Submitted:
22 September 2023
Posted:
26 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
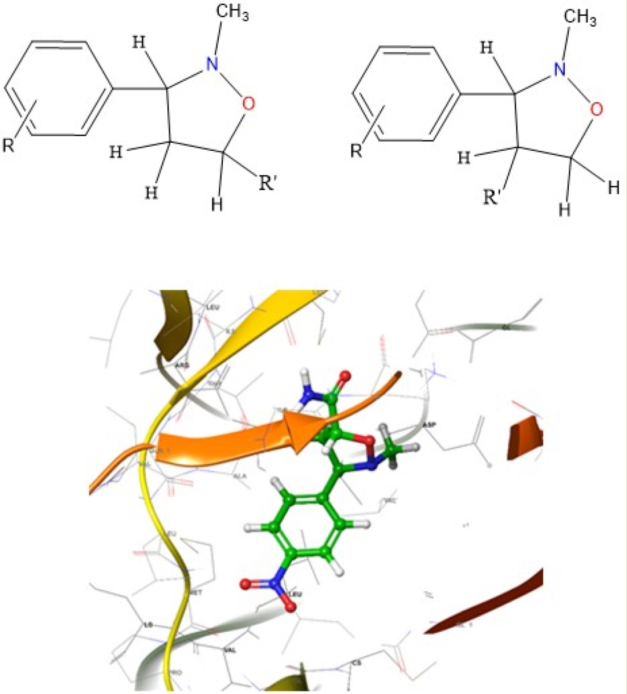
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
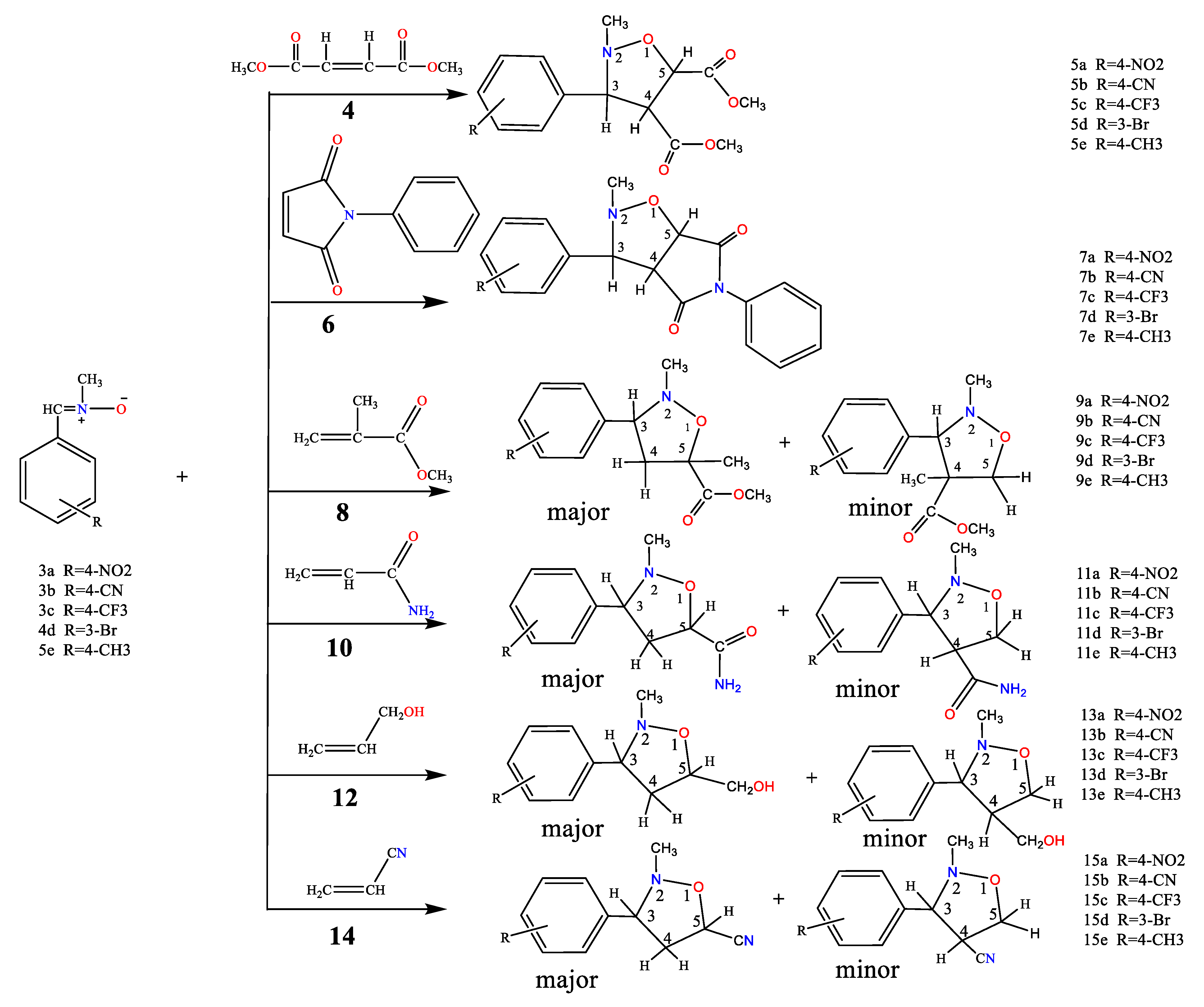
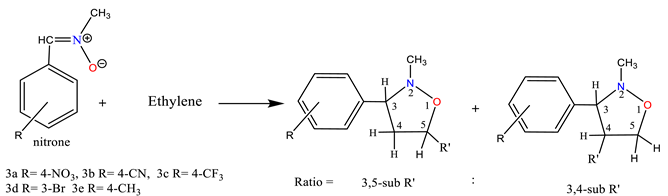
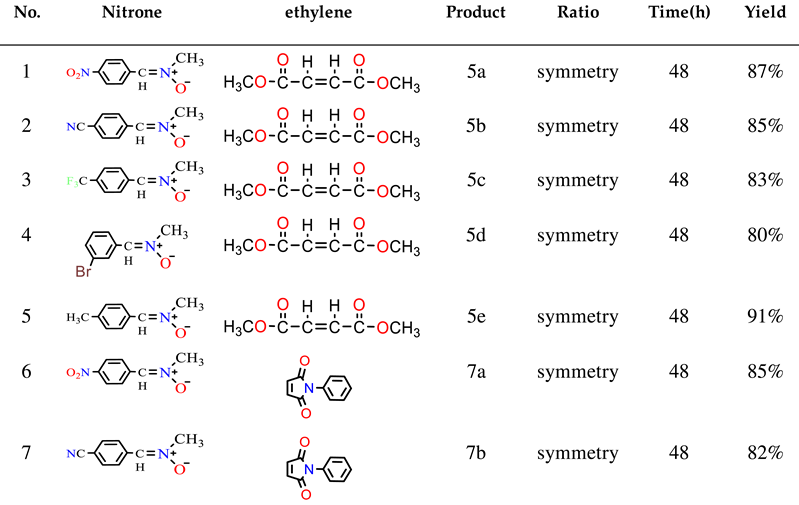
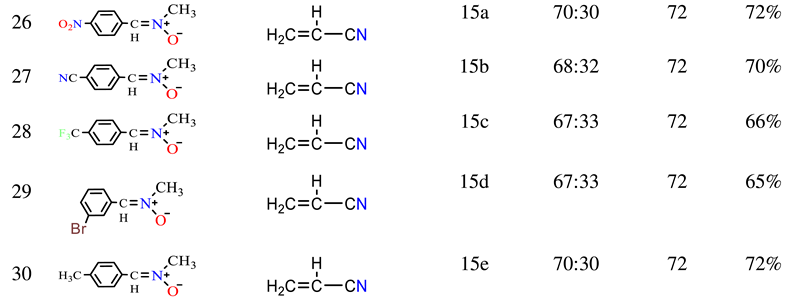
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Computational Investigations
2.2.1. ELF Analysis of Electronic Structures
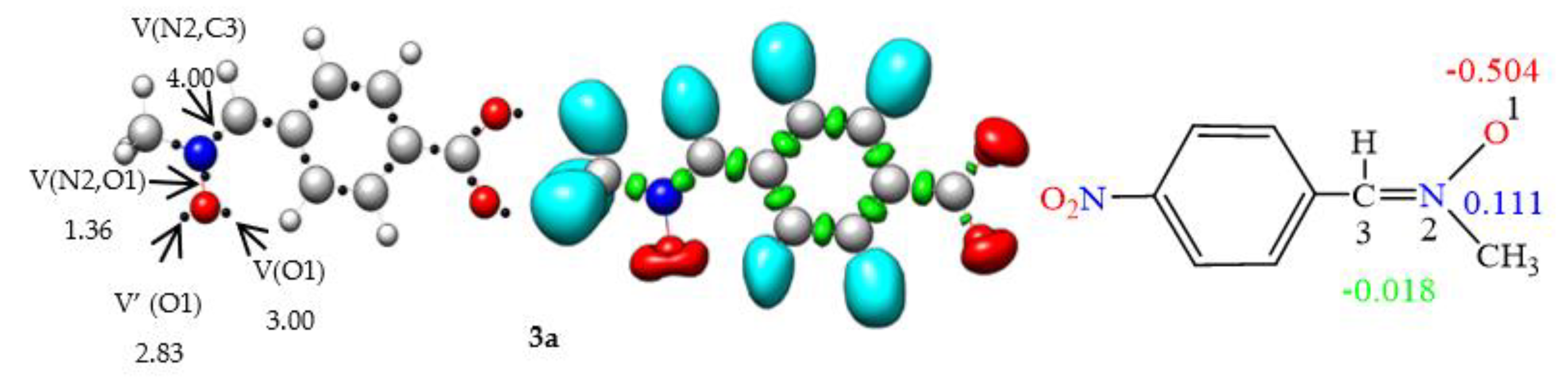
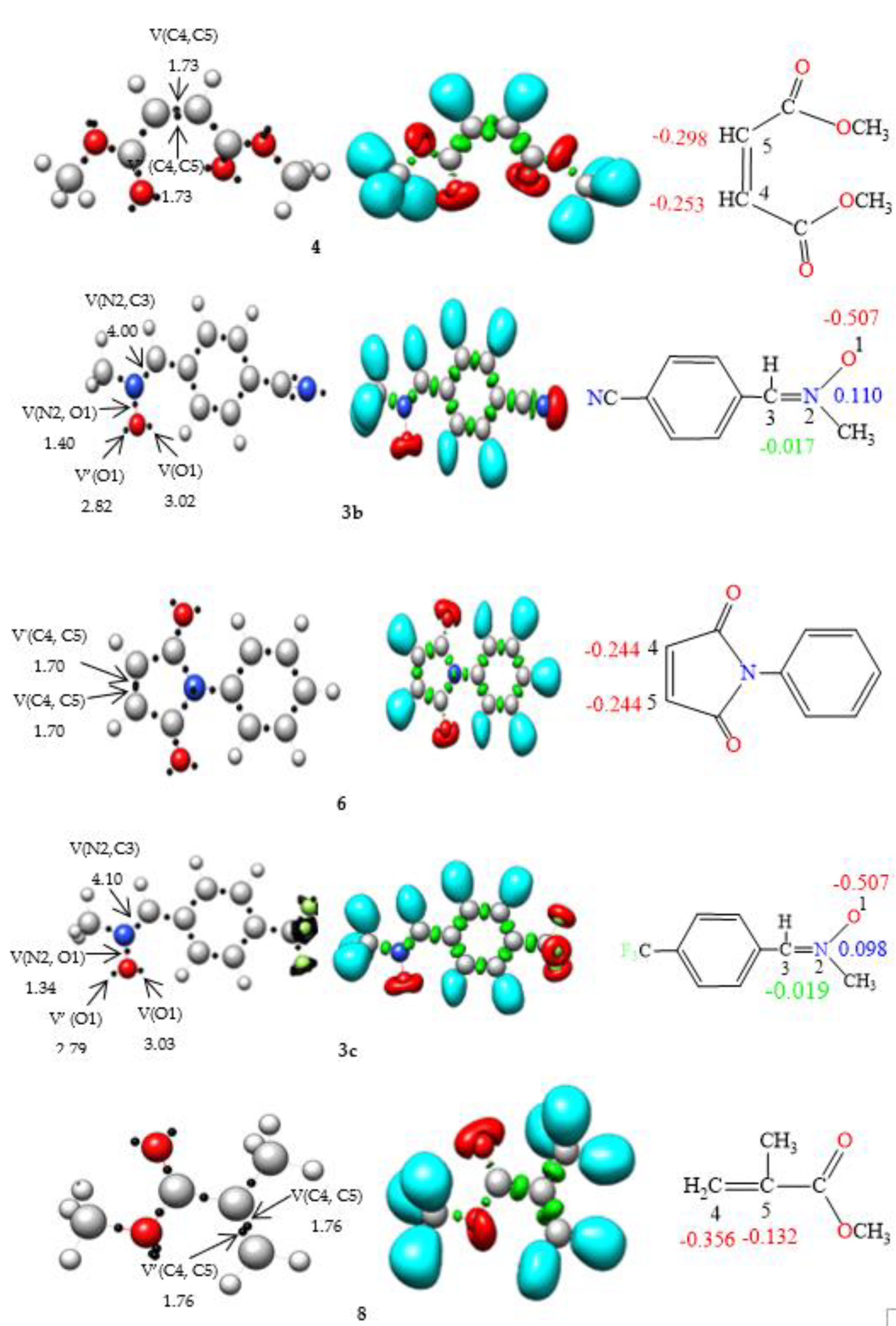
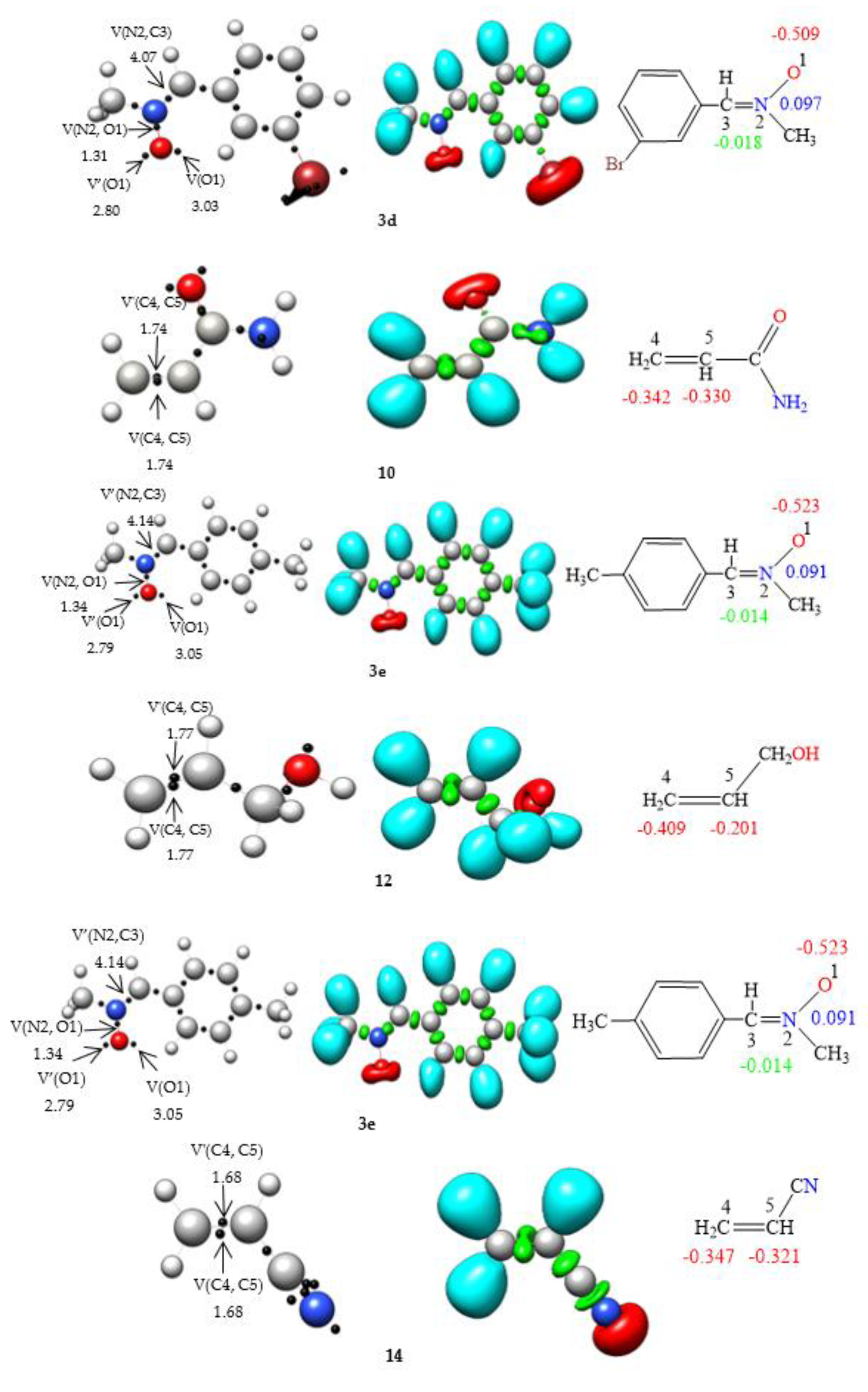
2.2.2. CDFT Reactivity Indices Analysis
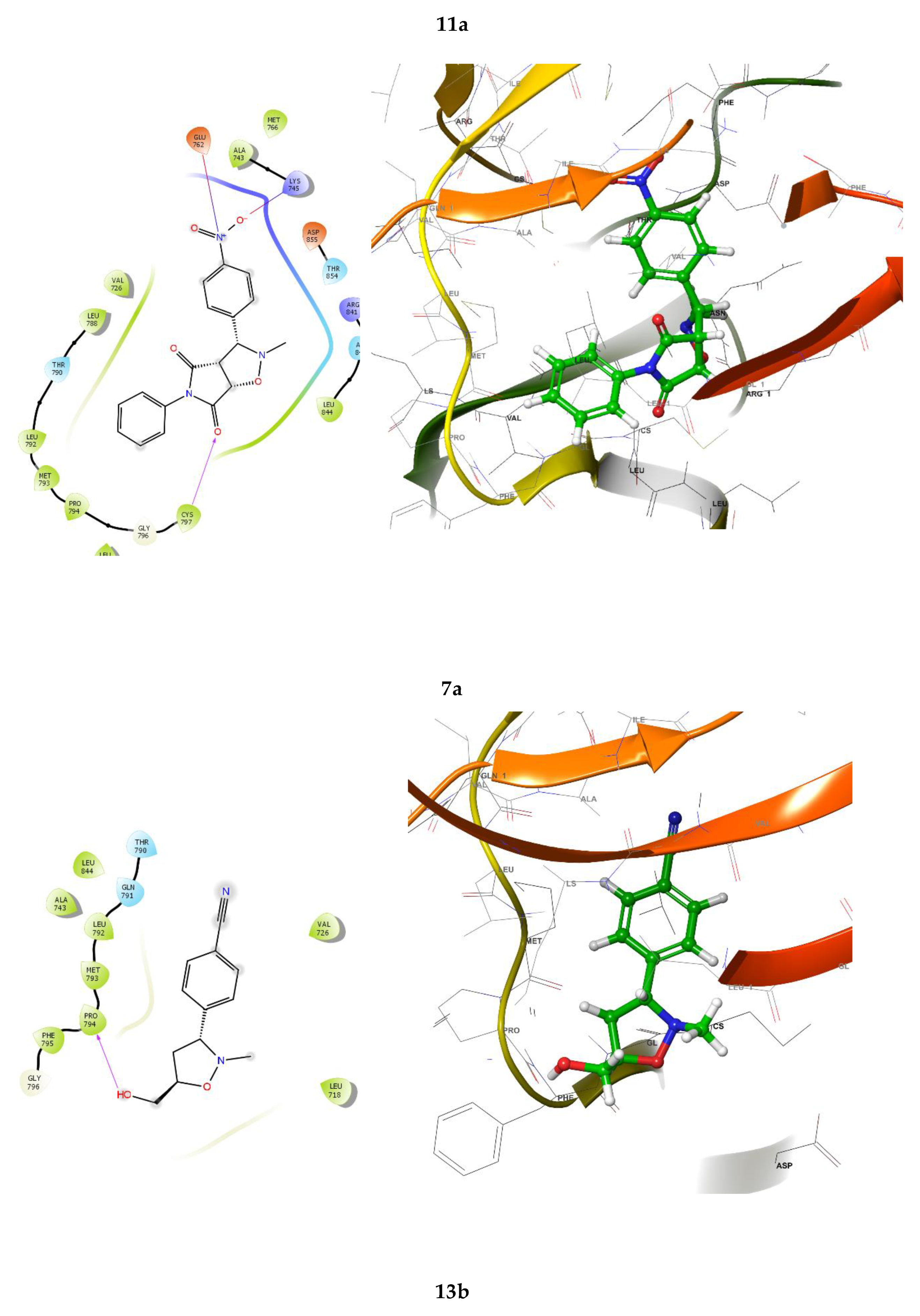
2.3. Molecular docking
3.4. Oral drug-likeness
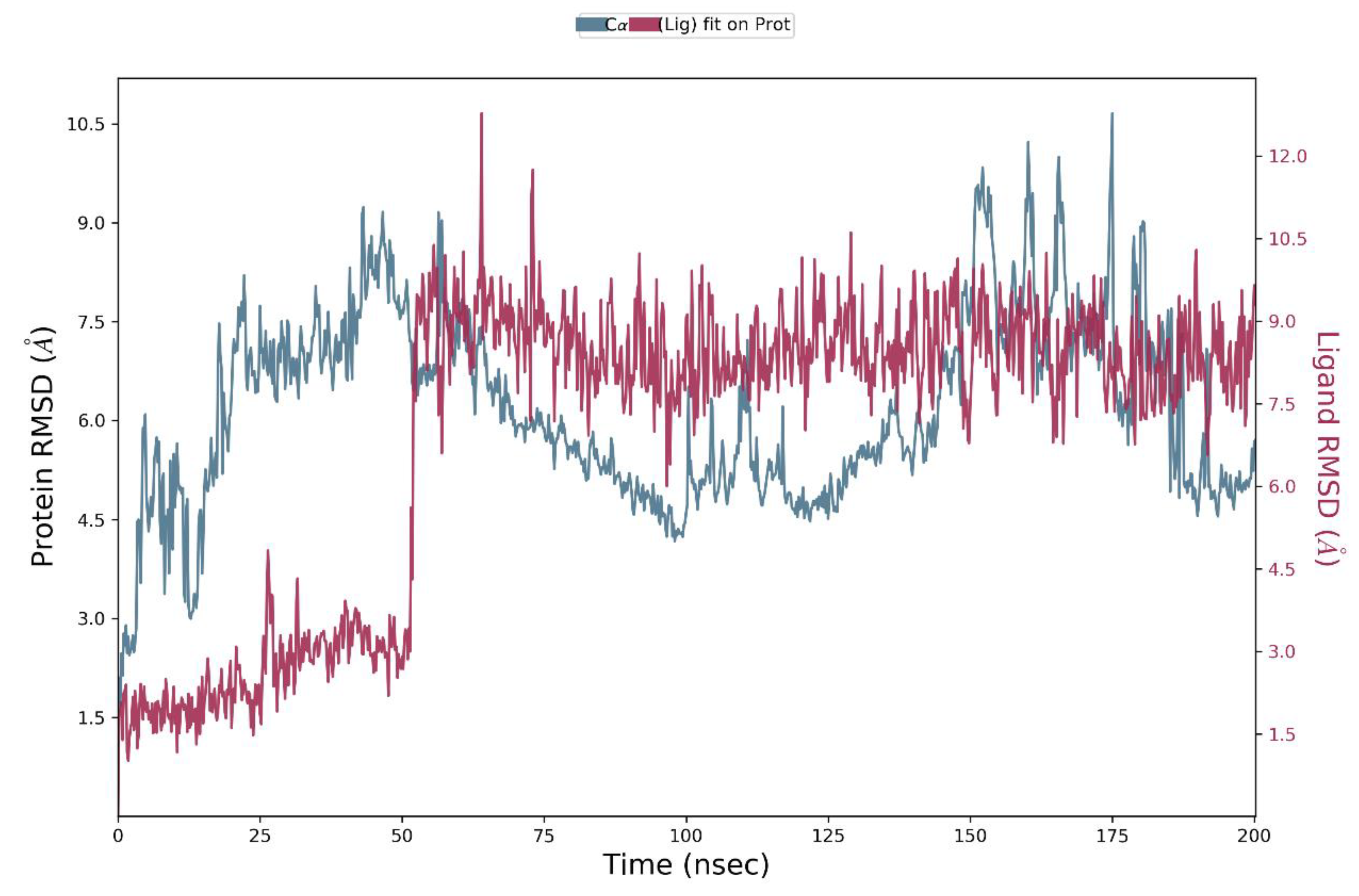
3.5. Molecular dynamics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Nitrone Derivatives.
3.2.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Isoxazolidine Derivatives.
3.3. Characterization
3.3.1. N-methyl-C-4-nitrophenyl-nitrone (3a)
3.3.2. N-methyl-C-4-cyanophenyl-nitrone (3b)
3.3.3. N-methyl-C-4-trifluoromethylphenyl-nitrone (3c)
3.3.4. N-methyl-C-3-bromophenyl-nitrone (3d)
3.3.5. N-methyl-C-4-methylphenyl-nitrone (3e)
3.3.6. Dimethyl 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylate (5a)
3.3.7. Dimethyl 3-(4-cyanomethylphenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylate (5b)
3.3.8. Dimethyl 3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylate (5c)
3.3.9. Dimethyl 3-(3-bromomethylphenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylate (5d)
3.3.10. Dimethyl 3-(4-methylmethylphenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-4,5-dicarboxylate (5e)
3.3.11. 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-methyl-5-phenyl-3a,6a-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[3,4-d] [1,2] oxazole-4,6-dione (7a)
3.3.12. 3-(4-cyanophenyl)-2-methyl-5-phenyl-3a,6a-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[3,4-d] [1,2] oxazole-4,6-dione (7b)
3.3.13. 3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-phenyl-3a,6a-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[3,4-d] [1,2] oxazole-4,6-dione (7c)
3.3.14. 3-(3-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-5-phenyl-3a,6a-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[3,4-d] [1,2] oxazole-4,6-dione (7d)
3.3.15. 3-(4-methylphenyl)-2-methyl-5-phenyl-3a,6a-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo [3,4-d] [1,2] oxazole-4,6-dione (7e)
3.3.16. Methyl 5-methyl-3-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carboxylate (9a)
3.3.17. Methyl 5-methyl-3-(4-cyanophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carboxylate (9b)
3.3.18. Methyl 5-methyl-3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-methyl-1,2 oxazolidine -5-carboxylate (9c)
3.3.19. Methyl 5-methyl-3-(3-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carboxylate (9d)
3.3.20. Methyl 5-methyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carboxylate (9e)
3.3.21. 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-5-carboxamide (11a)
3.3.22. 3-(4-cyanophenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-5-carboxamide (11b)
3.3.23. 3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-5-carboxamide (11c)
3.3.24. 3-(3-bromophenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-5-carboxamide (11d)
3.3.25. 3-(4-methylphenyl)-2-methylisoxazolidine-5-carboxamide (11e)
3.3.26. 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-methanol (13a)
3.3.27. 3-(4-cyanophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-methanol (13b)
3.3.28. 3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-methanol (13c)
3.3.29. 3-(3-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-methanol (13d)
3.3.30. 3-(4-methylphenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-methanol (13e)
3.3.31. 3-(4-nitrophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carbonitrile (15a)
3.3.32. 3-(4-cyanophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carbonitrile (15b)
3.3.33. 3-(4-trifluoromethylphenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carbonitrile (15c)
3.3.34. 3-(3-bromophenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carbonitrile (15d)
3.3.35. 3-(4-methylphenyl)-2-methyl-1,2-oxazolidine-5-carbonitrile (15e)
3.3. Computational methods
3.4. Molecular docking
3.4.1. Protein preparation
3.4.2. Docking
3.4.3. Oral drug-likeness
3.4.4. Molecular dynamics MD
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, R.D.; MacCoss, M.; Lawson, A.D. Rings in drugs: Miniperspective. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2014, 57, 5845–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, A.; et al. Synthesis, molecular modelling and biological evaluation of tetrasubstituted thiazoles towards cholinesterase enzymes and cytotoxicity studies. Bioorganic chemistry 2018, 78, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new piperazine substituted 3, 5-diarylisoxazolines. Current Organic Synthesis 2019, 16, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiacchio, M.; et al. Isoxazolidines as biologically active compounds. Current Organic Synthesis 2016, 13, 726–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannay, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, molecular properties and in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial potential of novel enantiopure isoxazolidine derivatives. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13, 2121–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaonkar, S.L.; Nagaraj, V.U.; Nayak, S. A review on current synthetic strategies of oxazines. Mini-Reviews in Organic Chemistry 2019, 16, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, M.; et al. Isoxazolidine: a privileged scaffold for organic and medicinal chemistry. Chemical Reviews 2016, 116, 15235–15283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyasami, G.; Arumugam, N.; Aldalbahi, A. Inexpensive ionic liquid mediated green synthetic approach of multi-functionalized regioselective β-lactam fused isoxazolidine heterocyclic hybrids. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouadi, K.; et al. New synthetic routes toward enantiopure (2S, 3R, 4R)-4-hydroxyisoleucine by 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition of a chiral nitrone to C4 alkenes. Synthesis 2007, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar]
- Aouadi, K.; et al. 1, 3-Dipolar cycloaddition of a chiral nitrone to (E)-1, 4-dichloro-2-butene: a new efficient synthesis of (2S, 3S, 4R)-4-hydroxyisoleucine. Tetrahedron Letters 2012, 53, 2817–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seerden, J.-P.G.; Boeren, M.M.; Scheeren, H.W. 1, 3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions of nitrones with alkyl vinyl ethers catalyzed by chiral oxazaborolidines. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 11843–11852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederickson, M. Optically active isoxazolidines via asymmetric cycloaddition reactions of nitrones with alkenes: applications in organic synthesis. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-T.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of N-heterocyclic indolyl glyoxylamides as orally active anticancer agents. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2003, 46, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmi, J.; et al. Unprecedented stereoselective synthesis of 3-methylisoxazolidine-5-aryl-1, 2, 4-oxadiazoles via 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition and study of their in vitro antioxidant activity. Synthetic Communications 2016, 46, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghannay, S.; et al. Stereoselective synthesis of enantiopure N-substituted pyrrolidin-2, 5-dione derivatives by 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition and assessment of their in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2017, 27, 2302–2307. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.R.R.; Mallesha, H.; Rangappa, K.S. Synthesis of novel isoxazolidine derivatives and their antifungal and antibacterial properties. Archiv der Pharmazie: An International Journal Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Chemistry 2003, 336, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, B.; et al. Inhibition of HIV-1 Replication by Isoxazolidine and Isoxazole Sulfonamides. Chemical Biology & Drug Design 2010, 75, 461–474. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.S.; et al. 1, 3-Dipolar cycloaddition of C-aryl-N-phenylnitrones to (R)-1-(1-phenylethyl)-3-[(E)-arylmethylidene] tetrahydro-4 (1H)-pyridinones: Synthesis and antimycobacterial evaluation of enantiomerically pure spiroisoxazolidines. European journal of medicinal chemistry 2010, 45, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.B.; et al. 1, 3-Dipolar cycloadditions of nitrones to heterosubstituted alkenes. Part 1: oxa and aza-substituted alkenes. Organic Preparations and Procedures International 2010, 42, 387–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; et al. Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2008, 455, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-F.; et al. High frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations with complex patterns in non–small cell lung cancers related to gefitinib responsiveness in Taiwan. Clinical Cancer Research 2004, 10, 8195–8203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, T.; et al. Mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in lung cancer: biological and clinical implications. Cancer research 2004, 64, 8919–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T.J.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non–small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. New England Journal of Medicine 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non–small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. New England Journal of Medicine 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): an open label, randomised phase 3 trial. The lancet oncology 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin–paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; et al. Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2005, 97, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, K.D.; et al. Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Cancer research 2006, 66, 8163–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, T., D. Bell, and R. Sordella, S. Gurubhagavatu la, RA Okimoto, BW Brannigan, PL Harris, SM Haserlat, JG Supko, FG Haluska, et al. N Engl J Med 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, V.; et al. Gold nanoparticles against respiratory diseases: oncogenic and viral pathogens review. Therapeutic Delivery 2020, 11, 521. [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, L.; Vickers, R. The Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds: Synthetic Applications of 1, 3-Dipolar Cycloaddition Chemistry Toward Heterocycles and Natural Products; Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 169–252. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; et al. Formation and reductive ring opening reactions of indolyl-isoxazolidines: access to novel natural product analogs and precursors. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; et al. Dipolar cycloadditions of HMF-based nitrones: Stepwise and multicomponent reactions, stereochemical outcome and structural scope. Green Chemistry 2020, 22, 7907–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Wazeer, M. The 13-dipolar cycloaddition reactions of 3456-tetrahydro-2h-azepine 1-oxide. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 7207–7218. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi, L.; et al. First 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition of Z-α-phenyl-N-methylnitrone with allylic fluorides: a stereoselective route to enantiopure fluorine-containing isoxazolidines and amino polyols. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2004, 15, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becke, A.D.; Edgecombe, K.E. A simple measure of electron localization in atomic and molecular systems. The Journal of chemical physics 1990, 92, 5397–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvi, B.; Savin, A. Classification of chemical bonds based on topological analysis of electron localization functions. Nature 1994, 371, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Gutiérrez, M.; Domingo, L.R. Unravelling the mysteries of the [3+ 2] cycloaddition reactions. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2019, 2019, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.; Weinstock, R.B.; Weinhold, F. Natural population analysis. The Journal of Chemical Physics 1985, 83, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.E.; Curtiss, L.A.; Weinhold, F. Intermolecular interactions from a natural bond orbital, donor-acceptor viewpoint. Chemical Reviews 1988, 88, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, L.R.; Ríos-Gutiérrez, M.; Pérez, P. Applications of the conceptual density functional theory indices to organic chemistry reactivity. Molecules 2016, 21, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerlings, P.; FProft, D.; Langenaeker, W. Conceptual density functional theory. Chemical reviews 2003, 103, 1793–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parr, R.G.; Yang, W. Book density functional theory of atoms and molecules; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, R.G.; Szentpály, L.V.; Liu, S. Electrophilicity index. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1999, 121, 1922–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, L.R.; et al. Quantitative characterization of the global electrophilicity power of common diene/dienophile pairs in Diels–Alder reactions. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 4417–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, L.R.; Chamorro, E.; Perez, P. Understanding the high reactivity of the azomethine ylides in [3+ 2] cycloaddition reactions. Letters in Organic Chemistry 2010, 7, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, L.R.; Pérez, P. The nucleophilicity N index in organic chemistry. Organic & biomolecular chemistry 2011, 9, 7168–7175. [Google Scholar]
- Ríos-Gutiérrez, M.; Sousa, A.S.; Domingo, L.R. Electrophilicity and nucleophilicity scales at different DFT computational levels. Journal of Physical Organic Chemistry 2023, e4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahayarayan, J.J.; et al. In-silico protein-ligand docking studies against the estrogen protein of breast cancer using pharmacophore based virtual screening approaches. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2021, 28, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.-Y.; et al. Identification of novel PPARα/γ dual agonists by pharmacophore screening, docking analysis, ADMET prediction and molecular dynamics simulations. Computational Biology and Chemistry 2019, 78, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, H.B. Optimization of equilibrium geometries and transition structures. Journal of computational chemistry 1982, 3, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, H. Advanced series in physical chemistry. Modern Electronic Structure Theory 1994, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Hehre, W.; Radom, L.; Schleyer, P.V.R.; Pople, J.A. Ab initio molecular orbital theory 1986, 228-251.
- Frisch, M.E.; et al. Gaussian 16, revision C. 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. Journal of computational chemistry 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; et al. UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. Journal of computational chemistry 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavi Sastry, G.; et al. Protein and ligand preparation: parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. Journal of computer-aided molecular design 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, J.R.; et al. Towards the comprehensive, rapid, and accurate prediction of the favorable tautomeric states of drug-like molecules in aqueous solution. Journal of computer-aided molecular design 2010, 24, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.A.; et al. Design, 3D QSAR modeling and docking of TGF-β type I inhibitors to target cancer. Computational biology and chemistry 2018, 76, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger, L. Schrödinger Release 2022-3: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Impact, S. , LLC, New York, NY, 2016; Prime, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2020. Google Scholar There is no corresponding record for this reference.
- Release, S. 1: Glide, Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, 2021. Schrödinger Release, 2021. 3.
- Maruthanila, V.; et al. In silico molecular modelling of selected natural ligands and their binding features with estrogen receptor alpha. Current computer-aided drug design 2019, 15, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Duffy, E.M. Prediction of drug solubility from structure. Advanced drug delivery reviews 2002, 54, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyna, G.J.; Klein, M.L.; Tuckerman, M. Nosé–Hoover chains: The canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics. The Journal of chemical physics 1992, 97, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. The Journal of chemical physics 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
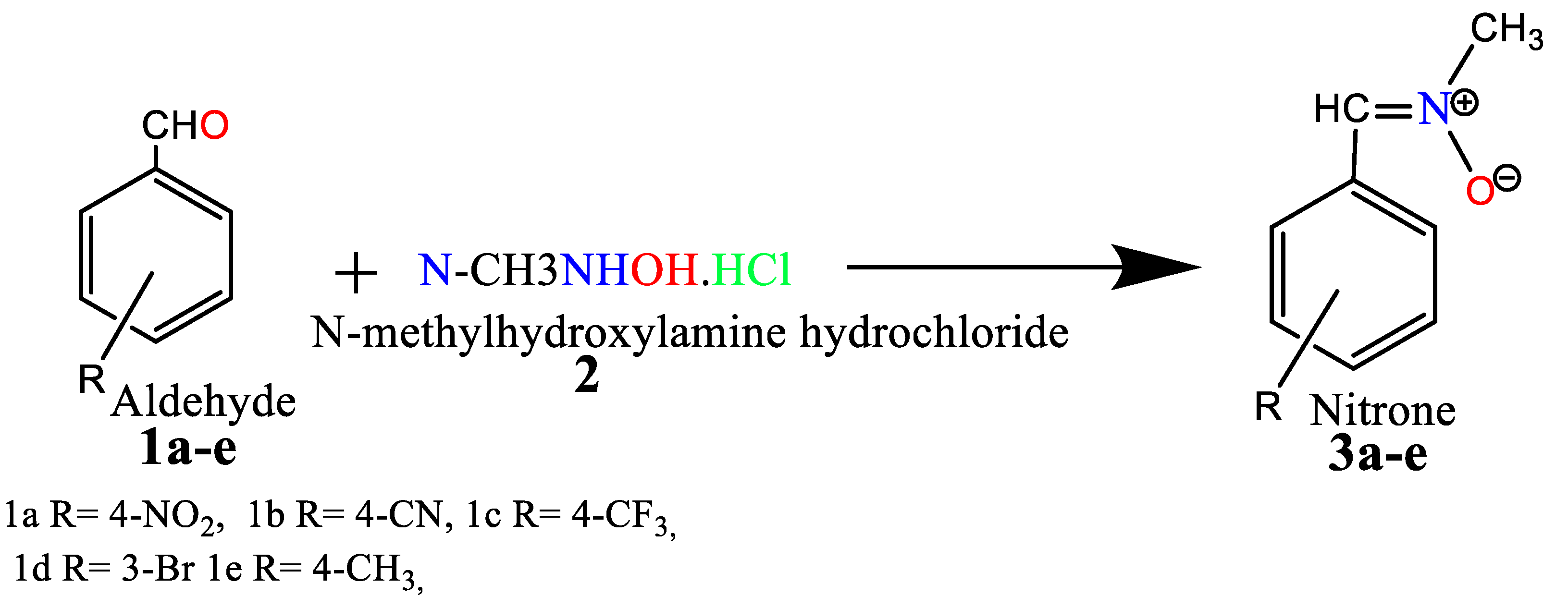

 | ||||||
 | ||||||
 |
| Reactant | η | µ | ω | N |
| 3a | 5.40 | -4.46 | 1.84 | 2.32 |
| 3b | 3.92 | -4.11 | 2.15 | 3.42 |
| 3c | 4.15 | -3.84 | 1.78 | 3.57 |
| 3d | 4.21 | -3.67 | 1.60 | 3.72 |
| 3e | 4.19 | -3.27 | 1.28 | 4.12 |
| 4 | 5.44 | -4.49 | 1.85 | 2.27 |
| 6 | 5.49 | -4.56 | 2.98 | 2.97 |
| 8 | 6.24 | -4.47 | 1.39 | 2.20 |
| 10 | 5.92 | -4.80 | 1.22 | 2.73 |
| 12 | 6.55 | -4.64 | 1.01 | 2.57 |
| 14 | 6.34 | -4.70 | 1.74 | 1.62 |
| Ligand | Affinity (kcal/mol) | H-Bonding | Interacting residues |
| 11a | -6.573 | 3 | ALA743, LEU788, MET793 |
| 11e | -6.523 | 2 | THR854, THR790 |
| 7c | -6.099 | 1 | CYC797 |
| 11d | -6.097 | 1 | PRO794 |
| 11 c | -6.835 | 2 | THR854, THR790 |
| 7 d | -6.08 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 13 b | -5.866 | 1 | PRO794 |
| 11 b | -5.803 | 2 | MET793, ASP800 |
| 9 d | -5.696 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 15 c | -5.606 | 0 | |
| 9 e | -5.536 | 1 | LYS745 |
| 7a | -5.506 | 3 | LYS745, GLU762, CYS797 |
| 13 e | -5.449 | 1 | PRO794 |
| 15 b | -5.437 | 0 | |
| 13 a | -5.392 | 1 | PHE795 |
| 15 a | -5.389 | 0 | |
| 7 b | -5.385 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 15 d | -5.37 | 0 | |
| 5 b | -5.362 | 2 | MET793, CYS797 |
| 13 c | -5.316 | 2 | MET793, MET793 |
| 5a | -5.234 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 15 e | -5.195 | 1 | LYS745 |
| 5 c | -5.129 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 7 e | -5.113 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 13 d | -5.114 | 1 | MET793 |
| 5 d | -5.105 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 9a | -5.022 | 1 | THR854 |
| 5 e | -4.798 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 9 c | -4.658 | 1 | CYS797 |
| 9 b | -4.493 | 1 | CYS797 |
| Lig. | Formula | MW (>500) | Accept HB (<=10) | Donor HB (<=5) | TPSA |
iLOGP w (<5) |
| 5a | C14H16N2O7 | 324.29 | 8 | 0 | 110.89 | 2.61 |
| 5b | C15H16N2O5 | 304.3 | 7 | 0 | 88.86 | 2.77 |
| 5c | C15H16F3NO5 | 347.29 | 9 | 0 | 65.07 | 3.21 |
| 5d | C14H16BrNO5 | 358.18 | 6 | 0 | 65.07 | 3.27 |
| 5e | C15H19NO5 | 293.32 | 6 | 0 | 65.07 | 3.16 |
| 7a | C18H15N3O5 | 353.33 | 6 | 0 | 95.67 | 2.13 |
| 7b | C19H15N3O3 | 333.34 | 5 | 0 | 73.64 | 2.51 |
| 7c | C19H15F3N2O3 | 376.33 | 7 | 0 | 49.85 | 2.78 |
| 7d | C18H15BrN2O3 | 387.23 | 4 | 0 | 49.85 | 2.94 |
| 7e | C19H18N2O3 | 322.36 | 4 | 0 | 49.85 | 2.76 |
| 9a | C13H16N2O5 | 280.28 | 6 | 0 | 84.59 | 2.26 |
| 9b | C14H16N2O3 | 260.29 | 5 | 0 | 62.56 | 2.73 |
| 9c | C14H16F3NO3 | 303.28 | 7 | 0 | 38.77 | 2.84 |
| 9d | C13H16BrNO3 | 314.18 | 4 | 0 | 38.77 | 3.04 |
| 9e | C14H19NO3 | 249.31 | 4 | 0 | 38.77 | 2.91 |
| 11a | C11H13N3O4 | 251.24 | 5 | 1 | 101.38 | 1.19 |
| 11b | C12H13N3O2 | 231.25 | 4 | 1 | 79.35 | 1.29 |
| 11c | C12H13F3N2O2 | 274.24 | 6 | 1 | 55.56 | 1.78 |
| 11d | C11H13BrN2O2 | 285.14 | 3 | 1 | 55.56 | 1.97 |
| 11e | C12H16N2O2 | 220.27 | 3 | 1 | 55.56 | 1.76 |
| 13a | C11H14N2O4 | 238.24 | 5 | 1 | 78.52 | 1.63 |
| 13b | C12H14N2O2 | 218.25 | 4 | 1 | 56.49 | 2.04 |
| 13c | C12H14F3NO2 | 261.24 | 6 | 1 | 32.7 | 2.47 |
| 13d | C11H14BrNO2 | 272.14 | 3 | 1 | 32.7 | 2.51 |
| 13e | C12H17NO2 | 207.27 | 3 | 1 | 32.7 | 2.43 |
| 15a | C11H11N3O3 | 233.22 | 5 | 0 | 82.08 | 1.51 |
| 15b | C12H11N3O | 213.24 | 4 | 0 | 60.05 | 1.84 |
| 15c | C12H11F3N2O | 256.22 | 6 | 0 | 36.26 | 2.35 |
| 15d | C11H11BrN2O | 267.12 | 3 | 0 | 36.26 | 2.27 |
| 15e | C12H14N2O | 202.25 | 3 | 0 | 36.26 | 2.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





