Submitted:
19 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study design, data collection, sampling and definition of cohorts.
Outcome variables
Statistical analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, W.J.; Liang, W.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.R.; Chen, Z.S.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, R.C.; Tang, C.L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis. Eur Respir J 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID 19) Dashboard. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/. (Accessed on 16 September 2023).
- Song, J.; Zeng, M.; Wang, H.; Qin, C.; Hou, H.Y.; Sun, Z.Y.; Xu, S.P.; Wang, G.P.; Guo, C.L.; Deng, Y.K.; Wang, Z.C.; Ma, J.; Pan, L.; Liao, B.; Du, Z.H.; Feng, Q.M.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.G.; Liu, Z. Distinct effects of asthma and COPD comorbidity on disease expression and outcome in patients with COVID-19. Allergy. 2021, 76, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espiritu, A.I.; Sucaldito, M.S.F.P.; Ona, D.I.D.; Apor, A.D.A.O.; Sy, M.C.C.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Jamora, R.D.G. Clinical outcomes in COVID-19 among patients with hypertension in the Philippine CORONA Study. Eur J Med Res 2023, 28, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anlacan, V.M.M.; Piamonte, B.L.C.; Sy, M.C.C.; Villanueva, E.Q.; Jamora, R.D.G.; Espiritu, A.I. Clinical outcomes of older persons and persons with dementia admitted for coronavirus disease 2019: findings from the Philippine CORONA Study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2022, 51, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamora, R.D.G.; Prado, M.B.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Sy, M.C.C.; Espiritu, A.I. Incidence and risk factors for stroke in patients with COVID-19 in the Philippines: an analysis of 10,881 cases. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022, 31, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espiritu, A.I.; Reyes, N.G.D.; Leochico, C.F.D.; Villanueva, E.Q.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Jamora, R.D.G. Body mass index and its association with COVID-19 clinical outcomes: findings from the Philippine CORONA Study. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2022, 49, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espiritu, A.I.; Larrazabal, R.B.; Sy, M.C.C.; Villanueva, E.Q.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Jamora, R.D. Outcomes and risk factors of patients with COVID-19 and cancer (ONCORONA): findings from the Philippine CORONA Study. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 857076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espiritu, A.I.; Chiu, H.H.C.; Sy, M.C.C.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; The Philippine CORONA Study Group, Jamora, R. D.G. The outcomes of patients with diabetes mellitus in The Philippine CORONA Study. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 24436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espiritu, A.I.; Bravo, S.L.R.; Sombilla, H.A.A.; Tantengco, O.A.G.; Sy, M.C.C.; Sy, A.D.R.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Jamora, R.D.G. Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 infection in pregnant and non-pregnant women: results from The Philippine CORONA Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease. Global strategy for prevention, diagnosis and management of COPD: 2023 report. Available online: https://goldcopd.org. (Accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Espiritu, A.I.; Sy, M.C.C.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Jamora, R.D.G.; Philippine CORONA Study Group, Investigators. COVID-19 Outcomes of 10,881 patients: Retrospective study Of Neurological symptoms and Associated manifestations (Philippine CORONA Study). J Neural Trans (Vienna) 2021, 128, 1687–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espiritu, A.I.; Sy, M.C.C.; Anlacan, V.M.M.; Jamora, R.D.G. The Philippine COVID-19 Outcomes: a Retrospective study Of Neurological manifestations and Associated symptoms (The Philippine CORONA Study): a protocol study. BMJ Open. 2020, 10, e040944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruma, Y.; Manabe, T.; Fujikura, Y.; Iikura, M.; Hojo, M.; Kudo, K. Effect of asthma, COPD, and ACO on COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS One. 2022, 17, e0276774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerayeli, F.V.; Milne, S.; Cheung, C.; Li, X.; Yang, C.W.T.; Tam, A.; Choi, L.H. ; Bae A; Sin D.D. COPD and the risk of poor outcomes in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2021, 33, 100789. [Google Scholar]
- Bonato, M.; Semenzato, U.; Tinè, M.; Bazzan, M.; Damin, M.; Biondini, D.; Casara, A.; Romagnoli, M.; Turato, G.; Cosio, M.G.; Saetta M., Baraldo, S. Risk factors for development and severity of COVID-19 in COPD patients. Front Med (Lausanne) 2021, 8, 714570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.M.; Niikura, M.; Yang, C.W.; Sin, D.D. COVID-19 and COPD. Eur Respir J. 2020, 56, 2002108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.M.; Yang, C.X.; Tam, A.; Shaipanich, T.; Hackett, T.L.; Singhera, G.K.; Dorscheid, D.R.; Sin, D.D. ACE-2 expression in the small airway epithelia of smokers and COPD patients: implications for COVID-19. Eur Respir J. 2020, 55, 2000688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotwica, A.; Knights, H.; Mayor, N.; Russell-Jones, E.; Dassios, T.; Russell-Jones, D. Intrapulmonary shunt measured by bedside pulse oximetry predicts worse outcomes in severe COVID-19. Eur Respir J 2021, 57, 2003841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Mathioudakis, A.G.; Higham, A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and COVID-19: interrelationships. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2022, 28, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Features | All patients | With COPD | Without COPD |
p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 10,881) | (n = 156) | (n = 10,725) | ||
| Socio-demographic data | ||||
| Age group | <0.001 | |||
| 19 – 59 y, n (%) | 7047 (64.7) | 33 (21.2%) | 7014 (65.4%) | |
| ≥ 60 y, n (%) | 3834 (35.2%) | 123 (78.8%) | 3711 (34.6%) | |
| Female, n (%) | 5099 (46.9%) | 25 (16.0%) | 5074 (47.3%) | <0.001 |
| Ever-smoker (past/ current), n (%) | 1026 (9.4%) | 82 (52.5%) | 944 (8.8%) | <0.001 |
| Non-neurologic comorbidities, n (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 3647 (33.5%) | 104 (66.7%) | 3543 (33.0%) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2191 (20.1%) | 61 (39.1%) | 2130 (19.8%) | <0.001 |
| Chronic cardiac diseasea | 512 (4.7%) | 29 (18.6%) | 483 (4.5%) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 611 (5.6%) | 17 (10.9%) | 594 (5.5%) | 0.004 |
| Chronic liver disease | 60 (0.6%) | 2 (1.2%) | 58 (0.5%) | 0.212 |
| Malignancy | 244 (2.2%) | 4 (2.5%) | 240 (2.2%) | 0.781 |
| HIV/ AIDS | 37 (0.3%) | - | 37 (0.3%) | 1.000 |
| Past neurologic history, n (%) | ||||
| Stroke/ cerebrovascular | 321 (3.0%) | 10 (6.4%) | 311 (2.9%) | 0.026 |
| Epilepsy | 27 (0.3%) | - | 27 (0.3%) | 1.000 |
| Neurodegenerativeb | 44 (0.4%) | 3 (1.9%) | 41 (0.4%) | 0.025 |
| Headache syndrome | 5 (0.1%) | - | 5 (0.1%) | 1.000 |
| Demyelinating disorder | 2 (0.0%) | - | 2 (0.0%) | 1.000 |
| Central nervous system infection | 5 (0.1%) | - | 5 (0.1%) | 1.000 |
| Peripheral nervous system disordersc | 15 (0.1%) | - | 15 (0.1%) | 1.000 |
| Respiratory and constitutional symptoms, n (%) | ||||
| Fever | 3927 (36.1%) | 80 (51.2%) | 3847 (35.9%) | <0.001 |
| Cough | 4411 (40.5%) | 114 (73.1%) | 4297 (40.1%) | <0.001 |
| Dyspnea | 2703 (24.8%) | 106 (67.9%) | 2597 (24.2%) | <0.001 |
| Rhinorrhea | 607 (5.6%) | 6 (3.9%) | 601 (5.6%) | 0.342 |
| Sputum production | 637 (5.9%) | 23 (14.7%) | 614 (5.7%) | <0.001 |
| Sore throat | 751 (6.9%) | 9 (5.8%) | 742 (6.9%) | 0.574 |
| Diarrhea | 597 (5.5%) | 5 (3.2%) | 592 (5.5%) | 0.208 |
| Fatigue | 713 (6.6%) | 15 (9.6%) | 698 (6.5%) | 0.119 |
| Others | 1674 (15.3%) | 16 (10.2%) | 1658 (15.4%) | 0.074 |
| New onset neurological symptoms, n (%) | ||||
| Headache | 607 (5.6%) | 5 (3.2%) | 602 (5.6%) | 0.193 |
| Nausea or vomiting | 158 (1.5%) | 2 (1.3%) | 156 (1.5%) | 1.000 |
| Seizure | 96 (0.9%) | 1 (0.6%) | 95 (0.9%) | 1.000 |
| Altered mental stated | 518 (4.7%) | 13 (8.3%) | 505 (4.7%) | 0.035 |
| Olfactory or taste dysfunction | 663 (6.1%) | 6 (3.9%) | 657 (6.1%) | 0.237 |
| Dysfunctions of other sensese | 166 (1.5%) | 1 (0.6%) | 165 (1.5%) | 0.735 |
| Bulbar symptomsf | 122 (1.1%) | 2 (1.3%) | 120 (1.1%) | 0.695 |
| Motor symptoms | 246 (2.2%) | 5 (3.2%) | 241 (2.3%) | 0.406 |
| Sensory symptoms | 53 (0.5%) | 1 (0.6%) | 52 (0.4%) | 0.536 |
| Myalgia | 256 (2.4%) | 6 (3.9%) | 250 (2.3%) | 0.186 |
| Othersg | 33 (0.3%) | 1 (0.6%) | 32 (0.3%) | 0.380 |
| New-onset neurological disorders/ complications, n (%) | ||||
| Encephalopathyh | 644 (5.9%) | 19 (12.1%) | 625 (5.8%) | 0.001 |
| Symptomatic seizure/ status epilepticus | 125 (1.2%) | 1 (0.6%) | 124 (1.1%) | 1.000 |
| Stroke/ cerebrovasculari | 367 (3.4%) | 9 (5.8%) | 358 (3.3%) | 0.095 |
| Central nervous system infectionj | 7 (0.07%) | - | 7 (0.07%) | 1.000 |
| Othersk | 14 (0.1%) | - | 14 (0.1%) | 1.000 |
| Treatment/s received, n (%) | ||||
| Glucocorticoids | 2844 (26.1%) | 87 (55.8%) | 2757 (25.7%) | <0.001 |
| Tocilizumab | 1029 (9.5%) | 24 (15.3%) | 1005 (9.4%) | 0.011 |
| Antivirall | 1902 (17.4%) | 46 (29.5%) | 1856 (17.3%) | <0.001 |
| Antibacterial | 9014 (82.8%) | 150 (96.2%) | 8864 (82.7%) | <0.001 |
| Othersm | 3905 (35.9%) | 75 (48.1%) | 3830 (35.7%) | 0.001 |
| aIncludes heart failure, coronary artery disease, prior history of myocardial infarction, and other cardiac conditions | ||||
| bIncludes dementia, and movement disorders | ||||
| cIncludes peripheral nerve disease, neuromuscular junction disorder, and muscle disorder | ||||
| dIncludes altered sensorium, and confusion | ||||
| eIncludes visual, hearing, and vestibular dysfunctions | ||||
| fIncludes facial paresthesia, facial weakness, dysarthria, dysphonia, dysphagia, tongue weakness, and neck weakness | ||||
| gIncludes tremor, dystonia, choreoathetosis, bradykinesia, ataxia, and meningisimus | ||||
| hIncludes encephalopathy and anoxic brain injury | ||||
| iAny acute cerebrovascular disease (no need to distinguish between infarction, hemorrhagic) | ||||
| jIncludes encephalitis, meningitis, and meningoencephalitis | ||||
| kIncludes acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, optic neuritis, sensory ganglionitis, radiculitis, anterior horn syndrome, peripheral neuritis (Guillain Barre Syndrome, other than Guillain Barre Syndrome), neuromuscular disorder, and myositis | ||||
| lIncludes remdesivir, lopinavir, and ritonavir | ||||
| mIncludes chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, convalescent plasma, and other therapies | ||||
| COPD – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; HIV/ AIDS – Human immunodeficiency virus/ Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome | ||||
| Outcomes | All patients | With COPD | Without COPD | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 10,881) | (n = 156) | (n = 10,725) | ||
| COVID-19 severity at nadir | <0.001 | |||
| Mild/ moderate, n (%) | 6690 (62.2%) | 43 (28.3%) | 6647 (62.7%) | |
| Severe, n (%) | 2354 (21.9%) | 58 (38.1%) | 2296 (21.7%) | |
| Critical, n (%) | 1707 (15.9%) | 51 (33.6%) | 1656 (15.6%) | |
| In-hospital mortality | 1702 (15.6%) | 60 (38.4%) | 1642 (15.3%) | <0.001 |
| Time to in-hospital mortality in days, median (IQR; range) | 15 (13; 1 to 78) | 20 (15.5; 2 to 65) | 15 (13; 1 to 78) | 0.004 |
| Respiratory failure, n (%) | 1608 (14.7%) | 59 (37.8%) | 1549 (14.4%) | <0.001 |
| Cause/sa | ||||
| Pneumonia | 891 (55.4%) | 30 (50.9%) | 861 (55.6%) | 0.472 |
| Acute respiratory distress syndrome | 845 (52.6%) | 43 (72.8%) | 802 (51.7%) | 0.001 |
| Shock | 140 (8.7%) | 3 (5.1%) | 137 (8.8%) | 0.315 |
| Central neurologic cause | 86 (5.4%) | 1 (1.7%) | 85 (5.5%) | 0.368 |
| Pulmonary edema | 32 (2.0%) | 1 (1.7%) | 31 (2.0%) | 1.000 |
| Pulmonary embolism | 19 (1.1%) | 2 (3.4%) | 17 (1.1%) | 0.152 |
| Time to respiratory failure in days, median (IQR; range) | 5 (4; 0 to 20) | 6 (4; 1 to 13) | 5 (4; 0 to 20) | 0.342 |
| Duration of invasive mechanical venticlation in days, median (IQR; range) | 13 (12; 0 to 75) | 15 (14; 1 to 62) | 13 (12; 0 to 75) | 0.150 |
| Admitted to ICU, n (%) | 1740 (15.99%) | 70 (44.87%) | 1670 (15.57%) | <0.001 |
| Time to ICU admission in days, median (IQR; range) | 5 (4; 0 to 20) | 5 (5; 0 to 17) | 5 (4; 0 to 20) | 0.290 |
| Length of ICU stay in days, median (IQR; range) | 15 (11; 0 to 77) | 15 (14; 1 to 64) | 15 (11; 0 to 77) | 0.923 |
| Length of hospital stayb in days, median (IQR; range) | 13 (9; 1 to 78) | 14 (10; 2 to 65) | 13 (9; 1 to 78) | 0.003 |
| Neurologic deficits, n (%) | 2291 (21.0%) | 35 (22.4%) | 2256 (21.0%) | 0.670 |
| Neurologic outcomec | <0.001 | |||
| Full/ partial improvement of neurologic deficits, n (%) | 1639 (88.0%) | 12 (57.1%) | 1627 (86.3%) | |
| No improvement of neurologic deficits, n (%) | 266 (13.9%) | 9 (42.8%) | 257 (13.6%) | |
| aNon-mutually exclusive | ||||
| bDerived from overall length of stay for patients who were never admitted to the ICU; excludes length of ICU stay for those who were admitted in the ICU | ||||
| cPatients with recorded data for neurologic outcome (n = 1905) | ||||
| COPD – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; COVID-19 – Coronavirus disease 2019; IQR – Interquartile range; ICU – intensive care unit | ||||
| Outcomes | Estimatea | 95% Confidence Interval | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dichotomous outcomes | |||
| Severe/ critical COVID-19 at nadirb | 4.26 | 2.99, 6.08 | <0.001 |
| Neurologic deficit/s | 1.09 | 0.74, 1.59 | 0.670 |
| Full/ partial improvement of neurologic deficit/s | 0.21 | 0.09, 0.50 | <0.001 |
| In-hospital mortality | 3.46 | 2.49, 4.79 | <0.001 |
| Respiratory failure | 3.60 | 2.60, 5.00 | <0.001 |
| ICU admission | 4.41 | 3.21, 6.08 | <0.001 |
| Time-to-event outcomes | |||
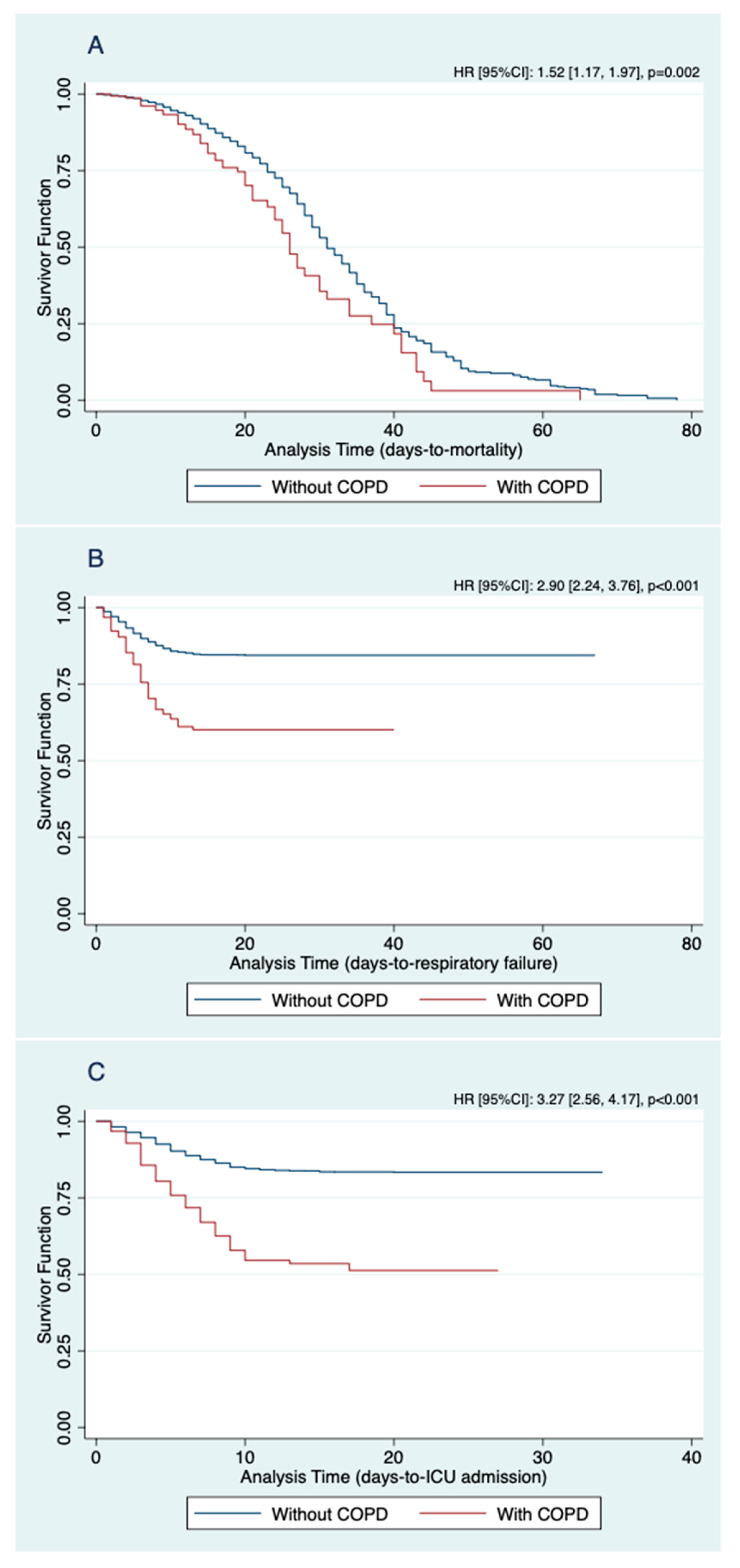
| In-hospital mortality | 1.52 | 1.17, 1.97 | 0.002 |
| Respiratory failure | 2.90 | 2.24, 3.76 | <0.001 |
| ICU admission | 3.27 | 2.56, 4.17 | <0.001 |
| Count outcomes | |||
| Days of invasive mechanical ventilation | 1.15 | 1.08, 1.22 | <0.001 |
| Days of ICU stay | |||
| Among mild/ moderate COVID-19 | 0.88 | 0.65, 1.21 | 0.435 |
| Among severe COVID-19 | 1.02 | 0.92, 1.13 | 0.688 |
| Among critical COVID-19 | 1.04 | 0.97, 1.12 | 0.273 |
| Days of hospital stay | |||
| Among mild/ moderate COVID-19 | 0.98 | 0.91, 1.06 | 0.656 |
| Among severe COVID-19 | 1.17 | 1.10, 1.23 | <0.001 |
| Among critical COVID-19 | 1.15 | 1.08, 1.22 | <0.001 |
| a Odds ratio for ordered and dichotomous outcomes, hazard ratio for time-to-event outcomes, and incidence rate ratio for count outcomes | |||
| b Dichotomized to mild/moderate, and severe/critical, due to violation of the proportional odds assumption of ordinal logistic regression for the three-level severity, i.e., mild/moderate, severe, and critical | |||
| COPD – Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; COVID-19 – Coronavirus disease 2019; ICU – Intensive care unit | |||
| Outcomes | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| COVID-19 severity at nadira | 1.78 | 1.58, 2.01 | <0.001 |
| In-hospital mortalityb | 1.90 | 1.63, 2.21 | <0.001 |
| a Ordered outcomes: mild/ moderate, severe, and critical | |||
| b Dichotomous outcomes: in-hospital mortality and discharged | |||
| COVID-19 – Coronavirus disease 2019; IQR – Interquartile range | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





