1. Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau, as the third pole of the Earth, is a zone of rapid topographic change characterized by plate collision and active tectonics[
1]. The eastern part of the plateau, in particular, is marked by complex topography, active plate tectonics and extremely high seismic intensity. The complex and varied geological conditions indicate the development of geohazards[2-7]. Early studies showed that most of the famous large-scale landslide disasters in the Tibetan Plateau occurred in the area of deeply incised valleys[8-12]. The routes for the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor are mostly located in the lower parts of the slopes along the river. Therefore, the stability of the slopes poses a considerable challenge to the alignment and design of the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor.
With the rapid development of various remote sensing technologies and the exponential increase in the number of successful cases of each technology in the investigation of geohazards, integrated remote sensing has become a popular method in the identification and monitoring of geohazards, and different remote sensing technologies have their own advantages in different aspects[
13,
14]. Common remote sensing techniques include high-precision optical remote sensing, light detection and ranging (LiDAR) remote sensing and interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR). High-resolution optical satellite remote sensing data have the advantages of originating from multiple sources and being acquired over multiple temporal scales with low acquisition costs and wide coverage; hence, optical data are widely used in railway route selection surveys and geohazard investigations for existing lines[
15,
16]. In contrast, LiDAR data have a higher resolution than optical data and provide more realistic surface information through the processing of point cloud data, making it possible to achieve the more detailed identification and interpretation of geohazard bodies[17-19]. Consequently, LiDAR technology offers irreplaceable advantages in railway surveys[20-23]. As another alternative, InSAR technology plays an important role in the rapid identification and monitoring of surface deformation along railway lines by virtue of its ability to acquire measurements at all times of day and under all weather conditions, and it can achieve a deformation monitoring accuracy up to the millimeter scale[24-30]. Although InSAR technology has many limitations, it has developed from the initial differential InSAR (D-InSAR) technique to subsequent time-series analysis technologies such as small baseline subset (SBAS) InSAR, persistent scatterer (PS) InSAR and Stacking-InSAR; this has been accomplished by continuously diminishing the influences of factors such as spatiotemporal decoherence, atmospheric delays, and noise. And by distinguishing and eliminating phases that are not related to the deformation phase, thereby obtaining more reliable deformation estimates[31-37]. Just as InSAR technology has various drawbacks, individual remote sensing techniques have their own shortcomings, whereas integrated remote sensing can make up for these disadvantages and provide a more comprehensive assessment of geological hazards. In previous disaster studies, integrated remote sensing techniques were mostly used for slopes that were undergoing slowness deformation, while less research was conducted for slopes with only morphological features but no deformation[
38]. In contrast, this study was conducted for the latter type of slopes.
In this paper, three remote sensing techniques, namely, optical remote sensing, airborne LiDAR, and InSAR, were integrated to detect the deformation of the slope of the Genie tunnel, which located in the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor. The high-resolution optical satellite images, airborne LiDAR derived data (DEM and hillshade), and Advanced Land Observing Satellite (ALOS)-1 and Sentinel-1A satellite data were collected. Then, the results of analyzing these three datasets were combined to evaluate the stability of the Genie slope and explain its formation mechanism.
2. Study Area
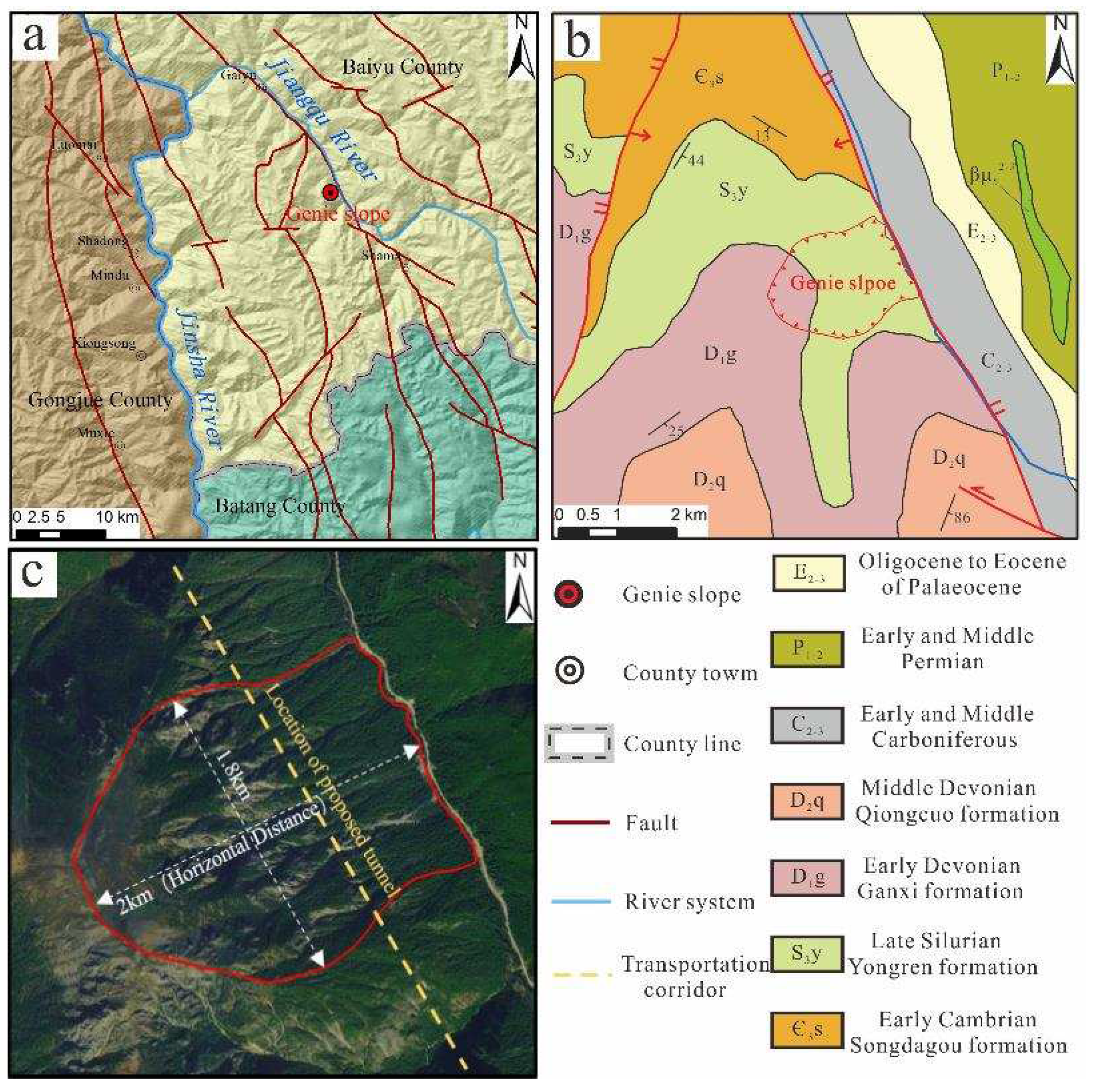
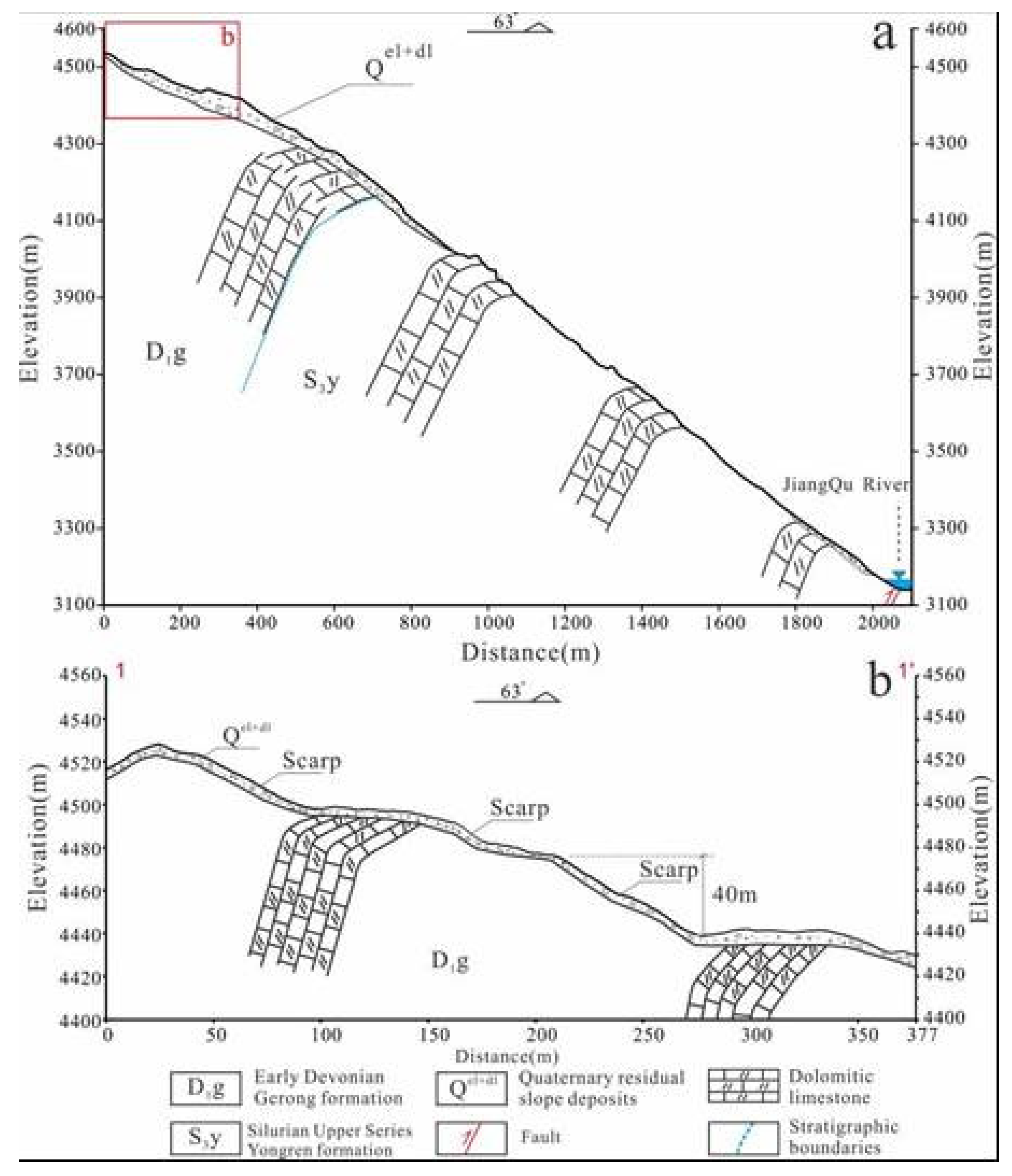
The Genie Slope is located approximately 4 km south of Huolong village, Gaiyu town, Baiyu County, Ganzi Prefecture, Sichuan Province. The slope is located on the left bank of the Jiangqu River within a typical alpine canyon area, with the NW-SE-trending Jinsha River east boundary fault passing through the foot of the slope (
Figure 1 a, b). The elevation of the top of the slope is 4535 m, and the elevation of the Jiangqu River, which flows through the foot of the front edge, is 3140 m. The relative height difference reaches 1395 m, and the average slope is 67%. The overall horizontal length of the slope is approximately 2 km, and the width is approximately 1.8 km (
Figure 1 c). The structure is an inverted, steeply inclined layered rock slope, the overlying soil layer on which is composed of Quaternary residues and slope deposits. The Lower Devonian Ganxi Formation (D
1g) strata are exposed in the upper part of the slope, and the Upper Silurian Yongren Formation (S
3y) strata are exposed in the middle and lower parts. The lithology of both groups of exposed strata is mainly dolomite limestone.
To cross the slope of Genie Mountain, the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor was designed to adopt a tunneling method. The proposed route is located in the middle and lower parts of the slope. Therefore, whether the slope is presence or absence of deformation constitutes a vital component in determining the feasibility of the design scheme.
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Datasets
3.1.1. Optical satellite imagery and airborne LiDAR data
For this research, true-color satellite optical image data with a resolution of 0.5 m taken by the WorldView-2 satellite in March 2015 were collected. The satellite optical image data is of good quality, with no cloud cover, and there are no large shadow areas in the image. The image perfectly covers the study area and clearly shows the morphological and deformation characteristics of the slope. The optical image was registered and geometrically rectified using high-precision DEM data. Accordingly, the data meet the requirements for visual interpretation.
In addition, 3D laser point cloud data acquired by SKYEYE SE-J1200B airborne LiDAR were collected. The point cloud density is about 50 points/m3, the level difference between point cloud air strips is better than 10 cm. the TerraScan and TerraModeler modules of Terrasolid software were used to automatically classify the raw point cloud data, and the point clouds were mainly classified into ground, vegetation and noise point types. Then the ground point cloud data were manually edited and corrected to obtain ground point cloud data, and a high accuracy real surface digital elevation model (DEM) and hillshade model were generated in ArcGIS software based on the ground point cloud data.
3.1.2. SAR data
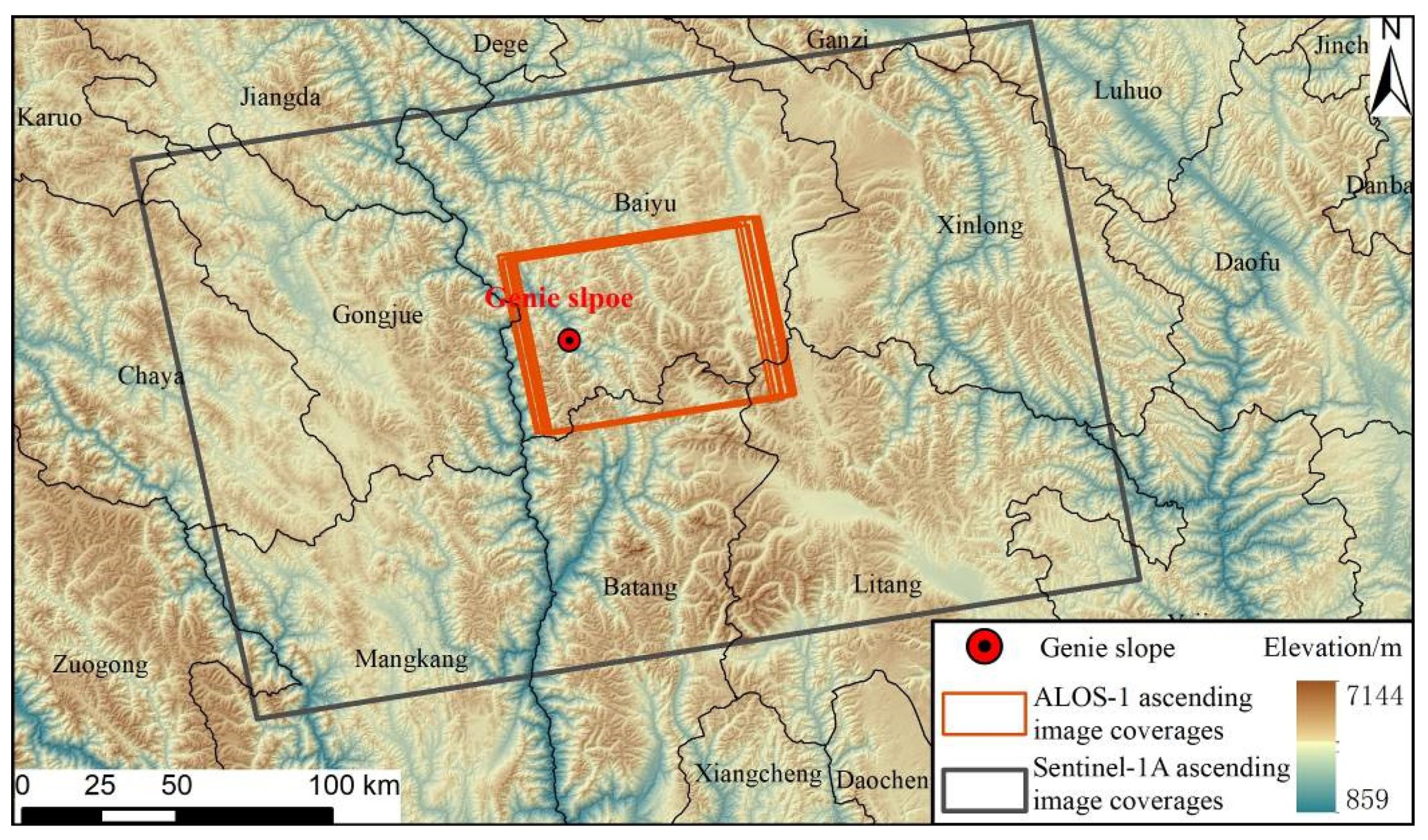
In this study, ascending L-band spaceborne SAR image data taken by the Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) sensor on board the ALOS-1 satellite launched by the Japan Aerospace Development and Research Agency (JAXA) were used for D-InSAR analysis. The time span of the collected ALOS-1 data is from January 2007 to December 2008. However, the satellite has a revisit period of 46 days, only 9 scenes of ascending data were collected within this time span due to the influence of the data source. Nevertheless, compared with other SAR image data, the wavelength of 23.6 cm enables the ALOS-1 data to maintain a certain degree of coherence over a longer time interval, so the nine collected data scenes meet the processing requirements of D-InSAR technology.
Furthermore, 108 scenes of ascending SAR image data acquired by the Sentinel-1A Earth-observing satellite launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) were acquired over the period from March 2017 to November 2020. The image interval between two adjacent scenes is 12 days, and the image time series are continuous, which is suitable for time-series InSAR analysis. The parameters of these two spaceborne SAR image datasets are summarized in
Table 1, and their spatial extents are shown in
Figure 2.
3.2. Methodology
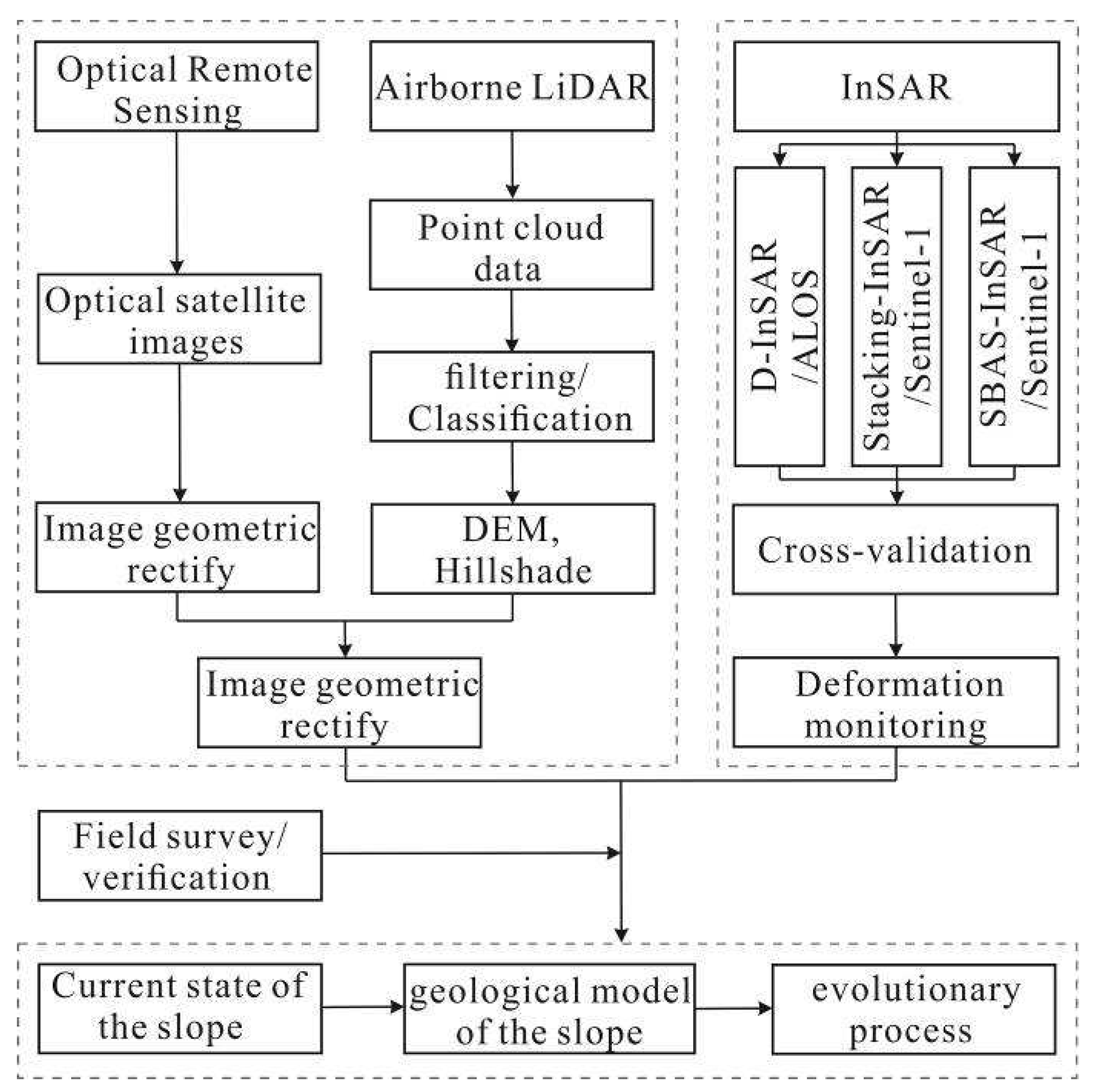
The slope morphological characteristics are analyzed using optical satellite image and airborne LiDAR DEM and hillshade data, while the deformation of the slope is monitored using three different InSAR techniques (D-InSAR, Stacking-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR). Based on the above studies, field investigations were conducted to verify the results of remote sensing analysis. Subsequently, the conclusions were summarized to analyze the current status of slope deformation and to establish a geological model to analyze the slope evolution process. The technical flowchart adopted in this study is shown in
Figure 3. The remote sensing analysis is divided into two main modules, namely, visual interpretation of slopes and deformation detection, as shown below.
3.2.1. Optical remote sensing and airborne LiDAR interpretation
Manual visual interpretation was adopted for both the optical remote sensing interpretation and the LiDAR 3D digital model interpretation. The morphological features of the Genie slope and all signs of deformation should be discerned when using optical remote sensing interpretation. The main identification targets include the slope boundary, local collapse in the area of strong deformation in the middle of the slope, and the development of cracks and scarps at the back edge of the slope.
High resolution DEM and hillshade data were used to decipher slope features in areas with high vegetation cover. The removal of vegetation resulted in more realistic hillshade data, detailing the topography in the middle of the slope and stacking features along the leading edge of the slope, while also providing support for measuring the structural surface of the slope.
3.2.2. InSAR deformation monitoring
Based on GAMMA SAR and Interferometric Processing Software, D-InSAR, Stacking-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR technologies were applied to carry out deformation monitoring research. D-InSAR was applied to every two adjacent scenes of ALOS-1 time-series data to obtain filtered differential interferograms, and the geocoded unwrapped differential interferograms were used to determine the deformation of the Genie slope according to the phase change characteristics. In addition, time-series analyses were conducted using Stacking-InSAR and SBAS-InSAR for the Sentinel-1A data. Stacking-InSAR performs a weighted superposition of a series of unwrapped differential interferograms to obtain the average deformation phase over a certain period of time, where the accuracy of the final deformation grows with the timespan and amount of superimposed data[
39,
40]. A maximum temporal baseline of 60 days was set for this study, and a total of 318 interferometric image pairs were generated. All the unwrapped interference image pairs were stacked year by year to obtain interferometric Stacking maps for 2017, 2018, 2019, and 2020, and the deformation of the Genie slope was evaluated through the four interferometric Stacking maps. SBAS-InSAR was also employed to further obtain the average deformation rate and historical displacement of the Genie slope over a period of three and a half years and to judge the deformation of the Genie slope by statistically analyzing the deformation rate and displacement of typical deformation points in the slope. In this paper, two different radar satellite data and three different InSAR techniques were used to analyze the slope deformation. The results of different data and different methods for deformation trend detection can play a good role in mutual verification, and the field survey further supports the deformation characteristics of the slope.
4. Results
4.1. Optical Remote Sensing and Airborne LiDAR Interpretation Results
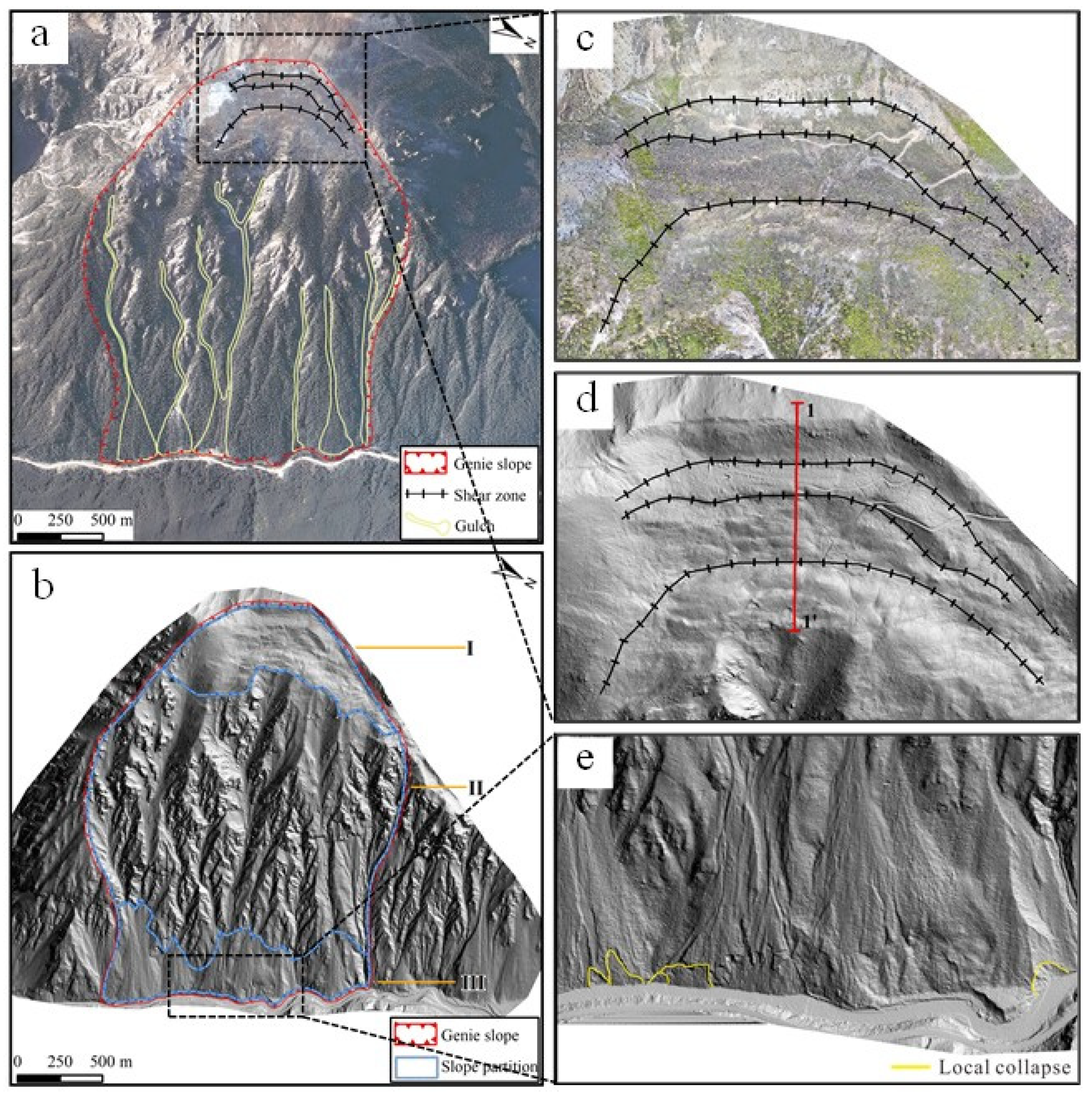
Based on the optical and LiDAR images, the Genie slope can be divided into three zones according to the geological and deformation characteristics (
Figure 4 a, b). The tensile cracking dislocation area along the trailing edge of the slope (Zone I) is crescent-shaped, and the rock mass is affected by bending, tensile cracking, and strong weathering. The rock masses in this area are extremely broken due to well-developed joints and fissures, and the slope surface is covered by Quaternary residual slope deposits. Three main dislocation zones divide the top area into three terraces (
Figure 4 c, d). The DEM was used with the vegetation removed to draw a 1-1’ geological profile (
Figure 5a, b), and the maximum measured displacement height was found to be approximately 40 m. The strongly deformed area at the center of the slope (Zone II) is characterized by exposed bedrock that is more fragmented, and small-scale collapses and rockfalls are generally developed in this area, with most of the rockfalls occurring along the seven major gullies that are fully developed. Finally, the erosion accumulation area at the foot of the slope (Zone III) is influenced by the erosion of the Jinsha River east boundary fault and the scouring of the Jiangqu River, and collapses and slope surface debris flows are locally developed. Many boulders and gravels soil are accumulated at the mouth of the gully, but the river channel is not blocked (
Figure 4e).
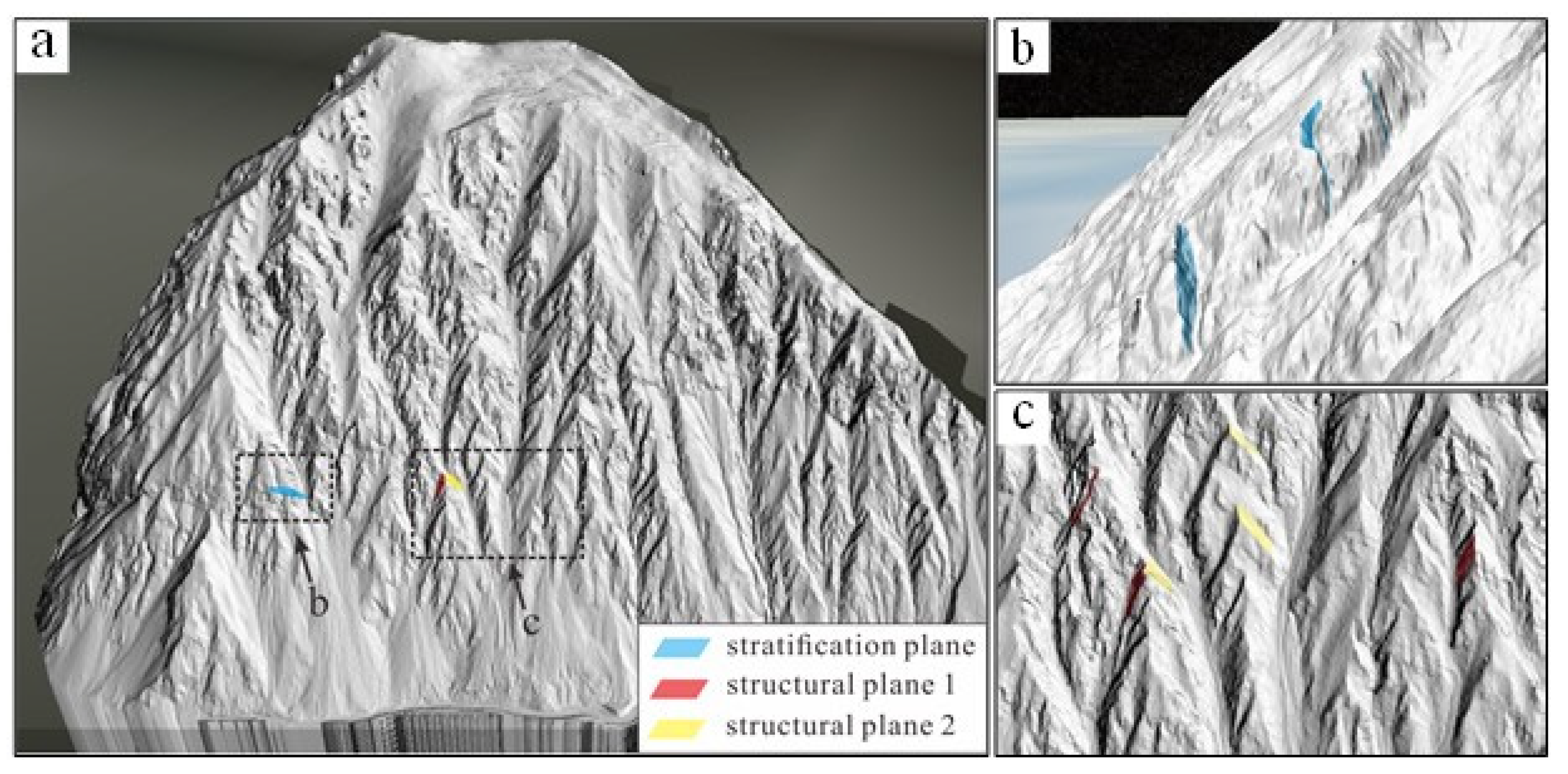
A three-dimensional analysis of the DEM and hillshade data after removing vegetation (
Figure 6a) reveals signs of outcropping rock layers in the lower and middle areas on the right side of the mountain.
Figure 6b shows the rock layers from the perspective of the strike direction of the slope. Using fitting the plane method, the attitude of the layer was measured to be 262°∠59°. Two sets of structural planes forming a set of conjugate planes are mainly exposed in the slope body in Zone II (
Figure 6c). Upon measuring the occurrence of these structural planes in a typical area (
Figure 6c), the occurrence of structural plane 1 was 164°∠48°, and that of structural plane 2 was 318°∠41°.
4.2. InSAR Deformation Detection Results
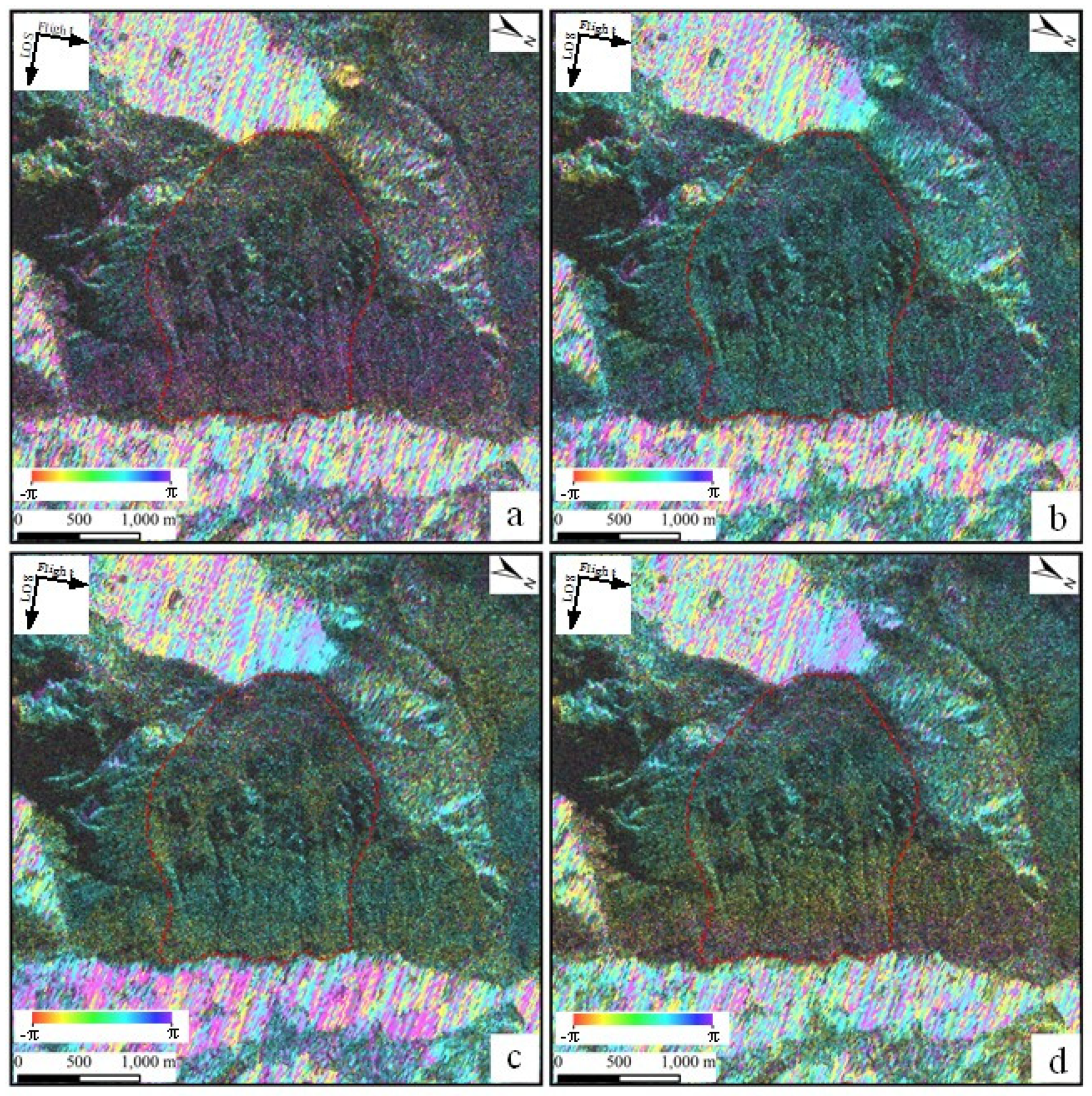
Four typical D-InSAR interferograms obtained from the ALOS-1 data were selected for display with the dates 31 Jan. 2007 and 18 Jun. 2007, 18 Jun. 2007 and 3 Aug. 2007, 3 Aug. 2007 and 3 Nov. 2007, 20 Sept. 2008 and 21 Dec. 2008 (
Figure 7). The differential interferogram of 2007.01.31-2007.06.18 has a lower quality due to the longer time interval, while the remaining three differential interferograms are of high quality. There is a small amount of residual noise phase in the four interferograms, but the remaining noise phase has a negligible influence on the overall result. The results show no clear and continuous periodic phase change in the whole range of the slope, indicating that these interferograms of the slope contain no deformation.
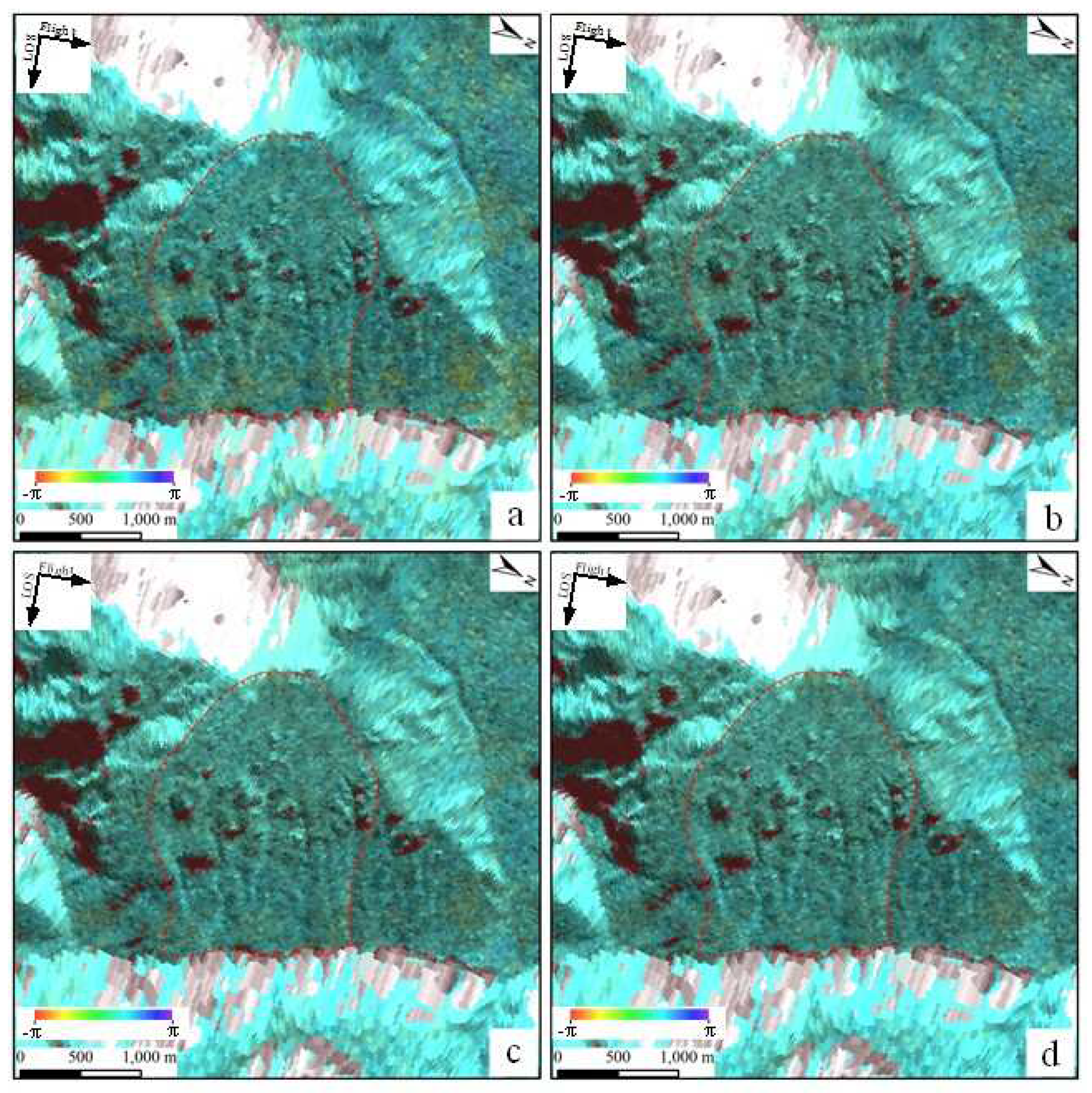
The Sentinel-1A data were processed by Stacking-InSAR, and the weighted average was calculated annually based on the temporal baseline starting from 2017. Weighted average interferometric stacking graphs were constructed from March 2017 to December 2017, March 2017 to December 2018, March 2017 to December 2019, and March 2017 to November 2020 (
Figure 8). During Stacking-InSAR processing, there may be a residual topographic phase and a noise phase due to the insufficient accuracy of external DEM data and the setting of the filter window size; these phases may introduce a small error into the estimated deformation rate, but this error is within an acceptable range. After removing the effects of topography and flattening and after filtering out noise and atmospheric effects, these four interferometric Stacking diagrams at different time intervals have a smooth phase transition, and there is no phase mutation information. This further confirms that the slope does not exhibit obvious deformation.
Furthermore, the deformation of the slope was analyzed by SBAS-InSAR, and the average deformation rate of the slope was plotted (
Figure 9). A negative deformation rate indicates that the surface moves away from the satellite sensor, while a positive value indicates movement toward the sensor. Combining the SBAS-InSAR results of the average deformation rate with the optical imagery, the vegetation coverage on the slope in Zone III is higher than that in Zones I and II, resulting in poor coherence in Zone III and a sparsity of points at which the deformation rate was obtained. However,
Figure 9 readily demonstrates that the deformation rates at all the points on the slope are concentrated near 0 mm/a.
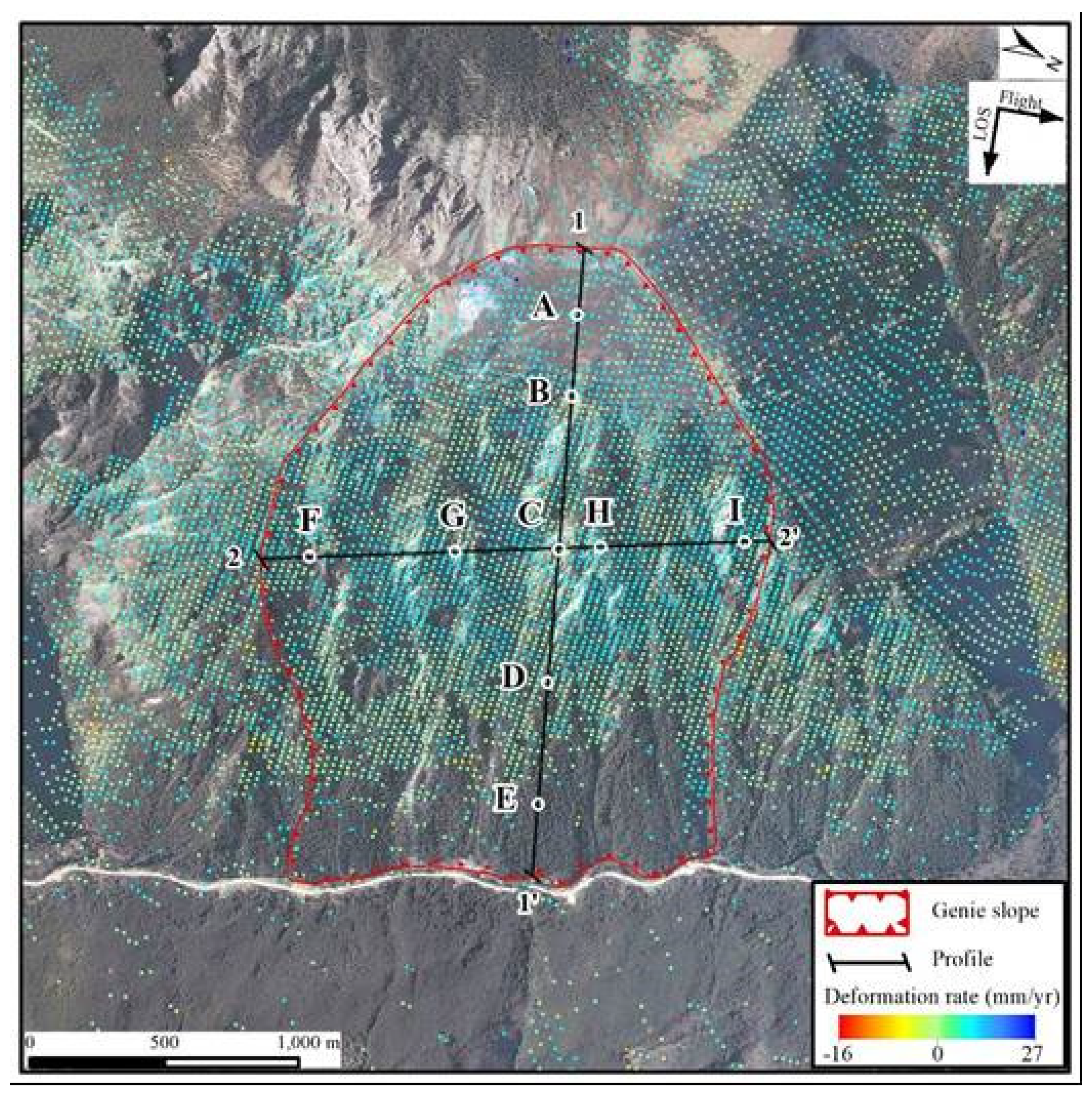
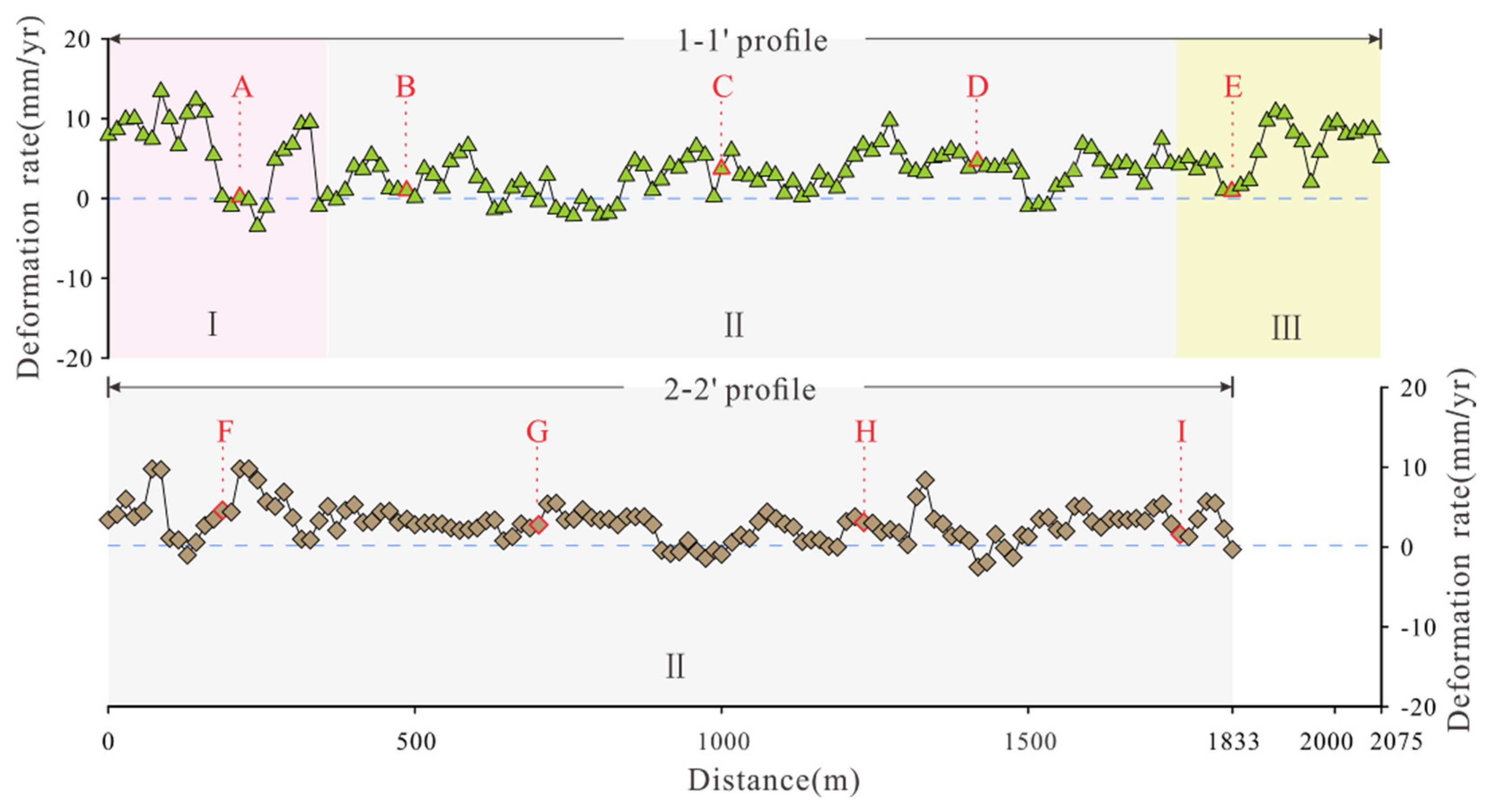
To further analyze the deformation of the slope, an along-dip profile (profile 1-1') was selected longitudinally along the slope surface, and an along-strike profile (profile 2-2') was established in the middle of the slope (
Figure 9); profile 1-1' runs through all three zones, while profile 2-2' runs transversely through Zone II. Five typical deformation points (A through E) were selected on profile 1-1', while four typical deformation points (F through I) were selected on profile 2-2'. The average deformation rate on each profile is plotted in
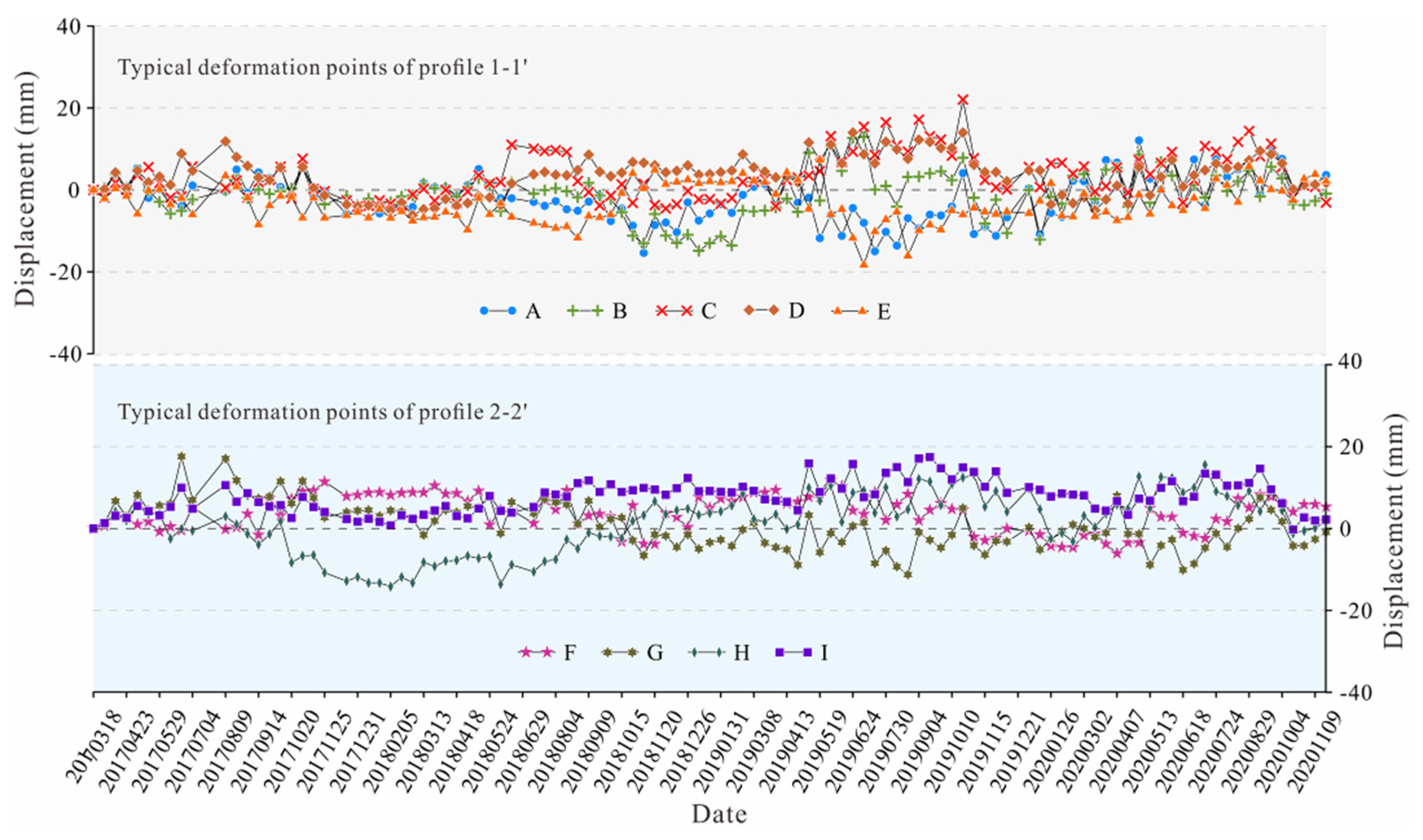
Figure 10, and the historical deformation curves at the typical deformation points between March 2017 and November 2020 are plotted in
Figure 11.
Table 2 shows the magnitudes cumulative deformation and average deformation rates at the nine typical deformation points over three and a half years and the zones in which they are located. As shown in
Figure 10, the deformation rates at individual points on the profiles are abnormal, but the deformation rates at most points on the two profiles are distributed in the range from -2 mm/a to 6 mm/yr, and the overall deformation rate is stable in the range of very small orders of magnitude. Moreover,
Figure 11 shows that the magnitudes of cumulative deformation at the nine typical deformation points fluctuate within the interval of approximately ±20 mm over the period of three and a half years. From the deformation analysis of profiles and typical points, it is easy to see that there are local jumps in both rate curves and deformation curves. The reason is that InSAR technology has been affected by irrelevant phases such as topography, atmosphere and noise, and the minimal residual topographic and atmospheric errors after processing can lead to local fluctuations in deformation monitoring results. The entire history of InSAR technology is the development history of continuously eliminating errors to obtain a closer approximation to the real surface deformation. Numerous studies have shown that the surface deformation monitored by InSAR is approximately linear and slow, so local fluctuations in the data cannot be considered as actual slope deformation when the overall deformation trend remains constant. In summary, the SBAS-InSAR results indicate that there is no significant deformation trend in the slope.
5. Discussion
Individual remote sensing techniques have limitations in assessing geohazards and can sometimes even lead to incorrect conclusions. In contrast, integrated remote sensing takes advantage of multiple remote sensing techniques by combining multiple sources of data, multiple indicators, multiple phenomena and multiple results to conduct a comprehensive analysis of geohazards from an overall perspective. The conclusions derived from this method are therefore more in line with the reality. Finally, the current state of the slope can be basically identified by combining the results of field survey and verification.
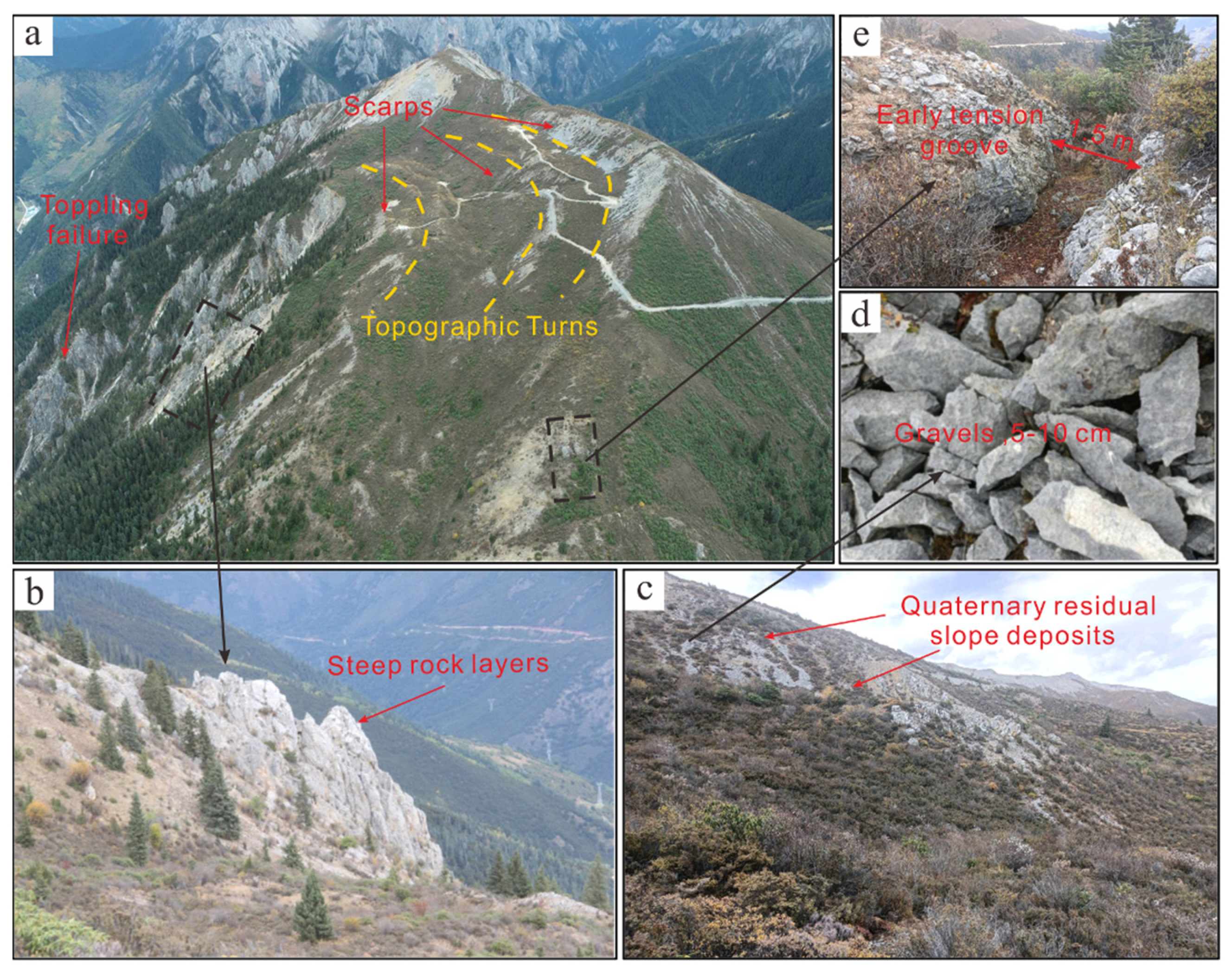
In this study, the optical interpretation reveals that the Genie slope exhibits morphological features and signs of deformation. Such as, the back edge of the slope is characterized by multiple stages of scarps, and the rock of the slope surface is fragmented, featuring many small-scale collapses and gullies. The interpretation of airborne LiDAR data indicates that the rock mass in the middle of the slope is cut by two sets of structural planes, thereby presenting a block structure as a whole, and the accumulated deposits at the corner of the slope are locally collapsed. The above intuitive factors, such as the local geomorphological features of the slope, reflect conditions conducive to slope failure. However, the D-InSAR monitoring results based on ALOS-1 data show no slope deformation between July 2007 and December 2008. Additionally, the time-series InSAR monitoring results based on Sentinel-1 data demonstrate that the slope did not experience any deformation between March 2017 and November 2020. Although InSAR deformation analysis is affected by factors such as the external DEM accuracy, filtering strength and atmospheric correction model, resulting in the incomplete identification and rejection of extraneous phases such as those pertaining to the terrain, noise and atmosphere, the errors are within acceptable limits and do not affect the confidence of the final results. Hence, the results of these three InSAR methods confirm the absence of deformation in the Genie slope. Subsequent field survey results verify that there are no fresh signs of slope deformation and that all the features currently exhibited by the slope can be attributed to the early evolution of the slope.
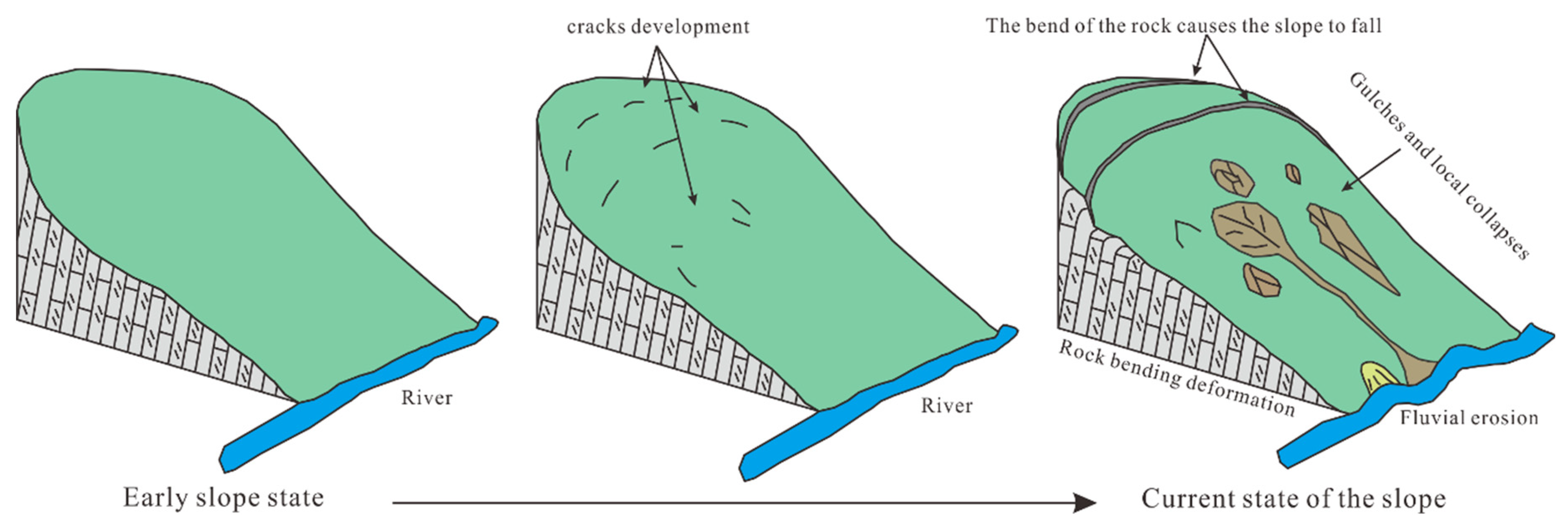
In summary, a comprehensive analysis of the results of optical remote sensing, airborne LiDAR, InSAR and field survey verification verifies that the Genie slope was essentially free of deformation during the study period. Thus, the morphological characteristics and signs of deformation exhibited by the slope appeared during its early formation and have persisted to this day. Combining the available geological information and remote sensing data, the formation mechanism of the Genie slope is inferred to be as follows (
Figure 14).
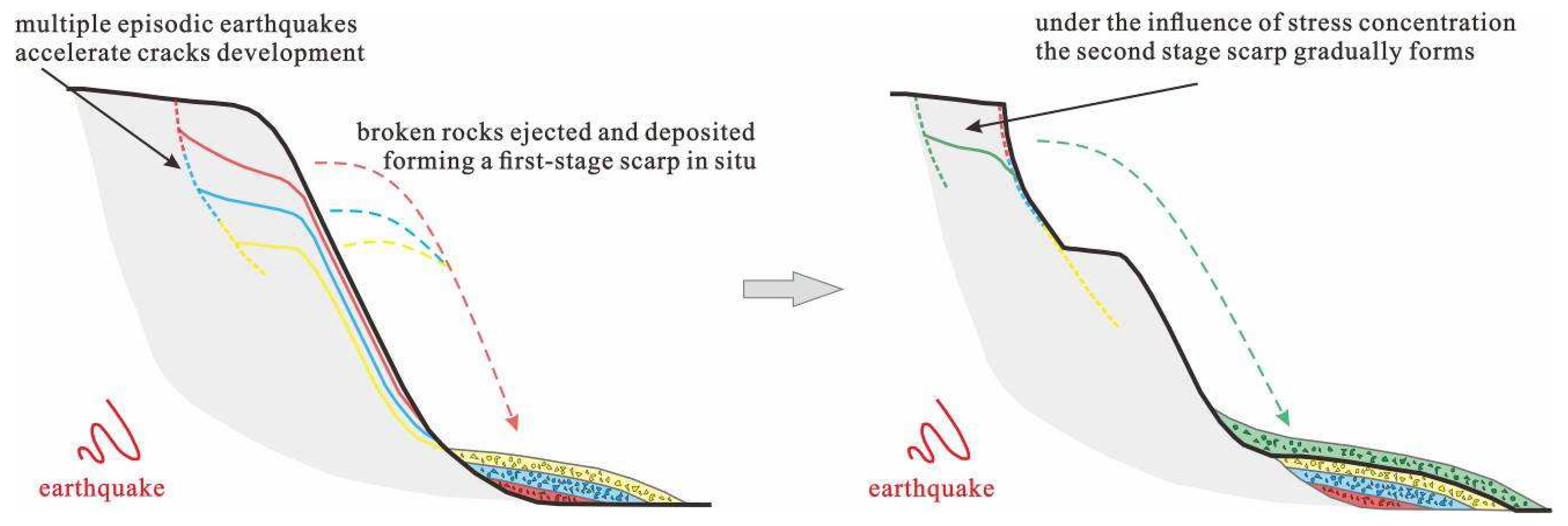
During the early formation process of the slope, the shallow inverted and steeply layered strata at the rear edge of the slope were folded and toppled in the direction of the free surface under the action of their self-weight bending moment; this process caused interlaminar dislocations and tension cracks to occur. Originally, under natural gravity and weathering conditions, the scarps at the back edge of the slope would have taken an extremely long time to form, but the tectonic activity of the region and episodic earthquakes greatly accelerated this process. The cyclic, opposite-direction tension and shear effects of the earthquakes exacerbated the development of the aforementioned cracks and interlaminar dislocations to greater depths, while the fractured rocks were ejected and deposited at the foot of the slope, forming a first-stage scarp in situ. After the first stage of scarp development reaches a certain height, another stage of scarp will be developed in the same pattern at the upper edge of the scarp due to stress concentration (
Figure 15). Currently, the exposure of the bedrock in the middle of the slope was controlled by the strata and two main groups of conjugate structural planes. Due to long-term weathering, the bedrock on the slope surface was continuously eroded, resulting in local collapse and rockfall events. Multiple gullies formed under the downslope movement of collapsing slope surface material and rockfalls, and the area of accumulated deposits at the foot of the slope locally collapsed due to long-term erosion by the river.
Only from the perspective of integrated remote sensing reveals that there is no deformation in Genie slope under natural conditions. However, the disturbance to the slope structure created by excavating a tunnel is not considered in this study. Therefore, a detailed geological survey should be carried out to assess the slope stability during the construction of subsequent tunnel projects to identify the magnitude of the impact on slope toppling deformation, and equipment should be arranged at the site for the real-time monitoring of slope dynamic changes.
6. Conclusions
Based on the interpretation of optical remote sensing, airborne LiDAR and InSAR deformation data, this paper conducted research on the slope of the Genie Tunnel on the Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor. The surface deformation of the Genie slope was judged by comprehensively analyzing the results of these various remote sensing techniques, and the slope formation mechanism was briefly evaluated. The following main conclusions can be drawn from this study.
The interpretation of optical and LiDAR remote sensing data shows that the Genie slope is composed of steeply dipping inverted strata. Multistage scarps are present in Zone I at the rear edge of the slope, rock mass structural planes in Zone II in the middle of the slope led to local collapses, and the accumulated deposits in Zone III at the foot of the slope are being eroded by the river. Hence, the Genie slope shows the morphological characteristics and deformation signs of a potentially unstable slope.
No significant deformation phases were detected in the D-InSAR processing results of ALOS-1 data or in the Stacking-InSAR processing results of Sentinel-1 data. Moreover, the SBAS-InSAR processing results of Sentinel-1 data showed that the cumulative deformation of the Genie slope from March 2017 to November 2020 and the mean deformation rates were stable at approximately 0 mm and 0 mm/a, respectively, with no significant trends. Hence, all three InSAR techniques employed herein indicate that the Genie slope is not deforming at present.
Based on the results of three remote sensing analyses, field survey verification and borehole data information, the current slope structures and morphological characteris-tics were created during the early formation of the Genie slope. In contrast, at present, the Genie slope is not experiencing deformation under natural conditions.
The selection and design of railway routes in high-elevation mountainous and canyon regions often encounter situations similar to the Genie slope, where the interpretation of optical or LiDAR data acquired individually over the slope would indicate a geo-hazard risk, whereas the results of InSAR analysis would suggest that the slope is not experiencing active deformation under natural conditions. In this case, it is difficult to make a qualitative judgment on whether the slope exists deformation by only a single remote sensing technique. This research demonstrates that the method of analyzing and determining the deformation of slopes in alpine canyon areas from multiple factors, multiple indicators and multiple perspectives by using integrated remote sensing is not only feasible but also highly advantageous.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.L. and W.Y.; methodology, W.Y.; software, W.Y.; validation, H.L.; formal analysis, W.Y.; investigation, D.W.; resources, Z.X., X.D and P.L.; data curation, W.Y; writing—original draft preparation, W.Y.; writing—review and editing, W.L.; visualization, W.Y.; supervision, W.L.; project administration, W.L.; funding acquisition, W.L.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Key Research and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41941019), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2021YFC3000401), the Key Research and Development Program of Sichuan Province (Grant No. 2023YFS0435), the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection Independent Research Project (Grant No. SKLGP2022Z007), the China Power Construction Group Research Project (Grant No. DJ-ZDXM-2020-3), and the Yangtze River Joint Research Phase II Program (Grant No. 2022-LHYJ-02-0201).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to ESA for Sentinel-1 data, X.D for airborne LiDAR data, and D.W, Z.X for field survey results.
References
- Peng, J.; Ma, R.; Lu, Q.; Li, X.; Shao, T. Geological hazards effects of uplift of qinghai-tibet plateau. Advance in Earth Sciences 2004, 19, 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Shi, J.; Meng, W.; Du, Y.; Ma, C. Discussion on the Environmental and Engineering Geological Problems Along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and Its Adjacent Area. Geoscience 2017, 31, 877–889. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Cui, P.; Zhuang, J. Challenges to engineering geology of SichuanTibet railway. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 2020, 39, 2377–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Kong, F.; Yang, W.; Qiu, D.; Su, M.; Fu, K.; Ma, X. Main unfavorable geological conditions and engineering geological problems along SichuanTibet railway. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 2020, 39, 445–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Ge, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Lei, Y.; Zhou, L.; et al. Scientific challenges in disaster risk reduction for the Sichuan-Tibet Railway. ENGINEERING GEOLOGY 2022, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Wang, D.; LI, G.; Tao, W.; Shi, S. Design Concept and Main Principles of Tunnel on Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Tunnel Construction 2021, 41, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Cai, C. Challenges and Countermeasures for Construction Safety during the Sichuan-Tibet Railway Project. ENGINEERING 2019, 5, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Su, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, L. Insights into some large-scale landslides in southeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Key Laboratory of Mountain Hazards and Earth Surface Processes, Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, 610041, China;China-Pakistan Joint Research Cente 2023, 15, 1960–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Xu, Q.; Alonso-Rodriguez, A.; Subramanian, S.; Li, W.; Zheng, G.; Dong, X.; Huang, R. Successive landsliding and damming of the Jinsha River in eastern Tibet, China: prime investigation, early warning, and emergency response. LANDSLIDES 2019, 16, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, R. Study on the Creep-Sliding Mechanism of the Giant Xiongba Ancient Landslide Based on the SBAS-InSAR Method, Tibetan Plateau, China. REMOTE SENSING 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Han, X.; Zhai, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, F. Comprehensive analysis of a paleo-landslide damming event on the upper reach of the Jinsha River, SE Tibetan Plateau. BULLETIN OF ENGINEERING GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT 2022, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Peng, J. Monitoring and Stability Analysis of the Deformation in the Woda Landslide Area in Tibet, China by the DS-InSAR Method. REMOTE SENSING 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lu, Z. Remote Sensing of Landslides A Review. REMOTE SENSING 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Li, W.; Xu, Q.; Dong, X.; Dai, C.; Wang, D. Early Detection of Landslides in the Upstream and Downstream Areas of the Baige Landslide,the Jinsha River Based on Optical Remote Sensing and InSAR Technologies. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2019, 44, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.; Tsao, T.; Huang, C.; Lee, C.; Lee, Y. Using Remote Sensing Techniques to Identify the Landslide Hazard Prone Sections along the South Link Railway in Taiwan. Procedia Engineering 2016, 143, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Shen, W.; Liu, X.; Ren, S. Remote Sensing Interpretation of Large Landslides Along Sichuan-Tibet Railway Based on Object-oriented Classification Method. Geoscience 2017, 31, 930–942. [Google Scholar]
- Glenn, N.; Streutker, D.; Chadwick, D.; Thackray, G.; Dorsch, S. Analysis of LiDAR-derived topographic information for characterizing and differentiating landslide morphology and activity. GEOMORPHOLOGY 2006, 73, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaboyedoff, M.; Oppikofer, T.; Abellan, A.; Derron, M.H.; Loye, A.; Metzger, R.; Pedrazzini, A. Use of LIDAR in landslide investigations: a review. NATURAL HAZARDS 2012, 61, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicani, R.; Argentiero, I.; Manzari, P.; Spilotro, G.; Marzo, C.; Ermini, R.; Apollonio, C. UAV and Airborne LiDAR Data for Interpreting Kinematic Evolution of Landslide Movements: The Case Study of the Montescaglioso Landslide (Southern Italy). Geosciences 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X. Application of multi-source remote sensing technology in the identification of debris flow source within complex mountainous areas in southeast Tibet. Geological Bulletin of China 2021, 40, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Tie, Y.; Xu, W.; Liang, J.; Meng, M.; Li, F.; Zhao, C. Characteristics of Kazila mountain landslide and its mitigation measures on the Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology 2021, 48, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilecka, E.; Szwarkowski, D.; Stanisz, J.; Blockus, M. Analysis of a Landslide on a Railway Track Using Laser Scanning and FEM Numerical Modelling. APPLIED SCIENCES-BASEL 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromer, R.; Hutchinson, D.; Lato, M.; Gauthier, D.; Edwards, T. Identifying rock slope failure precursors using LiDAR for transportation corridor hazard management. ENGINEERING GEOLOGY 2015, 195, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Leijen, F.; Chang, L.; Wu, J.; Hanssen, R. Monitoring Deformation along Railway Systems Combining Multi-Temporal InSAR and LiDAR Data. Remote Sensing 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y. InSAR technique applied to the monitoring of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway. NATURAL HAZARDS AND EARTH SYSTEM SCIENCES 2019, 19, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Qi, T.; Zhao, Y.; Dijkstra, T.; Shi, W.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Su, X.; Zhao, F.; Ma, J.; et al. Deformation of the Zhangjiazhuang high-speed railway tunnel: an analysis of causal mechanisms using geomorphological surveys and D-InSAR monitoring. JOURNAL OF MOUNTAIN SCIENCE 2021, 18, 1920–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Li, J. Early Landslide Detection in the Lancangjiang Region Along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway Based on SBAS-InSAR Technology. Geoscience 2021, 35, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Z. Landslide Detection in the Linzhi-Ya'an Section along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway Based on InSAR and Hot Spot Analysis Methods. REMOTE SENSING 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Zhang, L.; Song, C.; Li, Z.; Zhuo, G.; Xu, Q. Quantitative Analysis of Sentinel-1 Imagery Geometric Distortion and Their Suitability Along Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University 2021, 46, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xiong, X.; Tie, Y. Research on Early Identification of Landslide in Deeply Incised Valley of Sichuan-Tibet Railway. Journal of Catastrophology 2021, 36, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 1989, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Bock, Y.; Fang, P. Integrated satellite interferometry: Tropospheric noise, GPS estimates and implications for interferometric synthetic aperture radar products. JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH-SOLID EARTH 1998, 103, 27051–27067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.; Li, F.; Madsen, S.; Rodriguez, E.; Goldstein, R. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry - Invited paper. PROCEEDINGS OF THE IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON GEOSCIENCE AND REMOTE SENSING 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-Gonzalez, M.; Devanthery, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A review. ISPRS JOURNAL OF PHOTOGRAMMETRY AND REMOTE SENSING 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liu, G.; Li, Z.; Ma, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Tang, J.; Li, G. Monitoring Highway Stability in Permafrost Regions with X-band Temporary Scatterers Stacking InSAR. SENSORS 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Zhao, B.; Dai, K.; Dong, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; et al. Remote sensing for landslide investigations: A progress report from China. ENGINEERING GEOLOGY 2023, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.; Price, E. Phase gradient approach to stacking interferograms. JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH-SOLID EARTH 1998, 103, 30183–30204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strozzi, T.; Wegmuller, U.; Tosi, L.; Bitelli, G.; Spreckels, V. Land subsidence monitoring with differential SAR interferometry. PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING AND REMOTE SENSING 2001, 67, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Geographical and geological conditions of the study area. a. location of the study area; b. geological overview of the study area; c. remote sensing image of the Genie slope.
Figure 1.
Geographical and geological conditions of the study area. a. location of the study area; b. geological overview of the study area; c. remote sensing image of the Genie slope.
Figure 2.
The coverage of the SAR images.
Figure 2.
The coverage of the SAR images.
Figure 3.
The technical flowchart adopted in this study.
Figure 3.
The technical flowchart adopted in this study.
Figure 4.
Interpretation results based on optical satellite images and airborne LiDAR data. (a) High-resolution optical satellite image interpretation; (b) LiDAR hillshade data interpretation; (c) partial large sample of an orthoimage at the trailing edge of the slope; (d) partial large sample of the hillshade at the trailing edge of the slope; (e) partial large sample of the hillshade at the front edge of the slope.
Figure 4.
Interpretation results based on optical satellite images and airborne LiDAR data. (a) High-resolution optical satellite image interpretation; (b) LiDAR hillshade data interpretation; (c) partial large sample of an orthoimage at the trailing edge of the slope; (d) partial large sample of the hillshade at the trailing edge of the slope; (e) partial large sample of the hillshade at the front edge of the slope.
Figure 5.
The geological profiles of the Genie slope. (a) the overall geological profile of the slope; (b) the geological profile at the top of the slope.
Figure 5.
The geological profiles of the Genie slope. (a) the overall geological profile of the slope; (b) the geological profile at the top of the slope.
Figure 6.
3D analysis of the DEM and hillshade data. (a) rock strata interpretation; (b) local conjugate structural surfaces in Zone II.
Figure 6.
3D analysis of the DEM and hillshade data. (a) rock strata interpretation; (b) local conjugate structural surfaces in Zone II.
Figure 7.
D-InSAR interferograms obtained from the ALOS-1 data. (a) the differential interferogram between 31 Jan. 2007 and 18 Jun. 2007; (b) the differential interferogram between18 Jun. 2007 and 3 Aug. 2007; (c) the differential interferogram between3 Aug. 2007 and 3 Nov. 2007; (d) the differential interferogram between 20 Sept. 2008 and 21 Dec. 2008.
Figure 7.
D-InSAR interferograms obtained from the ALOS-1 data. (a) the differential interferogram between 31 Jan. 2007 and 18 Jun. 2007; (b) the differential interferogram between18 Jun. 2007 and 3 Aug. 2007; (c) the differential interferogram between3 Aug. 2007 and 3 Nov. 2007; (d) the differential interferogram between 20 Sept. 2008 and 21 Dec. 2008.
Figure 8.
Stacking-InSAR interferograms obtained from the Sentinel-1A data. (a) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2017; (b) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2018; (c) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2019; (d) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2020.
Figure 8.
Stacking-InSAR interferograms obtained from the Sentinel-1A data. (a) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2017; (b) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2018; (c) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2019; (d) the differential interferogram from Mar. 2017 to Dec. 2020.
Figure 9.
Average deformation rate by SBAS-InSAR.
Figure 9.
Average deformation rate by SBAS-InSAR.
Figure 10.
Average deformation rates along the profiles.
Figure 10.
Average deformation rates along the profiles.
Figure 11.
Cumulative deformation curves at typical deformation points.
Figure 11.
Cumulative deformation curves at typical deformation points.
Figure 12.
Field verification photos. (a) panoramic photo of the middle and rear of the slope; (b) morphological characteristics of slope bedrock; (c). residual slope deposit overlay; (d) strongly weathered gravels; e. rock mass tension groove.
Figure 12.
Field verification photos. (a) panoramic photo of the middle and rear of the slope; (b) morphological characteristics of slope bedrock; (c). residual slope deposit overlay; (d) strongly weathered gravels; e. rock mass tension groove.
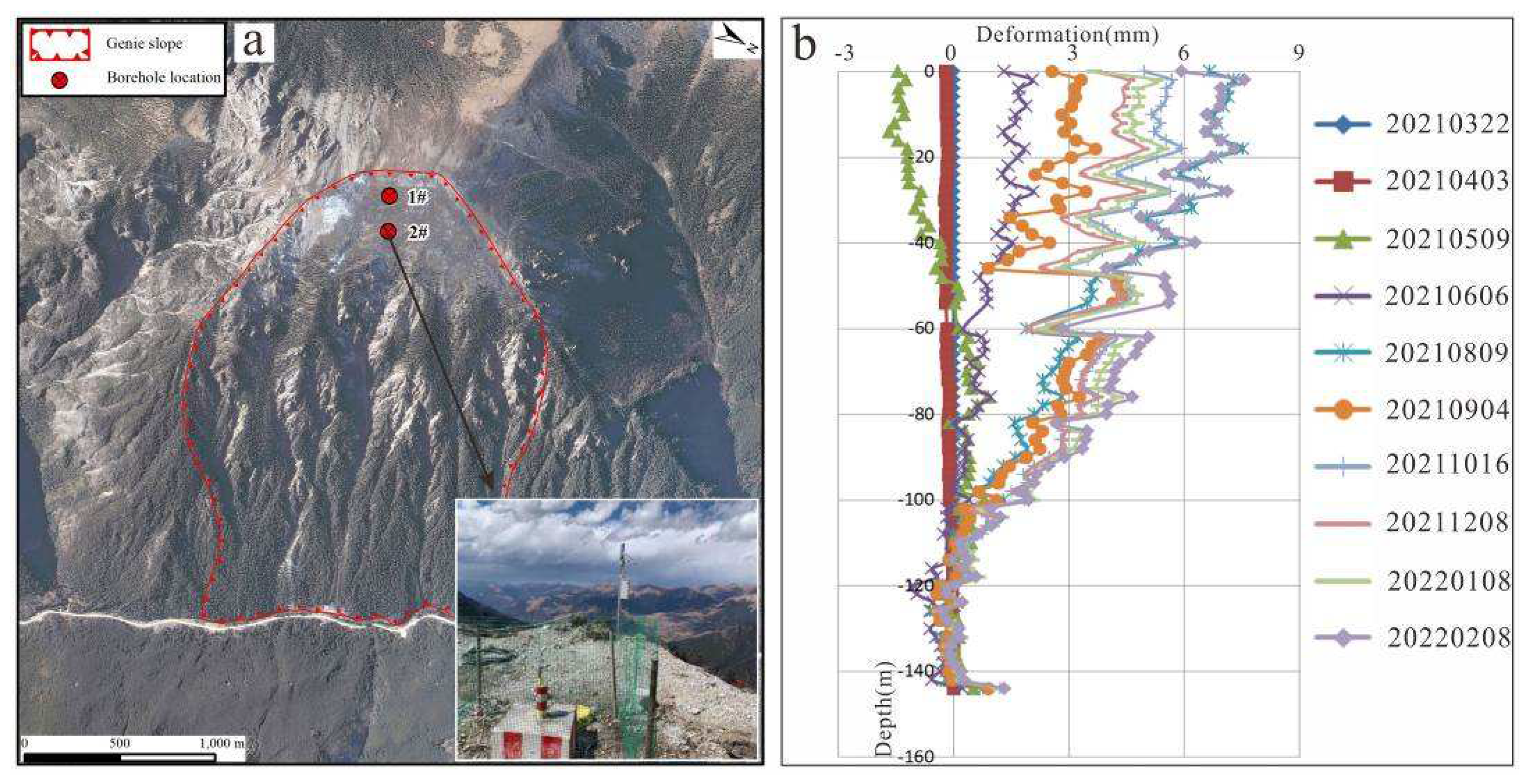
Figure 13.
Borehole information. (a) borehole location and monitoring device; (b) borehole displacement curve.
Figure 13.
Borehole information. (a) borehole location and monitoring device; (b) borehole displacement curve.
Figure 14.
Schematic diagram of the deformation mechanism of the Genie slope.
Figure 14.
Schematic diagram of the deformation mechanism of the Genie slope.
Figure 15.
Schematic diagram of multi-stage scarps mechanism.
Figure 15.
Schematic diagram of multi-stage scarps mechanism.
Table 1.
Parameters of the SAR image data.
Table 1.
Parameters of the SAR image data.
| Parameters |
SAR sensors |
| ALOS PALSAR-1 |
Sentinel-1A |
| Polarization mode |
HH |
VV |
| Spatial resolution / m |
10×10 |
5×20 |
| Incidence angle/ ° |
34.3 |
39.5 |
| Orbit |
Ascending |
Ascending |
| Band (Radar wavelength /cm) |
L (23.6) |
C (5.6) |
| Period |
Jul. 2007 - Dec. 2008 |
Mar. 2017 - Nov. 2020 |
| Number of images |
9 |
108 |
Table 2.
Typical deformation point parameters.
Table 2.
Typical deformation point parameters.
| parameters |
1-1' profile |
2-2' profile |
| point |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
G |
H |
I |
| Partition |
I |
II |
II |
II |
III |
II |
II |
II |
II |
| Average annual deformation rate (mm/yr) |
0.2 |
1.0 |
3.7 |
4.7 |
1.1 |
4.4 |
2.6 |
3.6 |
1.4 |
| Cumulative deformation (mm) |
3.6 |
-0.9 |
1.7 |
2.1 |
5.3 |
-3.1 |
-0.9 |
1.8 |
2.2 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).