Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
22 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
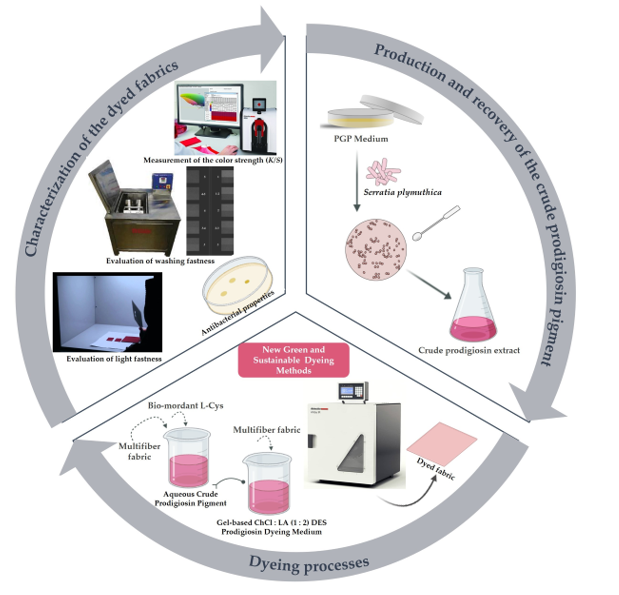
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of the color strength and equalization of the dyed fabrics
2.1.1. The effect of temperature
2.1.2. The effect of the dyeing aids addition
2.1.2.1. The addition of salts
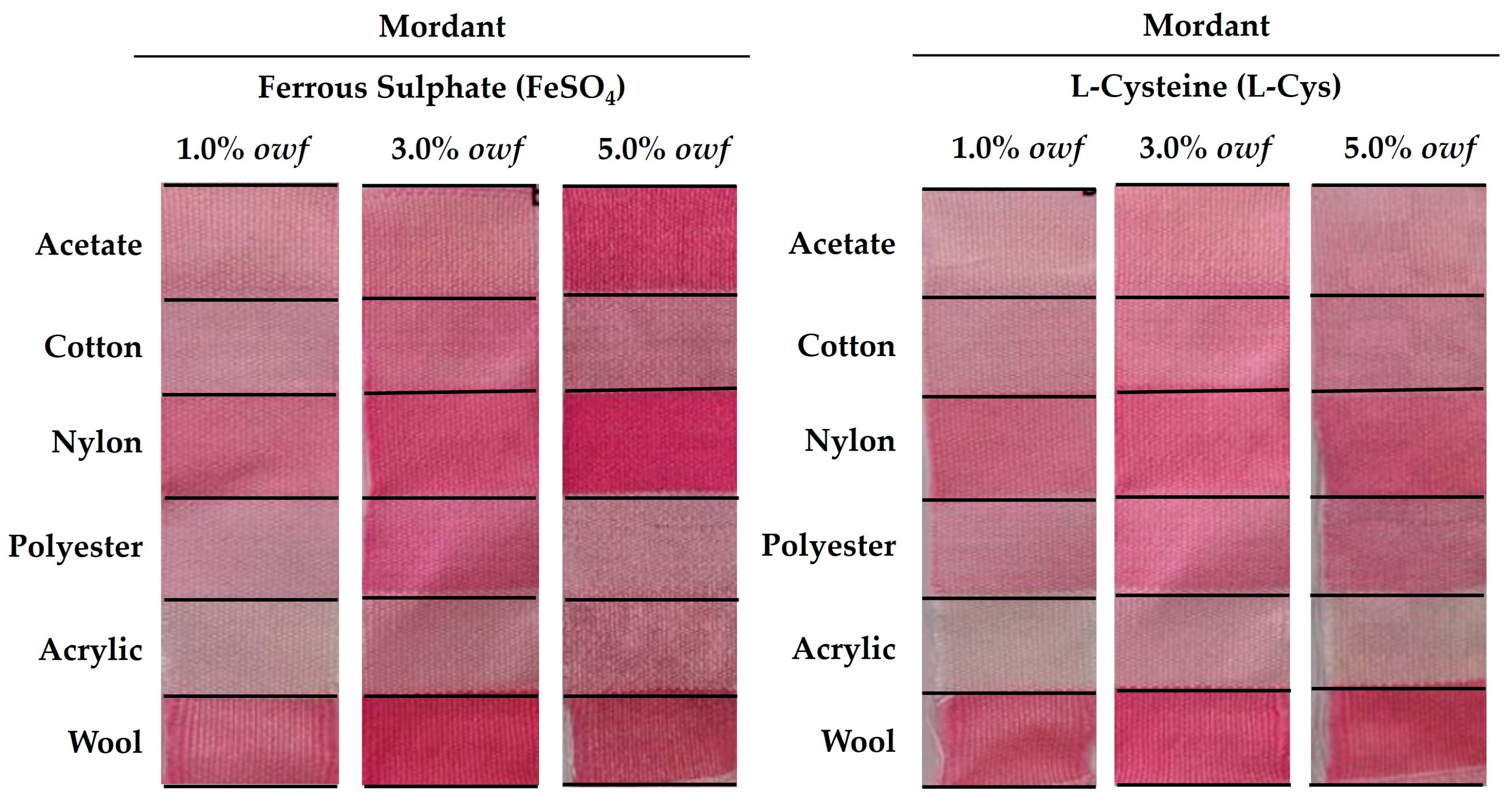
2.1.2.2. The addition of mordants
2.1.3. The effect of the use of gel-based deep eutectic solvents (DES) as a prodigiosin dyeing medium
2.2. Evaluation of fastness properties of dyed fabrics
2.2.1. Assessement of the washing fastness properties
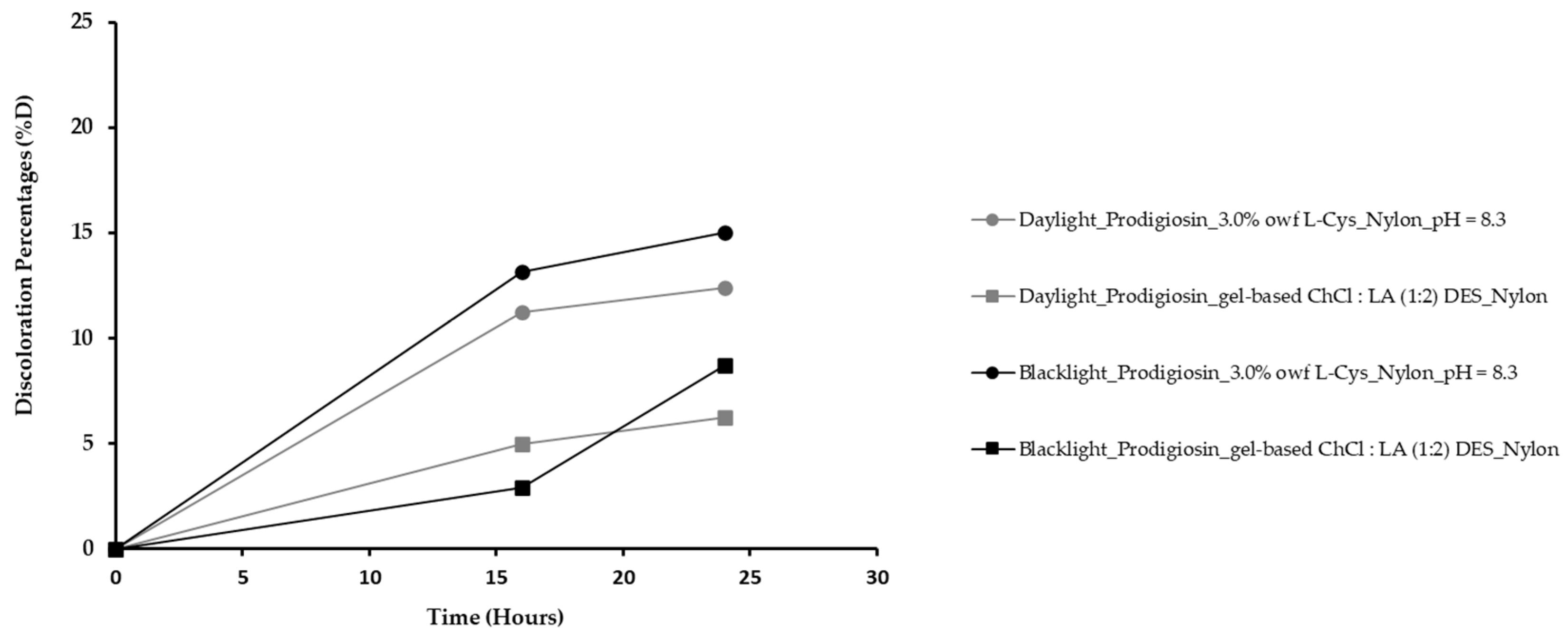
2.2.2. Assessement of the light fastness properties
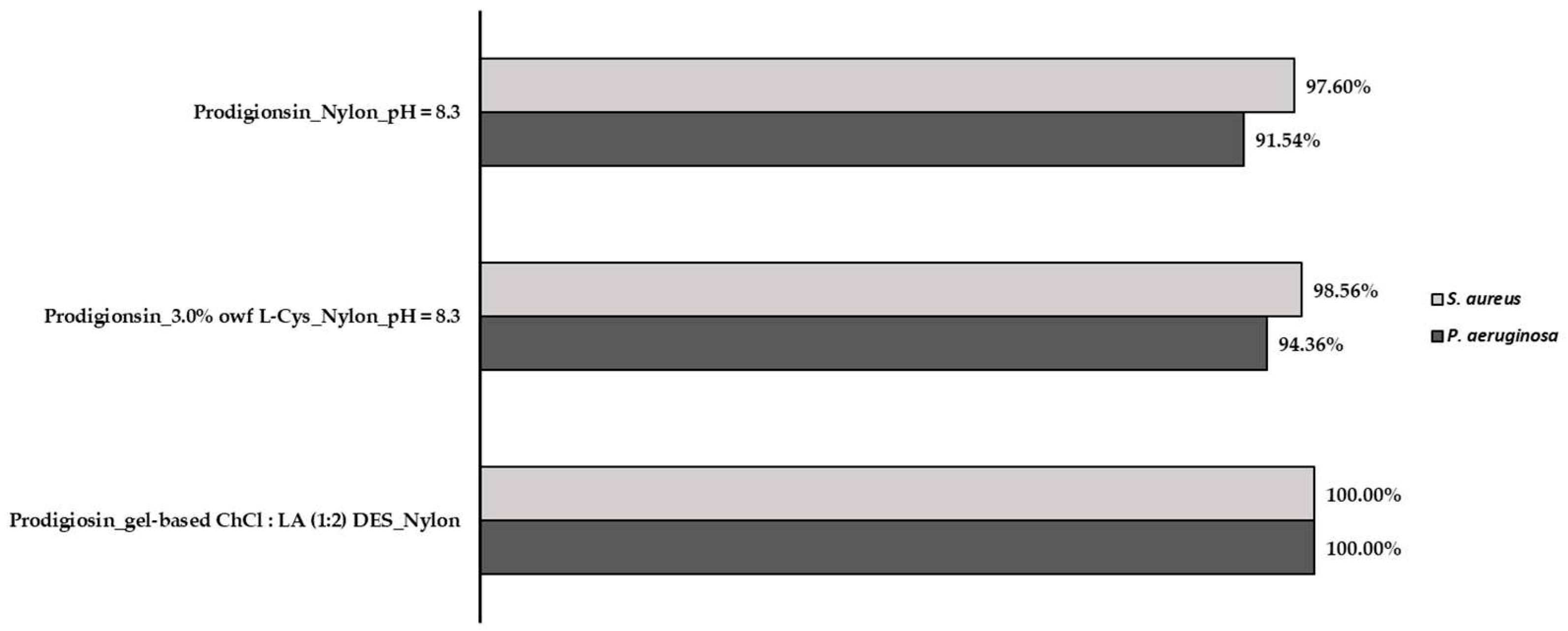
2.3. Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of dyed fabrics
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Production and recovery of prodigiosin pigment
4.3. Preparation of the crude gel prodigiosin pigment solution and dyeing process
4.3.1. Optimization of dyeing conditions
4.4. Characterization of the dyed fabrics
4.4.1. Color strength measurements of dyed fabrics
4.4.2. Evaluation of fastness properties of dyed fabrics
4.4.3. Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of dyed fabrics
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haji, A.; Naebe, M. Cleaner Dyeing of Textiles Using Plasma Treatment and Natural Dyes: A Review. J Clean Prod 2020, 265, 121866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramar, A.; Kostic, M.M. Bacterial Secondary Metabolites as Biopigments for Textile Dyeing. Textiles 2022, 2, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, L.; Sarker, S.K.; Khan, M.S. Evaluation of Present and Future Wastewater Impacts of Textile Dyeing Industries in Bangladesh. Environ Dev 2018, 26, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, R.A.; El Sikaily, A.; El-Sersy, N.A.; Ghozlan, H.A.; Sabry, S.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Textile Fabrics Dyed with Prodigiosin Pigment Extracted from Marine Serratia Rubidaea RAM_Alex Bacteria. The Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Research 2021, 47, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.M. dos S.; Fiaschitello, T.R.; Queiroz, R.S. de; Freeman, H.S.; Costa, S.A. da; Leo, P.; Montemor, A.F.; Costa, S.M. da Natural Dye from Croton Urucurana Baill. Bark: Extraction, Physicochemical Characterization, Textile Dyeing and Color Fastness Properties. Dyes and Pigments 2020, 173, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amutha, K.; Grace Annapoorani, S.; Sudhapriya, N. Dyeing of Textiles with Natural Dyes Extracted from Terminalia Arjuna and Thespesia Populnea Fruits. Ind Crops Prod 2020, 148, 112303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Z. A Novel and Eco-Friendly Approach for Dyeing Polyester Fabrics by Liquid Disperse Dyes Treated with Deep Eutectic Solvent. Coloration Technology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, M.; Wang, P.; Yu, Y. An Innovative, Low-Cost and Environment-Friendly Approach by Using a Deep Eutectic Solvent as the Water Substitute to Minimize Waste in the Textile Industry and for Better Clothing Performance. Green Chemistry 2022, 24, 5904–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruldass, C.A.; Aziz, A.; Venil, C.K.; Khasim, A.R.; Ahmad, W.A. Utilization of Agro-Industrial Waste for the Production of Yellowish-Orange Pigment from Chryseobacterium Artocarpi CECT 8497. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 2016, 113, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, R.; Kaur, S.; Panesar, P.S. Production of Microbial Pigments Utilizing Agro-Industrial Waste: A Review. Curr Opin Food Sci 2015, 1, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venil, C.K.; Devi, P.R.; Ahmad, W.A. Agro-Industrial Waste as Substrates for the Production of Bacterial Pigment. In Valorisation of Agro-industrial Residues – Volume I: Biological Approaches ; Springer, Cham, 2020; pp. 149–162.
- Amorim, L.F.A.; Fangueiro, R.; Gouveia, I.C. Characterization of Bioactive Colored Materials Produced from Bacterial Cellulose and Bacterial Pigments. Materials 2022, 15, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, L.F.A.; Mouro, C.; Riool, M.; Gouveia, I.C. Antimicrobial Food Packaging Based on Prodigiosin-Incorporated Double-Layered Bacterial Cellulose and Chitosan Composites. Polymers (Basel) 2022, 14, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arivizhivendhan, K. V.; Mahesh, M.; Boopathy, R.; Swarnalatha, S.; Regina Mary, R.; Sekaran, G. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Bioactive Prodigiosin Produces from Serratia Marcescens Using Agricultural Waste as a Substrate. J Food Sci Technol 2018, 55, 2661–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagwat, A.; Padalia, U. Optimization of Prodigiosin Biosynthesis by Serratia Marcescens Using Unconventional Bioresources. Journal of Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkenawy, N.M.; Yassin, A.S.; Elhifnawy, H.N.; Amin, M.A. Optimization of Prodigiosin Production by Serratia Marcescens Using Crude Glycerol and Enhancing Production Using Gamma Radiation. Biotechnology Reports 2017, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazic, J.; Skaro Bogojevic, S.; Vojnovic, S.; Aleksic, I.; Milivojevic, D.; Kretzschmar, M.; Gulder, T.; Petkovic, M.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Synthesis, Anticancer Potential and Comprehensive Toxicity Studies of Novel Brominated Derivatives of Bacterial Biopigment Prodigiosin from Serratia Marcescens ATCC 27117. Molecules 2022, 27, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.L.T.; Nguyen, T.C.; Do, T.T.; Vu, T.L.; Nguyen, T.T.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, T.H.T.; Le, T.H.; Trinh, D.K.; Nguyen, T.A.T. Study on the Anticancer Activity of Prodigiosin from Variants of Serratia Marcescens QBN VTCC 910026. Biomed Res Int 2022, 2022, 4053074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picha, P.; Kale, D.; Dave, I.; Pardeshi, S. Comparative Studies on Prodigiosin Production by Serratia Marcescens Using Various Crude Fatty Acid Sources-Its Characterization and Applications. Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci 2015, 254–267. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Gong, J.; Fu, R.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Cheng, X. Dyeing and Antibacterial Properties of Cotton Dyed with Prodigiosins Nanomicelles Produced by Microbial Fermentation. Dyes and Pigments 2017, 138, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venil, C.K.; Dufossé, L.; Velmurugan, P.; Malathi, M.; Lakshmanaperumalsamy, P. Extraction and Application of Pigment from Serratia Marcescens SB08, an Insect Enteric Gut Bacterium, for Textile Dyeing. Textiles 2021, 1, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Shen, Z.; Fan, B.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Peng, F.; Zhao, J.; Xue, B. Structure of Prodigiosin from Serratia Marcescens NJZT-1 and Its Cytotoxicity on TSC2-Null Cells. Food Science and Technology 2020, 41, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alihosseini, F.; Ju, K.S.; Lango, J.; Hammock, B.D.; Sun, G. Antibacterial Colorants: Characterization of Prodiginines and Their Applications on Textile Materials. Biotechnol Prog 2008, 24, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramar, A.; Ilic-Tomic, T.; Petkovic, M.; Radulović, N.; Kostic, M.; Jocic, D.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Crude Bacterial Extracts of Two New Streptomyces Sp. Isolates as Bio-Colorants for Textile Dyeing. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 2014, 30, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhu, C.; Xu, W.; Park, Y.; Zhou, H. Mutant Breeding of Serratia Marcescens Strain for Enhancing Prodigiosin Production and Application to Textiles. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 2013, 43, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, J.; Bhathena-Langdana, Z.; Adivarekar, R. V.; Nerurkar, M. Production, Partial Characterization, and Use of a Red Biochrome Produced by Serratia Sakuensis Subsp. Nov Strain KRED for Dyeing Natural Fibers. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2012, 166, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namazkar, S.; Garg, R.; Ahmad, W.Z.; Nordin, N. Production and Characterization of Crude and Encapsulated Prodigiosin Pigment. International Journal of Chemical Sciences and Applications 2013, 4, 116–129. [Google Scholar]
- Burkinshaw, S.M.; Kumar, N. The Mordant Dyeing of Wool Using Tannic Acid and FeSO4, Part 1: Initial Findings. Dyes and Pigments 2009, 80, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongkholrattanasit, R.; Kryštůfek, J.; Wiener, J.; Viková, M. UV Protection Properties of Silk Fabric Dyed with Eucalyptus Leaf Extract. The Journal of The Textile Institute 2011, 102, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G. Effects of Different Mordants on Silk Fabric Dyed with Onion Outer Skin Extracts. Journal of Textiles 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegarra, J.; Puente, P.; Valldeperas, J. The Dyeing of Textile Materials: The Scientific Bases and the Techniques of Application Available online:. Available online: https://books.google.pt/books/about/The_Dyeing_of_Textile_Materials.html?id=7rg6mgEACAAJ&redir_esc=y (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Cai, C.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Tan, Z. Deep Eutectic Solvents Used as the Green Media for the Efficient Extraction of Caffeine from Chinese Dark Tea. Sep Purif Technol 2019, 227, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Vega, J.; Gómez-Alonso, S.; Pastene-Navarrete, E.; Pérez-Navarro, J. Green Extraction of Alkaloids and Polyphenols from Peumus Boldus Leaves with Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Profiling by HPLC-PDA-IT-MS/MS and HPLC-QTOF-MS/MS. Plants (Basel) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawky, E.; Takla, S.S.; Hammoda, H.M.; Darwish, F.A. Evaluation of the Influence of Green Extraction Solvents on the Cytotoxic Activities of Crinum (Amaryllidaeae) Alkaloid Extracts Using in-Vitro-in-Silico Approach. J Ethnopharmacol 2018, 227, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhu, C.; Xu, W.; Park, Y.; Zhou, H. Mutant Breeding of Serratia Marcescens Strain for Enhancing Prodigiosin Production and Application to Textiles. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 2013, 43, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, B.A.; Remmele, R.L. Protect from Light: Photodegradation and Protein Biologics. J Pharm Sci 2007, 96, 1468–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, R.; Fränz, J. Der Einfluss Des Lichtes Und Ionisierender Strahlung Auf Die Autoxydation von Cystein Und Die Reaktion Zwischen Cystein Und 3, 4-Benzpyren. Int J Radiat Biol 1960, 2, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Gong, J.; Fu, R.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Lou, J.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Dyeing and Functional Properties of Polyester Fabric Dyed with Prodigiosins Nanomicelles Produced by Microbial Fermentation. J Clean Prod 2017, 148, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, I.C. Nanobiotechnology: A New Strategy to Develop Non-Toxic Antimicrobial Textiles for Healthcare Applications. J Biotechnol 2010, 150, 349–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouro, C.; Martins, R.; Gomes, A.P.; Gouveia, I.C. Upcycling Wool Waste into Keratin Gel-Based Nanofibers Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Gels 2023, Vol. 9, Page 661 2023, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.; Khan, N.A.; Ibrahim, T.; Khamis, M.; Khan, A.S.; Alharbi, A.M.; Alfahemi, H.; Siddiqui, R. Antimicrobial Activity of Novel Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sci Pharm 2023, 91, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giteru, S.G.; Ramsey, D.H.; Hou, Y.; Cong, L.; Mohan, A.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A. Wool Keratin as a Novel Alternative Protein: A Comprehensive Review of Extraction, Purification, Nutrition, Safety, and Food Applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 2023, 22, 643–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
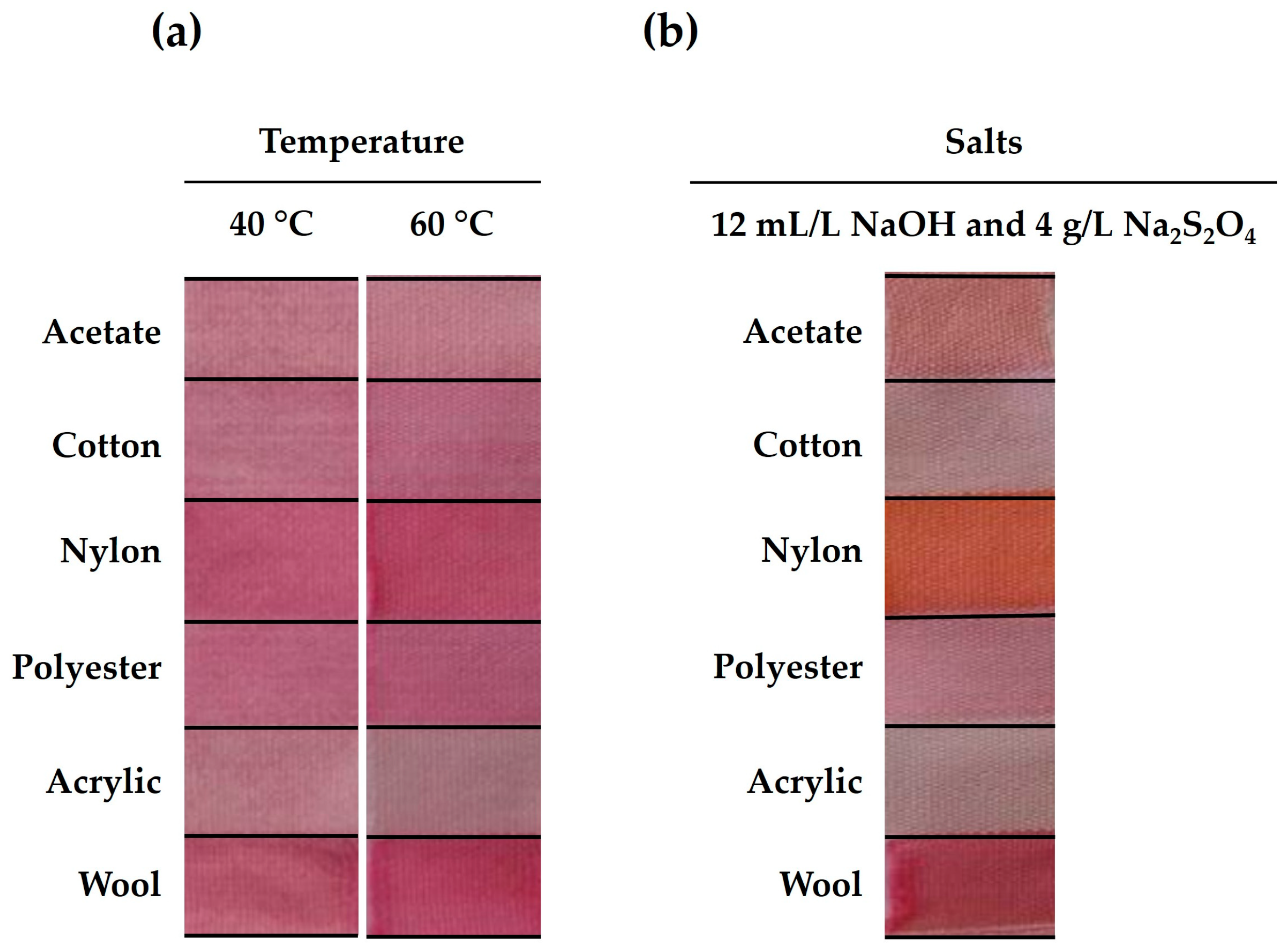



| (a) | Temperature (°C) | (b) | Salts | ||||||
| 40 | 60 | ||||||||
| Acetate | K/S | 0.49 | 0.47 | Acetate | K/S | 0.59 | |||
| dE | 0.10 | 0.07 | dE | 0.19 | |||||
| Cotton | K/S | 0.78 | 0.70 | Cotton | K/S | 0.25 | |||
| dE | 0.10 | 0.08 | dE | 0.16 | |||||
| Nylon | K/S | 1.17 | 1.20 | Nylon | K/S | 1.25 | |||
| dE | 0.16 | 0.04 | dE | 0.14 | |||||
| Polyester | K/S | 0.68 | 0.72 | Polyester | K/S | 0.39 | |||
| dE | 0.09 | 0.05 | dE | 0.07 | |||||
| Acrylic | K/S | 0.51 | 0.30 | Acrylic | K/S | 0.14 | |||
| dE | 0.06 | 0.03 | dE | 0.10 | |||||
| Wool | K/S | 1.56 | 1.38 | Wool | K/S | 1.60 | |||
| dE | 0.12 | 0.05 | dE | 0.05 | |||||
| Mordants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Sulphate (FeSO4) | L-Cysteine (L-Cys) | ||||||
| 1.0% | 3.0% | 5.0% | 1.0% | 3.0% | 5.0% | ||
| Acetate | K/S | 0.75 | 1.65 | 6.43 | 0.47 | 0.63 | 0.70 |
| dE | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 0.10 | |
| Cotton | K/S | 0.55 | 0.90 | 1.23 | 0.59 | 0.86 | 0.94 |
| dE | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.43 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.09 | |
| Nylon | K/S | 1.39 | 2.02 | 6.81 | 1.12 | 1.72 | 1.61 |
| dE | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 0.07 | |
| Polyester | K/S | 0.48 | 0.60 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.76 | 0.91 |
| dE | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.19 | |
| Acrylic | K/S | 0.27 | 0.66 | 0.92 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.35 |
| dE | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.55 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.12 | |
| Wool | K/S | 1.47 | 2.44 | 2.06 | 1.69 | 2.08 | 2.48 |
| dE | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.96 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.11 | |
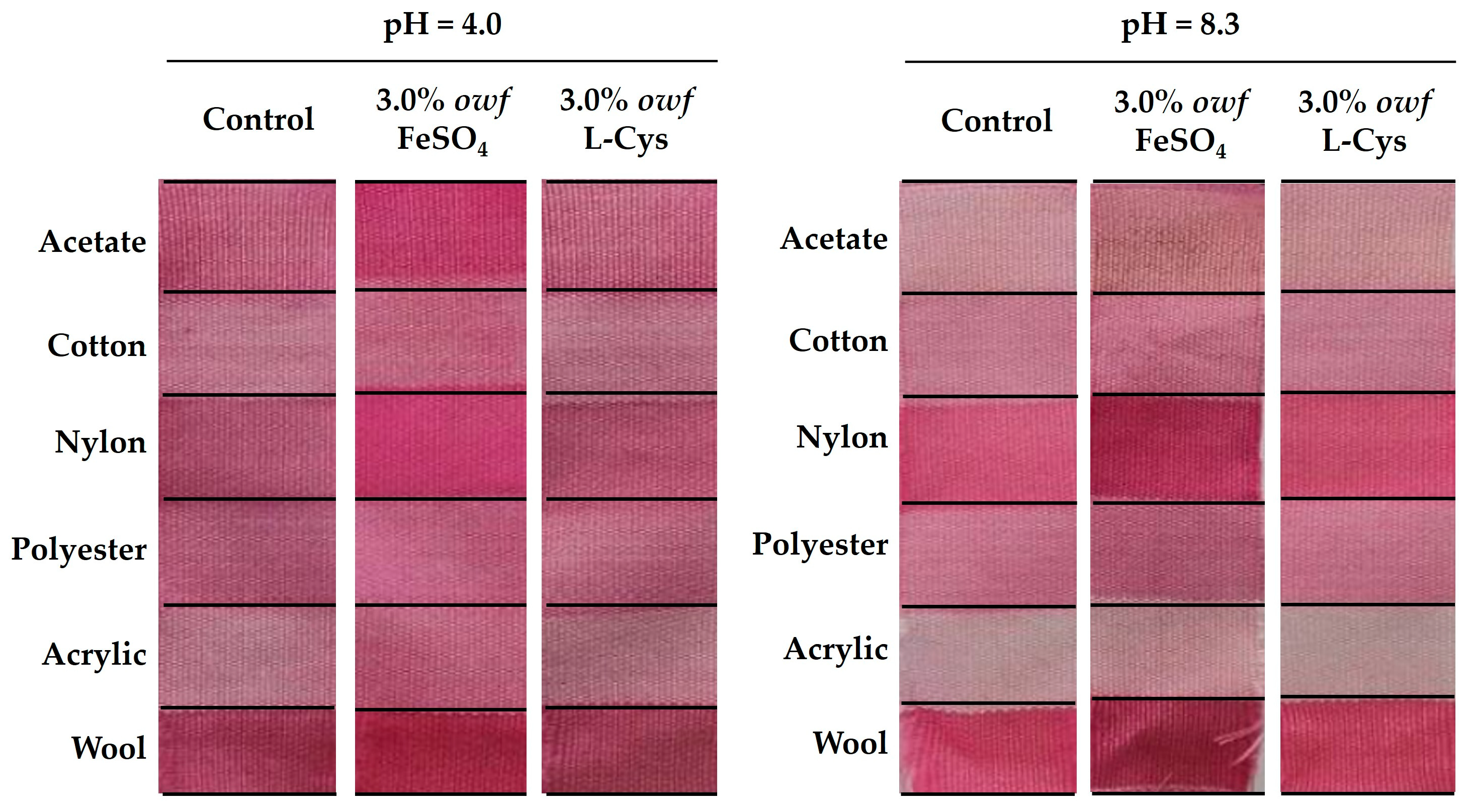
| pH | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.0 | 8.3 | ||||||
| Control | 3.0% owf FeSO4 | 3.0% owf L-Cys | Control | 3.0% owf FeSO4 | 3.0% owf L-Cys | ||
| Acetate | K/S | 1.71 | 3.81 | 1.53 | 0.51 | 1.01 | 0.58 |
| dE | 1.21 | 0.19 | 1.16 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 | |
| Cotton | K/S | 0.86 | 1.46 | 0.83 | 0.90 | 1.21 | 0.97 |
| dE | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.80 | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.13 | |
| Nylon | K/S | 1.73 | 3.30 | 1.59 | 1.87 | 3.67 | 2.30 |
| dE | 1.01 | 0.13 | 1.00 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.05 | |
| Polyester | K/S | 1.10 | 1.11 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 1.28 | 0.97 |
| dE | 0.41 | 0.22 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.11 | |
| Acrylic | K/S | 0.57 | 1.04 | 0.61 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 0.26 |
| dE | 0.17 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.11 | |
| Wool | K/S | 2.33 | 3.22 | 2.04 | 2.38 | 3.11 | 2.49 |
| dE | 0.70 | 0.35 | 0.84 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.27 | |
| Gel-based Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) | ||
|---|---|---|
| ChCl : LA (1 : 2) | ||
| Acetate | K/S | 2.76 |
| dE | 0.02 | |
| Cotton | K/S | 1.60 |
| dE | 0.02 | |
| Nylon | K/S | 3.33 |
| dE | 0.01 | |
| Polyester | K/S | 1.22 |
| dE | 0.01 | |
| Acrylic | K/S | 1.55 |
| dE | 0.01 | |
| Wool | K/S | 1.60 |
| dE | 0.01 | |
| ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | Fastness Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆Color | |||||
| Prodigionsin_3.0% owf L-Cys_Nylon_pH = 8.3 | 1.66 | -0.77 | 2.64 | 3.21 | 3 |
| Prodigiosin_3.0% owf L-Cys_Wool_pH = 8.3 | 3.31 | -6.56 | 2.86 | 7.88 | 2 |
| Prodigiosin_gel-based ChCl : LA (1 : 2) DES_Nylon | 11.12 | -1.15 | 1.09 | 10.77 | 1-2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





