1. Introduction
1.1. Digital Microfluidic Biochips (DMFBs)
Digital Microfluidic Biochips (DMFBs), a subtype of biochips, have transformed the biochemical processes industry with their capability to automatically execute operations on a miniature scale. These diminutive, efficient, and user-friendly devices, often referred to as "lab-on-chips," mark a significant improvement over traditional methodologies [
1,
2]. DMFBs serve a broad spectrum of applications, including DNA analysis, clinical diagnosis, and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) testing [
3,
4,
5]. The COVID-19 pandemic propelled DMFBs into the spotlight due to their ability to deliver rapid and reliable diagnostic results. For instance, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), a leading U.S. medical research agency, instituted the Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) initiative. RADx’s primary objective was to expedite the development, validation, and commercialization of innovative diagnostic technologies for COVID-19, with biochip technologies playing a pivotal role [
6].
From an aspect of research, not only error defections ways and droplet routing algorithms but also various kind of research are developing. For instance, biochip fabrication methodologies are constantly advancing [
7], and their integration with emergent technologies such as 5G communication, the Internet-of-Medical-Things (IoMT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and cloud computing are being explored [
8]. This convergence is aiding in the progress towards developing the concept of a hospital-on-chip (HOC).
As various types of biochips are being developed, DMFBs distinguish themselves from their predecessors by allowing for the manipulation of minuscule, discrete droplets on a device [
9,
10,
11]. They have capabilities to generate droplets from a reservoir, split droplets, mix different droplets, and move multiple droplets simultaneously [
12]. As illustrated in
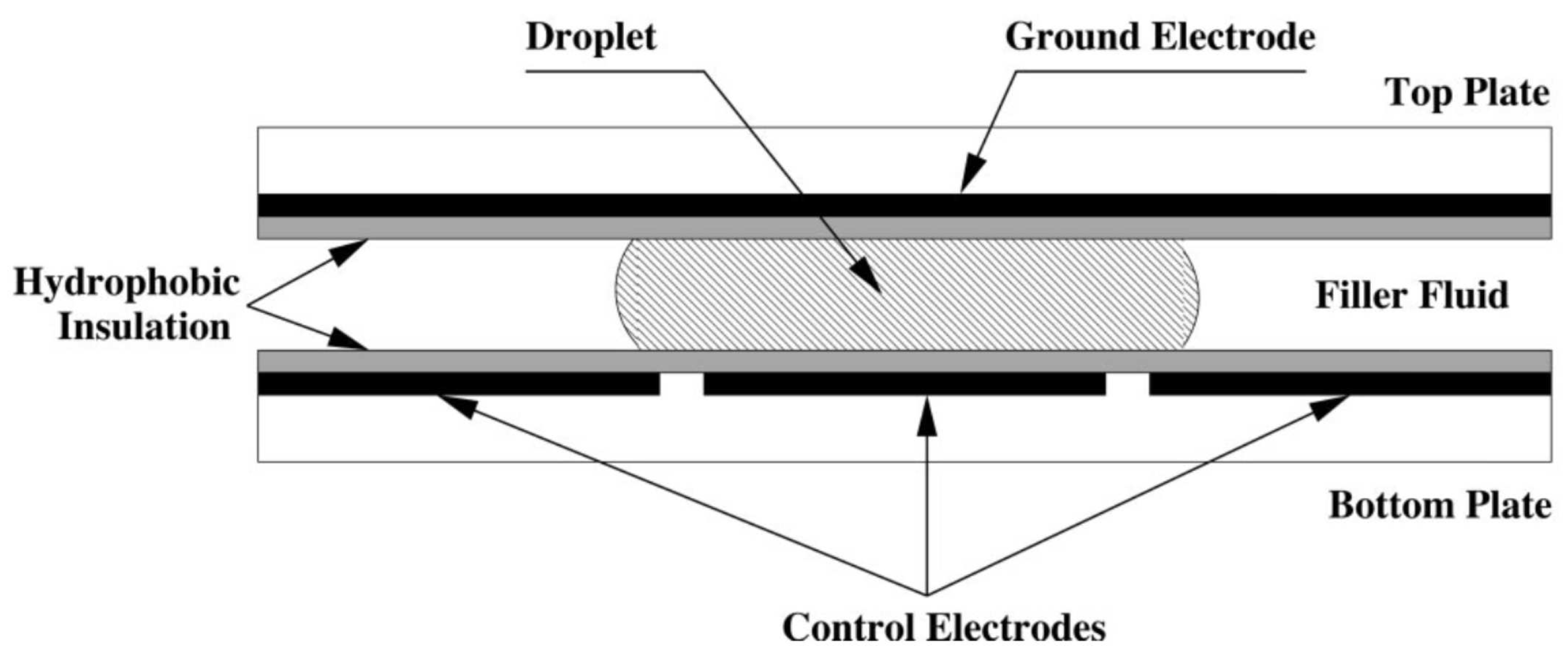
Figure 1, a droplet and hydrophobic insulation are placed between a ground electrode and a set of controllable electrodes. By varying the voltage across these controllable electrodes, DMFBs can manipulate droplets and perform a variety of movements. The Electrowetting-On-Dielectric (EWOD) technique, which manipulates the interfacial tension between a conductive fluid and a solid electrode via an applied electric field, is fundamental to the operation of DMFBs [
13].
However, despite these advancements, DMFB reliability is still a significant concern. Previous research has identified several potential error sources within DMFBs, classifiable as known or unknown errors [
14,
15,
16]. Known errors, such as cell degradation, droplet residue due to unexpected surface tension, and obstacles impeding droplet movement, can be identified prior to the routing process, often detected by sensors or cameras. While previous droplet routing algorithms have addressed these errors [
17,
18], unknown errors, such as electrode breakdown, unexpected electrode shorts with neighboring electrodes, or fluctuations in temperatures and heat that are undetectable by human or mechanical observers, are more elusive and challenging.
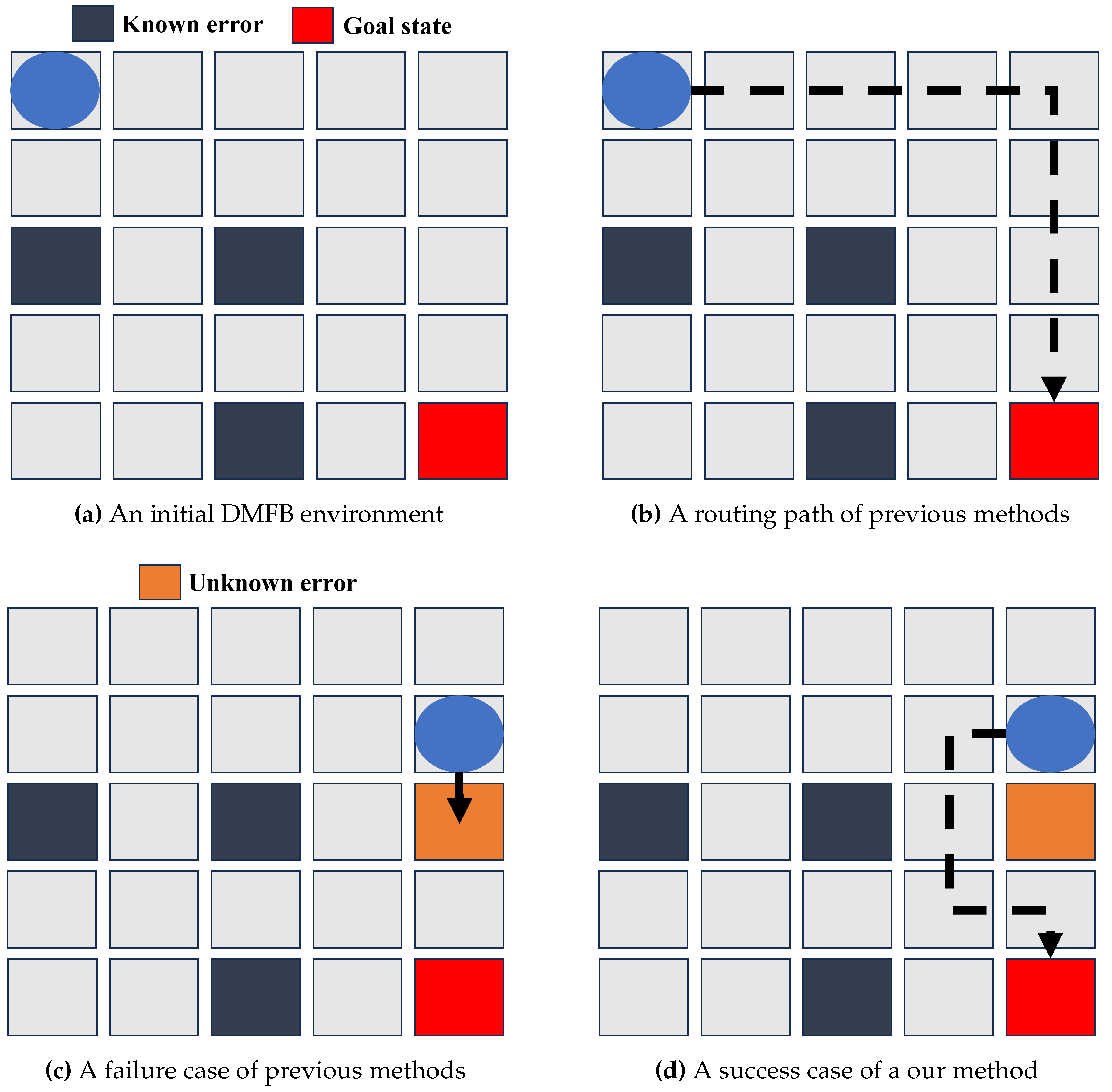
Certain unknown errors only surface during the routing process, and they pose significant challenges due to their unpredictability and difficulty to detect.
Figure 2 illustrates a practical scenario where conventional methods fall short in identifying and adapting to these unknown errors, which ultimately result in the failed routing. Traditional methods rely heavily on data provided by sensors or cameras prior to the routing, limiting their error detection capabilities to known issues like those depicted in
Figure 2. They consequently generate a routing path similar to what’s shown in
Figure 2. However, when an unknown error is present in the predetermined routing path, droplets become stuck in a single state. They persistently apply voltage to the unidentified erroneous cell, as portrayed in
Figure 2. This issue stems from the fact that these methods establish the routing path before the routing begins, utilizing information from sensors or cameras. Regrettably, unknown errors evade this detection system and only become evident during the routing process.
In actual biochip experiments, it’s crucial to accurately adapt not only known errors but also unknown errors in real-time since one of the most important factors of biochemical experiments is the reliability. Considering this issue, we propose an algorithm that considers both known and unknown errors, reflecting a more authentic biochip environment. By including not only known errors but also unknown ones in the training phase, our developed model can efficiently handle all types of errors, as shown in
Figure 2.
Not to consider all kinds of errors may lead to system failures or accidents. A case in point is Illumina’s NeoPrep device. Introduced in 2015, this
$40K instrument utilized DMFBs to automate DNA sequencing sample preparation [
19]. Despite its initial success in infectious disease testing and newborn disease detection, Illumina had to discontinue NeoPrep sales in 2017 due to significant reliability issues, which indicates the importance of error handlings in actual biochip experiments.
1.2. Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)
Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) is just the combination of two methodologies both Deep Learning (DL) and Reinforcement Learnig (RL). The main purpose of RL is to solve problems, intelligent agents performing actions and aiming to maximize the total rewards within the given environment [
20]. In addition to the RL approach, the development of DL significantly contributed to solving more complex tasks. For instance, in 2013, a Deep Q Learning algorithm was proposed as the first DRL algorithm [
21]. By adding two kinds of methods like experience replay and epsilon greedy strategies into the DRL algorithm, in 2015, the DRL model outperformed human experts in some Atari games [
22], which was the significant milestone of the development of DRL. Furthermore, the same year also witnessed the historical event of AlphaGO, a DRL model, which defeated a professional human Go player with a resounding score of 5-0 [
23]. This accomplishment demonstrated the impressive potential of DRL on a global states, as Go is a game known for its complexity and strategic dept. Today, the capabilities of DRL extend beyond game playing and into various complicated and high-stakes domains. The technology has been demonstrated in the StarCraft at the grand master level [
24], natural language processing [
25], predictions of 3D models of protein structures [
26] and so on.
1.3. Paper Contributions
This paper is an extended version of [
27], offering a more in-depth analysis of the algorithm’s performance and a broader range of experiments. The contributions of this paper are outlined below.
This paper presents a new deep reinforcement learning-based routing algorithm for Digital Microfluidic Biochips (DMFBs).
It contributes to the field by addressing the crucial issue of error management in DMFBs, specifically both known and unknown errors. It proposes and tests an algorithm that can effectively handle different types of errors, potentially boosting the reliability and efficiency of biochips.
In addition to proposing a new algorithm, this paper conducts extensive experiments to compare the performance of this algorithm against existing ones. The comprehensive results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm in terms of accuracy, optimality of the routing path, and error detection capability.
In this paper, we first introduce a new deep reinforcement learning-based routing algorithm for Digital Microfluidic Biochips (DMFBs) in
Section 3. We then provide a detailed description of the proposed framework in
Section 3.1, delving into the particulars of the environment in
Section 3.2 and the agent details in
Section 3.3. In the subsequent part of the paper, we focus on the verification of our proposition.
Section 4 contains a comprehensive account of the conducted experiments. The experimental setup is detailed in
Section 4.1 while
Section 4.2 elucidates the process of agent training. Subsequent to these,
Section 4.3 presents the results of the experiments. We finally draw the paper to a close in
Section 5 with the conclusion, providing a summary of the key research findings and their implications in the relevant field.
2. Related Works
Since 2004, the synthesis process of Digital Microfluidic Biochips (DMFBs) has involved several distinct steps. Initially, biologists developed a bioassay protocol [
28]. This protocol is subsequently mapped onto designated electrode areas, also known as fluidic modules, which facilitate the execution of fluidic operations [
29].
The transportation of droplets from one module to the next, known as droplets routing, is a critical part of the the synthesis process and developed in the past few decades. For instance, Huang et all introduced a fast routing method and performance-driven approach [
30]. They defined an entropy-based routing technique for the better routing method but were unable to efficiently manage the latest arrival time. To address blockages in biochips, Keszocze et all. introduced an exact routing method, which guaranteed optimal solutions for routing paths [
31]. Additionally, other strategies were implemented, such as calculating the Manhattan distance between the source and target to reduce pin count by Pan et al. [
32]. Even though these innovative approaches brought significant improvements, they came with a trade-off, specifically affecting resource efficiency in the system. Furthermore, a lot of routing methods have been proposed [
33,
34,
35]. These methods, however, are static and ignoring the fact that bichips have various kinds of errors like known errors and unknown errors [
14,
15,
16].
In order to address a degradation issue which is a type of known errors, an adaptive routing algorithm has been proposed [
18]. This algorithm’s primary function is to identify the health conditions of the electrodes, thereby facilitating reliable fluidic operations via a Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithm. However, this approach exhibits a limitation in its adaptability to unknown errors. This limitation stems from the fact that the method gets information about each electrode from the Charge-coupled Device (CCD) camera [
36,
37] before initiating the routing process. Consequently, this method falls short in handling unknown errors that may occur during the routing process or errors that remain undetectable by CCD cameras.
Another notable work in error management involves the proposal for the design of fault-tolerant and dynamically reconfigurable microfluidic biochips [
38]. The objective of this approach is to dynamically assign specific modules during the routing process while taking into account the fault tolerance of these modules. This strategy proves effective in detecting not just known errors but also unknown errors, while efficiently utilizing module placement. Despite these advantages, the method exhibits limitations in adapting to a comprehensive range of errors. For example, should an electrode fail during the routing process, a droplet will be immobilized, leading to the failure of the routing process. Additionally, the reassignment of modules to other cells reduces the number of cells available for other droplets to use in parallel.
3. Proposed DRL-based Routing Algorithm
3.1. Framework Description
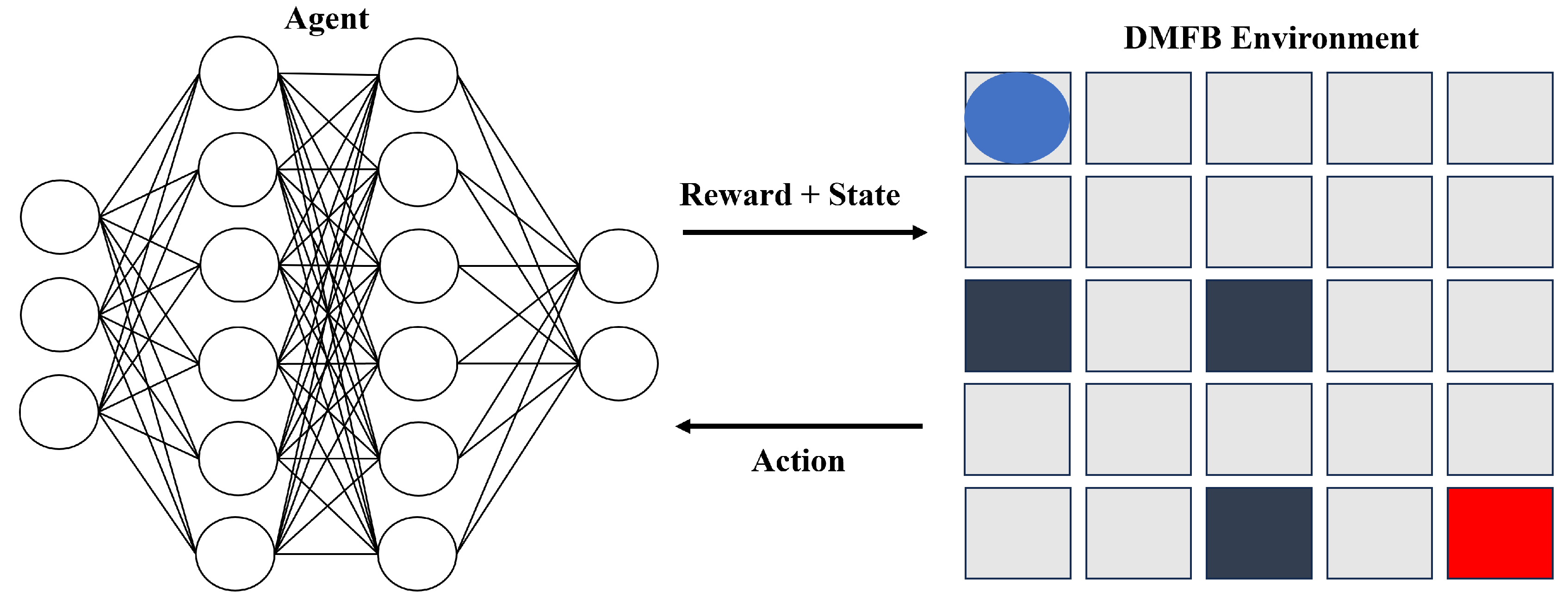
The framework we propose revolves around the interactive dynamics between an intelligent agent and a Digital Microfluidic Biochip (DMFB) environment. As illustrated in
Figure 3, the primary objective of this framework is to maximize the agent’s cumulative reward obtained from the DMFB environment.
3.2. Environment
An integral part of this proposed framework is the creation of a Digital Microfluidic Biochip (DMFB) environment. Initially, the DMFB environment designates the upper-left state as the starting point and the lower-right state as the goal. It also introduces both known and unknown errors at random positions to consider real DMFB environments having all kinds of errors. To ensure navigability, the DMFB environment employs the Breadth-First Search (BFS) algorithm. If the algorithm is unable to find a route from the start state to the goal state within the initially configured DMFB environment, the environment reinitializes itself. This process is repeated until at least one valid path from the starting state to the goal state is established.
Upon successful initialization, the DMFB environment begins its interaction with the agent. It accepts an action input from the agent and, in response, provides the corresponding reward and state updates. Given the nature of DMFB operations, a droplet has four possible movements at any given moment: up, down, right, and left. Therefore, the DMFB environment also offers these four action choices. The current state provided by the DMFB environment includes the droplet’s status, the goal state, and the presence of any known errors, which are provided from a CCD camera in real experiments [
36,
37]. Furthermore, if a droplet exhibits irregular movements, the DMFB environment incorporates unknown error information into the state. This ability to add unknown error information enhances the proposed algorithm’s adaptability in handling unexpected errors. The rewards provided by the DMFB environment to the agent are detailed in
Table 1. The maximum number of steps, as mentioned in the table, is calculated as 2 × (w + h), where ’w’ represents the width, and ’h’ denotes the height of the biochip. This framework allows the algorithm to navigate efficiently in a DMFB environment, making it an integral part of the system’s adaptive learning process.
3.3. Agent
In our proposed framework, the agent is represented by a Deep Neural Network (DNN), leveraging a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) [
39] architecture. The fundamental purpose of the learning process is to find the optimal configuration of parameters that best fits the model. This process dynamically interacts with the Digital Microfluidic Biochip (DMFB) environment, determining the agent’s behavior and its learning trajectory.
The CNN agent utilizes a 3D array input, which contains critical information pertaining to the current state of a droplet, the desired goal state, and the presence of any known errors. If we denote the size of the biochip as (w × h), the size of the input array is then configured as (w, h, 3). This structure guarantees a comprehensive representation of the DMFB environment, enabling the agent to make informed and effective decisions.
The detailed architecture of the CNN can be seen in
Table 2. It follows a layered structure, beginning with convolutional layers, which are primarily tasked with feature extraction. The first layer utilizes 32 filters, while the second and third layers use 64 filters each. All three layers employ the ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) activation function, introduced to add non-linearity into the model. Following the convolutional layers, two linear layers are deployed. The first possesses 256 nodes and also applies the ReLU activation function. The second linear layer, depending on its function, may have 4 nodes for the actor network or a single node for the critic network. The Softmax activation function is applied to this layer, enabling it to generate a probability distribution for the agent’s potential actions.
As the agent continually interacts with and adjusts to the DMFB environment, it refines its understanding of the system. This leads to the optimization of its actions, thereby maximizing the cumulative rewards. As a result, the agent’s performance in navigating the DMFB environment improves.
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
The experiments conducted in this study involve a rigorous exploration of the performance and response of varying sizes of biochips. To ensure a thorough understanding of the system behavior, a total of nine different biochip sizes were evaluated. The specific sizes selected for this study include: , , , , , , , , and .
In order to better understand the system’s robustness against errors and to simulate real-world conditions, error rates were systematically incorporated in the test cases. These error rates ranged from 0% to 10% for each biochip size. Specific combinations of known and unknown error rates were used, such as (0,5), (5,5), and (0,10). Each tuple represents the known error rate first, followed by the unknown error rate. The experiments were carried out on a machine with the following specifications:
4.2. Agent Training
In the training process, we leverage the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm [
40]. The PPO algorithm is an advanced form of policy gradient methods and amalgamates the principles of the Actor-Critic (A2C) method [
41]. It is an evolutionary development from the Trust Region Policy Optimization (TRPO) algorithm [
42] and is favored for its balance between algorithmic complexity and performance outcomes. Our training process is structured into epochs, with each epoch encompassing 10,000 games. Following the conclusion of each epoch, we undertake a comprehensive evaluation of the model against a set of 100 diverse test cases. The model’s performance is considered satisfactory if it can successfully discover a routing path in every single test case.
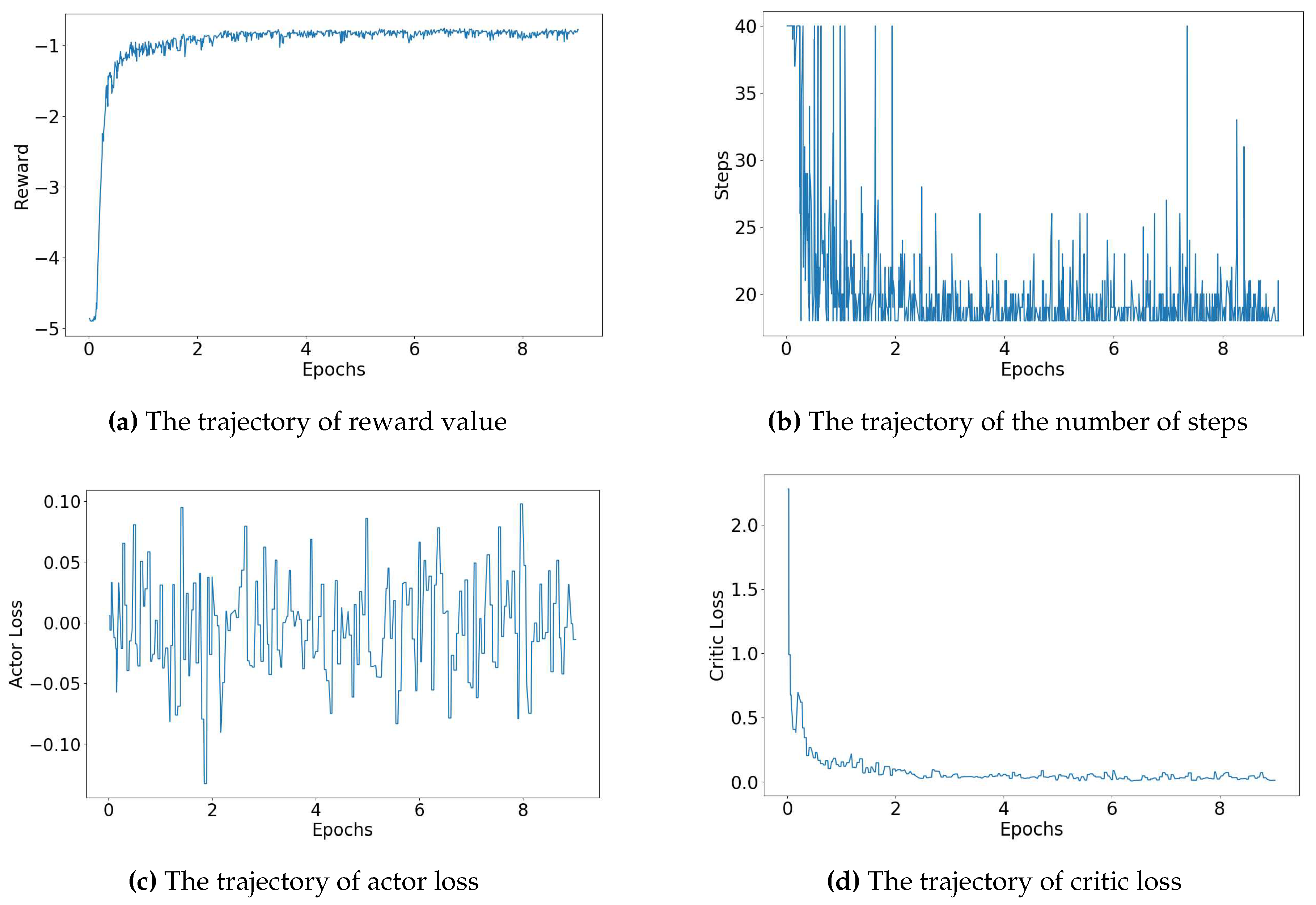
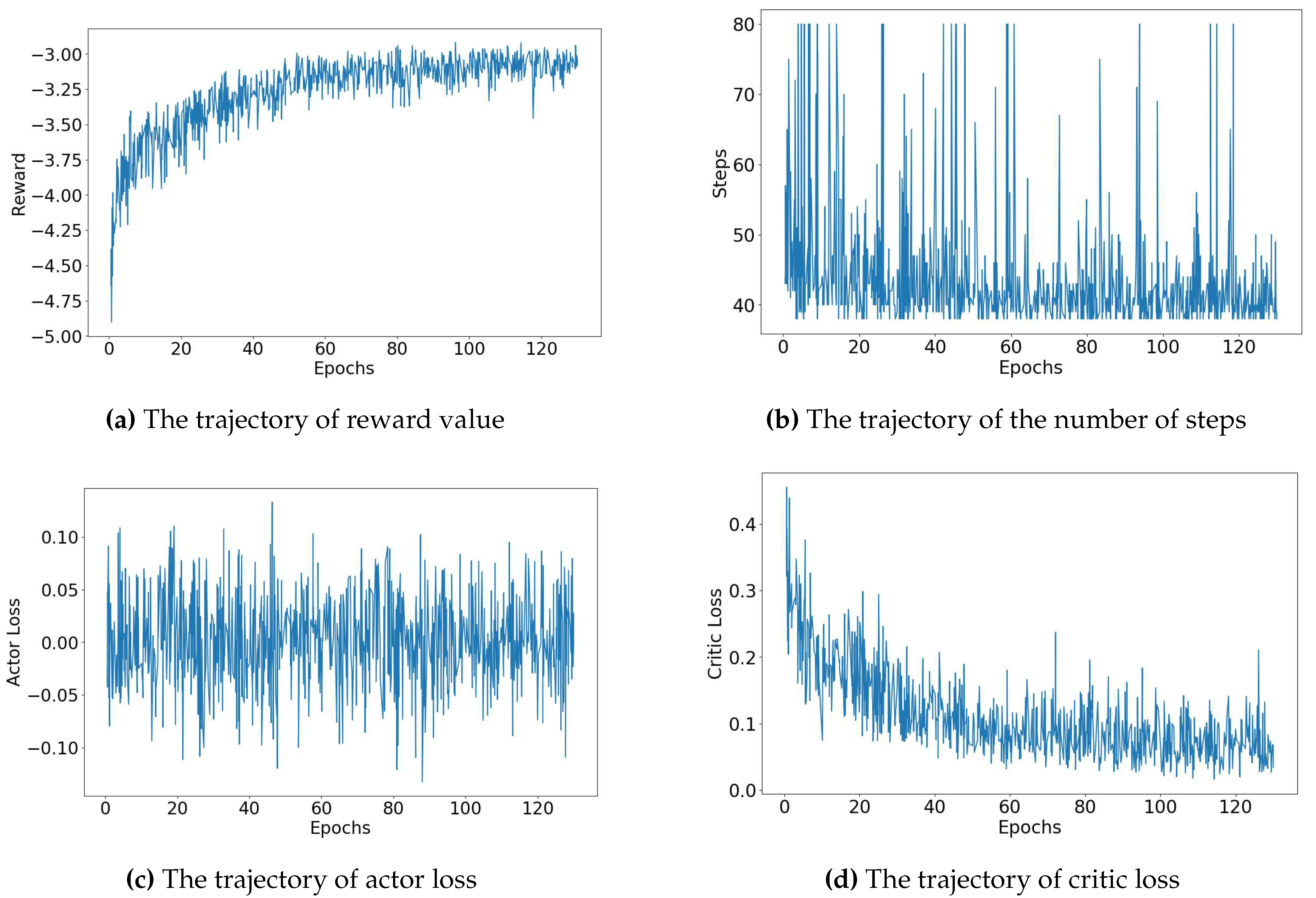
In
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, we provide a thorough depiction of the training trajectories, illustrating the accumulated rewards from the environment, the number of steps taken by the agent throughout the training process, and the loss of each network, actor and value network. These trajectories are shown for two different biochip sizes:
and
.
Figure 4 provides a detailed visual breakdown of the trajectories for the
biochip size, considering error rate denoted by (5, 5) - representing the rate of known errors and the rate of unknown errors respectively. The agent’s rewards, depicted in
Figure 4, gradually increase, suggesting the agent’s success in refining its policy to maximize rewards from the environment. Concurrently, the number of steps, displayed in
Figure 4, decreases, indicating that the agent learns to find the routing path more efficiently over the training period. The actor loss, exhibited in
Figure 4, corresponds to the loss of the actor network, which is responsible for guiding the agent’s policy. In contrast, the critic loss, displayed in
Figure 4, pertains to the loss of the critic network, which evaluates the agent’s value function. As shown in
Figure 4, both the total and critic losses decrease as the training process advances, while the actor loss hovers around zero. This trend indicates a continuous improvement in the agent’s performance, as it learns to balance exploration and exploitation. Remarkably, in the scenario of a
biochip size with an error rate denoted by (5, 5) - representing the rate of known errors and the rate of unknown errors, respectively - the agent required only approximately 22 minutes to satisfactorily accomplish the routing process across all test cases.
In comparison,
Figure 5 traces the trajectories for a larger
biochip size, also considering the same error rate denoted by (5, 5). In this case, the agent required 16 hours to satisfactorily complete the routing process across all test cases. Despite the difference in training times for the two biochip sizes, our reinforcement learning agent demonstrates promising training in handling both small and larger problem instances.
4.3. Experimental Results
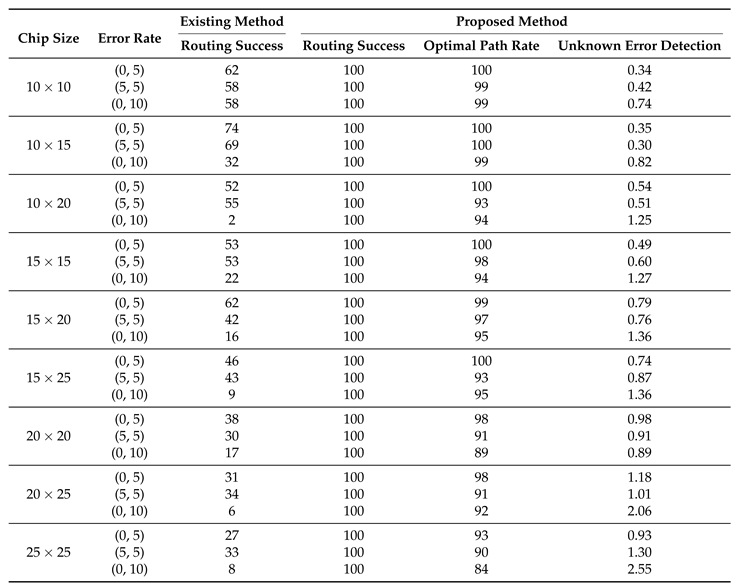
In
Table 3, we provide data on the performance of routing algorithms in the test cases. The table presents several experimental results that compare the performance of a proposed routing method [
18] versus an existing method across various chip sizes and error rates. The table includes six columns, each representing a different factor. ’Chip Size’ represents the physical dimensions of the chip being tested. ’Error Rate’ is the frequency of known and unknown errors occurring, represented as a pair of rate (known errors, unknown errors). ’Routing Success’ shows the success rate of the droplet reaching its target; this is divided into the proposed method and the existing one. ’Optimal Path Rate’ is the rate at which the droplet uses the shortest routing path, computed by the breadth-first search (BFS) algorithm. ’Unknown Error Detection’ measures how many unknown errors were detected during the routing process. We will now dive deeper into interpreting these results and evaluating their implications.
The experimental results showcase a significant comparison between the proposed routing algorithm and the existing methods across different chip sizes and error rates. The result makes it evident that the proposed algorithm outperforms the existing methods in almost all aspects and conditions.
Starting with the chip size of , for all error rates, the proposed algorithm showcases a perfect routing success rate of 100%. This is substantially higher than the routing success rates of the existing methods, which vary from 58% to 62%. Such results illustrate the robustness of the proposed algorithm even in the presence of errors. This trend is consistent across all chip sizes, where the proposed algorithm maintains a 100% success rate, while the existing methods show a decreased success rate with larger chip sizes and higher error rates. For instance, in the chip size with an error rate of (0,10), the existing method has a significantly lower success rate of 6%, compared to the 100% success rate of the proposed algorithm.
Further, the ’Optimal Path Rate’ shows how efficiently the routing is performed. A higher rate indicates that the routing is carried out using the minimum number of cells, which signifies a more efficient and optimal path. For all chip sizes and error rates, the proposed algorithm consistently outperforms the existing method, often achieving a 100% rate. This signifies that not only is the proposed algorithm more successful in routing, but it also does so in the most optimal way. However, it’s important to understand why the optimal path rate isn’t always 100%. The routing process is a dynamic one, and during this process, if an unknown error is detected in a state nearer to the droplet, the proposed algorithm smartly avoids this error. This detour results in a path that sometimes deviates from the originally calculated optimal path, which, in turn, lowers the optimal path rate. This mechanism allows for a safer and more reliable routing process, even if it means straying from the optimal path.
Lastly, ’Unknown Error Detection’ captures the number of unknown errors detected during the routing process. A higher value is desirable as it signifies better error detection capability. This is not just about managing current routing tasks. Detecting unknown errors plays a critical role in facilitating smoother routing in the future. As an error is detected, it becomes a known factor that the routing algorithm can account for in subsequent computations. This enables the algorithm to make more informed routing decisions, effectively avoiding previously detected error zones. It’s worth noting that as the chip size and error rates increase, the proposed algorithm tends to detect more unknown errors, ranging from 0.34 to 2.55. This robust error detection capability, therefore, ensures not just the success of the current routing process, but it also significantly enhances the efficiency and reliability of future routing operations.
Overall, the experimental results provide compelling evidence of the superior performance of the proposed algorithm over existing methods. This superiority is observed across various chip sizes and error rates, highlighting the proposed algorithm’s robustness, efficiency, and improved error detection capabilities. These attributes make it a highly promising alternative for routing in biochips, potentially leading to more accurate results and fewer process interruptions due to errors.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this research introduced a deep reinforcement learning-based routing algorithm for Digital Microfluidic Biochips (DMFBs). The significance of this work lies in the fact that it not only accounts for known errors but also effectively manages unknown errors, which have been a major reliability issue for biochips.
Our experimental results provide strong evidence of the algorithm’s superior performance in three key areas. Firstly, it demonstrated an impressive success rate in routing, consistently outperforming previous methods across all tested chip sizes and error rates. Secondly, the proposed algorithm showed exceptional proficiency in identifying the most efficient routing paths. Even in scenarios where unknown errors were detected during the routing process, the algorithm smartly adapted to the new circumstances, ensuring a successful routing outcome, even if it meant diverging from the initially computed optimal path. Finally, the algorithm’s capability to automatically detect unknown errors during the routing process was a critical asset. This feature didn’t just enhance the current routing process, it also improved the efficiency and reliability of future routing tasks. By turning unknown errors into known factors, the algorithm evolved to be more informed and adaptive, further strengthening its robustness. In terms of accuracy, optimality of the routing path, and the number of detected unknown errors during the routing process, the proposed algorithm outperformed existing ones, thus offering a substantial improvement for DMFB routing.
Given the critical role of DMFBs in various fields, including DNA analysis, clinical diagnosis, and PCR testing, the proposed algorithm’s superior performance and error management capability present a promising advance towards more reliable and efficient biochip operations. As we move forward, we aim to continue refining our algorithm and expanding its application to further enhance DMFB reliability and efficiency.
Acknowledge
This work is partly supported by KAKENHI 20H04160 and 20H00590.
References
- Azizipour, N.; Avazpour, R.; Rosenzweig, D.H.; Sawan, M.; Ajji, A. Evolution of biochip technology: A review from lab-on-a-chip to organ-on-a-chip. Micromachines 2020, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Chakrabarty, K. High-level synthesis of digital microfluidic biochips. ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems (JETC) 2008, 3, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sista, R.S.; Ng, R.; Nuffer, M.; Basmajian, M.; Coyne, J.; Elderbroom, J.; Hull, D.; Kay, K.; Krishnamurthy, M.; Roberts, C.; others. Digital microfluidic platform to maximize diagnostic tests with low sample volumes from newborns and pediatric patients. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Connolly, J.; Khlystov, A.; Fair, R.B. Digital microfluidics for the detection of selected inorganic ions in aerosols. Sensors 2020, 20, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguli, A.; Mostafa, A.; Berger, J.; Aydin, M.Y.; Sun, F.; Ramirez, S.A.S.d.; Valera, E.; Cunningham, B.T.; King, W.P.; Bashir, R. Rapid isothermal amplification and portable detection system for SARS-CoV-2. The National Academy of Sciences 2020, 117, 22727–22735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachter, S.C.; Dunlap, D.R.; Lam, W.A.; Manabe, Y.C.; Martin, G.S.; McFall, S.M. Future potential of Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx Tech) in molecular diagnostics. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics 2021, 21, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhar, D.S.; Kumari, R.; Malode, S.J.; Shetti, N.P.; Chandra, P. Integrated lab-on-a-chip devices: Fabrication methodologies, transduction system for sensing purposes. The Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2023, 223, 115120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Khanna, V.; Awan, H.T.A.; Singh, K.; Khalid, M.; Mishra, Y.K.; Bhansali, S.; Li, C.Z.; Kaushik, A. Towards hospital-on-chip supported by 2D MXenes-based 5th generation intelligent biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2023, 220, 114847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, T.; Maerkl, S.J.; Quake, S.R. Microfluidic large-scale integration. Science 2002, 298, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verpoorte, E.; De Rooij, N.F. Microfluidics meets MEMS. The IEEE 2003, 91, 930–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, M.G. Electrowetting-based microactuation of droplets for digital microfluidics; The Duke University, 2001.
- Cho, S.K.; Moon, H.; Kim, C.J. Creating, transporting, cutting, and merging liquid droplets by electrowetting-based actuation for digital microfluidic circuits. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems 2003, 12, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Pollack, M.G.; Fair, R.B.; Shenderov, A.D. Electrowetting-based actuation of liquid droplets for microfluidic applications. Applied Physics Letters 2000, 77, 1725–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, H.; Prins, M. Reversible electrowetting and trapping of charge: model and experiments. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6616–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, E.R.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Madison, A.; Fair, R.B. Picoliter DNA sequencing chemistry on an electrowetting-based digital microfluidic platform. Biotechnology Journal 2011, 6, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Chakrabarty, K.; Fair, R.B. Microfluidics-based biochips: technology issues, implementation platforms, and design-automation challenges. IEEE Transactions on Computer-aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 2006, 25, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chakrabarty, K. Cross-contamination avoidance for droplet routing in digital microfluidic biochips. IEEE Transactions on Computer-aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 2012, 31, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.C.; Zhong, Z. Adaptive droplet routing in digital microfluidic biochips using deep reinforcement learning 2020.
- Li, J.; others. Current commercialization status of electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD) digital microfluidics. Lab On A Chip 2020, 20, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S. Dyna, an integrated architecture for learning, planning, and reacting. ACM Sigart Bulletin 1991, 2, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Graves, A.; Antonoglou, I.; Wierstra, D.; Riedmiller, M. Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv, 2013; arXiv:1312.5602. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; others. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; Van Den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M.; others. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinyals, O.; Babuschkin, I.; Czarnecki, W.M.; Mathieu, M.; Dudzik, A.; Chung, J.; Choi, D.H.; Powell, R.; Ewalds, T.; Georgiev, P.; others. Grandmaster level in StarCraft II using multi-agent reinforcement learning. Nature 2019, 575, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Almeida, D.; Wainwright, C.; Mishkin, P.; Zhang, C.; Agarwal, S.; Slama, K.; Ray, A.; others. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2022, 35, 27730–27744. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; others. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, T.; Shiro, C.; Nishikawa, H.; Kong, X.; Tomiyama, H.; Yamashita, S. A Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Routing Algorithm for Unknown Erroneous Cells in DMFBs 2023. pp. 1–5.
- Su, F.; Chakrabarty, K. Architectural-level synthesis of digital microfluidics-based biochips 2004. pp. 223–228.
- Chakrabarty, K.; Fair, R.B.; Zeng, J. Design tools for digital microfluidic biochips: toward functional diversification and more than moore. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 2010, 29, 1001–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.W.; Ho, T.Y. A fast routability-and performance-driven droplet routing algorithm for digital microfluidic biochips 2009. pp. 445–450.
- Keszocze, O.; Wille, R.; Drechsler, R. Exact routing for digital microfluidic biochips with temporary blockages 2014. pp. 405–410.
- Pan, I.; Samanta, T. Weighted optimization of various parameters for droplet routing in digital microfluidic biochips 2014. pp. 131–139.
- Su, F.; Chakrabarty, K. Yield enhancement of reconfigurable microfluidics-based biochips using interstitial redundancy. ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies in Computing Systems (JETC) 2006, 2, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Chakrabarty, K. Integrated droplet routing in the synthesis of microfluidic biochips 2007. pp. 948–953.
- Zhao, Y.; Chakrabarty, K. Simultaneous optimization of droplet routing and control-pin mapping to electrodes in digital microfluidic biochips. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 2012, 31, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Chakrabarty, K.; Ho, T.Y. Error recovery in cyberphysical digital microfluidic biochips. IEEE Transactions on Computer-aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems 2012, 32, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willsey, M.; Stephenson, A.P.; Takahashi, C.; Vaid, P.; Nguyen, B.H.; Piszczek, M.; Betts, C.; Newman, S.; Joshi, S.; Strauss, K. ; others. Puddle: A dynamic, error-correcting, full-stack microfluidics platform 2019. pp. 183–197.
- Su, F.; Chakrabarty, K. Design of fault-tolerant and dynamically-reconfigurable microfluidic biochips 2005. pp. 1202–1207. pp. 2005, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2012, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Badia, A.P.; Mirza, M.; Graves, A.; Lillicrap, T.; Harley, T.; Silver, D.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Asynchronous
methods for deep reinforcement learning 2016. pp. 1928–1937.
- Schulman, J.; Levine, S.; Abbeel, P.; Jordan, M.; Moritz, P. Trust region policy optimization 2015. pp.
1889–1897.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).