was formed;
- Al-Mo-B(CN) coating has dense homogeneous with small drip inclusions structure with no columnar elements and without typical growth defects (nodal, point, cone-shaped and open voids) for the magnetron sputtering;
- Al-Mo-B(CN) coating has an amorphous structure;
- XPS analysis confirmed the formation of the MoB2 and AlN phase with an admixture of oxygen in the form of aluminum oxide, molybdenum oxide and boron oxide;
- the hardness of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating was 13.0±3.6 GPa, the elastic modulus was 114±5.8 GPa, the elastic recovery - 45%, H/E - 0.11, and H3/E2 = 0.17 GPa;
- Al-Mo-B(CN) coating has a friction coefficient of 0.8 against steel 100 Cr6 ball and failure mode was fatigue and abrasive;
- the adhesion strength of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating amounted to about 11 N, and the failure mode was cohesive.
The results of this work open up new prospects for the further elaboration of novel, facile and economical technology to make composite cathodes for magnetron sputtering and synthesize composite nanostructured coating.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.S.; Data curation, S.Z. and D.P.; Formal analysis, M.L., A.S.; Investigation, M.K., S.Z. and M.L.; Methodology, D.P., M.L. and M.K.; Writing – original draft, V.S. and M.K. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Russian Science Foundation, under grant No 21-19-00536. The studies were carried out on the equipment of the Centre for High Technologies of BSTU using a unique scientific installation No. 3552744, and the Joint Research Center of Belgorod State National Research University «Technology and Materials».
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V. , Bondarev, A.V., Shtansky, D.V. Levashov, E.A. Structure and properties of nanocomposite Mo-Si-B-(N) coatings. Prot.Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2015, 51, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosminska, Y.O. , Kornyushchenko, G.S., Gannych, Y.V., Perekrestov, V.I. Fabrication and physical properties of coatings belonging to W, Ta, Hf, Ti, Mo, Cr, Al and C based multicomponent systems. J. Superhard Mater. 2020, 42, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, H.H. , Tzeng, Y.C., Syu, J.H. Study of the strengthening mechanism of electrodeposited Ni-B thin films with ultra-low boron content. Mater. Lett. 2019, 238, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, R.A. , Genel, K., Gulmez, T. Effect of electroless Ni-B and Ni-WB coatings on the corrosion-fatigue behavior of 7075 Al alloy. Int. J. Fatigue. 2021, 144, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V. , Sytchenko, A.D., Gorshkov, V.A., Loginov, P.A., Sheveyko, A.N., Nozhkina, A.V., Levashov, E.A. Complex study of protective Cr3C2–NiAl coatings deposited by vacuum electro-spark alloying, pulsed cathodic arc evaporation, magnetron sputtering, and hybrid technology. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 10921–10931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, Y.; Li, H.; He, T.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, H. Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of pulse electrodeposited Ni-B/B4C composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovskii, A.L. Mechanical and electronic properties of diborides of transition 3d–5d metals from first principles: toward search of novel ultra-incompressible and superhard materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 184–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitterer, C. Borides in thin film technology. J. Solid State Chem. 1997, 133, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, T. , Zubar, T., Chizhik, S., Gilewicz, A., Lupicka, O., Warcholinski, B. Surface microstructure of Mo(C)N coatings investigated by AFM. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 5450–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedfors, N. , Primetzhofer, D., Wang, L., Lu, J., Hultman, L., Jansson, U. Characterization of magnetron sputtered Cr-B and Cr-B-C thin films for electrical contact applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 266, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, J.-T. , Park, I.-W., Moore, J.J., Kang, M.C., Kim, K.H. Syntheses and mechanical properties of Ti-B-C coatings by a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stüber, M. , Schier, V., Holleck, H. Properties and performance of new metastable Ti-BC-N hard coatings prepared by magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1995, 74-75, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallia, B. , Stüber, M., Dearnley, P.A. Character and chemical-wear response of high alloy austenitic stainless steel (Ortron 90) surface engineered with magnetron sputtered Cr-B-N ternary alloy coatings. Thin Solid Films. 2013, 549, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.F. , Yuan, Z.G., Liu, Q., Wang, X.P., Fang, Q.F. Characterization of Mo-Al-N nanocrystalline films synthesized by reactive magnetron sputtering. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S. , Qi, M.W., Kwang, H.K., and Shin, J.H. Microstructural evolution and tribological behavior of Mo-Cu-N coatings as a function of Cu content. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. , Kamiya, K., Hashimoto, K., Nakanishi, S. In Situ CO2- emission assisted synthesis of molybdenum carbonitride nanomaterial as hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinovskis, P. , Palisaitis, J., Persson, P.O.Å., Jansson, U., Lewin, E. Synthesis and characterization of Mo-B-C thin films deposited by non-reactive DC magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totemeier, T.C. , Wright, R.N., Swank, W.D. FeAl and Mo–Si–B intermetallic coatings prepared by thermal spraying. Intermetallics. 2004, 12, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Wang, D., Yan, J. Preparation and characterization of MoSi2/MoB composite coating on Mo substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 589, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warcholinski, B. , Gilewicz, A., Kuznetsova, T.A., Zubar, T.I., Chizhik, S.A., Abetkovskaia, S.O., Lapitskaya, V.A. Mechanical properties of Mo(C)N coatings deposited using cathodic arc evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 319, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashov, A.E. , Lebedev, D.N., Potanin, A.Y., Levashov, E.A. Structure and properties of coatings produced by pulsed electrospark deposition on nickel alloy using Mo-Si-B electrodes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 335, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, Ph.V., Kudryashov, A.E., Levashov, E.A. Recent achievements on oxidation-resistant Cr-(Al)-Si-B, Mo-(Al)-Si-B, Zr-(Al)-Si-B coatings obtained by magnetron sputtering and pulsed electrospark deposition (part 2). Galvanotechnik. 2018, 109, 1044–1050.
- Wen, S.H. , Zhou, C.G., Sha, J.B., Microstructural evolution and oxidation behaviour of Mo-Si-B coatings on an Nb-16Si-22Ti-7Cr-2Al-2Hf alloy at 1250°C prepared by spark plasma sintering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 352, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L., Zhu, Y., Ren, X., Zhang, P., Qiao, J., Feng, P. Microstructure, properties and oxidation behavior of MoSi2-MoB-ZrO2 coating for Mo substrate using spark plasma sintering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 375, 773–781. [CrossRef]
- Buršík, J. , Buršíková, V., Souček, P., Zábranský, L., Vašina, P. Nanostructured Mo-B-C coatings. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2016, 68, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Zábranský, L. , Buršíková, V., Souček, P., Vašina, P., Buršík, J. On the study of the mechanical properties of Mo-B-C coatings. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 75, 24716–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buršíková, V. , Sobota, J., Grossman, J., Fořt, T., Dupák, L., Zábranský, L., Souček, P., Vašina, P., Buršík, J. Study of fracture resistance of nanolaminate coatings using indentation and impact tests. Solid State Phenom. 2017, 258, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, Ph.V., Sytchenko, A.D., Potanin, A.Yu., Vorotilo, S.A., Levashov, E.A. Mechanical properties and oxidation resistance of Mo-Si-B and Mo-Hf-Si-B coatings obtained by magnetron sputtering in DC and pulsed DC modes. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 403, 126373. [CrossRef]
- Sanchette, F. , Billard, A. Special Issue “Magnetron Sputtering Deposited Thin Films and Its Applications”. Coatings. 2020, 10, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, F.V. , Sheveiko, A.N., Komarov, V.A., Blanter, M.S., Skryleva, E.A., Shirmanov, N.A., Levashov, E.A., Shtansky, D.V. Nanostructured Ti-Cr-B-N and Ti-Cr-Si-C- N coatings for hard-alloy cutting tools. Russ. J. Non-Ferrous Metals. 2011, 52, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtansky, D.V. , Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, Ph.V., Sheveyko, A.N., Mavrin, B.N., Rojas, T.C., Fernandez, A., Levashov, E.A. Comparative investigation of TiAlC(N), TiCrAlC(N), and CrAlC(N) coatings deposited by sputtering of MAX- phase Ti2−xCrxAlC targets. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 3595–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V. , Pierson, J.F., Kuptsov, K.A., Shtansky, D.V. Hard Cr–Al–Si–B–(N) coatings deposited by reactive and non-reactive magnetron sputtering of CrAlSiB target. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 314, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, P.V. Pulsed magnetron sputtering of ceramic SHS targets as a promising technique for deposition of multifunctional coatings. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2020, 56, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotskaia, A. , Avdeeva, V., Bazhin, P., Mikheev, M., Stolin, A., Novikov, V., Kovaleva, M., Sirota, V. Coatings prepared by electro-spark alloying with SHS electrode materials based on Ti-B-Fe-AlN. Coatings. 2023, 13, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, A.F. , Amosov, A.P., Ermoshkin, A.A., Lavro, V.N., Altukhov, S.I., Latukhin, E.I., Davydov, D.M. Composition, structure, and properties of SHS-compacted cathodes of the Ti-C-Al-Si system and vacuum-arc coatings obtained from them. Russ. J. Non-ferrous Metals. 2014, 55, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potanin, A.Yu., Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, Ph.V., Rupasov, S.I., Pogozhev, Yu.S., Levashov, E.A. Application of SHS for production of composite ceramic cathodes for PVD of high-temperature protective Mo-(Hf/Zr)-Si-B coatings. In Proceedings of International symposium on self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Russia, Book of abstracts. - Chernogolovka, 2019, №XV, 357-358. [CrossRef]
- Kunc, F. , Musil, J., Mayrhofer, P.H., Mitterer, C. Low-stress superhard Ti-B films prepared by magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 174, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mraz, S., Emmerlich, J., Weyand, F., Schneider, J.M. Angle-resolved evolution of the composition of Cr-Al-C thin films deposited by sputtering of a compound target. J. Phys. D. 2013, 46, 135501. [CrossRef]
- Vasyliev, V.V. , Luchaninov, A.A., Reshetnyak, E.N., Strel’nitskij, V.E., Tolmacheva, G.N., Pribytkov, G.A., Gurskikh, A.V., Krinitcyn, M.G. Application of powder cathodes for Ti-Si-N coatings deposition from the filtered vacuum-arc plasma. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 148–163. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Rueß, H. , to Baben, M., Mráz, S., Shang, L., Polcik, P., Kolozsvári, S., Hans, M., Primetzhofer, D., Schneider, J.M. HPPMS deposition from composite targets: Effect of two orders of magnitude target power density changes on the composition of sputtered Cr-Al-C thin films. Vacuum. 2017, 145, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirota, V., Zaitsev, S., Prokhorenkov, D., Limarenko, M., Skiba, A., Kovaleva, M. NiB-CrC coatings prepared by magnetron sputtering using composite ceramic NiCr-BC target produced by detonation spray coating. Nanomater 2022, 12, 3584. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaleva, M. , Goncharov, I., Novikov, V., Pavlenko, I., Yapryntsev, M., Vagina, O., Sirota, V., Tyurin, Yu., Kolisnichenko, O., Krasil’nikov, V. Oxidation behavior and microstructural evolution of ZrB2-35MoSi2-10Al composite coating. Coatings. 2021, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirota, V. , Pavlenko, V., Cherkashina, N., Kovaleva, M., Tyurin, Y., Kolisnichenko, O. Preparation of aluminum oxide coating on carbon/carbon composites using a new detonation sprayer. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. 2021, 2, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilik, N., Tyurin, Yu., Kolisnichenko, O. Method for gas-dynamic detonating speedup of powders and device for its implementation. RU Patent 2506341.11 (2012).
- Tyurin, Yu., Kolisnichenko, O., Jia, J., Vasilik, N., Kovaleva, M., Prozorova, M., Arseenko, M., Sirota, V. Performance and economic characteristics of multi-chamber detonation sprayer used in thermal spray technology. In Proceedings of the International Thermal Spray Conference and Exposition; 2016 May 10–12. Shanghai, China: ASM International, 2016, 630-634. [CrossRef]
- Moskal, G.J. The porosity assessment of thermal barrier coatings obtained by APS method. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. 2007, 20, 483–486. [Google Scholar]
- Natu, V. , Kota, S.S., Barsoum, M.W. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of the MAB phases, MoAlB, M2AlB2 (M = Cr, Fe), Cr3AlB4 and their binary monoborides. J. Eur. Ceram. 2020, 40, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C. , Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM-G-99-05 Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-on-Disk Apparatus; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010; Volume 03.02, p. 6.
- Standard test method for wear testing with a Pin-on-Disk apparatus, ASTM G99-05, Book of ASTM Standards, American Soc. for Metals, vol. 03.02, 2010, 6 p.
- Yuan, Z.G. , Yang, J.F., and Wang, X.P. Characterization and properties of quaternary Mo–Si–C–N coatings synthesized by magnetron sputtering technique. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 205, 3307–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J., Sui, X., Lu, X., Wang, W., Hao, J., Wan, Y., Liu, W. A New insight into friction transfer behavior of MoCN coatings: the tribo-activated formation of carbonitride based nano-twisted helix wear debris, 2022, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square. [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, M. , Sprenger, D., Lang, B., Mitterer, C., Lorenz, R. Chemical composition and properties of MoAl thin films deposited by sputtering from MoAl compound targets. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 2017, A 35, 041504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, J. and Zeman, P., Hard a-Si3N4/MeNx Nanocomposite Coatings with High Thermal Stability and High Oxidation Resistance. Solid State Phenom. 2007, 127, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A. , Heilmaier, M., Sossamann, T.A., Perepezko, J.H. Oxidation behavior of pack-cemented Si–B oxidation protection coatings for Mo–Si–B alloys at 1300°C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 266, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panjan, P. , Drnovšek, A., Gselman, P., Čekada, M., Panjan, M. Review of growth defects in thin films prepared by PVD techniques. Coatings. 2020, 10, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šímová, V. , Vlček, J., Zuzjaková, Š., Houška, J., Shen, Y., Jiang, J., Peřina, V. Magnetron sputtered Hf-B-Si-C-N films with controlled electrical conductivity and optical transparency, and with ultrahigh oxidation resistance. Thin Solid Films, 2018, 653, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.L. , Huang, C.S., Jao, J.Y. Microstructural, mechanical and wear properties of Cr–Al–B–N coatings deposited by DC reactive magnetron co-sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011; 205, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. , Zhang, Z., Jing, Z., Wang, H., Yao, W., Liang, X. Characteristics of (Mo-Ta-W)-C and (Nb-Ta-W)-C refractory multi-principal element carbide thin films by non-reactive direct current magnetron co-sputtering. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 936, 168260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. , Xu, M., Zhang, H., He, W., Lu, Z. Effect of silicon-doping on the wide-temperature tribological behavior and lubrication mechanism of WC/aC film. Wear. 2023, 516, 204614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberger, L. , Baird, R., Mccullen, E., Auner, G., Shreve, G. XPS analysisofaluminumnitridefilmsdepositedbyplasmasourcemolecularbeamepitaxy. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manova, D. , Dimitrova, V., Fukarek, W., Karpuzov, D. Investigation of d.c.-reactive magnetron-sputtered AlN thin films by electron microprobe analysis, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and polarised infra-red reflection. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1998; 106, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F., Adachi, K., Kato, K. Influence of deposition parameters on surface roughness and mechanical properties of boron carbon nitride coatings synthesized by ion beam assisted deposition. Thin Solid Films. 2006, 497(1-2), 210-217. [CrossRef]
- Vishnyakov, V.M. , Ehiasarian, A.P., Vishnyakov, V.V., Hovsepian, P., Colligon, J.S. Amorphous boron containing silicon carbo-nitrides created by ion sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.O., Hernandez-Rengifo, E., Caicedo, J.C. Analysis of the tribological evolution of nitride-based coatings, In: G. Pintaude, T. Cousseau, A. Rudawska (Eds.), Tribology of Machine Elements - Fundamentals and Applications, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.C. , Kustas, F.M., Coulter, K.E., Crawford, G.A. Dense VSiCN coatings deposited by flament-assisted reactive magnetron sputtering with varying amorphous phase precursor flow rates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 422, 127507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Samra, H., Staedler, T., Xia, J., Aronov, I., Jia, C., Wenclawiak, B., Jiang, X. Deposition and characterization of nanocrystalline Mo2N/BN composite coatings by ECR plasma assisted CVD. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204, 1919-1924. [CrossRef]
- Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, F.V. , Sheveyko,A.N., Levashov, E.A., Shtansky, D.V. Investigation of the Si–B–C–N thin coatings deposited using magnetron sputtering of SiBC targets. Izvestiya. Non-Ferrous Metallurgy. 2015, 4, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobzin, K. , Brögelmann, T., Kalscheuer, C., Thiex, M. Self-lubricating triboactive (Cr,Al)N+Mo:S coatings for fluid-free applications. J Mater Sci. 2021, 56, 15040–15060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evertz, S. , Pöllmann, P., Holzapfel, D.M., Mayer, E., Schneider, J.M. Low temperature synthesis of dense MoAlB thin films. J. Eur. Ceram., 2021, 41, 6302–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levashov, E.A. , Shtansky, D.V., Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, Ph.V., Petrzhik, M.I., Tyurina, M.Ya., Sheveiko, A.N. Multifunctional nanostructured coatings: Formation, structure, and the uniformity of measuring their mechanical and tribological properties. Russ. Metall. 2010, 10, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyland, A. , Matthews, A. On the significance of the H/E ratio in wear control: a nanocomposite coating approach to optimised tribological behavior. Wear, 2020; 246, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. , Munroe, P., Zhou, Z., Xie, Z. Nanostructured molybdenum nitride-based coatings: Effect of nitrogen concentration on microstructure and mechanical properties. Thin Solid Films. 2019, 682, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.H. , Weng, C.H., Lai, C.H., Lin, S.J. Study on adhesion and wear resistance of multi-element (AlCrTaTiZr) N coatings. Thin Solid Films. 2009, 517, 4989–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. , Wang, Y., Yu, Z., Planche, M.-P., Peyraut, F., Liao, H., LaSalle, A., Allimant, A., Montavon, G. Microstructural, mechanical and tribological properties of suspension plasma sprayed YSZ/h-BN composite coating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 4512–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.-H. , He, P.-F., Wang, H.-D., Liu, M., Chen, S.-Y., Xing, Z.-G., Ma, G.-Z., Lv, Z.-L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mo coating deposited by supersonic plasma spraying. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 86, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The AlMo-30B4C composite powder: SEM micrograph (a,b), XRD pattern (b), and particle size distribution (c).
Figure 1.
The AlMo-30B4C composite powder: SEM micrograph (a,b), XRD pattern (b), and particle size distribution (c).
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Figure 3.
AlMo-30B4C coatings (cross-section): SEM micrographs (back-scattered electron mode) (a), SEM EDX element distribution maps (b), and X-ray phase analysis (c).
Figure 3.
AlMo-30B4C coatings (cross-section): SEM micrographs (back-scattered electron mode) (a), SEM EDX element distribution maps (b), and X-ray phase analysis (c).
Figure 4.
Al-Mo-B(CN) coating on Si wafers: SEM image of the fracture (a), and the surface (b), and X-ray phase analysis (c).
Figure 4.
Al-Mo-B(CN) coating on Si wafers: SEM image of the fracture (a), and the surface (b), and X-ray phase analysis (c).
Figure 5.
XPS spectra of Al2p (a), Mo 3d (b), B1s (c), N1s (d), C1s (e) and O1s (f) electrons for Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Figure 5.
XPS spectra of Al2p (a), Mo 3d (b), B1s (c), N1s (d), C1s (e) and O1s (f) electrons for Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Figure 6.
AFM microstructure of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating (scanning area 1000 nm): image 3D (a) and height map (b).
Figure 6.
AFM microstructure of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating (scanning area 1000 nm): image 3D (a) and height map (b).
Figure 7.
Load–displacement curve of specimen deposited with Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Figure 7.
Load–displacement curve of specimen deposited with Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Figure 8.
Friction coefficient vs. the applied load during scratch testing. Microphotographs of the destruction areas of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating after scratch tests. Areas correspond to loads of 4, 8 and 11 N.
Figure 8.
Friction coefficient vs. the applied load during scratch testing. Microphotographs of the destruction areas of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating after scratch tests. Areas correspond to loads of 4, 8 and 11 N.
Figure 9.
Coefficient of friction (COF) of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating against steel 100Cr6 counterpart with a diameter of d = 10 mm.
Figure 9.
Coefficient of friction (COF) of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating against steel 100Cr6 counterpart with a diameter of d = 10 mm.
Figure 10.
SEM images of wear track (a) and surface of counterpart (d); EDS mapping of the wear track (c) and surface of counterpart after the tribological tests of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Figure 10.
SEM images of wear track (a) and surface of counterpart (d); EDS mapping of the wear track (c) and surface of counterpart after the tribological tests of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Table 1.
Parameters of AlMo-30B4C coating deposition by a robotic complex for detonation spraying of coatings.
Table 1.
Parameters of AlMo-30B4C coating deposition by a robotic complex for detonation spraying of coatings.
Barrel length,
mm |
Barrel
diameter, mm |
Deposition distance, mm |
Powder Feed Rate, g/h |
Flow Rate of Fuel Mixture
Components, m3/h |
| Oxygen |
Propane |
Air |
| 300 |
18 |
70 |
800 |
*2.44/
**3.01 |
*0.51/
**0.53 |
*1.18/
**1.4 |
| *Cylindrical form combustion chamber. **Combustion chamber in the form of a disk |
Table 2.
Parameters of deposition of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating using UNICOAT 200.
Table 2.
Parameters of deposition of the Al-Mo-B(CN) coating using UNICOAT 200.
| Parameters |
Meaning |
| Leaking |
0.06 cm3/min |
| Operating pressure |
0.17 Pa |
| Working gas |
Ar (99.999% purity) |
| N2 (99.999% purity) |
| Total flow in the chamber |
Ar |
74 sccm* |
| N2 |
4 sccm |
| Current/Voltage |
|
| Target |
AlMo-30B4C |
2 A/580 V |
| Carbon |
0.8 A/489 V |
| Frequency |
14 kHz |
| Cathode material |
AlMo-30B4C
Carbon (99.999% purity) |
| Bias |
1 A/40 V |
| Magnetron-sample distance |
70 mm |
| Deposition time |
50 min |
| *sccm – standard cubic centimeters per minute |
Table 3.
Chemical composition of the AlMo-30B4C powder and coating, and Al-Mo-B(CN) coating (SEM, Figures1, 3 and 4).
Table 3.
Chemical composition of the AlMo-30B4C powder and coating, and Al-Mo-B(CN) coating (SEM, Figures1, 3 and 4).
| Material |
Element composition, wt% |
| Al |
Mo |
B |
C |
O |
N |
| AlMo-30B4C |
|
| powder |
26.50 |
28.64 |
25.41 |
7.01 |
12.33 |
0.11 |
| coating |
20.26 |
32.10 |
21.73 |
6.32 |
19.37 |
0.22 |
| Al-Mo-B(CN) coating |
25.04 |
37.55 |
10.38 |
7.24 |
12.68 |
7.02 |
Table 4.
Mechanical properties of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Table 4.
Mechanical properties of Al-Mo-B(CN) coating.
Hardness,
GPa |
E,
GPa |
H/E |
H3/E2,
GPa |
We,
% |
| 13.0±3.6 |
114±5.8 |
0.11 |
0.17 |
45 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).