Submitted:
15 September 2023
Posted:
20 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The therapeutic properties of lutein’s biologic activity against disease
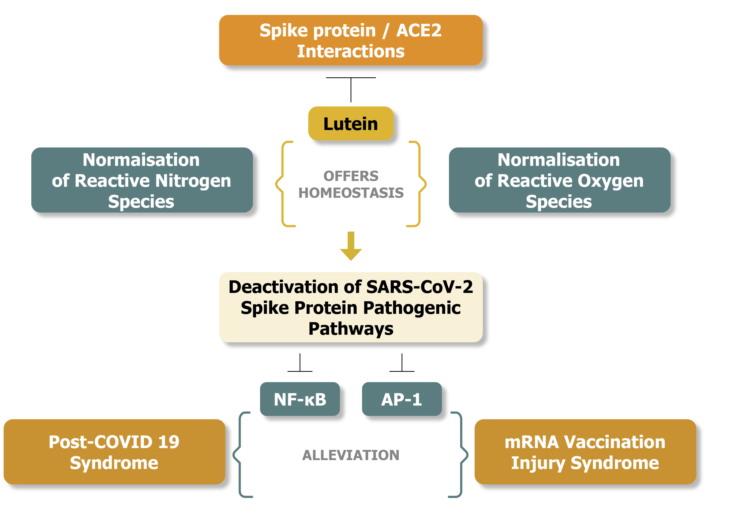
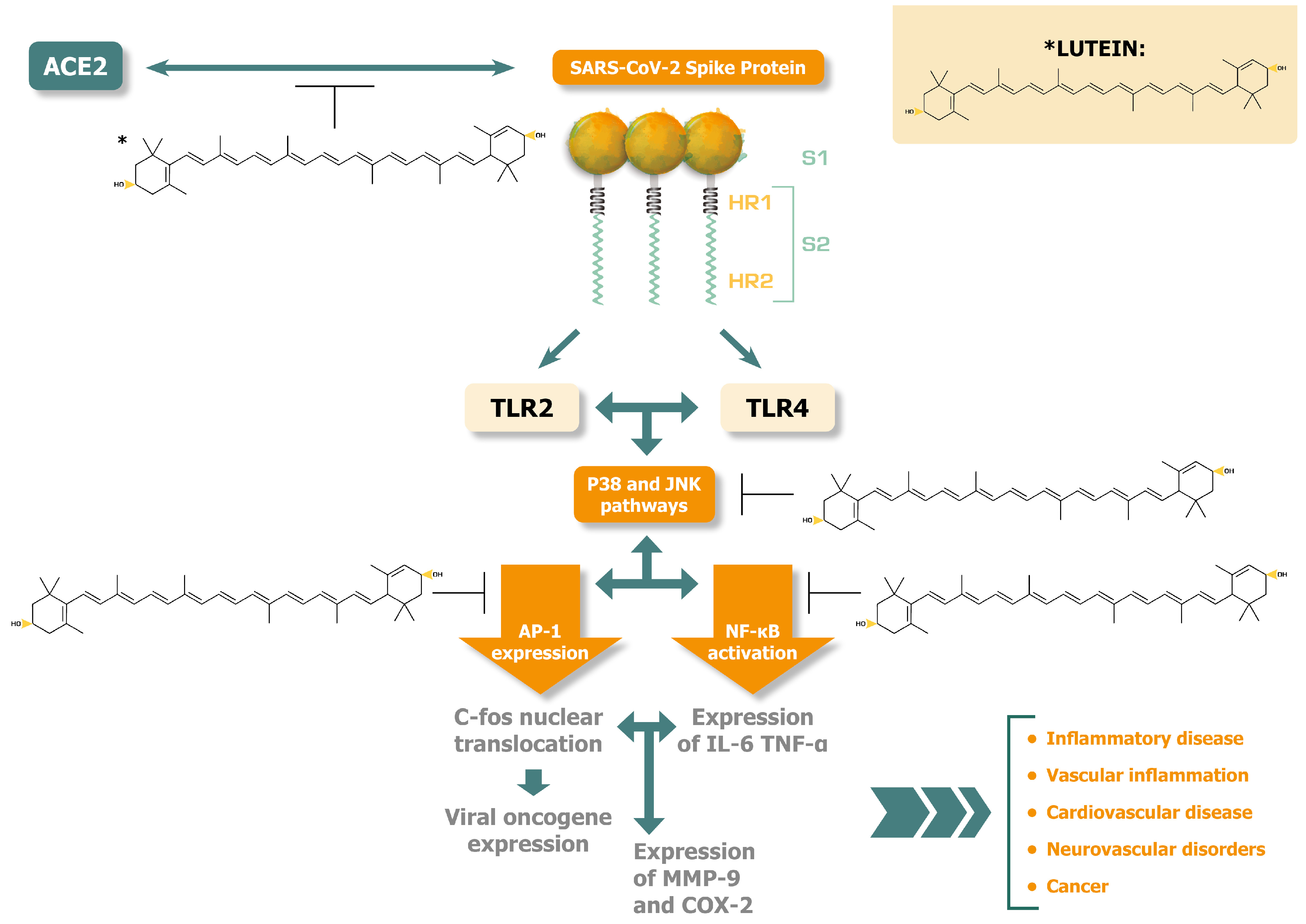
3. Beyond the ROS scavenging properties of lutein. Relations to alleviations of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induced pathology
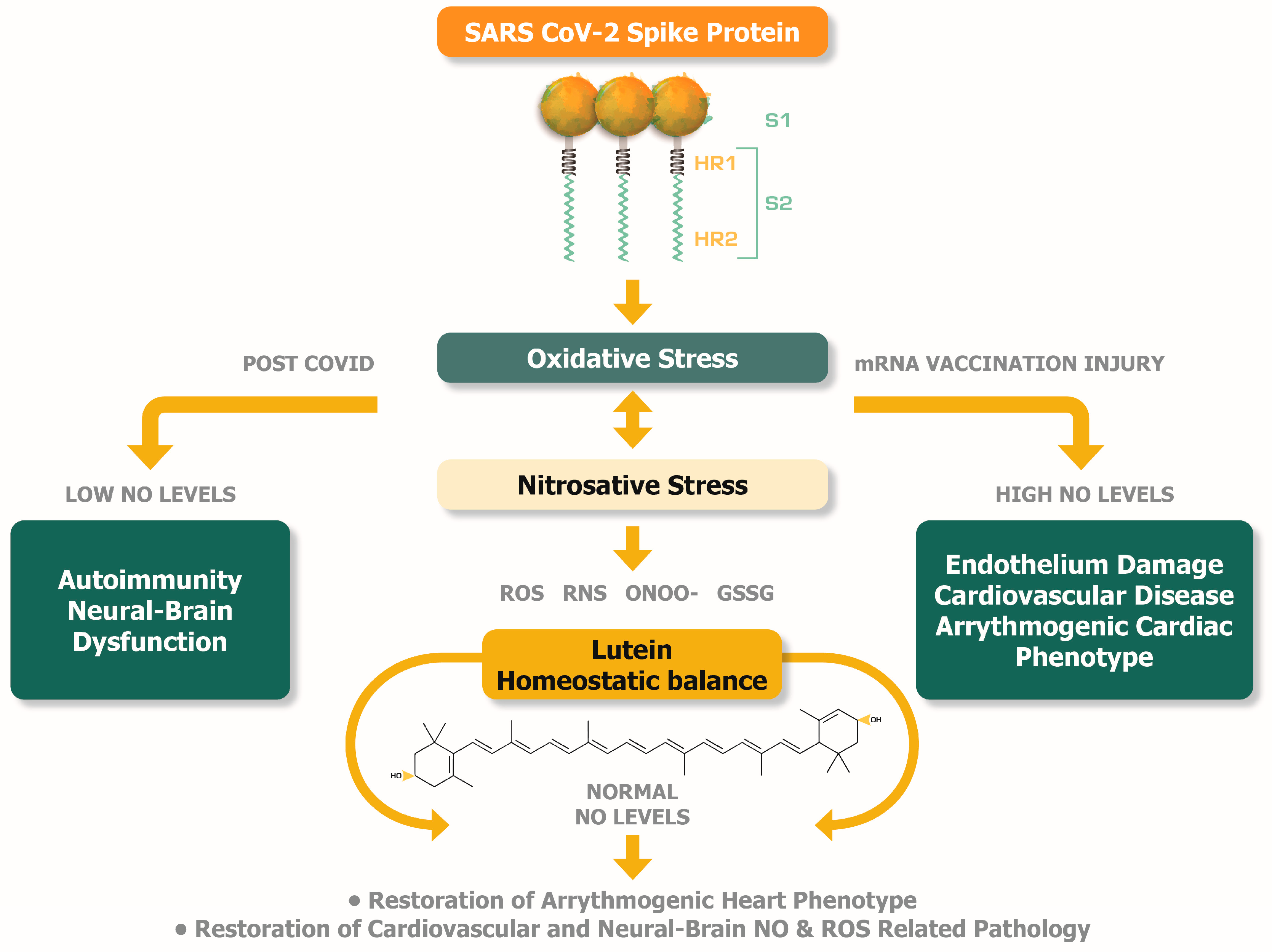
4. Lutein, oxidative stress, post-COVID syndrome, and mRNA vaccination injuries
5. The ROS and RNS imbalance during post-COVID and mRNA injury syndromes -- The potential therapeutic role of lutein
5.1. The redox buffering mechanism that protects from ROS-induced arrythmias
5.2. Abnormal levels of NO can reveal the underlying cardiovascular and brain pathologic conditions in post-COVID and mRNA injury syndrome
6. The nutritional supplementation of lutein can potentially alleviate the pathologic levels of NO found in post-COVID and mRNA injury syndromes.
7. Why lutein-rich food can be an ideal supplement
8. Synergy with other natural compounds against post-COVID and mRNA vaccination injuries
9. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitra S, Rauf A, Tareq AM, Jahan S, Emran TB, Shahriar TG, et al. Potential health benefits of carotenoid lutein: An updated review. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021; 154: 112328. [CrossRef]
- Leermakers ET, Darweesh SK, Baena CP, Moreira EM, Melo van Lent D, Tielemans MJ, Muka T, et al. The effects of lutein on cardiometabolic health across the life course: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;103(2):481-94. [CrossRef]
- Gandla K, Babu AK, Unnisa A, Sharma I, Singh LP, Haque MA, et al. Carotenoids: Role in neurodegenerative diseases remediation. Brain Sci. 2023; 13(3): 457. [CrossRef]
- Melo van Lent D, Leermakers ETM, Darweesh SKL, Moreira EM, Tielemans MJ, Muka T, et al. The effects of lutein on respiratory health across the life course: A systematic review. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2016;13:e1-e7. [CrossRef]
- Brahmi F, Vejux A, Ghzaiel I, Ksila M, Zarrouk A, Ghrairi T, et al. Role of diet and nutrients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Incidence on oxidative stress, Inflammatory Status and Viral Production. Nutrients. 2022 ;14(11):2194. 25 May. [CrossRef]
- Khalil A, Tazeddinova D, Aljoumaa K, Kazhmukhanbetkyzy ZA, Orazov A, Toshev AD. Carotenoids: Therapeutic strategy in the battle against viral emerging diseases, COVID-19: An overview. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2021; 26(3): 241-261. [CrossRef]
- Becerra MO, Contreras LM, Lo MH, Díaz JM, Herrera GC. Lutein as a functional food ingredient: Stability and bioavailability. Journal of Functional Foods. 2020; 66: 103771. [CrossRef]
- Korobelnik JF, Rougier MB, Delyfer MN, Bron A, Merle BMJ, Savel H, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation with lutein, zeaxanthin, and ω-3 on macular pigment: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017; 135(11): 1259-1266. [CrossRef]
- Azar G, Quaranta-El Maftouhi M, Masella JJ, Mauget-Faÿsse M. Macular pigment density variation after supplementation of lutein and zeaxanthin using the Visucam® 200 pigment module: Impact of age-related macular degeneration and lens status. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2017; 40(4): 303-313. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakeim HK, Al-Rubaye HT, Al-Hadrawi DS, Almulla AF, Maes M. Long-COVID post-viral chronic fatigue and affective symptoms are associated with oxidative damage, lowered antioxidant defenses and inflammation: A proof of concept and mechanism study. Mol Psychiatry. 2023; 28(2): 564-578. [CrossRef]
- Dursun AD, Saricam E, Sariyildiz GT, Iscanli MD, Cantekin ÖF. The evaluation of oxidative stress in the young addults with COVID-19 mRNA vaccines induced acute pericarditis- myopericarditis. Int J Gen Med. 2022; 15: 161-167. [CrossRef]
- Kim JK, Park SU. Current results on the potential health benefits of lutein. EXCLI J. 2016; 15: 308-14. [CrossRef]
- Algan AH, Gungor-Ak A, Karatas A. Nanoscale delivery systems of lutein: An updated review from a pharmaceutical perspective. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9): 1852. [CrossRef]
- Shechter A, Yelin D, Margalit I, Abitbol M, Morelli O, Hamdan A, et al. Assessment of adult patients with long COVID manifestations suspected as cardiovascular: A single-center experience. J Clin Med 2022; 11: 6123. [CrossRef]
- Seneff S, Nigh G, Kyriakopoulos AM, McCullough PA. Innate immune suppression by SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccinations: The role of G-quadruplexes, exosomes, and MicroRNAs. Food Chem Toxicol. 2022; 164: 113008. [CrossRef]
- Chew BP, Brown CM, Park JS, Mixter PF. Dietary lutein inhibits mouse mammary tumor growth by regulating angiogenesis and apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2003; 23(4): 3333-9.
- Gong X, Smith JR, Swanson HM, Rubin LP. Carotenoid lutein selectively inhibits breast cancer cell growth and potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic agents through ROS-mediated mechanisms. Molecules. 2018; 23(4): 905. [CrossRef]
- Chung RWS, Leanderson P, Lundberg AK, Jonasson L. Lutein exerts anti-inflammatory effects in patients with coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 2017; 262: 87-93. [CrossRef]
- Kim JE, Leite JO, DeOgburn R, Smyth JA, Clark RM, Fernandez ML. A lutein-enriched diet prevents cholesterol accumulation and decreases oxidized LDL and inflammatory cytokines in the aorta of guinea pigs. J Nutr. 2011; 141(8): 1458-63. [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh-Sharafabad F, Ghoreishi Z, Maleki V, Tarighat-Esfanjani A. Mechanistic insights into the effect of lutein on atherosclerosis, vascular dysfunction, and related risk factors: A systematic review of in vivo, ex vivo and in vitro studies. Pharmacol Res. 2019; 149: 104477. [CrossRef]
- Liu XH, Yu RB, Liu R, Hao ZX, Han CC, Zhu ZH, Ma L. Association between lutein and zeaxanthin status and the risk of cataract: a meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2014; 6(1): 452-65. [CrossRef]
- Buscemi S, Corleo D, Di Pace F, Petroni ML, Satriano A, Marchesini G. The effect of lutein on eye and extra-eye health. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9): 1321. [CrossRef]
- Junghans A, Sies H, Stahl W. Macular pigments lutein and zeaxanthin as blue light filters studied in liposomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001; 391(2): 160-4. [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana R, Raju M, Krishnakantha TP, Baskaran V. Lutein and zeaxanthin in leafy greens and their bioavailability: olive oil influences the absorption of dietary lutein and its accumulation in adult rats. J Agric Food Chem. 2007; 55(15): 6395-400. [CrossRef]
- Min JY, Min KB. Serum lycopene, lutein and zeaxanthin, and the risk of Alzheimer's disease mortality in older adults. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2014; 37(3-4): 246-56. [CrossRef]
- Wu W, Li Y, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Liu X. Lutein suppresses inflammatory responses through Nrf2 activation and NF-κB inactivation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 microglia. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015; 59(9): 1663-73. [CrossRef]
- Tan D, Yu X, Chen M, Chen J, Xu J. Lutein protects against severe traumatic brain injury through anti-inflammation and antioxidative effects via ICAM-1/Nrf-2. Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16(4): 4235-4240. [CrossRef]
- Muriach M, Bosch-Morell F, Arnal E, Alexander G, Blomhoff R, Romero FJ. Lutein prevents the effect of high glucose levels on immune system cells in vivo and in vitro. J Physiol Biochem. 2008; 64(2): 149-57. [CrossRef]
- Gopal SS, Eligar SM, Vallikannan B, Ponesakki G. Inhibitory efficacy of lutein on adipogenesis is associated with blockage of early phase regulators of adipocyte differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2021; 1866(1): 158812. [CrossRef]
- Fatani, A.J. , Al-Rejaie, S.S., Parmar, M.Y., Ahmed, O.M., Abuohashish, H.M. and Ahmed, M.M. 2017. Lutein attenuates diabetic-induced renal damage via inhibiting oxidative and nitrosative stresses. Progress in Nutrition. 2017; 19(1): 57–66. [CrossRef]
- Hu BJ, Hu YN, Lin S, Ma WJ, Li XR. Application of lutein and zeaxanthin in nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 2011; 4(3): 303-6. [CrossRef]
- Pap R, Pandur E, Jánosa G, Sipos K, Agócs A, Deli J. Lutein exerts antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory effects and influences iron utilization of BV-2 microglia. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021; 10(3): 363. [CrossRef]
- Chao SC, Nien CW, Iacob C, Hu DN, Huang SC, Lin HY. Effects of lutein on hyperosmoticity-induced upregulation of IL-6 in cultured corneal epithelial cells and its relevant signal pathways. J Ophthalmol. 2016; 2016: 8341439. [CrossRef]
- Elvira-Torales LI, García-Alonso J, Periago-Castón MJ. Nutritional importance of carotenoids and their effect on liver health: A review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019; 8(7): 229. [CrossRef]
- Kim JE, Clark RM, Park Y, Lee J, Fernandez ML. Lutein decreases oxidative stress and inflammation in liver and eyes of guinea pigs fed a hypercholesterolemic diet. Nutr Res Pract. 2012; 6(2): 113-9. [CrossRef]
- Sharavana G, Joseph GS, Baskaran V. Lutein attenuates oxidative stress markers and ameliorates glucose homeostasis through polyol pathway in heart and kidney of STZ-induced hyperglycemic rat model. Eur J Nutr. 2017; 56(8): 2475-2485. [CrossRef]
- Pang R, Tao JY, Zhang SL, Zhao L, Yue X, Wang YF, et al. In vitro antiviral activity of lutein against hepatitis B virus. Phytother Res. 2010; 24(11): 1627-30. [CrossRef]
- Rababi D, Nag A. Evaluation of therapeutic potentials of selected phytochemicals against Nipah virus, a multi-dimensional in silico study. 3 Biotech. 2023; 13(6): 174. [CrossRef]
- Kim E-A, Kang N, Heo S-Y, Oh J-Y, Lee S-H, Cha S-H, et al. Antioxidant, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory activities of lutein-enriched extract of Tetraselmis species. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(7): 369. [CrossRef]
- Behera SK, Mahapatra N, Tripathy CS, Pati S. Drug repurposing for identification of potential inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain: An in-silico approach. Indian J Med Res. 2021; 153(1 & 2): 132-143. [CrossRef]
- Kafi, D.K. , Ayyash, A.N. Density functional theory and molecular docking study to lutein molecule for COVID-19 protease inhibitors. Appl Nanosci. 2023; 13: 5477–5488. [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova VL, Zhang A, Miller MA, Tatineni M, Greenberg JP, Tsigelny IF. Potential SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-ACE2 interface inhibitors: Repurposing FDA-approved drugs. J Explor Res Pharmacol. 2022; 7(1): 17-29. [CrossRef]
- Krinsky NI, Johnson EJ. Carotenoid actions and their relation to health and disease. Mol Aspects Med. 2005; 26(6): 459-516. [CrossRef]
- Lin ZX, Zhang M, Yang R, Min Y, Guo PT, Zhang J, et al. The anti-inflammatory effect of lutein in broilers is mediated by regulating Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid-differentiation-factor 88 signaling pathway. Poult Sci. 2023; 102(6): 102622. [CrossRef]
- Vaure C, Liu Y. A comparative review of toll-like receptor 4 expression and functionality in different animal species. Front Immunol. 2014; 5: 316. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Y, Kuang M, Li J, Zhu L, Jia Z, Guo X, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein interacts with and activates TLR41. Cell Res. 2021; 31(7): 818-820. [CrossRef]
- Kircheis R, Planz O. Could a Lower Toll-like receptor (TLR) and NF-κB activation due to a changed charge distribution in the spike protein be the reason for the lower pathogenicity of omicron? Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(11): 5966. [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos AM, Nigh G, McCullough PA, Seneff S. Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation, p53, and autophagy inhibition characterize the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein induced neurotoxicity. Cureus. 2022; 14(12): e32361. [CrossRef]
- Francisco S, Arranz A, Merino J, Punzón C, Perona R, Fresno M. Early p38 activation regulated by MKP-1 Is determinant for high levels of IL-10 expression through TLR2 activation. Front Immunol. 2021; 12: 660065. [CrossRef]
- McCullough PA, Wynn C, Procter BC. Clinical rationale for SARS-CoV-2 base spike protein detoxification in post COVID-19 and vaccine injury syndromes. Journal of American Physicians and Surgeons 2023; 28(3): 90-94. [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos AM, Nigh G, McCullough PA, Seneff S. Proteolytic targets for SARS-CoV-2 spike protein degradation: Hope for systemic detoxification. Journal of American Physicians and Surgeons 2023; 28(3): 86-93.
- Khan S, Shafiei MS, Longoria C, Schoggins JW, Savani RC, Zaki H. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway. Elife. 2021; 10: e68563. [CrossRef]
- Iordanov M, Bender K, Ade T, Schmid W, Sachsenmaier C, Engel K, et al. CREB is activated by UVC through a p38/HOG-1-dependent protein kinase. EMBO J. 1997; 16(5): 1009-22. [CrossRef]
- Sheng M, McFadden G, Greenberg ME. Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron. 1990; 4(4): 571-82. [CrossRef]
- Bhosale PB, Kim HH, Abusaliya A, Vetrivel P, Ha SE, Park MY, et al. Structural and Functional properties of activator protein-1 in cancer and inflammation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022; 2022: 9797929. [CrossRef]
- Byrns CN, Saikumar J, Bonini NM. Glial AP1 is activated with aging and accelerated by traumatic brain injury. Nat Aging. 2021; 1(7): 585-597. [CrossRef]
- Wu Z, Nicoll M, Ingham RJ. AP-1 family transcription factors: a diverse family of proteins that regulate varied cellular activities in classical Hodgkin lymphoma and ALK+ ALCL. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2021; 10(1): 4. [CrossRef]
- Oh J, Kim JH, Park JG, Yi YS, Park KW, Rho HS, et al. Radical scavenging activity-based and AP-1-targeted anti-inflammatory effects of lutein in macrophage-like and skin keratinocytic cells. Mediators Inflamm. 2013; 2013: 787042. [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos AM, Nagl M, Baliou S, Zoumpourlis V. Alleviating promotion of inflammation and cancer induced by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Int J Inflam. 2017; 2017: 9632018. [CrossRef]
- Yabluchanskiy A, Ma Y, Iyer RP, Hall ME, Lindsey ML. Matrix metalloproteinase-9: Many shades of function in cardiovascular disease. Physiology (Bethesda). 2013; 28(6): 391-403. [CrossRef]
- Allport VC, Slater DM, Newton R, Bennett PR. NF-kappaB and AP-1 are required for cyclo-oxygenase 2 gene expression in amnion epithelial cell line (WISH). Mol Hum Reprod. 2000; 6(6): 561-5. [CrossRef]
- Brasier, AR. The nuclear factor-kappaB-interleukin-6 signalling pathway mediating vascular inflammation. Cardiovasc Res. 2010; 86(2): 211-8. [CrossRef]
- Eferl, R. , Wagner, E. AP-1: a double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 859-868. [CrossRef]
- Raveendran AV, Jayadevan R, Sashidharan S. Long COVID: An overview. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021; 15(3): 869-875. Erratum in: Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022; 16(5): 102504. Erratum in: Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2022; 16(12): 102660. [CrossRef]
- Xu E, Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Long-term neurologic outcomes of COVID-19. Nat Med. 2022; 28: 2406-2415. [CrossRef]
- Raman B, Bluemke DA, Lüscher TF, Neubauer S. Long COVID: post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 with a cardiovascular focus. Eur Heart J. 2022; 43(11): 1157-1172. [CrossRef]
- Tanni SE, Tonon CR, Gatto M, Mota GAF, Okoshi MP. Post-COVID-19 syndrome: Cardiovascular manifestations. Int J Cardiol. 2022; 369: 80-81. [CrossRef]
- Mörz, M. A case report: Multifocal necrotizing encephalitis and myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination against COVID-19. Vaccines (Basel). 2022; 10(10): 1651. [CrossRef]
- Schwab C, Domke LM, Hartmann L, Stenzinger A, Longerich T, Schirmacher P. Autopsy-based histopathological characterization of myocarditis after anti-SARS-CoV-2-vaccination. Clin Res Cardiol. 2023; 112(3): 431-440. [CrossRef]
- Efe C, Kulkarni AV, Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B, Magro B, Stättermayer A, Cengiz M, et al. Liver injury after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: Features of immune-mediated hepatitis, role of corticosteroid therapy and outcome. Hepatology. 2022; 76(6): 1576-1586. [CrossRef]
- Talotta, R. Do COVID-19 RNA-based vaccines put at risk of immune-mediated diseases? In reply to "potential antigenic cross-reactivity between SARS-CoV-2 and human tissue with a possible link to an increase in autoimmune diseases". Clin Immunol. 2021; 224: 108665. [CrossRef]
- Alqatari S, Ismail M, Hasan M, Bukhari R, Al Argan R, Alwaheed A, et al. Emergence of post COVID-19 vaccine autoimmune diseases: A single center study. Infect Drug Resist. 2023; 16: 1263-1278. [CrossRef]
- Giannotta G, Murrone A, Giannotta N. COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: The molecular basis of some adverse events. Vaccines (Basel). 2023; 11(4): 747. [CrossRef]
- Stufano A, Isgrò C, Palese LL, Caretta P, De Maria L, Lovreglio P, et al. Oxidative damage and post-COVID syndrome: A cross-sectional study in a cohort of Italian workers. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(8): 7445. [CrossRef]
- Hilgenberg LGW, Pham B, Ortega M, Walid S, Kemmerly T, O'Dowd DK, Smith MA. Agrin regulation of alpha3 sodium-potassium ATPase activity modulates cardiac myocyte contraction. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284(25): 16956-16965. [CrossRef]
- PHOSP-COVID Collaborative Group. Clinical characteristics with inflammation profiling of long COVID and association with 1-year recovery following hospitalisation in the UK: a prospective observational study. Lancet Respir Med. 2022; 10(8): 761-775. [CrossRef]
- Paul BD, Lemle MD, Komaroff AL, Snyder SH. Redox imbalance links COVID-19 and myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021; 118(34): e2024358118. [CrossRef]
- Damiano RF, Rocca CCA, Serafim AP, Loftis JM, Talib LL, Pan PM, et al. Cognitive impairment in long-COVID and its association with persistent dysregulation in inflammatory markers. Front Immunol. 2023; 14: 1174020. [CrossRef]
- Kılıç Y, Özer A, Tatar T, Zor MH, Kirişçi M, Kartal H, et al. Effect of picroside II on hind limb ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017; 11: 1917-1925. [CrossRef]
- Küçük A, Polat Y, Kılıçarslan A, Süngü N, Kartal H, Dursun AD, et al.Irisin protects against hind limb ischemia reperfusion injury. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021; 15: 361-368. [CrossRef]
- Ntouros PA, Kravvariti E, Vlachogiannis NI, Pappa M, Trougakos IP, Terpos E, et al. Oxidative stress and endogenous DNA damage in blood mononuclear cells may predict anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers after vaccination in older adults. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022; 1868(6): 166393. [CrossRef]
- Espino J, Pariente JA, Rodríguez AB. Oxidative stress and immunosenescence: therapeutic effects of melatonin. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012; 2012: 670294. [CrossRef]
- Dashwood A, Cheesman E, Beard N, Haqqani H, Wong YW, Molenaar P. Understanding how phosphorylation and redox modifications regulate cardiac ryanodine receptor type 2 activity to produce an arrhythmogenic phenotype in advanced heart failure. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020; 3(4): 563-582. [CrossRef]
- Won T, Gilotra NA, Wood MK, Hughes DM, Talor MV, Lovell J, et al. Increased interleukin 18-dependent immune responses are associated with myopericarditis after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination. Front Immunol. 2022; 13: 851620. [CrossRef]
- Lee JK, Kim SH, Lewis EC, Azam T, Reznikov LL, Dinarello CA. Differences in signaling pathways by IL-1beta and IL-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101(23): 8815-20. [CrossRef]
- Kunsch C, Medford RM. Oxidative stress as a regulator of gene expression in the vasculature. Circ Res. 1999; 85(8): 753-66. [CrossRef]
- Chiu SN, Chen YS, Hsu CC, Hua YC, Tseng WC, Lu CW, et al. Changes of ECG parameters after BNT162b2 vaccine in the senior high school students. Eur J Pediatr. 2023; 182(3): 1155-1162. [CrossRef]
- Genco L, Cantelli M, Noto M, Battista T, Patrì A, Fabbrocini G, et al. Alopecia Areata after COVID-19 vaccines. Skin Appendage Disord. 2023; 9(2): 141-143. [CrossRef]
- Prie BE, Voiculescu VM, Ionescu-Bozdog OB, Petrutescu B, Iosif L, Gaman LE, et al. Oxidative stress and alopecia areata. J Med Life. 2015; 8: 43-6.
- Pamukcu B, Lip GY, Shantsila E. The nuclear factor--kappa B pathway in atherosclerosis: a potential therapeutic target for atherothrombotic vascular disease. Thromb Res. 2011; 128(2): 117-23. [CrossRef]
- Meijer CA, Le Haen PA, van Dijk RA, Hira M, Hamming JF, van Bockel JH, et al. Activator protein-1 (AP-1) signalling in human atherosclerosis: results of a systematic evaluation and intervention study. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012; 122(9): 421-8. [CrossRef]
- Morris G, Maes M. Oxidative and nitrosative stress and immune-inflammatory pathways in patients with myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME)/chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Curr Neuropharmacol. 2014; 12(2): 168-85. [CrossRef]
- Ray PD, Huang BW, Tsuji Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 2012; 24(5): 981-90. [CrossRef]
- Nikolaienko R, Bovo E, Zima AV. Redox dependent modifications of ryanodine receptor: Basic mechanisms and implications in heart diseases. Front Physiol. 2018; 9: 1775. [CrossRef]
- Kiss A, Juhász L, Seprényi G, Kupai K, Kaszaki J, Végh A. The role of nitric oxide, superoxide and peroxynitrite in the anti-arrhythmic effects of preconditioning and peroxynitrite infusion in anaesthetized dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 2010; 160(5): 1263-72. [CrossRef]
- Raddino R, Caretta G, Teli M, Bonadei I, Robba D, Zanini G, et al. Nitric oxide and cardiovascular risk factors. Heart Int. 2007; 3(1): 18. [CrossRef]
- Sharma JN, Al-Omran A, Parvathy SS. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology. 2007; 15(6): 252-9. [CrossRef]
- Ueki Y, Miyake S, Tominaga Y, Eguchi K. Increased nitric oxide levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1996; 23(2): 230-6.
- Stephan BCM, Harrison SL, Keage HAD, Babateen A, Robinson L, Siervo M. Cardiovascular disease, the nitric oxide pathway and risk of cognitive impairment and dementia. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2017; 19(9): 87. [CrossRef]
- Wright AL, Zinn R, Hohensinn B, Konen LM, Beynon SB, Tan RP, et al. Neuroinflammation and neuronal loss precede Aβ plaque deposition in the hAPP-J20 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 2013; 8(4): e59586. [CrossRef]
- Sims NR, Anderson MF. Mitochondrial contributions to tissue damage in stroke. Neurochem Int. 2002; 40(6): 511-26. [CrossRef]
- Protonotarios A, Elliott PM. Arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: A disease or merely a phenotype? Eur Cardiol. 2020; 15: 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Yonker LM, Swank Z, Bartsch YC, Burns MD, Kane A, Boribong BP, et al. Circulating spike protein detected in post-COVID-19 mRNA vaccine myocarditis. Circulation. 2023; 147(11): 867-876. [CrossRef]
- Gumanova NG, Deev AD, Kots AY, Shalnova SA. Elevated levels of serum nitrite and nitrate, NOx, are associated with increased total and cardiovascular mortality in an 8-year follow-up study. Eur J Clin Invest. 2019; 49(3): e13061. [CrossRef]
- Wang F, Yuan Q, Chen F, Pang J, Pan C, Xu F, et al. Fundamental mechanisms of the cell death caused by nitrosative stress. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021; 9: 742483. [CrossRef]
- Clough E, Inigo J, Chandra D, Chaves L, Reynolds JL, Aalinkeel R, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics in SARS-CoV2 spike protein treated human microglia: Implications for neuro-COVID. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021; 16(4): 770-784. [CrossRef]
- Perrone S, Longini M, Marzocchi B, Picardi A, Bellieni CV, Proietti F, et al. Effects of lutein on oxidative stress in the term newborn: a pilot study. Neonatology. 2010; 97(1): 36-40. [CrossRef]
- Perrone S, Tei M, Longini M, Santacroce A, Turrisi G, Proietti F, et al. Lipid and protein oxidation in newborn infants after lutein administration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014; 2014: 781454. [CrossRef]
- Kuligowski J, Vento M. Metabolomics, oxidative, and nitrosative stress in the perinatal period. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022; 11(7): 1357. [CrossRef]
- Li SY, Fu ZJ, Ma H, Jang WC, So KF, Wong D, et al. Effect of lutein on retinal neurons and oxidative stress in a model of acute retinal ischemia/reperfusion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009; 50(2): 836-43. [CrossRef]
- Ruban AV, Pascal A, Lee PJ, Robert B, Horton P. Molecular configuration of xanthophyll cycle carotenoids in photosystem II antenna complexes. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277(45): 42937-42. [CrossRef]
- Rafi MM, Shafaie Y. Dietary lutein modulates inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) gene and protein expression in mouse macrophage cells (RAW 264.7). Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007; 51(3): 333-40. [CrossRef]
- Pap R, Pandur E, Jánosa G, Sipos K, Nagy T, Agócs A, Deli J. Lutein decreases inflammation and oxidative stress and prevents iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation at glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022; 11(11): 2269. [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T. Interleukin 6 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: a personal memoir. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010; 86(7): 717-30. [CrossRef]
- Sindhu ER, Preethi KC, Kuttan R. Antioxidant activity of carotenoid lutein in vitro and in vivo. Indian J Exp Biol. 2010; 48(8): 843-8.
- Krinsky NI, Landrum JT, Bone RA. Biologic mechanisms of the protective role of lutein and zeaxanthin in the eye. Annu Rev Nutr. 2003; 23: 171-201. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal el-SM, Akhtar H, Zaheer K, Ali R. Dietary sources of lutein and zeaxanthin carotenoids and their role in eye health. Nutrients. 2013; 5(4): 1169-85. [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathan R, Neuringer M, Snodderly DM, Schalch W, Johnson EJ. Macular lutein and zeaxanthin are related to brain lutein and zeaxanthin in primates. Nutr Neurosci. 2013; 16(1): 21-9. [CrossRef]
- Dwyer JH, Navab M, Dwyer KM, Hassan K, Sun P, Shircore A, et al. Oxygenated carotenoid lutein and progression of early atherosclerosis: the Los Angeles atherosclerosis study. Circulation. 2001; 103(24): 2922-7. [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Qi Z, Liu W, Wang W. (2015). Lutein protects against ischemia/ reperfusion injury in rat kidneys. Molecular Medicine Reports 2015; 11: 2179-2184. [CrossRef]
- Koushan K, Rusovici R, Li W, Ferguson LR, Chalam KV. The role of lutein in eye-related disease. Nutrients. 2013; 5(5): 1823-39. [CrossRef]
- Shi Z, Kong G, Wang F, Gao H, Wei A, Ren S, Yan X. Improvement in the stability and bioavailability of pumpkin lutein using β-cyclodextrin microcapsules. Food Sci Nutr. 2023; 11(6): 3067-3074. [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarieh M, Sacu S, Wedrich A. The role of the carotenoids, lutein and zeaxanthin, in protecting against age-related macular degeneration: a review based on controversial evidence. Nutr J. 2003; 2: 20. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Roger Illingworth D, Connor SL, Barton Duell P, Connor WE. Competitive inhibition of carotenoid transport and tissue concentrations by high dose supplements of lutein, zeaxanthin and beta-carotene. Eur J Nutr. 2010; 49(6): 327-36. [CrossRef]
- Bohn T, Desmarchelier C, El SN, Keijer J, van Schothorst E, Rühl R, Borel P. β-Carotene in the human body: metabolic bioactivation pathways - from digestion to tissue distribution and excretion. Proc Nutr Soc. 2019; 78(1): 68-87. [CrossRef]
- Johnson EJ, Maras JE, Rasmussen HM, Tucker KL. Intake of lutein and zeaxanthin differ with age, sex, and ethnicity. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010; 110(9): 1357-62. [CrossRef]
- Montesano D, Rocchetti G, Cossignani L, Senizza B, Pollini L, Lucini L, et al. Untargeted metabolomics to evaluate the stability of extra-virgin olive oil with added Lycium barbarum carotenoids during storage. Foods. 2019; 8(6): 179. [CrossRef]
- European Union. On the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis. Commission Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91. , 1991. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eur/1991/2568. 11 July.
- Mousavi S, Mariotti R, Stanzione V, Pandolfi S, Mastio V, Baldoni L, et al. Evolution of extra virgin olive oil quality under different storage conditions. Foods. 2021; 10(8): 1945. [CrossRef]
- Frankel, EN. Chemistry of extra virgin olive oil: adulteration, oxidative stability, and antioxidants. J Agric Food Chem. 2010; 58(10): 5991-6006. [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, AM. N-bromotaurine solutions and emulsions against abnormal. cells. Patent #10,772,855. September 15, 2020. https://uspto.report/patent/grant/10,772, 855.
- Kyriakopoulos AM, Nagl M, Gupta RC, Marcinkiewicz J. Taurine and N-bromotaurine in topical treatment of psoriasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022; 1370: 99-111. [CrossRef]
- Geromichalou EG, Geromichalos GD. In silico approach for the evaluation of the potential antiviral activity of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) bioactive constituents oleuropein and oleocanthal on spike therapeutic drug target of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules. 2022; 27(21): 7572. [CrossRef]
- Borkotoky S, Dey D, Hazarika Z. Interactions of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2) and SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD): a structural perspective. Mol Biol Rep. 2023; 50(3): 2713-2721. [CrossRef]
- Patterson BK, Francisco EB, Yogendra R, Long E, Pise A, Rodrigues H, et al. Persistence of SARS CoV-2 S1 protein in CD16+ monocytes in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) up to 15 months post-infection. Front Immunol. 2022; 12: 746021. [CrossRef]
- Imran M, Thabet HK, Alaqel SI, Alzahrani AR, Abida A, Alshammari MK, et al. The therapeutic and prophylactic potential of quercetin against COVID-19: An outlook on the clinical studies, inventive compositions, and patent literature. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022; 11(5): 876. [CrossRef]
- Nag A, Banerjee R, Paul S, Kundu R. Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study. Comput Biol Med. 2022; 146: 105552. [CrossRef]
- Suresh MV, Francis S, Aktay S, Kralovich G, Raghavendran K. Therapeutic potential of curcumin in ARDS and COVID-19. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2023; 50(4): 267-276. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty AJ, Mitra S, Tallei TE, Tareq AM, Nainu F, Cicia D, et al. Bromelain a potential bioactive compound: A comprehensive overview from a pharmacological perspective. Life (Basel). 2021; 11(4): 317. [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa T, Kiba Y, Yu J, Hsu K, Chen S, Ishii A, et al. Degradative effect of nattokinase on spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules. 2022; 27(17): 5405. [CrossRef]
- Lucock, M. Is folic acid the ultimate functional food component for disease prevention? BMJ. 2004; 328(7433): 211-4. [CrossRef]
| Therapeutic effect of lutein | Mechanisms of lutein activity to alleviate pathogenesis of disease |
|---|---|
| Anti-cancer | Regulation of apoptosis and angiogenesis [16]. Cell cycle arrest, apoptosis of cancer cells, inhibition of cancer cell proliferation [17]. |
| Cardiovascular: Cardio-protection Cardio-metabolic diseases (Health benefits provided with a lutein enriched diet) |
Lowers inflammation in coronary artery disease associated atherosclerosis. Lowers levels of IL-6 in monocytes and exerts anti-inflammatory activity by lowering IL-1β and TNF-α [18]. Lowers stroke incidence and mortality from cardiovascular disease and improves metabolic syndrome by reducing ROS and hyperinsulinemia [2]. Prevention of cholesterol build-up, reduction of blood pressure, reduction of arterial thickening, reduction of oxidized LDL [19,20]. |
| Oculo-protection and prevention of eye disease. Lutein-rich diet correlates with diminished risk of age-related macular degeneration-improves eye vision. (Preferably provided with a suitable source in a lutein-enriched diet [24]) |
Inhibition of nuclear cataracts [21]. Restoration of retinopathies due to antioxidant activities [22]. Filters blue light and reduces photoreceptor cell damage [23]. |
| Combats neuro-degenerative diseases. Improves cognitive function. Reduction of Alzheimer's disease (AD) mortality risk in the elderly [25]. Protection from severe traumatic brain injury (Lutein rich food). |
Reduction of oxidative stress. Inhibition of Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer activated B cells (NF-κB) signalling pathway and activation of Nrf2 [26]. Anti-oxidation exerted via the nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) and ICAM-1 downregulation. Downregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 activity [27]. |
| Stabilization of high glucose level effects in immune cells. | Reduction of oxidative stress induced by glucose. Reduction of nuclear factor-kappa beta (NF-κB) activity [28]. |
| Inhibition of obesity | Inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. Delay of adipose cells at G0/G1 phase of cell cycle [29]. |
| Diabetes: Diabetic nephropathy. Diabetic retinopathies. |
ROS scavenging. Reduction of serum and urine urea and creatinine. Decrease of TNF- α, IL-6 and IL-1 in renal tissues. Restoration of pro-inflammatory cytokines to normal in renal tissues and restoration of oxidative / nitrosative stress biomarkers [30]. Improvement in visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and macular oedema in diabetic retinopathy patients due to protection from visible light [31]. |
| Immunomodulation of inflammation. | Reduction of proinflammatory cytokine levels. Inhibition of chronic inflammation (increase of Il-10) [32]. Inhibition of hyperosmocity-induced secretion of IL-6 through the deactivation of p38, JNK and NF-κB pathways [33]. |
| Protection of liver health: Prevention of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) evolution from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). | Decrease of insulin resistance and lipogenesis. Prevents triglyceride synthesis, free fatty acid and cholesterol deposition and lipid peroxidation. Reduction of cytokine inflammatory response, and oxidative stress [34]. Decrease of hepatic TNF-α and NF-κB DNA binding activity in in vivo studies [35]. |
| Heart and kidney axis: Prevention of cardiac and renal injuries. |
Improves glucose tolerance. Restores balance of polyol pathway. Decreases malondialdehyde levels and increases reduced glutathione levels in the serum, heart and kidney. Modifies the antioxidant enzymatic activities of catalase, glutathione peroxidase, reductase and transferase, and superoxide dismutase in diabetes [36]. |
| Anti-viral effects. | Inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) transcription in vitro [37]. Inhibition by binding to Nipah virus protein in silico [38]. Inhibition of vaccinia virus in vitro [39]. |
| SARS-CoV-2 spike protein potential neutralization properties. Obtained from molecular docking and molecular dynamics in in silico simulation studies. |
Direct binding to the Lys417Asn position of spike protein, part of the spike-human angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) interface (Wuhan lineage variants) in silico [40]. Highest binding affinity amongst polyphenolic compounds (including quercetin and luteolin) against spike protein. Potential inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 protease active sites [41]. FDA selected drug candidate to block ACE2 binding affinity of spike protein [42]. |
| Potential anti-COVID-19 activity. | Reduction of oxidative stress and inflammatory injury. Lowering of pro-inflammatory cytokine mediators including IL-16 and TNF-α receptor-1 [6]. |
| Studies on post-COVID in relation to oxidative stress | |
|---|---|
| Scope of study | Findings on oxidative stress and inflammatory response |
| Analysis of oxidative stress biomarkers in post-COVID patients after a previous mild SARS-CoV-2 infection. | Malondialdehyde serum levels (MDA) (lipid peroxidation product) remain high in post-COVID patients compared to healthy controls [74]. |
| Inflammatory protein profiling in post-COVID patients, 5 months to 1 year after COVID-19 hospital discharge. | Systemic inflammation was evident in post-COVID patients with upregulated IL-6 and neuroinflammation. C-terminal fragment of agrin protein found elevated. Breakdown of agrin indicates cardiomyocyte and neuromuscular junction damages [75]. Prediction of neuropsychiatric symptoms correlated with antioxidant / pro-oxidant imbalance [76]. |
| Investigation of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome in post-COVID syndrome. | Redox imbalance. Increased levels of peroxides and superoxide. Elevated levels of pro-oxidants including nitrogen species. Nitrosative stress and abnormally high nitric oxide (NO) levels. High levels of homocysteine indicating impairment of reverse trans-sulfation enzyme activities. Inability to generate adenosine triphosphate [77]. |
| Investigation of post-COVID chronic fatigue, somatic and mental symptoms. | Increased peak body temperature predicting high C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. Low glutathione peroxidase (GPX) and zinc levels. Increased myeloperoxidase (MPO), NO and lipid peroxidase-associated aldehyde levels. Neuro-immune and neuro-oxidative stress associated inflammation [10]. |
| Investigations of cognitive impairment in post-COVID and associations with inflammatory markers | Cognitive impairment-associated neuro-oxidative stress inflammation parallels increased cytokine profile including IFN-α, TGF-β, TNF-β, IL-6, IL-7, IL-13, IL-15 and G-CSF. Cognitive impairment is significantly associated with CRP and D-dimer levels [10,78]. |
| Studies on mRNA vaccine injury syndrome in relation to oxidative stress | |
| Evaluations on mRNA-induced acute-pericarditis and myopericarditis in young adults and associations with oxidative stress. | Myopericarditis was associated with increased levels of troponin I, D-dimers and high sensitivity CRP (hsCRP). Oxidative stress index (TOS/TAS*) [79,80], and NO levels were lower in myopericarditis group compared to acute-pericarditis and control groups, indicating an inflammatory and pro-coagulant condition in the myopericarditis [11]. |
| Investigation of the mRNA vaccination effects of oxidative stress and DNA damage on blood mononuclear cells (BMC) in the young (aged 27-44 years) and the elderly (aged 80-88 years) population groups. | Increased oxidative and DNA damage in all population groups. Accumulation of double strand breaks (DSB) in the elderly peripheral BMCs as compared to younger population occurring with every mRNA (first and second shot) vaccination. Pro-oxidant / antioxidant imbalance was associated with reduced humoral response after mRNA vaccination. This was linked with immune senescence in the elderly population [81,82]. |
| Investigations on arrythmia and myocarditis. | Autopsies indicate acute arrythmogenic cardiac failure / lethal complication of mRNA vaccination [69,86] [68,85]. Possible redox / pro-oxidant / antioxidant imbalance resulting in sudden death [83]. |
| Investigations on electrocardiogram abnormalities after the mRNA vaccinations | Myopericarditis association with IL-18 NLRP3 inflammasome activation [84]. Potential upregulation of IL-18 / activator protein (AP-1) redox sensitive signaling via p38 MAPK activation [85]. Possible pro-oxidant stimuli, leading to vascular damage [86]. Mass (4928 students) screening study on electrocardiogram (ECG) parameters [87] revealed that depolarization and repolarization of heart (QRS duration and QT interval) reduced significantly after the second dose of mRNA vaccine, whilst the heart rate was increased. Arrythmia cases can be associated with Na+/Ca2+ exchanger redox imbalance, sarcolemma depolarization defects and ventricular arrythmia [83]. |
| mRNA vaccination related to autoimmune disorders that result in hair loss | Patients in complete remission (mean 1.8 years) from alopecia areata (AA), [(Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT): 0 (S0)], deteriorated after the first mRNA vaccine, showing stability of AA symptoms after the subsequent doses. One patient showed a booster effect of AA symptoms after subsequent doses [88]. Possible oxidative stress triggering, resulting in inflammatory process activation and hair loss [89]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





