1. Introduction
To protect the fragile ecosystem and economy, combat desertification, and control dust storms, the Chinese central and local governments have implemented a series of ecological engineering projects in China [
1], such as the Slope Land Conversion Project, China’s Natural Forest Protection Project, River Shelterbelt Project, and the Returning Farmland to Forest and Grassland [
2]. Ecological engineering slowed desertification and its expansion in China, significantly contributing to the world's “greening” trend [
3]. Chen et al. [
3] indicated that the global green leaf area has increased by 5% since the early 2000s. China and India contributed 25% and 6.8%, respectively, to the increase in greening on land.
However, this significant land cover change resulting from afforestation very strongly affected the ecological environment, especially the water resources [
4,
5,
6,
7]. It was confirmed that forests could increase regional evapotranspiration and reduce total runoff discharge compared to the absence of forests under the same precipitation conditions. Some studies pointed out that 10-40% of annual precipitation was lost by the canopy interception [
8] It was shown that the total canopy interception was calculated to be 76.6 mm in Shaanxi Province, northwest China, accounting for 18.6% of the gross precipitation. Moreover, in forests, the shallow roots extract soil water provided by precipitation while consuming groundwater by the deep roots during the dry period [
9].Karimov et al. [
10] found that shallow groundwater contribution to plant transpiration exceeds 60% in the upstream area of the Syrdarya River, in Central Asia. In the Ejina Basin, China,
Populus euphratica obtains 53% of its water from groundwater [
11]. In the dry season, the groundwater uptake accounts for 73.2% [
12]. Under the effects of canopy interception and transpiration from soil and aquifer layers, the effective precipitation and groundwater recharge in forests is much lower than in other areas [
13]. Keese et al. [
14] used an unsaturated flow modeling study that indicated the forests significantly decrease groundwater recharge by factors of 2 to 30 relative to the recharge for non-vegetated simulations [
14]. Therefore, it was concluded that large-scale tree planting in China could lead to regional water resource shortages. Xiao et al. [
15] indicated that since 2000, the water consumption of plantations has increased to 40.42 billion m
3 in southwest China. This amount accounts for 10.69% of the water resources for the entire year. Cao et al. [
16] used seven models and estimated that afforestation will increase net water consumption by 559-2354 m
3/ha annually compared with the amount of water potential natural vegetation would consume. Water resources are an important basis for maintaining the sustainability of ecosystem development in arid and semi-arid areas [
17,
18]. Due to climate change and water resources development and utilization, the spatial distribution of water resources changes [
19], leading to the risk of water supply - demand in regional ecosystems [
20].
Inner Mongolia is a perfect natural laboratory to study the forest’s effects on regional water resources. The forest areas of Inner Mongolia showed rapid increases through several large-scale ecological restoration projects implemented since 2000. Inner Mongolia is located in environmentally fragile arid and semi-arid regions that currently face water scarcity. However, informative reports about the impacts of forest dynamics on the variation in water resources at the regional scale remain unavailable. It is urgently necessary to study the dynamic changes and ecological risks on water resources to better regulate ecological engineering policies and provide benefits for human beings.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study area
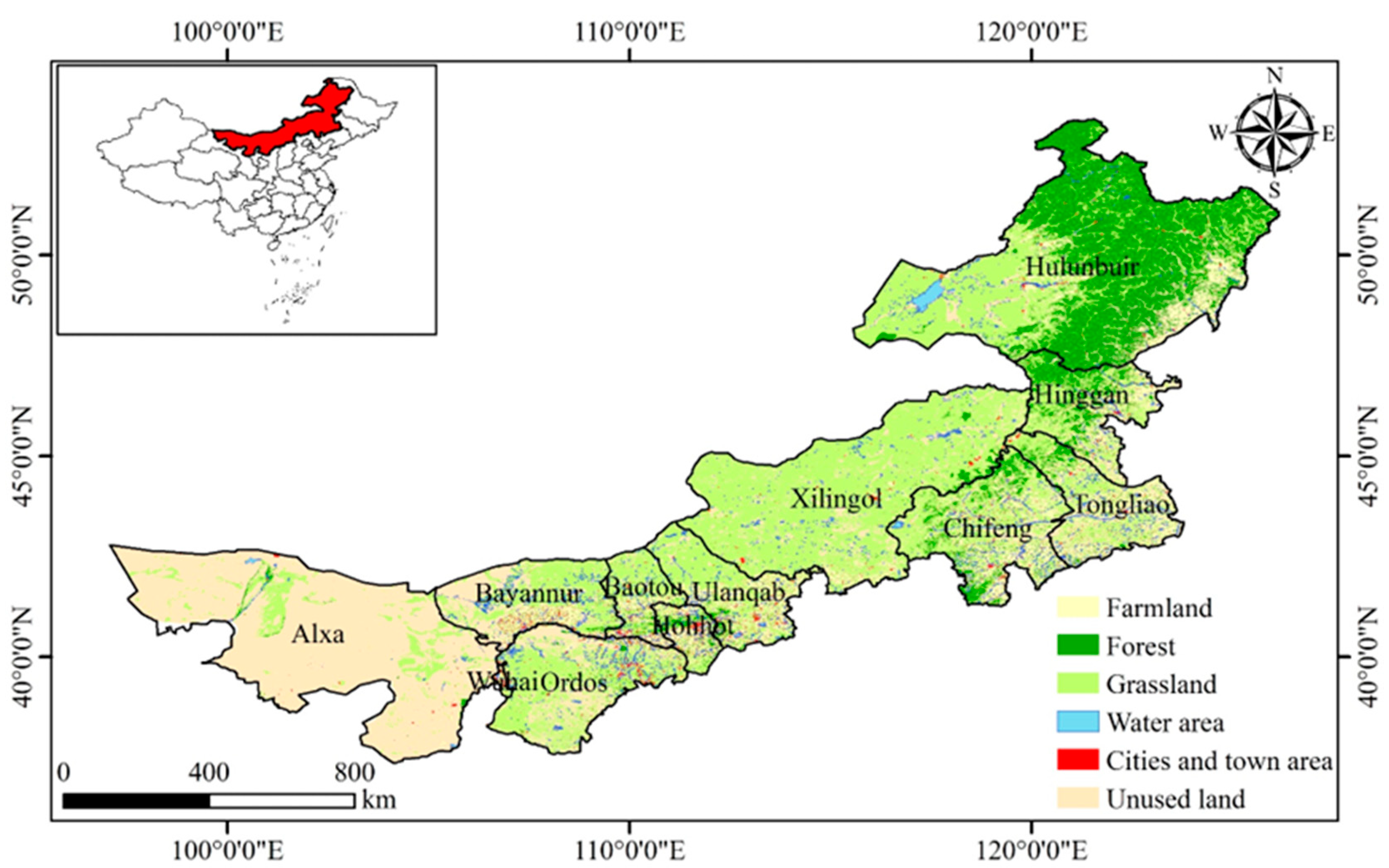
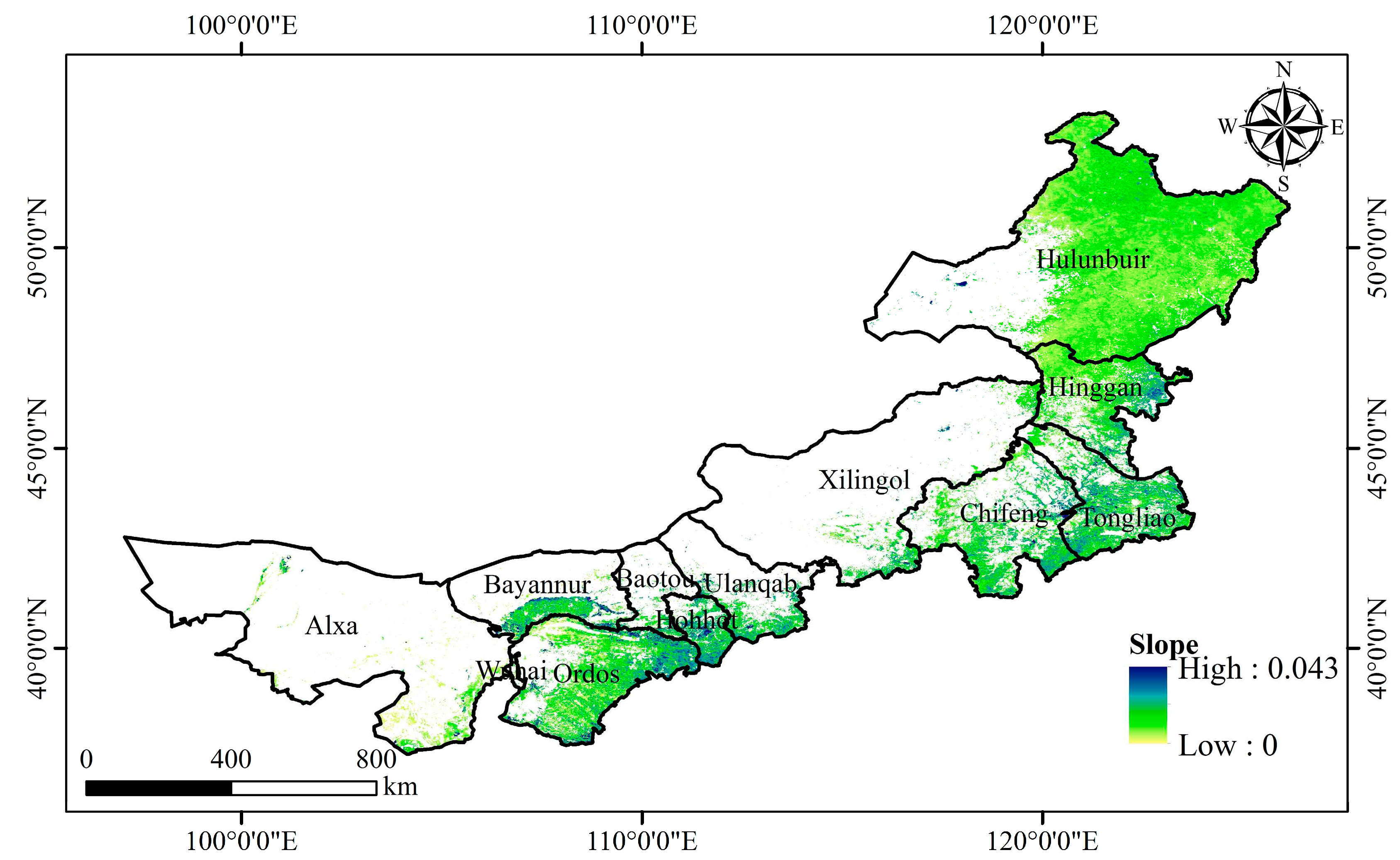
Inner Mongolia is located in northern China, covering an area of 1.18 million km
2, or 12.3% of the national terrestrial area [
21]. It extends from 97°E-126°E and 37°N–53°N (
Figure 1). The mean temperature is approximately 0-8 ℃. The average annual precipitation is only 50-450 mm and gradually increases from west to east; approximately 75% of the rainfall is concentrated between July and September [
22]. The main vegetation types are forested prairies, temperate prairies, desert steppes, and deserts intergrading from east to west (
Figure 1). Inner Mongolia contains the largest grassland and natural pasture in China. According to the results of the eighth forest resources inventory, the grassland area is 88 million hectares, accounting for ~74% of the total land area of Inner Mongolia and ~22% of the grassland area of the entire country. The forest land area is 45 million hectares, accounting for ~22% of the total land area of Inner Mongolia and ~14% of the forest area of the entire country. The ecology and environment of Inner Mongolia are fragile, very sensitive, and vulnerable to the water resource. Ecological restoration projects have been implemented to address land desertification and improve the environment, such as Returning Farmland to Forest, and Beijing-Tianjin Sand Control.
According to the Inner Mongolia Water Resource Bulletin, the area’s total water resources in 2020 were 503.93 × 108 m3, surface water resources were 354.19 × 108 m3, and groundwater resources were 243.94 × 108 m3. However, water resources are mainly concentrated in the northeastern part of the study region, Hulunbuir City. In contrast, the per capita water resources in the northwestern part are only one-fifth of the world average, and it is one of the most water-scarce regions in China. Water supply in Inner Mongolia includes surface water and groundwater. The surface water primarily comes from precipitation and Yellow River water diversion.
Based on our investigation and the data available, we summarized three major water resource uses in Inner Mongolia. Agricultural irrigation and industrial water consumption accounted for 70.8% of total water consumption. Ecological and people’s livelihoods accounted for 15.1% and 6.0% of the total water consumption, respectively.
2.2. Data Collection
The meteorological data mainly included monthly precipitation and temperature from 2000 to 2020. The meteorological data from 37 stations were collected from the Chinese National Meteorological Information Center (
http://data.cma.cn). Land use/land cover remote sensing monitoring data in China from 2000 to 2020 were collected from the Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC,
http://www.resdc.cn). The NDVI dataset originated from the Global Inventory Modeling and Mapping Studies (GIMMS) covering the period from 2000 to 2020 was collected from the Ecological Forecasting Lab of NASA’s Ames Research Center (
https://ecocast.arc.nasa.gov). The annual evapotranspiration (ET) data (MOD16 data product) from 2000 to 2020 was obtained from the Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (
https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/). The MOD16 evapotranspiration datasets is based on the logic of the Penman-Monteith equation, which includes inputs of daily meteorological data and MODIS remote sensing data products such as vegetation property dynamics and land cover [
23]. We obtained afforestation data from annually published China forestry statistical yearbooks from 2000 to 2020 (State Forestry Agency of the People’s Republic of China). We obtained the water resource data from the Inner Mongolia Water Resource Bulletin (2000-2020,
http://slt.nmg.gov.cn/).
2.3. Methods
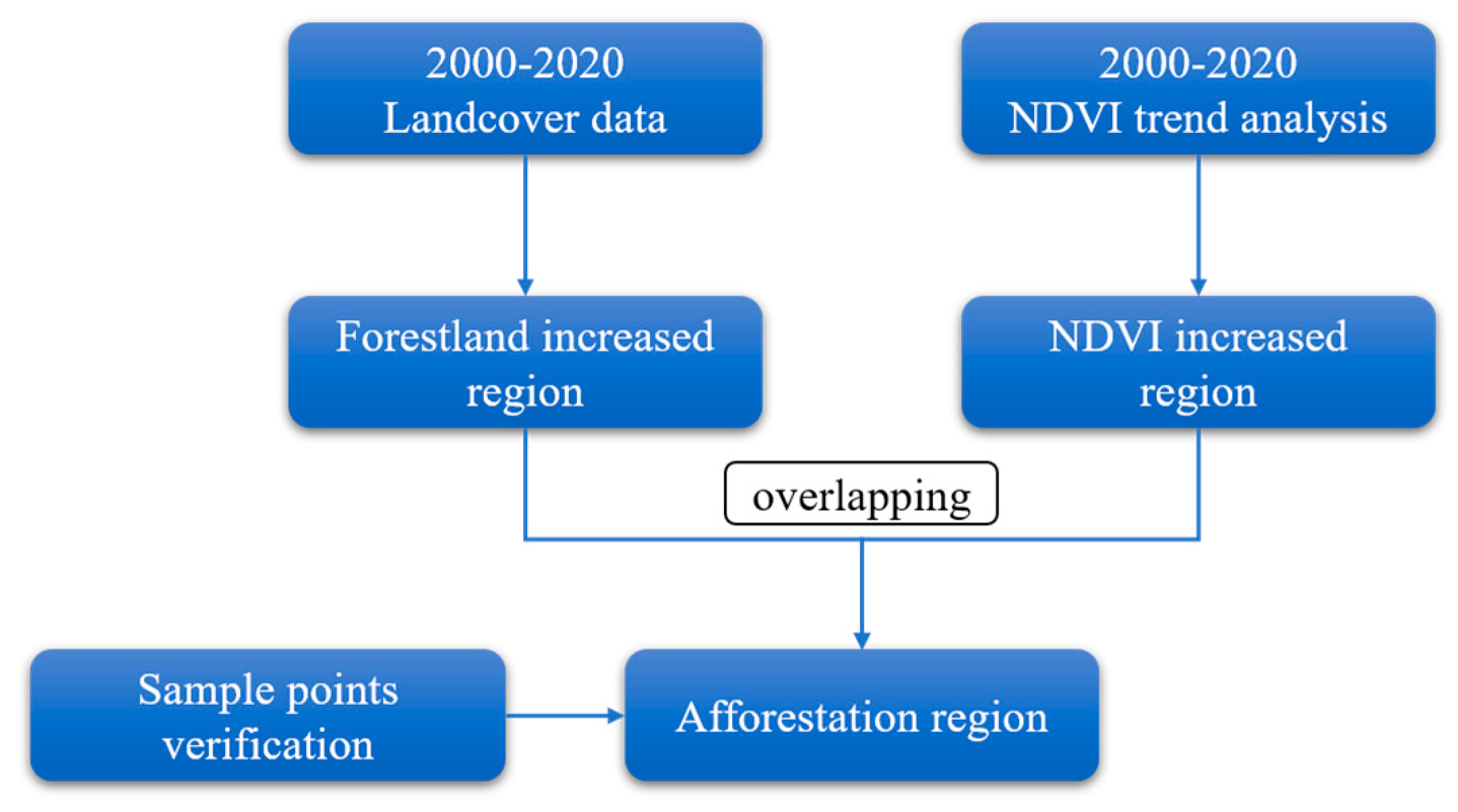
2.3.1. Identifying the afforestation regions
The identification of afforestation regions is an important prerequisite to evaluate the ecological risk of water resources caused by afforestation [
24,
25]. Compared with natural forest land, NDVI of artificial forest land is more easily affected by human activities, and the change trend is more obvious [
26]. In this study, NDVI and land cover data were used to analyze the spatial characteristics of vegetation and forest land, and afforestation areas were identified through the combination of the two, and finally sample points were used to verify the results (
Figure 2). The main steps are as follows:
(1) Trend analysis was used to identify areas with significant increase in NDVI in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2020. Trend analysis is a linear regression analysis of time-dependent variables [
27,
28]. The constantly changing properties of the vegetation may be reflected in the trend of the change in NDVI for each grid by applying linear trend analysis. In this study, the trend of NDVI change in the Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2020 was determined using a unitary linear regression model, and the slope of the trend was calculated using the least squares method:
where:
refers to the trend of vegetation change,
is the number of years studied (
= 21 in this study),
is the ordinal number of a given year, and
denotes the NDVI value for year
; in the case of a
> 0, this indicates the NDVI tends increasing.
A significance test is often used to assess the accuracy of the trend change. In this study, we assess the significance of trends using the F-test (p<0.05). The calculation's formula is as follows:
where:
refers to the sum of squares of errors,
is the regression square sum,
is the NDVI value for year
,
is the NDVI regression value for fear
;
is the average NDVI value in n year; and
is the ordinal number of a given year.
(2) Five periods of land cover data (2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, 2020) were used to identify forestland increased region in 2000-2020. The histogram analysis method was used to calculate the NDVI values of the forestland increased region, and the NDVI range of 20%-80% was taken as the NDVI threshold of the afforestation regions.
(3) Extract afforestation area by overlapping the results derived in the prior two steps. The NDVI increased region within the NDVI threshold of afforestation region is identified as afforestation area. Finally, the extraction results were verified by using 23 afforestation sample points obtained from field investigation in Ulanqab. The overall identification accuracy was 73.9%.
2.3.2. Water balance
To understand the influence of afforestation on water resources in Inner Mongolia, the water balance equation was used to calculate the change of water resources in afforestation regions[
29], which can be described as follows:
where:
refers to the water resource (mm);
is the precipitation (mm);
is the actual evapotranspiration (mm);
indicates to basin water resource change (mm), which is generally assumed to be zero in a long term.
In order to detect the change trend of water resources caused by afforestation during the 2000-2020, the least square linear regression model can be used.
2.3.3. Ecological risk
Water resources Security Index (WSI) was used to evaluate the ecological risk of water resources caused by afforestation, which quantified regional water security from the perspective of regional supply and demand balance [
30]. The equation is as follows:
where:
refers to the water resource supply (mm), we assume that the afforestation only has precipitation supply;
is the water resource requirement (mm), the
was taken as the water resource requirement of the afforestation. In the case of
< -0.5, this indicates high risk; -0.5 ≤
< 0, this indicates low risk; 0 ≤
< 0.5, this indicates low security; 0.5 ≤
< 1, this indicates high security.
3. Results
3.1. The spatial distribution of afforestation in Inner Mongolia
According to the change trend of NDVI in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2020, ~ 65% of the region's NDVI shows an increasing trend, vegetation coverage has improved significantly, mainly distributed in the central and eastern part of Inner Mongolia (
Figure 4). Within these NDVI-increased significantly land areas, their forest cover was designated as afforestation.
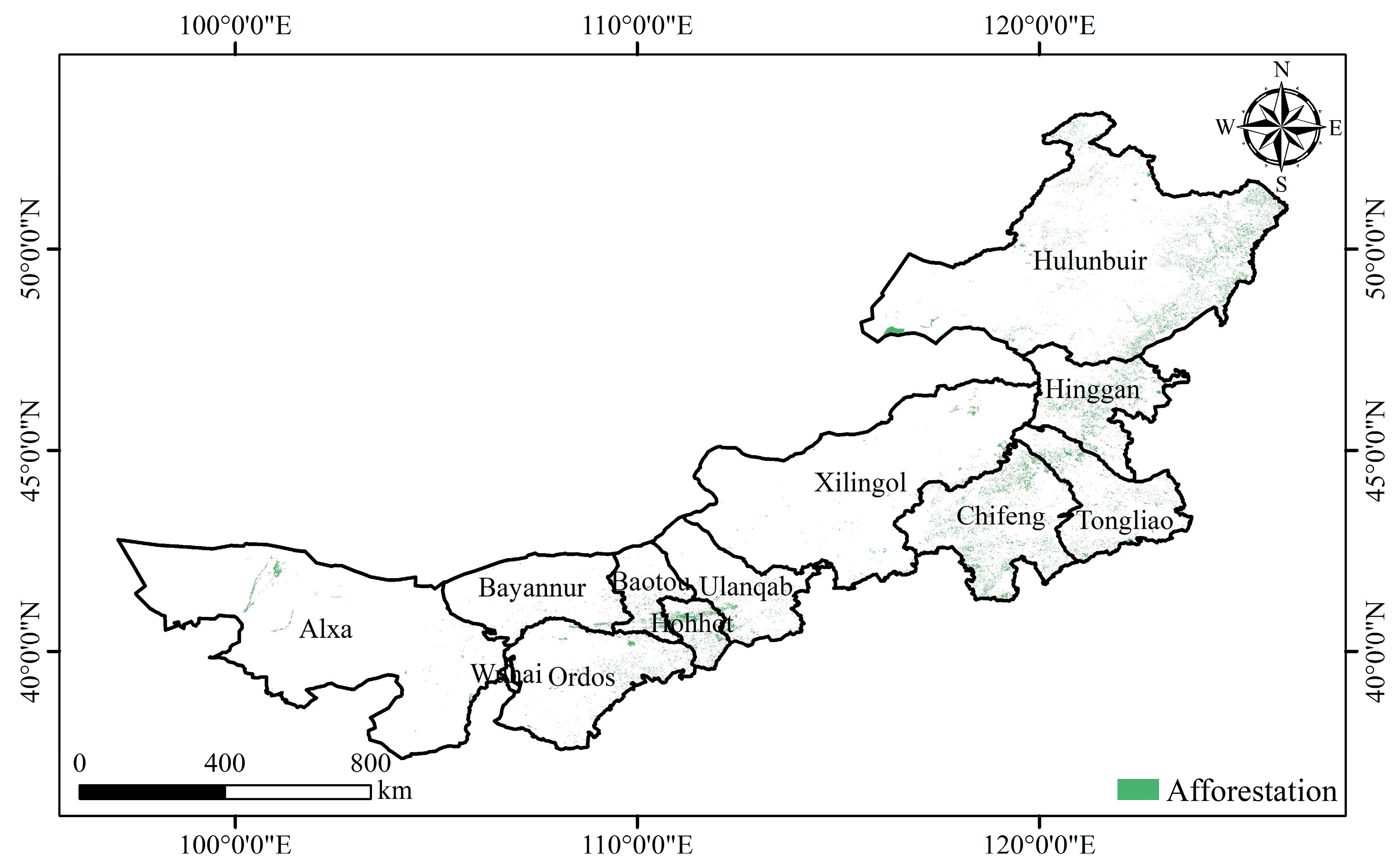
The spatial distribution of afforestation showed pronounced spatial heterogeneity, and afforestation is mainly distributed in the eastern part of Inner Mongolia (
Figure 5). The forest cover area in the study area increased from 20.74 × 10
4 km
2 in 2000 to 26.11 × 10
4 km
2 in 2020.The afforestation area in Inner Mongolia was 5.37 × 10
4 km
2 from 2000 to 2020. The growth rate was 0.27 × 10
4 km
2/a. The forest coverage rate increased from 17.53% to 22.07%. Hulunbuir has the largest afforestation area, with an area of 2.46 × 10
4 km
2, accounting for 45.81% of the total afforestation area. The afforestation area of Chifeng is second only to Hulunbuir, accounting for 10.75% of the total afforested area. The afforestation area of Wuhai and Alxa in western Inner Mongolia was relatively small, accounting for 0.24% and 1.57% respectively.
3.2. ET comparison between artificial forest land and natural forest land
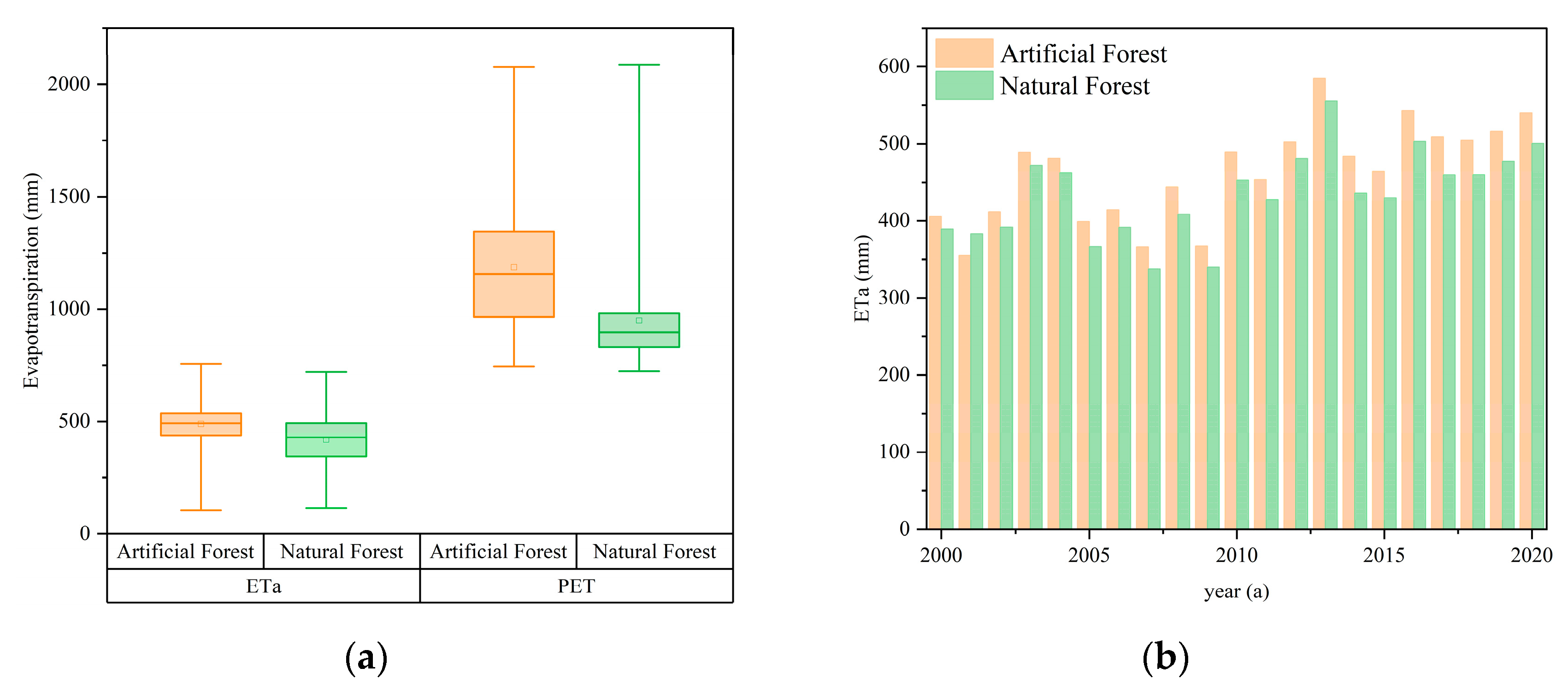
The effects of afforestation on regional water resources were studied by comparing ET changes of artificial forest and natural forest. The annual ETa of the artificial forest in Inner Mongolia was 488.77mm, slightly higher than that of the natural forest (418.82mm), and the potential ET (PET) of the artificial forest was 1186.19mm, much higher than that of the natural forest (950.14mm) (
Figure 6a). Under the background of climate change warming and wetting in the Inner Mongolia Plateau [
31], ET showed an obvious increasing trend from 2000 to 2020, with increasing at a rate of 7.15mm/ year in artificial forest and 5.25mm/ year in natural forest. The consumption of water resources in the artificial forest is greater than that in the natural forest.
3.3. Changes in water resources caused by afforestation
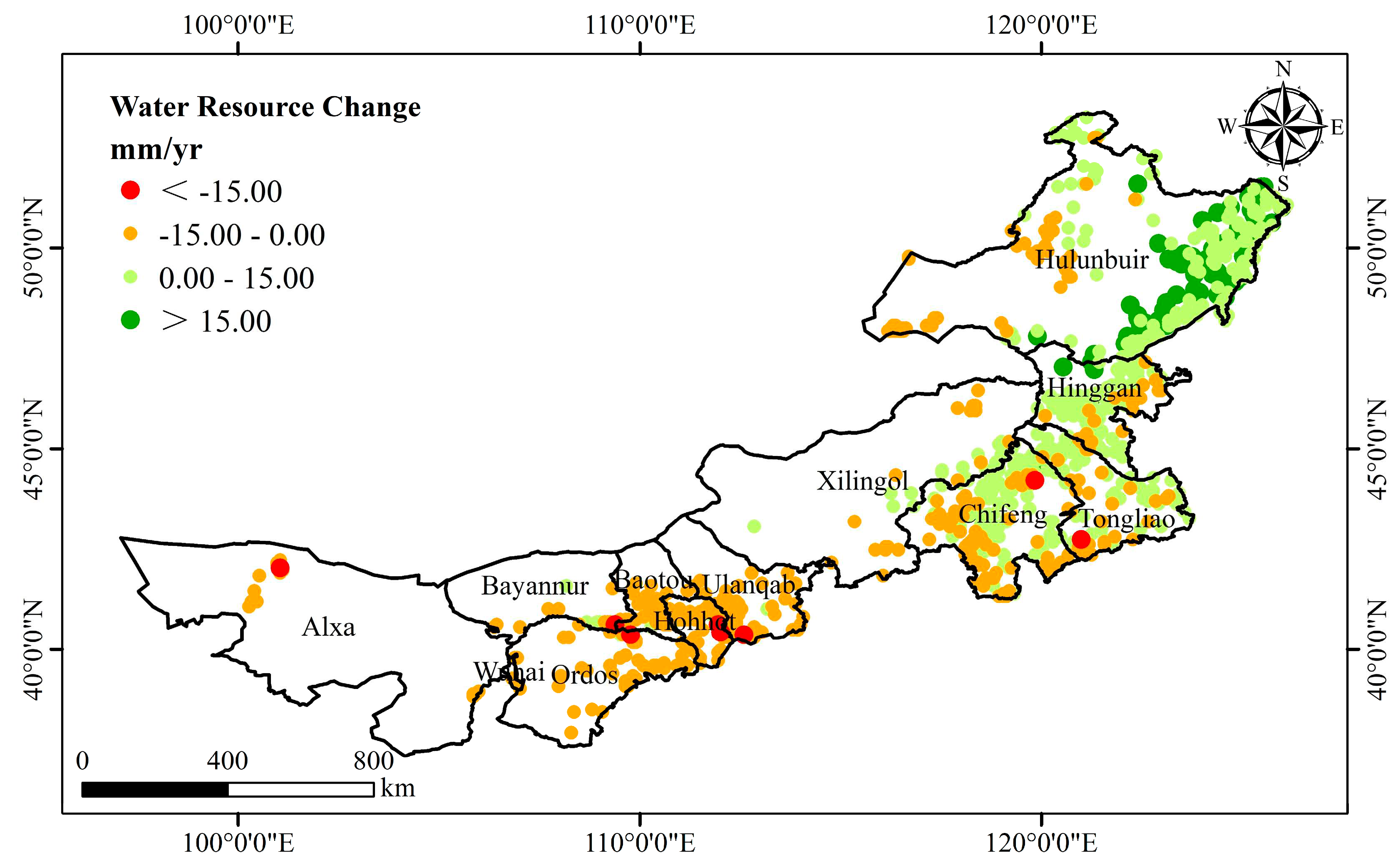
The water resources change caused by afforestation during 2000-2020 was calculated by the water balance equation (
Figure 7). The results showed that the change of water resources in Inner Mongolia caused by afforestation showed a decreasing trend, and showed obvious spatial heterogeneity. ~43% of the afforestation regions showed an increasing trend of water resources, mainly distributed in the eastern areas with sufficient precipitation, especially Hulunbuir and Hinggan; ~57% of the afforestation regions showed a decreasing trend of water resources change, mainly distributed in the central and western regions with insufficient precipitation, especially in Alxa, Ordos, Hohhot, Baotou and Ulanqab.
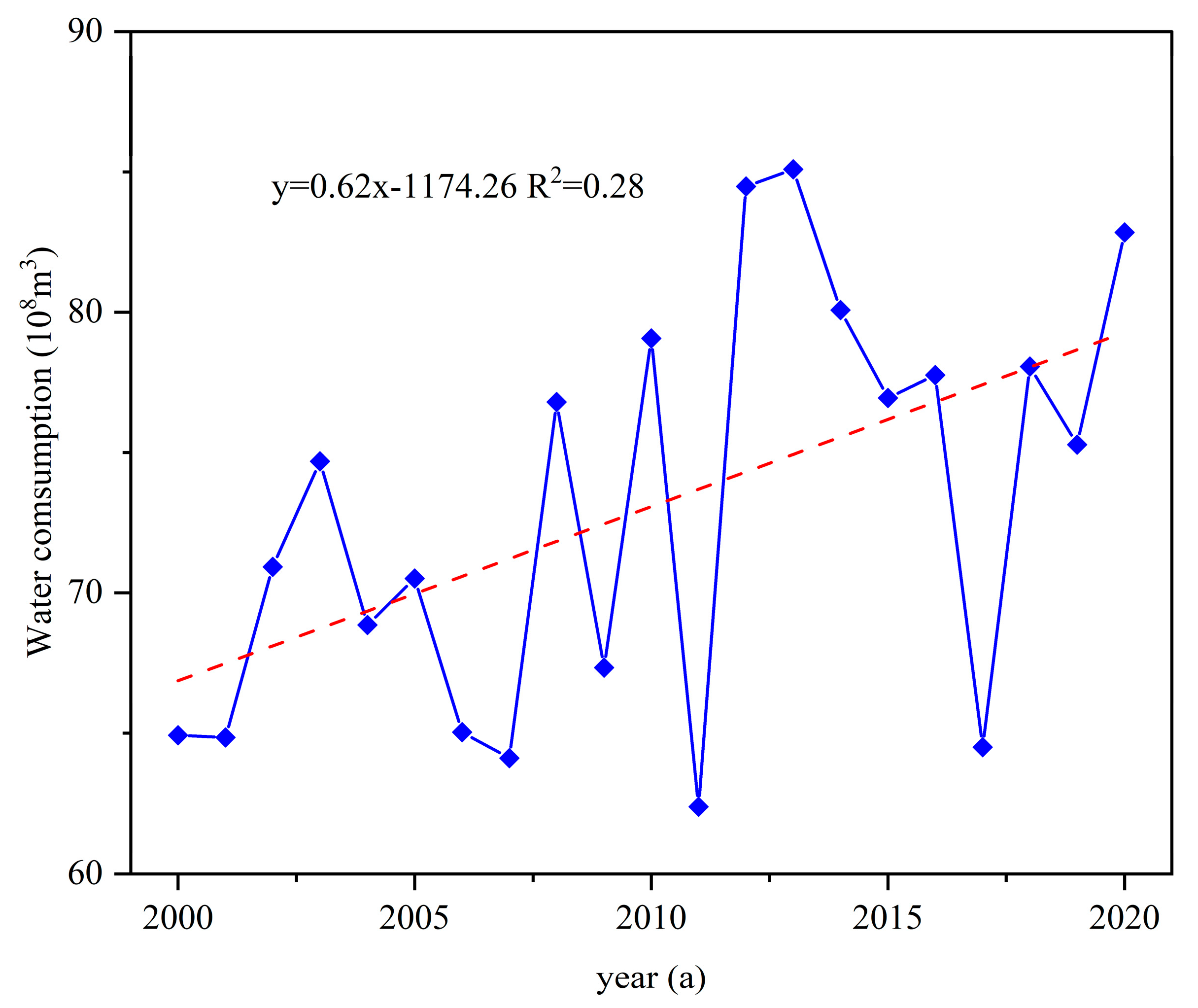
From the time change trend of water resources consumption in afforestation (
Figure 8), it can be seen that the water resources consumption in afforestation was between 60-90 × 10
8 m
3 from 2000 to 2020, showing an increasing trend, with a change rate of 0.62 × 10
8 m
3/ years, of which the water resources consumption in 2011 was the smallest, the minimum value was 62.40 × 10
8 m
3, and the water resources consumption in 2013 was the largest, the maximum value was 85.10 × 10
8 m
3, and the mean value of multi-years was 73.07 × 10
8 m
3.
3.4. Ecological risk of water resources in afforestation area
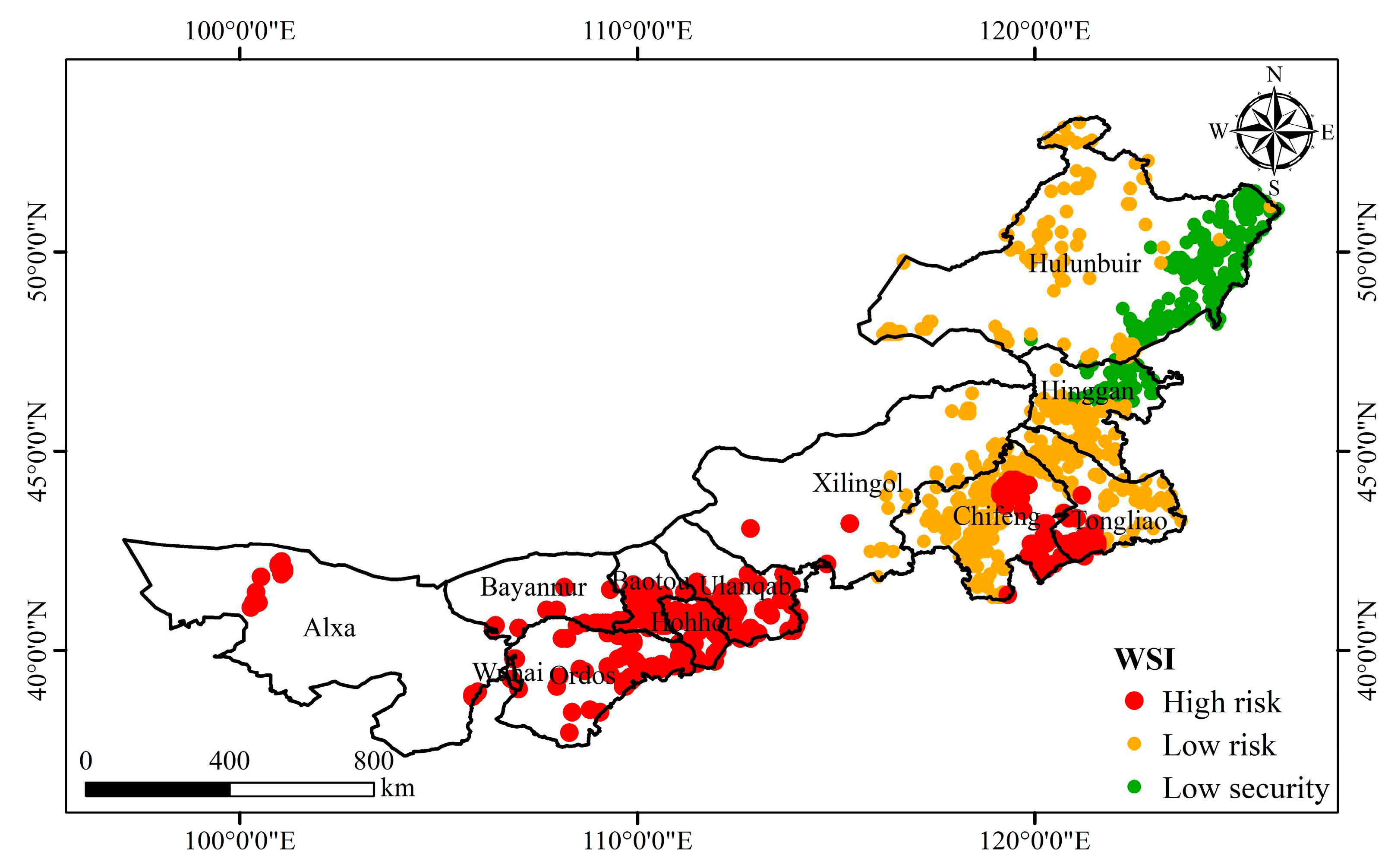
The ecological risk caused by afforestation was calculated from the perspective of water supply by WSI. Under the assumption that only precipitation supply is considered, most areas in the study area face ecological risks caused by afforestation (
Figure 9). The ecological risk increased from east to west, indicative of spatial heterogeneity. ~24% of the afforestation regions are at high risk, mainly in the central and western parts of Inner Mongolia; ~bout 52% of the afforestation regions are at low risk, mainly in the eastern part of Inner Mongolia, especially Chifeng and Tongliao. ~24% of the afforestation regions are at low security, mainly in the eastern part of Hulunbuir. There is no high security of afforestation in Inner Mongolia.
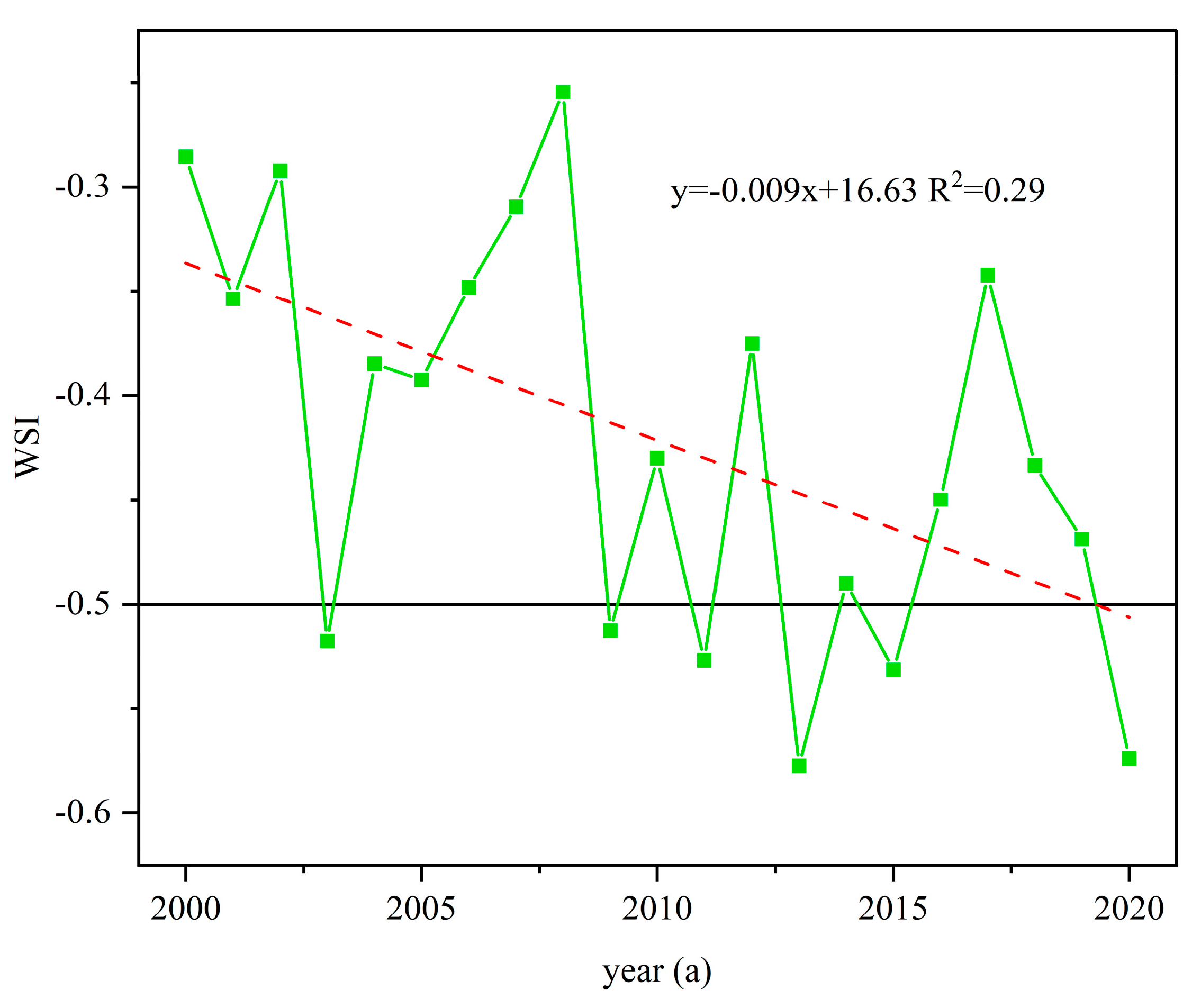
From the temporal change trend of WSI in afforestation (Figure 10), it can be seen that the WSI in afforestation has gradually changed from low risk to high risk from 2000 to 2020, showing a decreasing trend. In 2008, the WSI was the largest at -0.25. The WSI in 2013 and 2020 were the smallest, which is -0.57, and the ecological risk of water resources caused by afforestation was the largest. The ecological risk was at high risk in 2003, 2009, 2011, 2013, 2015 and 2020.
Figure 8.
Ecological Risks Arising for the Afforestation in Inner Mongolia.
Figure 8.
Ecological Risks Arising for the Afforestation in Inner Mongolia.
Figure 9.
Variations of WSI for afforestation region (2000-2020).
Figure 9.
Variations of WSI for afforestation region (2000-2020).
4. Discussion
4.1. Identification of afforestation
Inner Mongolia is one of the key regions targeted by Chinese ecological restoration programs [
21], and ecological restoration projects such as afforestation have a significant impact on regional water resources. It is an important basis for calculating and evaluating the ecological risk of water resources to accurately identify the afforestation regions. In this study, the change characteristics of land cover data and NDVI data were combined to identify the afforestation areas in Inner Mongolia. The afforestation area, growth rate and spatial distribution characteristics were consistent with previous research results [
21,
24,
25,
32], indicating that the large-scale ecological restoration project has made certain progress since 2000. Due to the large study area, the identification of forest land and shrub vegetation with low vegetation coverage is poor, and the actual afforestation area may be underestimated. In future studies, we plan to combine fieldwork, deep learning methods with high-resolution remote sensing data to extract afforestation at different time scales and analyze afforestation at different time and space scales [
33,
34,
35,
36].
4.2. Impacts of climate change on large-scale afforestation
Forest plays an important role in regulating regional climate and has significant influence on regional hydrological cycle [
37]. Afforestation can not only increase the carbon sink capacity of ecosystems, reduce the impact of climate change [
38], but also decline the surface temperature and reduce the occurrence of drought events [
39]. The spatial heterogeneity of precipitation results in the change of afforestation activities from east to west in Inner Mongolia. From east to west, the planting of tree species has changed from trees to shrubs, and the ecological function has changed from water conservation to wind protection and sand fixation [
40,
41]. The suitable density of afforestation was related to climate, it was determined by the water balance of the soil-vegetation system: a part of the rain falls on the soil and evaporates into the atmosphere, and the other part of the rain penetrates the soil to replenish the groundwater and maintain the normal growth of plants [
42]. When the density of afforestation exceeds the water supply capacity of the region, it means that groundwater was consumed faster, which affects the survival of vegetation and creates greater ecological risks [
43,
44].
4.3. The impact of large-scale afforestation on the water resources and ecological environment
Some studies show that the water consumption associated with afforestation is greater than that of natural vegetation [
45]. The forests’ water consumption increases significantly, resulting in regional ecological water resources imbalance [
2,
16,
46]. In addition, afforestation in arid and semi-arid areas, where precipitation is insufficient, will have an impact on groundwater recharge [
47]. The precipitation is less in western Inner Mongolia than in eastern Inner Mongolia, and the vegetation is more dependent on groundwater. Afforestation increases vegetation coverage. Water consumption through vegetation canopy interception and vegetation transpiration increase as vegetation coverage increases. The soil water mainly moves upward, decreasing the groundwater recharge and groundwater table [
7,
48]. It is very difficult to restore the groundwater level once the water table depth has decreased [
49], which suggests that these changes may lead to permanent decreases in the ground's capacity to store water [
16,
50]. At the same time, other studies have shown that afforestation can alleviate groundwater depletion in areas with sufficient precipitation [
43,
51,
52]. Next, we will study the influence of afforestation on groundwater in different climate areas of Inner Mongolia.
Large-scale afforestation increases water consumption and may exacerbate land degradation, especially by planting fast-growing and short-lived vegetation [
53]. In arid and semi-arid regions with sparse precipitation and large evaporation, the stability of the ecosystem is poor due to the simple species composition and structure. A large-scale vegetation restoration destroys the original stable state of the ecosystem [
5]. In this process, the planted vegetation competes with the original vegetation for water, which changes the regional eco-hydrological processes and causes more severe ecological problems [
54]. The decrease in groundwater depth causes the degradation of surface vegetation and land degradation [
55]. In future studies, we will pay more attention to the impact of afforestation on regional groundwater depth.
4.4. Future ecological risks to afforestation
Afforestation in China, an expensive ecological restoration policy, has yielded far fewer returns than expected, with only 5-34% survival rates in the northwestern provinces [
16,
50]. According to China's ecological plan for the next 15 years, in order to achieve carbon neutrality and carbon peak, the national forest coverage rate will reach 26% by 2035, which indicates that China will continue its afforestation program in the future. Therefore, we suggest that: (1) To avoid afforestation in arid and semi-arid areas, so as not to cause a permanent decline in regional water storage capacity; (2) Selecting suitable vegetation according to local conditions is an important prerequisite for promoting ecological restoration and sustainable development [
56]; (3) The formulation of an optimized groundwater extraction plan is one of the most effective management strategies to protect and maintain the current ecological environment and ecosystem [
57,
58,
59]; (4) As the climate of the Inner Mongolia Plateau is warmer and wetter, the increase of precipitation in the future may reduce the ecological risks caused by afforestation [
31,
60].
5. Conclusions
Base on the land cover data, NDVI data and meteorological data, this study analyzed the ecological risks of water resources caused by afforestation in Inner Mongolia from 2000 to 2020. The results show that afforestation in Inner Mongolia had a specific impact on regional water resources. Water resources are scarce in Inner Mongolia, which cannot support the sustainable growth of large-scale forestland. Large-scale afforestation increases total water consumption, leading to regional water resource consumption and becoming a potential source of ecological risks in the region. Developing optimized afforestation schemes and improving water resource utilization efficiency are crucial to avoid potential ecological risks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, P.C.; writing—review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition, R.M. and J.S.; investigation, data curation, visualization, L.S., L.Z. and J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by “Geological Survey Projects Foundation of Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology (DD20221773)”, and “Investigation of Groundwater Environment in Ordos (Phase II) (ESZC-G-F-220140)”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the useful comments and suggestions rendered by the editors and reviewers, which are essential for us to further improve the quality of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lu, F.; Hu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, P.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; et al. Effects of National Ecological Restoration Projects on Carbon Sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2018, 115, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; A, G.; Zhang, J.; Velicogna, I.; Liang, C.; Li, Z. Ecological Restoration Impact on Total Terrestrial Water Storage. Nat Sustain 2021, 4, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India Lead in Greening of the World through Land-Use Management. Nat Sustain 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.W.; Nisbet, T.R.; Broadmeadow, S.B. The Impacts of Conifer Afforestation and Climate on Water Quality and Freshwater Ecology in a Sensitive Peaty Catchment: A 25 Year Study in the Upper River Halladale in North Scotland. Forest Ecology and Management 2021, 502, 119616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Xiao, J.; Ma, X. The Impact of Large-Scale Afforestation on Ecological Environment in the Gobi Region. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 14383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Yang, X.; Fang, N.; Shi, Z. Large-Scale Afforestation Significantly Increases Permanent Surface Water in China’s Vegetation Restoration Regions. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2020, 290, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Gong, C.; Zhao, M.; Franssen, H.-J.H.; Brunner, P. Salix Psammophila Afforestations Can Cause a Decline of the Water Table, Prevent Groundwater Recharge and Reduce Effective Infiltration. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 780, 146336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Wenninger, J.; Zhang, E.; Hou, G.; Dong, J. Interaction between Groundwater and Trees in an Arid Site: Potential Impacts of Climate Variation and Groundwater Abstraction on Trees. Journal of Hydrology 2015, 528, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Meng, T.; Wu, W.; Si, B.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Wu, S.; Feng, H.; Siddique, K.H.M. Evaluating Potential Groundwater Recharge in the Unsteady State for Deep-Rooted Afforestation in Deep Loess Deposits. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 858, 159837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, A.Kh.; Šimůnek, J.; Hanjra, M.A.; Avliyakulov, M.; Forkutsa, I. Effects of the Shallow Water Table on Water Use of Winter Wheat and Ecosystem Health: Implications for Unlocking the Potential of Groundwater in the Fergana Valley (Central Asia). Agricultural Water Management 2014, 131, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.; Skaggs, T.H.; Lü, H.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Fang, X. Simulation of Populus Euphratica Root Uptake of Groundwater in an Arid Woodland of the Ejina Basin, China. Hydrological Processes 2009, 23, 2460–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, C.A.; Nadezhdina, N.; David, J.S.; Kurz-Besson, C.; Caldeira, M.C.; Henriques, M.O.; Monteiro, F.G.; Pereira, J.S.; David, T.S. Transpiration in Quercus Suber Trees under Shallow Water Table Conditions: The Role of Soil and Groundwater. Hydrological Processes 2014, 28, 6067–6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owuor, S.O.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Guzha, A.C.; Rufino, M.C.; Pelster, D.E.; Díaz-Pinés, E.; Breuer, L. Groundwater Recharge Rates and Surface Runoff Response to Land Use and Land Cover Changes in Semi-Arid Environments. Ecological Processes 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keese, K.E.; Scanlon, B.R.; Reedy, R.C. Assessing Controls on Diffuse Groundwater Recharge Using Unsaturated Flow Modeling. Water Resources Research 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Sun, X. Ecological Risks Arising from the Impact of Large-Scale Afforestation on the Regional Water Supply Balance in Southwest China. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, T. Ecosystem Water Imbalances Created during Ecological Restoration by Afforestation in China, and Lessons for Other Developing Countries. Journal of Environmental Management 2016, 183, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Su, X. Challenges and Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystems in Arid Areas – A Case Study of the Nalenggele Alluvial Fan in NW China. Journal of Hydrology 2019, 573, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Optimization of Groundwater Exploitation in an Irrigation Area in the Arid Upper Peacock River, NW China: Implications for Sustainable Agriculture and Ecology. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asoka, A.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Mishra, V. Relative Contribution of Monsoon Precipitation and Pumping to Changes in Groundwater Storage in India. Nature Geosci 2017, 10, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, M.M.; Biswas, T.; Housman, I.W.; Campbell, L.S.; Klausmeyer, K.R.; Howard, J.K. A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Groundwater Levels in California Reveals Ecosystems at Risk. Frontiers in Earth Science 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Pflugmacher, D.; Li, A.; Li, Z.; Hostert, P. Land Use and Land Cover Change in Inner Mongolia - Understanding the Effects of China’s Re-Vegetation Programs. Remote Sensing of Environment 2018, 204, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Dang, D.; Li, X.; Lyu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, S. Mapping Ecosystem Services Bundles for Analyzing Spatial Trade-Offs in Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Cleaner Production 2020, 256, 120444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Algorithm. Remote Sensing of Environment 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, D.; Xu, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y. Assessing the Water Footprint of Afforestation in Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Arid Environments 2020, 182, 104257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, D.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Y. Quantifying the Influences of Natural and Human Factors on the Water Footprint of Afforestation in Desert Regions of Northern China. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 780, 146577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, V.B.; Dedoussi, I.C. Annual Satellite-Based NDVI-Derived Land Cover of Europe for 2001–2019. Journal of Environmental Management 2022, 302, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, J. Detecting Sustainability of Desertification Reversion: Vegetation Trend Analysis in Part of the Agro-Pastoral Transitional Zone in Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Quan, Q.; Wu, B.; Mo, S. Response of Vegetation Dynamics in the Three-North Region of China to Climate and Human Activities from 1982 to 2018. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiao, Q. Impact of Large-Scale Tree Planting in Yunnan Province, China, on the Water Supply Balance in Southeast Asia. Environ Monit Assess 2018, 191, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y. Application of Ecosystem Service Flows Model in Water Security Assessment: A Case Study in Weihe River Basin, China. Ecological Indicators 2021, 120, 106974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, G.; Zhang, W.; Tu, Z.; Tan, W. Change Features of Time-Series Climate Variables from 1962 to 2016 in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Arid Land 2020, 12, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Y.; Guna, A.; Bao, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations of Land Use/Cover Changes in Inner Mongolia (China) during 1980–2015. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, T.; Yang, F.; Sun, H.; Guan, Y. An Improved Optimum-Path Forest Clustering Algorithm for Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Computers & Geosciences 2018, 112, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, Md.S.; Hafsa, B. Multi-Decadal Land Cover Change Analysis over Sundarbans Mangrove Forest of Bangladesh: A GIS and Remote Sensing Based Approach. Global Ecology and Conservation 2022, 37, e02151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, E.A.; Caccetta, P.; Lowell, K.; Mitchell, A.; Zhou, Z.-S.; Held, A.; Milne, T.; Tapley, I. SAR and Optical Remote Sensing: Assessment of Complementarity and Interoperability in the Context of a Large-Scale Operational Forest Monitoring System. Remote Sensing of Environment 2015, 156, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ramirez, C.; McElhaney, M.; Evans, K. F3: Simulating Spatiotemporal Forest Change from Field Inventory, Remote Sensing, Growth Modeling, and Management Actions. Forest Ecology and Management 2018, 415–416, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liang, S.; Yao, Y.; Jia, K.; Meng, S.; Li, J. Detection and Attribution of Changes in Hydrological Cycle over the Three-North Region of China: Climate Change versus Afforestation Effect. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2015, 203, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ťupek, B.; Lehtonen, A.; Mäkipää, R.; Peltonen-Sainio, P.; Huuskonen, S.; Palosuo, T.; Heikkinen, J.; Regina, K. Extensification and Afforestation of Cultivated Mineral Soil for Climate Change Mitigation in Finland. Forest Ecology and Management 2021, 501, 119672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálos, B.; Mátyás, C.; Jacob, D. Regional Characteristics of Climate Change Altering Effects of Afforestation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 044010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Xie, X.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Y. The Relative Contribution of Vegetation Greening to the Hydrological Cycle in the Three-North Region of China: A Modelling Analysis. Journal of Hydrology 2020, 591, 125689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z.; You, X.; Zhang, X.; Song, A. The Dynamics of Sand-Stabilization Services in Inner Mongolia, China from 1981 to 2010 and Its Relationship with Climate Change and Human Activities. Ecological Indicators 2018, 88, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liang, W. Regulation of Stand Density Alters Forest Structure and Soil Moisture during Afforestation with Robinia Pseudoacacia L. and Pinus Tabulaeformis Carr. On the Loess Plateau. Forest Ecology and Management 2021, 491, 119196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Jin, W.; Leininger, T.D.; Feng, G.; Yang, J. Impacts of Afforestation on Groundwater Resource: A Case Study for Upper Yazoo River Watershed, Mississippi, USA. Hydrological Sciences Journal 2021, 66, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jia, Z. Soil Water Utilization Characteristics of Haloxylon Ammodendron Plantation with Different Age during Summer. Acta Ecologica Sinica 2011, 31, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilske, B.; Lu, N.; Wei, L.; Chen, S.; Zha, T.; Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Noormets, A.; Huang, J.; Wei, Y.; et al. Poplar Plantation Has the Potential to Alter the Water Balance in Semiarid Inner Mongolia. Journal of Environmental Management 2009, 90, 2762–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, T. Effects of Large-Scale Afforestation Project on the Ecosystem Water Balance in Humid Areas: An Example for Southern China. Ecological Engineering 2016, 89, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Pang, Z.; Yang, S.; Yin, L. Impact of Afforestation on Atmospheric Recharge to Groundwater in a Semiarid Area. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2020, 125, e2019JD032185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yeh, T.J.; Qiao, G.; Wang, W.; Duan, L.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wen, J.-C. Flow Dynamics in Vadose Zones with and without Vegetation in an Arid Region. Advances in Water Resources 2017, 106, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, J.B.; Edmunds, W.M.; Darling, W.G.; Ma, J.; Pang, Z.; Young, A.A. Conceptual Model of Recharge to Southeastern Badain Jaran Desert Groundwater and Lakes from Environmental Tracers. Applied Geochemistry 2008, 23, 3519–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhao, T.; Shi, X.; Cao, S. Ecological Restoration by Afforestation May Increase Groundwater Depth and Create Potentially Large Ecological and Water Opportunity Costs in Arid and Semiarid China. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 176, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, R.; Schwaab, J.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Sprenger, M.; Lewis, E.; Davin, E.L. Empirical Estimate of Forestation-Induced Precipitation Changes in Europe. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Peng, S.; Liu, G.; Ducharne, A.; Ciais, P.; Prigent, C.; Li, X.; Tang, X. Trade-off between Tree Planting and Wetland Conservation in China. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Labzovskii, L. Challenging the Land Degradation in China’s Loess Plateau: Benefits, Limitations, Sustainability, and Adaptive Strategies of Soil and Water Conservation. Ecological Engineering 2019, 127, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Xie, Z.; Ma, X.; Huete, A. Water Loss Due to Increasing Planted Vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Remote Sensing 2018, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Yang, X. Landscape Spatial Patterns in the Maowusu (Mu Us) Sandy Land, Northern China and Their Impact Factors. CATENA 2016, 145, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, G.; Chen, L. Assessing Effects of Afforestation Projects in China: Cao and Colleagues Reply. Nature 2010, 466, 315–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Wu, B.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, N. A Trade-off Method between Environment Restoration and Human Water Consumption: A Case Study in Ebinur Lake. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 217, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejduk, L.; Kaznowska, E.; Wasilewicz, M.; Hejduk, A. Dynamics of the Natural Afforestation Process of a Small Lowland Catchment and Its Possible Impact on Runoff Changes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozma, Z.; Decsi, B.; Ács, T.; Kardos, M.K.; Hidy, D.; Árvai, M.; Kalicz, P.; Kern, Z.; Pinke, Z. Supposed Effects of Wetland Restoration on Hydrological Conditions and the Provisioning Ecosystem Services—A Model-Based Case Study at a Hungarian Lowland Catchment. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S. Effects of Multi-Temporal Scale Drought on Vegetation Dynamics in Inner Mongolia from 1982 to 2015, China. Ecological Indicators 2022, 136, 108666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).