Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
20 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
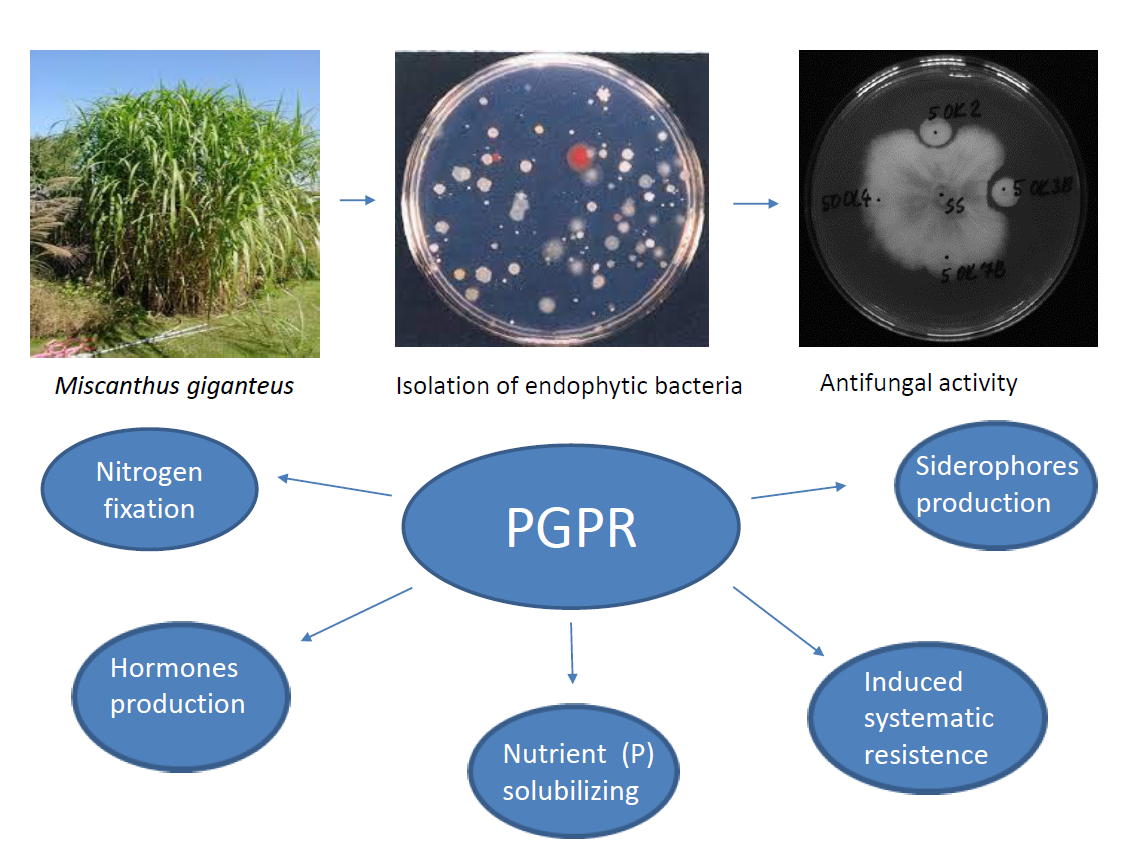
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation of Bacterial Endophytes
2.2. Identification of Bacterial Isolates
2.3. Antifungal Activity of Endophytic Bacteria (Dual Culture Plate Test)
2.4. Detection of ACC-Deaminase Activity
2.5. Siderophore Production
2.6. Phosphate Solubilization
2.7. Nitrogenase Activities
2.8. Phytohormones Detection
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of Endophytic Bacteria from Leaves and Roots of the Miscanthus Giganteus
3.2. Antifungal Activity of Bacterial Isolates
| Isolates from plant tissue | Identification | Score* | Botrytis cinerea |
Fusarium sporotri chioides |
Sclerotinia sclerotiniorum | Sphaerodes fimicola |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 OK 2 | Pseudomonas fluorescent | 2.179 | +/- | + | +/- | - |
| 50 OK 3 | Pseudomonas libanensis | 2.202 | + | + | + | + |
| 50 OK 5 | Variovorax paradoxus | 2.003 | + | + | + | + |
| 50 OK 6 | Pseudomonas marginalis | 2.223 | + | + | + | + |
| 50 OK 7 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.238 | + | + | + | +/- |
| 50 OK 14A | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.277 | + | + | +/- | +/- |
| 5 OK 3B | Pseudomonas azotoformans | 2.138 | + | + | + | + |
| 5 OK 5A | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.198 | + | + | + | + |
| 5 OK 7A | Pseudomonas libanensis | 2.300 | + | + | + | + |
| 5 OK 7B | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.178 | + | + | - | +/- |
3.3. Plant growth promoting potential of bacterial isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahle, P.; Beuch, S.; Boelcke, B.; Leinweber, P.; Schulten, H. R. Cropping of Miscanthus in Central Europe: biomass production and influence on nutrients and soil organic matter. European Journal of Agronomy 2001, 15, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, D.Y.; Palumbo, J.D. Bacterial endophytes and their effects on plants and uses in agriculture. In Microbial endophytes; Bacon, C.W., White, J.F., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, USA, 2000; pp. 199–233. [Google Scholar]
- Mercado-Blanco, J.; Lugtenberg, B.J.J. Biotechnological Applications of Bacterial Endophytes. Current Biotechnology 2014, 3, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, K.L.; Kour, D.; Kaur, T. Endophytic microbes: biodiversity, plant growth-promoting mechanisms and potential applications for agricultural sustainability. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 1075–1107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunjal, A.; Waghmode, M.; Patil, N. , B. Endophytes and Their Role in Phytoremediation and Biotransformation Process. In Microbial Biotechnology in Environmental Monitoring and Cleanup, IGI Global. Editor Sharma A., Eds.; Publisher: Engineering Science Reference, Harshey, USA, 2018; pp. 238–251. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblueth, M.; Martínez–Romero, E. Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2006, 19, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glick, B.R. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: Mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012, 963401. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, G.; Panwar, J.; Akhtar, M.S.; Jha, P.N. Endophytic nitrogen-fixing bacteria as biofertilizer. Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 2012, 11, 183–221. [Google Scholar]
- Gaiero, J.R.; McCall, C.A.; Thompson, K.A.; Day, N.J.; Best, A.S.; Dunfield, K.E. Inside the root microbiome: Bacterial root endophytes and plant growth promotion. American Journal of Botany 2013, 100, 1738–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Malfanova, N.V. Endophytic bacteria with plant growth promoting and biocontrol abilities. Ph.D. thesis, Leiden University, Leiden, Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, M.L.E.; Glick, B.R. Applications of plant growth-promoting bacteria for plant and soil systems. In Application of Microbial Engineering; Editor Gupta, V.K., Schmoll, M., Mazutti, M.A., Maki M., Tuohy, M.G., Eds., Publisher: CRC Press, Boca Raton, USA, 2013; pp. 181–228. [Google Scholar]
- Afzal, M.; Khan, Q.M.; Sessitsch, A. Endophytic bacteria: Prospects and applications for the phytoremediation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, C.S.; Lovecká, P.; Mrnka, L.; Vychodilová, A.; Strejček, M.; Fenclová, M.; Demnerová, K. Distinct communities of poplar endophytes on an unpolluted and a risk elements-polluted site and their plant growth promoting potential in vitro. Microbial Ecology 2017, 75, 955–969. [Google Scholar]
- Koubek, J.; Uhlík, O.; Ječná, K.; Junková, P.; Vrkoslavová, J.; Lipov, J.; Kurzawová, V.; Macek, T.; Macková, M. Whole-cell MALDI-TOF: rapid screening method in environmental microbiology. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation 2012, 69, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Chang, S.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; An, Q. A colorimetric assay of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) based on ninhydrin reaction for rapid screening of bacteria containing ACC deaminase. Letters in Applied Microbiology 2011, 53, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Louden, B.C.; Haarmann, D.; Lynne, A.M. Use of Blue Agar CAS Assay for Siderophore Detection. Journal of Microbiology and Biology Education 2011, 12, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jasim, B.; Jimtha, C.J.; Jyothis, M.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Plant growth promoting potential of endophytic bacteria isolated from Piper nigrum. Plant Growth Regulation 2013, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dadarwal, K.R.; Kundu, B.S.; Tauro, P. In vitro and in vivo nitrogenase aktivity of Rhizobium mutants and their symbiotic effectivity. Journal of Biosciences 1981, 3, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hajšlová, J.; Fenclová, M.; Zachariašová, M. Methodology for the rapid screening of isolates of endophytic microorganisms and identification of strains with phytohormonal activity [in Czech]. ISBN 978-80-7080-869-6, 2013.
- Schmidt, C.S.; Mrnka, L.; Frantík, T.; Loveckaá, P.; Vosádka, M. Plant growth promotion of Miscanthus × giganteus by endophytic bacteria and fungi on non-polluted and polluted soils. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 2018, 34, 48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manka, M.; Visconti, A.; Chełkowski, J.; Baottalico, A. Pathogenicity of Fusarium Isolates from Wheat, Rye and Triticale Towards Seedlings and their Ability to Produce Trichothecenes and Zearalenone. Journal of Phytopathology 2008, 113, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Loper, J.E.; Gross, H. Genomic analysis of antifungal metabolite production by Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5. European Journal of Plant Pathology 2007, 119, 265–278. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, T.A.; Venter, S.N. Pantoea ananatis: an unconventional plant pathogen. Molecular Plant Pathology 2009, 10, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ercolani, G.L. Pseudomonas savastanoi and other bacteria colonizing the surface of olive leaves in the field. Journal of the General Microbiology 1978, 109, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInroy, J.A.; Kloepper, J.W. Survey of indigenous bacterial endophytes from cotton and sweet corn. Plant and Soil 1995, 173, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Earl, A.M.; Losick, R.; Kolter, R. Ecology and genomics of Bacillus subtilis. Trends in Microbiology 2008, 16, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scales, B.S.; Dickson, R.P.; LiPuma, J.J.; Huffnagle, G.B. Microbiology, genomics, and clinical significance of the Pseudomonas fluorescens species complex, an unappreciated colonizer of humans. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2014, 27, 927–948. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhu, N.N.; Zhai, Z.H.; Zhang, Q. Endophytic bacterial diversity in roots of Phragmites australis in constructed Beijing Cuihu Wetland (China). FEMS Microbiology Letters 2010, 309, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreani, N.A.; Martino, M.E.; Fasolato, L.; Carraro, L.; Montemurro, F.; Mioni, R.; Bordin, P.; Cardazzo, B. Reprint of ’Tracking the blue: A MLST approach to characterise the Pseudomonas fluorescens group´. Food Microbiology 2015, 45, 148–158. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston-Monje, D.; Raizada, M.N. Conservation and diversity of seed associated endophytes in Zea across boundaries of evolution, ethnography and ecology. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, P.; Yadav, A.N.; Kazy, S.K.; Saxena, A.K.; Suman, A. Evaluating the diversity and phylogeny of plant growth promoting bacteria associated with wheat (Triticum aestivum) growing in central zone of India. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences 2014, 3, 432–447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qian, M.; Sheng, X. Characterization of ACC deaminase-producing endophytic bacteria isolated from copper-tolerant plants and their potential in promoting the growth and copper accumulation of Brassica napus. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, P.; Spann, T.; Wang, N. Isolation and characterization of beneficial bacteria associated with citrus roots in Florida. Microbial Ecology 2011, 62, 324–336. [Google Scholar]
- Belimov, A.A.; Safronova, V.I.; Sergeyeva, T.A.; Egorova, T.N.; Matveyeva, V.A.; Tsyganov, V.E.; Borisov; A. Y., Tikhonovich, I.A.; Kluge, C.; Preisfeld, A.; Dietz, K.; Stepanok, V.V. Characterization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria isolated from polluted soils and containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 2011, 47, 642–652. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, C.A.; Alves, V.M.C.; Marriel, I.E.; Gomes, E.A.; Scotti, M.R. .; Carneiro, N.P.; Guimaraes, C.T.; Schaffert, R.E.; Sá, N.M.H. Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms isolated from rhizosphere of maize cultivated in an oxisol of the Brazilian Cerrado Biome. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2009, 41, 1782–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornelis, P. Iron uptake and metabolism in pseudomonads. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2010, 86, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Dodd, I.C.; Theobald, J.C.; Belimov, A.A.; Davies, W.J. The rhizobacterium Variovorax paradoxus 5C-2, containing ACC deaminase, promotes growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana via an ethylene-dependent pathway. Journal of Experimental Botany 2013, 64, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Persson, B.C. , Esberg, B., Ólafso,n Ó., Björk, G.R. Synthesis and function of isopentenyl adenosine derivatives in tRNA. Biochimie 1994, 76, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakakibara, H. Cytokinins: activity, biosynthesis, and translocation. Annual Review of Plant Biology 2006, 57, 431–449. [Google Scholar]
- Kido, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Matsumoto, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Takikawa, Y. Pantoea ananatis strains are differentiated into three groups based on reactions of tobacco and welsh onion and on genetic characteristics. Journal of General Plant Pathology 2010, 76, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martínez, I.; Zhao, Y.; Murillo, J.; Sundin, G.W.; Ramos, C. Global genomic analysis of Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi plasmids. Journal of Bacteriology 2008, 190, 625–635. [Google Scholar]
- Kochar, M.; Upadhyay, A.; Srivastava, S. Indole-3-acetic acid biosynthesis in the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas fluorescens Psd and plant growth regulation by hormone overexpression. Research in Microbiology 2011, 162, 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, A.; Cromey, M. Identifying disease threats and management practices for bio-energy crops. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2011, 3, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
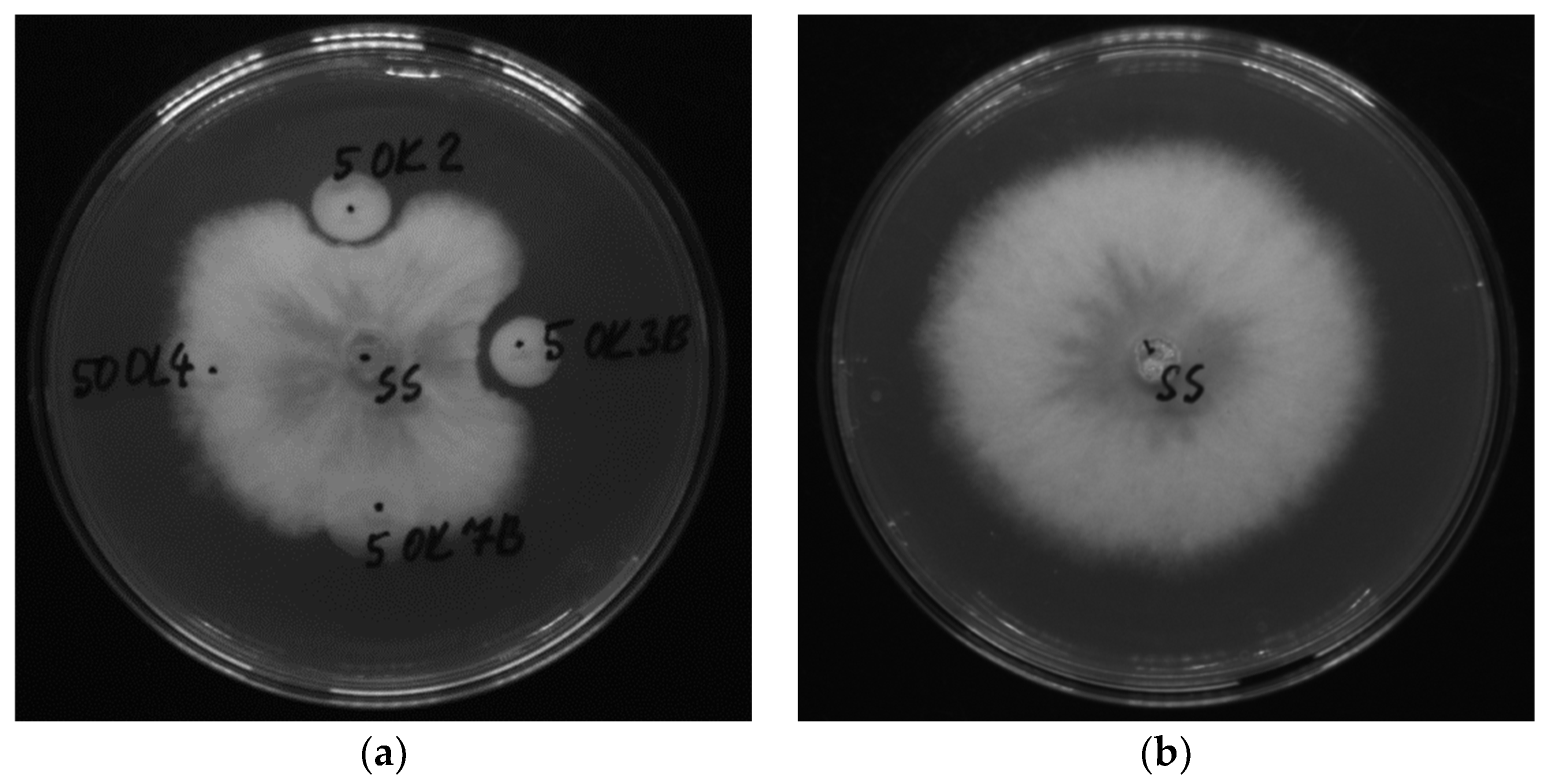
| Isolates from plant tissue | Identification | Score* |
Botrytis cinerea |
Fusarium sporotri- chioides |
Sclerotinia scleroti- niorum |
Sphaerodes fimicola |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 OL 2 | Pantoea ananatis | 2.386 | + | + | + | - |
| 50 OL 4 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.109 | + | +/- | - | - |
| 50 OL 5 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.056 | +/- | + | +/- | - |
| 50 OL 6 | Ps. libanensis | 2.117 | + | - | + | - |
| 50 OL 7 | Pseudomonas sp. | 1.990 | + | - | - | - |
| 5 OL 1 | Pantoea ananatis | 2.299 | + | + | +/- | - |
| 5 OL 2 | Pantoea ananatis | 2.381 | + | +/- | + | - |
| 5 OL 3 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.029 | +/- | + | + | - |
| 5 OL 4 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.111 | +/- | - | - | - |
| 5 OL 5 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.095 | +/- | + | - | - |
| 5 OL 6 | Pantoea ananatis | 2.368 | + | +/- | +/- | - |
| 5 OL 7 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.086 | +/- | + | - | - |
| 5 OL 8 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.106 | +/- | +/- | - | - |
| 5 OL 11 | Pseudomonas sp. | 2.108 | +/- | - | - | - |
| 5 OL 12 | Pantoea ananatis | 2.277 | + | + | +/- | - |
| Isolates from plant tissue | Identification | ACCd | P-SOL | SID | NITRO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 OK 3 | Pseudomonas libanensis | + | - | +++ | +++ |
| 50 OK 5 | Variovorax paradoxus | + | - | +++ | + |
| 50 OK 6 | Pseudomonas marginalis | - | + | +++ | ++ |
| 5 OK 7A | Pseudomonas libanensis | - | +++ | + | ++ |
| 50 OL 2 | Pantoea ananatis | + | ++ | +++ | + |
| Isolates from plant tissue | Identification | Phytohormons (ng.mL−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| iP | iPR | IAA | ||
| 50 OK 3 | Pseudomonas libanensis | 5.5 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 50 OK 5 | Variovorax paradoxus | 3.8 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 50 OK 6 | Pseudomonas marginalis | 3.7 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 5 OK 7A | Pseudomonas libanensis | 11.7 | 8.9 | 12.6 |
| 50 OL 2 | Pantoea ananatis | 1.1 | n.d. | n.d. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





