1. Introduction
In December 2019, a novel virus was identified in Wuhan, Hubei Province, China (1). A coronavirus, from a betacoronavirus family, named as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (2). The disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 is highly transmissible and potentially fatal. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused more than 770,563.467 cases and 6,957,216 deaths worldwide. Despite the vaccines against COVID-19, approximately 17.576 cases are reported weekly (3). SARS-CoV-2 infects the upper and lower airways, causing mild symptoms such as fever, cough, fatigue, runny nose, and sneezing, and can evolve with severe symptoms, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), hypoxemic respiratory failure, shock, multiple organ failure, and death (4). Evidence suggests that the exacerbated inflammatory process induced by the SARS-CoV-2 infection plays a key role in the severity of COVID-19 and mortality (5–7). Severe COVID-19 is associated with high levels of circulating mediators, including pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and lipid mediators; profound lymphopenia; and substantial infiltration of mononuclear cells into the lungs, heart, spleen, lymph nodes, and kidneys (8–10).
Recent studies have shown that critically ill patients with SARS-CoV2 infection present dysregulated inflammatory responses, including lipid mediators production (11–14). Thus, the modulation of lipid mediators may be a therapeutic target for SARS-CoV-2. Among these lipid mediators, leukotrienes (LTs) and lipoxins (LXA) have been highlighted because they can affect prognosis and play a dual role in the pathogenesis of several chronic inflammatory diseases, including bacterial, parasitic, and viral infections in experimental models (15–17). Zileuton (Zi) is a selective inhibitor of the enzyme 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO), which is involved in intracellular pathways that trigger the production of both LTs and LXA. Zi is approved for use in patients with asthma (18,19).
We hypothesized that Zi could have a protective effect against beta-coronavirus-induced diseases. Here, we first used a model of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV)-3 infection, a murine beta-coronavirus that emulates severe COVID-19 in mice (20). Zi treatment significantly improved clinical scores, weight loss, cardiopulmonary function, and survival rates compared with vehicle-treated infected littermates. Zi-treated mice showed reduced inflammatory scores in the lungs, reduced dendritic cell-producing tumor necrosis factor (TNF), and increased neutrophil-producing interleukin (IL)-10 in the lungs 3 days after infection (dpi), the peak of lung damage. At 5dpi, the peak of systemic disease manifestation, increased Th2-, Treg CD4+-, and Treg CD8+-producing IL-10, and reduced Th1 infiltrating cells were observed in the lungs of treated mice. Similar protective effects were observed upon Zi treatment in transgenic mice expressing the human angiotensin I-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor driven by the cytokeratin-18 (K18) gene promoter (K18-hACE2) infected by SARS-CoV2. Interestingly, the effects of Zi were independent of the control of viral titers in the lungs.
These findings suggest that Zi treatment controls the exacerbated deleterious inflammatory responses in the lungs of mice infected with both MHV-3 and SARS-CoV-2 without affecting the host’s ability to deal with the infection. Finally, using Zi along with an antiviral drug may be beneficial for treating betacoronavirus-induced diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell, virus, and plaque assay
L929 cells purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC ® CCL-1) were cultured in a controlled atmosphere (37° C, 5% CO2) in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM, Gibco, BLR Life Technologies) supplemented with 7% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Cultilab, Campinas, Brazil), and 100 U/mL of penicillin (Gibco) and 100 μg/mL of streptomycin (Gibco). The MHV-3 strain was kindly provided and sequenced (GenBank accession number MW620427.1. (21) by Dr. Clarice Arns and Dr. Ricardo Durães-Carvalho from the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP, Brazil) and propagated in L929 cells. For viral titration, 100 μL of serially diluted virus suspension, plasma samples, and tissue homogenates (1:9; tissue:DMEM) were inoculated onto a confluent monolayer of L929 cells grown in 24-well plates. After gentle agitation for 1 h (4 x 15 min), the samples were harvested, and the culture medium was replaced (DMEM containing 1.6% carboxymethylcellulose, 2% FBS, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin-glutamine) and maintained for two days at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Then, cells were fixed with 10% neutral-buffered formalin for 1 h and stained with 0.1% crystal violet. Viral titers were determined as plaque-forming units (PFU).
2.2. Mouse strains
C57/BL6 obtained from the Central Animal House at the Federal University of Minas Gerais (UFMG) and hK18 human angiotensin I-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) purchased from the Jackson Laboratories and maintained at the Immunopharmacology Lab at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences (ICB)/UFMG were housed in individually ventilated cages placed in an animal facility at 24 ± 2 °C on a 12/12 h light/dark cycle, receiving ad libitum access to water and food. All experimental procedures were performed with mixed groups (male and female) of mice aged 6–9 weeks at the NB2 and NB3 facilities and were approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation of the UFMG (Approval nº. 190/2020).
2.3. MHV-3 and SARS-CoV-2 infections
Mice were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of ketamine (Syntec, 50 mg/kg): xylazine (Syntec, 5 mg/kg) and received an intranasal inoculation of 30 μL of loaded or unloaded sterile saline (mock controls) with MHV-3 (3 × 10³ PFU) or SARS-CoV-2 (clinical isolate from a nasopharyngeal swab obtained from a confirmed case of COVID-19 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, GenBank accession no. MT710714, Gamma variant, 2 x 104 PFU). Symptoms of illness, including goosebumps, arching of the back, weight loss, facial swelling, and lack of activity, were monitored daily for five or ten days post-inoculation (dpi).
2.4. Treatment with Zi
For the treatment, mice were divided into three groups: mock, vehicle, and treated. Mock animals received an intranasal inoculation of 30 μL of sterile saline. In contrast, mice in the vehicle and treated groups received an intranasal inoculation of 30 μL loaded with MHV-3 or SARS-COV-2. Then, 24 h after infection, the treated group received a solution containing 1, 5, 3, 15, or 30 mg/kg of Zi, diluted in 100 µL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) by oral gavage. The treatment was administered orally for ten days, and the animals received the drug every 12 h. The vehicle group received 100 µL of carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) 0.5% for ten days, every 12 h.
2.5. Tissue collection
After anesthesia (ketamine: xylazine, 80 mg/kg:10 mg/kg, i. p.), control (mock), infected, and infected and treated mice at 3 and 5 dpi were euthanized. Blood samples were collected from the abdominal cava vein and placed in tubes coated with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA; Vacuplast). The lungs were harvested and quickly rinsed with cold, sterile saline, and the right lobes were frozen. The left lobe was fixed by immersion in a 10% neutral buffered formalin solution (Synth).
2.6. Hematological evaluation
The numbers of circulating platelets, leukocytes, red cells, granulocytes, and lymphocytes were determined in blood samples using a Celltac MEK-6500K hemocytometer (Nihon Kohden).
2.7. Histopathology
Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues were sectioned into 5-µm thickness slices, stained with hematoxylin-eosin (H&E), and examined under light microscopy. Inflammation-mediated injury in mouse lungs was determined by a pathologist (CMQJ) blinded to the experiment by employing a scoring system encompassing (i) airway inflammation (up to 4 points); (ii) vascular inflammation (up to 4 points); (iii) parenchyma inflammation (up to 5 points); and (iv) general neutrophil infiltration (up to 5 points) (22). Fundamental pathological lesions, including signs of inflammation (i.e., inflammatory cell infiltration and edema), cell death (i.e., necrosis), tissue hyperplasia, and hemorrhage, were evaluated regarding intensity and extension and graded according to the adapted score.
2.8. Cytokine assay
Lung homogenates were prepared by homogenizing 40 mg of frozen tissue in 400 mL of cold cytokine extraction buffer (100 mM Tris pH 7.4, 150 MM NaCl, 1 mM EGTA, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM Triton X-100, 1% sodium deoxycholate, 0.5%, and protease inhibitor cocktail 1%. After centrifugation at 14000 g for 15 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was collected, and the concentration of TNF, IFN-γ, IL- 10, IL-6, IL-17, IL-1β, TGF- β, CCL2, and CXCL1 was measured using the mouse DuoSet ELISA System (R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.9. Respiratory mechanics
To measure respiratory system compliance, full-range pressure-volume (PV) curves were constructed similar to those in our previous study (20) and adapted from (23,24). Briefly, the mice were divided into three groups, and three days dpi, the animals were deeply anesthetized until respiratory arrest. The mice were tracheostomized, and a polyethylene tube (P50) was inserted into the trachea. The PV curve was generated by injecting air volume in a continuous manner using a 3 mL syringe and an automated syringe pump (Bonther, Ribeirao Preto, Brazil) at a rate of 3 mL/min until the intratracheal pressure peaked at approximately 35 cmH2O. At peak pressure, the syringe pump was manually switched for the deflation limb, deflated at the same rate until the pressure reached approximately 15 cmH2O, and finally inflated again to the resting lung volume (23). Both volume and pressure signals were acquired and recorded using PowerLab software (LabChart v7, AdInstruments, NSW, Australia). At least two consecutive sequences of inflation and deflation were performed, and full-range PV curves for each animal were obtained. If leaks or inappropriately high pressures were detected, the animal was excluded from the analysis. Vital capacity was determined by maximum insufflation (lung volume at 35 cmH2O), and static compliance of the respiratory system (expressed in mL/cmH2O) was measured at the steepest point of the deflation limb of the PV curve (23–25).
2.10. ECG recording
A six-channel non-invasive electrocardiograph (InCardio X, Inpulse Animal Health®, Florianópolis, Santa Catarina, Brazil) was used. The recordings were made without anesthesia once anesthetic drugs were recognized to influence the ECG markers, as highlighted previously (26). The study ensured precise positioning by manually restraining the rodents in a dorsal recumbent stance on a plastic-covered wooden table, followed by the application of conductive electrocardiographic gel and attachment of four alligator clip electrodes on the forelimbs and hind limbs, as established previously (27). All the procedures were performed in a quiet room to mitigate stress. For lead second frontal plane deviation (DII), readings were captured at a standard speed of 100 mm/s, with sensitivity calibrated to 3N.
2.11. Flow cytometry
Mice infected or uninfected with MHV-3 were sacrificed at 3 and 5 dpi. The spleens were removed and processed as previously described (28). The lungs were removed and processed as previously described (29). Purified cells from the lungs and spleen were plated and incubated with refeldin A (10 μg/mL) (Invitrogen) for 3 h at 37 ºC in the presence of 5% CO2. Cells were blocked with Fc Block (antibody CD16/CD32 in PBS/BSA 1%), followed by stain using specific combinations of antibodies for cell surface molecule labeling: CD3, CD11b (APC-Cy7); CD4, Ly6C (PE-Cy7); CD8, Ly6G, SinglecF (BV421); CD25, CD45 (PerCP-Cy5.5); F4/80 (FITC); CD11c (V500), and isotype controls (all from BD Biosciences). For intracellular staining, the following antibodies were added: IFNγ (Alexa 488), IL-17, forkhead box P3 (FOXP3) (PE), TNF (PE), and IL-10 (APC). A total of 30,000 cells (events) were acquired using a FACSCanto II cytometer (Becton, Franklin Lakes, San Jose, USA) and analyzed using the FlowJo software (version 10).
2.12. Statistical Analysis
The statistical significance of differences in values between the control and treated/infected groups was assessed using Student’s t-test, Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), with Sidak’s post-test. Differences were considered statistically significant at p ≤ 0.05. GraphPad Prism software (version 7.0) was used for statistical analyses.
3. Results
3.1. Treatment with Zi improves survival rates of MHV-3-infected mice regardless a control of viremia.
Zi is capable of inhibiting the production of LTs and LXs, which are eicosanoids with pro and anti-inflammatory/pro-resolving actions, respectively. Selective blockade of the main enzyme (5-LO) in the pathway producing these mediators by this drug is a promising target for several diseases, including COVID-19. First, the effect of Zi in an animal model of respiratory coronavirus (MHV-3) infection was investigated through a dose-dependent treatment with Zi (1.5, 3, 15, and 30 mg/kg) (
Figure 1A). Animals treated with the highest dose of Zi (30 mg/kg) were able to delay and partially prevent lethality (
Figure 1A), reduce weight loss (
Figure 1B), and improve clinical scores (
Figure 1C) induced by MHV-3-infection, when compared to vehicle-treated animals. Considering that a dose of 30 mg/kg showed the best effects, it was chosen for further experiments. Since the infected animals showed a significant reduction in weight loss from 3 day after infection (dpi) (
Figure 1B) and began to succumb to infection at 6 dpi (
Figure 1A), we chose to carry out the subsequent analysis at 3 and 5 dpi. To understand how Zi protects mice, the number of plaque-forming units (PFU) in the plasma of animals was verified. Both the infected groups showed elevated viremia. No difference was observed between the Zi- and vehicle-treated groups (
Figure 1D), demonstrating that the delay and increased survival rates were not dependent on viremia control. Subsequently, we evaluated the clinical disease. On the 3rd and 5th dpi, hematological analyzes performed at, which showed that the infection caused severe leukopenia (
Figure 1E) and lymphopenia (Figure F) compared to control animals. Among other parameters, it was observed that on the 5th dpi, there was a reduction in platelets in both groups (
Figure 1G), but a reduction in granulocytes was observed only in untreated infected animals (
Figure 1H), suggesting that Zi can regulate granulocyte numbers during MHV-3 infection.
3.2. Zi treatment prevent lung tissue damage regardless of viral load control.
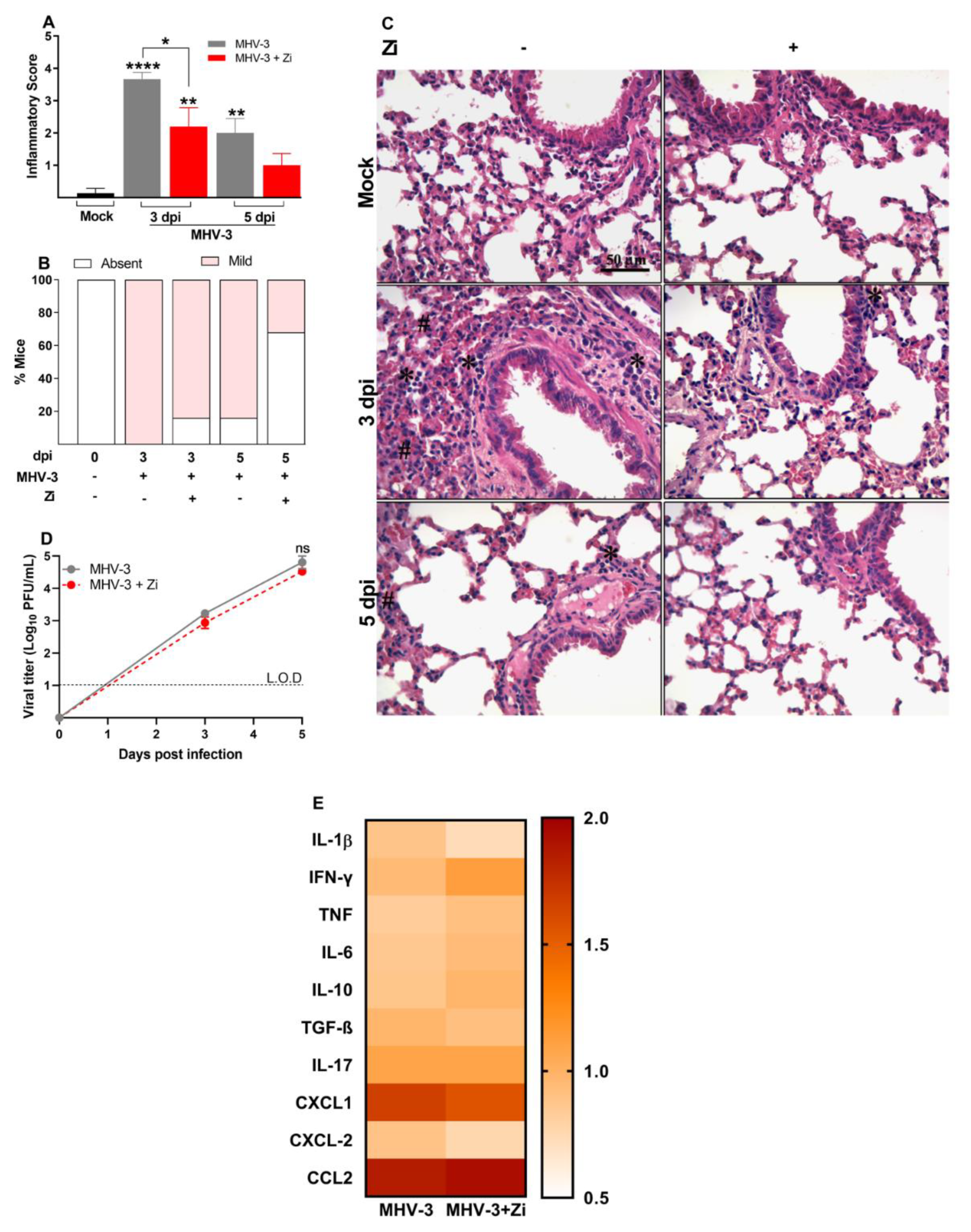
To observe the effect of Zi treatment on lung tissue, histopathological analyses were performed at 3 and 5 dpi. The results demonstrated that at 3 dpi, there was more pronounced tissue damage than at 5 dpi in both groups (
Figure 2 A), however, treatment with Zi significantly reduced the inflammatory scores at 3 dpi when compared to the infected and vehicle-treated groups. At 5 dpi, the Zi-treated group no longer presented a statistically significant difference from the mock-treated group (Figs. 2A and 2C). Moreover, at 3 dpi, 100% of the infected, untreated animals presented with lesions in the lung tissue, whereas this percentage was reduced to 80% in the treated group. At 5 dpi, this difference increased to 80% in the untreated group versus only 30% in the Zi-treated group (
Figure 2B). Notably, the amount of PFU was similar in this tissue between the treated and untreated animals on days 3 and 5, demonstrating that the improvement in lung tissue was independent of the number of viral particles present (
Figure 2D). Considering that the exacerbated production of inflammatory cytokines is a major hallmark of severe disease, the levels of cytokines in the lung tissue were verified. Zi-treated mice presented at 3 dpi a higher mean level of IFN-γ, TNF, and IL-10 when compared to the untreated group, however, a reduction in CXCL-2, IL-1β, and CXCl-1 was observed (
Figure 2E).
3.3. Zi reduces the severity of cardiopulmonary complications during MHV-3 infection.
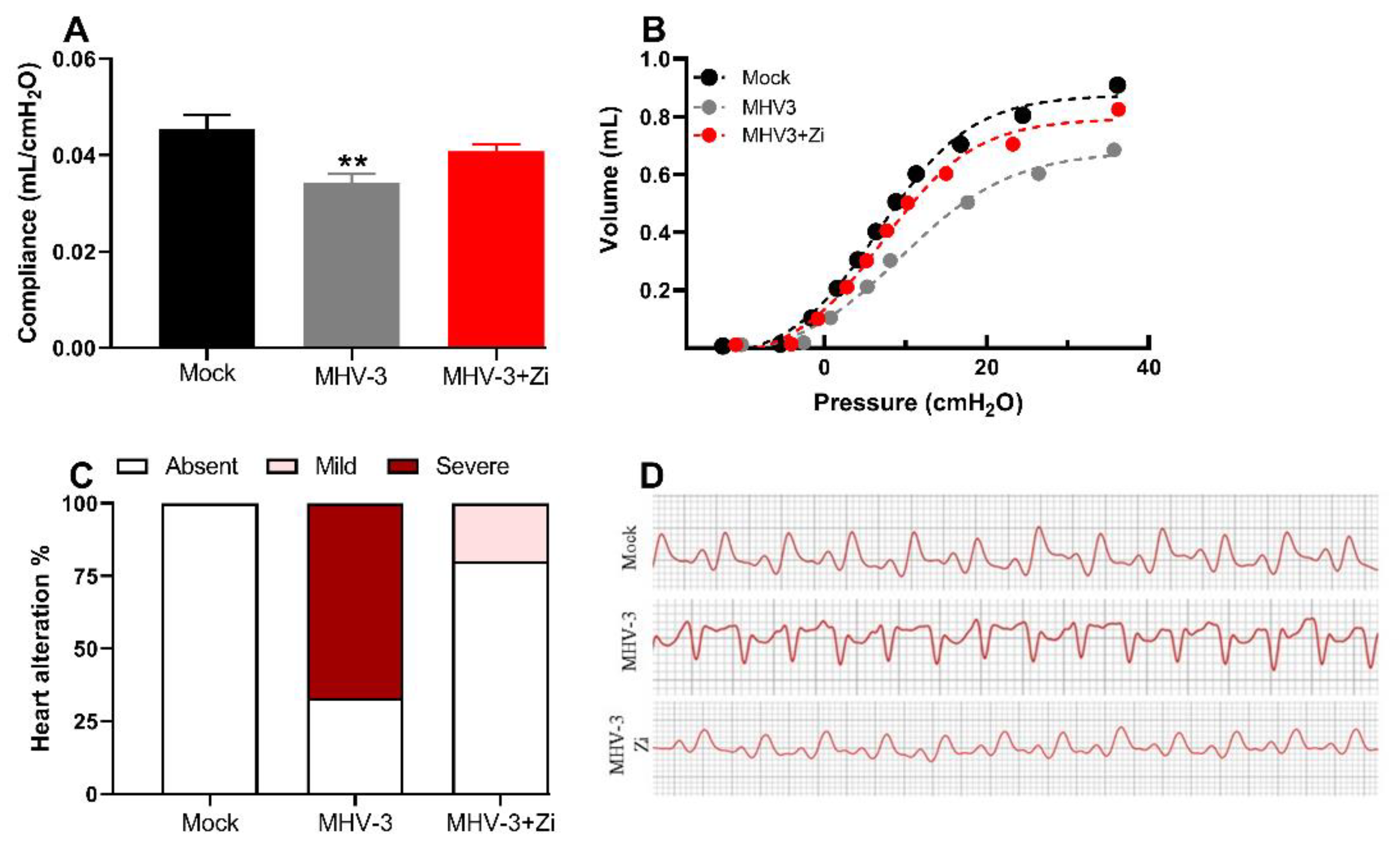
Considering the reduction in inflammation in the lungs, we evaluated whether treatment with Zi would improve the pathophysiological conditions caused by infection. In addition to lung function, cardiac function was also analyzed because the heart is physiologically connected to the lungs and undergoes the consequences of viral infection.
Figure 3A–B demonstrated that at 3 dpi, when infected, untreated mice presented a more pronounced lesion in the lungs, a significant reduction in lung compliance was observed compared to the mock group. This effect was observed in the PV curves of representative animals from each experimental group (
Figure 3B). Notably, treatment with Zi protected lung function, maintaining the compliance of the respiratory system closer to that of the mock group (
Figure 3A, B).
Electrocardiogram analysis revealed that treated animals exhibited minor cardiac alterations, whereas the untreated group displayed pronounced alterations (
Figure 3C). Furthermore, Zi treatment helped maintain a heart pattern more closely resembling that observed in the mock animals (
Figure 3D).
3.4. Zi treatment was associated with an increased expansion of IL-10 producing neutrophils in the Lungs of MHV-3 infected-mice
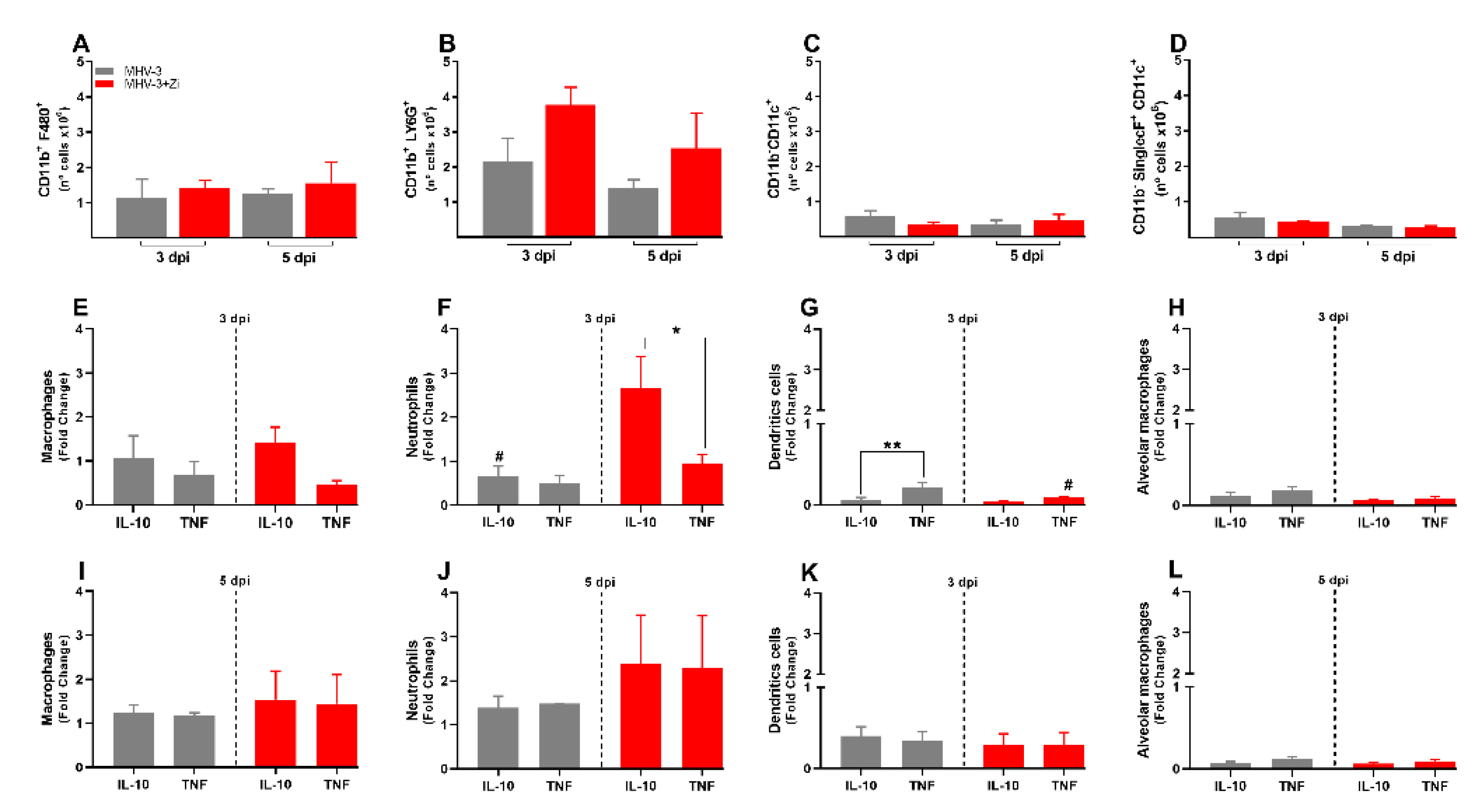
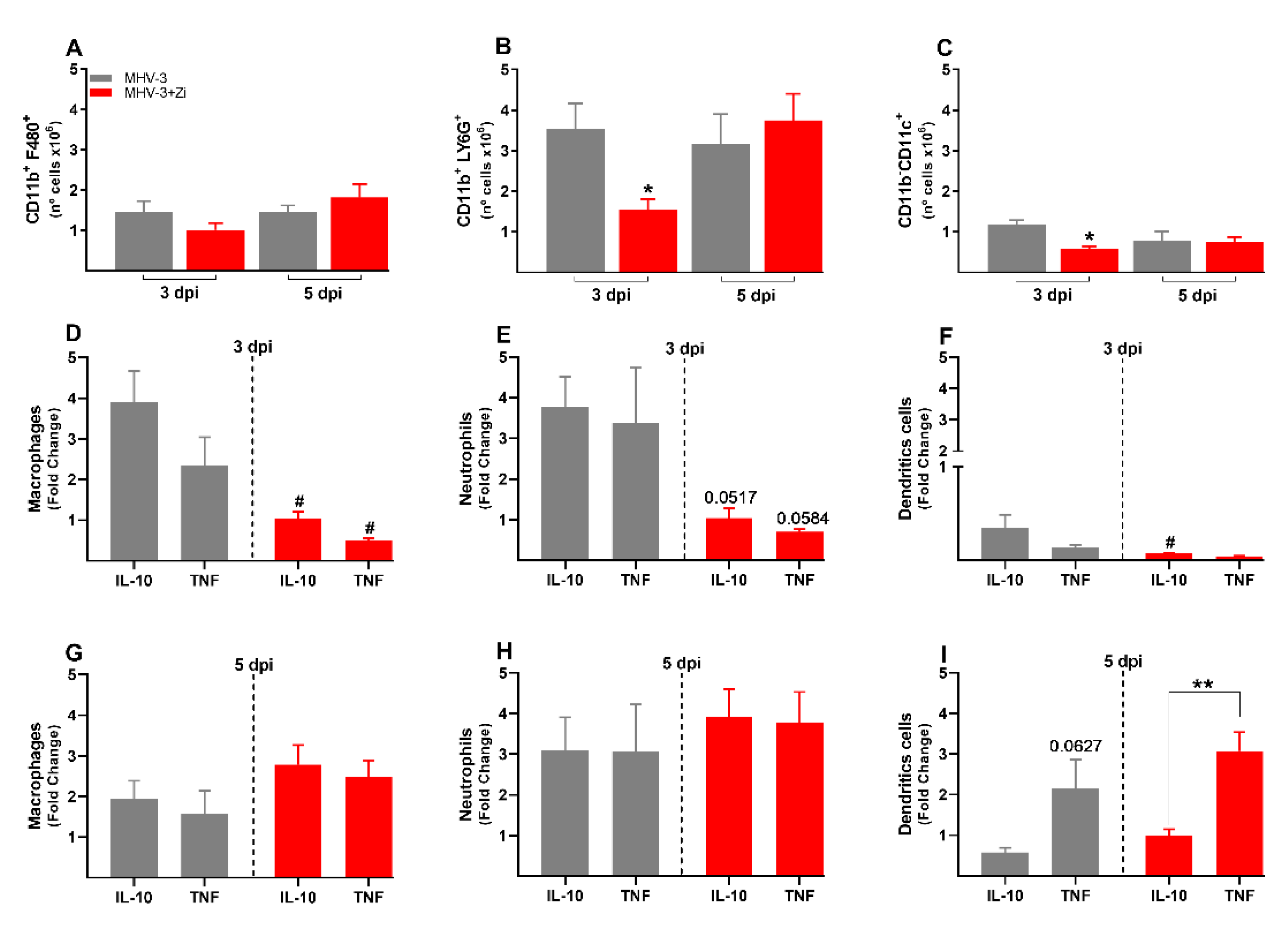
To better understand the protection of lung function during Zi treatment, the profiles of infiltrating cells in this tissue were investigated. In the lungs, were not observed significant differences in the number of cells of the innate immune response: macrophages (CD11b+F480+,
Figure 4A); neutrophils (CD11b+LY6G+,
Figure 4B); dendritic cells (CD11b-CD11c+,
Figure 4C), and alveolar macrophages (CD11b-SinglecF+CD11c+,
Figure 4D). However, the cytokine profiles differed between the untreated and Zi-treated groups. Zi treatment did not alter the numbers of macrophages and alveolar macrophages producing IL-10 or TNF (Figs. 4E and 4H), but resulted in a significant increase in the number of IL-10-producing neutrophils (
Figure 4F) and reduced the number of TNF-producing dendritic cells at 3dpi (
Figure 4G). No differences were observed at 5 dpi among these groups (
Figure 4K–L).
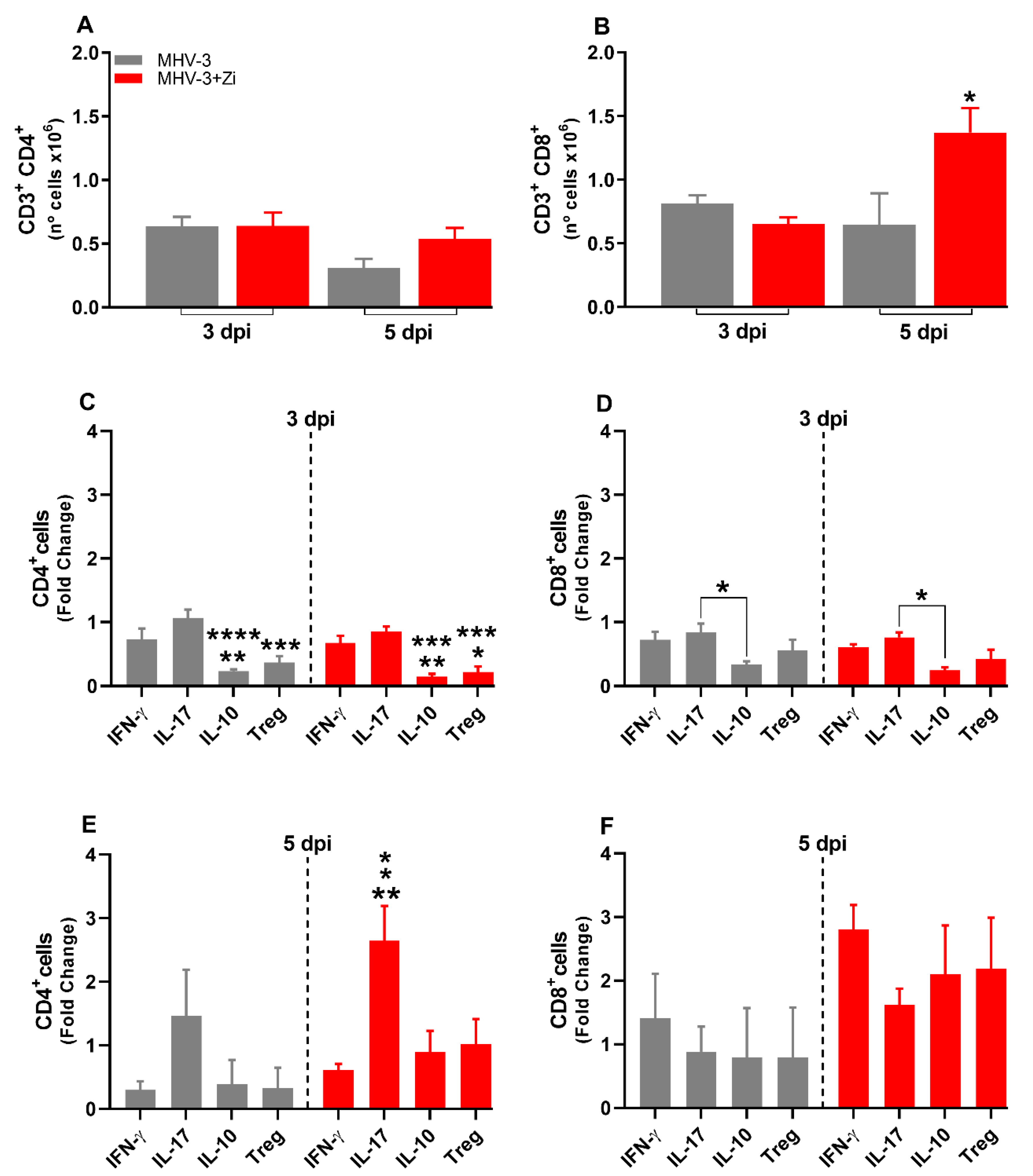
3.5. Treatment with Zi promotes the increasing Treg cells producing IL-10 into lung tissue during MHV-3 infection
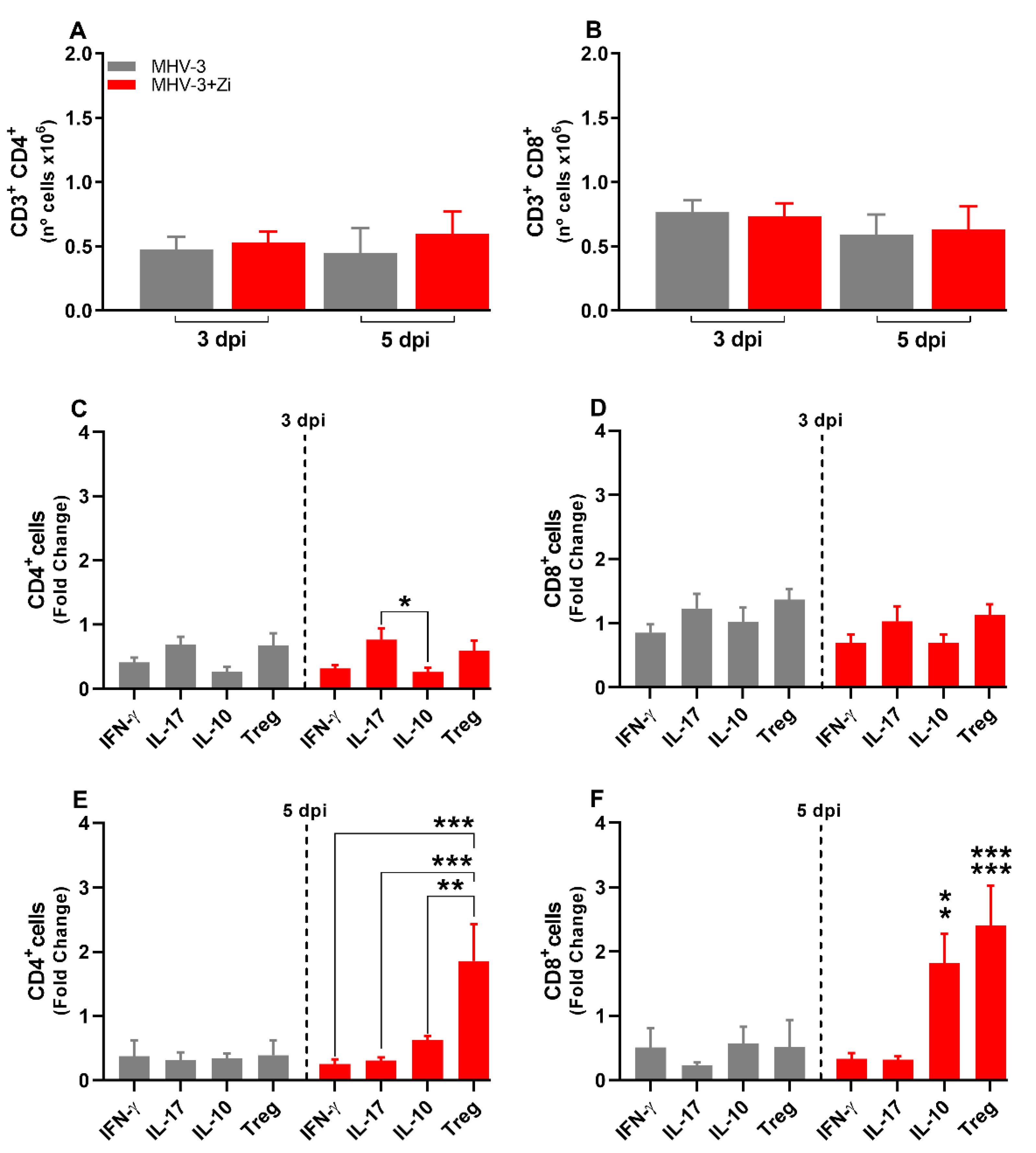
The adaptive immune response is characterized by delayed and specific actions. No difference in the numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes was observed at 3 and 5 dpi (Figs. 5A and B), but the profiles of these cells were different, mainly at 5 dpi (Figs. 5C-F). Animals treated with Zi showed more Th17 cells than IL-10 producing CD4+ T cells at 3 dpi (
Figure 5C). At 5dpi, CD4+ T cells from untreated infected animals did not show differences among their populations (
Figure 5E); however, CD4+ T cells from Zi-treated animals showed a higher number of Treg cells (FOXP3+ IL-10+) than their other cell subtypes (
Figure 5E). Notably, the Zi treatment also resulted in significant increase of the CD8+ T-producing IL-10 and CD8+ Tregs (FOXP3+ IL-10+) cells, when compared with CD8+ T producers of IL-17 and IFN-γ (
Figure 5F).
3.6. Zi treatment reduced the number of innate immune cells in the spleen during MHV-3 infection.
At 3dpi, but not at 5 dpi, there was a reduced number of neutrophils and dendritic cells, but not macrophages, in the spleens of animals treated with Zi compared to that in the untreated infected group (
Figure 6A–C). Notably, at 3 dpi, but not 5 dpi, treatment with Zi reduced the numbers of macrophages and neutrophils producing IL-10 and TNF-, and dendritic cells producing IL-10 (
Figure 6 D–I).
3.7. Zi treatment modulates the expansion/generation of T cells in the spleen during MHV-3 infection.
In the spleen, at 3dpi there was no difference between the groups in the numbers of TCD4+ and TCD8+ lymphocytes (
Figure 7A and B), whereas at 5dpi an increased number of CD8+ T cells was observed upon Zi treatment compared to that in the untreated infected group (
Figure 7B). Checking the profile of these lymphocytes, we observed that at 3dpi the CD4+ T cells of both groups were more polarized to Th1 and Th17 profiles than to Th2 (IL-10) and Tregs (
Figure 7C). Notably, among the CD8+ T cells in both groups, there were more IL-17 producers than IL-10 producers (
Figure 7D). At 5 dpi, an increase in Th17 cells was observed in the treated group compared to the Th1, Th2, and Treg profiles (
Figure 7E). However, no differences were observed in the CD8+ T cell profiles in either group (
Figure 7F).
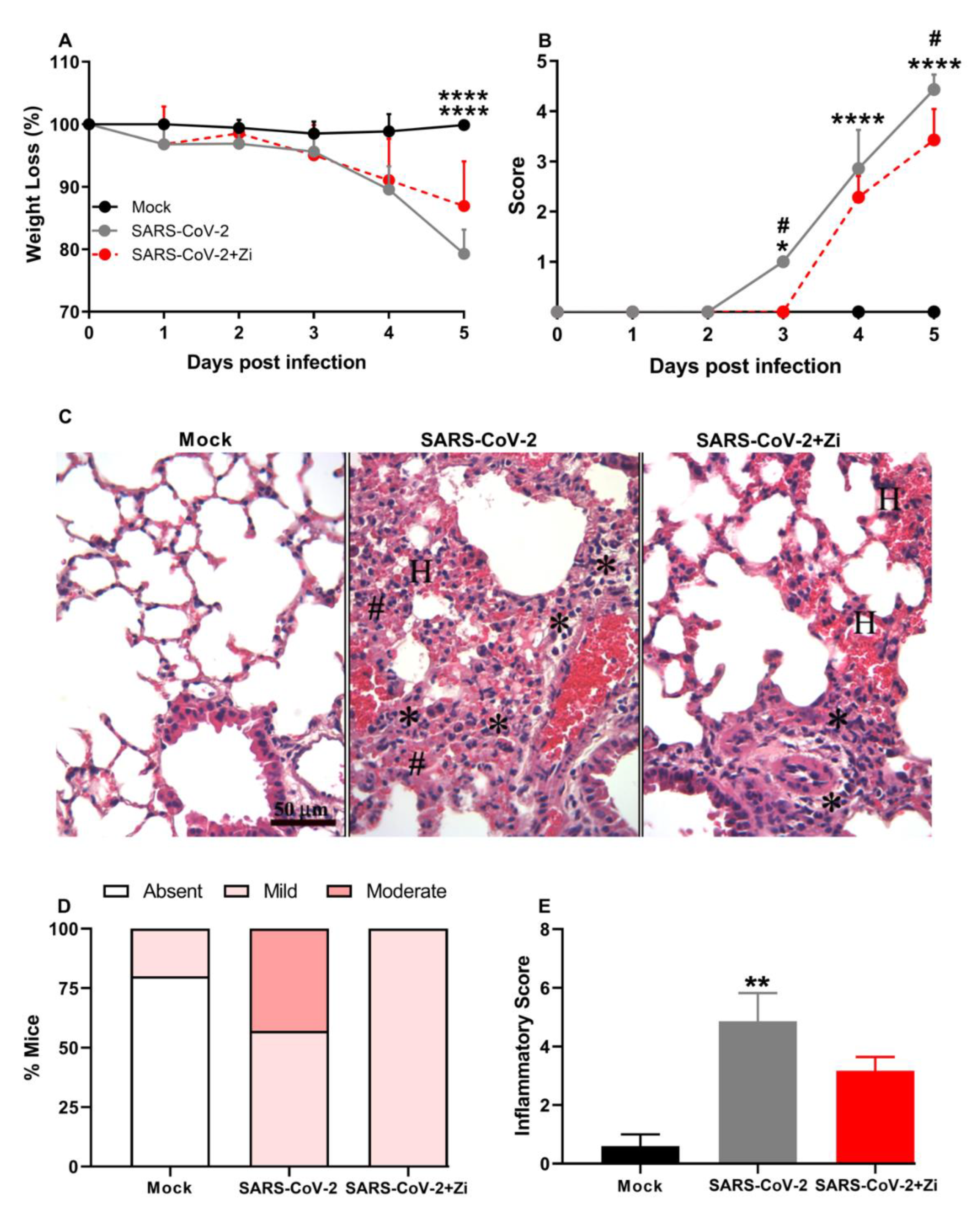
3.7. Zi improves clinical parameters and protects hK18ACE2 mice from lung injury induced by SARS-CoV2.
We validated the effects of Zi treatment in a translational model of SARS-COV2 infection. Therefore, we investigated the effects of Zi treatment on SARS-CoV2 infection in transgenic animals expressing the human angiotensin I-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor. Treatment with Zi reduced weight loss and significantly improved the clinical score compared to untreated animals (
Figure 8A and B). Notably, during coronavirus infection, treatment with Zi significantly reduced the inflammatory score in the lungs (
Figure 8C,D), improving the histopathological pattern (
Figure 8D), with a higher percentage of animals having mild lesions than the untreated group (
Figure 8E).
4. Discussion
Ecosanoids or eicosanoids (from the Greek eikosi for “twenty”) are important lipid mediators for body homeostasis (30). These mediators are oxygenated metabolites from the metabolism of Arachidonic Acid (AA), which acts at small concentrations on target cells, usually via G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) (31). Eicosanoids were initially described for their ability to promote biological responses such as platelet aggregation, edema, and smooth muscle contraction; however, other functions, such as participation in inflammation, cancer, and immune responses, have been attributed to them (32). Examples of eicosanoids include thromboxanes (TXAs), prostaglandins (PGs), leukotrienes (LTs) and lipoxin (LXAs) (30). PGs and TXAs are pro-inflammatory lipid mediators produced by the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway. LTs and LXAs have pro- and anti-inflammatory activities, respectively, and are produced via the lipoxygenase pathway, mainly involving the activity of 5-lipoxygenase enzyme (5-LO) (33).
Of great relevance, studies have shown that LTs play a key role in the development of respiratory distress syndrome (SDRA), which is knowing to be one of the most important clinical consequences of COVID-19 (11). We and others have suggested that in SARS-CoV-2-mediated SDRA, agents such as 5-LO inhibitors could reduce the consequences of virus-induced cytopathic effects by immediate action on critical immune cells, which are associated with cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19 (17). Thus, we sought to verify the effect of the selective 5-LO inhibitor, Zi, against infection in murine models of SDRA induction, which is extremely useful for studies of viral pathogenesis and antiviral therapy.
Initially, our results demonstrated that treatment with Zi improved clinical parameters and delayed the mortality of the animals, and a dose of 30 mg/kg promoted approximately 20% survival. The model used here was described by our group as a model of severe COVID-19, where 100% of the animals died, presenting with severe pneumonia and an increase in several cytokines in lung tissue (20). Notably, the protection conferred by Zi in this model was of great relevance, mainly because we observed that this protection was not dependent on a reduction in viremia. Treatment with Zi did not protect the animals against leukopenia, lymphopenia, and thrombocytopenia caused by the virus; however, the treated animals did not present a reduction in granulocytes observed in the untreated group, suggesting that Zi is able to regulate the number of granulocytes during MHV3 infection. Several studies have shown that uncontrolled inflammation is key to the severity of disease caused by SARS-COV-2, this inflammation initially occurs in the lungs and can become systemic, causing shock, multiple organ failure, and death(4–7). Here, we demonstrated that Zi significantly reduced the inflammatory process in the lungs caused by the murine coronavirus. In fact, Zi, being a selective 5-LO inhibitor, leads to the reduction of LTs, which are mediators with pro-inflammatory actions. LTs are divided into two classes: chemoattractant LTB4, which contains only hydroxyl fractions, and cysteinyl LTs (CysLTs: LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4), which contain amino acid fractions(34,35). LTB4 is a potent monocyte-macrophage and neutrophil chemoattractant that is involved in T cell migration, increases the activity of dendritic cells, and promotes their migration by draining lymph nodes. It also increases TNF-α production and acts synergistically with IL-4 to activate B lymphocytes. LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 induce tissue edema, mucus secretion and bronchoconstriction(17). Blocking LTs caused a change in the cytokine expression profile in infiltrating cells of the lung tissue. At 3dpi was found a greater proportion of IL-10, TNF-α and IFN-γ, these cytokines play extremely important roles both in inflammatory processes and in the physiological processes of the body. TNF-α is an extremely important cytokine that has pleiotropic actions. In the inflammatory process it regulates apoptosis, cell proliferation and promotes the production of other chemokines and cytokines, in physiological processes it becomes important for antitumor responses and homeostasis of the immune system, so the presence of TNF-α, depending its levels, does not necessarily constitute a bad prognosis (36,37) IL-10 is notably a cytokine known for its anti-inflammatory and Th1-type response inhibitory effects (38), while IFN-γ performs antiparasitic, antiviral, antitumor and immunomodulatory functions, playing an important role in the immune response. In the innate immune system, IFN-γ-promotes the activation of macrophages (MOs), and in the adaptive immune response, it increases the proliferation of CD8+ T cells (39). Notably, the presence of cytokines at the site of inflammation does not constitute a problem because they are necessary to contain the offending agent; however, their exacerbated production promotes deleterious effects, as observed in COVID-19 (6,40,41). Some studies have shown that the balanced secretion of anti-inflammatory and pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 and IL-6, is characteristic of asymptomatic infections, whereas in symptomatic infections, there is a predominance of pro-inflammatory cytokines (42–44). As an exacerbated inflammatory process can cause damage to the host and loss of function in the affected tissue, we sought to observe whether the physiological functions of the infected animals would be affected. Remarkably, our results demonstrated that Zi treatment induces higher levels of IL-10 and IL-6 in the lungs.
As demonstrated by Andrade et al. in 2021 (20), infection with MHV-3 promotes an increase in the viral load in the cardiac tissue and damages the lung tissue, thereby reducing the compliance of the respiratory system. Compliance can be defined as the ability to expand, lower respiratory compliance, and a more rigid system becomes (45). In this context, measuring the PV curve in mice offers a method for tracking the development of pathophysiological alterations over time and assessing the potential impact of therapeutic interventions (23,24,45). Lung function can be altered by the fibrotic process that occurs after exaggerated inflammation or by the extent of edema caused by acute inflammation (20,23). In the present study, MHV-3 infection reduced respiratory compliance, as previously reported in an experimental model (20) and in human patients affected by COVID-19 (46). Importantly, we observed maintenance of lung function in the Zi-treated group, in which compliance was not significantly decreased. The lower inflammatory score in the lung tissue of Zi-treated animals was likely responsible for the lack of impaired respiratory compliance.
Within the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection, various cardiac manifestations have been documented. These include atrial arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, sinus node dysfunction, atrioventricular conduction irregularities, ventricular tachyarrhythmias, sudden cardiac arrest, and cardiovascular dysautonomia (47). The etiology of these manifestations encompasses a spectrum of factors including direct viral intrusion, hypoxemia, localized and systemic inflammation, shifts in ion channel physiology, immune activation, and autonomic dysregulation (47).
Cardiac alterations significantly influence infection pathogenicity. Hospitalized COVID-19 patients with ventricular or atrial arrhythmias have an elevated risk of mortality, underscoring the clinical importance of these findings (48). Consequently, the milder cardiac alterations observed in the treated animals serve as an additional indication of the efficacy of Zi in protecting against infection.
For the course of infection to occur in such a way that the virus is eliminated without extreme damage to the host, it is necessary that the innate immune response is robust enough to eliminate the pathogen but balanced to the point of not being deleterious to the tissue (7). The innate immune response is known to provide the first line of defense against parasitic, viral, and bacterial infections. Among the cells of the innate immune response, neutrophils are among the first to migrate to the site of infection (49). Studies have shown that neutrophils are increased in the nasopharyngeal epithelium and bronchoalveolar fluid of patients with severe COVID-19, and robust evidence suggests that these patients have elevated levels of extracellular neutrophil traps (NETs) in the plasma, serum aspirates from the trachea and lungs, and lung biosia (50–52), suggesting that neutrophils can play a critical role in this infection (6). Here, treatment with Zi promoted an increase in IL-10-producing neutrophils, suggesting that the drug promotes the polarization of NEs towards a more anti-inflammatory profile, which may be one of the mechanisms by which it protects the lung tissue. Along with the increase in IL-10-producing NEs, was observed a reduction in TNF-α-producing DCs, a fact that could influence the presentation and activation of T lymphocytes, since DCs play a fundamental role in the connection between innate and adaptive immune responses. No major changes were observed in the innate immune response at 5 dpi, probably because this part of the immune system is more prominent at the beginning of the infection (3 dpi). In contrast, significant changes in adaptive immune responses were observed at 5dpi. Adaptive immune response cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, play crucial roles in the antiviral response. CD4+ T cells can differentiate into several subsets (Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg are examples) and help CD8+ T cells release cytokines that activate and recruit more cells of the innate immune response, improve antiviral activities, and facilitate tissue repair, thus presenting functionality in broad aspects of the immune response (53). We observed that the treatment did not cause differences in the number of CD4+ T cells in the lung at 3 and 5 dpi; however, at 3 dpi, there was an increase in IL-17 producing CD4 T cells (Th17) compared to IL-10 producing cells. Th17 cells play a variety of roles, including antimicrobial protective responses; maintenance of barriers in the skin, intestine, and lungs; and recruitment of NEs by stimulating the secretion of cytokines such as CXCL1 (54). Interestingly, IL-17 has been associated with the presence of several pulmonary pathogens, which led us to believe that its presence in this infection is a precise way to delay viral dissemination. However, it is important to note that excess IL-17 could cause damage to lung tissue, as this cytokine promotes cell migration; thus, a fine adjustment to avoid exacerbating the proinflammatory response would be beneficial. Our data showed that Zi promotes an increase in IL-10, a cytokine with great anti-inflammatory potential, at 3 dpi; therefore, it is likely that Zi promotes this balance between cytokines to improve lung tissue and prevent viral perpetuation, which seems to be reflected in the reduction of the inflammatory score, maintenance of the pulmonary tissue, and clinical improvement observed here. Treatment with Zi promoted a change in the profile of CD4 + and CD8 + lymphocytes at 5 dpi, increasing the number of IL-10-and FOXP3+IL-10+ (Treg)-producing cells, which are thought to promote the regulation of the immune response (55) and is probably one reason for the increased survival observed in the treated group.
Seeking to observe organs involved in the generation/expansion of immune response, was found that the profile of the immune response in the spleen differs between infected and treated infected animals. At 3dpi the innate immune cells, mainly NE cells, was reduced in the treated animals, suggesting that these cells migrated to the target organ of the infection. Notably, increased levels of chemokines and cytokines were observed, which are important for the recruitment of cells to infected tissues. However, at 5dpi was observed treatment increased the number of CD8+ T-cells in the spleen. Our collaborators (20) demonstrated that at 5dpi the virus was already present in the bloodstream, and several studies have demonstrated that CD8+ T cells are important for viral containment (56). In COVID-19, virus-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes are associated with better prognoses; therefore, this increase evidenced by us could be beneficial for viral containment (57).
Finally, it was observed that Zi also influences lung inflammation caused by SARS-CoV-2, showing that treatment with this drug improves the adjustment of the inflammatory response during infection with different strain of SARV-Cov-2 virus.
5. Conclusion
Our findings showed that the 5-LO inhibitor, Zi, modulates local and systemic immune responses, restrains pulmonary inflammation, ameliorates clinical disease, and enhances survival rates without interfering with the host’s ability to deal with MHV-3 and betacoronaviruses-induced SARS-CoV-2 infections. Finally, evaluating whether the combination of Zi with an antiviral drug is an ideal treatment for coronavirus infection is important.
Funding
This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) [Grant nº 307828/2022-0 for FSM], the National Institute of Science and Technology in Dengue and Host-Microorganism Interaction (INCT em Dengue) sponsored by CNPq [Grant nº 465425/2014-3], and the Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) Rede Mineira de Imunobiológicos [Grant nº RED-00140-16], and the Rede de Investigação em Mucosas e Pele [Grant nº RED-00096-22]. In addition, the FAPEMIG supported this study (Processes nº 25036, APQ 02281-18, and APQ-02618-23) and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Programa: 9951 - Programa Estratégico Emergencial de Prevenção e Combate a Surtos, Endemias, Epidemias e Pandemias [Grant nº 0688/2020 - 88881.504421/2020-01 and 0641/2020 - 88881.507175 /2020 -01).
Data availability
Data are available upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jacqueline Barbosa de Oliveira Viana, Frankcineia Aparecida de Assis, Ilma Marçal de Souza, Rosemeire Oliveira and Tânia Colina, and Domenico Romano Romani for their technical assistance.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Chams, N.; Chams, S.; Badran, R.; Shams, A.; Araji, A.; Raad, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Stroberg, E.; Duval, E.J.; Barton, L.M.; et al. COVID-19: A Multidisciplinary Review. Front. Public Heal. 2020, 8, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner RW, Majjouti M, Alcazar MAA, Mahabir E. Of Mice and Men: The Coronavirus MHV and Mouse Models as a Translational Approach to Understand SARS-CoV-2. Viruses. 2020 Aug 12;12(8):880.
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 27 July 2023).
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J.; on behalf of theHLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet Lond Engl. 2020 Feb 15;395(10223):497–506.
- Arish, M.; Qian, W.; Narasimhan, H.; Sun, J. COVID-19 immunopathology: From acute diseases to chronic sequelae. J. Med Virol. 2022, 95, e28122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed A, Kalle AM, Reddanna P. Managing SARS-CoV2 Infections Through Resolution of Inflammation by Eicosanoids: A Review. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:4349–58.
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, R.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, L.; et al. Human kidney is a target for novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citron F, Perelli L, Deem AK, Genovese G, Viale A. Leukotrienes, a potential target for Covid-19. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2020 Oct;161:102174.
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of COVID-19 Patient Sera. Cell 2020, 182, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Chu, H.; Yang, D.; Sze, K.-H.; Lai, P.-M.; Yuan, S.; Shuai, H.; Wang, Y.; Kao, R.Y.-T.; Chan, J.F.-W.; et al. Characterization of the Lipidomic Profile of Human Coronavirus-Infected Cells: Implications for Lipid Metabolism Remodeling upon Coronavirus Replication. Viruses 2019, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, U.N. Bioactive Lipids in COVID-19-Further Evidence. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Chiang, N.; Van Dyke, T.E. Resolving inflammation: dual anti-inflammatory and pro-resolution lipid mediators. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basil, M.C.; Levy, B.D. Specialized pro-resolving mediators: endogenous regulators of infection and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayola-Serrano, N.C.; Roy, N.; Fathah, Z.; Anwar, M.M.; Singh, B.; Ammar, N.; Sah, R.; Elba, A.; Utt, R.S.; Pecho-Silva, S.; et al. The role of 5-lipoxygenase in the pathophysiology of COVID-19 and its therapeutic implications. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill KA, Busse WW. Zileuton. Lancet Lond Engl. 1996 Aug 24;348(9026):519–24.
- Hammock BD, Wang W, Gilligan MM, Panigrahy D. Eicosanoids: The Overlooked Storm in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)? Am J Pathol. 2020 Sep;190(9):1782–8.
- Andrade ACDSP, Campolina-Silva GH, Queiroz-Junior CM, de Oliveira LC, Lacerda L de SB, Gaggino JCP, et al. A Biosafety Level 2 Mouse Model for Studying Betacoronavirus-Induced Acute Lung Damage and Systemic Manifestations. J Virol. 2021 Oct 27;95(22):e0127621.
- Garcia, A.B.; de Moraes, A.P.; Rodrigues, D.M.; Gilioli, R.; de Oliveira-Filho, E.F.; Durães-Carvalho, R.; Arns, C.W. Coding-Complete Genome Sequence of Murine Hepatitis Virus Strain 3 from Brazil. Genome Announc. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, J.C.; Beagley, K.W.; Wade, M.A.; Preston, J.A.; Hansbro, N.G.; Hickey, D.K.; Kaiko, G.E.; Gibson, P.G.; Foster, P.S.; Hansbro, P.M. Neonatal Chlamydial Infection Induces Mixed T-Cell Responses That Drive Allergic Airway Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limjunyawong N, Fallica J, Horton MR, Mitzner W. Measurement of the Pressure-volume Curve in Mouse Lungs. J Vis Exp JoVE. 2015 Jan 27;(95):52376.
- Robichaud, A.; Fereydoonzad, L.; Limjunyawong, N.; Rabold, R.; Allard, B.; Benedetti, A.; Martin, J.G.; Mitzner, W. Automated full-range pressure-volume curves in mice and rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 123, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soutiere, S.E.; Mitzner, W. On defining total lung capacity in the mouse. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 96, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintaku, T.; Ohba, T.; Niwa, H.; Kushikata, T.; Hirota, K.; Ono, K.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Imaizumi, T.; Kuwasako, K.; Sawamura, D.; et al. Effects of Propofol on Electrocardiogram Measures in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 126, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, A.F.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Soto-Blanco, B.; Melo, M.M. Computerized electrocardiography in healthy conscious guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus). 2016, 36, 1203–1208. [CrossRef]
- Brant, F.; Miranda, A.S.; Esper, L.; Rodrigues, D.H.; Kangussu, L.M.; Bonaventura, D.; Soriani, F.M.; Pinho, V.; Souza, D.G.; Rachid, M.A.; et al. Role of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in the Immune Response Profile and Development of Pathology during Plasmodium berghei Anka Infection. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3127–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claser C, Nguee SYT, Balachander A, Wu Howland S, Becht E, Gunasegaran B, et al. Lung endothelial cell antigen cross-presentation to CD8+T cells drives malaria-associated lung injury. Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 18;10(1):4241.
- Tessaro, F.H.G.; Ayala, T.S.; Martins, J.O. Lipid Mediators Are Critical in Resolving Inflammation: A Review of the Emerging Roles of Eicosanoids in Diabetes Mellitus. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drachman, D.B.; Rothstein, J.D. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 protects motor neurons in an organotypic model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, T.G.; Peters-Golden, M. Activation and Regulation of Cellular Eicosanoid Biosynthesis. Sci. World J. 2007, 7, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoxha M. What about COVID-19 and arachidonic acid pathway? Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;76(11):1501–4.
- Luster, A.D.; Tager, A.M. T-cell trafficking in asthma: lipid mediators grease the way. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomizo, T.; Izumi, T.; Shimizu, T. Leukotriene B4: Metabolism and Signal Transduction. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2001, 385, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Ling, K.; Cai, C.; Wang, W.; Ye, D. Targeting TNF-α for COVID-19: Recent Advanced and Controversies. Front. Public Heal. 2022, 10, 833967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, W.; O’garra, A. IL-10 Family Cytokines IL-10 and IL-22: from Basic Science to Clinical Translation. Immunity 2019, 50, 871–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, L.B. IFNγ: signalling, epigenetics and roles in immunity, metabolism, disease and cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams AE, Chambers RC. The mercurial nature of neutrophils: still an enigma in ARDS? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Feb;306(3):L217-230.
- Li, X.; Geng, M.; Peng, Y.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan M, Rabaan AA, Fawarah MMA, Almuthree SA, Alsubki RA, Alfaraj AH, et al. Updated Insights into the T Cell-Mediated Immune Response against SARS-CoV-2: A Step towards Efficient and Reliable Vaccines. Vaccines. 2023 Jan 1;11(1):101.
- Le Bert N, Clapham HE, Tan AT, Chia WN, Tham CYL, Lim JM, et al. Highly functional virus-specific cellular immune response in asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Exp Med. 2021 May 3;218(5):e20202617.
- Grau-Expósito J, Sánchez-Gaona N, Massana N, Suppi M, Astorga-Gamaza A, Perea D, et al. Peripheral and lung resident memory T cell responses against SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun. 2021 May 21;12(1):3010.
- Mortola, J.P. How to breathe? Respiratory mechanics and breathing pattern. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2018, 261, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattinoni L, Chiumello D, Caironi P, Busana M, Romitti F, Brazzi L, et al. COVID-19 pneumonia: different respiratory treatments for different phenotypes? Intensive Care Med. 2020 Jun;46(6):1099–102.
- Saha, S.A.; Russo, A.M.; Chung, M.K.; Deering, T.F.; Lakkireddy, D.; Gopinathannair, R. COVID-19 and Cardiac Arrhythmias: a Contemporary Review. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 24, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Qin, M.; Shen, B.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, F.; Gong, W.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Association of Cardiac Injury With Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C. Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras FP, Pontelli MC, Silva CM, Toller-Kawahisa JE, de Lima M, Nascimento DC, et al. SARS-CoV-2-triggered neutrophil extracellular traps mediate COVID-19 pathology. J Exp Med. 2020 Dec 7;217(12):e20201129.
- Panda, R.; Castanheira, F.V.; Schlechte, J.M.; Surewaard, B.G.; Shim, H.B.; Zucoloto, A.Z.; Slavikova, Z.; Yipp, B.G.; Kubes, P.; McDonald, B. A functionally distinct neutrophil landscape in severe COVID-19 reveals opportunities for adjunctive therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo Y, Yalavarthi S, Shi H, Gockman K, Zuo M, Madison JA, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps in COVID-19. JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 4;5(11):e138999, 138999.
- Sette A, Crotty S. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Cell. 2021 Feb 18;184(4):861–80.
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Miyara, M.; Costantino, C.M.; Hafler, D.A. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.; Pamer, E.G. CD8 T Cell Responses to Infectious Pathogens. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 29–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva MJA, Ribeiro LR, Lima KVB, Lima LNGC. Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1001198.
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier survival curve of control (Mock), untreated MHV-3-infected, and zileuton (Zi) treated MHV-3-infected mice (Zi: 1.5; 3.0, 15, and 30 mg/mL) (a). Body weight change after infection was assessed by bidirectional repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Sidak’s multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (b). Clinical scoring of control, infected, and Zi-treated infected animals was performed daily until the end of the experiment (c). Viral load was determined in plasma collected from mice infected with MHV-3 using the plaque assay and/or infected and treated with Zi (30 mg/mL). Results are presented as log 10 PFU/µL of plasma. Differences between the groups were assessed using the post hoc Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn test (d). Differential blood count highlighting leukocytes (e), lymphocytes (f), platelets (g), and granulocytes (h), observed on 3 and 5 dpi. Differences between the control, infected, and/or infected-treated groups were assessed by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. LOD, limit of detection. ns, not significant. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: MHV-3, mouse hepatitis virus 3; PFU, plaque-forming units.
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier survival curve of control (Mock), untreated MHV-3-infected, and zileuton (Zi) treated MHV-3-infected mice (Zi: 1.5; 3.0, 15, and 30 mg/mL) (a). Body weight change after infection was assessed by bidirectional repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Sidak’s multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (b). Clinical scoring of control, infected, and Zi-treated infected animals was performed daily until the end of the experiment (c). Viral load was determined in plasma collected from mice infected with MHV-3 using the plaque assay and/or infected and treated with Zi (30 mg/mL). Results are presented as log 10 PFU/µL of plasma. Differences between the groups were assessed using the post hoc Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn test (d). Differential blood count highlighting leukocytes (e), lymphocytes (f), platelets (g), and granulocytes (h), observed on 3 and 5 dpi. Differences between the control, infected, and/or infected-treated groups were assessed by one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. LOD, limit of detection. ns, not significant. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: MHV-3, mouse hepatitis virus 3; PFU, plaque-forming units.
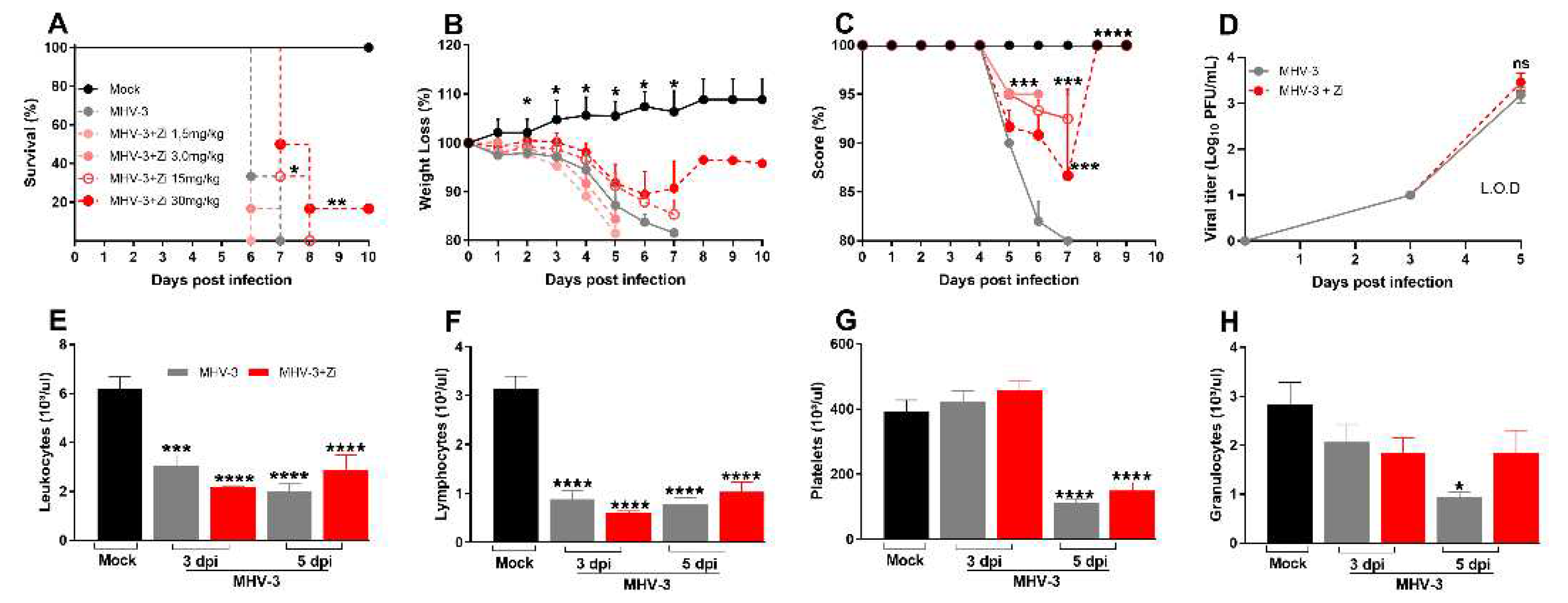
Figure 2.
Histopathological evaluation regarding the general inflammatory score. Comparisons between the sham and infected groups were performed using the post hoc Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn test (a). Percentages of mice according to the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration (b). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung sections showing signs of inflammatory lesion in infected mice (c). * foci inflammatory, # hyperplasia, and H hemorrhage. Viral load was determined in lung extracts of mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with zileuton (Zi) using the plaque assay. Results are presented as log 10 PFU/g of tissue (d). Differences between the groups were assessed using the Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn post hoc test. LOD, limit of detection. ns, not significant. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001.
Figure 2.
Histopathological evaluation regarding the general inflammatory score. Comparisons between the sham and infected groups were performed using the post hoc Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn test (a). Percentages of mice according to the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration (b). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung sections showing signs of inflammatory lesion in infected mice (c). * foci inflammatory, # hyperplasia, and H hemorrhage. Viral load was determined in lung extracts of mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with zileuton (Zi) using the plaque assay. Results are presented as log 10 PFU/g of tissue (d). Differences between the groups were assessed using the Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn post hoc test. LOD, limit of detection. ns, not significant. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ****, p < 0.0001.
Figure 3.
Analysis of compliance of the respiratory system (a) in control mice, mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with zileuton (Zi). Compliance was calculated from the steepest point of the deflation limb of the pressure-volume (PV) curve. Representative PV curves of animals from each experimental group (mock, MHV-3, and MHV3+Zi) (b). Percentage of cardiac changes in control mice and mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with Zi (c). Computerized electrocardiogram tracings of control mice and mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with Zi. Demonstration of the second frontal plane deviation (DII) records, with a speed of 50 mm/s and amplitude 2 N (d). **, p < 0.01.
Figure 3.
Analysis of compliance of the respiratory system (a) in control mice, mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with zileuton (Zi). Compliance was calculated from the steepest point of the deflation limb of the pressure-volume (PV) curve. Representative PV curves of animals from each experimental group (mock, MHV-3, and MHV3+Zi) (b). Percentage of cardiac changes in control mice and mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with Zi (c). Computerized electrocardiogram tracings of control mice and mice infected with MHV-3 and/or infected and treated with Zi. Demonstration of the second frontal plane deviation (DII) records, with a speed of 50 mm/s and amplitude 2 N (d). **, p < 0.01.
Figure 4.
Flow cytometry analyses showing the total cell numbers in the lung at 3 and 5 dpi among groups of macrophages (CD11b+ F480+) (a), neutrophils (CD11b+ LY6G+) (b), dendritic (CD11b-CD11c+) (c), and macrophages alveolar (CD11b+SinglecF+CD11c+) (d). Macrophages (e and i), neutrophils (f and j), dendritic (g and k), and alveolar macrophages (h and l)-producing IL-10 and TNF-α at 3 and 5 dpi. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; (* representation among the same groups); (# representation between different groups). Abbreviations: IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Figure 4.
Flow cytometry analyses showing the total cell numbers in the lung at 3 and 5 dpi among groups of macrophages (CD11b+ F480+) (a), neutrophils (CD11b+ LY6G+) (b), dendritic (CD11b-CD11c+) (c), and macrophages alveolar (CD11b+SinglecF+CD11c+) (d). Macrophages (e and i), neutrophils (f and j), dendritic (g and k), and alveolar macrophages (h and l)-producing IL-10 and TNF-α at 3 and 5 dpi. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; (* representation among the same groups); (# representation between different groups). Abbreviations: IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Figure 5.
Flow cytometric analyses showing the total cell numbers in the lung at 3 and 5 dpi between the CD3+CD4+ (a) and CD3+CD8+ (b) groups. CD4+ (c and e) and CD8+ (d and f) cells-producing IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-10, and FOXP3+ IL-10+ (Treg) at 3 and 5 dpi. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Abbreviations: FOXP3, forkhead box P3; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IL, interleukin.
Figure 5.
Flow cytometric analyses showing the total cell numbers in the lung at 3 and 5 dpi between the CD3+CD4+ (a) and CD3+CD8+ (b) groups. CD4+ (c and e) and CD8+ (d and f) cells-producing IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-10, and FOXP3+ IL-10+ (Treg) at 3 and 5 dpi. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. Abbreviations: FOXP3, forkhead box P3; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IL, interleukin.
Figure 6.
Flow cytometric analyses showing the total cell numbers in the spleen at 3 and 5 dpi among macrophages (CD11b+ F480+) (a), neutrophils (CD11b+ LY6G+) (b), and dendritic (CD11b-CD11c+) (c) groups. Macrophages (d and g), neutrophils (e and h), and dendritic cells (f and i)-producing IL-10 and TNF-α at 3 and 5 dpi. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 (* representation among the same groups); (# representation between different groups). Abbreviations: IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Figure 6.
Flow cytometric analyses showing the total cell numbers in the spleen at 3 and 5 dpi among macrophages (CD11b+ F480+) (a), neutrophils (CD11b+ LY6G+) (b), and dendritic (CD11b-CD11c+) (c) groups. Macrophages (d and g), neutrophils (e and h), and dendritic cells (f and i)-producing IL-10 and TNF-α at 3 and 5 dpi. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 (* representation among the same groups); (# representation between different groups). Abbreviations: IL, interleukin; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
Figure 7.
Flow cytometric analyses showing total cell numbers in the spleen at 3 and 5 dpi between the CD3+CD4+ (a) and CD3+CD8+ (b) groups. CD4+ (c and e) and CD8+ (d and f) cells-producing IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-10, and Treg at 3 and 5 dpi. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IL, interleukin.
Figure 7.
Flow cytometric analyses showing total cell numbers in the spleen at 3 and 5 dpi between the CD3+CD4+ (a) and CD3+CD8+ (b) groups. CD4+ (c and e) and CD8+ (d and f) cells-producing IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-10, and Treg at 3 and 5 dpi. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IL, interleukin.
Figure 8.
Body weight change after SARS-CoV-2 infection was evaluated using bidirectional repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Sidak’s multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (a). Clinical scoring of control animals, mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 and infected and treated with zileuton (Zi), was performed daily until the end of the experiment (b). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung sections showing signs of the inflammatory lesions in infected mice (c); * foci inflammatory, # hyperplasia and H hemorrhage. Percentages of mice according to the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration (d). Histopathological evaluation regarding the general inflammatory score. Comparisons between the sham and infection groups were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn post hoc test (e). *, p < 0.05; **, p<0.01; ****, p < 0.0001. (* representation among the same groups); (# representation between different groups).
Figure 8.
Body weight change after SARS-CoV-2 infection was evaluated using bidirectional repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Sidak’s multiple comparison test. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) (a). Clinical scoring of control animals, mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 and infected and treated with zileuton (Zi), was performed daily until the end of the experiment (b). Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung sections showing signs of the inflammatory lesions in infected mice (c); * foci inflammatory, # hyperplasia and H hemorrhage. Percentages of mice according to the degree of inflammatory cell infiltration (d). Histopathological evaluation regarding the general inflammatory score. Comparisons between the sham and infection groups were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn post hoc test (e). *, p < 0.05; **, p<0.01; ****, p < 0.0001. (* representation among the same groups); (# representation between different groups).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).