Submitted:
26 September 2023
Posted:
28 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
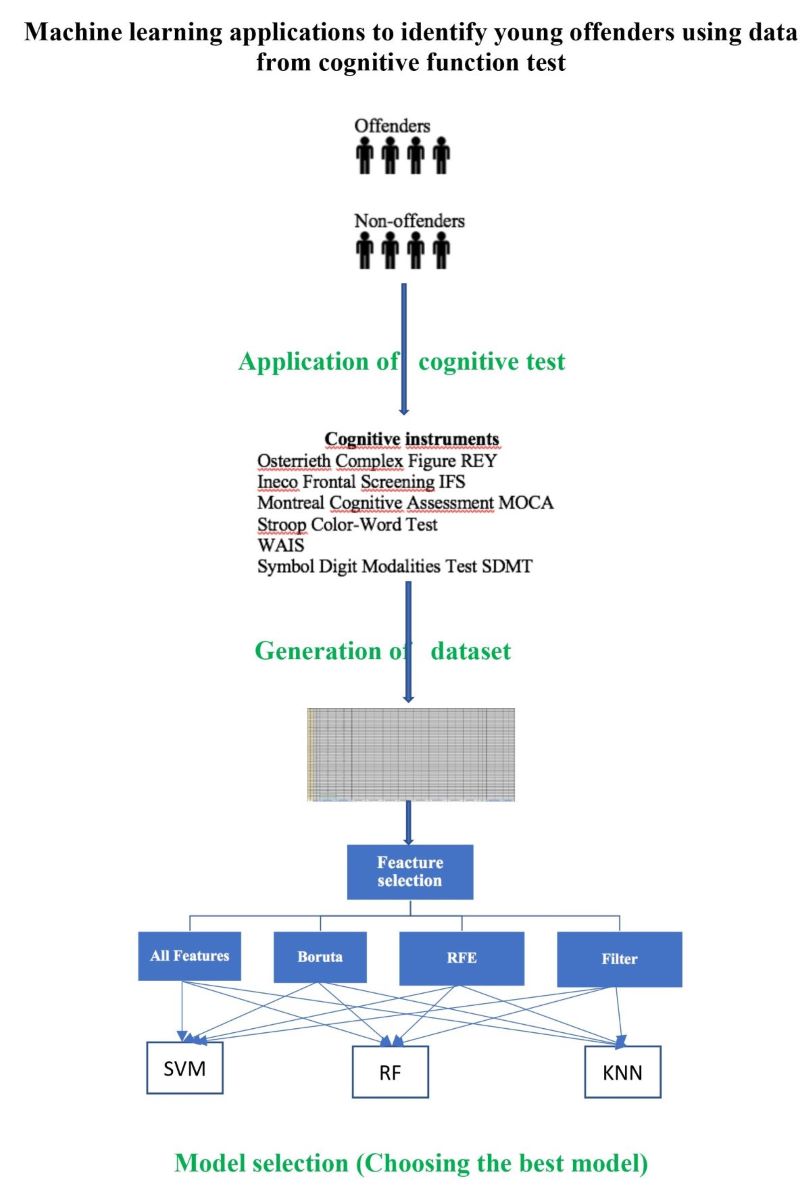
2. Materials and Methods
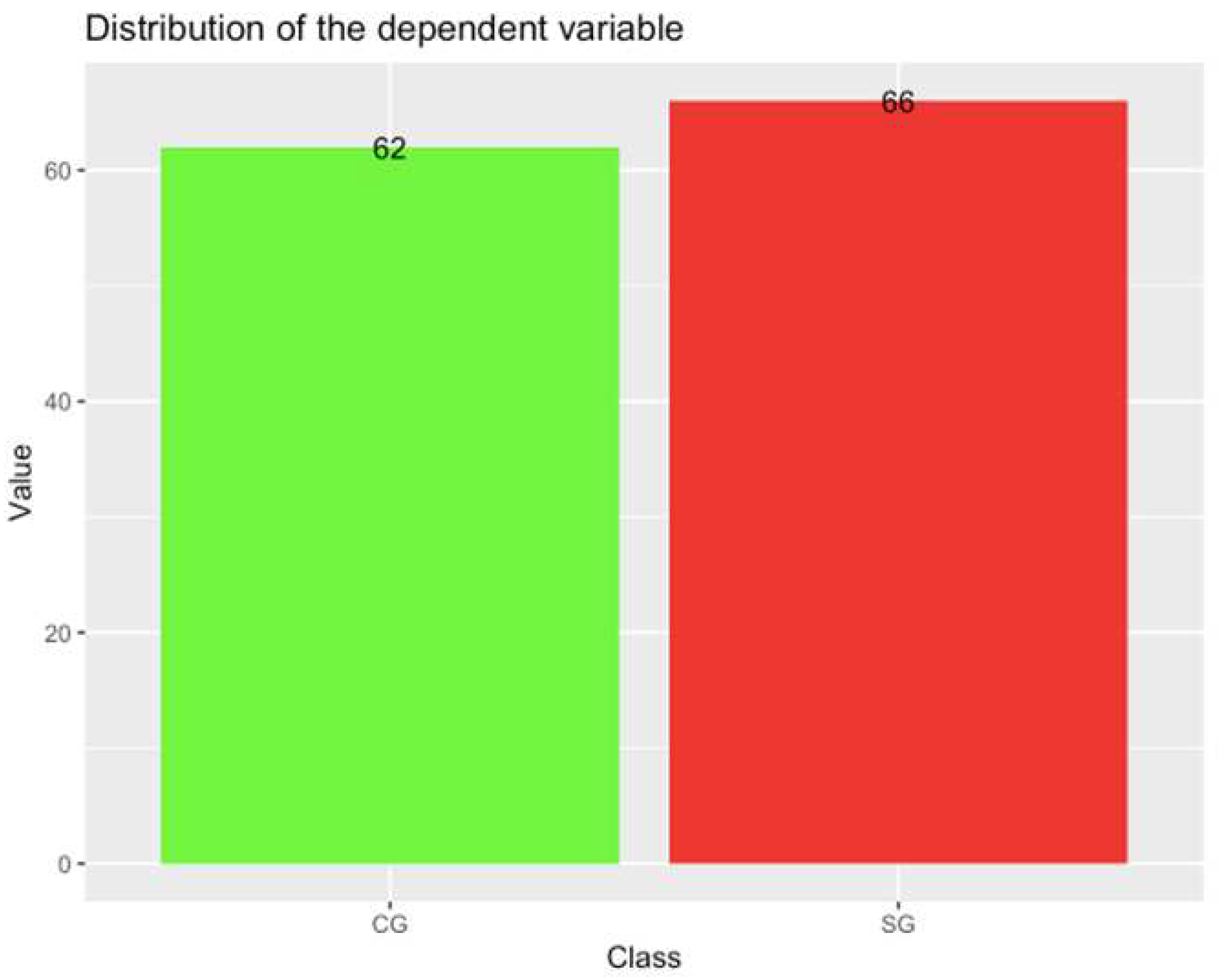
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Feature selection
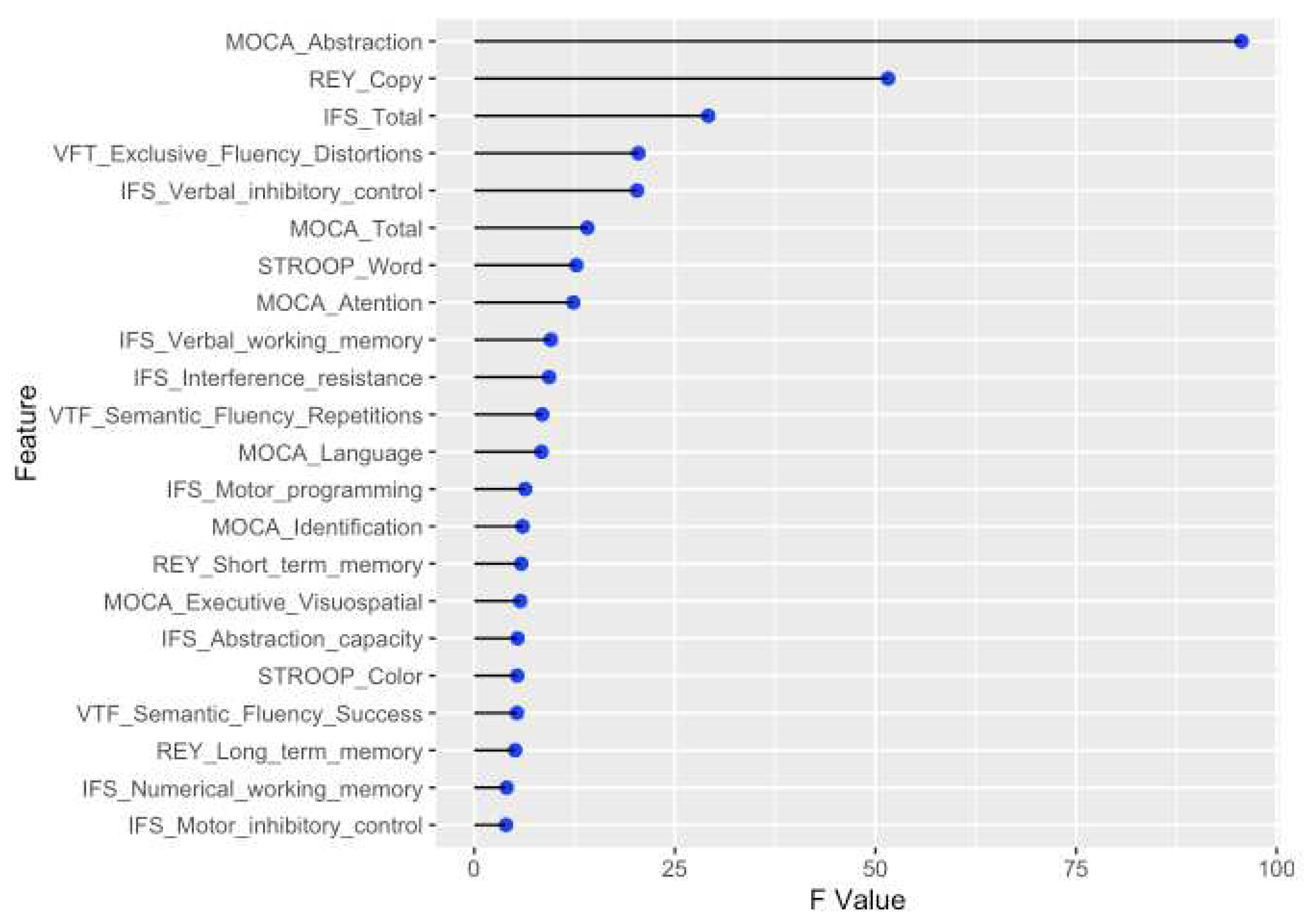
2.2.1. Features that are significantly different among groups
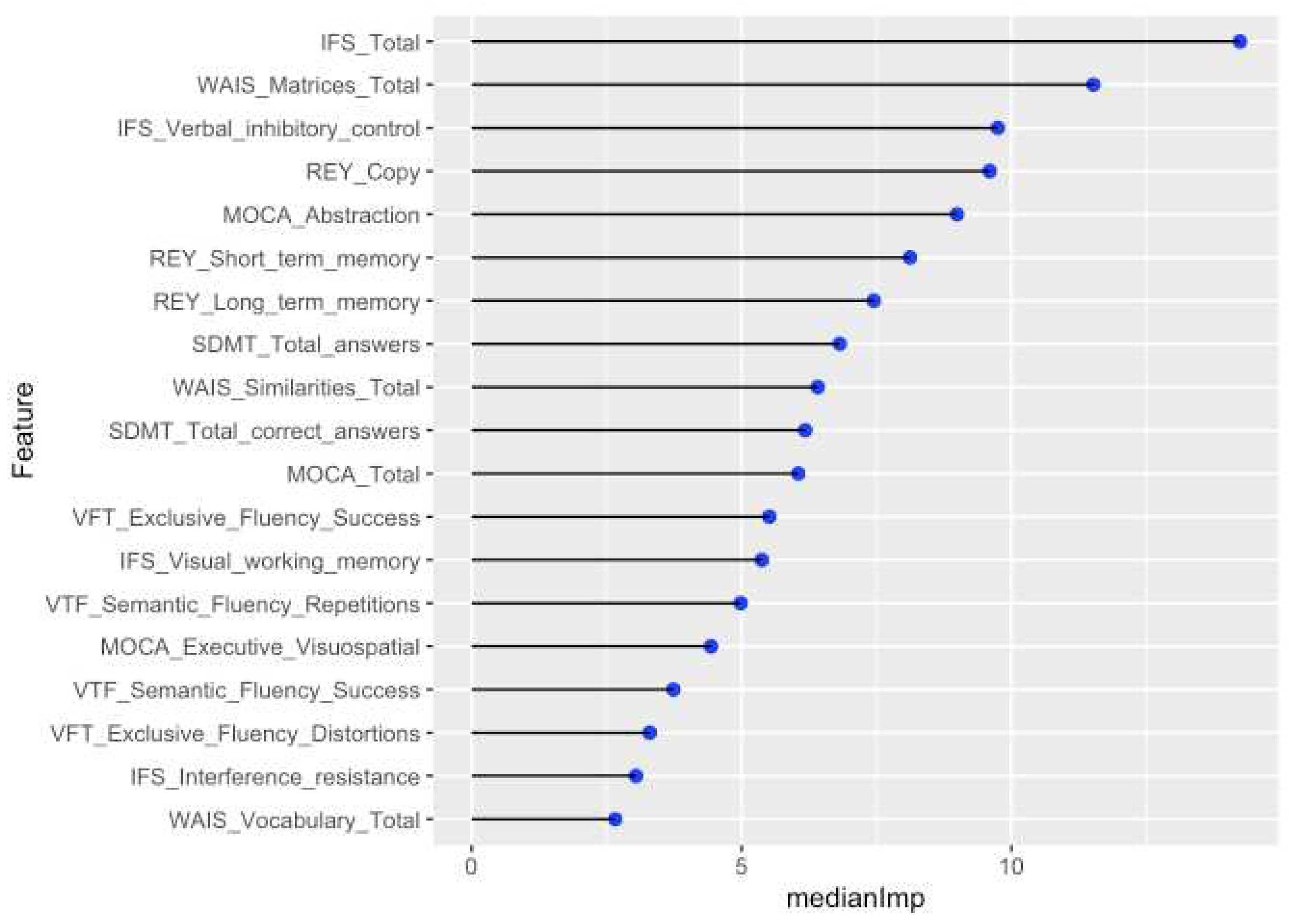
2.2.2. Boruta algorithm
2.2.3. Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE) Algorithm
2.2.4. Filter Algorithm
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masho, S. W., Schoeny, M. E., Webster, D., & Sigel, E., Outcomes, Data, and Indicators of Violence at the Community Level. Journal of Primary Prevention, 2016, 37(2), 121–139. [CrossRef]
- Voith, L., Salas, M., Sorensen, A., Thomas, T. J., Coulton, C., & Barksdale, E., Identifying Risk Factors and Advancing Services for Violently Injured Low-Income Black Youth, Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Douglas, T., Pugh, J., Singh, I., Savulescu, J., & Fazel, S., Risk assessment tools in criminal justice and forensic psychiatry : The need for better data, European Psychiatry, 2017, 42, 134–137. [CrossRef]
- Rolin, S.A., Bareis, N., Bradford, J.M., Rotter, M., Rosenfeld, B., Pauselli, L., Compton, M.T., Stroup, T.S., Appelbaum, P.S., Dixon, L.B., Violence Risk Assessment for Young Adults Receiving Treatment for Early Psychosis, 2021, 76: 101701. [CrossRef]
- De Vogel, V., De Beuf, T., Shepherd, S., Schneider, R.D., Violence Risk Assessment with the HCR-20V3 in Legal Contexts: A Critical Reflection, Journal of Personality Assessment, 2022, 104:2, 252-264. [CrossRef]
- Barzman, D., Ni, Y., Griffey, M., Bachtel, A., Lin, K., Jackson, H., Sorter, M., DelBello, M., Automated Risk Assessment for School Violence: a Pilot Study, Psychiatric Quarterly, 2018, Vol. 89, pp. 817–828. [CrossRef]
- Singh, J. P., Desmarais, S. L., Hurducas, C., Arbach-lucioni, K., Condemarin, C., Dean, K, Doyle, M., Folino, J. O., Godoy-cervera, V., Grann, M., Mei, R., Ho, Y., Matthew, M., Nielsen, L. H., Pham, T. H., Rebocho, M. F., Reeves, K. A., Rettenberger, M., Ruiter, C. De, Ruiter, C. De., International Perspectives on the Practical Application of Violence Risk Assessment : A Global Survey of 44 Countries, International Journal of Forensic Mental Health, 9013, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Tortora, L., Meynen, G., Bijlsma, J., Tronci, E., & Ferracuti, S., Neuroprediction and A.I. in Forensic Psychiatry and Criminal Justice: A Neurolaw Perspective, Frontiers in Psychology, 11(March), 2020, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Coid, J., Mickey, N., Kahtan, N., Zhang, T., & Yang, M., Patients discharged from medium secure forensic psychiatry services: Reconvictions and risk factors, British Journal of Psychiatry, 190(MAR.), 2007, 223–229. [CrossRef]
- Watts, D., Cardoso, T. D. A., Librenza-garcia, D., Ballester, P., & Passos, I. C., Predicting criminal and violent outcomes in psychiatry : a meta- analysis of diagnostic accuracy, Translational Psychiatry, 2022, September. [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, L. A., Lau, S., & Kirchebner, J, Advantages of Machine Learning in Forensic Psychiatric Research—Uncovering the Complexities of Aggressive Behavior in Schizophrenia. Applied Sciences (Switzerland), (2022), 12(2). [CrossRef]
- Cockerill, R. G, Ethics implications of the use of artificial intelligence in violence risk assessment. Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law, 2020, 48(3), 345–349. [CrossRef]
- Trinhammer, M. L., Merrild, A. C. H., Lotz, J. F., & Makransky, G, Predicting crime during or after psychiatric care: Evaluating machine learning for risk assessment using the Danish patient registries, Journal of Psychiatric Research, 2022, 152(June), 194–200. [CrossRef]
- Watts, D., Mamak, M., Moulden, H. Upfold, C., De Azevedo Cardoso, T., Kapczinski, F., Chaimowitz, G., The HARM models: Predicting longitudinal physical aggression in patients with schizophrenia at an individual level, Journal of Psychiatric Research, 2023, Vol. 161, pp. 91-98. [CrossRef]
- Watts, D., Moulden, H., Mamak, M., Upfold, C., & Chaimowitz, G., Predicting offenses among individuals with psychiatric disorders - A machine learning approach, Journal of Psychiatric Research, 2021, 138(October 2020), 146–154. [CrossRef]
- Günther, M. P., Kirchebner, J., & Lau, S, Identifying Direct Coercion in a High Risk Subgroup of Offender Patients With Schizophrenia via Machine Learning Algorithms, Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2020, 11(May), 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Kirchebner, J., Lau, S., & Machetanz, L, Offenders and non-offenders with schizophrenia spectrum disorders: Do they really differ in known risk factors for aggression?, Frontiers in Psychiatry, 2023, 14(April), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Koppe, G., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., & Durstewitz, D, Deep learning for small and big data in psychiatry, Neuropsychopharmacology, 2021, 46(1), 176–190. [CrossRef]
- Menger, V., Spruit, M., Est, R. Van, Nap, E., & Scheepers, F., Machine Learning Approach to Inpatient Violence Risk Assessment Using Routinely Collected Clinical Notes in Electronic Health Records. JAME Network Open, 2019, 2(7), 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Parmigiani, G., Barchielli, B., Casale, S., Mancini, T., & Ferracuti, S., The impact of machine learning in predicting risk of violence : A systematic review, 2022, December. [CrossRef]
- Sonnweber, M., Kirchebner, J., Philipp, M., Kappes, J. R., & Lau, S., Exploring substance use as rule-violating behaviour during inpatient treatment of offender patientes with schizophrenia, Criminal Behaviour and Mental Health., 2022. [CrossRef]
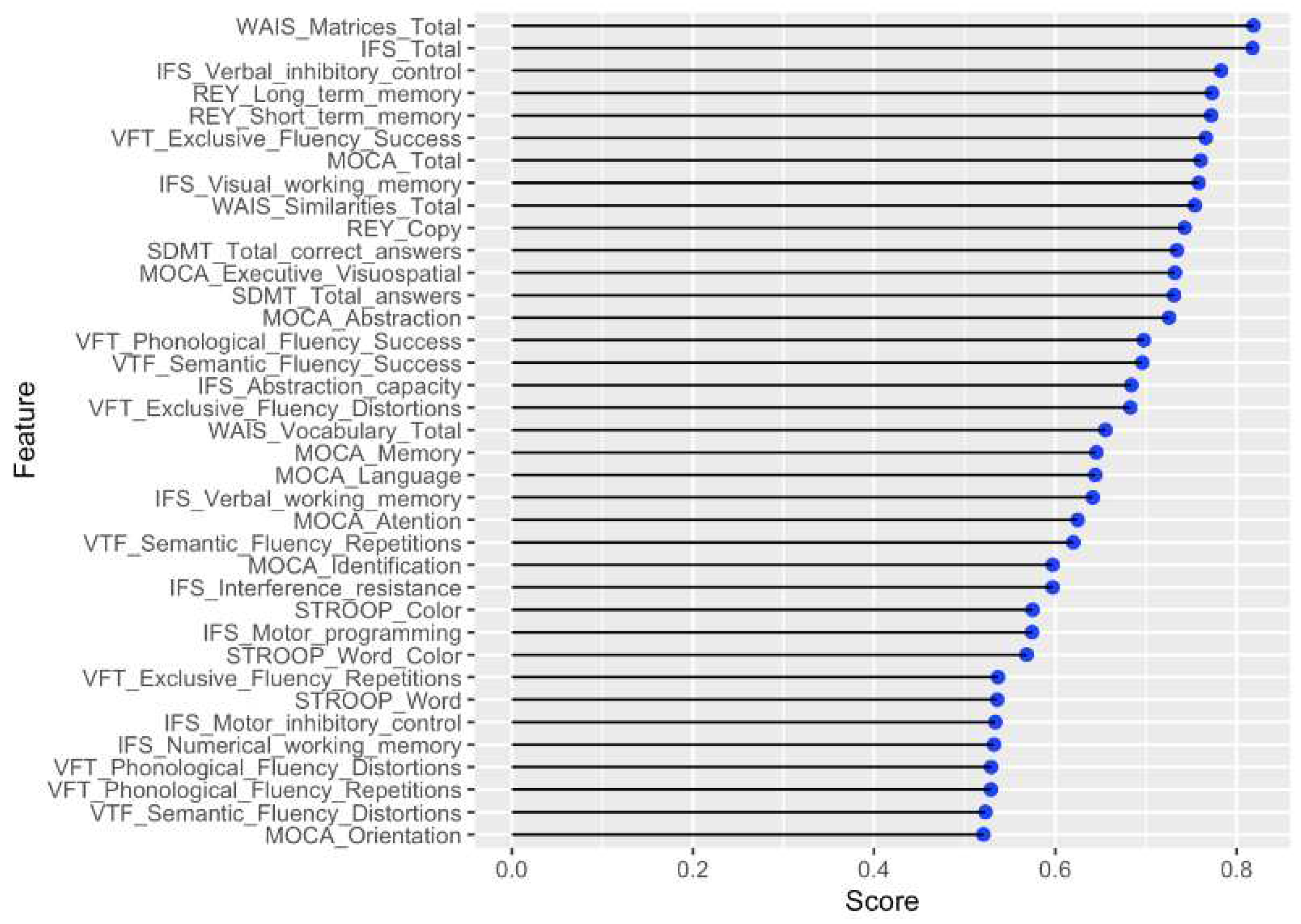
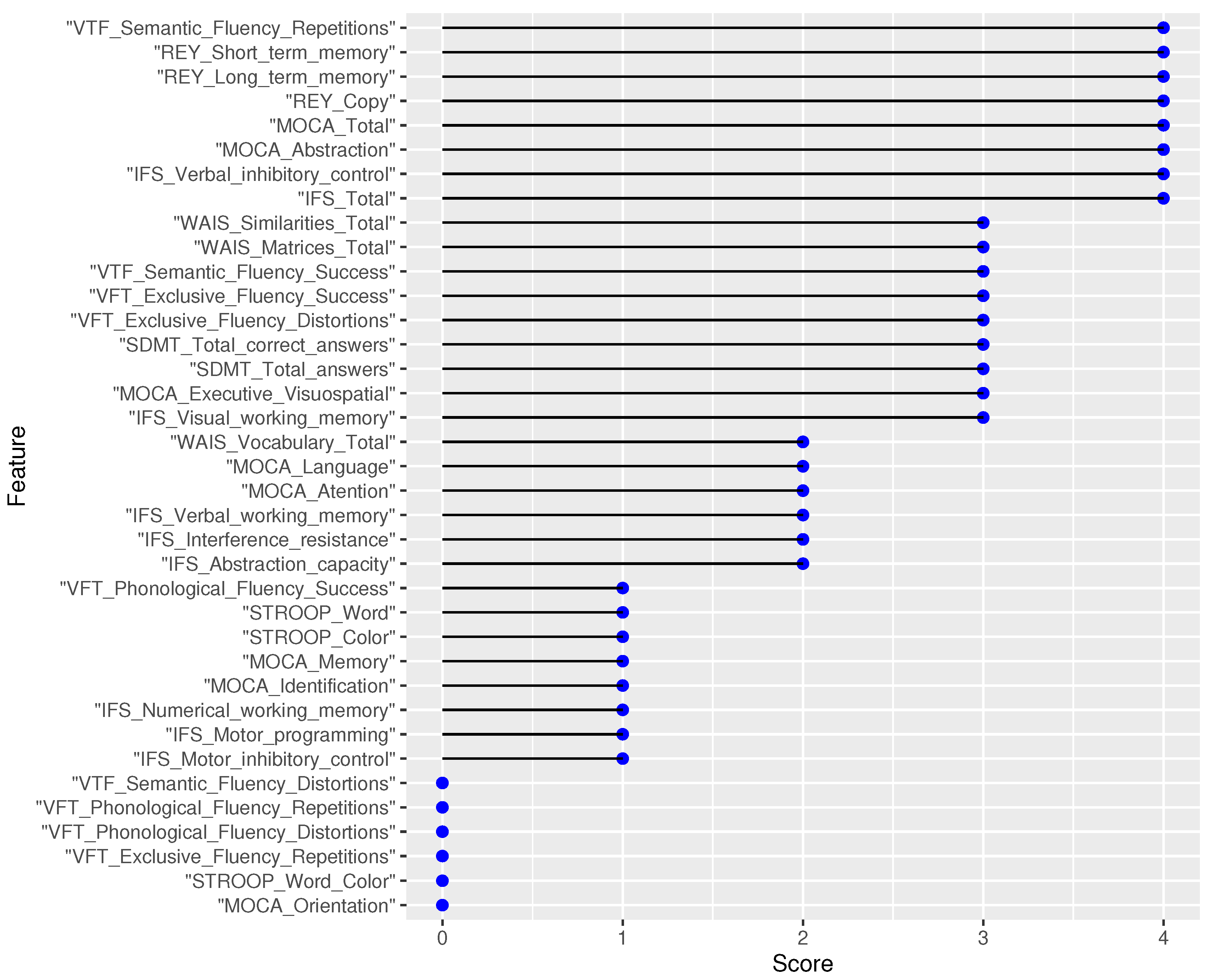
| Cognitive tests | Features |
|---|---|
| Osterrieth Complex Figure | Copy Short-term memory Long-term memory |
| Ineco Frontal Screening (IFS) | Motor programming Interference resistance Motor inhibitory control Verbal inhibitory control Verbal working memory Numerical working memory Visual working memory Abstraction capacity IFS Total |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA) | Executive Visuospatial Identification Memory Attention Language Abstraction Orientation MOCA Total |
| STROOP | Word |
| Color | |
| Word-Color | |
| VFT (Verbal Fluency Test) | Phonological Fluency Success |
| Phonological Fluency Repetitions | |
| Phonological Fluency Distortions | |
| Semantic Fluency Success | |
| Semantic Fluency Repetitions | |
| Semantic Fluency Distortions | |
| Exclusive Fluency Success | |
| Exclusive Fluency Repetitions Exclusive Fluency Distortions |
|
| WAIS (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale) | Matrices Similarities Vocabulary |
| SDMT (Symbol Digit Modalities Test) | Total correct answers Total answers |
| Cognitive tests | Features | Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Osterrieth Complex Figure | Copy Short-term memory Long-term memory |
4 7 9 |
| Ineco Frontal Screening (IFS) | Verbal inhibitory control Visual working memory IFS Total |
3 13 1 |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA) | Abstraction MOCA Total |
5 12 |
| VFT (Verbal Fluency Test) | Semantic Fluency Repetitions Exclusive Fluency Success |
11 14 |
| WAIS (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale) | Matrices_Total Similarities_Total |
2 10 |
| SDMT (Symbol Digit Modalities Test) | Total correct answers Total answers |
8 6 |
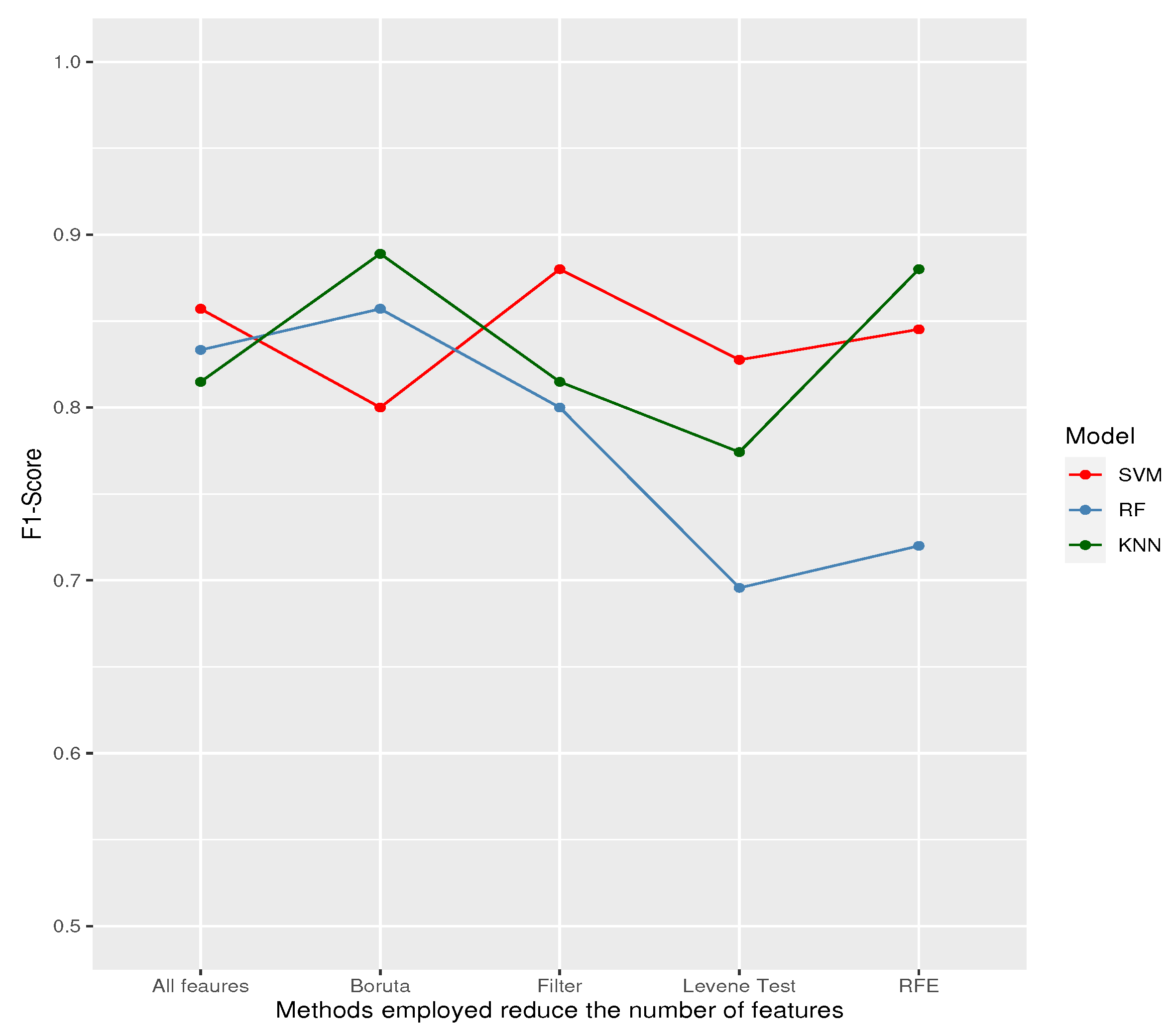
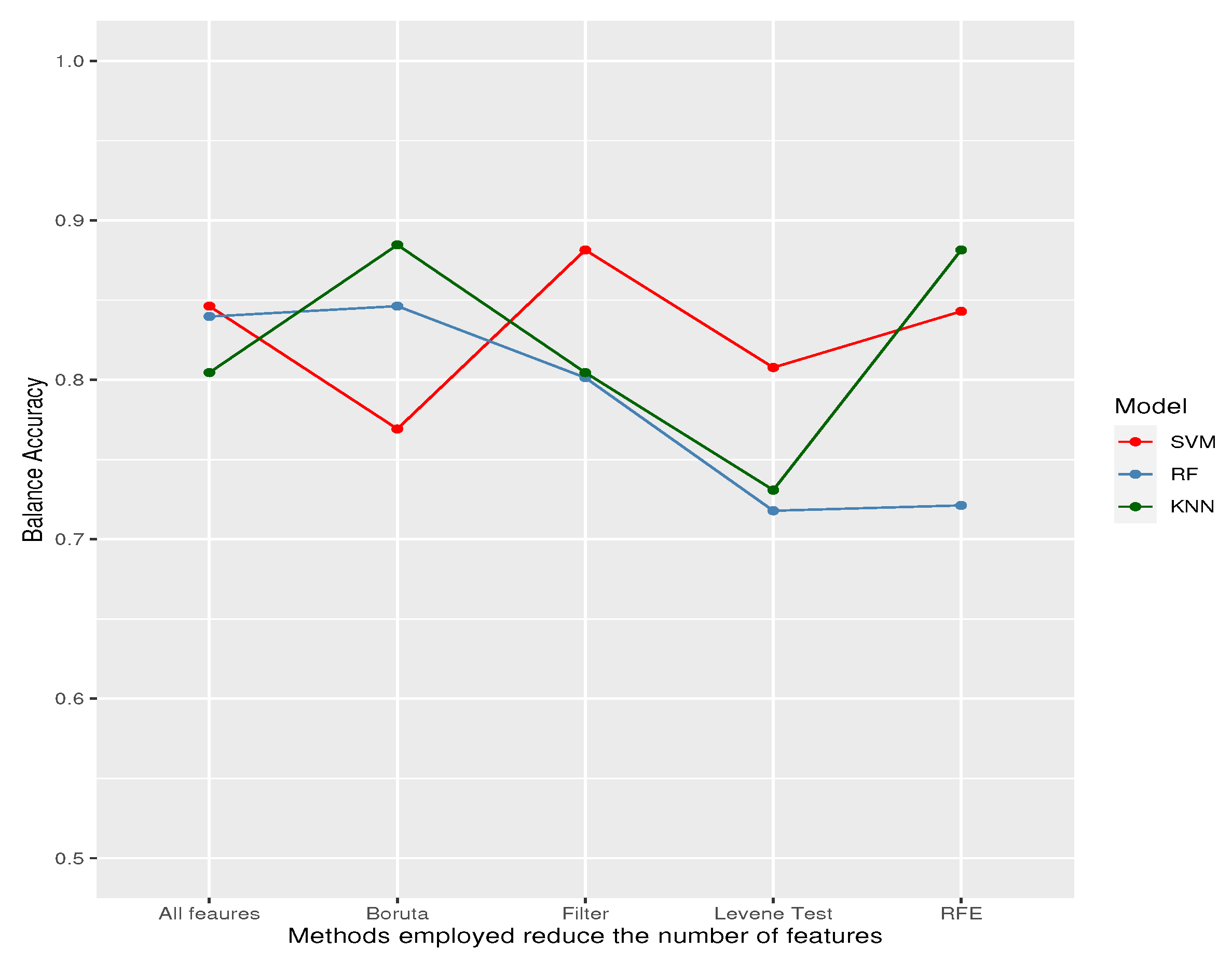
| Features selected by | ||||||
| Model | Metric | All Features | Levene test | Boruta | RFE | Filter |
| Sensitivity/Recall | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9167 | 0.9167 | |
| SVM | Specificity | 0.6923 | 0.6154 | 0.5385 | 0.7692 | 0.8462 |
| F1 | 0.8571 | 0.8276 | 0.8000 | 0.8452 | 0.8800 | |
| Balance Accuracy | 0.8462 | 0.8077 | 0.7692 | 0.8429 | 0.8814 | |
| Sensitivity/Recall | 0.8333 | 0.6667 | 1.0000 | 0.7500 | 0.8333 | |
| RF | Specificity | 0.8462 | 0.7692 | 0.6923 | 0.6923 | 0.7692 |
| F1 | 0.8333 | 0.6957 | 0.8571 | 0.7200 | 0.8000 | |
| Balance Accuracy | 0.8397 | 0.7179 | 0.8462 | 0.7212 | 0.8013 | |
| Sensitivity/Recall | 0.9167 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.9167 | 0.9167 | |
| KNN | Specificity | 0.6923 | 0.4615 | 0.7692 | 0.8462 | 0.6923 |
| F1 | 0.8148 | 0.7742 | 0.8889 | 0.8800 | 0.8148 | |
| Balance Accuracy | 0.8045 | 0.7308 | 0.8846 | 0.8814 | 0.8045 | |
| Cognitive tests | Features |
|---|---|
| Osterrieth Complex Figure | Copy Short-term memory Long-term memory |
| Ineco Frontal Screening (IFS) | Verbal inhibitory control IFS Total |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA) | Abstraction MOCA Total |
| VFT (Verbal Fluency Test) | Semantic Fluency Repetitions |
| Cognitive tests | Features |
|---|---|
| Osterrieth Complex Figure | Copy Short-term memory Long-term memory |
| Ineco Frontal Screening (IFS) | Verbal inhibitory control Visual working memory IFS Total |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA) | Abstraction MOCA Total |
| VFT (Verbal Fluency Test) | Semantic Fluency Repetitions Exclusive Fluency Success |
| WAIS (Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale) | Matrices Similarities |
| SDMT (Symbol Digit Modalities Test) | Total correct answers Total answers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





