Submitted:
21 September 2023
Posted:
25 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2.1. Overview of Plastics
2.2. Plastics in High Demand of the World Today
2.4.2. Factors Affecting Petro-Polymer (Synthetic Plastic) Biodegradation
| Plastic Polymer | Density (g/L) | Crystallinity | Life Span (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 1.35 | 0-50 | 450 |
| LDPE | 0.91-0.93 | 50 | 10-600 |
| HDPE | 0.94-0.97 | 70 | >600 |
| PS | 1.03-1.09 | 0 | 50-80 |
| PP | 0.90-0.91 | 50 | 10-600 |
| PVC | 1.35-1.45 | 0 | 50-150 |
2.5. Plastic Waste; the Global Environmental Issue

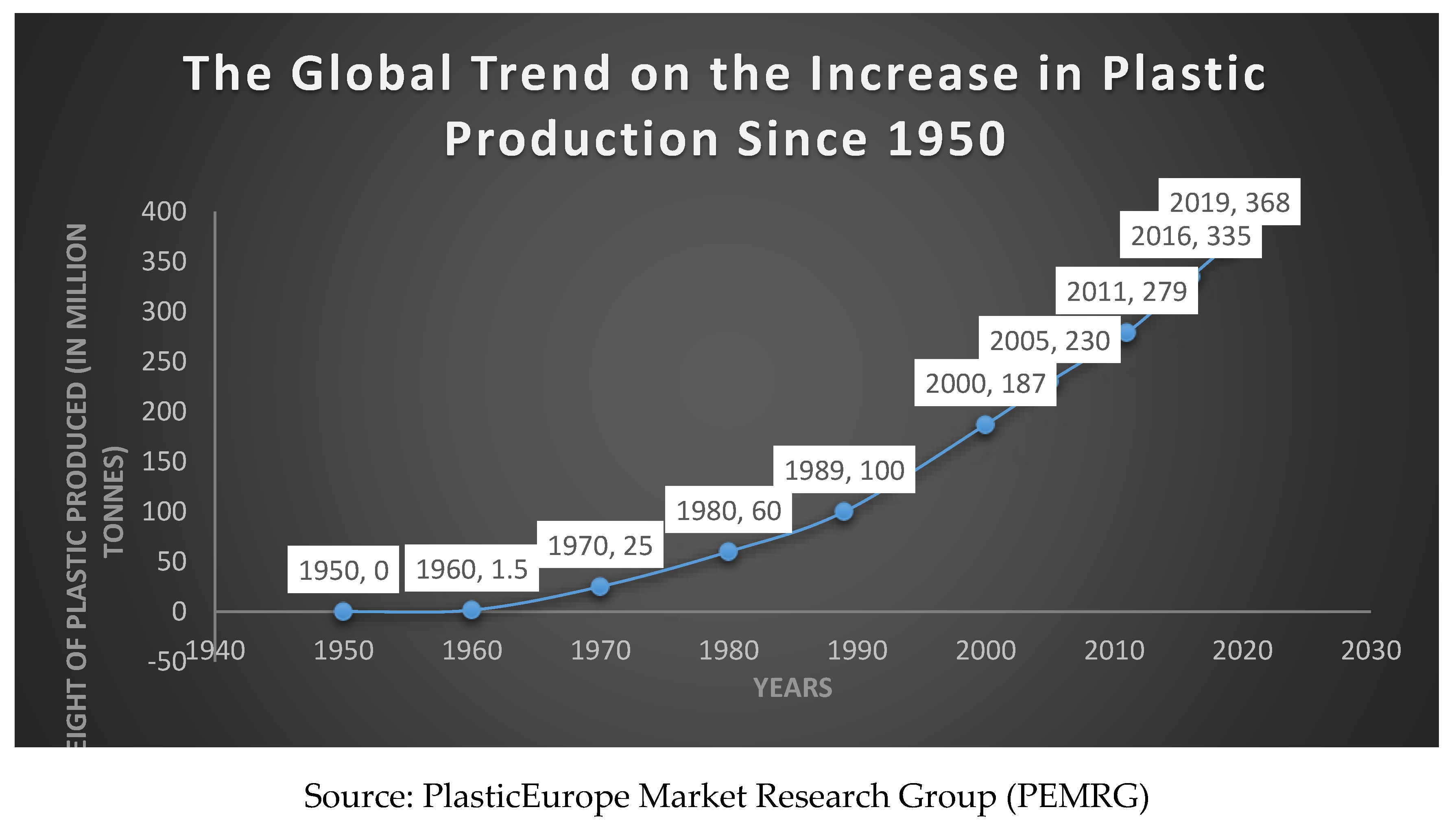
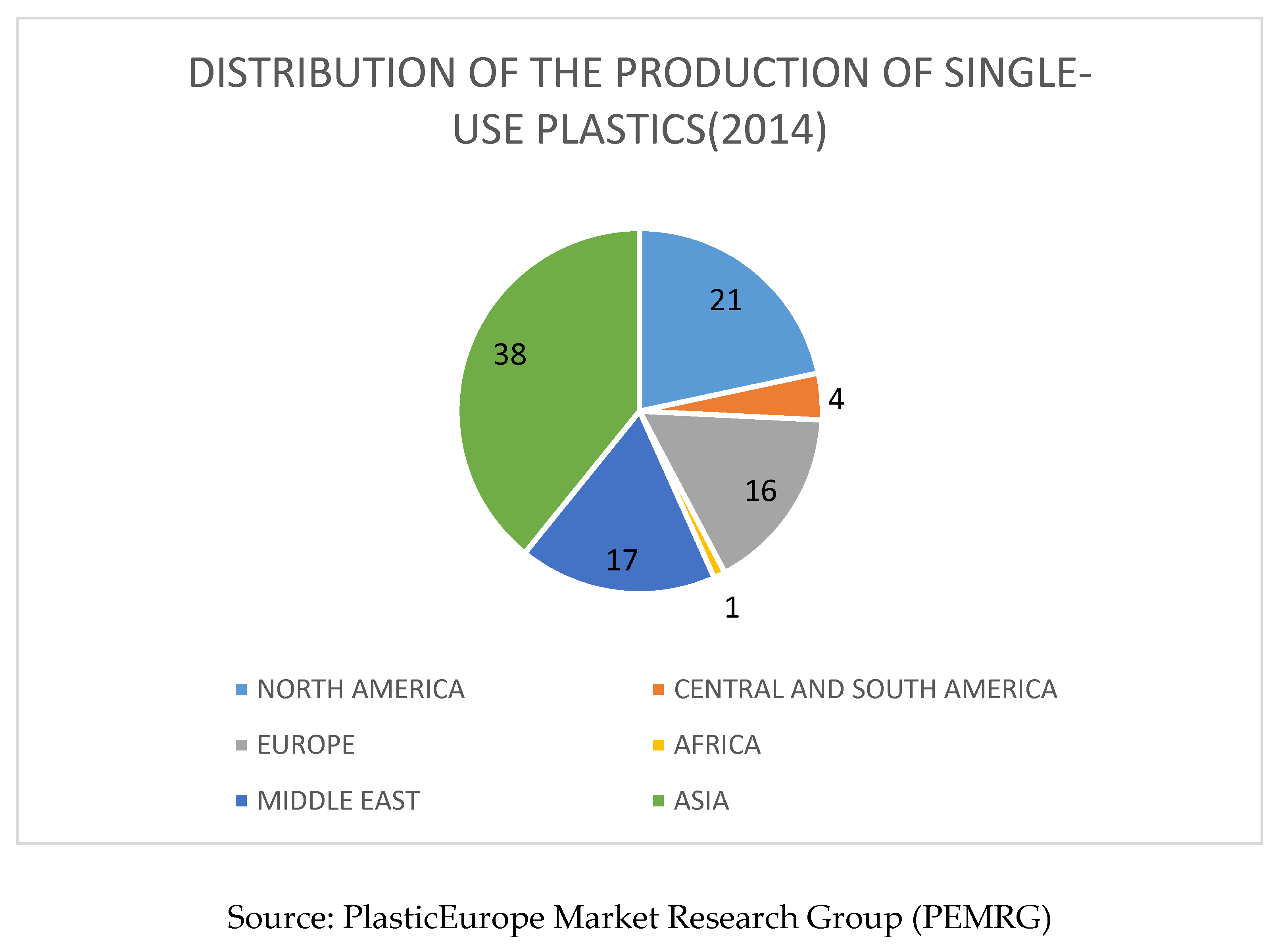
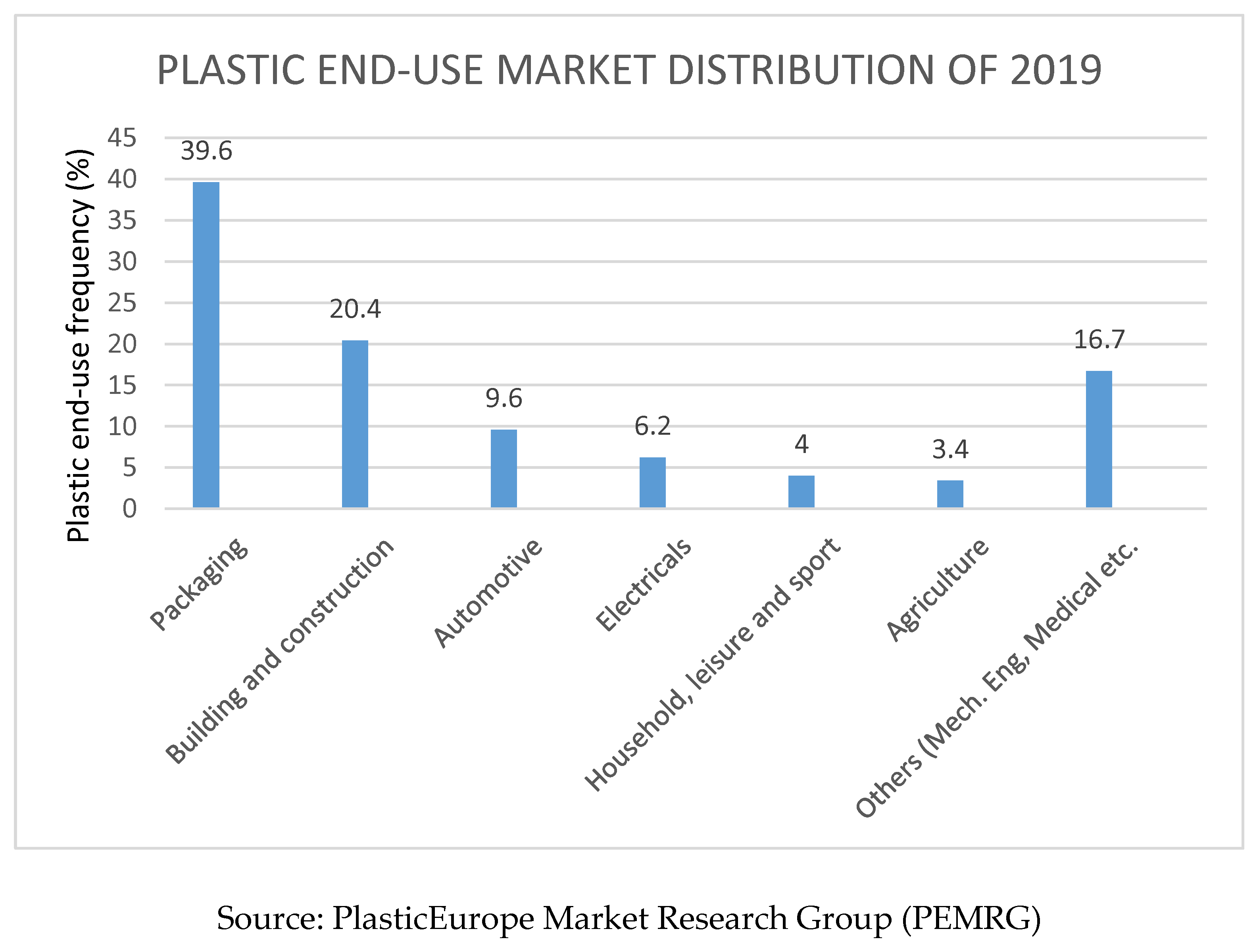
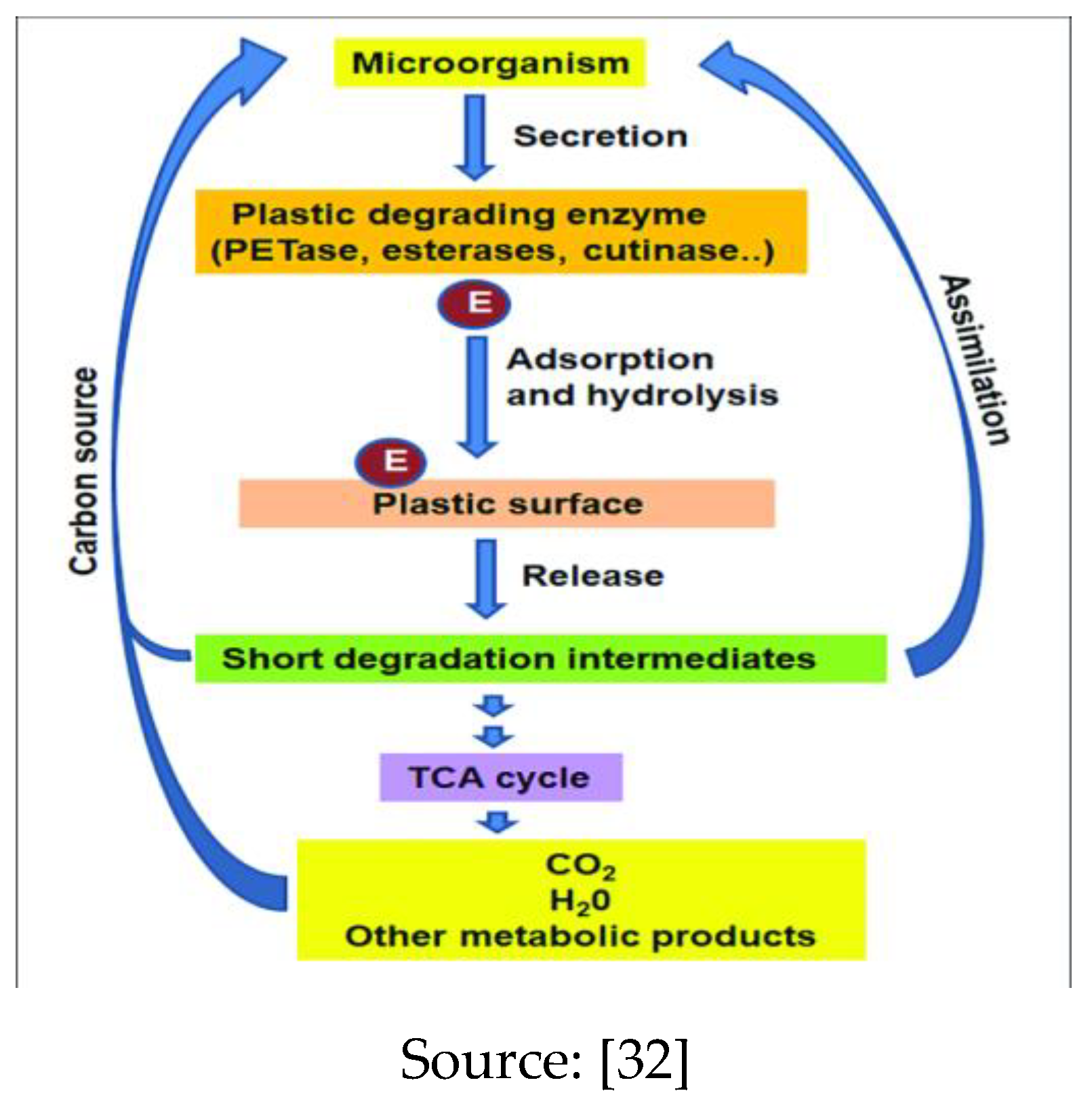
2.6. Mechanism of Biological Degradation of Polyethylene
2.7.1. Pictures of the Types of Plastics Materials

2.8. Factors, Methods and Approaches for Enhancing the Bio-Degradation of Conventional Plastics (Non-Biodegradable Plastics)
2.8.2. Modifications in Growth Medium
2.8.3. Use of Engineered Strains
| Bacteria | Type of Plastic | Source of Material | Degradation Efficiency (%) | Days / Month | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus | Polyethylene | Dumpsite soil | 7.2-7.4 | [42] | |
| Pseudomonas putida | Milk cover | Garden soil | 75.3 | 1 month | [30] |
| Streptomyces sp. | LDPE | Garden soil | 46.7 | [43] | |
| Pseudomonas sp. | Natural and synthetic polyethylene | Sewage sliding Dumping site |
46.2 29.1 |
[44] | |
| Pseudomonas sp. | Natural and synthetic polymer | Household garbage Dumping site |
31.4 16.3 |
[44] | |
| Pseudomonas sp. | Polyethylene | Textile effluent Drainage site |
39.7 19.6 |
[44] | |
| Pseudomonas sp. | Polyethylene | Mangrove soil | 20.54 | [45] | |
| Bacillus cereus | LDPE | Municipal composite yard | 17.036 | [46] | |
| Staphylococcal sp. | LDPE | Not stated | 22 | [47] | |
| Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 | LDPE | Municipal solid waste dumping ground soil | 5 ± 1 | 45 days | [35] |
| Bacillus subtilis | PS | Soil | 58.825 | 4 months | [1] |
| Bacillus subtilis | PET | Soil | 74.59 | 4 months | [1] |
| Bacillus amylolyticus | Polyethylene | Municipal waste water | 31 | 1 month | [37] |
| Microorganism | Plastic substrate | Method | Mutations | Outcome | References |
| Cutinase modification | |||||
| Thermobifida alba AHK119 | PBSA, PBS, PCL, PLA, and PET | Introducing proline residues | A68V/T253P | Increase of Tm value from 74 to 79°C compared with the A68V variant | [48] |
| Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190 | PET | Introducing proline residues | S226P | Increase of Tm value by 3.7°C with higher compared with the wild-type enzyme | [49] |
| Fusarium solani pis | PET and PA | Enlarging the opening size of active site clef | L182A | Fivefold increase in enzyme activity compared with the wild-type enzyme | [50] |
| Thermobifida fusca | PET | Increasing both the opening size and hydrophobicity of active site | Q132A/T101A | Higher hydrolysis efficiency than the wild-type enzyme Increased |
[51] |
| PETase modification | |||||
| Ideonella sakaiensis | PET | Forming hydrogen bond | S121E/D186H | Increase of Tm value by 7.21°C and improved enzyme activity at elevated temperature relative to wild-type PETase | [52] |
| Ideonella sakaiensis | PET | Increasing the hydrophobicity of active site | L88F and I179F | 2.1 and 2.5 times increased improvement in catalytic efficiency compared with the wild-type enzyme | [53] |
| Esterase | |||||
| Clostridium botulinum | PET | Modulating the surface hydrophobicity | Truncation of 17 residues at the N-terminus | Enhanced hydrolysis efficiency relative to the wild-type enzyme Up |
[54] |
| Hydrolase | |||||
| Pseudomonas aestusnigr | PET | Enlarging the opening size of active site cleft | Y250S | Improved PET degradation activity as well as the capability of hydrolyzing crystalline PET from commercial bottle | [55,56] |
Conclusions
References
- Asmita K, Shubhamsingh T, Tejashree S, Road DW, Road DW. Isolation of Plastic Degrading Micro-organisms from Soil Samples Collected at Various Locations in Mumbai, India. Adu-boahen, K, Atampugre, G, Antwi, K B, & Osman, A (2014) Waste management practices in Ghana: challenges and prospect, Jukwa Central Region International Journal of Development and Sustainability, 3(3), 530–546. 2015;4(3):77–85.
- Plastic Atlas. Facts and figures about the world of synthetic polymers. Lili Fuhr, Heinrich Böll Foundation Matthew Franklin BFFP, editor. Heinrich Böll Foundation, Berlin, Germany and Break Free from Plastic; 2019. pp. 1-52.
- Tsakona M, Baker E, Rucevska L, Maes T, Raubenheimer K, Langeard R, et al. Drowning in Plastics: Marine Litter and Plastic Waste Vital Graphics Youth brain drain and transnational migration View project BEAST BONUS project View project [Internet]. 2021. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355467650.
- Tsakona M. Plastic value chain is complex. 2018.
- Malthus T. An Essay on the Principle of Population [Internet]. 1998. Available from: http://www.esp.org.
- Ebenezer OS, Osumanu IK, Yahaya AK. An analysis of plastic waste collection and wealth linkages in Ghana. An Analysis of the Plastic Waste Collection and Wealth Linkages in Ghana [Internet]. Article in International Journal of Current Research. 2013. Available from: http://www.journalcra.com.
- Gomiero T. Soil degradation, land scarcity and food security: Reviewing a complex challenge. Vol. 8, Sustainability (Switzerland). MDPI; 2016. [CrossRef]
- Vijaya C, Reddy R. Impact of soil composting using municipal solid waste on biodegradation of plastics. Indian J Biotechnol. 2008 Apr;7(April):235–9.
- Ohwo O. Spatial Analysis of the Quality of Borehole Water Supply in Warri-Effurun Metropolis, Delta State, Nigeria. Ikogho. A Multi-disciplinary Journal. 2011; volume 9(103):91–112.
- Issahaku I, Nyame FK, Brimah AK. Waste Management Strategies in an Urban Setting Example from the Tamale Metropolis, Ghana. Journal of Waste Management. 2014; 2014:1–7. [CrossRef]
- Adu-boahen K, Atampugre G, Antwi KB, Osman A. Waste management practices in Ghana: challenges and prospect, Jukwa Central Region. International Journal of Development and Sustainability. 2014;3(3):530–46.
- Kanhai LDK, Johansson C, Frias JPGL, Gardfeldt K, Thompson RC, O’Connor I. Deep Sea sediments of the Arctic Central Basin: A potential sink for microplastics. Deep Sea Res 1 Oceanogr Res Pap. 2019 Mar 1; 145:137–42. [CrossRef]
- Kanhai G, Agyei-mensah S, Mudu P. Population awareness and attitudes toward waste- related health risks in Accra, Ghana. Int J Environ Health Res. 2019;00(00):1–17. [CrossRef]
- Asase, M., Yanful, E.K., Mensah, M., Stanford, J. & Amponsah S. “Comparison of municipal solid waste management sys- tems in Canada and Ghana: a case study of the cities of London, Ontario, and Kumasi, Ghana,” Waste Management. 2009; vol.29(10):2779–2786.
- Marqu M, Domingo JL. Concentrations of PCDD / Fs in Human Blood: A Review of Data from the Current Decade. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(3566):2–18.
- Hopewell J, Dvorak R, Kosior E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Vol. 364, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. Royal Society; 2009. p. 2115–26.
- Central Pollution Control Board. ANNUAL REPORT 2013-14. 2014.
- Janatunaim RZ, Fibriani A. Construction and Cloning of Plastic-degrading Recombinant Enzymes (MHETase). Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2020 Mar 11;14(3):229–34. [CrossRef]
- Nicholson J and, Leighton G. Plastics come of age. Haper’s Magazine. 1942;306.
- Chalmin P. The history of plastics: from the capitol to the the history of plastics. The journal of field actions. 2019;(19):6–11.
- Trulli E, Ferronato N, Torretta V, Piscitelli M, Masi S, Mancini I. Sustainable mechanical biological treatment of solid waste in urbanized areas with low recycling rates. Waste Management. 2018; 71:556–64. [CrossRef]
- Raziyafathima M, Praseetha PK, S RIR. Microbial Degradation of Plastic Waste: A Review. Journal of Pharmaceutical, Chemical and Biological Sciences. 2016;4(August):231–42.
- PlasticEurope. Plastics – the Facts 2020, An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. 2020.
- PlasticEurope. Plastic - the Facts 2019. An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. 2019;
- PlasticEurope. Plastics – the Facts 2016. 2016;
- PlasticEurope. An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. 2018.
- Lau, Y.W.Winnie, Shiran, Yonathan, Balley, M.Richard, Cook, Ed, Stuchey, R. Martin, Koskella, Julia, Velis, A. Costas, Godfrey, Linda, Boucher, Julien, Murphy, B. Margaret, Thompson, C. Richard, Jankowska, Emilia, Castillo, Castillo Arturo, Pilditch, D. T EJ. Evaluating Scenarios towards Zero Plastic Pollution. Human Relations. 2020;3(1):1–8.
- Mohanan N, Montazer Z, Sharma PK, Levin DB, Levin DB. Microbial and Enzymatic Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. A Review. Front Microbiol. 2020; 11:1–22. [CrossRef]
- Grover A, Gupta A, Chandra S, Kumari A, Khurana SMP. Polythene and environment. Int J Environ Sci. 2015;5(6):1091–105.
- Saminathan P, Sripriya A, Nalini K, Sivakumar T, Thangapandian V. Biodegradation of Plastics by Pseudomonas putida isolated from Garden Soil Samples. Journal of Advanced Botany and Zoology. 2014;1(3):3–6.
- Raziyafathima M, Praseetha P, Rimal Isaac RS, Author C. Impact Factor (GIF): 0.615 Impact Factor (SJ IF): 2.092 Microbial Degradation of Plastic Waste: A Review. J Pharm Chem Biol Sci. 2016;4(2):231–42.
- Mohanan N, Montazer Z, Sharma PK, Levin DB. Microbial and Enzymatic Degradation of Synthetic Plastics. Vol. 11, Frontiers in Microbiology. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2020. [CrossRef]
- Sanin SL, Sanin FD, Bryers JD. Effect of star v ation on the adhesi v e properties of xenobiotic degrading bacteria. 2003;38:909–14.
- Singh B, Sharma N. Mechanistic implications of plastic degradation. Polym Degrad Stab. 2007;93(2008):1–25. [CrossRef]
- Tribedi P, Sil AK. Low-density polyethylene degradation by Pseudomonas sp AKS2 biofilm. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2013;20(6):4146–53. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki T, Ichihara Y, Yamada M, Tonomura K. Some Characteristics of Pseudomonas 0-3 which Utilizes. Agr Biol Chem. 1973;37(4):747–56.
- Singh KK, Gautam K, Vaishya RC. Plastic-Degrading Bacteria From Municipal Wastewater. International Journal of Scientific Progress and Research. 2016;21(3):147–54.
- Sekiguchi1 T, Sato T, Enoki2 M, Kanehiro H, Uemats K, Kato C. Isolation and characterization of biodegradable plastic degrading bacteria from deep-sea environments. Jamstec Rep Res Dev. 2010;11(September):1–7.
- Urbanek AK, Rymowicz W, Miro AM. Degradation of plastics and plastic-degrading bacteria in cold marine habitats. A mini-review. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018;102(2018):7669–78. [CrossRef]
- Austin HP, Allen MD, Donohoe BS, Rorrer NA, Kearns FL, Silveira RL, et al. Characterization and engineering of a plastic-degrading aromatic polyesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 8;115(19):E4350–7. [CrossRef]
- Jayasekara SK, Joni HD, Jayantha B, Dissanayake L, Mandrell C, Sinharage MMS, et al. Trends in in-silico guided engineering of efficient polyethylene terephthalate (PET) hydrolyzing enzymes to enable bio-recycling and upcycling of PET. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Jun; [CrossRef]
- Sowmya H, Ramalingappa, Krishnappa’ M, Thippeswamy. Biodegradation of Polyethylene by Bacillus cereus. Advances Polymer Science Technoogy international journal. 2014;4(2):28–32.
- Deepika S JMR. Biodegradation of low density polyethylene by micro- organisms from garbage soil. journal of experimental biology and africulture science. 2015;3(1):15–21.
- Nanda S, Snigdha Smiti S, Abraham. J. Studies on the biodegradation of natural and synthetic polyethylene by Pseudomonas sp. Journal of Appl ied Science and Environmental Management. 2010;14(2):57–60.
- Kathiresan K. Polythene and plastic degrading microbes from mangrove soil. International Journal of Tropical Biology and Conservation. 2003; 51:629–40.
- Suresh B, Maruthamuthu S, Palanisamy S, Ragunathan R, Pandiyaraj KN. Investigation on biodegradability of polyethylene by Bacillus cereus strain Ma- Su isolated from compost soil. 2011; International Research Journal of Microbiology. 2011; 2:292-302.
- Chatterjee S, Roy B, Roy D, Banerjee R. Enzyme-mediated biodegradation of heat treated commer95cial polyethylene by Staphylococcal species. Polym Degrad Stab. 2010; 95:195–200.
- Thumarat U, Kawabata T, Nakajima M, Nakajima H, Sugiyama A, Yazaki K, et al. Comparison of genetic structures and biochemical properties of tandem cutinase-type polyesterases from Thermobifida alba AHK119. J Biosci Bioeng. 2015 Nov 1;120(5):491–7. [CrossRef]
- Kawai F, Kawabata T, Oda M. Current knowledge on enzymatic PET degradation and its possible application to waste stream management and other fields. Vol. 103, Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. Springer Verlag; 2019. p. 4253–68. [CrossRef]
- Araújo SJ, Cela C, Llimargas M. Tramtrack regulates different morphogenetic events during Drosophila tracheal development. Development. 2007 Oct;134(20):3665–76.
- Silva R V., De Brito J, Saikia N. Influence of curing conditions on the durability-related performance of concrete made with selected plastic waste aggregates. Cem Concr Compos. 2013 Jan;35(1):23–31. [CrossRef]
- Son HF, Cho IJ, Joo S, Seo H, Sagong HY, Choi SY, et al. Rational Protein Engineering of Thermo-Stable PETase from Ideonella sakaiensis for Highly Efficient PET Degradation. ACS Catal. 2019 Apr 5;9(4):3519–26. [CrossRef]
- Ma Y, Yao M, Li B, Ding M, He B, Chen S, et al. Enhanced Poly (ethylene terephthalate) Hydrolase Activity by Protein Engineering. Engineering. 2018 Dec 1;4(6):888–93. [CrossRef]
- Biundo A, Ribitsch D, Guebitz GM. Surface engineering of polyester-degrading enzymes to improve efficiency and tune specificity. Vol. 102, Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. Springer Verlag; 2018. p. 3551–9. [CrossRef]
- Pasula RR, Lim S, Ghadessy FJ, Sana B. The influences of substrates’ physical properties on enzymatic PET hydrolysis: Implications for PET hydrolase engineering. Engineering Biology. 2022 Mar;6(1):17–22. [CrossRef]
- Bollinger A, Thies S, Knieps-Grünhagen E, Gertzen C, Kobus S, Höppner A, et al. A Novel Polyester Hydrolase from the Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas aestusnigri – Structural and Functional Insights. Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 13;11. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





