Submitted:
26 September 2023
Posted:
26 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
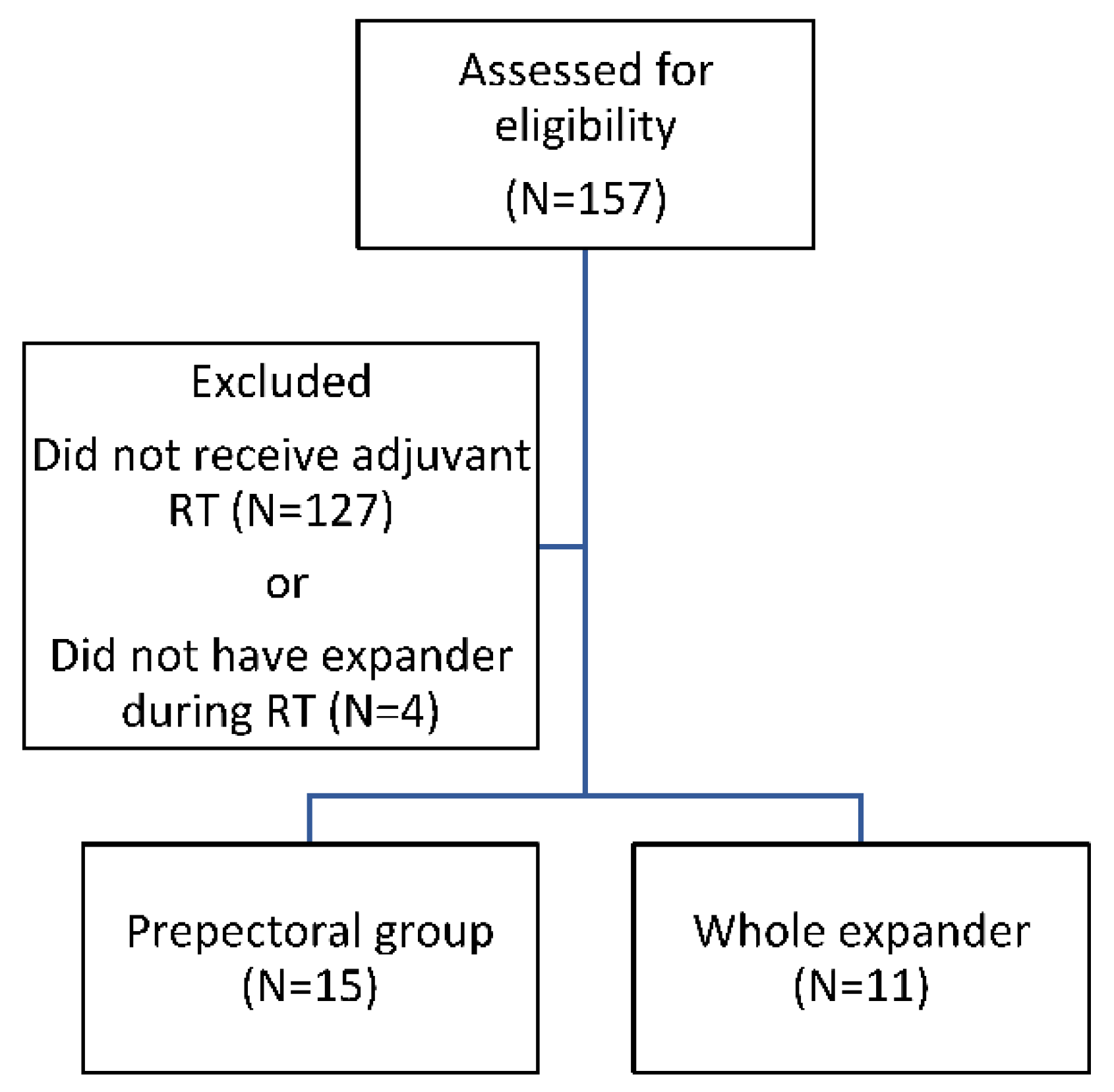
2.1. Patient Population
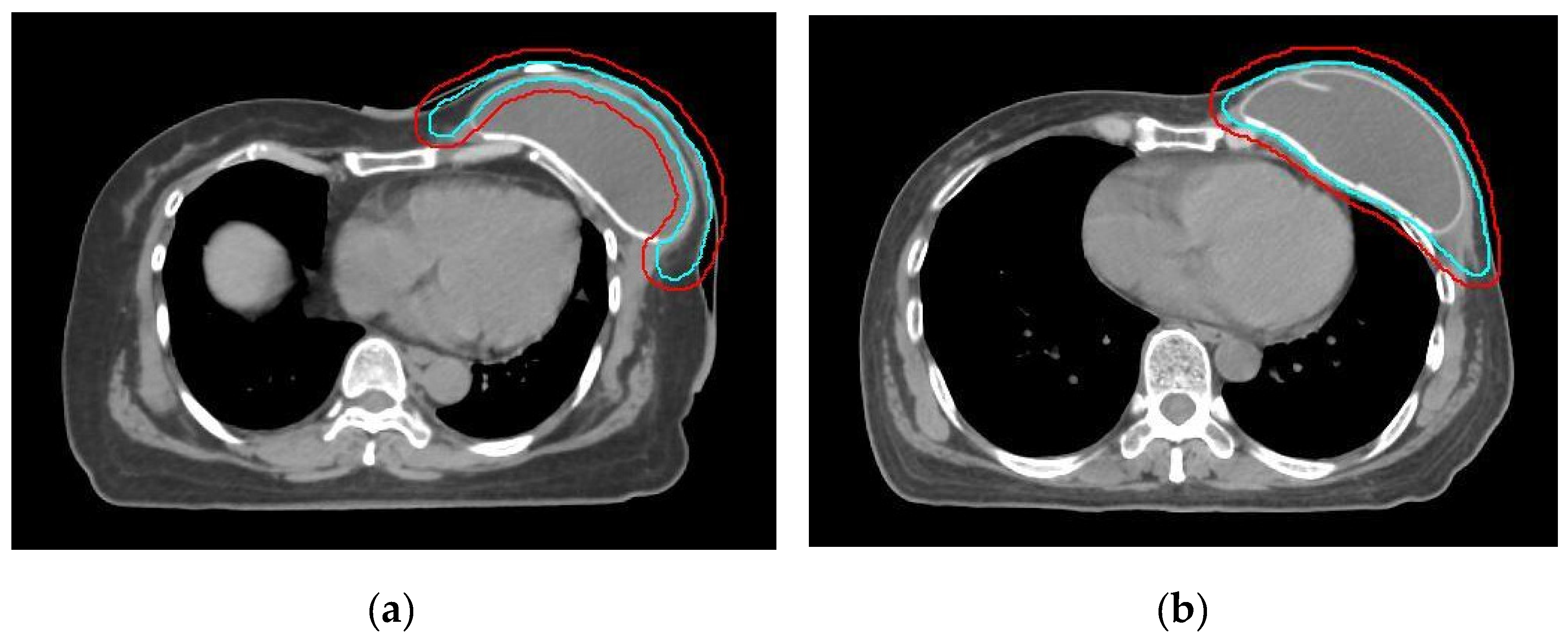
2.2. RT Treatment Plan
2.3. Reconstruction Complication
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
3.2. Comparisons of Dosimetric Outcomes
3.3. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, M.B.; Benson, J.R.; Audretsch, W.; Blondeel, P.; Catanuto, G.; Clemens, M.W.; Cordeiro, P.G.; De Vita, R.; Hammond, D.C.; Jassem, J. International multidisciplinary expert panel consensus on breast reconstruction and radiotherapy. Journal of British Surgery 2019, 106, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momoh, A.O.; Griffith, K.A.; Hawley, S.T.; Morrow, M.; Ward, K.C.; Hamilton, A.S.; Shumway, D.; Katz, S.J.; Jagsi, R. Post-mastectomy breast reconstruction: Exploring plastic surgeon practice patterns and perspectives. Plastic and reconstructive surgery 2020, 145, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billig, J.; Jagsi, R.; Qi, J.; Hamill, J.B.; Kim, H.M.; Pusic, A.L.; Buchel, E.; Wilkins, E.G.; Momoh, A.O. Should immediate autologous breast reconstruction be considered in women who require post-mastectomy radiation therapy? A prospective analysis of outcomes. Plastic and reconstructive surgery 2017, 139, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyam, B.V.; Shah, C.; Woody, N.M.; Reddy, C.A.; Weller, M.A.; Juloori, A.; Naik, M.; Valente, S.; Grobmyer, S.; Durand, P. Long-term outcomes after autologous or tissue expander/implant–based breast reconstruction and postmastectomy radiation for breast cancer. Practical Radiation Oncology 2019, 9, e497–e505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaverien, M.V.; Macmillan, R.D.; McCulley, S.J. Is immediate autologous breast reconstruction with postoperative radiotherapy good practice?: a systematic review of the literature. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 2013, 66, 1637–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, R.; Moustaki, M.; Harris, S.; Roblin, P.; Farhadi, J. Does post-mastectomy radiotherapy affect the outcome and prevalence of complications in immediate DIEP breast reconstruction? A prospective cohort study. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 2015, 68, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidar-Person, O.; Offersen, B.V.; Hol, S.; Arenas, M.; Aristei, C.; Bourgier, C.; Cardoso, M.J.; Chua, B.; Coles, C.E.; Damsgaard, T.E. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline for target volume delineation in the setting of postmastectomy radiation therapy after implant-based immediate reconstruction for early stage breast cancer. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2019, 137, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.J.; Kang, S.G.; Kim, E.K.; Song, S.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jin, U.S. Current status of and trends in post-mastectomy breast reconstruction in Korea. Archives of plastic surgery 2020, 47, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbaum, A.; Nakhla, M.; Seo, Y.J.; Dobaria, V.; Attai, D.J.; Baker, J.L.; Thompson, C.K.; DiNome, M.L.; Benharash, P.; Lee, M.K. National trends and predictors of mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction. The American Journal of Surgery 2021, 222, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, V.P.; Laikhter, E.; Manstein, S.M.; Comer, C.D.; Veeramani, A.; Shiah, E.; Xun, H.; Lin, S.J.; Lee, B.T. A national analysis of outpatient mastectomy and breast reconstruction trends from 2013 through 2019. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 2022, 75, 2920–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayaratna, N.; Nguyen, C.L.; Spillane, A.; Mak, C.; Warrier, S.K.; Dusseldorp, J.R. Trends and variations in post-mastectomy breast reconstruction rates in Australia over 10 years. ANZ Journal of Surgery 2023, 93, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott, C.J.; Persing, S.M.; Pronovost, M.; Hodyl, C.; McConnell, D.; Ott Young, A. Impact of postmastectomy radiation therapy in prepectoral versus subpectoral implant-based breast reconstruction. Annals of Surgical Oncology 2018, 25, 2899–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, C.; Kraenzlin, F.; Aravind, P.; Kokosis, G.; Yesantharao, P.; Sacks, J.M.; Rosson, G.D. Prepectoral breast reconstruction is safe in the setting of post-mastectomy radiation therapy. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 2022, 75, 3041–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.P.; Shaw, J.; Pusic, A.; Wyld, L.; Morrow, M.; King, T.; Mátrai, Z.; Heil, J.; Fitzal, F.; Potter, S. Oncoplastic breast consortium recommendations for mastectomy and whole breast reconstruction in the setting of post-mastectomy radiation therapy. The Breast 2022, 63, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rose, F.; Fogliata, A.; Franceschini, D.; Cozzi, S.; Iftode, C.; Stravato, A.; Tomatis, S.; Masci, G.; Torrisi, R.; Testori, A. Postmastectomy radiation therapy using VMAT technique for breast cancer patients with expander reconstruction. Medical Oncology 2019, 36, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, C.; McClure, J.A.; Baxter, N.N.; Brackstone, M. Complications From Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy in Patients Undergoing Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Population-Based Study. Advances in Radiation Oncology 2023, 8, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.; Fried, D.; Marks, L.B.; Gupta, G.P.; Jones, E.; Elmore, S.; Pearlstein, K.; Downs-Canner, S.; Gallagher, K.; Spanheimer, P.M. Dosimetric and Clinical Factors Associated With Breast Reconstruction Complications in Patients Receiving Postmastectomy Radiation. Practical Radiation Oncology 2022, 12, e169–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, C.F.P.M.; Neto, E.S.; Chen, M.J.; Silva, M.L.G.; Abrahão, C.H.; Ramos, H.; Fogaroli, R.C.; de Castro, D.G.; Favareto, S.L.; Pinto, P.J.J. Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy Bolus Associated Complications in Patients Who Underwent 2-stage Breast Reconstruction. Advances in Radiation Oncology 2022, 7, 101010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Song, S.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Lew, D.H.; Roh, T.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Keum, K.C.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, Y.B. Influence of radiation dose to reconstructed breast following mastectomy on complication in breast cancer patients undergoing two-stage prosthetic breast reconstruction. Frontiers in oncology 2019, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoum, G.E.; Ioakeim, M.I.; Shui, A.M.; Salama, L.; Colwell, A.; Ho, A.Y.; Taghian, A.G. Radiation modality (Proton/Photon), timing, and complication rates in patients with breast cancer receiving 2-stages Expander/Implant reconstruction. Practical Radiation Oncology 2022, 12, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, M.B.; Pennati, A.E.; Lozza, L.; Spano, A.; Zambetti, M.; Catanuto, G. Outcome of Different Timings of Radiotherapy in Implant-Based Breast Reconstructions. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2011, 128, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, P.G.; Albornoz, C.R.; McCormick, B.; Hudis, C.A.; Hu, Q.; Heerdt, A.; Matros, E. What is the optimum timing of post-mastectomy radiotherapy in two-stage prosthetic reconstruction: radiation to the tissue expander or permanent implant? Plastic and reconstructive surgery 2015, 135, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, J.A.; Epstein, S.; Momoh, A.O.; Lin, S.J.; Singhal, D.; Lee, B.T. A meta-analysis of implant-based breast reconstruction and timing of adjuvant radiation therapy. Journal of Surgical Research 2017, 218, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santosa, K.B.; Chen, X.; Qi, J.; Ballard, T.N.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Bensenhaver, J.M.; Pusic, A.L.; Wilkins, E.G. Post-Mastectomy Radiation Therapy (PMRT) and Two-Staged Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: Is There a Better Time to Radiate? Plastic and reconstructive surgery 2016, 138, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momoh, A.O.; Griffith, K.A.; Hawley, S.T.; Morrow, M.; Ward, K.C.; Hamilton, A.S.; Shumway, D.; Katz, S.J.; Jagsi, R. Patterns and correlates of knowledge, communication, and receipt of breast reconstruction in a modern population-based cohort of patients with breast cancer. Plastic and reconstructive surgery 2019, 144, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Prepectoral (n = 15) | Whole Expander (n = 11) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (SD) (range) |
50 (7.6) (32-58) | 50 (11.6) (27-65) | 0.61 |
| Rt side | 9 | 6 | 0.78 |
| Lt side | 6 | 5 | |
| Pathology | |||
| IDC | 15 | 10 | 0.42 |
| ILC | 0 | 1 | |
| Grade | 0.95 | ||
| Gr1+2 | 7 (1+6) | 5 (1+4) | |
| Gr3 | 8 | 6 | |
| Stage | 0.11 | ||
| Stage 1+2 | 5 (0+5) | 8 (1+7) | |
| Stage 3+4 | 10 (9+1) | 3 (3+0) | |
| pTis+T1+T2 | 13 (0+2+11) | 10 (1+2+7) | 1 |
| pT3+T4 | 2 (2+0) | 1 (1+0) | |
| pN0+1 | 6 (1+5) | 8 (2+6) | 0.13 |
| pN2+3 | 9 (6+3) | 3 (3+0) | |
| Clinical or pathological M1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| ER positive | 12 | 9 | 1 |
| PR positive | 12 | 7 | 0.41 |
| HER-2 positive | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| Chemotherapy | 15 | 10 | 0.42 |
| Target therapy | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| Anti-hormone therapy | 12 | 8 | 1 |
| Immunotherapy | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Smoking | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Characteristics | Prepectoral (n = 15) | Whole Expander (n = 11) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| RT technique | 0.61 | ||
| Hybrid+IMRT | 3 (2+1) | 1 (0+1) | |
| VMAT+Helical tomotherapy | 12 (8+4) | 10 (5+5) | |
| RT total dose (Gy) (SD) (range) |
50 (5.4) (45-60) |
55 (6.9) (40-61) |
0.26 |
| Number of fractions (SD) (range) |
25 (3.2) (20-33) |
30 (5.2) (15-33) |
0.22 |
| Conventional fractionation: N (%) | 14 | 10 | 1 |
| Hypofractionation: N (%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Heart Mean dose (Gy) (SD) (range) |
2.8 (1.67) (0.74-6.36) |
2.64 (4.35) (1.02-14.98) |
0.72 |
| Ipsilateral Lung Mean dose (Gy) (SD) (range) |
10.2 (2.86) (3.54-12.72) |
11.1 (3.75) (6.76-19.72) |
0.06 |
| Contralateral Breast Mean dose (Gy) (SD) (range) |
2.89 (1.19) (0.82-5.05) |
2.47 (1.44) (1.32-6.13) |
0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




