Submitted:
26 September 2023
Posted:
27 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
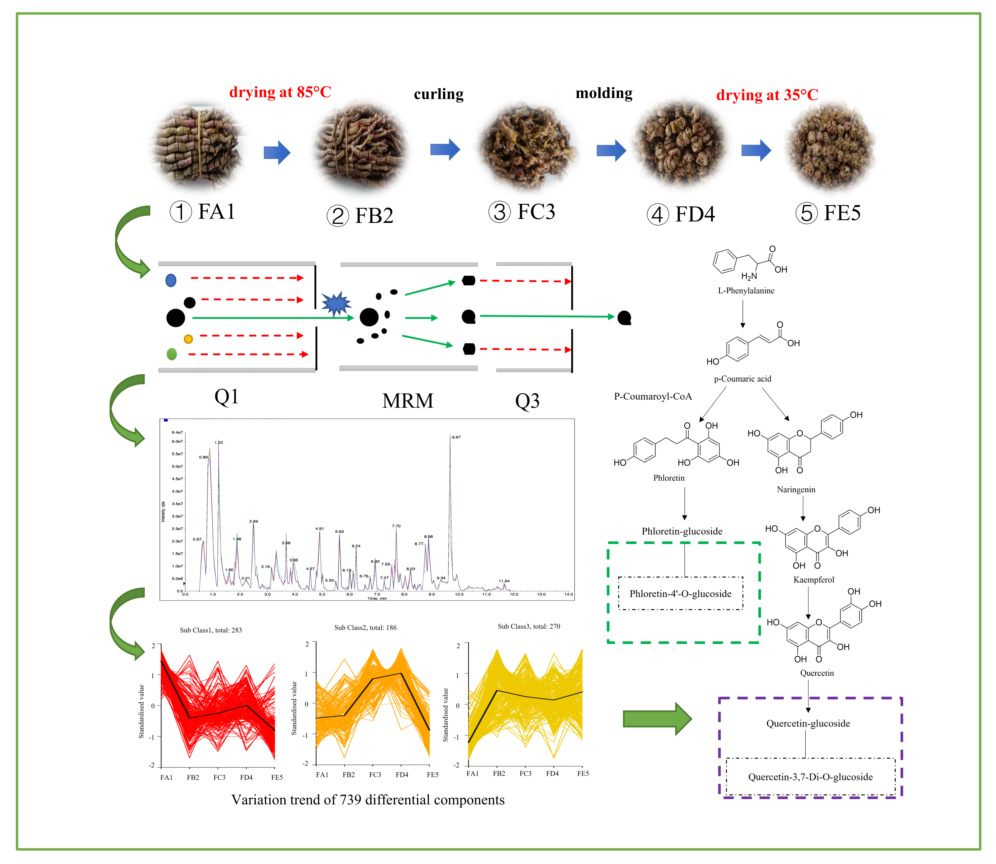
2.1. DO samples in different processing stages
2.2. Sample preparation and extraction
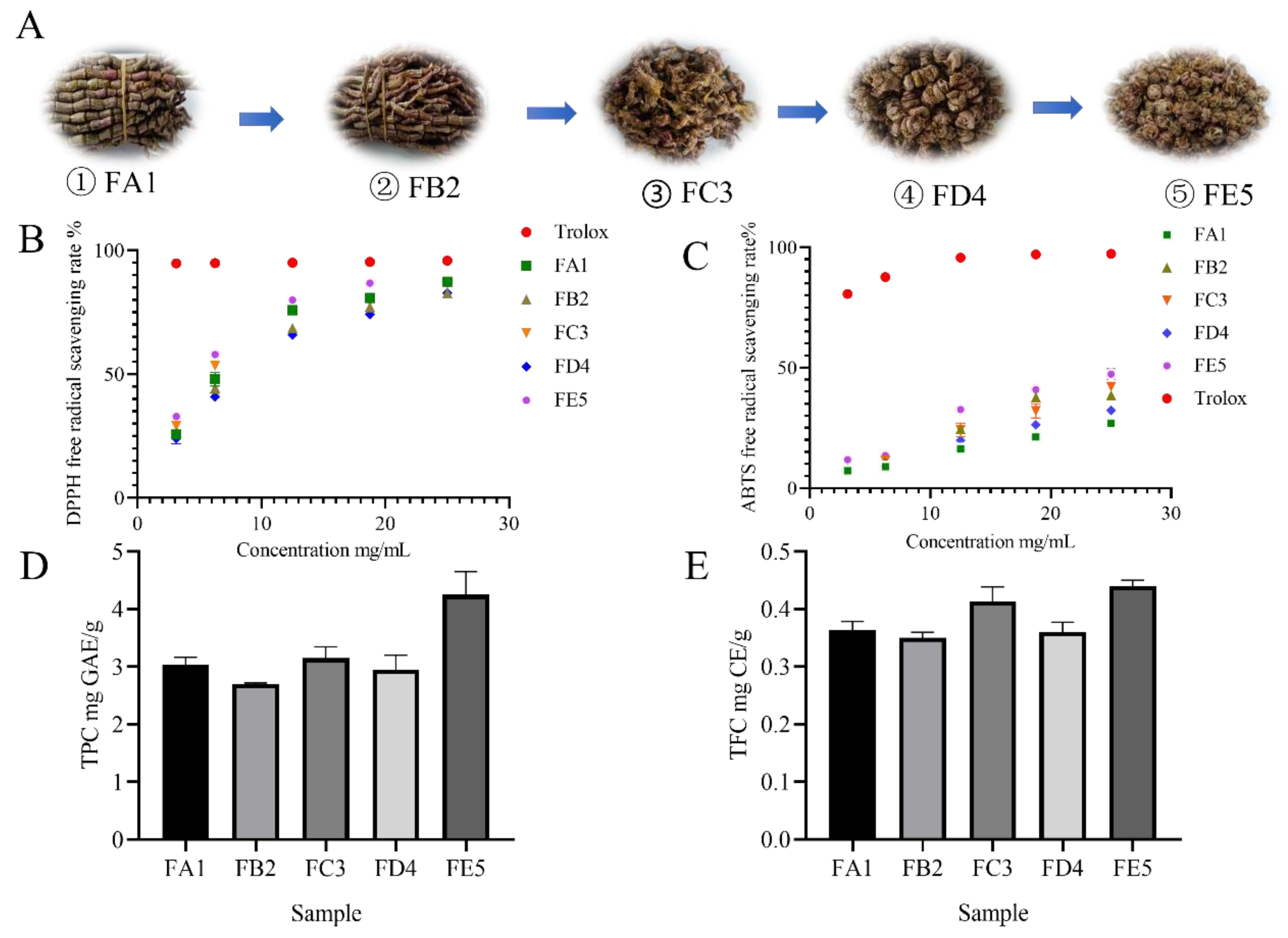
2.3. Antioxidant Activity
2.3.1. DPPH radical scavenging activity assay
2.3.2. ABTS radical scavenging activity assay
2.4. Total Phenolics and total flavonoid Quantification
2.5. UHPLC-MS conditions
2.6. Qualitative and statistical analysis of ingredients
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Effect of DO samples on antioxidant activity
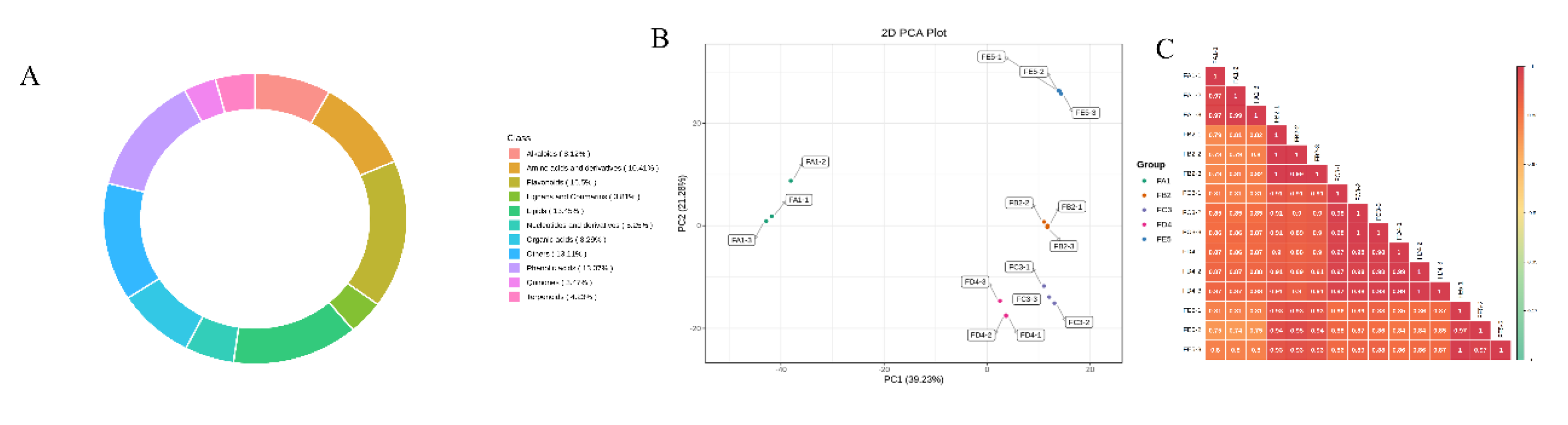
3.2. Overview of the profile of ingredients
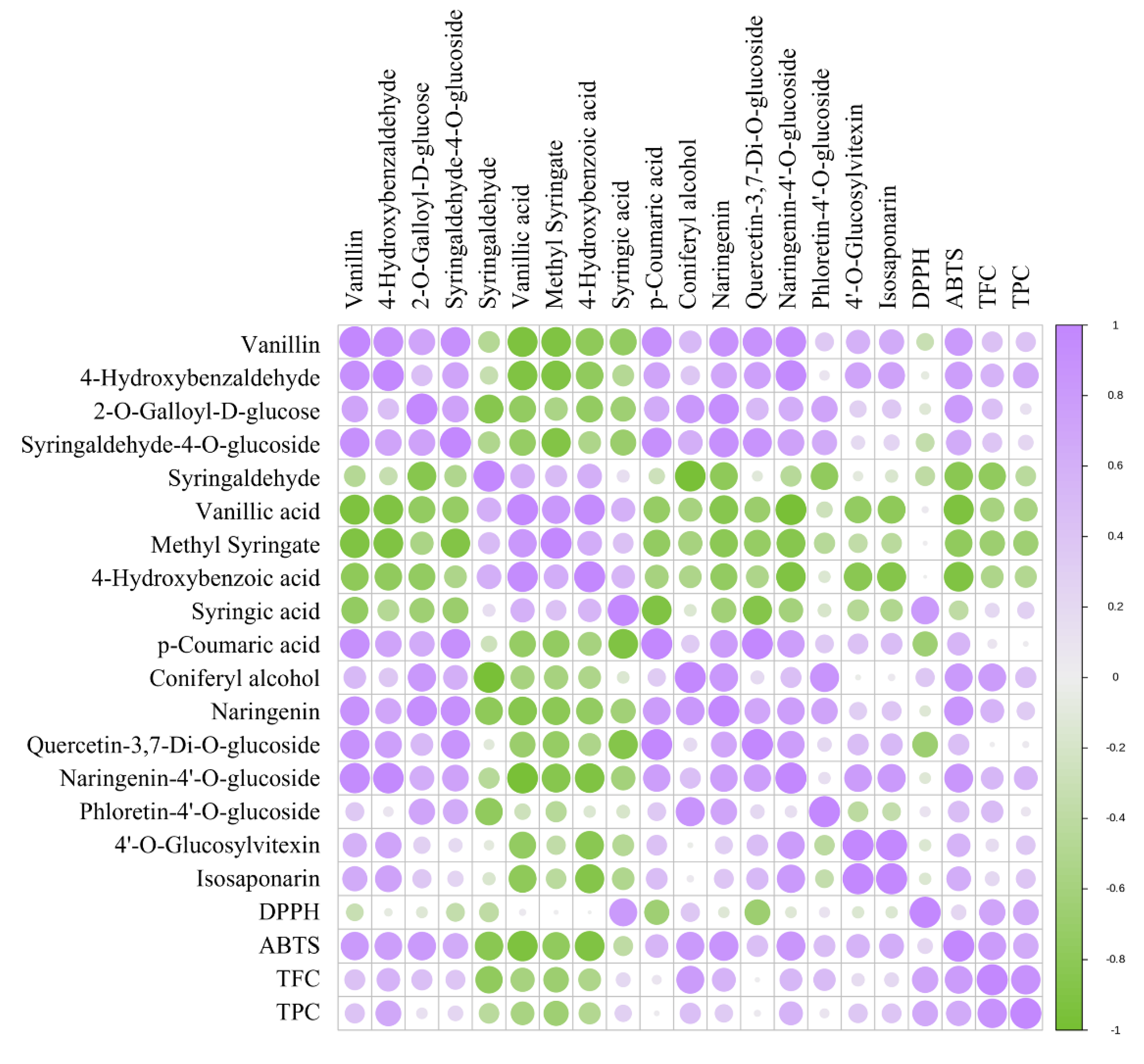
3.3. Multivariate statistical analysis
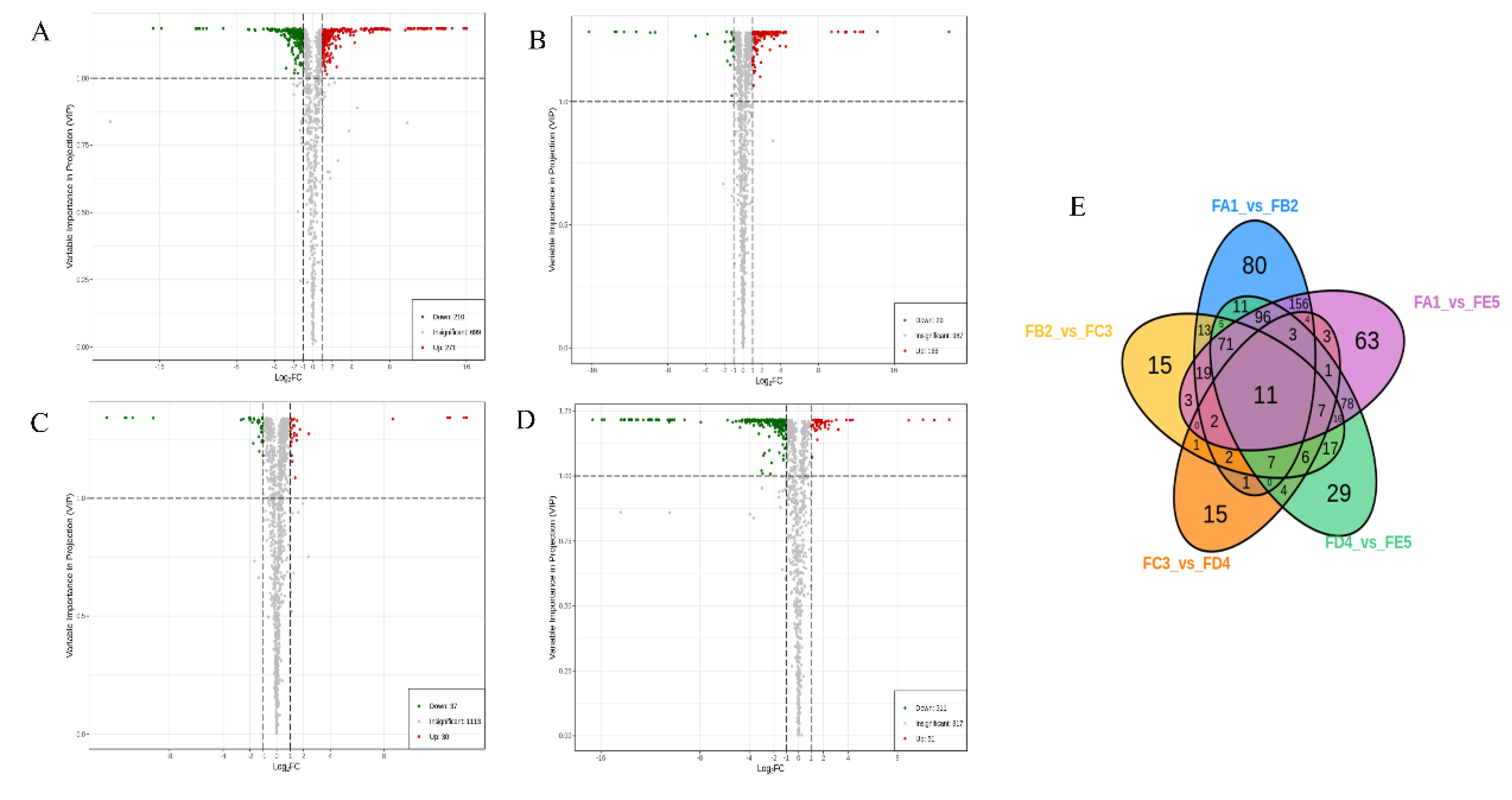
3.3. Identification of differential chemical ingredients
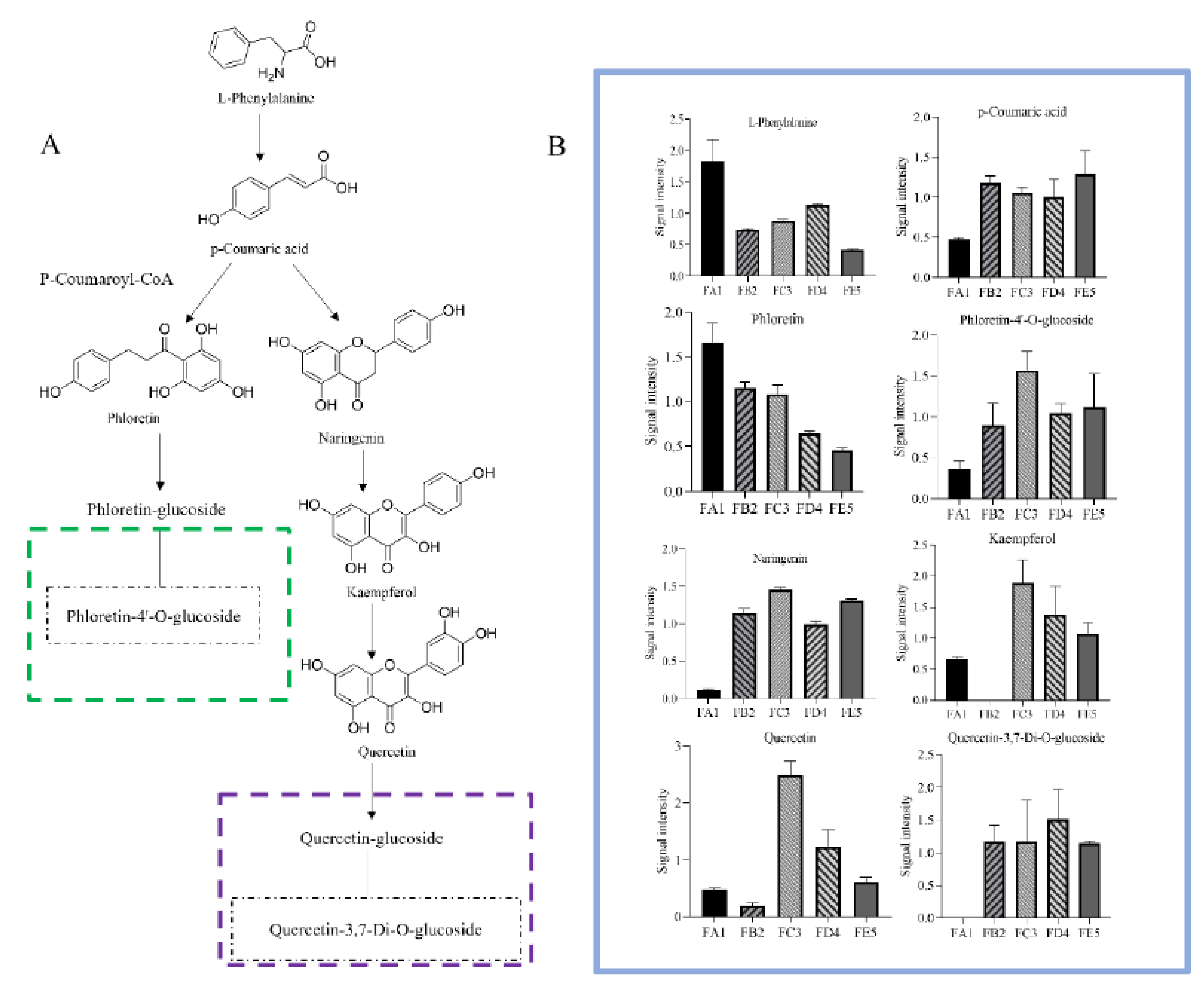
3.3.1. Changes in Phenolic acids Profile
3.3.2. Changes in flavonoids Profile
3.3.3. Changes in amino acids and derivatives profile
3.3.4. Changes in Lipids Profile
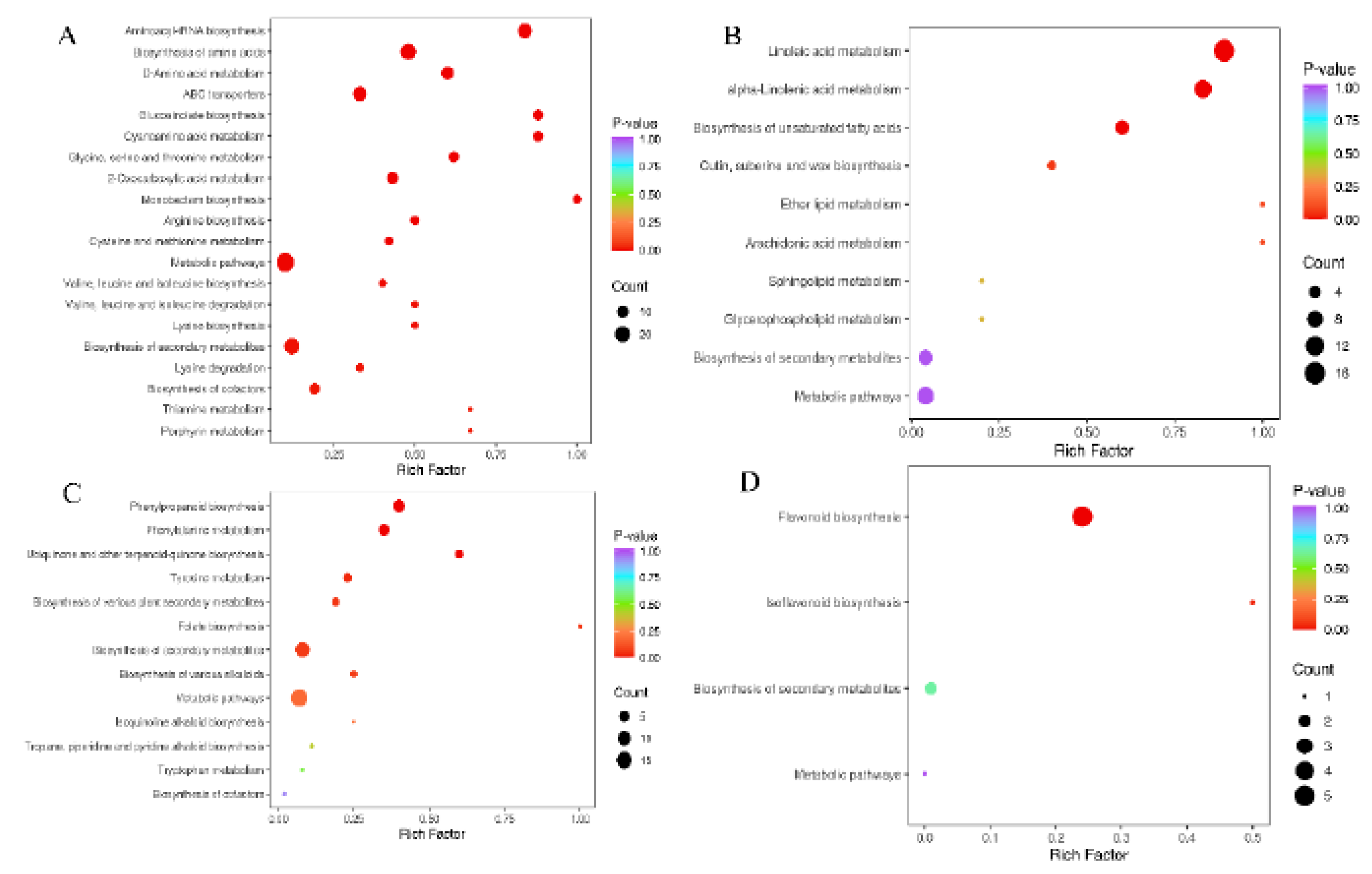
3.4. KEGG function annotation and enrichment analysis
3.5. Processing-induced chemical transformation mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Ding, B.; Chu, Q.; Zhou, G.; Ding, G.; Sun, G. Genetic diversity analysis and conservation of the endangered Chinese endemic herb Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo (Orchidaceae) based on AFLP. Genetica. 2008, 133, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Li, T.; Pedersen, H. A.; Kongstad, K.T.; Yan, J.Z.; Staerk, D. Antidiabetic constituents of Dendrobium officinale as determined by high-resolution profiling of radical scavenging and α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition combined with HPLC-PDA-HRMS-SPE-NMR analysis. Phytochemi. Lett. 2019, 31, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeniran, O.H.; Ademiluyi, A.O.; Oboh, G. African mistletoe (Tapinanthus bangwensis Lor.) infestation improves the phenolic constituents, antioxidative and antidiabetic effects of almond (Terminalia catappa Linn.) host leaf in sucrose-rich diet-induced diabetic-like phenotypes in fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster Meigen). Food Front. 2021, 2, 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, L.; Nie, Q.; Huang, M.; Luo, C.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yu, J.; Du, F. HPLC-based metabolomics of Dendrobium officinale revealing its antioxidant ability. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, C. Effects of microwave heating of wheat on its functional properties and accelerated storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Nie, Q.; Huang, X.; Nie, S. Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide ameliorates the liver metabolism disorders of type II diabetic rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1939–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, P.; Chen, L.; Shen, C.; Sun, C. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveal the regulation mechanism underlying MeJA-induced accumulation of alkaloids in Dendrobium officinale. J. Plant Res. 2019, 132, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.M. Therapeutic orchids: Traditional uses and recent advances—An overview. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 102–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, Y.M.; Loh, C.S.; Ong, B.L. Regulation of flower development in Dendrobium crumenatum by changes in carbohydrate contents, water status and cell wall metabolism. Scientia Horti-amsterdam. 2008, 119, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.F.; Fan, B.; Liu, X.D.; Yang, Y.; Lu, C.; Tong, L.T.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.Z. Comparison of different components of Dendrobium officinale Fengdou before and after processing. J. Nucl. Agric. Biol. 2022, 36, 2412–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.R.; Fan, H.R.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, L.F. Effect of drying methods on physico-chemical properties and antioxidant activity of Dendrobium officinale. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Fan, J.; Liu, Q.; Luo, H.; Tang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X. Phytochemical profiles of edible flowers of medicinal plants of Dendrobium officinale and Dendrobium devonianum. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6575–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Ding, S.; Han, W.; He, R.; Ren, Z.; Wei, G. Anti-colon cancer effects of Dendrobium officinale Kimura & Migo revealed by network pharmacology integrated with molecular docking and metabolomics studies. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 879986–880008. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Pan, L.; Xu, P.; Zhu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhu, W.; Hu, Y.; Gao, H. An NMR-based metabolomic approach to unravel the preventive effect of water-soluble extract from Dendrobium officinale Kimura & Migo on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice. Molecules 2017, 22, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. J.; Liu, Z. P.; Zhang, X. F.; Si, J. P. Effects of various processing methods on the metabolic profile and antioxidant activity of Dendrobium catenatum lindley leaves. Metabolites. 2021, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, L.; Izzo, L.; Lombardi, S.; Gaspari, A.; De Pascale, S.; Grosso, M.; Ritieni, A. Analysis of Polyphenolic compounds in Water-Based Extracts of Vicia faba L.: A Potential Innovative Source of Nutraceutical Ingredients. Antioxidants (Basel) 2022, 11, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, L.; Nie, Q.; Huang, M.; Luo, C.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yu, J.; Du, F. HPLC-based metabolomics of Dendrobium officinale revealing its antioxidant ability. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1060242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Ni, H.; Wu, L.; Weng, S.Y.; Li, L.; Chen, F. Analysis of aroma-active volatiles in an SDE extract of white tea. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraglio, S.K.T.; Hernández-Velásquez, B.S.; Osses-Millar, M.E.; Malverde-Muñoz, B.Y.; Guerra-Valle, M.E.; Pavez-Guajardo, C.; Moreno, J. Processing of Enriched Pear Slices with Blueberry Juice: Phenolics, Antioxidant, and Color Characteristics. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023, 12, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahukhandi, A.; Barola, A.; Sekar, K. C. Antioxidant Activity and Polyphenolics of Fragaria nubicola: A Wild Edible Fruit Species of Himalaya. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 90, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyło, A.; Oszmiański, J. Antioxidant Activity Modulated by Polyphenol Contents in Apple and Leaves during Fruit Development and Ripening. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020, 9, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paramita, V.; Yulianto, M. Response surface analysis on the microwave integrated-rumen based extraction of natural vanillin from cured vanilla pods. JPCS. 2019, 1295, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, A.; Sawano, T.; Yazama, F.; Ito, H. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of vanillin by using multiple antioxidant assays. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1810, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.M.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.Y.; Hou, B.K. Cloning of poplar phenolic acid glycosyltransferase gene PtSGT1 and identification of its enzymatic activity. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 52, 957–966. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.S.; Chen, L.M.; Xu, Z.S.; Chen, W.Q. Synthesis of ethyl vanillin-β-D-glucopyranoside. Flavors & Fragrances Cosmetics. 2018, 2018, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.G. Exploring the mechanism of ester formation in the brewing process of white wine. Brewing Sci. & Tech. 2022, 2022, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ti, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; Wei, Z.; Chi, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of extrusion on phytochemical profiles in milled fractions of black rice. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Z. Post-Harvest Processing Methods Have Critical Roles in the Contents of Active Ingredients of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. Molecules 2022, 27, 8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Gao, B.; Qian, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Si, J. Identification and quantitative analysis of phenolic glycosides with antioxidant activity in methanolic extract of Dendrobium catenatum flowers and selection of quality control herb-markers. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 732–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lu, S.; Du, H.; Cao, Y. Antioxidant capacity of flavonoids from Folium Artemisiae Argyi and the molecular mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; and Jiang, B.L. Study on the stability of flavonoids in twin-screw extruded puffed cereals. Food Sci. & Tech. 2006, 2006, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Roldan, M.; Loebner, J.; Degen, J.; Henle, T.; Antequera, T.; Ruiz-Carrascal, J. Advanced glycation end products, physico-chemical and sensory characteristics of cooked lamb loins affected by cooking method and addition of flavour precursors. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisan, A.J.; Almeida, L.D.; Sampaio, G.R.; Soares, R.A.; Markowicz, B.D. Influence of home cooking conditions on Maillard reaction products in beef. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmes, C.; Fischer, A. Role of amino acids and glucose in development of burnt off-flavours in liver sausage during heat processing. Meat Sci. 1997, 47, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, L.K.; Miao, W.J.; Wu, Q.F.; Liu, Y.X.; Sun, Y.; Gao, C. Thermal versus microwave inactivation kinetics of lipase and lipoxygenase from wheat germ. J. Food Process Eng. 2015, 39, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblado-Maldonado, A.F.; Pike, O.A.; Sweley, J.C.; Rose, D.J. Key issues and challenges in whole wheat flour milling and storage. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, C. Effects of microwave heating of wheat on its functional properties and accelerated storage. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 54, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Xing, J.J.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X. Changes of lipids in noodle dough and dried noodles during industrial processing. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 3517–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Z.X.; Cui, F.; Zhang, Q.N.; Song, P.P.; Li, B.; Tang, Z.S.; Hu, F.D.; Shi, X.F. Characterization of chemical composition variations in raw and processed Codonopsis Radix by integrating metabolomics and glycomics based on multiple chromatography-mass spectrometry technology. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2375–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, C.; Ma, X.; Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zeng, M. Functional characterization of a flavonoid glycosyltransferase in sweet orange (Citrus sinensis). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number | Compounds | Formula | m/z | Factor | Fold Change | VIP | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acids | |||||||
| 1 | 1-O-Sinapoyl-β-D-glucose | C17H22O10 | 386.3506 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.89E+00↑ | 1.173 | 7.30E-03 |
| 2 | Dihydrocaffeoylglucose | C15H20O9 | 344.3139 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 9.27E+03↑ | 1.185 | 2.41E-03 |
| 3 | Syringaldehyde-4-O-glucosid | C15H20O9 | 344.3139 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 8.44E+03↑ | 1.185 | 4.56E-03 |
| 4 | Sinapinaldehyde | C11H12O4 | 208.2106 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.47E+00↑ | 1.172 | 6.90E-05 |
| 5 | Isovanillin | C8H8O3 | 152.1473 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 4.52E+00↑ | 1.174 | 9.44E-03 |
| 6 | 1-O-Feruloyl-β-D-glucose | C16H20O9 | 356.3246 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 1.22E+01↑ | 1.180 | 4.84E-05 |
| 7 | 2-(Formylamino)benzoic acid | C8H7NO3 | 165.1461 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.48E+00↑ | 1.167 | 2.46E-04 |
| 8 | Caffeic aldehyde | C9H8O3 | 164.1580 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.04E+00↑ | 1.106 | 3.50E-03 |
| 9 | Vanillin | C8H8O3 | 152.1473 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 4.52E+00↑ | 1.181 | 2.61E-04 |
| 10 | p-Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | 164.1580 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.51E+00↑ | 1.178 | 3.37E-03 |
| 11 | 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde | C7H6O2 | 122.1213 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.14E+00↑ | 1.156 | 2.85E-03 |
| 12 | Methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate | C8H8O3 | 152.1743 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 4.82E+00↑ | 1.181 | 6.34E-06 |
| 13 | Gallacetophenone | C8H8O4 | 168.1467 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 1.23E+04↑ | 1.185 | 1.43E-04 |
| 14 | Cinnamic acid | C9H8O2 | 148.1586 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 6.44E+00↑ | 1.168 | 1.99E-03 |
| 15 | 2-O-Galloyl-D-glucose | C13H16O10 | 332.2601 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 6.02E+04↑ | 1.185 | 5.85E-05 |
| 16 | 1-O-(3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxy-benzoyl)-glucoside | C14H18O10 | 346.2867 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.65E-01↓ | 1.151 | 3.58E-02 |
| 17 | 2-Acetyl-3-hydroxyphenyl-1-O-glucoside | C15H20O7 | 312.3151 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 3.48E-01↓ | 1.166 | 1.34E-02 |
| 18 | Vanillin acetate | C10H10O4 | 194.1840 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 3.26E-01↓ | 1.135 | 5.10E-02 |
| 19 | 2,5-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde | C7H6O3 | 138.1207 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 7.29E-05↓ | 1.193 | 6.80E-04 |
| 20 | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | C7H6O3 | 138.1207 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 4.79E-01↓ | 1.211 | 7.53E-04 |
| 21 | Ferulic acid methyl ester | C11H12O4 | 208.2106 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 2.45E-01↓ | 1.199 | 1.77E-03 |
| 22 | Methyl syringate | C10H12O5 | 212.1993 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 3.90E-01↓ | 1.173 | 3.03E-02 |
| 23 | Vanillic acid | C8H8O4 | 168.1467 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 4.46E-01↓ | 1.215 | 4.53E-04 |
| 24 | 4-O-Methylgallic Acid | C8H8O5 | 184.1461 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 4.09E-01↓ | 1.102 | 3.26E-03 |
| 25 | Eudesmic acid | C10H12O5 | 212.1993 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 1.29E-01↓ | 1.159 | 1.78E-03 |
| 26 | 3-(3-Hydroxyphenyl)-3-hydroxypropanoic acid | C9H10O4 | 182.1733 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 4.16E-01↓ | 1.145 | 2.41E-02 |
| 27 | 4-Methylphenol | C7H8O | 108.1378 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 4.55E-02↓ | 1.178 | 9.79E-03 |
| 28 | Methyl 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate | C10H12O3 | 180.2005 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 6.99E-04↓ | 1.208 | 1.03E-01 |
| Flavonoids | |||||||
| 29 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-sophoroside | C28H32O17 | 640.5435 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 3.29E+00↑ | 1.148 | 4.77E-04 |
| 30 | Butin | C15H12O5 | 272.2528 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 9.44E+00↑ | 1.185 | 2.00E-04 |
| 31 | 7-Methoxy-3-[1-(3-pyridyl) methylidene]-4-chromanone | C16H13NO3 | 267.2793 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.41E+00↑ | 1.142 | 4.64E-03 |
| 32 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside-4'-O-glucoside | C34H42O21 | 786.6847 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.50E+00↑ | 1.147 | 5.82E-03 |
| 33 | 3,4'-Dihydroxyflavone | C15H10O4 | 254.2375 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 1.02E+03↑ | 1.185 | 1.91E-03 |
| 34 | 6,7,8-Tetrahydroxy-5-methoxyflavone | C16H12O6 | 300.2629 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.07E+00↑ | 1.133 | 1.95E-03 |
| 35 | Tangeretin | C20H20O7 | 372.3686 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 3.43E+00↑ | 1.215 | 2.67E-04 |
| 36 | Naringenin | C15H12O5 | 272.2528 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 9.79E+00↑ | 1.184 | 1.09E-03 |
| 37 | 3,5,7,3'4'-Pentamethoxyflavone | C20H20O7 | 372.3686 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 2.87E+00↑ | 1.205 | 3.37E-04 |
| 38 | Quercetin-3-O-(6''-O-p-coumaroyl) sophoroside-7-O-rhamnoside | C42H46O23 | 918.8008 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 3.72E+00↑ | 1.175 | 1.37E-02 |
| 39 | Apigenin-7,4'-dimethyl ether | C17H14O5 | 298.2901 | FD4 vs. FE5 | 3.11E+00↑ | 1.189 | 3.72E-03 |
| 40 | Quercetin-3-O-glucosyl (1→4) rhamnoside-7-O-rutinoside | C39H50O25 | 918.7993 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 3.12E+00↑ | 1.165 | 1.53E-02 |
| 41 | 5,6,7,3',4',5'-hexanmethoxyflavone | C21H22O8 | 402.3946 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 5.91E+00↑ | 1.181 | 1.73E-03 |
| 42 | Eriodictyol-3'-O-glucoside | C21H22O11 | 450.3928 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 3.88E+00↑ | 1.169 | 4.17E-03 |
| 43 | 1,8-dihydroxy-2,6-dimethylxanthen-9-one | C15H12O4 | 256.2534 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 1.34E+04↑ | 1.185 | 1.12E-02 |
| 44 | Pinocembrin | C15H12O4 | 256.2534 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 4.11E+00↑ | 1.129 | 1.16E-02 |
| 45 | Quercetin-3,7-di-O-glucoside | C27H30O17 | 626.5169 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.57E+03↑ | 1.184 | 1.55E-02 |
| 46 | Naringenin-4'-O-glucoside | C21H22O10 | 434.3934 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.02E+00↑ | 1.163 | 1.46E-02 |
| 47 | Trilobatin | C21H24O10 | 436.4093 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 2.43E+00↑ | 1.039 | 6.96E-02 |
| 48 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-sophoroside-7-O-rhamnoside | C34H42O21 | 786.6847 | FA1 vs. FB2 | 4.43E+00↑ | 1.147 | 8.48E-03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





