1. Introduction
Despite the growth of vehicle automation, the
number of car crashes is still unacceptably high. It seems that safety critical
events related to human driving have become more complex and partially
uncontrolled due to unexpected circumstances. Studies of human driving behavior
are needed to design traffic baselines for mixed traffic, involving traditional,
automated and autonomous vehicles. Human driving behavior is affected by
various factors such as weather conditions, which reduce visibility in
longitudinal car-following (CF) driving behavior [2,10].
Car-following behavior refers to how a car- following a leading car
reacts to the motion of the lead vehicle. The Car- following behavior describes
how a following vehicle reacts to the lead vehicle in the same lane. The
limitations of previous works in car-following models, particularly in their
assumptions of homogeneous drivers. In reality, drivers exhibit significant
heterogeneity in terms of their driving experience, gender, character, emotion,
and other sociological, psychological, and physiological aspects. Ignoring this
heterogeneity can lead to an incomplete understanding of car-following behavior
and limit the accuracy and applicability of the models. The incorporation of
driver heterogeneity is crucial for developing more realistic and accurate
car-following models in mixed traffic. By considering the individual
differences among drivers, such as their risk-taking tendencies, reaction
times, decision-making processes, and driving styles, one can better capture
the complexities of real-world driving scenarios. Furthermore, categorizing
drivers into just a few types (e.g., aggressive, normal, and inattentive)
oversimplifies the richness and diversity of driver characteristics. This
simplistic approach fails to capture the nuances and subtleties that exist
within different driver profiles. Instead, a more comprehensive approach is
needed to account for the wide range of characteristics and behaviors exhibited
by individual drivers. Addressing these limitations requires developing models
that can effectively incorporate the external heterogeneity between different
drivers and the internal heterogeneity within a single driver. The proposed
model is based on personalized cognitive agent. Each driver is assigned
a personalized cognitive agent that can represent the driver profile with
accessing local information and learn the driver characteristics. The
personalized cognitive agent is based on individual user preferences,
characteristics, and needs. The goal of a personalized cognitive agent is to
provide tailored and customized experiences to cognitive vehicle, taking into
account the unique requirements and individual preferences of occupants inside
autonomous vehicle to better understand the driving behavior of all surrounding
vehicles in mixed traffic. The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 gives an overview of related
research; section 3 describes the methodology; and sections 4 and 5 present a
performance evaluation and conclude the paper.
2. Related Research
Several different driving models have been
developed in the literature [1]. Many driving
models try to approximate the real driver’s road tracking performance, assuming
certain driver inputs and outputs. Models of models of driving behavior attempt
to capture the driver's decision-making process and behavior, such as how they
respond to changes in the road and traffic under external factors, how a
driving maneuver is recognized by a cognitive vehicle, observing (by its
onboard sensors) the driving behavior of surrounding vehicles [7]. It is expected that there is some level of
uncertainty associated with models of driving behavior, as they are based on
assumptions and approximations of real-world driver behavior as well as with
the inherited uncertainties of onboard sensor measurements and consecutive
feature extraction, characterizing the surrounding objects. This uncertainty
can have a significant impact on the performance of control systems that are
designed using these models. One way to address this uncertainty is by
developing a model for the driver model uncertainty [3].
Uncertainty modeling of driving refers to
predicting and managing the uncertainty that comes with driving. This includes
modeling human factors, driving behaviors (of human driver, automated or
autonomous vehicles), external factors and other factors that can affect
driving performance. Driving behaviors are the
main cause of road accidents and one of the main sources of insurance claims [14]. Wang and Lu [11] found that the that the difference in driving behavior
between males and females remained unchanged, or even increased in some
aspects. The differences involved traffic accidents and offenses, although the
driving times, attitudes, education, and other background factors were
controlled. Furthermore, all drivers involved in traffic accidents and fatalities,
however, Younger drivers have the highest rate of accidents. The study of Hiang
and Ming [13]
aimed to investigate the relationship between age and gender with speeding
driving behavior. Results showed young and male drivers averagely travelled at
higher velocity before entering the roundabout and at the same time accelerate
to higher velocity upon exiting the roundabout compared to old and female
drivers. Lee
et al. [15]
proposed the purpose of this research is (1) to investigate the relationship
between crash severity and the age and gender of the at-fault driver, the
socio-economic characteristics of the surrounding environment, and road
conditions. This research adopts the logit model to investigate how age impacts
accident severity and to uncover when age has little effect, using age as a
continuous variable. Shahverdy et al [12], introduced a deep learning method for analyzing the
driver behavior focused on driving signals, including acceleration and speed to
recognize five types of driving styles, including normal, aggressive,
distracted, drowsy, and drunk driving. The
study [16] examined the factors influencing
aggressive driving behavior, considering human factors, personality traits, and
demographic characteristics. Regression analysis was used to explore the impact
of age and driving experience and their interactions with other variables on
aggressive driving behaviors.
Aggressive driving behavior is influenced by a
combination of human factors, including age and driving experience, as well as
personality traits and demographic characteristics. The analysis revealed a
negative correlation between age and aggressive driving behaviors. This implies
that as individuals grow older, they tend to engage in fewer aggressive driving
behaviors on average. There was a positive correlation found between the
personality trait of neuroticism and aggressive driving behaviors. Individuals
with higher levels of neuroticism, characterized by emotional instability and
heightened negative emotions, are more likely to exhibit aggressive driving
tendencies. Significant associations were identified between age, driving
experience, and depression. This suggests that older, more experienced drivers
may be less prone to depression, potentially reducing their likelihood of
engaging in aggressive driving behaviors.
In the context of car-following models,
artificial intelligence tools can be used to represent different aspects and
behaviors of drivers. A non-monotonic logic-based approach for car- following
in autonomous vehicles has been proposed [4,5].
The study develops a reasoning system that incorporates non-monotonic inference
mechanisms to handle uncertainties and exceptions in car- following scenarios.
The experimental results demonstrate improved adaptability and decision-making
performance compared to traditional rule-based systems. An adaptive car-
following system that utilizes non-monotonic logic has been introduced to
enhance reasoning and decision-making capabilities. The study incorporates
context-dependent rules and non-monotonic inference mechanisms to handle
exceptions and conflicting information during car- following. Simulation
results show improved safety and efficiency in various traffic scenarios. This
research investigates the integration of non-monotonic logic into existing car-
following algorithms as illustrates
Figure 1.
The study proposes an architecture that combines rule-based reasoning with
non-monotonic inference mechanisms to handle uncertainties and adapt the
behavior of autonomous vehicles during car following. Experimental evaluations
demonstrate improved performance and adaptability in dynamic traffic
conditions. The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the challenges and
opportunities of applying non-monotonic reasoning in car- following for
autonomous vehicles. It discusses the limitations of traditional rule-based
systems and highlights the benefits of non-monotonic logic in handling
uncertainties, conflicting data, and context-dependent reasoning. The study
also identifies future research directions and potential applications of
non-monotonic reasoning in autonomous driving.
3. Methodology
3.1. CNN Reasoning model
Convolutional neural network (CNN) reasoning refers
to the application of CNNs in the context of reasoning and decision-making
tasks [6]. The traditional CNN Architecture
typically consist of multiple convolutional layers followed by fully connected
layers. These layers learn hierarchical representations of input data, enabling
the network to capture complex patterns and features. CNNs can be extended or
combined with other components to enable reasoning capabilities. This often
involves incorporating additional layers, such as recurrent neural networks
(RNNs) [6] or attention mechanisms, to capture
temporal or spatial dependencies and enable sequential reasoning. Furthermore,
CNNs can be employed for visual reasoning tasks, where the model is trained to
reason about relationships between objects. The model learns to extract
meaningful features from input data and use them to infer relationships and
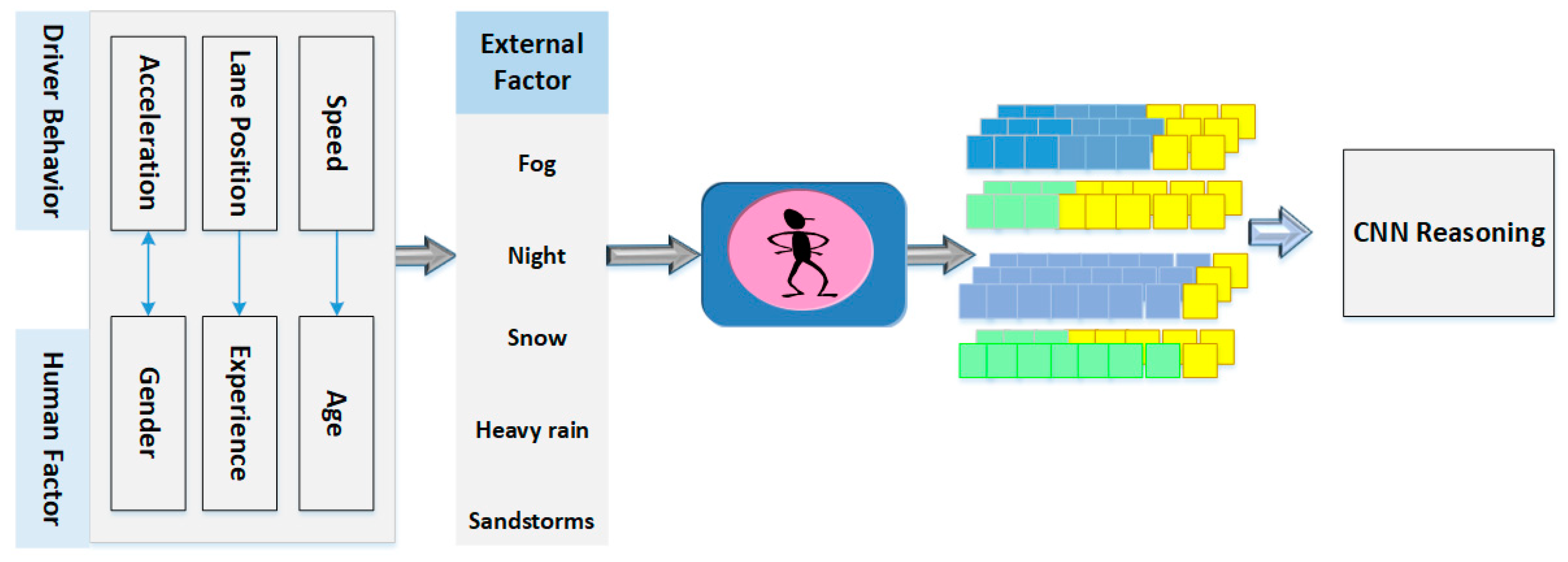
make logical deductions. This paper proposed a hybrid
approach that combines multiple techniques to create more accurate and robust
driver models as illustrated in
Figure 2.
A hybrid model uses a deep learning to find causal relationship between human
factor and driving behavior based on feature extraction and a statistical model
to predict a driver's speed and acceleration, but also incorporate rule-based
logic to handle unexpected situations.
3.2. Data collection
The dataset used in this research is based on
naturalistic driving data taken from the L3Pilot database
[8]. A European
research project L3Pilot, which tests the viability of automated
driving as a safe and efficient means of transportation on public roads, has
developed a common data format (CDF) for both data collection and processing
and has implemented a consolidated database for processed data collection. The
data consist of performance indicators for four driving scenarios, free
driving, following a lead vehicle, driving in traffic jams and changing lanes.
The used data for training the deep learning algorithm is involving cleaning
and formatting the data, selecting relevant features, and splitting the dataset
into training, validation, and testing sets.
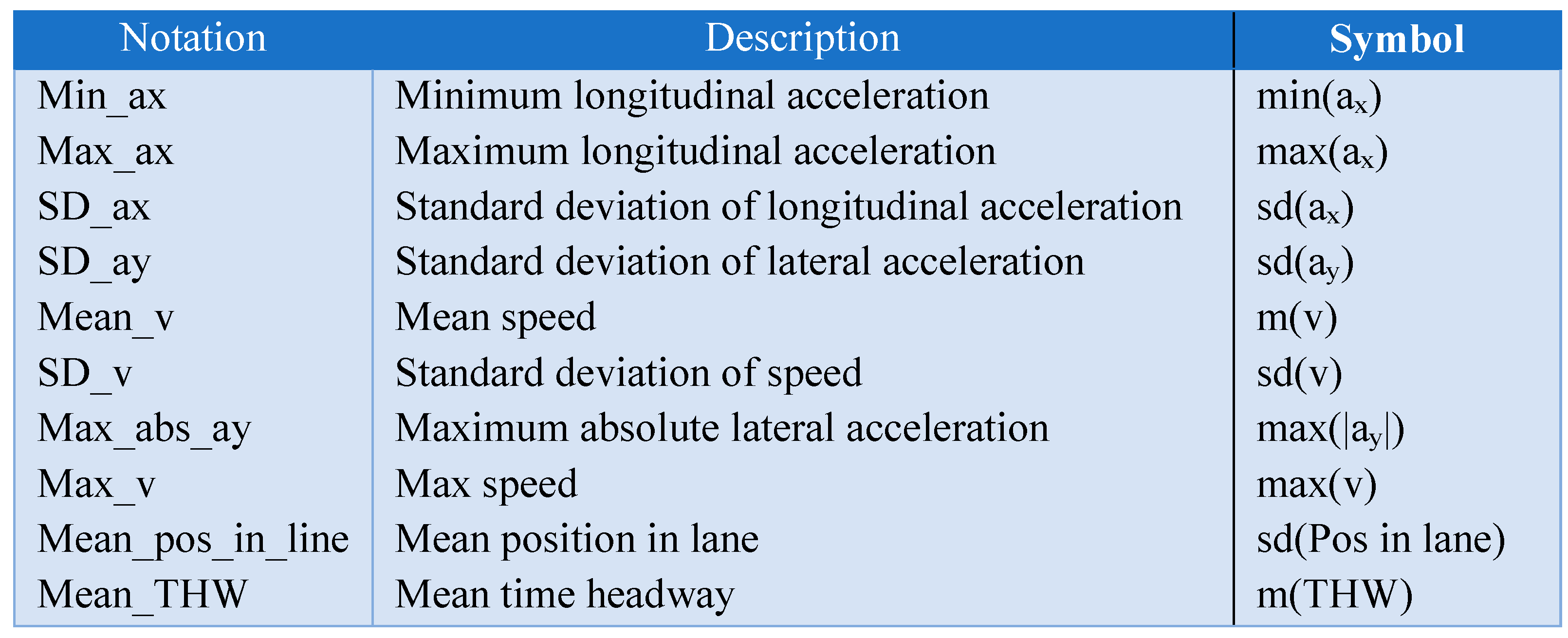
Table
1 summarized the main notation that is used in this paper.
3.3. Algorithm Description
The algorithm is a hybrid model that consists of a
deep learning scheme and statistical tools as illustrated in
Figure 3. The deep learning is a subset of
machine learning that involves training artificial neural networks to recognize
patterns in data. By applying deep learning techniques to analyze large
datasets of human behavior and vehicle behavior, you can identify complex
patterns and causal relationships that may be difficult to detect using
traditional statistical methods. The statistical tools are applied to evaluate
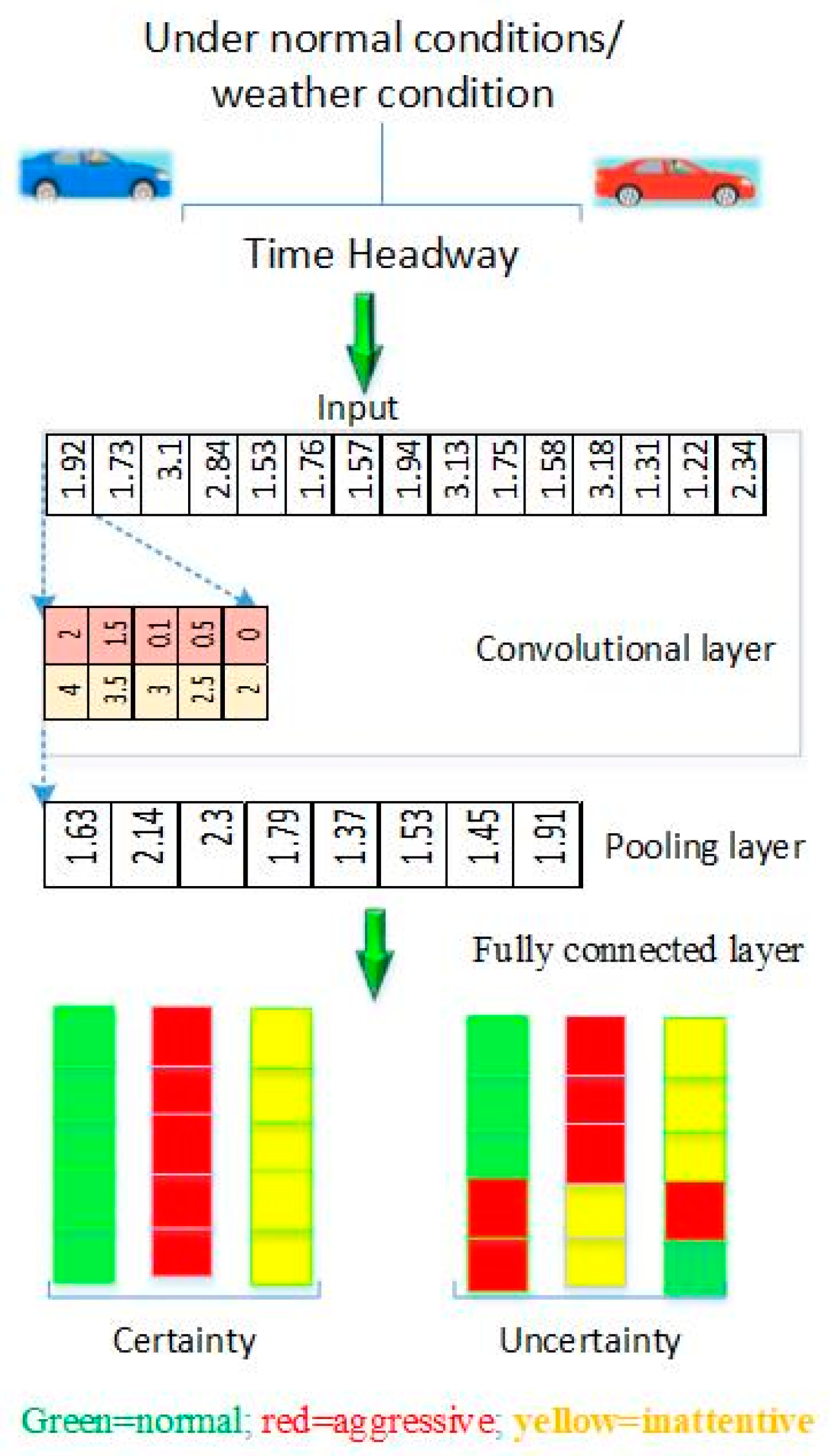
the performance of the prediction scheme. The prediction model of drivers’
behavior during car- following can be performed for certainty and uncertainty.
Driver’s certainty during car- following can increase when the driver is familiarity with the situation, consistent behavior of
the leading vehicle by maintains a steady speed, consistent acceleration and
deceleration, and follows traffic rules. In other hand, there are several
factors that contribute to driver’s uncertainty during car- following
such as Unpredictable behavior of the leading
vehicle: Uncertainty arises when the leading vehicle exhibits erratic or
unexpected actions, such as sudden braking, lane changes without signaling, or
unpredictable acceleration. In additions lack of information or incomplete
information about the road conditions, traffic situation, or intentions of the
leading vehicle, Furthermore, a driver in weather conditions, these factors can
contribute to uncertainty during car-following and driver is feeling
anxious and stressed due to external factors.
3.4. Feature Extraction
One approach is to use deep learning models to
extract features from the data, and then use these features as input to various
machine learning schemes, like Nearest Neighbor, Random Forest, Naïve Bayesian
network (NBN), Decision Table, etc. Feature extraction based on naturalistic
driving data is important for the analysis of driving behavior related to
safety-critical events. Human driving behavior can be identified however, it
is difficult to control because, although human drivers are affected by external
factors that can be estimated and predicted, there are internal factors
affecting human cognition which cannot be distinguished or controlled. However,
for AVs, both internal and external factors are predictable.
Figure 4.
Driving behavior Identification.
Figure 4.
Driving behavior Identification.
The trained CNN can recognize the driver profile
based on time headway. The CNN classifies the driver profile in three groups
normal, inattentive and aggressive. To evaluate and validate the quality of
data clustering results, we used the silhouette, a statistical technique [9] to present graphically how well each object has
been classified. For each driver, we calculate its silhouette score using the
following formula:
Where ai, is the average distance from the 𝑖th
point to the other points in the same cluster as 𝑖.
And bi is the minimum average distance from the 𝑖th
point to points in a different cluster,minimized over all clusters. The
silhouette value is an internal criterion, which is used for interpretation and
validation of consistency within a cluster of data and for each point measures
how similar that point is to points in its cluster when compared to points in
other clusters. Furthermore, we assigned a score according to driver
aggressivity degree.
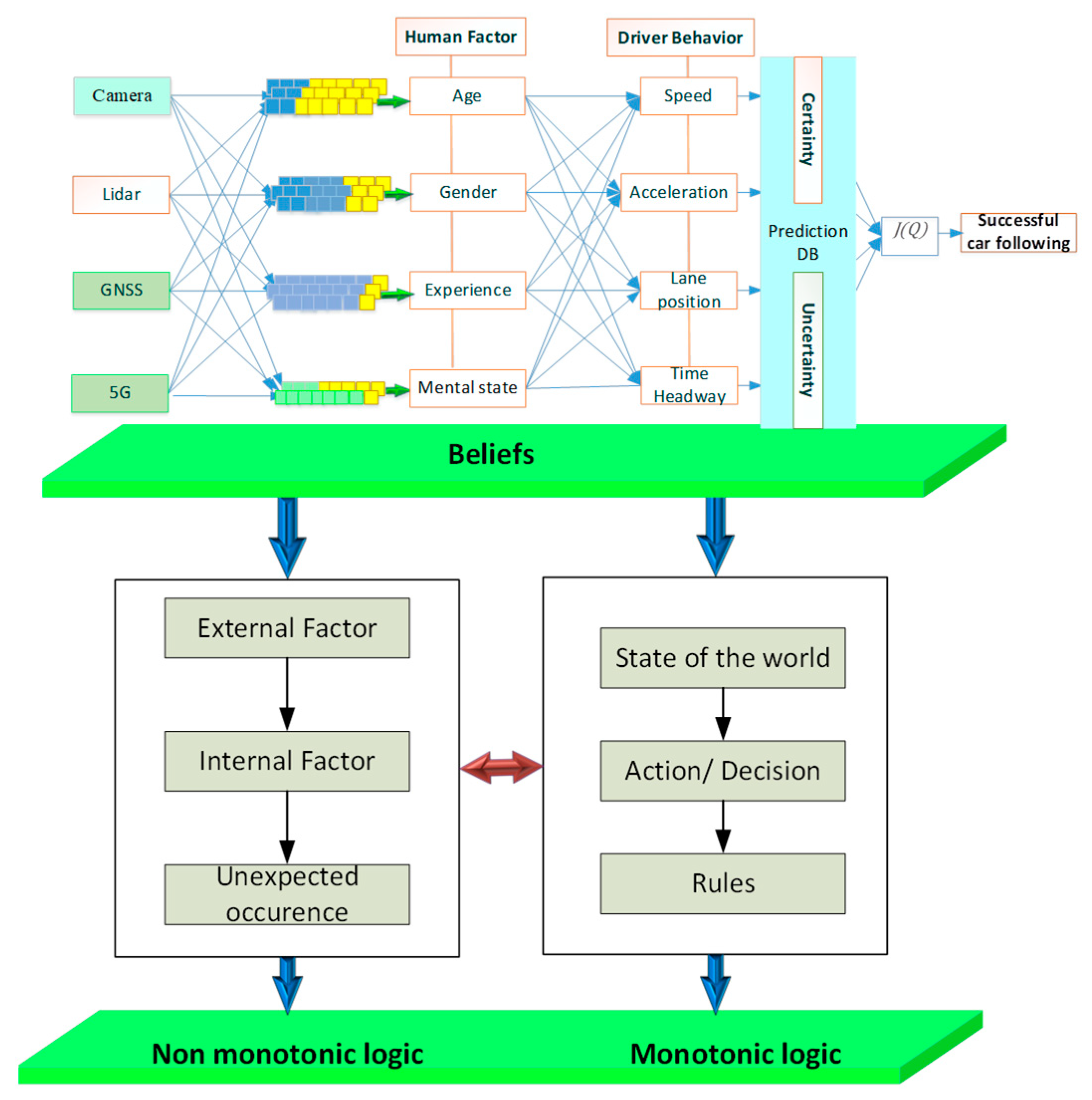
3.5. Reasoning based non-monotonic logic
To overcome these limitations of monotonic logic,
this paper proposes the application of non-monotonic logic as a promising
approach to enhance the reasoning capabilities of autonomous vehicles during
car- following. Non-monotonic logic allows for flexible and adaptive reasoning,
accommodating exceptions and context-specific information. By incorporating
non-monotonic logic into autonomous vehicles, they can make plausible
inferences, handle conflicting data, and adapt their behavior to ensure safe
and efficient car- following. Thus, the degree of beliefs for driver profiles
is clustered into the following stated:
The degree of beliefs for the occurrence of
accidents is dependent on the driver profiles (A, B, C), and is expressed as
follows.
The degree of beliefs for the occurrence of
accidents is dependent on the joint probability of driver profile (A, B, C) and
driving related experience (E) and is computed as follows and the probabilities
of the state are dependent on the weights as obtained from CNN training:
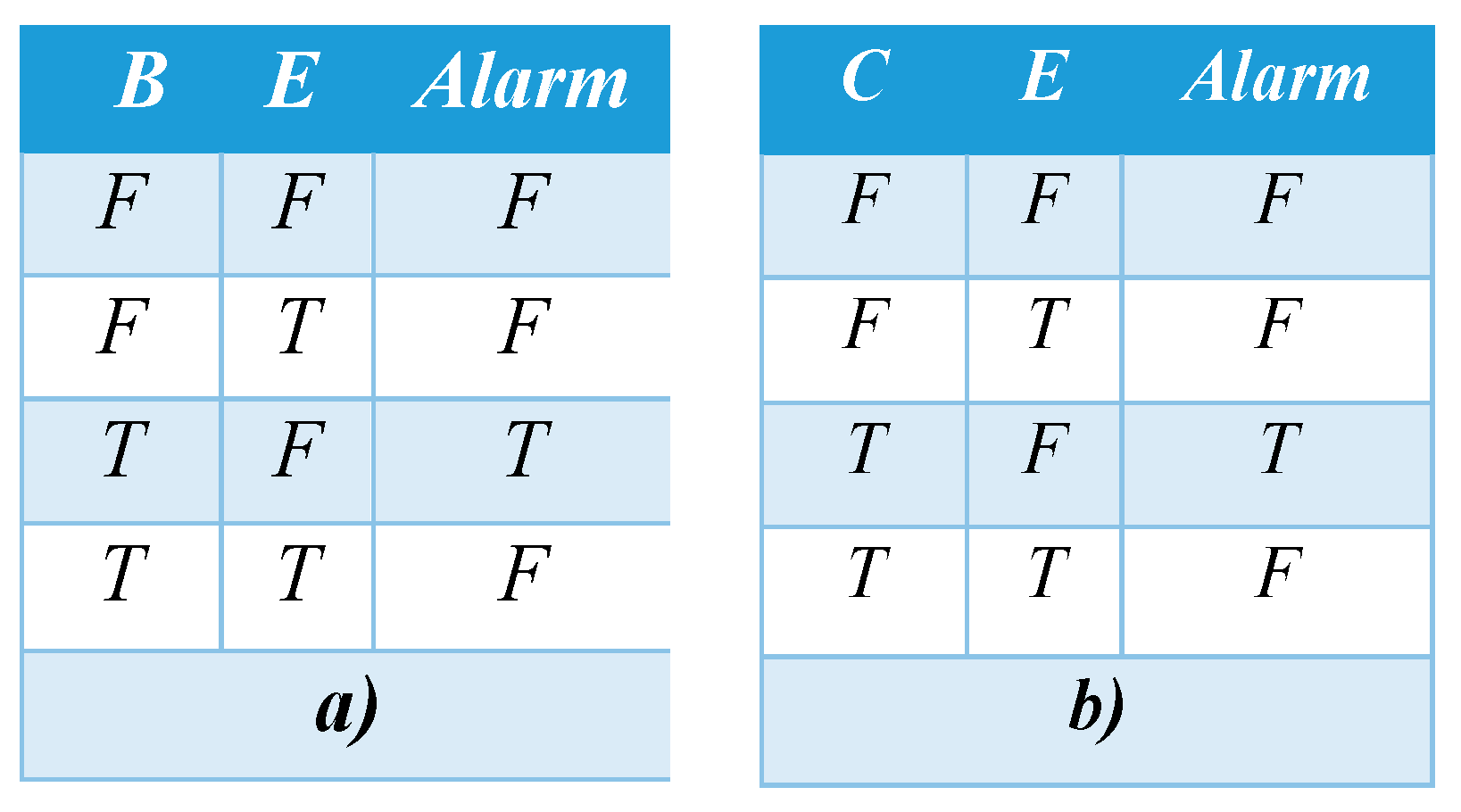
The personalized cognitive agent alerts the
autonomous control system based on causal relationship between human factors
and driver behavior related to time headway. This alert (which is denoted as
Alarm) can be represented as combinatorial combination of the involved Boolean
variables as showed in
Table 2.
The personalized cognitive agent creates rules based on
obtained beliefs. However, the traditional rule-based systems and
monotonic logic have been extensively used for decision-making in autonomous
vehicles. However, these approaches often struggle when faced with the
non-deterministic and dynamic nature of car -following scenarios. Monotonic
logic typically operates under the assumption that additional information does
not change the validity of previously drawn conclusions. This limitation poses
challenges in dealing with exceptions, conflicting data, and context-dependent
reasoning, which are prevalent in car- following situations. To overcome these
limitations, this paper proposes the application of non-monotonic logic as a
promising approach to enhance the reasoning capabilities of autonomous vehicles
during car- following. Non-monotonic logic allows for flexible and adaptive
reasoning, accommodating exceptions and context-specific information. By
incorporating non-monotonic logic into autonomous vehicles, they can make
plausible inferences, handle conflicting data, uncertain data, incomplete data
and adapt their behavior to ensure safe and efficient car- following.
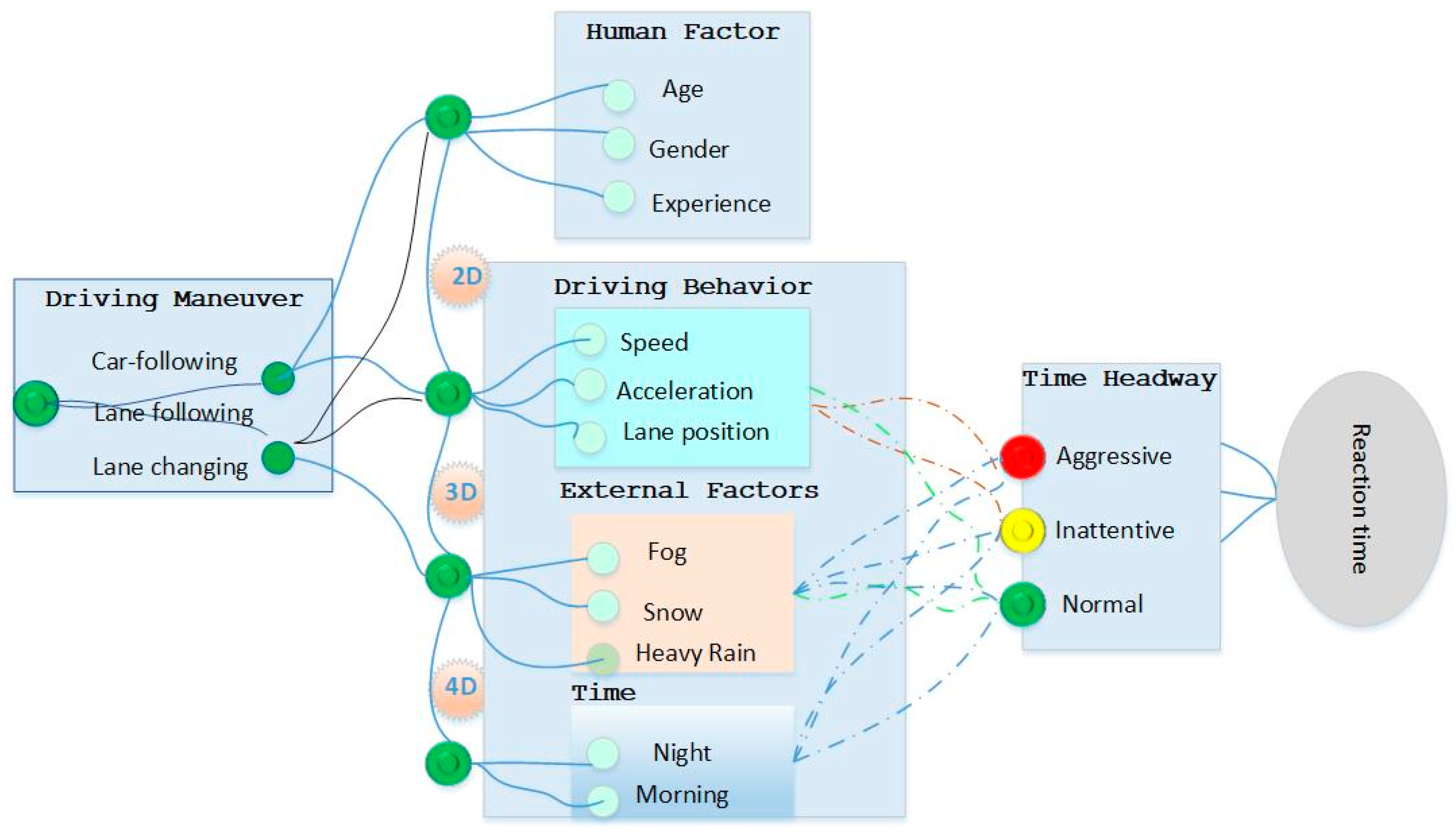
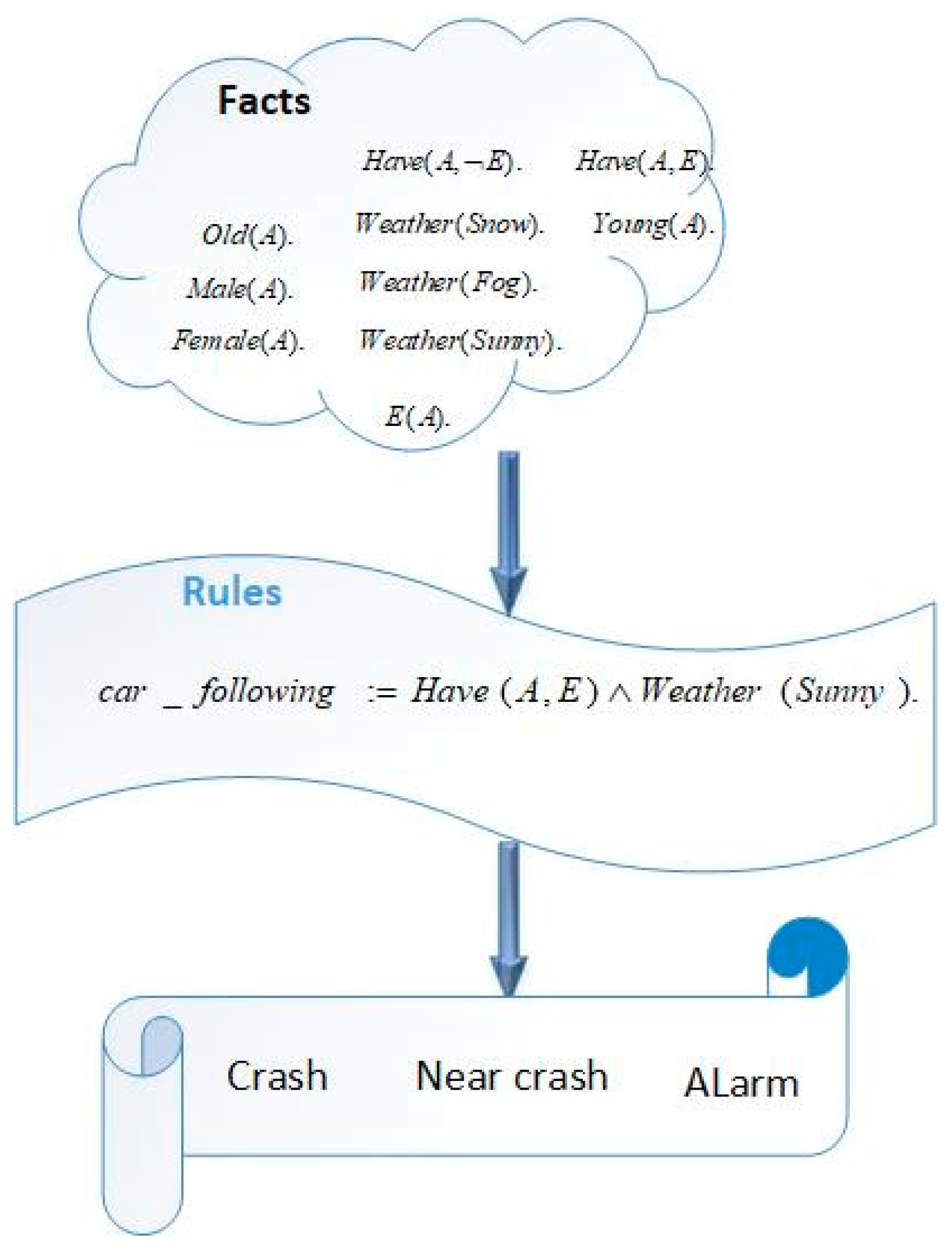
The primary goal of this research is to explore the
potential benefits and challenges associated with integrating non-monotonic
logic into autonomous vehicles for car- following by considering human factor,
driving behaviors and external factors. The personalized cognitive agent is
designing the rules based on defining the relationships between human factors
and driving behaviors and logical statements based on the facts to represent
knowledge and infer new information as illustrated in
Figure 5.
4. Discussion and Analysis
In this section, we discuss the modeling the causal
dependencies between human factors, driving behavior for car-following tasks
with the aim of keeping a time headway (time distance between a lead and a
follow-vehicle). The data provides evidence on the heterogeneity of human
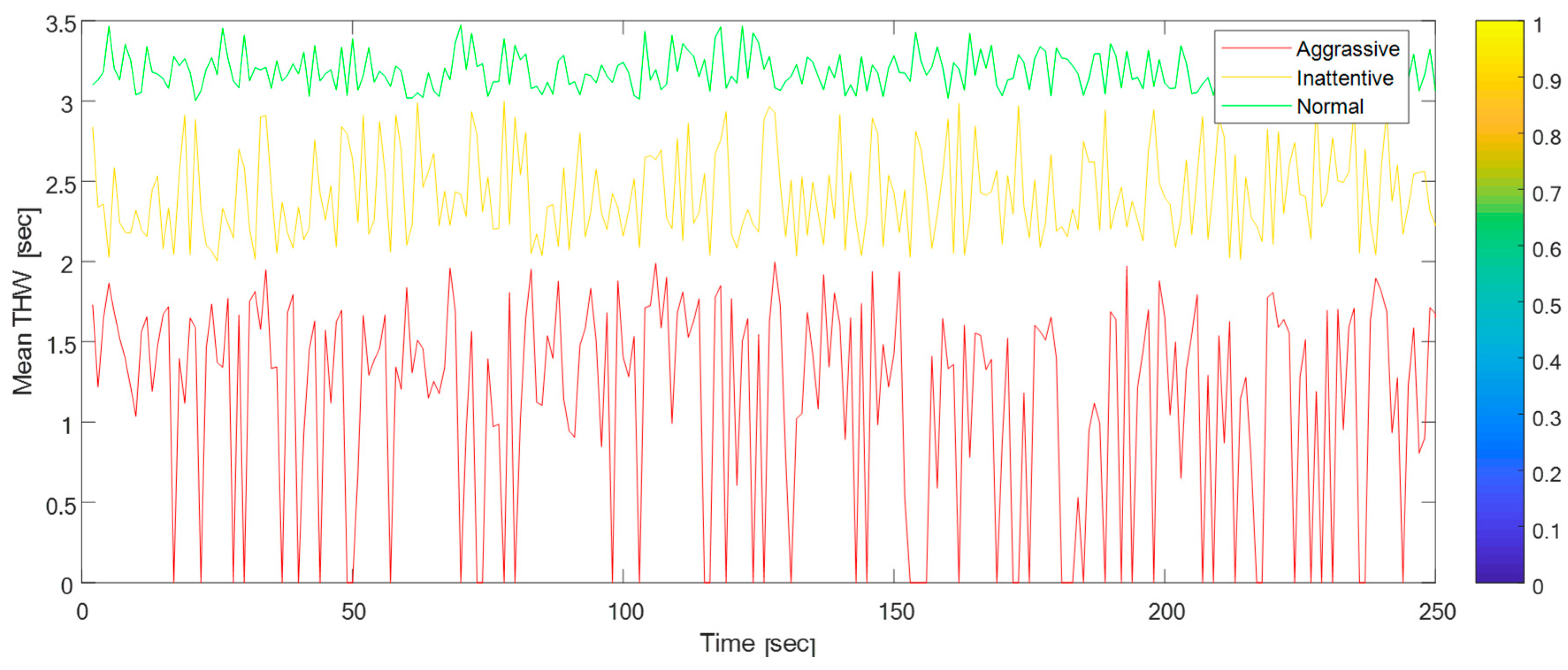
driving profiles as the mean THW ranges from near 0s to 5s and
the minimum of THW ranges from near 0s to more than 3s. Based on these
preliminary findings, we propose the definition of three profiles:
- (i)
’aggressive’: shorter car time-headway, (0-2 sec)
- (ii)
’inattentive’: longer reaction time (2-3 sec),
and
- (iii)
’normal’ for intermediate values of reaction time
and car time-headway (bigger than 3sec), i.e. keeping adaptive cruise
control, which is expressed by adaptive relative distance [m] and constant
relative speed [m/s].
The definitions of the two driver profiles
(aggressive inattentive) are formalized below.
- ⃝
Aggressive driver
profile: A driver
i is considered to be aggressive with respect to a
threshold t
* on the time headway THW if
- ⃝
Inattentive driver profile (drivers with long reaction time): A driver
i is considered to be inattentive (with a long reaction time) with respect to a threshold
on the time headway THW if
- ⃝
Normal driver profile: the drivers whose profiles are neither aggressive or inattentive are called normal. They have intermediate values (e.g., < 1 s) of reaction time headway.
Combination between HF and DB
Driving behaviors, such as time headway, speed and acceleration are depended on human factors, such as age, gender, experience and external factors, such as weather condition. However, in this paper, it is considered the human factors. The probability to occur accident is expressed as following,
The weight of each human factors is calculated according naturalistic driving.
The personalized cognitive agent can estimate the probability of accident occurrence according to minimization of the weights. The type of minimization objective function is referred to a loss function, which is also known as cost function. Neural network learning algorithms are formulated with the use of a loss function. The goal was always to minimize the error in prediction L by minimizing the number of misclassifications with respect to all training instances in a data set D containing feature-label pairs
The cost function is a special type of functions that helps to minimize error and approach as close as possible to the expected output. It uses two parameters to calculate error: one is an estimated output of the CNN model (also called the prediction) and other is the actual output. The mean squared error (MSE) is indeed a commonly used loss function in various machine learning tasks, including regression problems. Other loss functions, such as root mean square error (RMSE) and mean absolute error (MAE), are also commonly used depending on the specific problem and requirements.
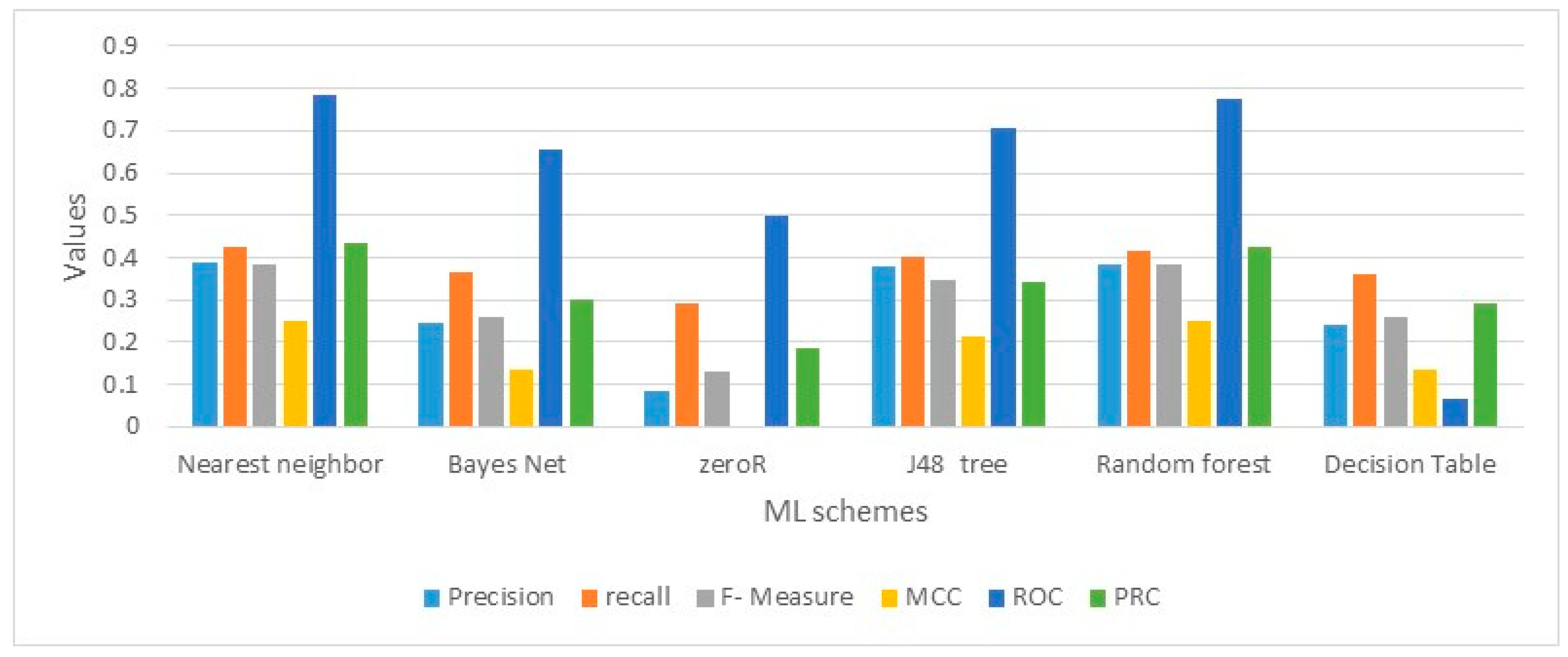
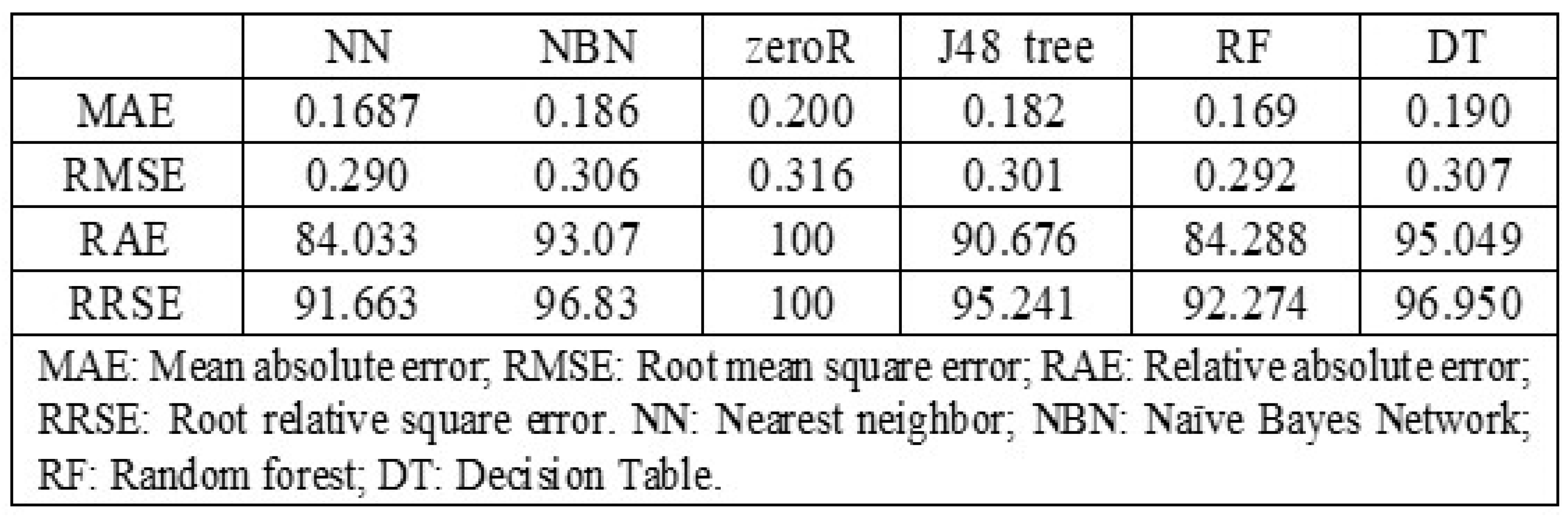
Table 3 illustrates a comparison between various machine learning schemes based on statistical measurements error. Nearest neighbor and random forest provide the best classification performance compared to others ML schemes. Furthermore, the two schemes provide the highest accuracy as illustrated in
Figure 6.
5. Simulation Results
The causal relationship between human factors and driver behavior related to time headway is complex and influenced by various factors. Human factors can play a significant role in determining how drivers perceive, interpret, and respond to the need for maintaining a proper time headway
. Figure 7 illustrates the driver profile which has been classified in aggressive, inattentive and normal according to time headway. Drivers with an aggressive driving style may be more inclined to follow vehicles closely and maintain shorter time headways
. Experienced drivers often have a better understanding of lane discipline and the importance of staying within their designated lane. They are more likely to maintain a consistent and centered lane position. However, inexperienced drivers may have a limited understanding of lane discipline which is increasing the risk of collisions.
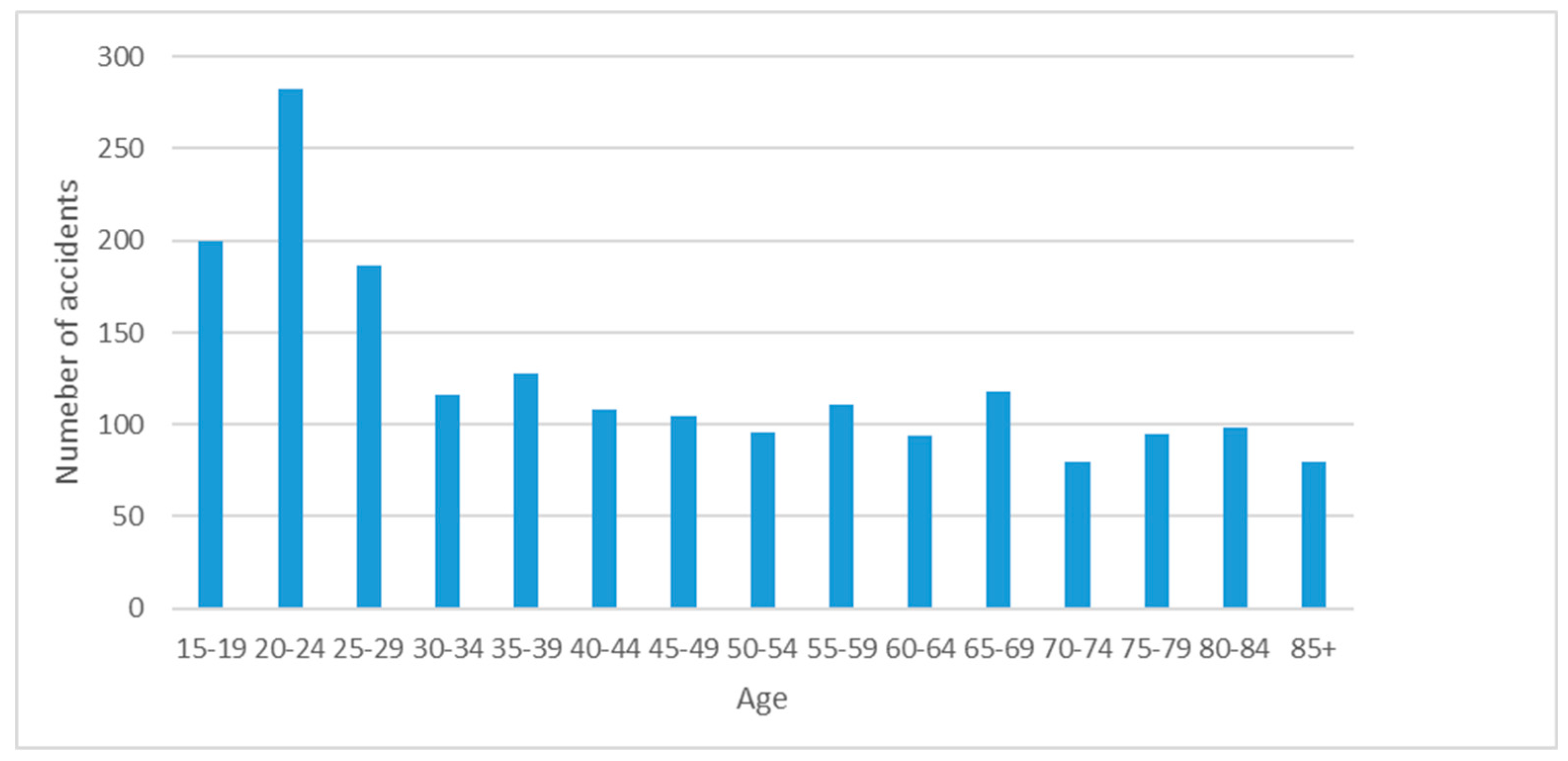
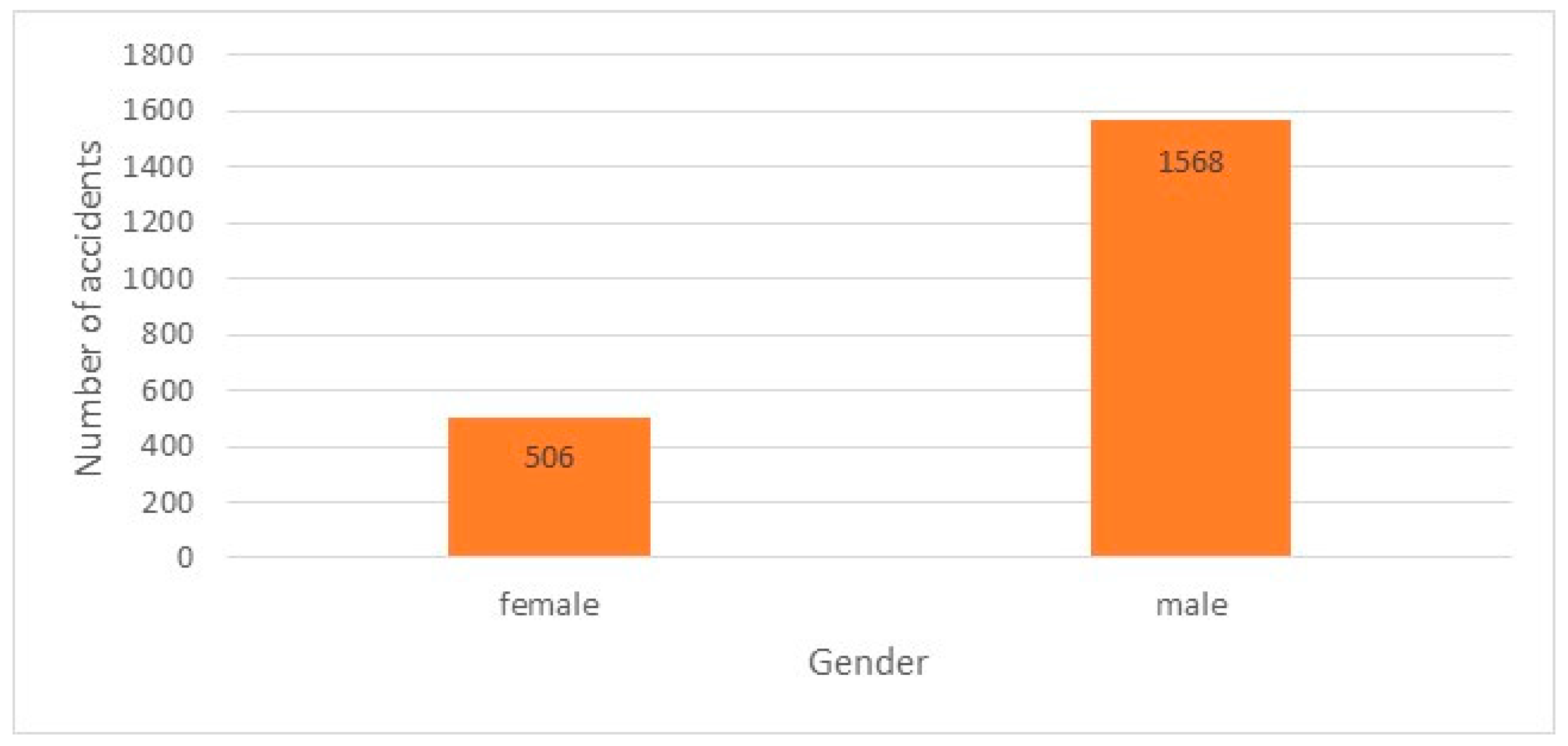
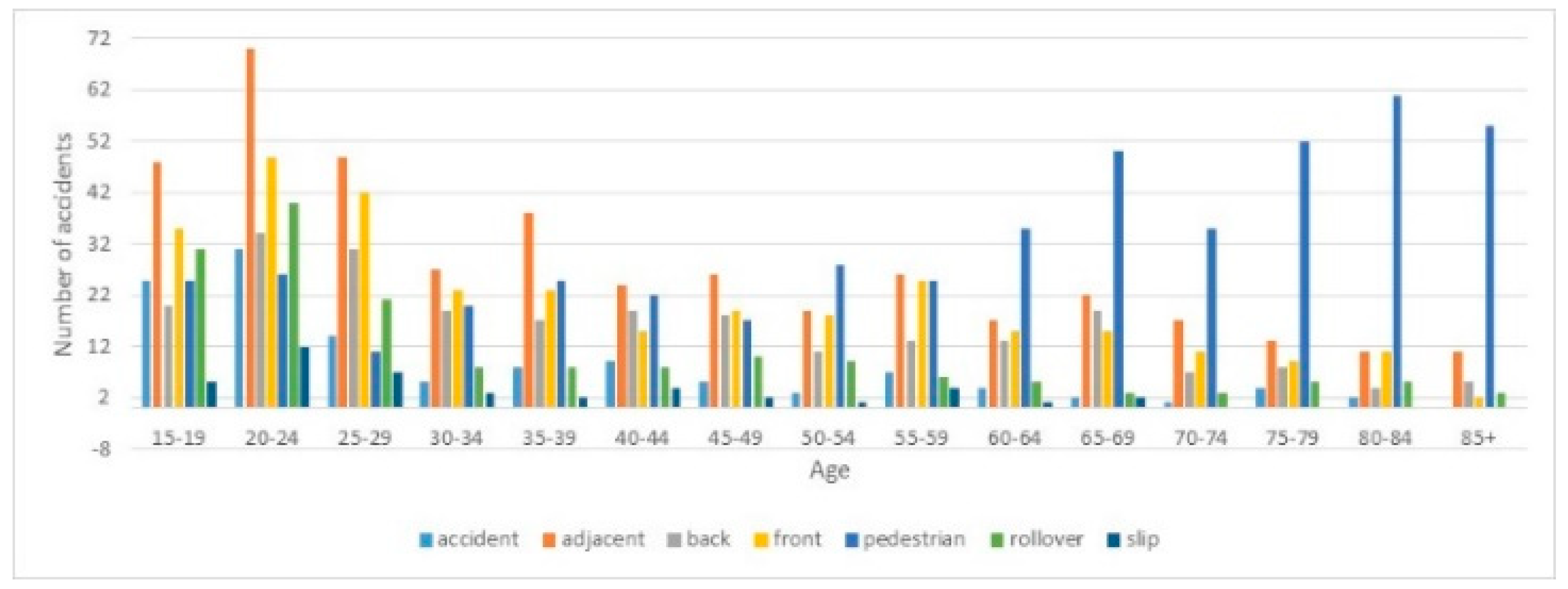
Inexperienced drivers may find the acceleration of a vehicle thrilling or exhilarating, especially if it's their first time driving or if they are not yet accustomed to the sensation. In addition, Inexperienced drivers may feel nervous or anxious during acceleration, particularly in situations where they are still learning to control the vehicle's speed and acceleration smoothly. Figure 8 illustrates the involvement of young driver in age between 20-24 in car accidents. Figure 9 illustrates that females are involved in car accident less than the males. Figure 10 illustrates that the type of car accident and the most accident occur with adjacent car.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of non-monotonic logic in autonomous vehicles' reasoning for car- following holds great potential for enhancing safety, adaptability, and decision-making in dynamic traffic environments. Traditional rule-based systems and monotonic logic often struggle to handle exceptions, conflicting data, and context-dependent reasoning, which are prevalent in car- following scenarios. By employing non-monotonic logic, autonomous vehicles can overcome these limitations and achieve more robust and intelligent behavior. Through the application of non-monotonic logic, autonomous vehicles can handle uncertainties, adapt to changing conditions, and make plausible inferences based on incomplete or uncertain information. The incorporation of non-monotonic logic allows for the modeling of non-monotonic dependencies of driver behavior, enabling the autonomous vehicle to respond effectively to unexpected actions, variable speeds, and context-specific behaviors exhibited by human drivers. This improves safety, efficiency, and the overall performance of the autonomous driving system. Furthermore, the use of AI characteristics, such as sensor fusion, perception, decision-making, predictive analytics, and continuous learning, enhances the safety of autonomous vehicles. AI enables the vehicles to perceive the environment, make informed decisions, and monitor their performance in real-time. The combination of non-monotonic logic and AI characteristics provides a comprehensive approach to develop cognitive and safe autonomous vehicles. However, it is important to continue researching and addressing challenges associated with integrating non-monotonic logic and AI in autonomous vehicles. These challenges include the interpretation and handling of complex scenarios, the validation and verification of non-monotonic reasoning, and the development of robust and reliable AI algorithms. Future work will combine features describing the human factors and vehicle behavior into cognitive hypotheses of a hierarchical cognitive Bayesian network. This will represent an extension of the approach of [
7] for recognition of vehicle behavior, like car-following, lane following and lane changing. By addressing these challenges, we can further improve the safety, reliability, and acceptance of autonomous vehicles on our roads.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bouhsissin, S.; Sael, N.; Benabbou, F. Driver Behavior Classification: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2013, 11, 14128–14153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarlagadda, J.; Pawar, D.S. Heterogeneity in the Driver Behavior: An Exploratory Study Using Real-Time Driving Data, Hindawi Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2022, 2022, 4509071. [CrossRef]
- Abdar, M.; Pourpanah, F.; Hussain, S.; Rezazadegan, D.; Liu, L.; Ghavamzadeh, M.; Fieguth, P.; Cao, X.; Khosravi, A.; Acharya, R.; Makarenkov, V.; Nahavandi, S. A Review of Uncertainty Quantification in Deep Learning: Techniques, Information Fusion 2021, 76. 243-297. [CrossRef]
- Riley, H.; Sridharan, M. Integrating Non-monotonic Logical Reasoning and Inductive Learning With Deep Learning for Explainable Visual Question Answering, Front. Robot. AI, 11 December 2019 Sec. Computational Intelligence in Robotics, Volume 6 - 2019. [CrossRef]
- Szalas, Decision-making support using non-monotonic probabilistic reasoning. In Intelligent Decision, Technologies 2019 - Proceedings of the 11th KES International Conference on Intelligent Decision Technologies (KES-IDT 2019), Volume 1, Malta, June 17-19, 2019, volume 142 of Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies, pages 39–51.
- Raiyn, J.; Weidl, G. Naturalistic Driving Studies Data Analysis Based on a Convolutional Neural Network, in Proceedings of 9th international Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, ISBN 978-989-758-652-1, ISSN 2184-495X, pages 248-256.
- Weidl, G.; Madsen, A.L.; Wang, S.R.; Kasper, D.; Karlsen, M. Early and Accurate Recognition of Highway Traffic Maneuvers Considering Real-World Application: A Novel Framework Using Bayesian Networks, June 2018, IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine 10(3):146 – 158. 20 June.
- L3pilot automation driving. Available online: https://l3pilot.eu/.
- Rousseeuw, P. J. Silhouettes: a Graphical Aid to the Interpretation and Validation of Cluster Analysis, Computational and Applied Mathematics, 1987. 20: 53-65. [CrossRef]
- Zhai and W. Wu, “A new car-following model considering driver’s characteristics and traffic jerk”, Nonlinear Dyn, 2018. 93:2185–2199. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. ; Li, K; Lu, X-Y. Effect of Human Factors on Driver Behavior, Advances in Intelligent Vehicles, 2013, 111-155.
- Shahverdy, M. , Fathy, M. , Berangi, R., Sabokrou, R. Driver behavior detection and classification using deep convolutional neural networks, Expert Systems with Applications 2020, 149, 113240. [Google Scholar]
- Hiang, T.S. , Ming, G. L.: Speeding driving behavior: Age and gender experimental analysis, MATEC Web of Conferences 2016, 74, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargavi, R. Road Rage and Aggressive Driving Behavior Detection in Usage-Based Insurance Using Machine Learning, International Journal of Software Innovation 2019, 11, 1-29. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Guldmann, J.-M.; von Rabenau, B. Impact of Driver’s Age and Gender, Built Environment, and Road Conditions on Crash Severity: A Logit Modeling Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X-K.; Chen, S-L.; Huang, D-L.; Jiang, Z-S.; Jiang, Y-T.; Liang, L-J.; Qin, L-L. The Influence of Personality and Demographic Characteristics on Aggressive Driving Behaviors in Eastern Chinese Drivers. Psychology Research and Behavior Management 2022, 15, 193–212. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).