1. Introduction
Ischaemic stroke is the most prevalent type of stroke and is characterised by a series of pathological events including the blood-brain barrier (BBB) damage triggered by arterial occlusion. Patients with bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO) have a particularly poor prognosis as a result of a high subsequent stroke prevalence rate (66% in bilateral internal carotid artery occlusion and 71% in bilateral common carotid artery occlusion) [
1]. Following stroke, the BBB is damaged leading to degraded proteins being released into the blood circulation. These circulating biomarkers are progressively being assessed for their role in the diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of brain ischaemia [
2]. The BBB is formed by brain microvascular endothelial cells interconnected by tight junctions (TJs), which selectively exclude most blood-borne substances from entering the brain. Endothelial cells, in conjunction with their neighbouring cells such as pericytes and astrocytes, are critical for maintaining the normal physiology and function of the BBB [
3]. BBB plays an important role in maintaining the microenvironment for normal brain function and signalling [
3]. Several studies have found that ischaemic stroke leads to changes in neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia as immediate primary ischaemic damage. The BBB is rapidly broken down as a result of secondary damage [
4] leading to increased BBB permeability. BBB leakage may also indicate massive dysfunction of microvessels, which could lead to poor outcomes after brain ischaemia [
5].
In the endothelial cells, the zonula occludens (ZO) belong to the large family of membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK)-like proteins and the actin cytoskeleton is involved in the regulation of the integrity of cytoplasmic TJs. ZO-1 is a well-known TJ protein and its damage reflects the severity of the pathological change of BBB [
6]. Occludin, a member of the TJ proteins, is also a key structural component of the BBB that has recently become an important focus of research in BBB damage [
7,
8]. Liu et al. (2012) have observed a rapid loss of Occludin in the ischaemic cerebral microvessels in a rat ischaemic stroke model [
8]. Occludin degradation has been observed in both human and animal studies with acute ischaemic stroke leading to BBB breakdown [
7]. Claudin-5 is the most dominant isoform of the Claudin family that decreases para-cellular small molecule diffusion, making it a promising target for selective drug delivery through the BBB [
9,
10]. However, several studies have shown that claudin-5 concentrations remained unchanged following the middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats [
11,
12].
During an ischaemic stroke, degradation of TJs occurs in a multistep time-dependent fashion, involving several interdependent signalling mechanisms. However, during the reperfusion phase of cerebral ischaemia and reperfusion (I/R) injury, reactive hyperaemia and loss of cerebral autoregulation lead to the acute opening of BBB TJs [
13]. Regardless of the type of stroke, these processes are associated with neuronal death, glial cell alterations and BBB damage. Furthermore, after ischaemia, sudden restoration of blood flow causes cerebral I/R injury, which aggravates inflammation, oxidative stress and cell death leading to haemorrhagic transformation [
14].
Recently, an emerging circulating biomarker strategy in differentiating between stroke patients and stroke mimics has shown promising results in stroke diagnosis[
15]. Different biomarker panels have been investigated in determining molecular characteristics of human cerebral I/R with variable results, as well as being considered as an assisting tool in the diagnosis of stroke. However, a deeper investigation of cerebral I/R-induced brain cells and BBB damage is required for better diagnosis, prognosis, and early treatment of ischaemic stroke.
Earlier studies including our group have shown that transient BCCAO followed by reperfusion in mice produces consistent and reproducible brain injury and neurological dysfunction [
6,
16,
17]. In our previous study, we have optimised the mouse model of transient BCCAO to study cerebral I/R-induced neuronal death, astrogliosis in the brain and memory dysfunction [
16]. The present study aims to examine the changes in neuronal, glial and BBB TJ proteins in the hippocampus and determine the level of relevant circulating biomarkers following cerebral I/R injury in this optimised mouse BCCAO model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A murine model for cerebral ischaemia and reperfusion
All experiments were performed on 10-to 12-week-old (25–30 g) male C57BL/6J mice (n = 54) Harlan-Olac, Bicester, UK) according to the ARRIVE guidelines, as specified in the U.K. Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986 and European Communities Council Directive of 24 November 1986 (86/609/EEC). The animals were housed under a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle and were provided with pellet food and water ad libitum to provide post-stroke support in mice [
18,
19]. Cerebral ischaemia in mice (n = 28) was induced by transient BCCAO, according to our previously published method [
16]. We used 15 min BCCAO followed by 5 days reperfusion as in our previous study we have shown that this produces consistent cellular damage in the brain of ischaemic mice [
16] Sham-operated mice (n =26) underwent the same procedure except that the carotid arteries were not occluded.
Neurological assessment was performed in BCCAO and sham-operated mice by neurological deficit signs as described in our previous published paper [
16] i.e., 0, no observable deficit; 1, drowsiness and circling; 2, torsion of the neck and disappearance of the righting reflex; 3, seizure; 4, no spontaneous movement or coma. Two animals were excluded from our analysis due to incomplete occlusion.
2.2. Tissue processing for immunohistochemistry:
Following 5 days survival time, BCCAO and sham-operated mice were perfused trans-cardially with 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1M phosphate buffer (PB, pH 7.4). Brains were post-fixed in PB overnight and stored in 0.1M phosphate buffer saline (PBS) at 4°C. Brain sections (20-μm) were cut using a cryostat (Leica, Bensheim, Germany) and processed for immunohistochemistry.
2.3. Primary antibody specificity
The specificities of antibodies were determined previously by the suppliers. In particular, an antibody against NeuN (Abcam, code number ab104224) was prepared by immunising mice with N terminal peptide 1B7. Recombinant fragment corresponding to NeuN aa 1-100 (N terminal). Sequence: MAQPYPPAQYPPPPQNGIPAEYAPPPPHPTQDYSGQTPVPTEHGMTLYTPAQTHPEQPG-EASTQPIAGTQTVPQTDEAAQTDSQPLHPSDPTEKQQPKR. Antibody against GFAP (Invitrogen, code number 131-17719) was prepared by immunising mice with 131-17719. Antibody against Occludin (Life technologies, code number OC-3F10) was prepared by immunising mice with C terminal peptide OC-3F10. Antibody against ZO-1(Invitrogen, code number 40-2200) was prepared by immunising the rabbit with a synthetic peptide found in the ZO-1 protein's middle region. Antibody against Claudin-5 (Invitrogen, code number 34-1600) was prepared by immunising rabbits with synthetic peptides from the Claudin-5 C-terminus.
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
The brain sections were placed in wells of the tray and treated with Liberate L.A.B. Solution (antigen retrieval solution, Polysciences Inc.) for 10 min to wipe off excessive fixative and minimize protein cross-linking. Then, the sections were washed with PBS containing 0.01% Triton-X100 (PBS-T) for 5 minutes followed by incubation in 10% horse or donkey serum (Sigma-Aldrich, Poole, Dorset, UK) diluted in PBS-T) at room temperature on a shaker (Bio Dancer, New Brunswick Scientific, Edison N.J USA) for 30 min with gentle agitation to block any non-specific binding and decrease background staining. Following that, sections were transferred to the appropriate primary antibodies. The primary antibodies used are - NeuN (Abcam-ab104224), GFAP (Invitrogen-A21282), Occludin (Life Technologies-331511), Claudin-5 (Invitrogen-34-1600), ZO-1 (Invitrogen-40-2200), CD31 (Abcam-ab28364), and CD31 (Invitrogen-14-0311-82). Sections were incubated overnight in these antibodies that were diluted in PBS-T with 10% horse serum at 40C. The dilutions of these antibodies used were - 1/4000 (NeuN), 1/1000 (GFAP), 1/50 (Occludin), 1/500 (Claudin-5), and 1/100 (ZO-1). Sections were washed three times for 5 min each on a shaker table for gentle agitation. Sections were then transferred to the appropriate (rabbit or mouse) secondary antibodies conjugated to Cy3 (red fluorescence) (Jackson Immunosearch Laboratories-115-167-003) or Alexa488 (green fluorescence) (Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories-115-545-003) (diluted 1:1000 in PBS-T with 10% horse serum) and incubated at room temperature on the shaker table for 4 hours. Since the secondary antibodies are light-sensitive, the tray was covered with foil. Finally, sections were washed three times each for 5 min, mounted on slides and cover-slipped using Vectashield mounting medium with or without DAPI (Vector Laboratories Inc., Burlingame, CA 94010).
The analysis of brain sections was done using Zeiss Axioskop.2 or AxioImager.Z1 fluorescence microscopes. Multiple digital images were taken with the imaging system (Acquis (Axioskop.2) or an Axiovision (AxioImager.Z1)).
2.5. Stereological method for quantification of immunolabelled profiles
We analysed data from the hippocampus to obtain consistent results as our previous study reported that 15 minutes of BCCAO followed by 5 days of reperfusion produces consistent and reproducible neuronal death and astrocyte activation in this region [
16]. The number of NeuN immunoreactive neuronal cells, GFAP immunoreactive glial cells and processes per unit volume of tissue in the hippocampus was estimated using a three-dimensional counting method, based on our previously published method [
16]. In brief, areas of the hippocampus were located by examining immunolabelled sections under the fluorescence microscope, at magnification of x10 objectives. Analysis was conducted unilaterally as the mice in our study showed hippocampal and cortical damage in both hemispheres. Images were captured into Axiovision, using the x10 objective. Each captured image corresponded to an area of tissue measuring 450 x 350 um. An acetate sheet with a standard unbiased counting frame [
20,
21], each side equivalent to 200 um at this magnification, was laid over the image on the monitor, to form a counting box for the image. All counts were performed blindly on coded slides by a single observer.
2.6. Western Blotting
Western blotting analysis was conducted from hippocampal regions of the forebrain. In brief, the mice were executed by decapitation under anaesthesia. Brains were removed and frozen rapidly on dry ice. The hippocampal tissue samples (25-35 mg) from both brain sides were collected at the forebrain level corresponding to bregma −0.22 to −2.06 mm [
22] with 1 mm corer under a × 5 dissecting microscope according to our previously published method [
16,
23]. The hippocampal tissues were homogenised using a Blunt 20-gauge blunt needle and extracted using 300 μL of lysis buffer (ThermoFisher Scientific, 87787).
Harvested hippocampal tissues were sonicated using the FB120 probe-sonicator from Fisher Scientific, in an ice bath, twice at 5 seconds and centrifuged for 30 minutes at 13000 rpm at 4 degrees C, before performing protein concentration measurements by BCA assay (Pierce Protein Quantification Kit) using the supernatant. Equal amounts of cellular protein were resolved on 12 % SDS polyacrylamide gels (Invitrogen) and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes (Millipore) and incubated for 1 hour in TBS-T (Tris-buffered saline and 0.1% Tween 20) containing 5% non-fat milk. Membranes were then immunoblotted and incubated overnight at 4°C with appropriate primary antibodies: GFAP, ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-5 (diluted 1:1000) against beta-Actin (1:1000) [
46]. Membranes were washed in TBS-T three times (15 min each) on a shaker and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature with corresponding HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology; 1:1000). The membranes were washed in TBS-T once for 15 min and then incubated in Anti-western-C marker (Streptactin) (BIO-RAD) diluted in TBS-T (1:25,000) for 10 min. The membranes were washed in TBS-T twice (15 min each). The membranes were developed with the Immobion Western HRP substrate luminol reagent with peroxide reagent (Millipore). The Syngene densitometry (Syngene Gel Documentation) system, GeneSys application was used to quantify the immunoblots. Densitometric quantification analysis of blots was performed using GeneTools analysis software along with Excel software. Data are shown as mean ± SEM, Mann Whitney U test p< 0.05.
2.7. Analysis and measurement of blood biomarkers using the ELISA method
Blood samples were collected in a gel clot active tube (Gold Hemogard closure) from the inferior vena cava from 8 BCCAO stroke and 8 sham-operated mice (~1ml blood from each mouse). Blood samples were collected after 5 days of BCCAO and sham operation. The blood samples were centrifuged (Bifug Pico) at 1500 g for 10 mins within two hours of collection. After that, samples were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored in a freezer at −80°C until analysis. For measurement of blood biomarkers, mouse GFAP ELISA Kit (Fine test, EM0335), mouse Occludin ELISA Kit (AVIVA Systems Biology, OKEH 07095), mouse Claudin-5 ELISA kit ( DL EVELOP, DL-CLDN5-Mu) and mouse TJP1(Tight junction protein ZO-1) ELISA Kit (Elabscience, E-EL-M1161) were used and the protocols were followed according to the attached guidance of the respective company.
Table 1 shows the detection range, sensitivity, and specificity for each previously mentioned ELISA kit. In brief, 100 μL of the serially standard sample (serum or plasma) and control (zero) solutions were added to each well and incubated for 90 minutes in GFAP and ZO-1 assays and 2 hours in Occludin and Claudin-5 assays at 37°C. Then, the liquid was removed and 100μL of Biotin-detection antibody was added to each well for 60 minutes at 37°C. Following that, the plate was washed three times and 100μL of HRP Conjugate (SABC) was added to each well and incubated for 30 minutes in GFAP, Occludin and ZO-1 assay and 1 hour in Claudin-5 assay at 37°C. The plate was then washed five times and 90μL of TMB substrate was added to each well for 15 minutes at 37°C. Finally, 50μL of Stop Solution was added followed by immediate optimal density determination at 450 nm with a plate reader. In ELISA analysis, the serum concentration of each biomarker (GFAP, Occludin, Claudin-5 and ZO-1 were analysed by unpaired t-test to compare the mean values from serum concentration/optical density. p< 0.05 is considered significantly different.
2.8. Statistical analysis
Data were shown as mean ± SEM. Excel program and GraphPad Prism 9 software (GraphPad, San Diego, California) were used for statistical analysis and visualisation. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Quantification of immunolabelled profiles data were analysed using an unpaired t-test to determine statistical significance and a multiple comparison test was used for post-hoc comparisons. Spearman’s correlation, a non-parametric test that is usually performed to measure the association degree between two variables [
24] was used to assess the linear relationships. The significance of the correlation was obtained by performing the 2-tailed Student’s t-test against the null hypothesis.
2.9. Study approval
All mouse procedures were approved by the University of Leeds project licence according to the ARRIVE guidelines as specified in the U.K. Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986 and the European Communities Council Directive of 24 November 1986 (86/609/EEC).
3. Results
3.1. Immunohistochemical analysis of immunoreactive cells and profiles
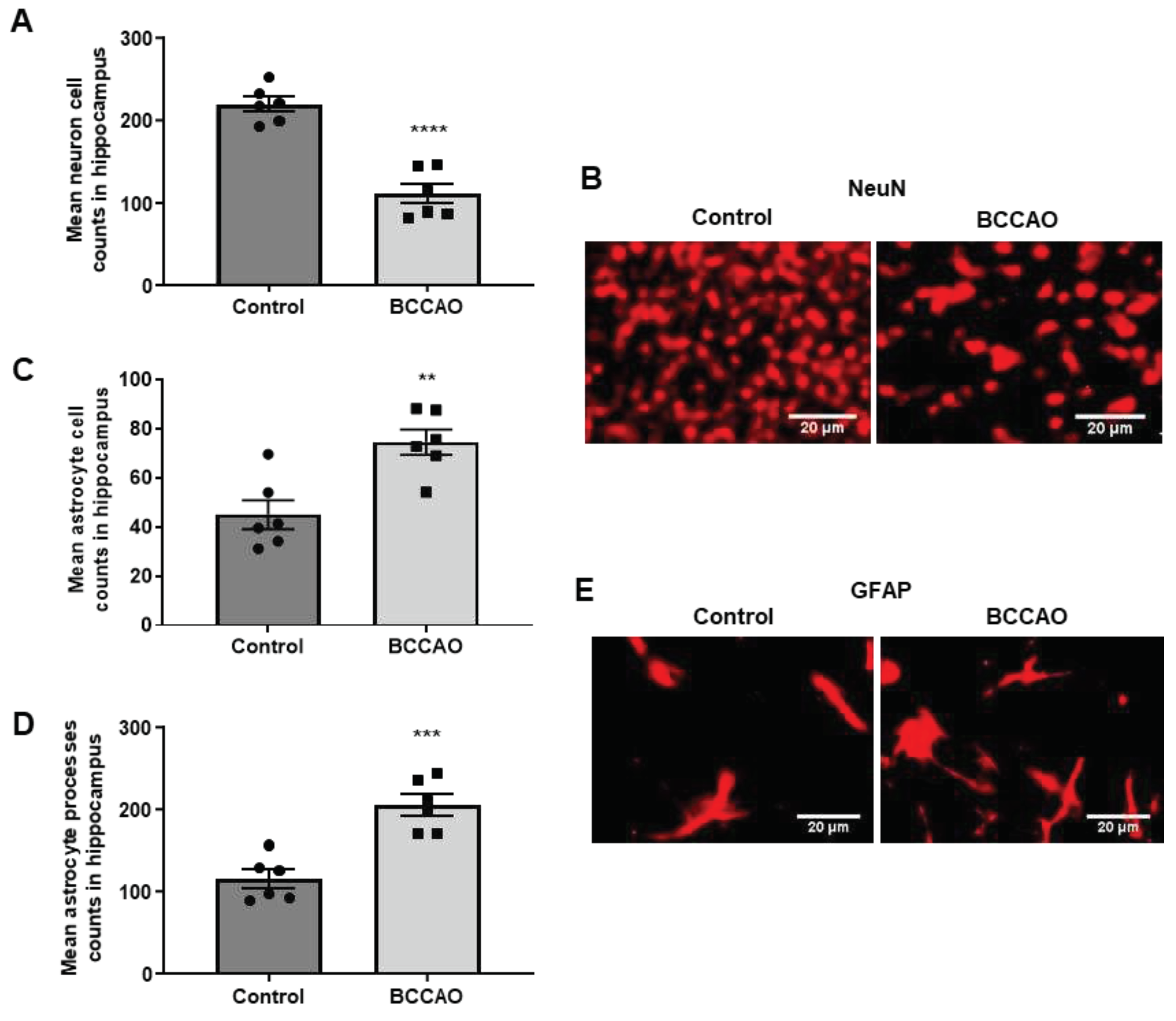
NeuN, a neuronal-specific nuclear protein that is commonly used as a marker of mature neurones [
25], was used to determine the extent of neuronal death in the hippocampus. The results showed that 15 minutes of ischaemia and 5 days of reperfusion-induced considerable loss of NeuN-labelled neurones in the hippocampus confirming our previous study where detailed analyses were performed to assess neuronal death in the CA1, CA2 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus [
16]. Quantitative analysis showed that the NeuN-positive cells were significantly decreased in the ischaemic brains when compared to the sham-operated group (p<0.0001,
Figure 1 A).
Figure 1 B shows NeuN-labelled cells in the CA1 area of the hippocampus of sham-operated and BCCAO mice, respectively.
Antibodies to GFAP, an intermediate filament protein that is predominantly expressed by astrocytes, were used to label changes in glial cells and processes following ischaemia. The results showed an increase in astrocytes and processes in the hippocampus of the BCCAO mice compared to the sham-operated mice (
Figure 1 E). The numbers of both GFAP positive glial cells (
Figure 1 C, p=0.0375) and GFAP positive glial processes (
Figure 1 D, p=0.0003) were significantly increased in the hippocampus of the BCCAO mice compared to the sham-operated mice.
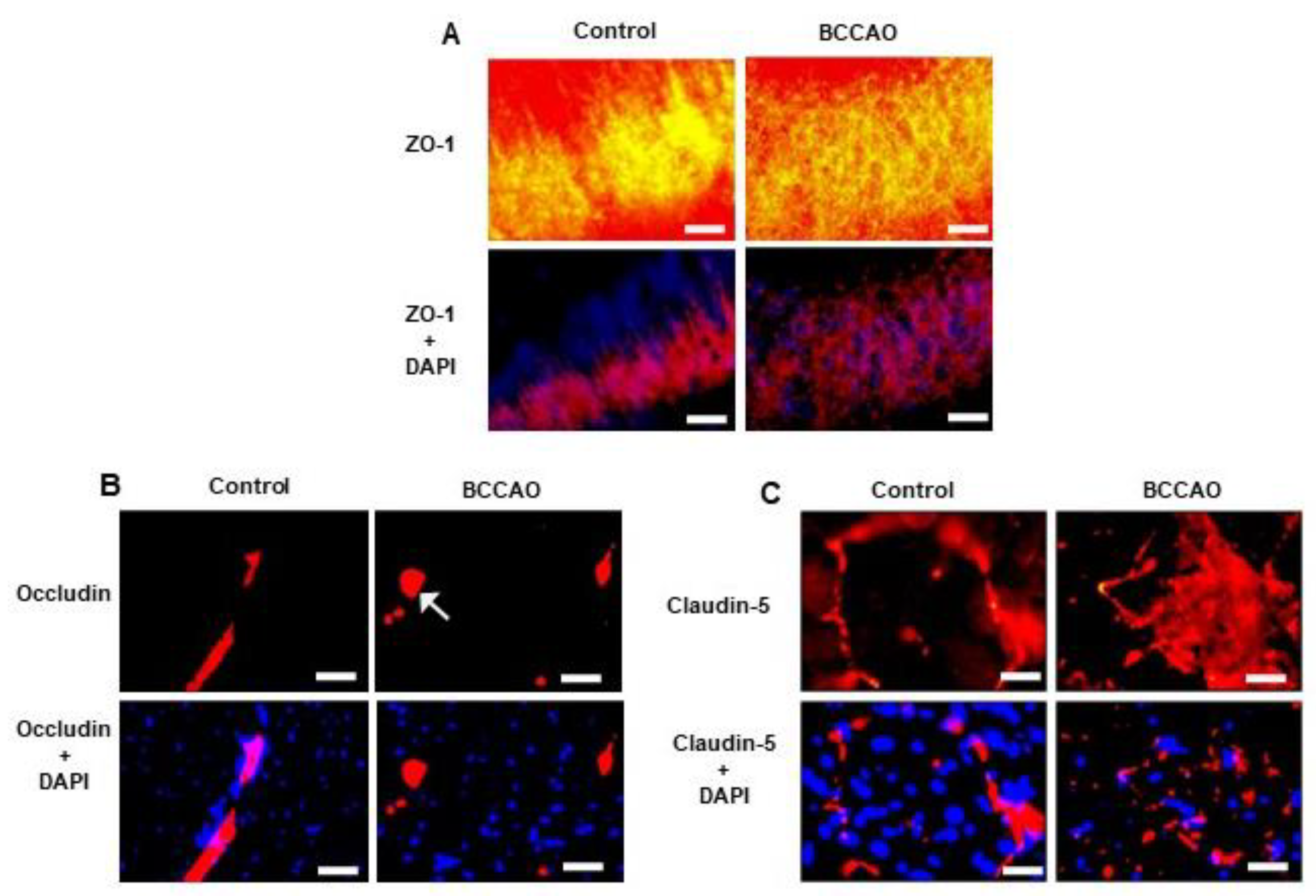
Qualitative immunohistochemical analysis showed ZO-1 (
Figure 2 A); Occludin (
Figure 2 B) and Claudin-5 (
Figure 2 C) immunoreactivity were reduced in the hippocampus of the BCCAO mice compared to sham-operated mice. There were disruptions and discontinuity in the distribution of immunoreactive profiles in the hippocampus of the BCCAO mice; whereas immunoreactive profiles remained intact in the sham-operated mice
3.2. Western Blotting analysis of protein expressions after ischaemia
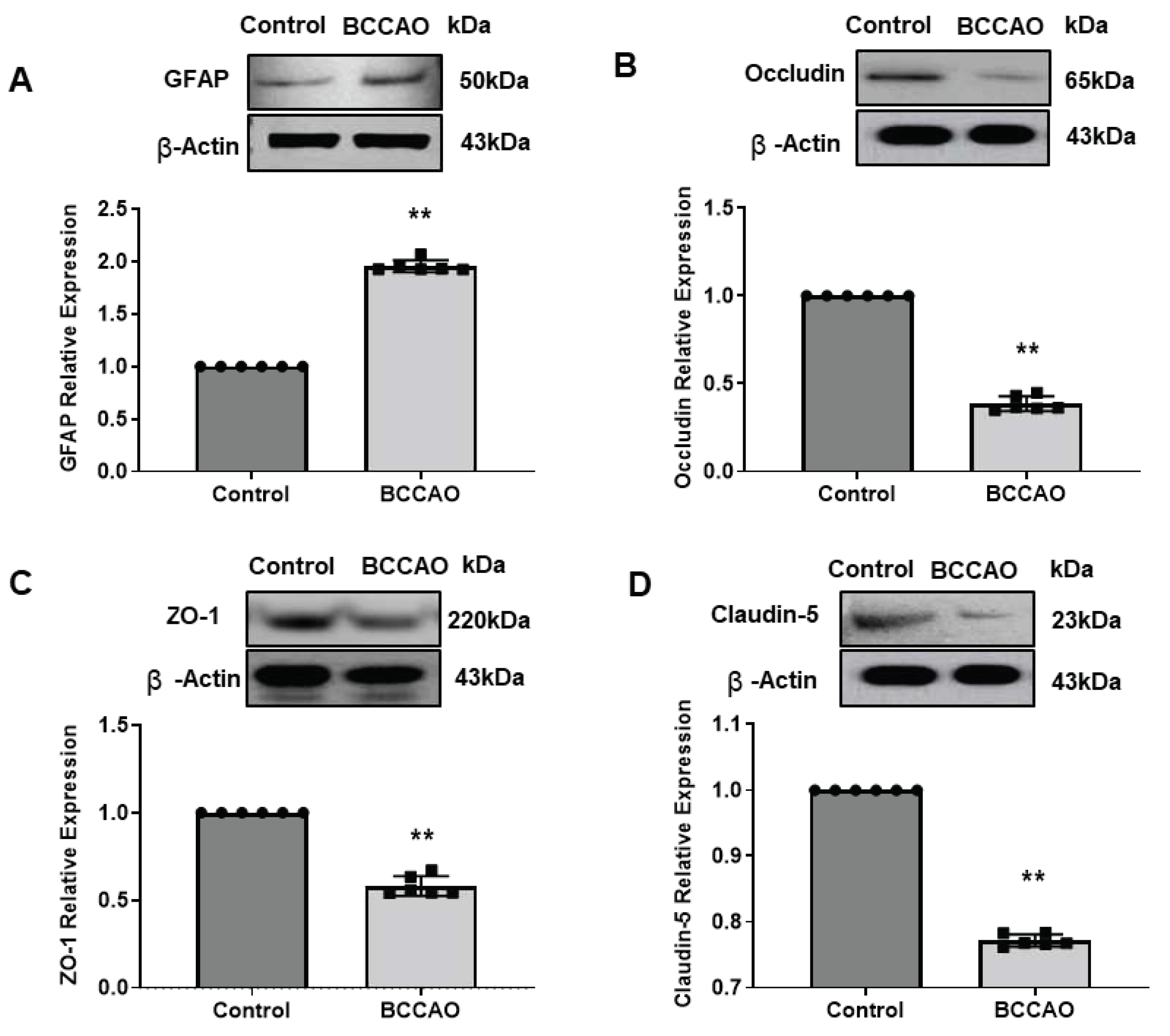
Quantitative Western Blotting (WB) analysis of GFAP expression in hippocampus tissues showed a significant increase in GFAP protein in the hippocampus of ischaemic mice compared to the control mice (Mann Whitney U test, p=0.0022,
Figure 3 A). This WB result was consistent with the observed immunostaining data.
The expression levels of the BBB TJs proteins in the hippocampus of the BCCAO mice were significantly lower (Occludin, p=0.0022,
Figure 3 B; ZO1, p=0.0022,
Figure 3 C and Claudin-5, p=0.0022,
Figure 3 D) compared to the sham-operated mice confirming our qualitative immunohistochemical results.
Our WB analysis suggests that the expression levels of all three TJ proteins were reduced significantly in the hippocampus following cerebral ischaemia confirming disruption of BBB integrity as determined by immunohistochemistry.
3.3. Analysis of markers in blood serum
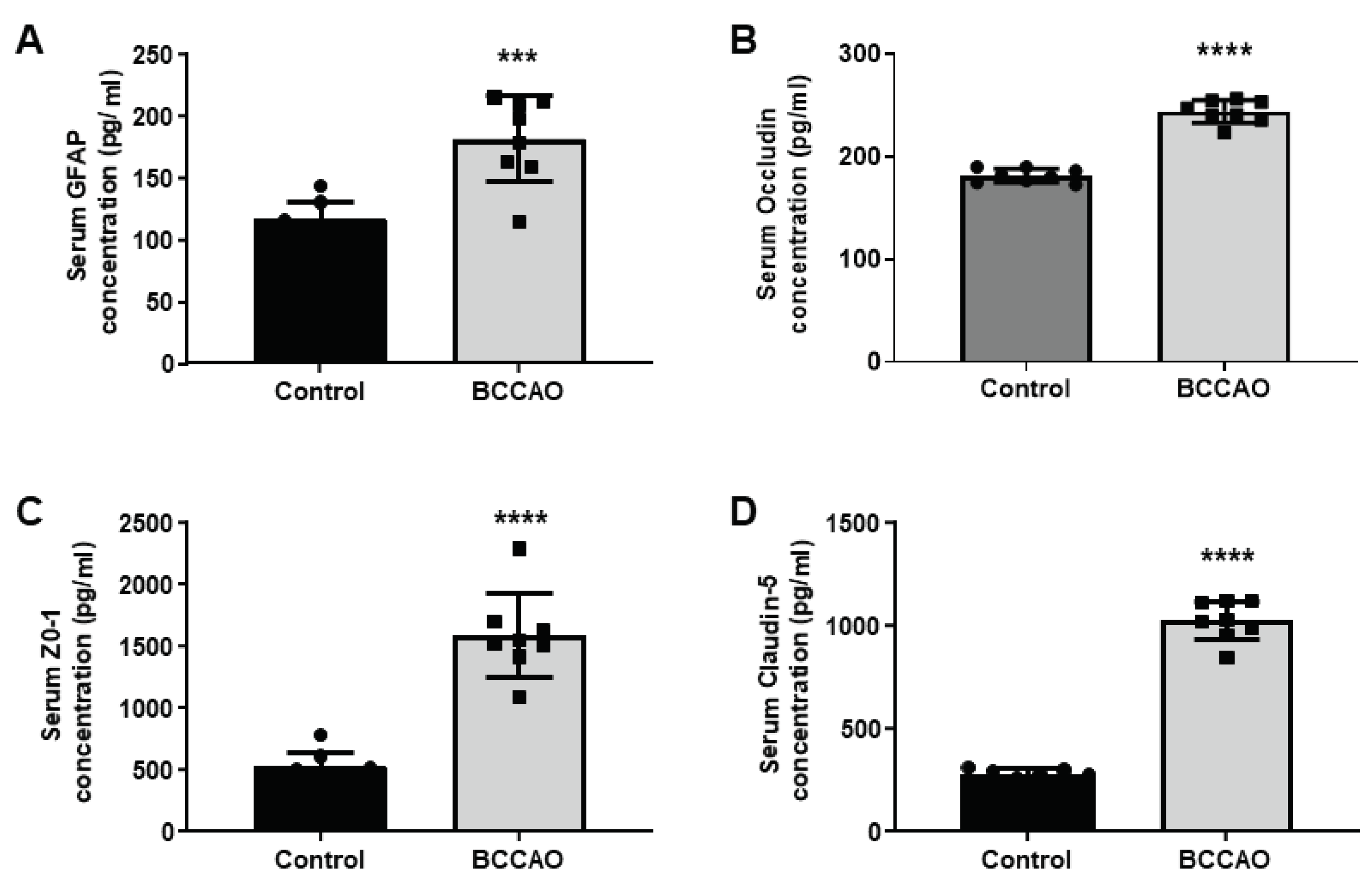
The serum levels of GFAP, ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-5 from BCCAO and sham-operated mice were quantified. The quantitative statistical analysis showed a significant increase of 1.5-fold in GFAP level (Control vs BCCAO, 116.8±13.8 vs 182.1±34.6; p=0.0002,
Figure 4 A), a 1.34-fold increase in Occludin level (Control vs BCCAO, 181±6.7 vs 243±11.1; p<0.0001,
Figure 4 B), a 3-fold increase in the ZO-1 level (Control vs BCCAO, 527.9±125.4 vs 1595±337.4; p<0.0001,
Figure 4 C) and ~ 3.6-fold increase in the level of Claudin-5 (Control vs BCCAO, 278.3±30.4 vs 1028±96.5; p<0.0001,
Figure 4 D) in the ischaemic group of mice compared to the sham-operated mice.
3.4. Correlation between expression of markers in serum and brain
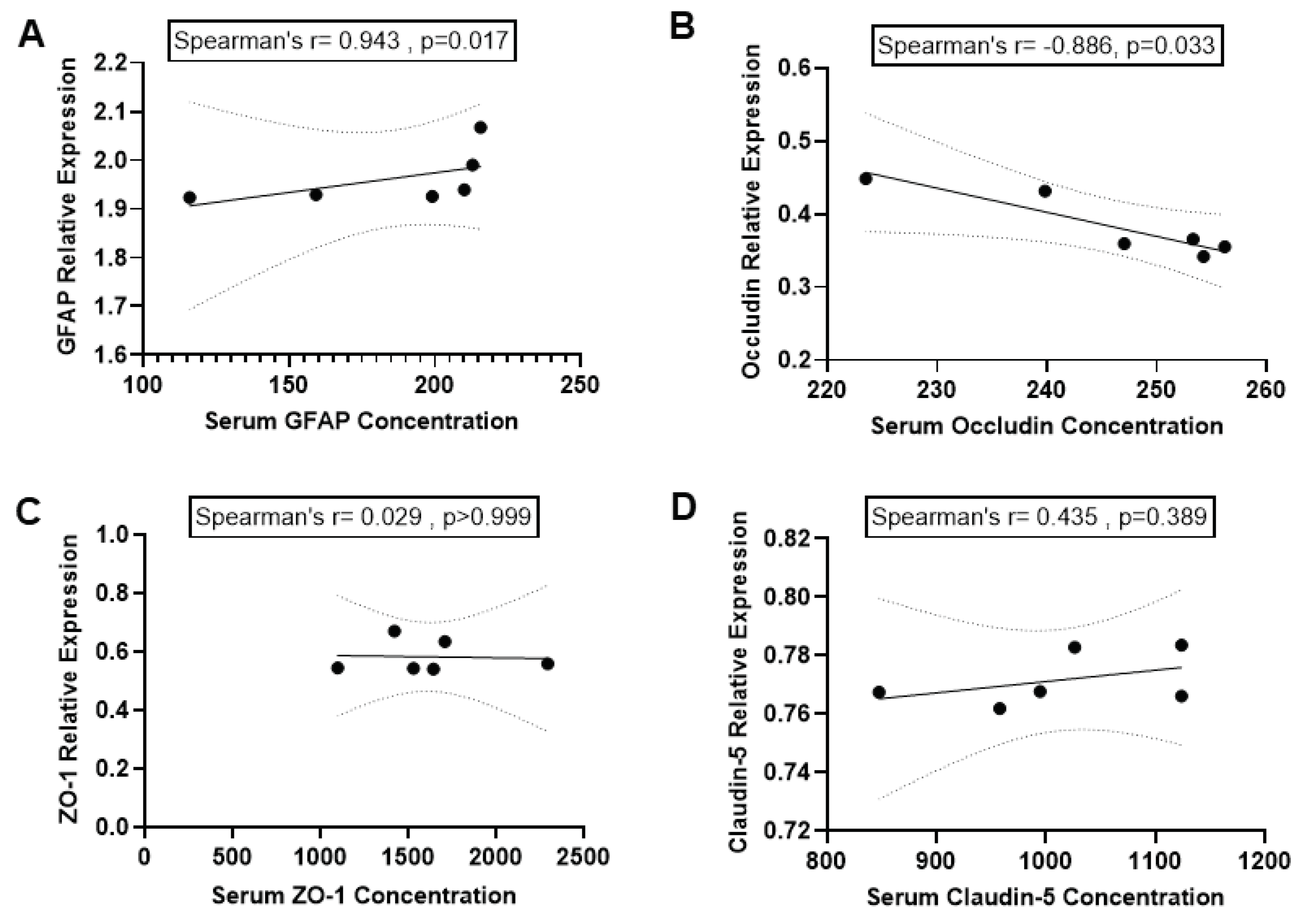
We investigated the correlation between GFAP levels in blood serum and the expression of GFAP in the hippocampus. The results of the Spearman correlation indicated a significant positive correlation between GFAP expression in the hippocampus, as determined by WB and serum GFAP level as determined by ELISA following BCCAO (r = 0.943, p=0.017) (
Figure 5 A).
We also tested whether serum levels of TJ proteins (Occludin, ZO-1 and Claudin-5) are correlated to the expressions of these proteins in hippocampal tissue in the brain after BCCAO. The Spearman correlation analysis indicated a significant negative correlation between Occludin expressions in the hippocampus and Occludin levels in blood serum after BCCAO (r = -0.886, p=0.033;
Figure 5 B). This indicated that serum Occludin level could reflect the reduction of Occludin protein expressions in the hippocampal tissue in the ischaemic brain.
In contrast, the Spearman correlation indicated no significant association between ZO-1 expressions in the hippocampus and serum ZO-1 levels after BCCAO (r = 0.029, p>0.999;
Figure 5 C). Similarly, results of the Spearman correlation showed no association between Claudin-5 expressions in the hippocampus and serum Claudin-5 levels after BCCAO (r = 0.435, p=0.389;
Figure 5 D).
4. Discussion
The present study is the first systematic study investigating detailed changes in neuronal and glial cells together with BBB junctional proteins (ZO1, Occludin, Claudin-5) in the hippocampus in the forebrain following cerebral I/R induced by BCCAO and reperfusion in C57BL/6J mice. This novel study also quantifies the expressions of GFAP, ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-5 in the hippocampus in this model. The levels of these protein concentrations in the brain were found to be correlated with their levels in the blood serum of Ischaemic mice, suggesting that these proteins could be used as potential biomarkers of ischaemic stroke.
We have used C57BL/6 mice, as our previous study [
16] along with others [
26,
27] showed transient BCCAO in these mice developed consistent and selective neuronal death in the CA1, CA2 and CA3 areas of the hippocampus and motor, somatosensory and insular cortex with a higher survival rate [
16,
26,
27]. The reduction in the neuronal cell number in the stroke group was due to the high sensitivity of neurons to ischaemic effects and the blood supply reduction, causing neuronal death in these brain areas [
28].
Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis showed a significant increase in GFAP-labelled astrocyte processes and cells following cerebral I/R in the hippocampus confirming our previous study [
16]. The results also confirmed studies that reported the altered morphology of astrocytes after stroke is related to the increased expression of GFAP [
29,
30]. GFAP up-regulation is one of the most important features of astrogliosis (an abnormal increase in the astrocyte number following ischaemia) [
31]. Astrocyte processes identified by GFAP immunostaining in the hippocampus of the BCCAO mice appeared to be rearranged and have become thicker, an indication of reactive gliosis [
32,
33]. This may contribute to CNS circuit dysfunction, defining maladaptive synaptic plasticity in the glial-neuronal network and leading to abnormal synaptic transmission [
34]. Increased levels of GFAP in blood in mice following cerebral I/R observed in the present study confirmed previous clinical studies that investigated the role of serum GFAP as a diagnostic tool for ischaemic stroke patients by showing increased circulatory GFAP levels in ischaemic patients [
35,
36].
The present study demonstrated disruption of BBB TJ proteins (ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-5) in the ischaemic brain compared to the sham brain. The significant reduction in TJ protein expressions in the hippocampus was reported previously in the rat brain following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) [
37,
38], However, to our knowledge, it is the first study in mice.
Significant increases in these three TJ proteins were found in blood serum in stroke mice compared to the control mice. The increased concentrations of these three TJ proteins in blood serum reflected the disarrangements and reductions of these proteins in the brain.
ZO-1 is one of the main TJ proteins that reduce cerebral vessel permeability by restricting the free molecular exchange between blood and brain tissues [
39]. Previous studies using brain microvessel endothelial cells showed dissociation of ZO-1 from the TJs complex has been linked to increased permeability of BBB suggesting that the ZO-1-transmembrane protein connection is crucial for the stability and function of the BBB [
40,
41].
Increased serum levels of Occludin after ischaemia observed in the present study in mice also confirm previous works in a rat model of MCAO and reperfusion (11-42). Occludin is also one of the main TJ proteins that is an integral part of the BBB structure [
43]. Changes in the Occludin expression are reported to be linked to the disruption in regulatory mechanisms of BBB [
44]. In the present study, we observed disruption of Claudin-5-immunoreactivity in the hippocampus and an increased level of Claudin-5 in the blood serum of ischaemic mice compared to the sham-operated mice. However, earlier studies in a rat model of MCAO reported that the blood levels of Claudin-5 did not change considerably during the first 4.5 hours [
11]. In the present study, we used the mouse BCCAO model and did not determine the time course level of these proteins following cerebral I/R, making it difficult to compare our results with earlier studies. Disruptions in Claudin-5 expressions are linked to a large increase in paracellular solute permeability as shown in a previous study in rats following MCAO [
8]. Claudin-5 has also been shown to be one of the integral components of the BBB TJs that control BBB permeability [
45,
46].
The correlation analysis in this study interestingly showed a significant correlation between circulating GFAP and the expression of this protein in the hippocampus in BCCAO mice. A negative correlation between circulating Occludin and the expression of Occludin in the hippocampus after BCCAO suggests that blood Occludin levels observed after BCCAO may accurately represent the expression of Occludin released from the ischaemic brain, which might be closely related to BBB disruption confirming earlier results in rat MCAO [
47]. In the present study we did not observe any correlation between circulating ZO1 and Claudin-5 levels and the expressions of these proteins in the hippocampus. However, more studies in different time points of cerebral I/R are needed to determine the exact roles of these BBB markers in ischaemic stroke. Previous studies suggested that Claudin-5 along with other BBB TJ proteins might be a potential marker for haemorrhagic stroke [
9,
48]. Claudin-5 has been reported to disappear in brain endothelial cells from 24h to 7 days after MCAO in rats and reappear in newly formed brain endothelial cells [
49].
Even though our data show increases in the TJ proteins: (ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-5) in blood serum in the BCCAO model, further studies on these biomarkers in different ischaemic models and in human samples at different time points are required to understand the mechanisms of ischemia-induced BBB damage. The data confirmed that brain and BBB-specific biomarkers are released in blood following 5 days of cerebral I/R in the BCCAO model. The results, however, cannot be directly related to earlier events of human stroke. Nevertheless, this study provides a valuable information on ischaemic changes in astrocytic and BBB proteins in the brain as well as in the circulation and represents an important step forward in investigating brain-derived proteins in the blood serum differentiating stroke from stroke mimics. The results suggest that implementation of blood GFAP in combination with BBB markers may be a promising approach for improving the precision of stroke diagnosis. However, more research is needed before implementing the biomarker strategies in clinical stroke scenarios.
In conclusion, our novel data not only confirmed the cerebral ischaemia-induced neuronal death and astrogliosis combined with BBB TJ disruptions in the brain after stroke in a murine model of cerebral I/R as compared to the sham-operated mice but also for the first time showed the association of expression of GFAP, ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-5 proteins in the ischaemic brain tissue with an increased level of these proteins in the serum of ischaemic mice. The results suggest that GFAP, ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-5 can potentially be used as potential biomarkers for evaluating BBB damage following cerebral I/R. The results are also helpful for further understanding the underlying mechanisms of stroke and developing new diagnostic biomarker strategies and therapeutic approaches targeting the BBB. These data, however, need validation with other models, such as the MCAO model in mice and the effectiveness of these biomarkers be conclusively proven in clinical studies.
Author Contributions
MA conducted histological, immunohistochemical, immunoblot, ELISA experiments, and data analysis and wrote the manuscript. NYY performed all surgical procedures. HV supervised the immunoblot experiments and data analysis. PK and TK contributed to the artwork. SS conceived and designed the study, supervised experimental work and proofread the manuscript with input from all authors.
Funding
This research is part of a PhD project supported by a scholarship from the "Research Center of the Female Scientific and Medical Colleges", Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (or Ethics Committee) of the U.K. Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986 and the European Communities Council Directive of 24 November 1986 (86/609/EEC). All experiments were performed on 10-to 12-week-old (25–30 g) male C57BL/6J mice (Harlan-Olac, Bicester, UK) according to the ARRIVE guidelines. No human samples or subjects were used in this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study is part of a PhD project supported by a scholarship from the "Research Center of the Female Scientific and Medical Colleges", Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lai SL, Chen YC, Weng HH, Chen ST, Hsu SP, Lee TH. Bilateral common carotid artery occlusion - A case report and literature review. J Neurol Sci. 2005;238(1-2):101-104. [CrossRef]
- Maas MB, Furie KL. Molecular biomarkers in stroke diagnosis and prognosis. Biomark Med. 2009;3(4):363-383. [CrossRef]
- Liebner S, Dijkhuizen RM, Reiss Y, Plate KH, Agalliu D, Constantin G. Functional morphology of the blood–brain barrier in health and disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2018;135(3):311-336. [CrossRef]
- Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA. Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(5):399-414. [CrossRef]
- Jiang X, Andjelkovic A V., Zhu L, et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2018;163-164:144-171. [CrossRef]
- The Role of Circulating Tight Junction Proteins in Evaluating Blood Brain Barrier Disruption following Intracranial Hemorrhage. Dis Markers. 2015;2015. [CrossRef]
- Yuan S, Liu K, Qi Z. Occludin regulation of blood–brain barrier and potential therapeutic target in ischemic stroke. Brain Circ. 2020;6(3):152. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Jin X, Liu KJ, Liu W. Matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated occludin degradation and caveolin-1-mediated claudin-5 redistribution contribute to blood-brain barrier damage in early ischemic stroke stage. J Neurosci. 2012;32(9):3044-3057. [CrossRef]
- Lv J, Hu W, Yang Z, et al. Focusing on claudin-5: A promising candidate in the regulation of BBB to treat ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 2018;161:79-96. [CrossRef]
- Haseloff RF, Dithmer S, Winkler L, Wolburg H, Blasig IE. Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at the blood-brain barrier: Structural and functional aspects. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;38:16-25. [CrossRef]
- Pan R, Yu K, Weatherwax T, Zheng H, Liu W, Liu KJ. Blood Occludin Level as a Potential Biomarker for Early Blood Brain Barrier Damage Following Ischemic Stroke. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):40331. [CrossRef]
- Shi S, Qi Z, Ma Q, et al. Normobaric Hyperoxia Reduces Blood Occludin Fragments in Rats and Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke. 2017;48(10):2848-2854. [CrossRef]
- Sandoval KE, Witt KA. Blood-brain barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis. 2008;32(2):200-219. [CrossRef]
- Granger DN, Kvietys PR. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015;6:524-551. [CrossRef]
- Tiedt S, Brandmaier S, Kollmeier H, et al. Circulating Metabolites Differentiate Acute Ischemic Stroke from Stroke Mimics. Ann Neurol. 2020;88(4):736-746. [CrossRef]
- Khan S, Yuldasheva NY, Batten TFC, Pickles AR, Kellett KAB, Saha S. Tau pathology and neurochemical changes associated with memory dysfunction in an optimised murine model of global cerebral ischaemia - A potential model for vascular dementia? Neurochem Int. 2018;118(April):134-144. [CrossRef]
- Yuan Y, Zhang Z, Wang ZG, Liu J. MiRNA-27b Regulates Angiogenesis by Targeting AMPK in Mouse Ischemic Stroke Model. Neuroscience. 2019;398:12-22. [CrossRef]
- Lourbopoulos A, Mamrak U, Roth S, et al. Inadequate food and water intake determine mortality following stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017;37(6):2084-2097. [CrossRef]
- Kestner R-I, Harms C, Michalski D, et al. Gene Expression Dynamics at the Neurovascular Unit During Early Regeneration After Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Williams RW, Rakic P. Three-dimensional counting: An accurate and direct method to estimate numbers of cells in sectioned material. J Comp Neurol. 1988;278(3):344-352. [CrossRef]
- Gundersen HJG. Notes on the estimation of the numerical density of arbitrary profiles: the edge effect. J Microsc. 1977;111(2):219-223. [CrossRef]
- Paxinos G, Franklin. KBJ. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th Edition-Braintree Scientific, Inc. 4th Editio.; 2012. https://www.braintreesci.com/prodinfo.asp?number=mous-dlx4. Accessed March 23, 2020.
- Ketheeswaranathan P, Turner NA, Spary EJ, Batten TFC, McColl BW, Saha S. Changes in glutamate transporter expression in mouse forebrain areas following focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2011;1418:93-103. [CrossRef]
- Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA. Correlation coefficients: Appropriate use and interpretation. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(5):1763-1768. [CrossRef]
- Gusel’nikova V V, Korzhevskiy DE. NeuN As a Neuronal Nuclear Antigen and Neuron Differentiation Marker. Acta Naturae. 2015;7(2):42-47. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26085943. Accessed June 17,2019.
- Murakami K, Kondo T, Kawase M, Chan PH. The development of a new mouse model of global ischemia: Focus on the relationships between ischemia duration, anesthesia, cerebral vasculature, and neuronal injury following global ischemia in mice. Brain Res. 1998;780(2):304-310. [CrossRef]
- Yang G, Kitagawa K, Matsushita K, et al. C57BL/6 strain is most susceptible to cerebral ischemia following bilateral common carotid occlusion among seven mouse strains: Selective neuronal death in the murine transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res. 1997;752(1-2):209-218. [CrossRef]
- Kudabayeva M, Kisel A, Chernysheva G, Smol’Yakova V, Plotnikov M, Khodanovich M. The increase in the number of astrocytes in the total cerebral ischemia model in rats. J Phys Conf Ser. 2017;886(1). [CrossRef]
- Lebkuechner I, Wilhelmsson U, Möllerström E, Pekna M, Pekny M. Heterogeneity of Notch signaling in astrocytes and the effects of GFAP and vimentin deficiency. J Neurochem. 2015;135(2):234-248. [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew M V. Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32(12):638-647. [CrossRef]
- Pekny M, Eliasson C, Siushansian R, et al. The impact of genetic removal of GFAP and/or vimentin on glutamine levels and transport of glucose and ascorbate in astrocytes. Neurochem Res. 1999;24(11):1357-1362. 1357. [CrossRef]
- Burda JE, Sofroniew M V. Reactive gliosis and the multicellular response to CNS damage and disease. Neuron. 2014;81(2):229-248. [CrossRef]
- Pekny M, Nilsson M. Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia. 2005;50(4):427-434. [CrossRef]
- Papa M, De Luca C, Petta F, Alberghina L, Cirillo G. Astrocyte-neuron interplay in maladaptive plasticity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014;42:35-54. [CrossRef]
- Luger S, Witsch J, Dietz A, et al. Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Serum Levels Distinguish between Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Cerebral Ischemia in the Early Phase of Stroke. Clin Chem. 2017;63(1):377-385. [CrossRef]
- Schiff L, Hadker N, Weiser S, Rausch C. A Literature Review of the Feasibility of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein as a Biomarker for Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injury. Mol Diagn Ther. 2012;16(2):79-92. [CrossRef]
- 37. Ren C, Li N, Wang B, et al. Limb ischemic perconditioning attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption by inhibiting activity of MMP-9 and occludin degradation after focal cerebral ischemia. Aging Dis. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Rosenberg GA. MMP-mediated disruption of claudin-5 in the blood-brain barrier of rat brain after cerebral ischemia. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;762:333-345. [CrossRef]
- Itoh M, Bissell MJ. The organization of tight junctions in epithelia: Implications for mammary gland biology and breast tumorigenesis. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003;8(4):449-462. [CrossRef]
- Mark KS, Davis TP. Cerebral microvascular changes in permeability and tight junctions induced by hypoxia-reoxygenation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2002;282(4):H1485. 1485. [CrossRef]
- Fischer S, Wobben M, Marti HH, Renz D, Schaper W. Hypoxia-induced hyperpermeability in brain microvessel endothelial cells involves VEGF-mediated changes in the expression of zonula occludens-1. Microvasc Res. 2002;63(1):70-80. [CrossRef]
- Liu P, Zhang R, Liu D, et al. Time-course investigation of blood–brain barrier permeability and tight junction protein changes in a rat model of permanent focal ischemia. J Physiol Sci. 2018;68(2):121-127. [CrossRef]
- Hawkins BT, Davis TP. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(2):173-185. [CrossRef]
- Sandoval KE, Witt KA. Blood-brain barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis. 2008;32(2):200-219. [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki S, Sato S, Yamaguchi H, Kamoi M, Asashima T, Terasaki T. Exogenous expression of claudin-5 induces barrier properties in cultured rat brain capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2007;210(1):81-86. [CrossRef]
- Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, et al. Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 2003;161(3):653-660. [CrossRef]
- Liu W, Hendren J, Qin XJ, Shen J, Liu KJ. Normobaric hyperoxia attenuates early blood-brain barrier disruption by inhibiting MMP-9-mediated occludin degradation in focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 2009;108(3):811-820. [CrossRef]
- Nicolae MANOLESCU B, Biochemist L, Jickling GC, Nicolae Manolescu B, Nenitescu C. Maedica-a Journal of Clinical Medicine New Approach to Identify Ischemic Stroke Patients at Risk to Develop Hemorrhagic Transformation. Vol 7.; 2012.
- Yang Y, Thompson JF, Taheri S, et al. Early inhibition of MMP activity in ischemic rat brain promotes expression of tight junction proteins and angiogenesis during recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(7):1104-1114. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Neuronal death and changes in astrocytes following BCCAO. (A, C and D) Quantitative analysis shows significant differences in the number of NeuN-positive cells (A) and GFAP labelled astrocyte cells (C and D) in the hippocampus of sham-operated and stroke mice (n=6). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 unpaired Student’s t-test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (B and E) Representative photomicrographs showing immunofluorescence staining of NeuN-labelled cells (B) and GFAP-labelled astrocytes (E) in the CA1 area of the hippocampus in control and stroke mice. Scale bars: 20 μm, magnification × 40 (B, E) and the images are taken at the level of Bregma -2.06mm.
Figure 1.
Neuronal death and changes in astrocytes following BCCAO. (A, C and D) Quantitative analysis shows significant differences in the number of NeuN-positive cells (A) and GFAP labelled astrocyte cells (C and D) in the hippocampus of sham-operated and stroke mice (n=6). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 unpaired Student’s t-test. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. (B and E) Representative photomicrographs showing immunofluorescence staining of NeuN-labelled cells (B) and GFAP-labelled astrocytes (E) in the CA1 area of the hippocampus in control and stroke mice. Scale bars: 20 μm, magnification × 40 (B, E) and the images are taken at the level of Bregma -2.06mm.
Figure 2.
Changes in TJ proteins following BCCAO. Representative photomicrographs showing immunofluorescence staining for ZO-1 with anti-ZO-1 (A), Occludin with anti-Occludin (B), and Claudin-5 with anti-Claudin-5 (C), and DAPI-labelled nuclei in the CA1 area of the hippocampus of control and stroke mice. The labelled TJs are disrupted in the stroke brain (arrows) compared to the intact TJs in the control. Scale bar=10 μm, magnification × 60, and the images are taken at the level of Bregma-2.06mm.
Figure 2.
Changes in TJ proteins following BCCAO. Representative photomicrographs showing immunofluorescence staining for ZO-1 with anti-ZO-1 (A), Occludin with anti-Occludin (B), and Claudin-5 with anti-Claudin-5 (C), and DAPI-labelled nuclei in the CA1 area of the hippocampus of control and stroke mice. The labelled TJs are disrupted in the stroke brain (arrows) compared to the intact TJs in the control. Scale bar=10 μm, magnification × 60, and the images are taken at the level of Bregma-2.06mm.
Figure 3.
WB analysis of protein expressions following BCCAO. Western blotting (WB) analysis of (A) GFAP, (B) Occludin, (C) ZO-1 and (D) Claudin-5 expressions in the hippocampus of sham-operated and BCCAO mice (n=6). The analysis includes band density and quantification analysis. ß-actin was used as a loading control. (**P < 0.01, Mann-Whitney test). Data presented as mean ± SD. The Control group was set as 1 in comparison to the BCCAO group.
Figure 3.
WB analysis of protein expressions following BCCAO. Western blotting (WB) analysis of (A) GFAP, (B) Occludin, (C) ZO-1 and (D) Claudin-5 expressions in the hippocampus of sham-operated and BCCAO mice (n=6). The analysis includes band density and quantification analysis. ß-actin was used as a loading control. (**P < 0.01, Mann-Whitney test). Data presented as mean ± SD. The Control group was set as 1 in comparison to the BCCAO group.
Figure 4.
Analysis of biomarkers in serum. Serum levels of A: GFAP, B: Occludin, C: ZO-1 and D: Claudin-5 in control and BCCAO stroke mice (n=8). A significant difference in the serum levels of biomarkers in control and BCCAO mice (A: GFAP, p=0.0002), (B: Occludin, p<0.0001), (C: ZO-1, p<0.0001) and (D: Claudin-5, p<0.0001). ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.001 unpaired Student’s t-test.
Figure 4.
Analysis of biomarkers in serum. Serum levels of A: GFAP, B: Occludin, C: ZO-1 and D: Claudin-5 in control and BCCAO stroke mice (n=8). A significant difference in the serum levels of biomarkers in control and BCCAO mice (A: GFAP, p=0.0002), (B: Occludin, p<0.0001), (C: ZO-1, p<0.0001) and (D: Claudin-5, p<0.0001). ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.001 unpaired Student’s t-test.
Figure 5.
Correlation between expression of biomarkers in serum and hippocampus. Correlation between serum levels (pg/ml) of A: GFAP, B: Occludin, C: ZO-1 and D: Claudin-5 and these proteins’ expressions in hippocampal tissue of the brain. Spearman correlation was used. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant; 2-tailed, unpaired t-test.
Figure 5.
Correlation between expression of biomarkers in serum and hippocampus. Correlation between serum levels (pg/ml) of A: GFAP, B: Occludin, C: ZO-1 and D: Claudin-5 and these proteins’ expressions in hippocampal tissue of the brain. Spearman correlation was used. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant; 2-tailed, unpaired t-test.
Table 1.
Detection range, sensitivity and specificity for mouse ELISA kits used.
Table 1.
Detection range, sensitivity and specificity for mouse ELISA kits used.
| ELISA kit name and catalogue number |
Detection range |
Sensitivity |
Specificity |
| Mouse GFAP ELISA Kit (Fine test, EM0335) |
15.625 -1000 pg/ml |
<9.375pg/ml |
For quantitative detection of GFAP in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates andother biological fluids. |
| Mouse Occludin ELISA Kit (AVIVA Systems Biology, OKEH 07095), |
0.156 – 10 ng/ml |
<0.078 ng/ml |
Mouse Occludin UniProt ID: Q61146 GeneID: 18260 Target Alias: AI503564, Occludin, Ocl. |
| Mouse Claudin-5 ELISA kit (DL EVELOP, DL-CLDN5-Mu) |
0.312-20ng/ml |
<0.127ng/ml |
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for the detection ofCLDN5. |
| Mouse TJP1 (Tight junction protien ZO-1) ELISA Kit (Elabscience, E-EL-M1161) |
78.13-5000pg/ml |
46.88pg/ml |
This kit recognizes Mouse TJP1 in samples. |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).