1. Introduction
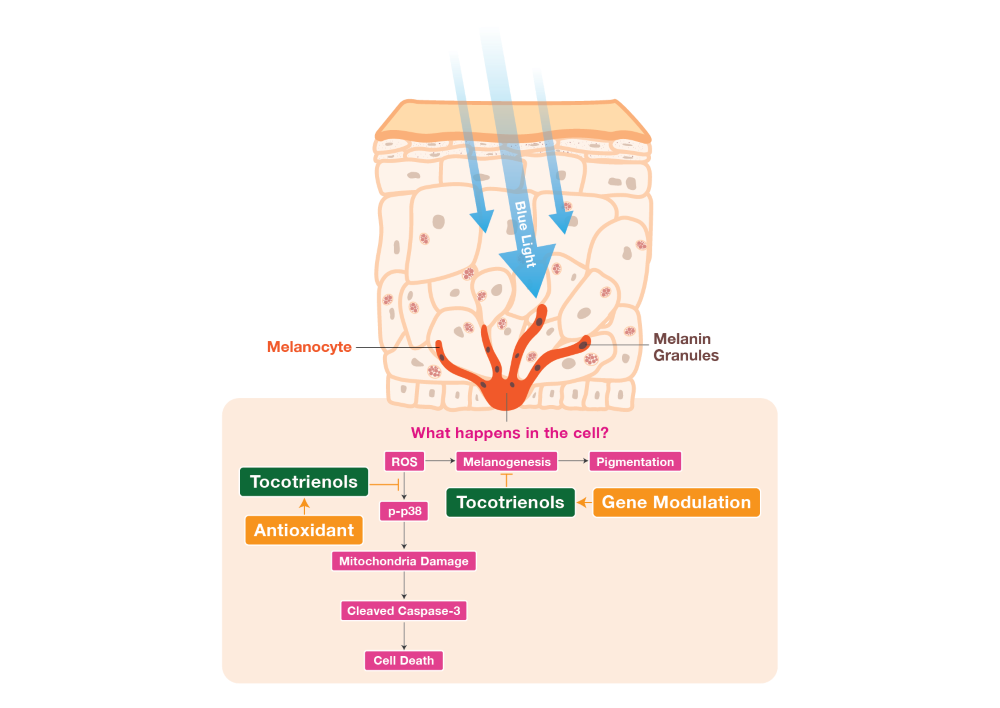
Our skin acts as a crucial barrier between the body and the external environment, protecting it from various environmental factors, such as solar radiation and air pollution (1). It serves as the primary defence and repair mechanism for the body, while also contributing to the maintenance of normal homeostasis. It is made up of 3 layers; the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Melanocytes, which are located in the basal layer of the epidermis, are an integral type of skin cell. These specialized cells synthesize melanin through complex enzymatic process, which gives rise to skin, eye and hair colour in humans and animals (2, 3). Sunlight, which is essential for the survival of most living organisms, consists of a range of wavelengths. The solar spectrum includes ultra-violet (UV) rays, visible light and infrared rays, that enter the terrestrial environment. Among these, UV rays comprises only 2% of solar spectrum, while visible light and infrared rays accounts for nearly half (4). Numerous studies have focused on understanding the skin protective measures required against UV, as they have the shortest wavelength (100 to 400 nm) and highest energy as compared to visible light (400 to 780 nm) and infrared rays (780 to 3000 nm), which have longer wavelengths and lower energy (5). Despite having lower energy, visible light is known to penetrate deeper into the skin due to its longer wavelength. The visible light spectrum consists of various colours, in increasing order of wavelengths: violet, blue, green, yellow, orange and red light. Blue light (BL; 450 to 485nm) is one of the most extensively studied visible light wavelengths (4). BL can be found in sunlight and artificially in devices such as light emitting diodes (LED) screens (laptop, mobile and tablet screens) or compact fluorescent lamp devices. (6). Recent studies have shown that BL can have detrimental effects on the skin, including the induction of skin pigmentation and photoaging (7, 8). BL has also been extensively studied for its potential in phototherapy against skin diseases such as melanoma as it can slow cell growth and promote apoptosis in melanoma cells. The effects are attributed to the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) molecules, such as superoxide, which can lead to mitochondrial membrane alterations and cell death (9, 10). As such, prolonged exposure to BL on healthy skin may result in irreversible damages to the skin. Therefore, it is widely acknowledged that exposure to artificial BL in modern times may have detrimental effects on skin health, leading to oxidative stress and pigmentation. Consequently, further studies are necessary to investigate protective measures for melanocytes against the damaging effects of BL
In such circumstances, antioxidants can effectively prevent damage caused by oxidative stress by maintaining a balanced cellular redox environment (11). Vitamin E has a well-established history of use in dermatology, cardiovascular health and neuroprotection due to its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It can be found from various food sources, such as plant oil and seeds (12). Studies have shown that vitamin E can alleviate inflammatory skin diseases and provide significant photoprotective effects (13, 14). Vitamin E primarily exists in eight isoforms, including: α-, β-, γ-, and δ-tocopherol (TP) and α-, β-, γ-, and δ-tocotrienol (T3). Both TPs and T3s differ in terms of their structural form, where T3s have the presence of an unsaturated side chain that enables better penetration into fatty tissues, making them more potent antioxidants compared to TPs (15). T3s have also been shown to protect the skin from oxidative stress-induced damage caused by particulate matter, and exhibit whitening effect by suppressing tyrosinase activity in UV-induced melanocytes, as reported in our previous studies (16, 17). In this study, we investigated the protective effects of T3s against the harmful effects of BL exposure on murine melanoma cells B16-F1. Our study utilized tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF), which comprises four T3 isoforms (α-, β-, γ- and δ-T3s) and αTP. The other vitamin E comparator used in this study was αTP, a commonly abundant form of vitamin E in the body (15). Although several studies have investigated the benefits of T3s for skin health, there is lack of studies specially focused on the effects of T3s on BL exposure. Given the potent antioxidative activities of T3s, it is hypothesized that T3s can protect the skin from excessive ROS generation, thereby alleviating cell death and skin hyperpigmentation. Therefore, our study aimed to elucidate the protective effects of T3s against BL exposure by investigating the antioxidative and anti-pigmentating mechanisms. To achieve this, the effects of TRF on BL-induced melanocytes were examined through a cell viability assay. Subsequent experiments revealed the presence of apoptosis, ROS formation, mitochondria damage, increase in melanin levels and elevated tyrosinase activity induced by BL. Additionally, an upregulation of activated p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and cleaved caspase-3 protein were observed. Collectively, these results illustrate the protective abilities of TRF against BL-induced damage and pigmentation in melanocytes.
2. Results
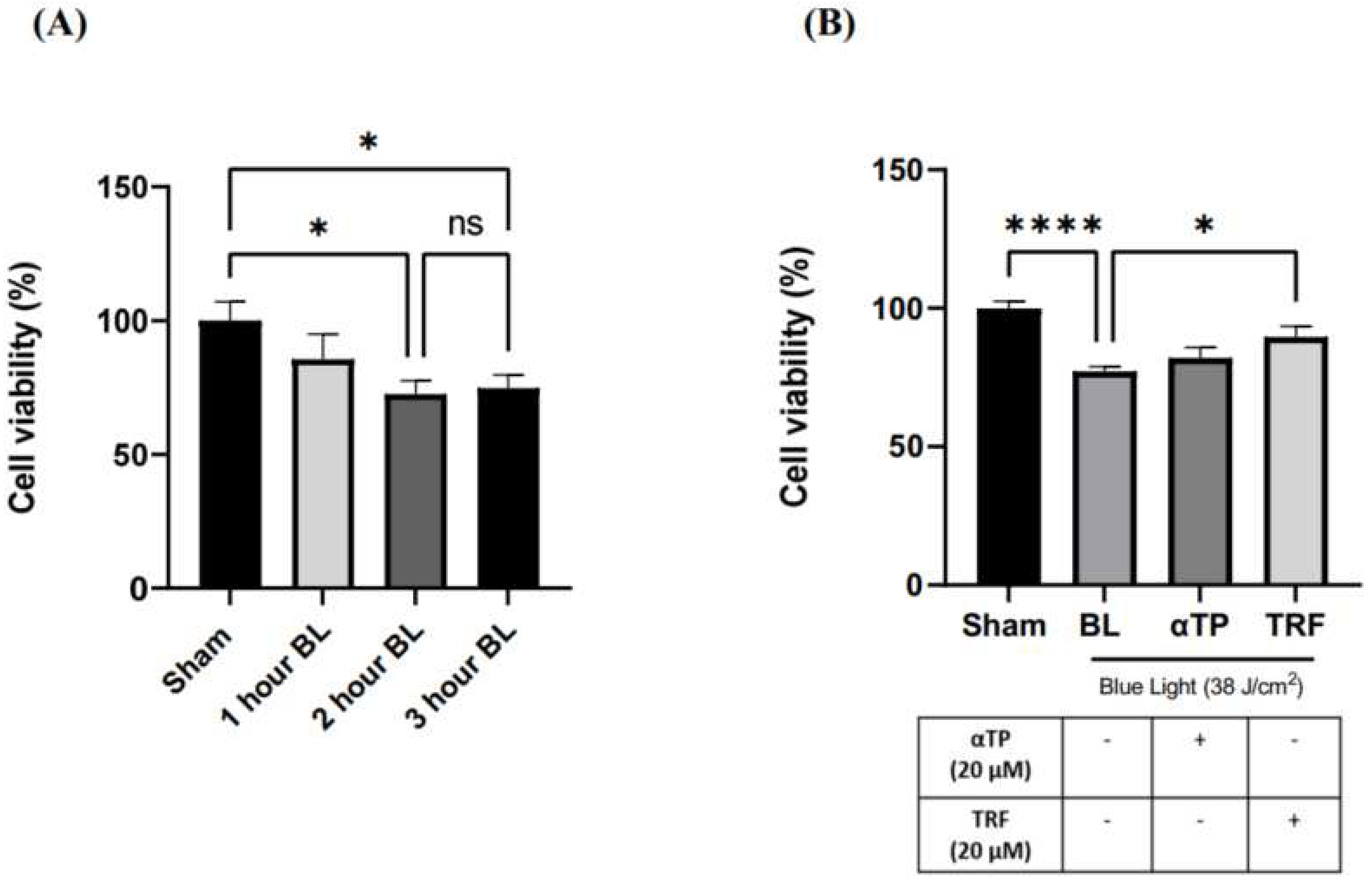
2.1. TRF Improved Cell Viability of BL-Induced melanocytes
To determine the optimal dosage of BL exposure for the cells, we performed cell irradiation at 3 different time points: 1 hour (12 J/cm
2), 2 hours (25 J/cm
2) and 3 hours (38 J/cm
2), using a 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5- diphenyltetrazoliumbromide (MTT) assay. Our results show a dose-dependent decrease in cell viability, with no significant difference between 25 and 38 J/cm
2 (
Figure 1A). Thus, 38 J/cm
2 was selected for our experiment to better represent real life BL exposure. This dosage is equivalent to approximately 300 hours of BL exposure from electronic devices at 100% screen brightness (18). Additionally, previous study has indicated that this dosage induces minimal lethal oxidative stress in cells, making it suitable for accurate experimentation (7). We further assessed the effect of TRF on the cell viability and found that treatment with 20 µM of TRF significantly increased the cell viability of BL-treated B16-F1 cells compared to αTP, where only a modest increase was shown (
Figure 1B).
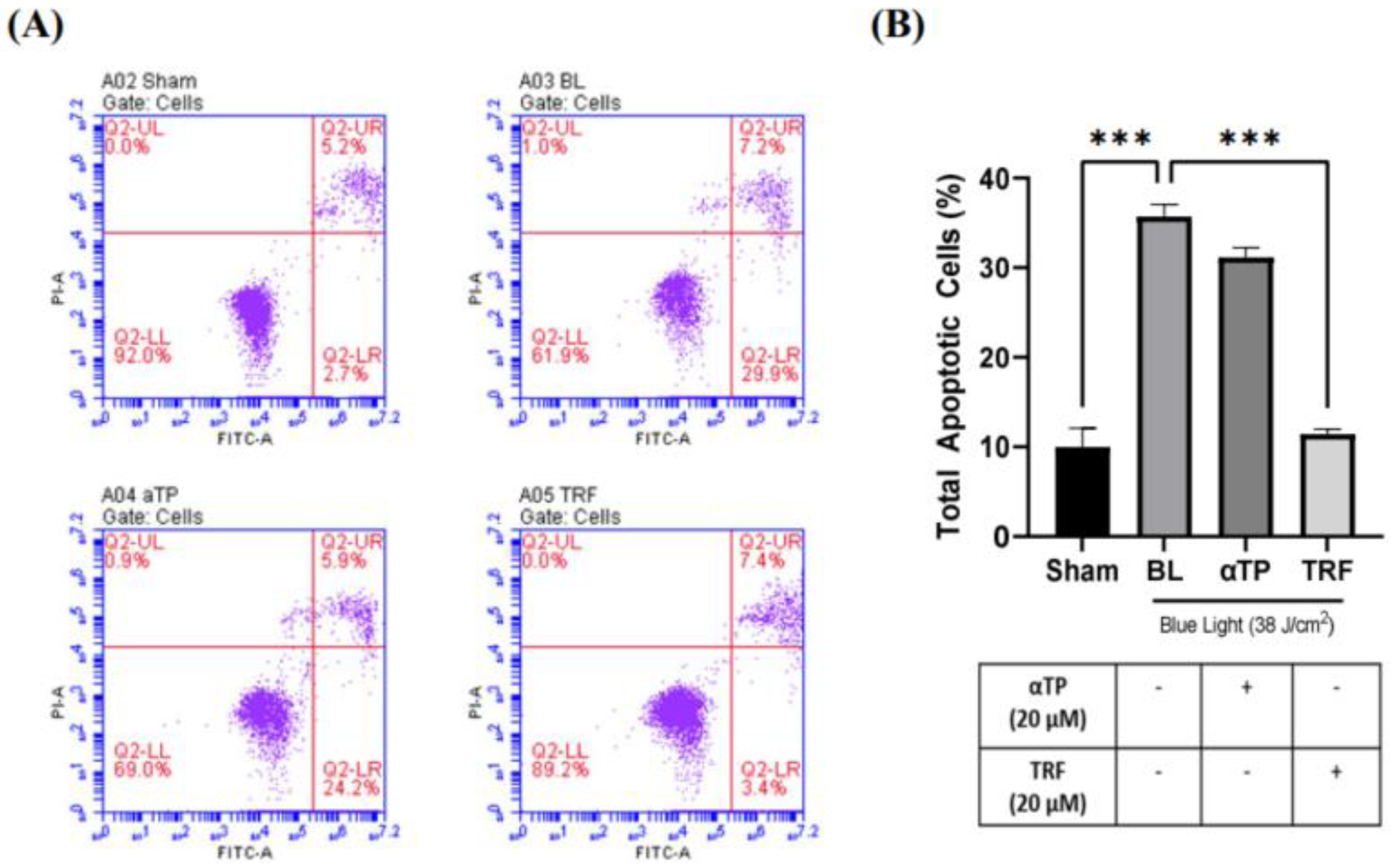
2.2. TRF inhibited BL-induced Cell Apoptosis
To provide further evidence supporting our findings, we conducted a flow cytometric assay to assess the population of apoptotic cells in both BL-induced and treated groups. A previous study has showed that BL induced cellular apoptosis as observed in B16-F10 cells (9). In our study, we used an Annexin V/Propidium Iodide (PI) double-staining assay to measure the population of apoptotic and necrotic cells. Our results showed a significant increase in the population of total apoptotic cells, particularly in the early apoptotic group, in the BL-induced melanocytes (
Figure 2A). Notably, the cells treated with TRF exhibited a rescue effect, as the number of apoptotic cells were significantly lower compared to the BL-irradiated cells (
Figure 2B).
2.3. TRF Exhibited Antioxidative Effects against Oxidative Stress Induced by BL
To examine the presence of oxidative stress in B16-F1 cells exposed to blue light, we used 2’, 7’-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFDA) fluorescent probe and captured images using fluorescence microscopy. We observed a stronger fluorescence signal in cells irradiated with BL compared to sham (negative control). However, treatment with αTP and TRF resulted in a reduction of the fluorescence signal, with TRF demonstrating a higher degree of reduction (
Figure 3A). To determine the levels of intracellular ROS, we measured the fluorescence intensity and normalized it to sham group. Both treatments showed protection against ROS, with TRF showing a higher antioxidative capacity compared to αTP (
Figure 3B).
2.4. TRF Regulated BL-Induced Mitochondria Membrane Potential Alterations
The effect of BL irradiation on the mitochondrial membrane potential of B16-F1 cells was evaluated using the JC-1 mitochondria staining kit. The presence of JC-1 monomers are indicated by green fluorescence and indicates a healthy mitochondrion, while the presence of JC-1 aggregates, represented by red fluorescence, indicates an unhealthy mitochondrion. Therefore, the ratio of red to green fluorescence can serve as an indicator of the membrane potential (19). Upon BL induction, a stronger intensity of green fluorescence was observed compared to red fluorescence. However, treatment with TRF exhibited a rescuing effect on the mitochondrial membrane potential, as evidenced by a significant restoration of the ratio of red to green fluorescence (
Figure 4A). As shown in
Figure 4B, there was a significant reduction in the red:green fluorescent ratio following BL exposure, suggesting mitochondria membrane depolarization. The ratio significantly improved back to baseline with TRF treatment, while this effect was not observed in the αTP group.
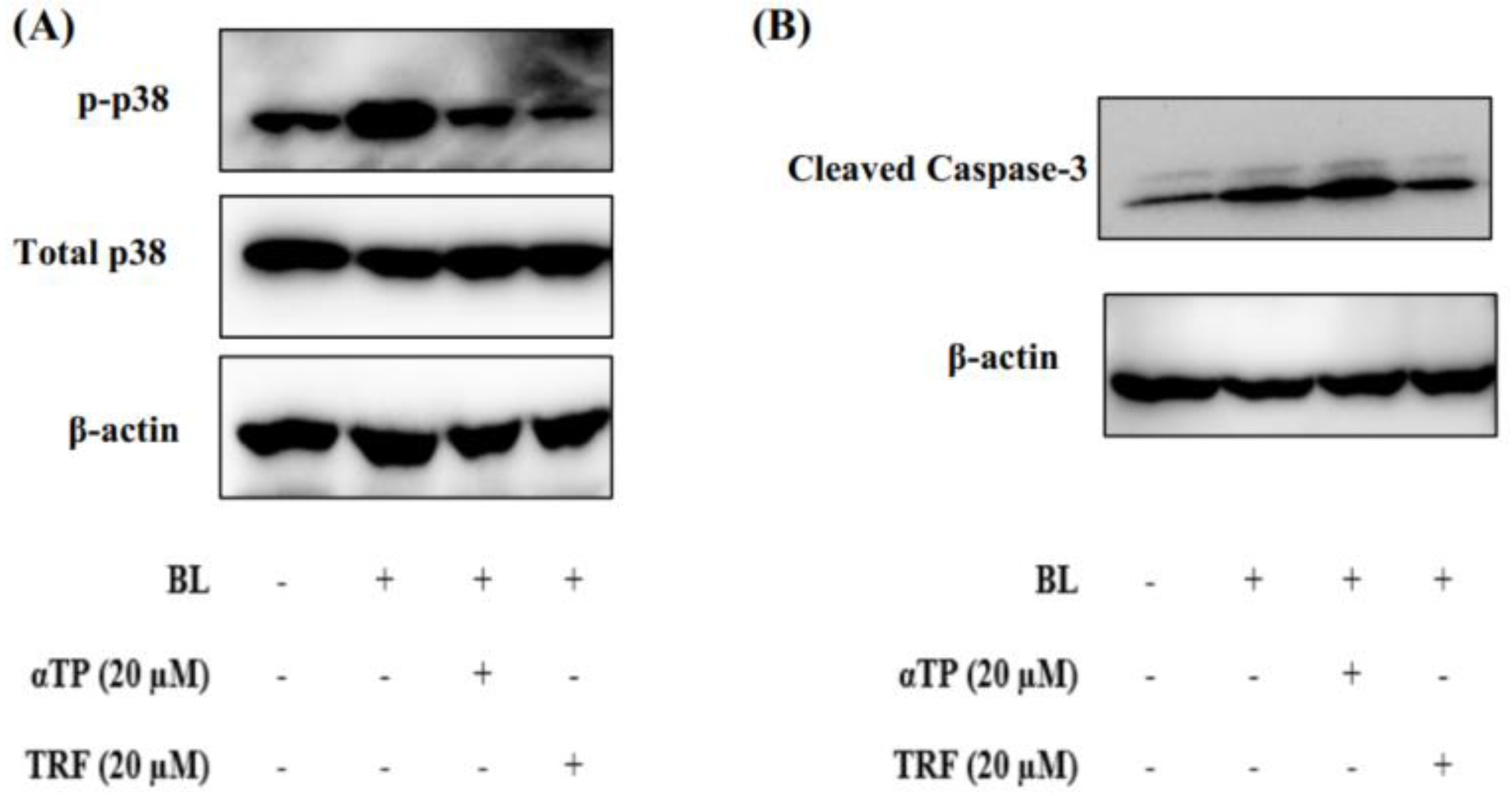
2.5. TRF Attenuated Cellular Death through Modulation of p38-MAPK Regulated Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway
Based on the results presented in the above sections, it can be theorized that mitochondrial dysfunction induced by BL may contribute to the observed cellular death. To understand the molecular mechanisms underlying this phenomenon, we studied the expression of proteins involved in the p38-MAPK regulated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway, namely p38 and caspase-3 (20). Upon BL induction, there was an extensive activation of p38, as evidenced by increased phosphorylation. However, treatment with αTP and TRF resulted a significant reduction in levels of phosphorylated p38 (
Figure 5A).
Additionally, we also investigated the expression levels of caspase-3 in B16-F1 cells exposed to BL. Activation of procaspase-3, indicated by the presence of cleaved caspase-3, was observed. Notably, treatment with TRF, but not αTP, significantly decreased the levels of cleaved caspase-3 (
Figure 5B). These results align with the results obtained from Annexin-V/PI and JC-1 assays, suggesting TRF may protect the cells from mitochondrial mediated apoptosis by preserving the mitochondrial membrane potential
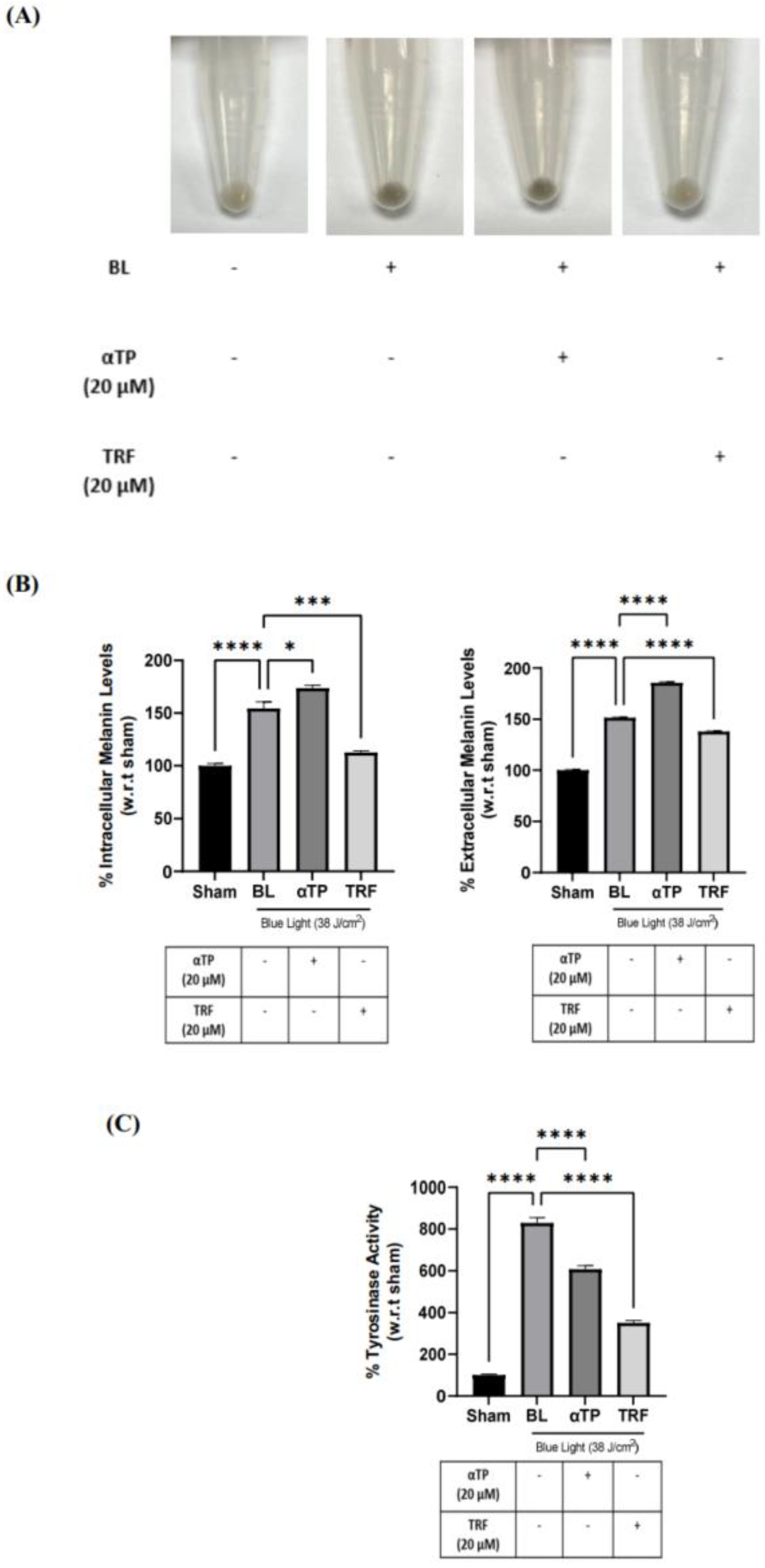
2.6. TRF Prevented Pigmentation Induced by BL through Regulation of Tyrosinase Activity
The pigmentation effect of BL on B16-F1 cells was investigated by observing changes in cell pellet colour and measuring intracellular and extracellular melanin content. BL exposure induced a visible darkening of the cell pellets , which was reversed by treatment with TRF (
Figure 6A). This finding is corroborated by the quantification of intra- and extracellular melanin levels, which showed a significant reduction in melanin levels in the TRF treated groups (
Figure 6B). To further elucidate the anti-pigmenting function of TRF, we assessed the tyrosinase activities in BL-induced cells. There was a drastic increase in tyrosinase activity after BL exposure. While both αTP and TRF were able to decrease the activity level, TRF appeared to exhibit a more pronounced effect (
Figure 6C).
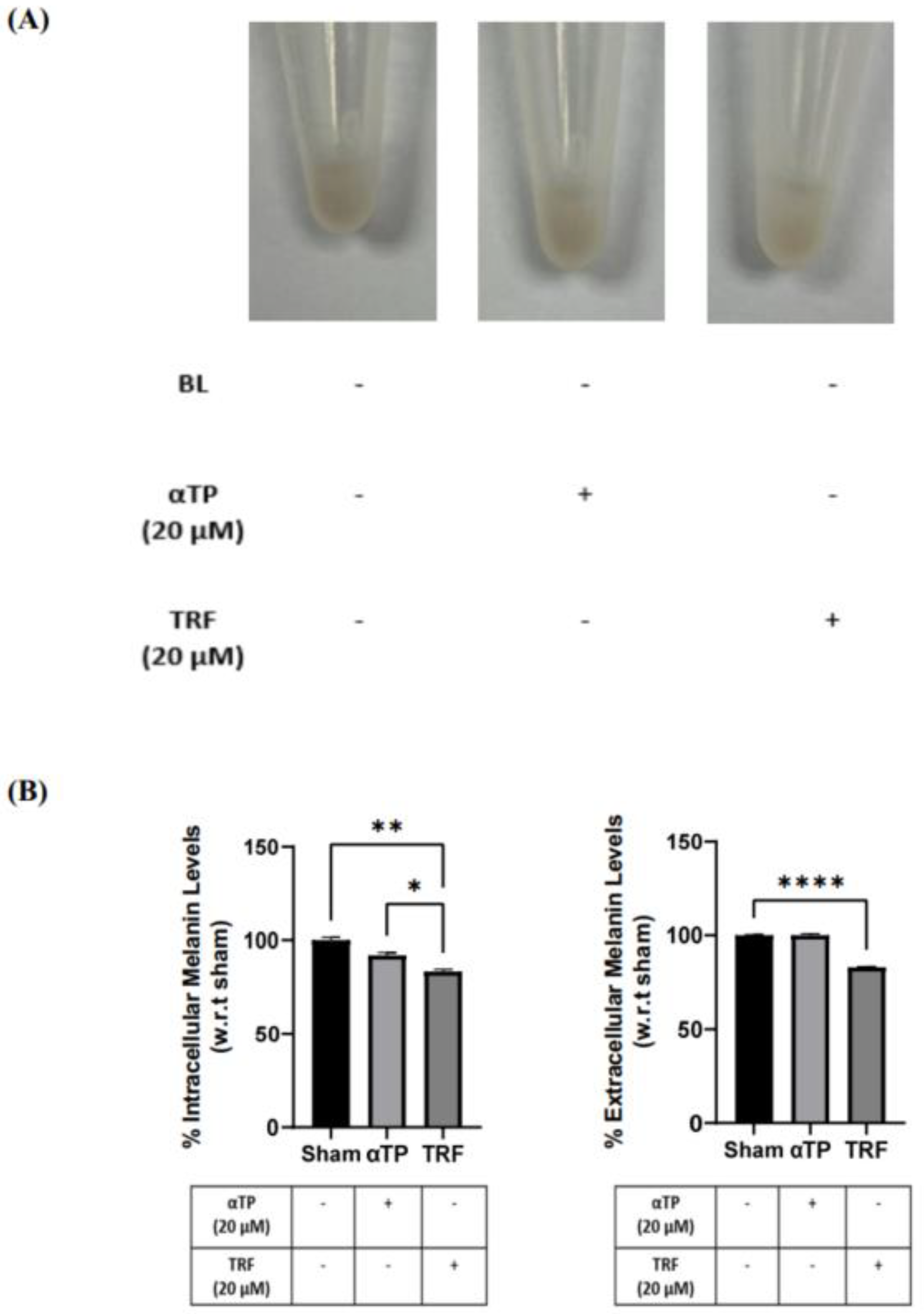
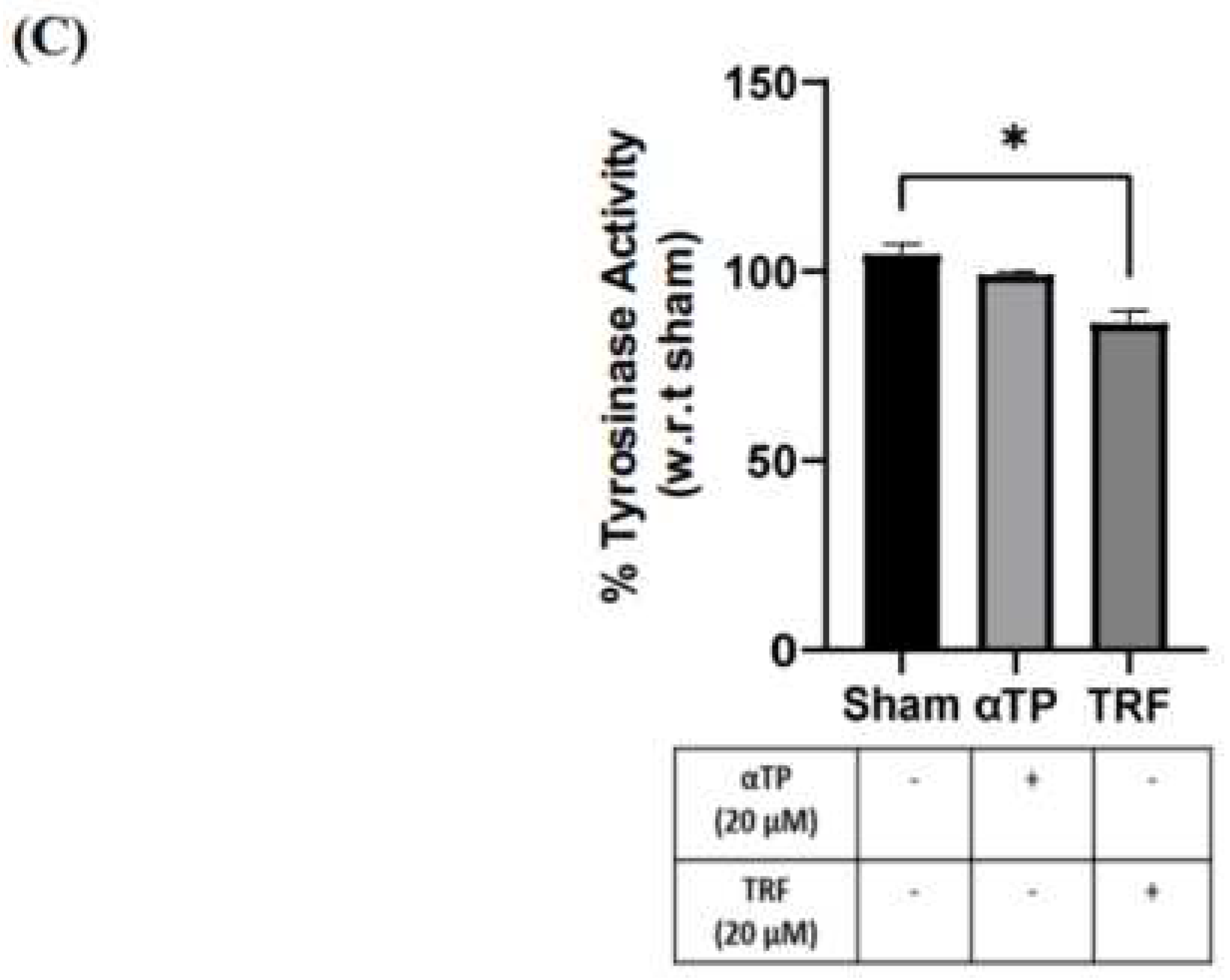
2.7. TRF exhibited Anti-Melanogenic Effects
To further investigate the effects of TRF on pigmentation, B16-F1 cells were treated with αTP and TRF in the absence of BL induction. Similar to previous experiment, changes of cell pellet colour, melanin levels, and tyrosinase activity were measured. TRF-treated cells exhibited a lighter pellet colour compared to the non-treated and αTP-treated cells (
Figure 7A). This finding is supported by the quantification levels of intra- and extracellular melanin levels, accompanied by the measurement of tyrosinase activity in the cells. Remarkably, TRF treatment resulted in a significant reduction in melanin levels and tyrosinase activity (
Figure 7B). These findings demonstrate that TRF may exhibit anti-melanogenic properties by modulating tyrosinase activity in the cells.
3. Discussion
In our modern, fast-paced and digitalized world, we are constantly surrounded by devices that emit blue light (BL), leading to an increase in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Melanin, a photoprotective and redox-active pigment, is produced in response to the increase oxidative stress caused by exposure to ROS. This pro-oxidative state triggers an upregulation of melanin production, resulting in skin darkening and hyperpigmentation (21). Our study investigated the antioxidative, anti-apoptotic and anti-melanogenic properties of TRF in BL exposed B16-F1 melanocytes. Additionally, we also aim to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying BL-induced apoptosis and pigmentation.
BL exposure is known to generate a significant amount of superoxide ROS, leading to cellular inflammation and oxidative stress. Under normal circumstances, our cells possess their own antioxidative systems that can eliminate the ROS generated. However, BL is known to oxidize the antioxidants produced by the cell, compromising the cell’s antioxidative capacity (22). When a cell undergoes oxidative stress, it can result in irreversible damage. If the cell’s endogenous repair mechanisms are unable to rapidly address this damage, it can accumulate and ultimately lead to cell death (23). In our study, we observed an increase in ROS levels in B16-F1 cells exposed to BL. However, both treatments, αTP & TRF, were effective in reducing the ROS produced, with TRF exhibiting a more significant protective effect. T3s acts as a potent antioxidant, scavenging free radicals more effectively than αTP due to their structural differences, which allow for better penetration. Furthermore, γT3s and TRF have been reported to possess various antioxidative properties, such as preventing the reduction of the enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) (24, 25). Regulation of SOD activity is crucial, as it is the only enzymes that exclusively interact with superoxide, keeping to maintain the levels of ROS at a minimal in cells (26). Therefore, our treatment with TRF might be beneficial in suppressing the formation of BL-induced superoxide, thereby protecting the cells from a pro-oxidative state.
The accumulation of ROS in cells can activate various signalling pathways, including apoptosis or necrosis pathways (27). One of the major pathways involved in cellular apoptosis is the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. MAPK signalling cascade plays a role in numerous physiological processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, inflammation and apoptosis. Among the different MAPK subgroups, p38 is often activated in response to oxidative stress, inflammation and DNA damage (28, 29). Activation of the p38 molecule is denoted by phosphorylation and can lead to either an intrinsic apoptotic pathway, activated by internal cell stresses, or an extrinsic apoptotic pathway, typically activated by external stimulus (30). Oxidative stress within cells, as part of the intrinsic pathway, can contribute to the activation of pro-apoptotic factors, resulting in mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and alteration of the mitochondrial membrane potential. This triggers a cascade of signalling events, including the release of the apoptogenic factor cytochrome c from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm. Cytochrome c in the cytosol then forms a complex with apoptotic protease activating factor-1 and caspase-9, further activating caspases such as caspase-3, and ultimately leading to cellular destruction (9, 31).
In this study, we investigated the effect of TRF on the activity of p38 MAPK molecule and the mitochondrial-mediated apoptotic pathway. Our results showed that TRF effectively abolished the activation of p38 molecule, improved the mitochondrial membrane potential and reduced the expression of cleaved caspase-3. Previous research by Satyamitra et al. (32) has reported that γT3s, an isomer found in TRF, can suppress the activities of caspase-3 and caspase-7, but do not affect the levels of cytochrome c. This suggests that γT3s may not directly rescue mitochondria function. Additionally, a previous study substantiates our findings by showing that treatment with TRF can lower levels of ROS and MAPK proteins, which are precursors of oxidative stress (16). Based on these observations, we theorize that TRF rescues B16-F1 cells exposed to BL due to its antioxidative nature, thereby terminating the downstream apoptotic signalling cascade. Further studies are warranted to fully understand the mechanisms by which TRF in modulates mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.
Our study demonstrated that prolonged BL exposure increased the rate of melanogenesis in B16-F1 cells by modulating tyrosinase activity. Tyrosinase and dopachrome tautomerase are the key liming enzymes involved in melanogenesis, which is the process of skin pigmentation (33). During melanogenesis, the formation of dopaquinone (DQ) is a rate-limiting step and is produced when L-tyrosine is oxidized by tyrosinase. The produced DQ then undergoes subsequent reactions to produce either pheomelanin or eumelanin, making tyrosinase a key enzyme in melanogenesis (34). In addition to tyrosinase, melanin synthesis in melanocytes is regulated by microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), which is the master gene of melanocyte development and can be activated by various external stimulus, including the MAPK signalling pathway (35).
In our study, TRF exhibited anti-melanogenic properties by reducing the levels of intra- and extracellular melanin produced upon BL induction. This could be attributed to the antioxidative functions of TRF. Furthermore, our results also established that TRF inhibited melanogenesis by modulating tyrosinase activity, suggesting that TRF may have a direct effect on melanin synthesis. Although the expression of MITF would be crucial in discussing the melanogenic pathways, our findings showed a significant decrease in tyrosinase activity with TRF treatment. Considering that tyrosinase expression is tightly regulated by MITF, it is plausible to consider that TRF may also exert an inhibitory effect on MITF expression (36).
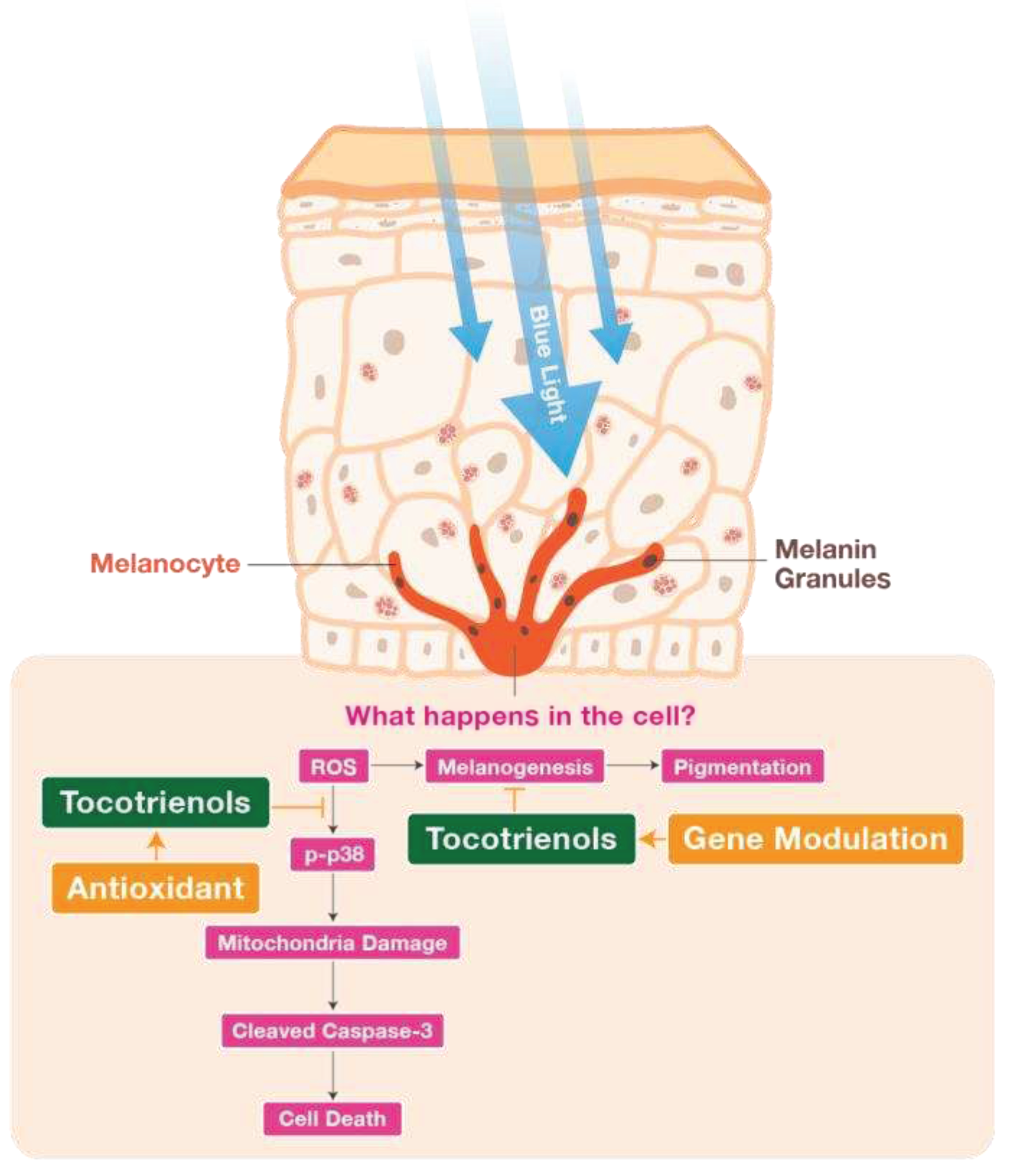
Prolonged BL exposure to skin can disrupt skin health by generating ROS and causing hyperpigmentation, which can accelerate skin ageing (37). BL also has detrimental effects on the mitochondrial health, leading to a decline in cell function and eventually cell death (38). Our study demonstrated that BL exposure induced cell death and hyperpigmentation in melanocytes. However, treatment with TRF was able to protect melanocytes from cell death and hyperpigmentation, potentially through the regulation of ROS and mitigation of mitochondria damage. TRF treatment also provided anti-pigmentation properties by regulating tyrosinase activity. In summary, our results indicate that TRF exhibits more robust protective effects against BL-induced damage in melanocytes compared to αTP, through a combination of antioxidative and anti-melanogenic mechanisms (
Figure 8). These findings support the potential of TRF as an active agent for protecting melanocytes from BL-induced damage. Future research, including human clinical trials, are warranted to validate the effects of TRF on human skin.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
Murine melanoma B16-F1 cell line (CRL-6323) was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA). Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; Nacalai Tesque Inc., Kyoto Japan) supplemented with 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (HyClone Laboratories, Logan, UT, USA) and 1% (v/v) penicillin G (100 U/mL) and streptomycin (100 µg/mL) (gibco, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Cells were grown and maintained at 37°C with 5% CO2 and humidity. Monoclonal antibodies against phospho-p38, total p38 and cleaved caspase 3 were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). Monoclonal antibody against β-actin was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Phosphate buffered saline (PBS), 0.05% trypsin and phenol red-free DMEM were purchased from gibco (Thermo Scientific). Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was purchased from Kanto Chemical Co. (Tokyo, Japan). Methanol and absolute ethanol were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Thermo Scientific). MTT, αTP, synthetic melanin, l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA), bovine serum albumin (BSA), DCFDA and JC-1 kit were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). TRF with a purity of > 95% was supplied by Davos Life Science Sdn Bhd (DavosLife E3, Malaysia).
4.2. Natural Extract and Cell Treatment
The TRF and αTP stock solution were prepared in absolute ethanol at a concentration of 100 mM, and stored at -20°C. The stocks were then diluted in complete DMEM or phenol red-free DMEM to a final concentration of 20 µM for each treatment. The B16-F1 cells were incubated with the respective treatments for 24 hours before irradiation, during the irradiation and after irradiation where necessary.
4.3. Cell Irradiation
The B16-F1 cells were subjected to artificial BL irradiation with the aim of inducing oxidative stress and melanin synthesis within the melanocytes. The BL source was a panel of LED light bulbs (15x15) with a power of 3.6 mW/cm2, emitting light at 465 nm (HQRP, Harrison, NJ, USA) placed in a customized WCI-40 CO2 incubator (Bio Laboratories Pte Ltd, Singapore). The B16-F1 cells were exposed to a BL irradiation dosage of 38 J/cm2, which is equivalent to 3 hours of in vitro BL exposure. Immediately after irradiation, fresh medium with the respective treatments were added and the cells were maintained in the CO2 incubator.
4.4. MTT Cell Viability Assay
The B16-F1 cells were cultured in individual wells of a 96-well plate at a density of 5 x 103 cells/well for 24 hours. Cell viability of the cells was measured 24 hours after BL irradiation. MTT solution (0.5 mg/mL) was added into each well for 2 hours and incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2 and humidity. The formazan crystals were dissolved in 200 µL of DMSO and the absorbance was measured at 595 nm using the Enspire® Multimode Plate Reader (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
4.5. Annexin-V Assay by Flow Cytometry
Cellular death was assessed by using the Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit with Annexin V (Thermo Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Cells were cultured in 60-mm petri dishes at a density of 2 x 105 cells/dish for 24 hours. At the end of 24 hours after BL, cells were harvested by trypsinization, washed twice in ice cold PBS and resuspended in 1X annexin-binding buffer at a concentration of 1 x 106 cells/mL. Samples were then used for flow cytometric analysis using the Accuri™ C6 Plus System (Becton Dickson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
4.6. Intracellular ROS assay
B16-F1 cells were cultured in 6-well plates at a density of 0.8 x 106 cells/well for 24 hours. Immediately after BL irradiation, the cell culture medium was aspirated and the cells were incubated with 10 µM of DCFDA dye for 30 minutes in the dark at 37°C. Cells were then washed twice in PBS and microscopic images were obtained using the EVOS M5000 Imaging System (Thermo Scientific) with a green excitation filter. Fluorescence intensity was then analysed using ImageJ version 1.8.0_172 (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) and data were normalized with respect to its respective sham values.
4.7. Mitochondria Membrane Potential
To assess the mitochondria membrane potential, the JC-1 assay was conducted. B16-F1 cells were cultured in 60-mm petri dishes at a density of 2 x 105 cells/dish for 24 hours. Immediately after BL irradiation, the cell culture medium was aspirated and the cells were incubated with 5 ug/mL of JC-1 dye for 20 minutes in the dark at 37°C. Subsequently, the cells were washed twice in incomplete DMEM. Microscopic images were obtained using an inverted microscope (Eclipse TE2000-U, Nikon, Minato City, Tokyo, Japan) with orange-red and green filters emitted from a Nikon Intensilight C-HGFI. Images were captured using a Nikon Digital Sight DS-U2. Fluorescence intensity was analysed using ImageJ version 1.8.0_172 (National Institutes of Health) and data were normalized with respect to its respective sham values.
4.8. Intracellular and Extracellular Melanin Content
The B16-F1 cells were cultured in 60-mm petri dishes at a density of 2 x 105 cells/dish for 24 hours. After 24 hours, the cells were harvested by scraping and the cell culture medium were collected. The cells were then incubated at 60°C at 1 hour in 1 M NaOH and vortexed to solubilize the melanin pigments. Following that cell suspensions and culture medium were centrifuged at 1,500 x rpm for 15 minutes. The absorbance was then measured at 405 nm using the EnSpire® Multimode Plate Reader (Perkin Elmer) and compared to a standard curve prepared using synthetic melanin. Thereafter, the intracellular and extracellular melanin content was determined based on absorbance/µg of protein. The protein content was determined using the DC protein assay kit (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
4.9. Tyrosinase Activity
Cellular tyrosinase activity was determined as reported by Lee et al, with slight modifications (39). The cells were cultured in 60-mm petri dishes at a density of 2 x 105 cells/dish for 24 hours. At the end of 24 hours post irradiation and treatment, cells were washed with PBS and collected with lysis buffer. The cells were then ruptured by freezing for 30 minutes in -80°C followed by thawing on ice. Afterwards, the lysate was clarified by centrifugation at 13,000 x rpm for 20 minutes at 4°C. The protein content was determined using the DC protein assay (Bio-Rad). An equal amount of protein was then added into each well of a 96-well plate, followed by 10% of 2 mg/mL L-DOPA prepared in phosphate solution. The well plate was then incubated at 37°C for 1 hour and the absorbance of the mixture was measured using the EnSpire® Multimode Plate Reader (Perkin Elmer).
4.10. Western Blot
Whole lysates were collected by resuspending the cell pellets with RadioImmunoPrecipitation Assay (RIPA) lysis buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 150 mM sodium chloride, 1 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 1% v/v nonidet P-40, 0.5% v/v sodium deoxycholate and 0.1% v/v sodium dodecyl sulfate, supplemented with protease and phosphatase cocktail inhibitors (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). The protein concentration was determined using the DC Protein Assay Kit (Bio-Rad) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and protein standards were prepared using BSA. The protein samples were then prepared and loaded onto polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis at 20 mA for 1 hours using the Mini-PROTEAN 3 Cell (Bio-Rad). The membrane was then blocked with 10% v/v non-fat milk in Tris-buffered Saline (TBS) supplied with 0.1% v/v Tween-20 (TBS-T). Subsequently, the blots were washed twice with TBS-T, and then incubated with the respective antibodies at 4°C overnight. The blots were then washed thrice with TBS-T to remove the unbound primary antibodies before exposure to IgG-HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies in 5% v/v non-fat milk in TBS-T for 1 hour at room temperature (25°C). The unbound secondary antibodies were removed by washing thrice with TBS-T. Chemiluminescent protein bands were then visualized by ECL Select Western Blot Detection Reagent (Amersham, Piscataway, NJ, USA) using the ChemiDoc MP Imaging System and ImageLab TM software (both from Bio-Rad) was used for densitometric analysis.
4.11. Statistical Analysis
All results are expressed as the mean + standard error of the mean (SEM) and the data obtained were statistically evaluated by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test using GraphPad Prism 9.4.1 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). A p value of < 0.05 (*) was considered to be statistically significant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.N.Y. and Y.W.U.; Methodology, J.R.E.N. and W.N.Y.; Validation, J.R.E.N. and W.N.Y.; Formal Analysis, J.R.E.N.; Investigation, J.R.E.N. and W.N.Y; Data Curation, J.R.E.N.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, J.R.E.N.; Writing – Review & Editing, J.R.E.N, W.N.Y., Y.W.U.; Supervision, W.N.Y.; Project Administration, J.R.E.N. and C.W.L.T.; Funding Acquisition, W.N.Y and Y.W.U.
Funding
This work was supported financially by a research fund from KL-Kepong Oleomas (KLK Oleo) to Davos Life Science Pte Ltd.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to extend special thanks to Mr Vincent Boey Ying Shiun for the graphical abstract.
Conflicts of Interest
Juvenia Rui En Neo and Wei Ney Yap works for Davos Life Science (a subsidiary of KLK Oleo). Cheryl Wei Ling Teo is an ex-employee of Davos Life Science. Yee Wei Ung works for KLK Oleo, a manufacturer of tocotrienols.
References
- Krutmann, J.; Bouloc, A.; Sore, G.; Bernard, B.A.; Passeron, T. The skin aging exposome. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 85, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Vukmanovic-Stejic, M. Skin barrier immunity and ageing. Immunology 2019, 160, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passeron, T.; Coelho, S.G.; Miyamura, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Hearing, V.J. Immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization in the study of human skin melanocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assis, L.V.M.; Tonolli, P.N.; Moraes, M.N.; Baptista, M.S.; Castrucci, A.M.d.L. How does the skin sense sun light? An integrative view of light sensing molecules. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 2021, 47, 100403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenese, A.; Korpinen, L.; Gobba, F. Solar Radiation Exposure and Outdoor Work: An Underestimated Occupational Risk. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Hagan, J.B.; Khazova, M.; A Price, L.L. Low-energy light bulbs, computers, tablets and the blue light hazard. Eye 2016, 30, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorrio S, Rodriguez-Luna A, Delgado-Wicke P, Mascaraque M, Gallego M, Perez-Davo A, et al. Protective Effect of the Aqueous Extract of Deschampsia antarctica (EDAFENCE((R))) on Skin Cells against Blue Light Emitted from Digital Devices. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21.
- Portillo M, Mataix M, Alonso-Juarranz M, Lorrio S, Villalba M, Rodriguez-Luna A, et al. The Aqueous Extract of Polypodium leucotomos (Fernblock((R))) Regulates Opsin 3 and Prevents Photooxidation of Melanin Precursors on Skin Cells Exposed to Blue Light Emitted from Digital Devices. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10.
- Oh, P.-S.; Na, K.S.; Hwang, H.; Lim, S.; Sohn, M.-H.; Jeong, H.-J. Effect of blue light emitting diodes on melanoma cells: Involvement of apoptotic signaling. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2015, 142, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Minai, Y.; Watanabe, H. Effect of monochromatic visible light on intracellular superoxide anion production and mitochondrial membrane potential of B16F1 and B16F10 murine melanoma cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.; Lee, M.-G. Oxidative stress and antioxidant strategies in dermatology. Redox Rep. 2016, 21, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Zaffarin AS, Ng SF, Ng MH, Hassan H, Alias E. Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics of Vitamin E: Nanoformulations to Enhance Bioavailability. Int J Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 9961–9974. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardesca, E.; Cameli, N. Vitamin E supplementation in inflammatory skin diseases. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, J.J.; Ekanayake-Mudiyanselage, S. Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Mol. Aspects Med. 2007, 28, 646–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanchi, M.M.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Rane, G.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P. Tocotrienols: the unsaturated sidekick shifting new paradigms in vitamin E therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1765–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, J.R.E.; Teo, Z.N.; Yeo, J.S.E.; Ng, C.K.S.; Teo, C.W.L.; Ung, Y.W.; Yap, W.N. Tocotrienols improve urban particulate matter-induced skin damages by regulating skin barrier function and ROS/MAPK signalling pathway in keratinocytes. Atmospheric Pollut. Res. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, W.N.; Zaiden, N.; Xu, C.H.; Chen, A.; Ong, S.; Teo, V.; Yap, Y.L. Gamma- and delta-tocotrienols inhibit skin melanin synthesis by suppressing constitutive and UV-induced tyrosinase activation. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2010, 23, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rascalou, A.; Lamartine, J.; Poydenot, P.; Demarne, F.; Bechetoille, N. Mitochondrial damage and cytoskeleton reorganization in human dermal fibroblasts exposed to artificial visible light similar to screen-emitted light. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 91, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivandzade, F.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. Analysis of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Using the Cationic JC-1 Dye as a Sensitive Fluorescent Probe. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3128–e3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Nian, Q.; Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Z. Ghrelin ameliorates A549 cell apoptosis caused by paraquat via p38-MAPK regulated mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Toxicology 2019, 426, 152267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, F. Photoprotection and Skin Pigmentation: Melanin-Related Molecules and Some Other New Agents Obtained from Natural Sources. Molecules 2020, 25, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima, Y.; Ohta, S.; Wolf, A.M. Blue light-induced oxidative stress in live skin. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Yepes J, Burns M, Anandhan A, Khalimonchuk O, del Razo LM, Quintanilla-Vega B, et al. Oxidative stress, redox signaling, and autophagy: cell death versus survival. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 66–85. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q. Natural forms of vitamin E: metabolism, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities and their role in disease prevention and therapy. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; Mathai, M.; Zulli, A. Revisiting the therapeutic potential of tocotrienol. BioFactors 2022, 48, 813–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Branicky, R.; Noë, A.; Hekimi, S. Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, G.L.; Lapadat, R. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways Mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 Protein Kinases. Science 2002, 298, 1911–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräb, J.; Rybniker, J. The Expanding Role of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Programmed Host Cell Death. Microbiol. Insights 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, E.; Eaves, C.J. Paradoxical roles of caspase-3 in regulating cell survival, proliferation, and tumorigenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2022, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satyamitra M, Ney P, Graves J, 3rd, Mullaney C, Srinivasan V. Mechanism of radioprotection by delta-tocotrienol: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and modulation of signalling pathways. Br J Radiol. 2012, 85, e1093-103.
- Lee, A.-Y. Skin Pigmentation Abnormalities and Their Possible Relationship with Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Namasivayam, V. Skin whitening agents: medicinal chemistry perspective of tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim SY, Lee YE, Lee M. Antioxidant Compounds, Kirenol and Methyl ent-16alpha, 17-dihydroxy-kauran-19-oate Bioactivity-Guided Isolated from Siegesbeckia glabrescens Attenuates MITF-Mediated Melanogenesis via Inhibition of Intracellular ROS Production. Molecules 2021, 26.
- Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Qu, B.; Wang, M.; Yu, X.; Chen, J. Mitf Involved in Innate Immunity by Activating Tyrosinase-Mediated Melanin Synthesis in Pteria penguin. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suitthimeathegorn, O.; Yang, C.; Ma, Y.; Liu, W. Direct and Indirect Effects of Blue Light Exposure on Skin: A Review of Published Literature. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 35, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godley, B.F.; Shamsi, F.A.; Liang, F.-Q.; Jarrett, S.G.; Davies, S.; Boulton, M. Blue Light Induces Mitochondrial DNA Damage and Free Radical Production in Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21061–21066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.; Choi, H.I.; Kim, C.D.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.D. Downregulation of NFAT2 promotes melanogenesis in B16 melanoma cells. Anat. Cell Biol. 2010, 43, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).