1. Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic and chronic autoimmune disorder that affects musculoskeletal joints resulting in persistent synovitis, hyperplasia, autoantibody production, cartilage and joint destruction, erosion, and functional impairment [
1]. Extra-articular involvement of other organs (or symptoms that occur beyond the obvious joints) in RA frequently results in dermatological, neurological, cardiovascular, pulmonary, renal, and gastrointestinal pathology [
2].
RA has a global prevalence of 0.24-1%. It has a prevalence rate of approximately 1% in the UK with an incidence of 1.5 and 3.6 per 100,000 in men and women, respectively, indicating a predilection towards women [
3,
4]. It is estimated that over 430,000 adults in the UK have rheumatoid arthritis [
5]. The disorder can occur at any age, but the average age of onset is between 30-50 years [
6].
Multiple genetic factors interacting with the environment are associated with the onset of RA. Alleles of the Human Leukocyte antigen (HLA) and other genes such as CTLA4, STAT4 and IL-6 are associated with developing the disorder [
7]. Environmental risk factors include smoking, air pollution, obesity, infections, vitamin D deficiency, immunisations, oral contraceptives, and socioeconomic status [
8,
9].
Clinical manifestations of the disorder include symmetrical small joint pain and swelling, predominantly of the hands and feet, with associated early morning stiffness lasting for >30 mins and often leading to limited function and mobility [
10]. Further features may include but not limited to rheumatoid nodules, tenosynovitis, rashes, fever, and weight loss [
11]. Early diagnosis within an optimal therapeutic window of between 3-6 months is identified to be key in achieving the most desirable and cost-effective outcome [
12]. Early diagnosis and management is vital to suppress inflammation before joint damage occurs. This poses a challenge as it focuses heavily on clinical evidence obtained from patient’s history and physical assessment accompanied by blood tests, and imaging analysis.
This review aims to summarise current treatment practices of rheumatoid arthritis and highlight the pressing need for alternative approaches to new drug discovery by elucidating the relationships between drugs, genes and disease pathology and ultimately developing further effective and safe therapeutic options. This review discusses how computational approaches such as connectivity mapping can identify existing FDA approved drugs, that can be repurposed to be beneficial in alternate disease areas beyond their original treatment indication. This paper will overview the challenges and limitations of this approach as well as the opportunities and potential benefits.
2. Discussion
2.1. Current RA treatments
Currently, treatment and management of RA is aimed at gaining control of inflammation and alleviating pain while maximising joint function with the long-term goal of achieving remission or low disease activity. Treatment plans usually consist of medications, exercise, physiotherapy and occupational therapy [
13]. These treatment plans are tailored to each patient according to their age, current disease state, occupation, compliance, and overall health [
13]. Treat-to-target (T2T) is a medical strategy that was established in 2010 to guide clinicians to help patients achieve the goal of clinical remission or low disease activity. It advocates early diagnosis and concomitant therapy implementation, followed by regular monitoring of disease activity and adaptation of therapy accordingly, as well as providing education and support for self-management [
12,
14].
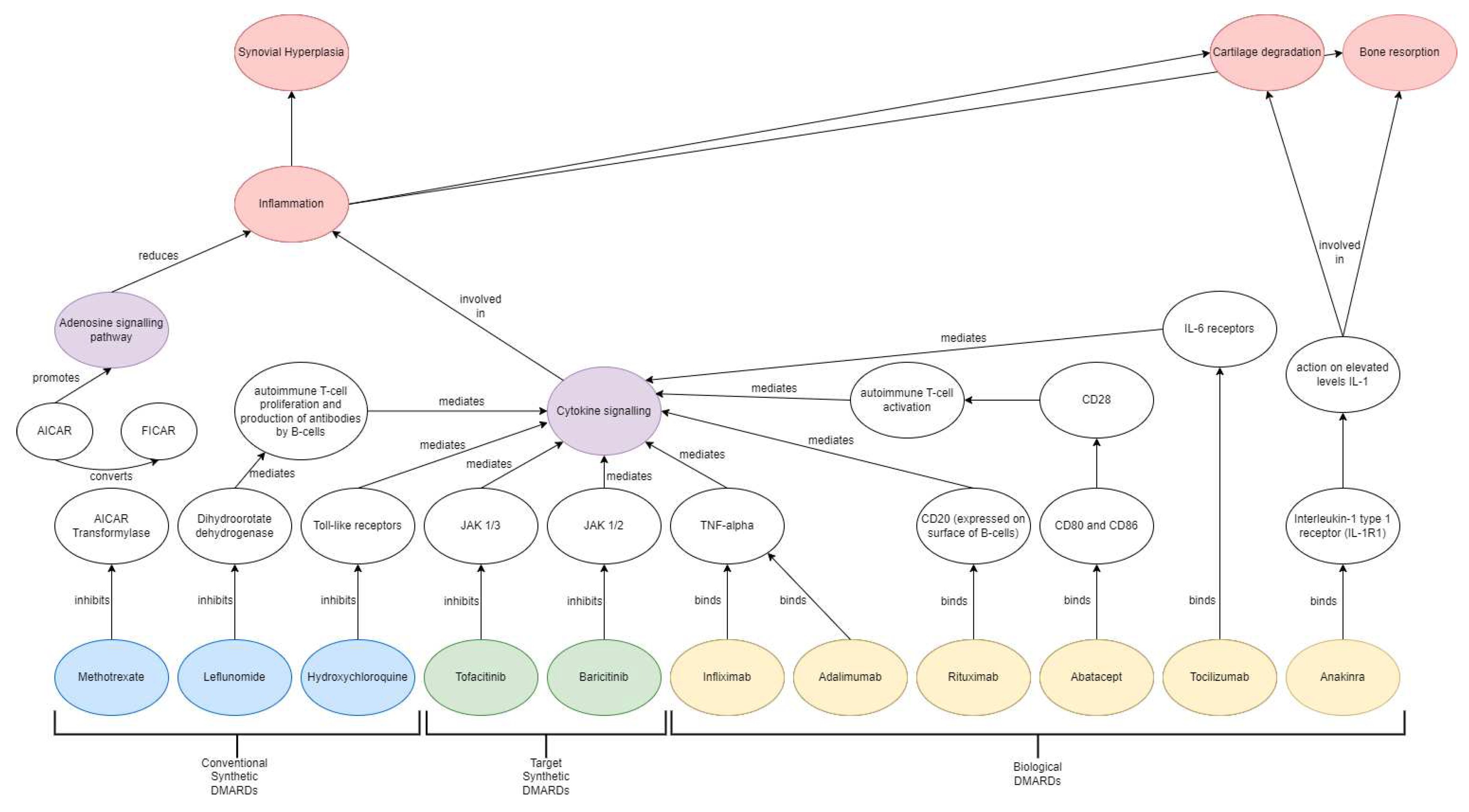
Main drug classes include conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-Rheumatic drugs (csDMARDs), biological DMARDs (bDMARDs) and target synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) (
Figure 1).
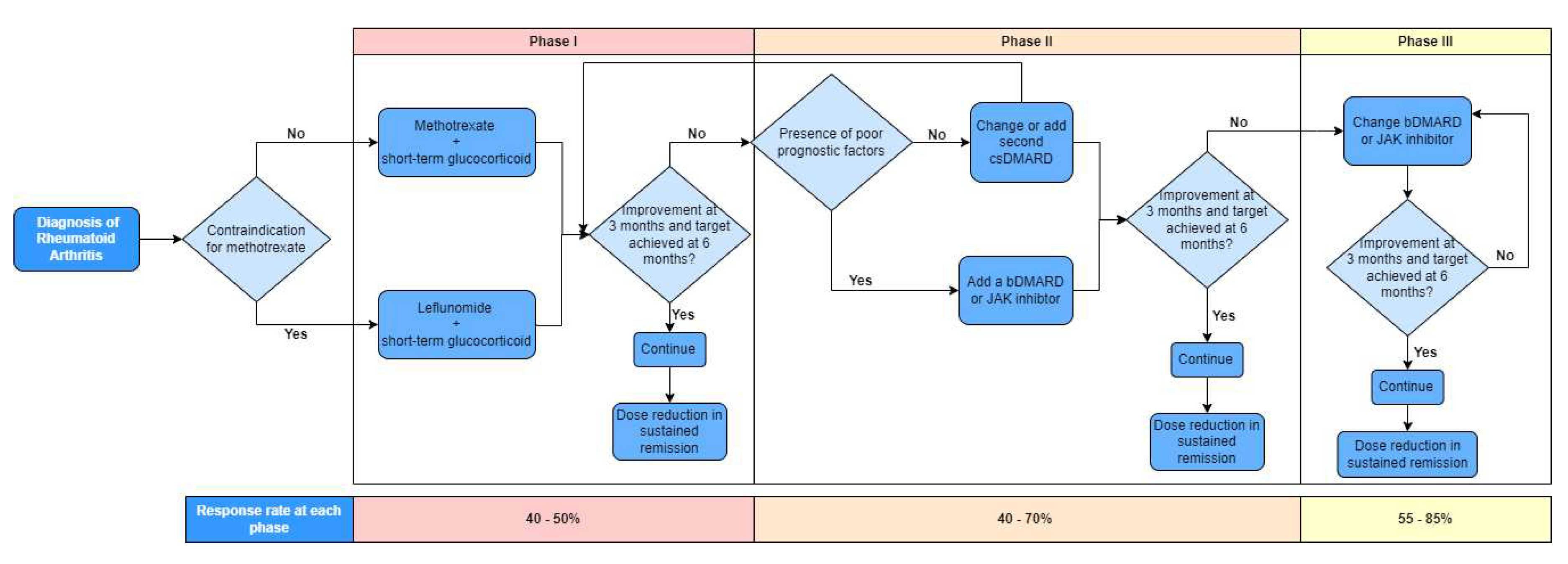
Figure 2 depicts the treatment algorithm based on the 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations on RA management allowing sequential use of drugs from the main classes [
15]. Recommendations are separated into 3 phases with regular monitoring of disease activity at 3-month intervals. Treatment is continued if there is improvement at 3 months and target achieved at 6 months followed by potential dose reduction in sustained remission. No improvement results in progression to next phase of treatment. Phase I treatment recommends methotrexate or leflunomide and short-term glucocorticoids to combat the inflammation. Phase II recommends change or addition of a second csDMARD or, in the presence of poor prognostic factors, addition of a bDMARD or JAK inhibitor. Phase III recommends change of bDMARD or JAK inhibitor.
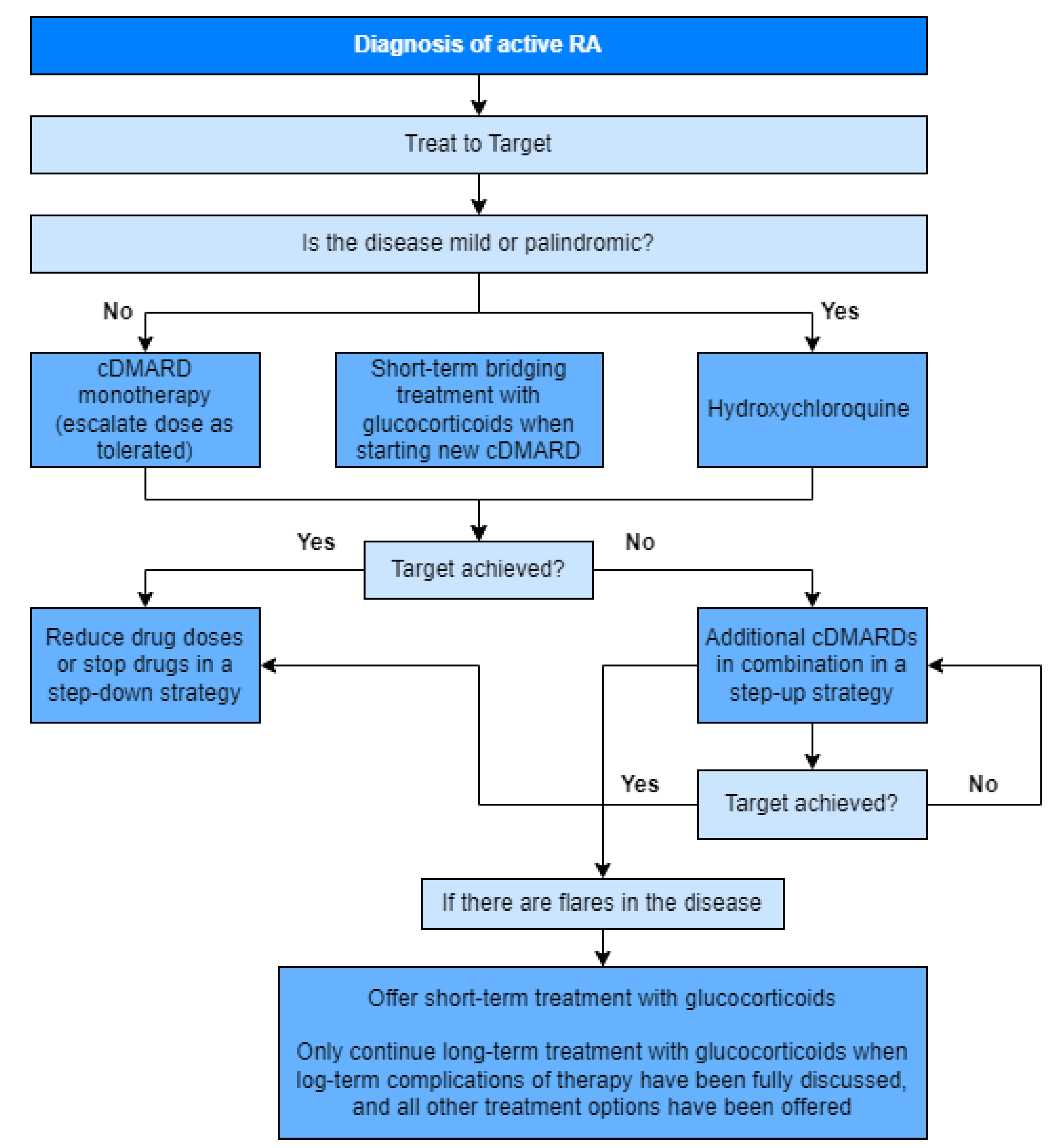
Figure 3 depicts the treatment algorithm based on the 2020 update of the NICE guidelines [
16].
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids are initially administered to decrease inflammation and alleviate the pain and stiffness in the joints [
17]. However, NSAIDs are reported to increase risk of gastric damage and cardiovascular disease [
18]. Although EULAR recommends the use of corticosteroids in combination with DMARDs immediately after diagnosis and they are frequently continued longer term at a lower dose to retain control of inflammation, there is no real clarity regarding their effectiveness and safety for the treatment of RA to justify extended use [
19]. Results of the SEMIRA trial involving patients in remission and treated with conventional synthetic DMARDs in combination with glucocorticoids for more than 6 months showed approximately two thirds of patients achieved treatment success within 24 weeks once they were tapered off glucocorticoids. This suggests that discontinuation or tapering of glucocorticoids should be considered for patients in remission and only reintroduced in the case of a flare [
19].
2.1.1. Conventional Synthetic DMARDs
Methotrexate, leflunomide and sulfasalazine are the most common csDMARDs used as first line therapy administered both as monotherapy and in combination with other DMARDs. Methotrexate is a folate antagonist which functions by inhibiting 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR)-transformylase from converting AICAR to 5-formyl-AICAR (FICAR), which increases adenosine levels and initiates an anti-inflammatory state [
20,
21]. Leflunomide on the other hand functions by inhibiting dihydroorotate dehydrogenase and tyrosine kinase essential for pyrimidine synthesis via de novo pathway and therefore inhibiting autoimmune T-cells proliferation and autoantibody B-cell production [
22]. Sulfasalazine is another anti-rheumatic drug where the exact mechanism of action is not fully understood; however, it is postulated to regulate osteoblasts and osteoclasts by inhibiting NF-kB ligand (RANKL) expression [
6]. Common side effects of csDMARDs include gastrointestinal problems, headache, nausea, alopecia, and deranged liver function tests [
23]. Folic acid supplementation is shown to reduce risks of adverse events due to methotrexate therapy [
20]. It is estimated only 40-50% of patients achieve a good response to treatment with csDMARDs [
24]. A study conducted in China reported that treatment with methotrexate, leflunomide and sulfasalazine resulted in 39.6%, 33.7% and 48.6% patients, respectively, experiencing adverse events [
25].
2.1.2. Biological DMARDs (bDMARDs)
bDMARDs are a class of highly effective drugs with targeted mechanism of action that can rapidly reduce the progression of joint destruction [
13]. Infliximab and adalimumab are recombinant monoclonal antibodies that binds to all forms of TNF-α and inhibits inflammatory cytokine production and apoptotic pathway initiation [
26]. Rituximab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to presenting CD20 antigens on B-cells surface and activates the complement system which eliminates the B-cells from blood circulation. Tocilizumab is a recombinant monoclonal antibody that functions as an IL-6 receptor antagonist, thereby inhibiting IL-6 mediated signalling and expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines [
27]. Side effects of bDMARDs are dependent on the mechanism of the drug employed but may include increased infection, mucocutaneous reactions, hypercholesterolaemia, nasopharyngitis and gastrointestinal perforations [
28]. It is estimated only 40-50% of patients achieve a good response to treatment with bDMARDs [
24].
2.1.3. Target Synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs)
tsDMARDs are a relatively novel drug class of orally administered small molecules targeted at intercellular kinase and phosphodiesterases inhibitions. Janus-Kinase (JAK) inhibitors are a class of tsDMARDs that interfere with the ATP-binding sites of JAKs, resulting in suppression of downstream signalling pathways, which can have immunomodulatory effects in a wide range of pathological processes [
29]. Tofacitinib, baricitinib and upadacitinib are approved by the FDA for therapeutic use in RA management [
29]. JAK inhibitors are reported to have achieved greater improvements in pain when compared to anti-TNF treatments with similar mechanism of action [
30]. Side effects of JAK inhibitors may include hyperlipidaemia, viral infection, rashes and perhaps a slight increase risk of cardiovascular events and venous thromboembolism [
31]. It is estimated 50-70% of patients with inadequate response to csDMARDs and bDMARDs achieve a good response to treatment with tsDMARDs [
24]. Analyses of an RA cohort from the BIOBADASER III registry found that 24% of patients discontinued treatment with b/tsDMARDs due to adverse events [
32].
2.2. Clinical need
There is significant impact on quality of life and work capacity for individuals with RA. Studies evidence that functional capacity of people living with RA deteriorates with time as disease activity increases [
33]. There is also 15-46% increased mortality in people living with rheumatoid arthritis compared to the general population. Around 1 in 6 people have major depressive disorder which is associated with increased levels of pain and function. 30-50% of people within the first year of diagnosis have to remove themselves from the workplace, which can become a permanent inability to work, leading to personal financial problems. Approximately 68% of RA patients in the UK are physically inactive which becomes a vicious cycle of disease progression and increased pain, thus affecting both physical and mental health [
34].
It is clear therefore that no drug is effective in every patient and there is significant variability and overlap between treatments in terms of response and toxicity. Some patients are non-responsive to the treatment while experiencing side effects that can be severely detrimental to the patient’s health and quality of life. Another important factor contributing to treatment failure and is often overlooked is drug resistance caused by poorly understood underlying biological mechanisms.
Clinicians in the UK currently work on guidelines set by NICE, EULAR and the British Society of Rheumatology by cycling through the various drug combinations from the csDMARDs through biologic DMARDs to new targeted synthetic DMARDs. This approach is essentially a trial-and-error prescribing approach with minimal new guidance in instances of non-response, other than that emerging from ongoing fundamental mechanistic research and clinical trials to resolve which combinations are effective and safe.
Studies report that although T2T is recommended as a standard practice of care and some aspects of the strategy are widely used, full implementation remains uncommon and adherence to the approach is low [
35]. This is mainly due to the lack of understanding and knowledge among healthcare providers on how to determine right target and treatment for individual patients such a complex disease that requires a multi-faceted treatment approach [
36,
37]. This is often exacerbated by the lack of resources to deliver a tight control/T2T service. Despite the advancements and enhanced knowledge gained from innovative research, translation of these into therapeutic benefits have not been fully realised. A study in Brazil found the average time lag from clinical development to application of biological drugs was 11.3 years [
38]. Upadacitinib is the most recently treatment approved for RA with clinical trials to determine safety and efficacy in 2015 and approved for use in the UK in April 2021 [
39].
Drug development is a time consuming and expensive process with many pitfalls for pharmaceutical companies. A study assessing 640 phase 3 trials found a 54% failure rate due to reasons such as inadequate efficacy, concerns with safety and lack of funding [
40]. The cost to successfully complete drug development to bring a drug to market is estimated at approximately
$2.5 billion [
41]. Therefore, failure at a later stage of the process results in substantial financial loss which could have been spent pursuing another potential therapeutic candidate.
There is prescient need for alternative drug discovery approaches which exploit relationships between drugs, genes and disease pathways to identify alternate therapeutic candidates with efficacy and safety profiles suited to heterogenous diseases such as RA. Clinicians require a reliable approach to efficiently identify and administer a highly effective therapy that can minimise disease activity, reduce disease burden and is also cost-effective. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly require discovery approaches with potential to increase confidence in drug candidates ahead of clinical trials, to reduce the associated development timescales and costs by prioritising compounds or molecules with enhanced precision and efficacy.
2.3. Connectivity Mapping
Connectivity mapping (CMap) is a bioinformatic approach pioneered by Lamb et al. in 2006 with the basic concept of comparing a reference database of drug-related gene expression profiles with a query gene signature specific to a disease or a response to a treatment in a disease [
42]. This allows for identification of associations between drugs and disease-related genes with the ultimate aim of predicting potential therapeutic options effective in that disease. Applications of CMap in pharmacogenomics includes discovery of novel phenotypic relations, elucidation of drug mechanism of action, drug repurposing and identification of drug combinations [
42].
CMapBatch is a parallel approach to connectivity mapping adapted by Fortney et al. [
43]. This approach is similar to meta-analysis as it applies CMAP to multiple gene signatures for the same disease and then combine the resulting outcomes [
43]. Analysis of lung cancer data revealed that CMapBatch produces a more stable list of drugs when compared to individual gene signatures. Despite the fact that CMapBatch was only tested for lung cancer, the proposed meta-analysis can be used for any disease phenotype to prioritise therapeutics. For example, multiple colorectal cancer datasets were analysed to compile a gene signature consisting of 148 genes. CMap analysis with this signature identified 10 candidate compounds, including existing chemotherapies such as irinotecan and etoposide [
44]. Other studies utilising CMap show promise by identifying candidate compounds and combination therapies for the treatment of breast cancer [
45] and gastric cancer [
46].
Cystic fibrosis and Huntington’s disease studies validated the effectiveness of the CMap approach to identify small molecules with potential to inhibit the disease state or regulate the expression of a small number of genes. For instance, A20 was identified as a key target to down-regulate the pro-inflammatory NF-kB pathway and the connectivity mapping approach predicted ikarugamycin and quercetin, FDA-approved drugs with anti-inflammatory effects, to induce A20 expression and therefore reduce the inflammatory response in cystic fibrosis [
47]. Deferoxamine and chlorzoxazone, FDA-approved antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents, were identified to reduce mutant HTT toxicity and HTT-induced caspase activation in PC12 cells which can delay onset or progression in Huntington’s disease [
48].
2.4. Drug repurposing and sensitisation
Drug repurposing is a concept that has attracted considerable attention in recent years. The term drug repurposing is broadly defined as investigating drugs which are already approved for specific disease indications, but may have utility in alternate diseases. The established safety profile of such drugs is a significant advantage, in addition to bypassing the time and cost involved with the de novo development of new compounds.
On the other hand, the principle of drug sensitisation is when a drug exhibits synergistic effects with another drug to produce enhanced anti-disease efficacy that could not be achieved by using either drug in isolation [
49]. The rationale behind this combined therapeutic approach is to target more than one disease associated pathway during treatment. One suggested mechanistic hypothesis behind such an approach is that a combination of therapies simultaneously administered to engage multiple pathways can evoke a higher response than those achieved with monotherapy. Another suggestion is that treatment with one drug can evoke a dynamic response resulting in sensitivity to treatment with a second drug. It is believed that combinations of repurposed already approved drugs have good potential to achieve greater efficacy, desired efficacy at lower dosage and overcome drug resistance [
50]. Implementation of synergistic combination therapy can raise concerns about synergistic toxicity as a result of targets and molecular mechanisms being shared between the combined drugs. Careful considerations and strategies are required to minimise toxicity without compromising drug efficacy.
There are many drugs used for treatment of RA and some of their mechanisms of action are understood, however, their combinational effects are still being explored.
2.5. Bioinformatics Pipelines to identify potential therapeutics
Bioinformatics is now more widely implemented within drug discovery for immune mediated and inflammatory diseases. Recent studies illustrate the potential of bioinformatic approaches to exploit increasing volumes of data generated from clinical trials and studies carried out globally. Bioinformatic methods have been used to create data warehouses, algorithms, networks, and programs to analyse ‘big data’ [
51]. Development of a workflow or pipeline using bioinformatic resources and techniques holds strong potential to accelerate identification of candidate drugs, avoid unwanted side effects and predict drug resistance [
52].
For example, a drug discovery strategy was developed to identify potential therapeutic agents for inflammatory bowel disease. Data involving the NF-κB/RelA pathways were curated from multiple sources including sequencing data, text-mining of relevant abstracts, genome wide association studies and HumanPSD database [
53]. Potential target genes within the pathways were classified as master regulators for pathway analysis. Prediction of activity spectra was used to assess the association between the chemical structure of compounds and their biological activities to identify potential novel drugs for IBD treatment. Results of the study indicated that clarithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, has potential to act as an inhibitor of the NF-κB signalling pathway in the gastrointestinal tract. This finding complements existing clinical literature as macrolides are already used to treat inflammatory conditions, such as panbronchiolitis [
54] and atopic dermatitis [
55]. The antibacterial and immunomodulatory properties of macrolides have shown promise in inhibiting the production and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines [
55]. Additional studies investigating the effect of macrolide in combination with rifabutin for treatment of Crohn’s disease indicate significant improvement in patient outcomes and disease activity [
56]. This drug discovery approach incorporated an intentional bias toward target genes involved in the NF-κB signalling pathways which resulted in corticosteroids and NSAIDs as the majority of predicted drugs.
An integrative computational modelling approach was developed to identify effective therapeutic agents for CD4+T cell mediated immune disorders. Multi-omic data was used to construct genome-scale metabolic models of CD4+ T cells to show perturbation in rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and primary biliary cholangitis. In silico simulations were performed on these models to predict drug targets from existing FDA-approved drugs and compounds with potential to downregulate effector CD4+ T cells. 68 potential drug targets were identified and validated in vitro to propose several drugs that can be repurposed for RA, multiple sclerosis, and primary biliary cholangitis treatment [
57].
The above studies demonstrate the power of implementing an in silico drug discovery model to identify repurposable candidate drugs and highlights the importance of incorporating steps to orthogonally validate results to determine which drugs to pursue for further experimental investigations.
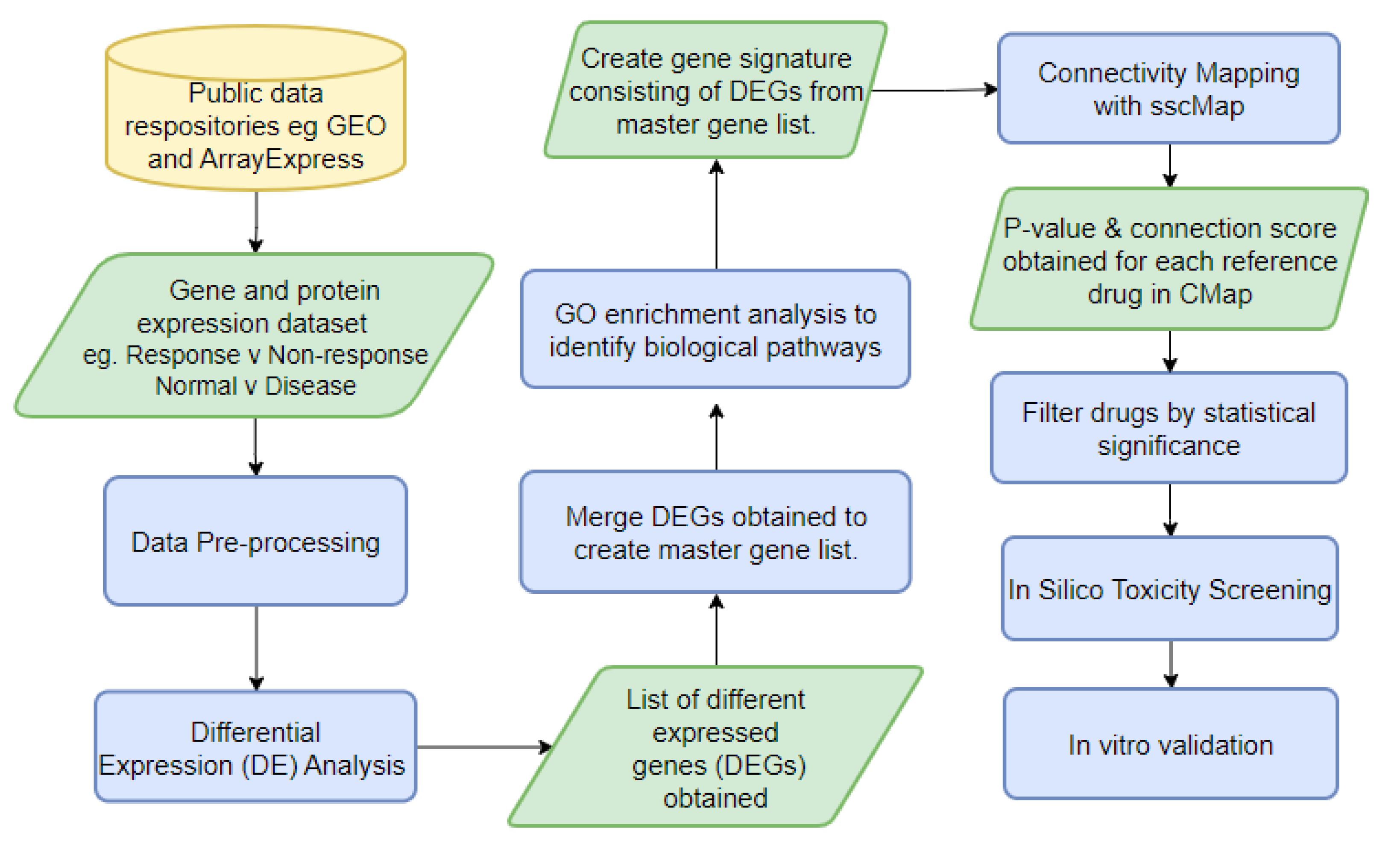
As an examplar approach, we have developed a novel bioinformatic pipeline (
Figure 4), DrugExpress, which integrates connectivity mapping platform ssCMap (statistically significant connectivity map) [
58] and ZhangScore [
59,
60]. DrugExpress will identify drug combinations, dosage regimens and already FDA approved drugs that can be repurposed in rheumatoid arthritis. This pipeline also incorporates the novel concept of drug sensitisation by predicting drugs that will act as a sensitiser to another drug, to produce synergistic effects which enhance therapeutic efficacy, by targeting multiple disease pathways. Suitable candidate drugs will be identified and shortlisted based on their abilities to shift the transcriptomic (gene expression) profiles of treatment naïve disease and sensitize non-responding patient sub-groups towards more favourable ‘response-like’ transcriptome profiles. Candidate drugs subsequently undergo toxicity screening and pathway analysis. The final list of candidate drugs then require validation in vitro in RA model systems.
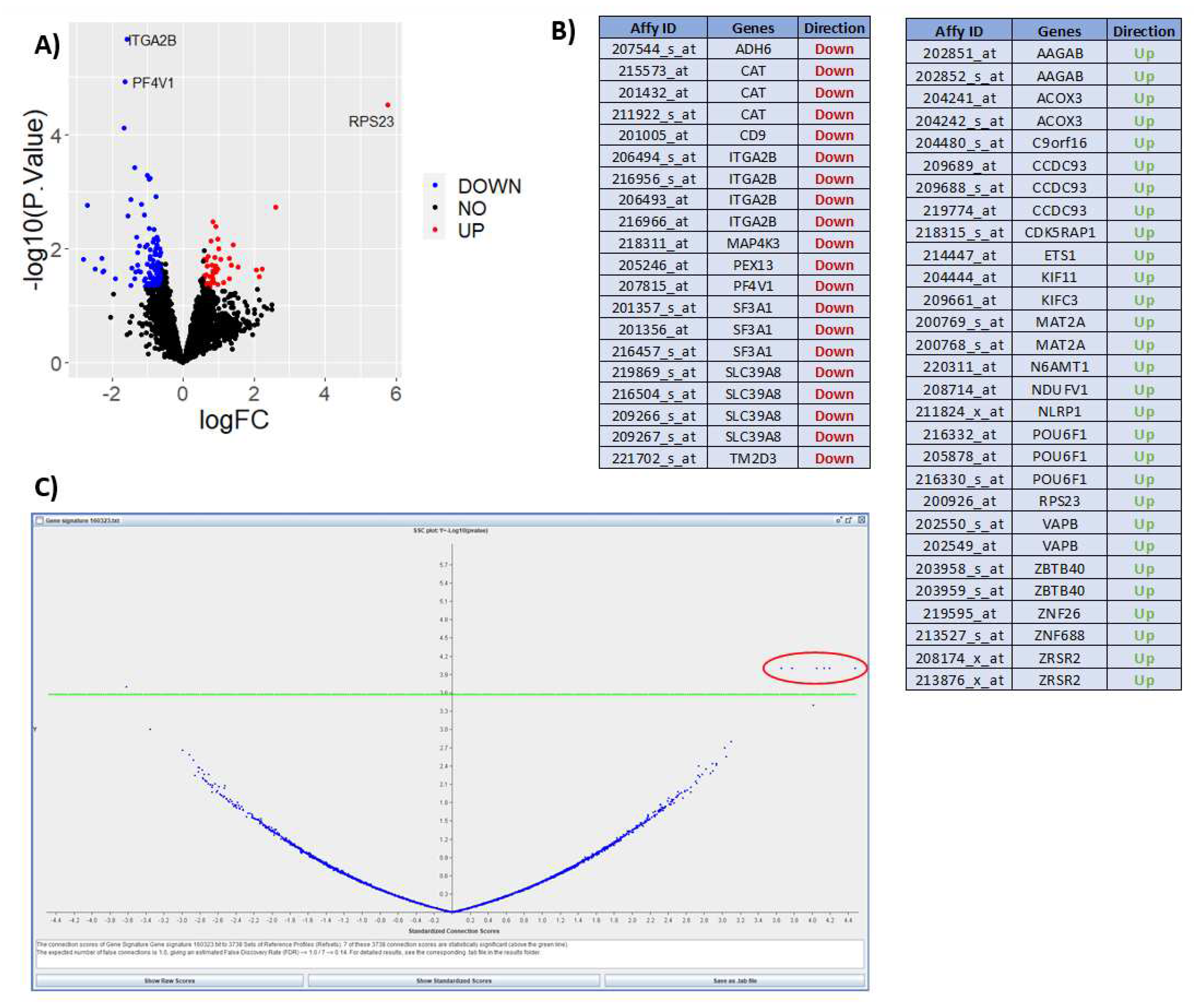
Figure 5 shows results from expression data after interrogation using the DrugExpress pipeline. Public datasets such as Gene Expression Omnibus and ArrayExpress are mined to gather a collection of suitable datasets and pre-processed manually using Microsoft Excel and R programming. The datasets are filtered, sorted and selected using a pre-determined criteria, followed by differential expression analysis to obtain a list of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) characteristic of treatment response. DEGs from multiple datasets are merged to create a master gene list subsequently mapped to Affymetrix probeset IDs to create a treatment response gene signature. Connectivity mapping (CMap) analysis is used to establish networks between DEGs in the response gene signature and FDA approved drugs. P-value and connection score of each reference drug in the CMap was obtained and used to identify 6 statistically significant candidate compounds with high probability of inducing therapeutic response. The next step is to perform in silico toxicity screening on the list of candidate compounds ahead of in vitro verification on optimal compounds to assess efficacy and ability to reduce gene expression I key pathways and cell proliferation associated with lower disease activity. This illustrates how publicly available expression datasets can be used to predict theoretical effect of drug candidates and prioritise novel compounds with maximal potential to reduce disease activity.
3. Conclusions
RA is a disorder with considerable heterogeneity in disease severity and trajectory which affects the accuracy of a patient’s prognosis. Clinicians require novel therapeutic options to improve outcome for people living with RA who are refractory to current treatments. This calls for a more reliable drug discovery pipeline to better inform new drug trials, which will optimise the potential to reduce disease activity and reduce disease burden, whilst also being cost effective in pharmaceutical development and for healthcare providers and payers.
3.1. Application of similar approaches in RA
Drug repurposing and use of aritifical intelligence (AI) to accelerate discovery in legacy data is a concept that has garnered growing interest from pharmaceutical companies and research organisation in recent years, with several RA focussed studies conducted proposing a computation-based drug discovery approach. One such study integrated drug-related and disease-related data to construct a genetic disease network to develop a drug ranking algorithm. This algorithm discovered innovative drugs from diseases genetically related to RA that can be repositioned to treat RA [
61]. Another study introduced a systems approach to identify potential targets for diagnosis and treatment of RA. RA-associated genes were initially identified and used to construct a RA-perturbed network illustrating the associations between these genes. This provided an insight into the role of the genes in the pathogenesis of the disease and allowed the identication of molecular targets that can be used to shift RA-perturbed processes towards normality [
62]. A pre-clinical study demonstrated that repurposing of pirfenidone, a drug originally used to treat anti-pulmonary fibrosis, can inhibit inflammation and angiogenesis through multiple pathways in collagen-induced arthritic rats. This finding supports literature proposing the use of pirfenidone in RA, however, it is to be further studied in humans to unveil the potential of being used as a therapeutic in rheumatoid arthritis [
63].
A further study used bioinformatic approaches to establish a transcriptional regulatory network to identify tissue-specific repurposing drug candidates for RA. The candidate drugs were reviewed and ranked based on supporting evidence obtained from extensive literature searches using text mining analyses. Momelotinib, ibrutinib, and sodium butyrate were suggested as promising drug candidates, however further comprehensive validation and clinical studies are required to fully elucidate their therapeutic effects in patients with RA [
64].
Numerous studies analysing treatment regimens in RA show that double and triple therapy leads to greater clinical outcome than DMARD monotherapy. Combination therapy adminstered early in the course of the disease has been found to significantly decrease disease activity [
65]. This finding aligns with the rationale behind the concept of drug sensitisation that administering multiple drugs in combination engages multiple pathways to evoke a higher treatment response. However, current evidence on combination therapy is limited with knowledge gaps that can only be filled with further research and randomised controlled trials of adequate power.
3.2. Application in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era
Remdesivir (GS-5734) is anti-viral drug that got emergency approval from the regulatory authorities of different countries for repositioned use in COVID-19 patients. The drug shows therapeutic efficacy in viruses such as Ebola, Nipah, SARS-CoV-2, MERS CoV, and SARS-CoV. Remdesivir shows in vitro activity by binding to the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and it acts as a terminator for RNA elongation. Recent studies show that it may be helpful for clinical improvement against SARS-CoV-2 as it shortened the time to recovery in hospitalized adults with COVID-19 [
66].
Monoclonal antibody treatments such as tocilizumab and mavrilimumab have been repurposed for use in COVID-19 and has been associated with reducing the incidence of severe infections and decreasing the duration of vasopressor support needed in severe patients. Studies on mavrilimumab concluded it was associated with improved clinical outcomes for severe COVID-19 patients with systemic hyper-inflammation and pneumonia. JAK inhibitor, baricitinib, speeds up the viral clearance and augments patients’ discharge rates compared to COVID-19 patients who are having standard-of-care. A recent randomized clinical trial with 1033 patients showed a better therapeutic outcome of combined therapy of baricitinib with remdesivir for COVID-19 hospitalized patients compared to only remdesivir [
67]. It has been noted that a good number of candidates have been identified through computational drug repurposing for COVID-19 patients.
CoV-KGE is an integrative, network-base, AI methodology developed to discover candidate drugs that can be repurposed for COVID-19. This approach aimed to shorten the gap between preclinical testing and clinical outcomes, allowing for rapid development of efficient treatment strategies during the COVID-19 pandemic. This methodology resulted in discovering 41 high-confidence drug candidates which were validated by an enrichment analysis of gene expression and proteomics data in SARS-CoV-2 infected human cells [
68]. The network tools used in this powerful methodology can be translated and applied to rapidly develop effective repurposable treatment strategies for other complex diseases and emerging infectious diseases.
As highlighted above, the majority of recent research conducted in drug repurposing has focussed on finding drugs that could combat the effects of the SARS-COV-2 virus infection. Therefore, there is now a unique opportunity to apply similar principles in RA, a chronic and frequently treatment refractory disease, to identify effective treatments which reduce disease activity and disease burden. The proposed DrugExpress pipeline allows for independent in silico validation of emerging candidate drugs using new RNAseq analyses of suitable samples from treated RA cohorts held in biobanks. A final list of robust sensitising drugs generated by DrugExpress will be carried forward for novel drug and combination drug screening performed on inflamed synovial cells in vitro.
3.3. Challenges and Benefits
There are several potential challenges or limitations that are to be acknowledged with this approach of computational drug discovery. While this computational approach can be widely generalised for many human disease and performed using multiple omics data, the unavailability of large, reliable data warehouses and high-quality datasets required for comprehensive analysis contributes to some limitations [
57]. Potential data noises generated from incorporating multiple different datasets may influence the performance of the pipeline. Issues such as varying standards for annotation, formatting, storage, and access may also affect the performance and results obtained [
69].
On the other hand, potential benefits include identification of novel drug combinations, dosage regimens and application of already established treatments in a new index disease that can be used as priority candidates for further in vitro and in vivo biological validation [
69].
3.4. Conclusion
RA is a chronic debilitating disorder that affects a significant proportion of the global population, that when refractory to current therapies leads to considerable societal, clinical and financial burden. It is important that novel effective therapies are identified more efficiently, trialled, and approved to help reduce growing disease and financial burden associated with unresponsive disease. This review illustrates the substantial opportunity AI approaches present to incorporate disease-related data and drug-related data to streamline the development of new treatments with favourable outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z. and D.G.; methodology, J.R.; software, S.Z. and J.R.; validation, J.R. formal analysis, J.R. investigation, J.R.; data curation, J.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.R.; writing—review and editing, S.Z, D.G, A.B and S.M.; visualization, J.R.; supervision, S.Z., D.G. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
DrugExpress pipeline was developed as part of a PhD project funded by the Department of Economy and Northern Ireland Rheumatism Trust.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Heidari, B. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Early diagnosis and treatment outcomes. 2011, 2, 161–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Figus, F.A.; Piga, M.; Azzolin, I.; McConnell, R.; Iagnocco, A. Rheumatoid arthritis: Extra-articular manifestations and comorbidities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, J.H.; Verstappen, S.M.M.; Hyrich, K.L.; Chipping, J.R.; Marshall, T.; Symmons, D.P.M. The incidence of rheumatoid arthritis in the UK: comparisons using the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and the 1987 ACR classification criteria. Results from the Norfolk Arthritis Register. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 72, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevalence and incidence | Background information | Rheumatoid arthritis | CKS | NICE. Available online: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/rheumatoid-arthritis/background-information/prevalence-incidence/ (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Versus Arthritis The State of MSK Health 2021. 2021.
- Köhler, B.M.; Günther, J.; Kaudewitz, D.; Lorenz, H.-M. Current Therapeutic Options in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deane, K.D.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Kelmenson, L.B.; Kuhn, K.A.; Norris, J.M.; Holers, V.M. Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Therneau, T.M.; Gabriel, S.E. Is the incidence of rheumatoid arthritis rising?: Results from Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1955-2007. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Alfredsson, L. Modifiable environmental exposure and risk of rheumatoid arthritis—current evidence from genetic studies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.; Rizvi, S.A.; Saleh, A.M.; Ahmed, S.S.; Do, D.P.; Ansari, R.A.; Ahmed, J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Overview of the Treatment. Med Princ. Pr. 2018, 27, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, L.; Buch, M. The ‘therapeutic window’ and treating to target in rheumatoid arthritis. 2013, 13, 387–390. [CrossRef]
- Bullock, J.; Rizvi, S.A.; Saleh, A.M.; Ahmed, S.S.; Do, D.P.; Ansari, R.A.; Ahmed, J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Overview of the Treatment. Med Princ. Pr. 2018, 27, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiel, M.H. Treat to Target Strategy in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Real Benefits. 2013, 9, 101–105. [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; de Wit, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Rheumatology 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE rheumatoid arthritis guideline. Available online: https://www.guidelines.co.uk/musculoskeletal-and-joints-/nice-rheumatoid-arthritis-guideline/454370.article (accessed on 24 June 2023).
- Moura, M.D.G.; Lopes, L.C.; Silva, M.T.; Barberato-Filho, S.; Motta, R.H.L.; Bergamaschi, C.d.C. Use of steroid and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Robson, J. The dangers of NSAIDs: look both ways. Br. J. Gen. Pr. 2016, 66, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, C.; Buttgereit, F.; Combe, B. Glucocorticoids in rheumatoid arthritis: current status and future studies. RMD Open 2020, 6, e000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, B.; Cronstein, B. Methotrexate mechanism in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 86, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoui, Y.; Guillot, X.; Sélambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Ralandison, S.; Gasque, P. Methotrexate an Old Drug with New Tricks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Yan, X.; Xiang, Z.; Ding, H.-F.; Cui, H. Leflunomide Reduces Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Neuroblastoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e71555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Dai, S.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z. Investigating the safety and compliance of using csDMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis treatment through face-to-face interviews: a cross-sectional study in China. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 40, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Xie, D.; He, D.; Lu, A.; Liang, C. Toward Overcoming Treatment Failure in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 755844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Dai, S.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z. Investigating the safety and compliance of using csDMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis treatment through face-to-face interviews: a cross-sectional study in China. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 40, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482425/?report=classic (accessed on 24 June 2023).
- Scott, L.J. Tocilizumab: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin Onecia, G.A., Lappin Sarah Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARD), Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing: 2022; 2022.
- Tanaka, Y.; Luo, Y.; O’shea, J.J.; Nakayamada, S. Janus kinase-targeting therapies in rheumatology: a mechanisms-based approach. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.S.; Taylor, P.C.; Choy, E.H.; Sebba, A.; Quebe, A.; Knopp, K.L.; Porreca, F. The Jak/STAT pathway: A focus on pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 51, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, R.; Al Nokhatha, S.A.; Conway, R. JAK Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Evidence-Based Review on the Emerging Clinical Data. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020, 14, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior-Español, A.; Sánchez-Piedra, C.; Campos, J.; Manero, F.J.; Pérez-García, C.; Bohórquez, C.; Busquets-Pérez, N.; Blanco-Madrigal, J.M.; Díaz-Torne, C.; Sánchez-Alonso, F.; et al. Clinical factors associated with discontinuation of ts/bDMARDs in rheumatic patients from the BIOBADASER III registry. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa-Gonçalves, D.; Bernardes, M.; Costa, L. Quality of life and functional capacity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis – Cross-sectional study. 2018, 14, 360–366. [CrossRef]
- Versus Arthritis The State of Musculoskeletal Health 2019. 2019.
- Huang, H.; Xie, W.; Geng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z. AB0171 TOWARDS A BETTER IMPLEMENTATION OF TREAT-TO-TARGET STRATEGY IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS: A COMPARISON OF TWO REAL-WORLD COHORTS. Rheumatology 2022, 81, 1215–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vollenhoven, R. Treat-to-target in rheumatoid arthritis — are we there yet? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lu, B.; Agosti, J.; Bitton, A.; Corrigan, C.; Fraenkel, L.; Harrold, L.R.; Losina, E.; Katz, J.N.; Solomon, D.H. Implementation of Treat-to-Target for Rheumatoid Arthritis in the US: Analysis of Baseline Data From a Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupatini, E.d.O.; Zimmermann, I.R.; Barreto, J.O.M.; da Silva, E.N. How long does it take to translate research findings into routine healthcare practice?—the case of biological drugs for rheumatoid arthritis in Brazil. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 738–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Pangan, A.L.; Song, I.; Mysler, E.; Bessette, L.; Peterfy, C.; Durez, P.; Ostor, A.J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Upadacitinib Versus Placebo or Adalimumab in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate: Results of a Phase III, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, D.B. Factors associated with clinical trials that fail and opportunities for improving the likelihood of success: A review. Contemp. Clin. Trials Commun. 2018, 11, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMasi, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. The Cost of Drug Development. New Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1972–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, A.; Ghoraie, L.S.; Zhang, S.-D.; Galzko, G.; Yli-Harja, O.; Dehmer, M.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Emmert-Streib, F. A review of connectivity map and computational approaches in pharmacogenomics. Briefings Bioinform. 2017, 19, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortney, K.; Griesman, J.; Kotlyar, M.; Pastrello, C.; Angeli, M.; Sound-Tsao, M.; Jurisica, I. Prioritizing Therapeutics for Lung Cancer: An Integrative Meta-analysis of Cancer Gene Signatures and Chemogenomic Data. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; O'Reilly, P.; Dunne, P.D.; Lawler, M.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Hamilton, P.; Zhang, S.-D. Connectivity mapping using a combined gene signature from multiple colorectal cancer datasets identified candidate drugs including existing chemotherapies. BMC Syst. Biol. 2015, 9, S4–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, E.; Zhang, X. Identification of breast cancer hub genes and analysis of prognostic values using integrated bioinformatics analysis. Cancer Biomarkers 2018, 21, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kang, W.; Lu, X.; Ma, S.; Dong, L.; Zou, B. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis and connectivity map identifies lovastatin as a treatment option of gastric cancer by inhibiting HDAC2. Gene 2018, 681, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcomson, B.; Wilson, H.; Veglia, E.; Thillaiyampalam, G.; Barsden, R.; Donegan, S.; El Banna, A.; Elborn, J.S.; Ennis, M.; Kelly, C.; et al. Connectivity mapping (ssCMap) to predict A20-inducing drugs and their antiinflammatory action in cystic fibrosis. 2016, 113, E3725–E3734. [CrossRef]
- Smalley, J.L.; Breda, C.; Mason, R.P.; Kooner, G.; Luthi-Carter, R.; Gant, T.W.; Giorgini, F. Connectivity mapping uncovers small molecules that modulate neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease models. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 94, 235–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehár, J.; Krueger, A.S.; Avery, W.; Heilbut, A.M.; Johansen, L.M.; Price, E.R.; Rickles, R.J.; Iii, G.F.S.; E Staunton, J.; Jin, X.; et al. Synergistic drug combinations tend to improve therapeutically relevant selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Zhu, F.; Ma, X.; Cao, Z.W.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Y.Z. Mechanisms of drug combinations: interaction and network perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooller, S.K.; Benstead-Hume, G.; Chen, X.; Ali, Y.; Pearl, F.M. Bioinformatics in translational drug discovery. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. Bioinformatics and Drug Discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1709–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, K.; Papoutsopoulou, S.; Smith, E.; Stegmaier, P.; Bergey, F.; Morris, L.; Kittner, M.; England, H.; Spiller, D.; White, M.H.R.; et al. Using systems medicine to identify a therapeutic agent with potential for repurposing in inflammatory bowel disease. Dis. Model. Mech. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Lu, J.; Yang, M.; Dong, B.R.; Wu, H.M. Macrolides for diffuse panbronchiolitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD007716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwiatkowska, B.; Maślińska, M. Macrolide Therapy in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2012, 2012, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, G.P.; Thomas, P.R.; Tizard, M.L.; Lake, J.; Sanderson, J.D.; Hermon-Taylor, J. Two-year-outcomes analysis of Crohn's disease treated with rifabutin and macrolide antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 39, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puniya, B.L.; Amin, R.; Lichter, B.; Moore, R.; Ciurej, A.; Bennett, S.J.; Shah, A.R.; Barberis, M.; Helikar, T. Integrative computational approach identifies drug targets in CD4+ T-cell-mediated immune disorders. npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2021, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-D.; Gant, T.W. sscMap: An extensible Java application for connecting small-molecule drugs using gene-expression signatures. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 236–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zou, L.; Xiao, Z.-X.; Yang, J. Transcriptome-based drug repositioning identifies TPCA-1 as a potential selective inhibitor of esophagus squamous carcinoma cell viability. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Li, L.; Dai, Y.; Wang, H.; Teng, S.; Bao, X.; Lu, Z.J.; Wang, D. A comprehensive evaluation of connectivity methods for L1000 data. Briefings Bioinform. 2019, 21, 2194–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Wang, Q. A genomics-based systems approach towards drug repositioning for rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.; Cho, C.-S.; Lee, I.; Hood, L.; Hwang, D.; Kim, W.-U. A Systems Approach to Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e51508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.; Cheng, W.; Ke, L.; Sun, A.R.; Jia, Q.; Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, P. Repurposing of Pirfenidone (Anti-Pulmonary Fibrosis Drug) for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, U.; Comertpay, B.; Demirtas, T.Y.; Gov, E. Drug repurposing for rheumatoid arthritis: Identification of new drug candidates via bioinformatics and text mining analysis. Autoimmunity 2022, 55, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steunebrink, L.M.M.; Versteeg, G.A.; Vonkeman, H.E.; Klooster, P.M.T.; Kuper, H.H.; Zijlstra, T.R.; van Riel, P.L.C.M.; van de Laar, M.A.F.J. Initial combination therapy versus step-up therapy in treatment to the target of remission in daily clinical practice in early rheumatoid arthritis patients: results from the DREAM registry. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frediansyah, A.; Nainu, F.; Dhama, K.; Mudatsir, M.; Harapan, H. Remdesivir and its antiviral activity against COVID-19: A systematic review. Clin. Epidemiology Glob. Heal. 2020, 9, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Bhattacharya, M.; Agoramoorthy, G.; Lee, S.-S. The Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Clinical Trials Provide Very Effective Therapeutic Combinations: Lessons Learned From Major Clinical Studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 704205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Song, X.; Ma, T.; Pan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, K.; Karypis, G.; Cheng, F. Repurpose Open Data to Discover Therapeutics for COVID-19 Using Deep Learning. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4624–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Zhu, Y. The Challenges of Data Quality and Data Quality Assessment in the Big Data Era. Data Sci. J. 2015, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).