Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. Deep Belief Network (DBN)
3.2. Simple Deep Neural Network (SDNN)
3.3. LSTM based network (LSTM)
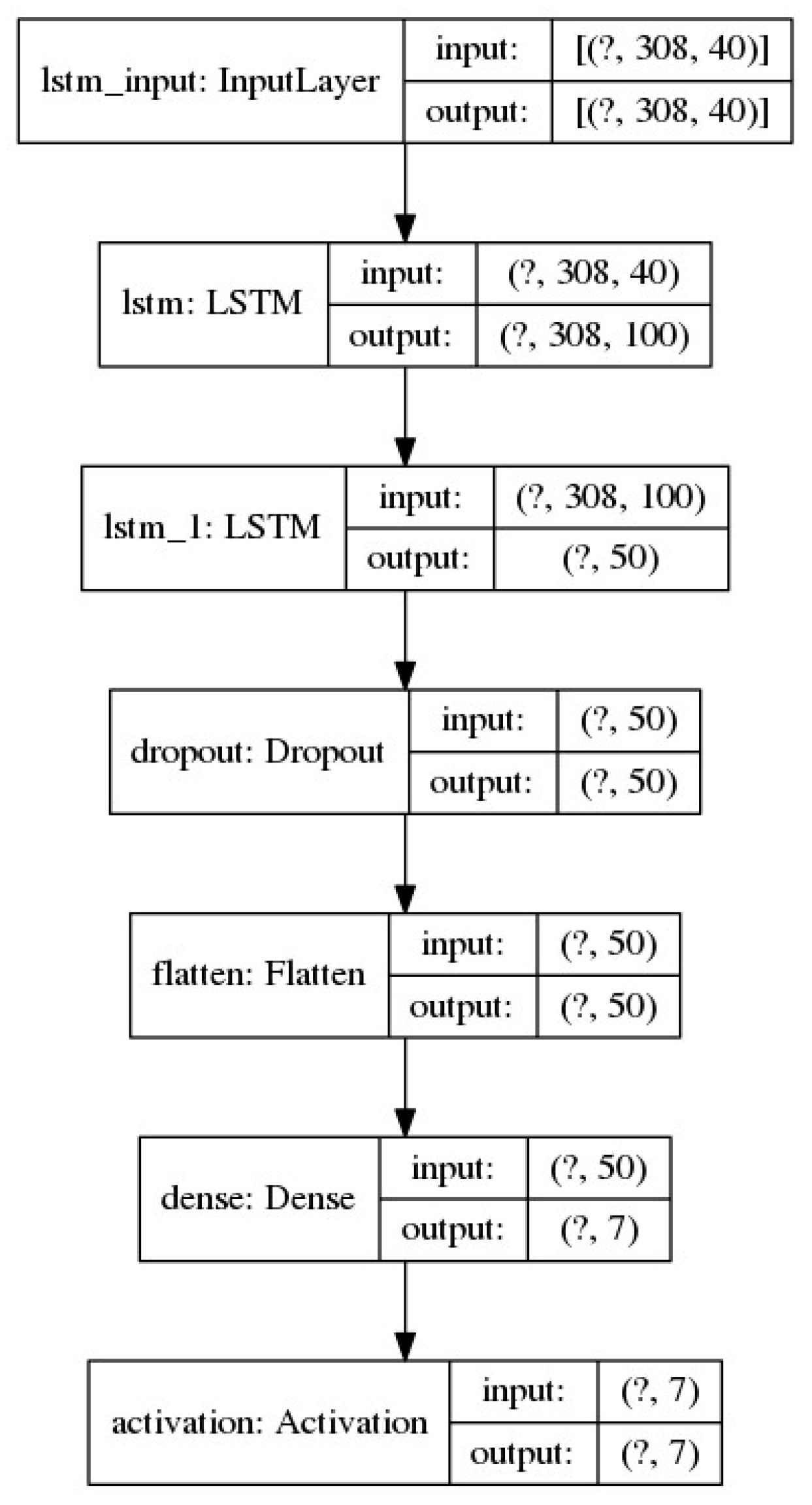
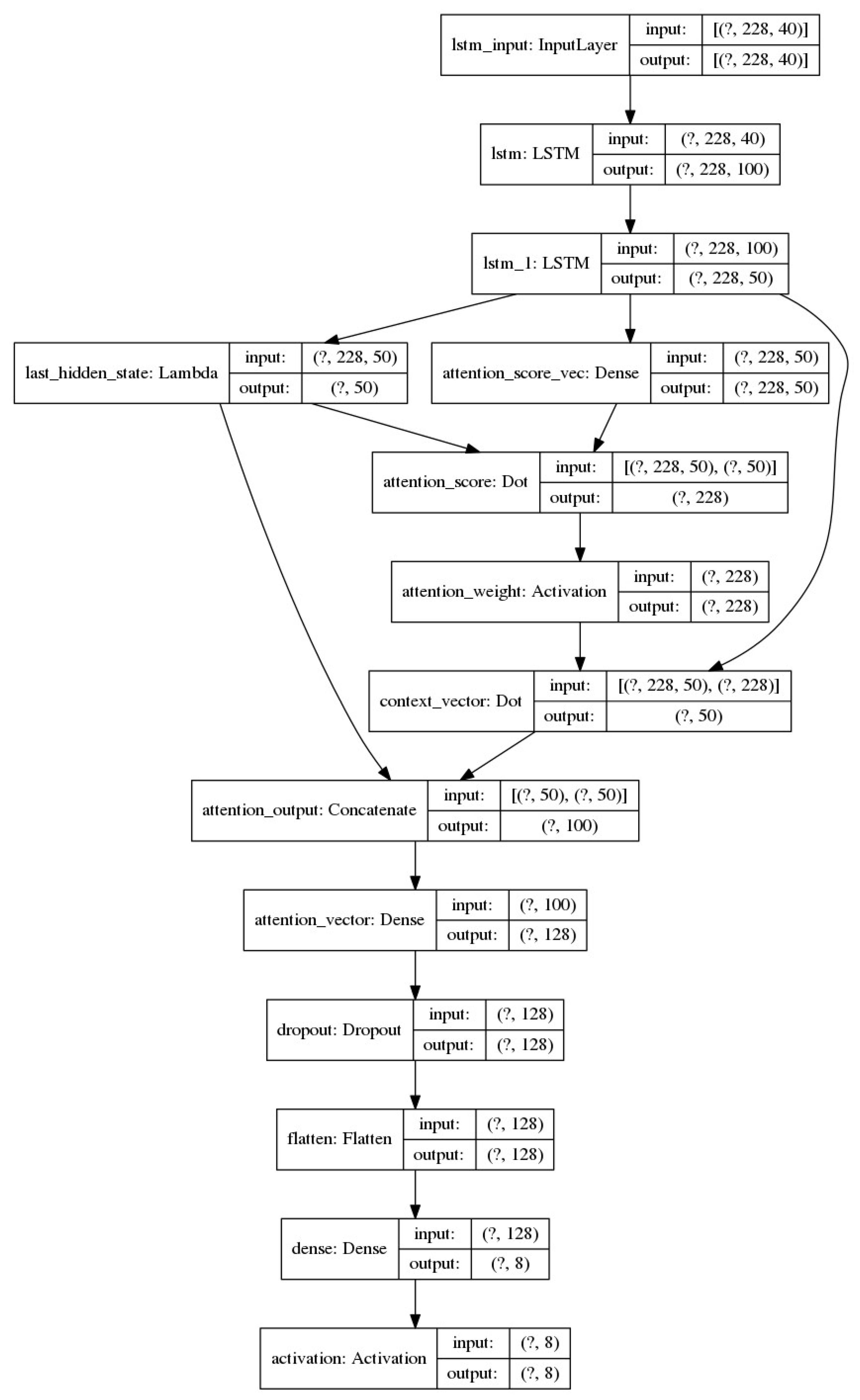
3.4. LSTM based Network with Attention Mechanism (LSTM-ATN)
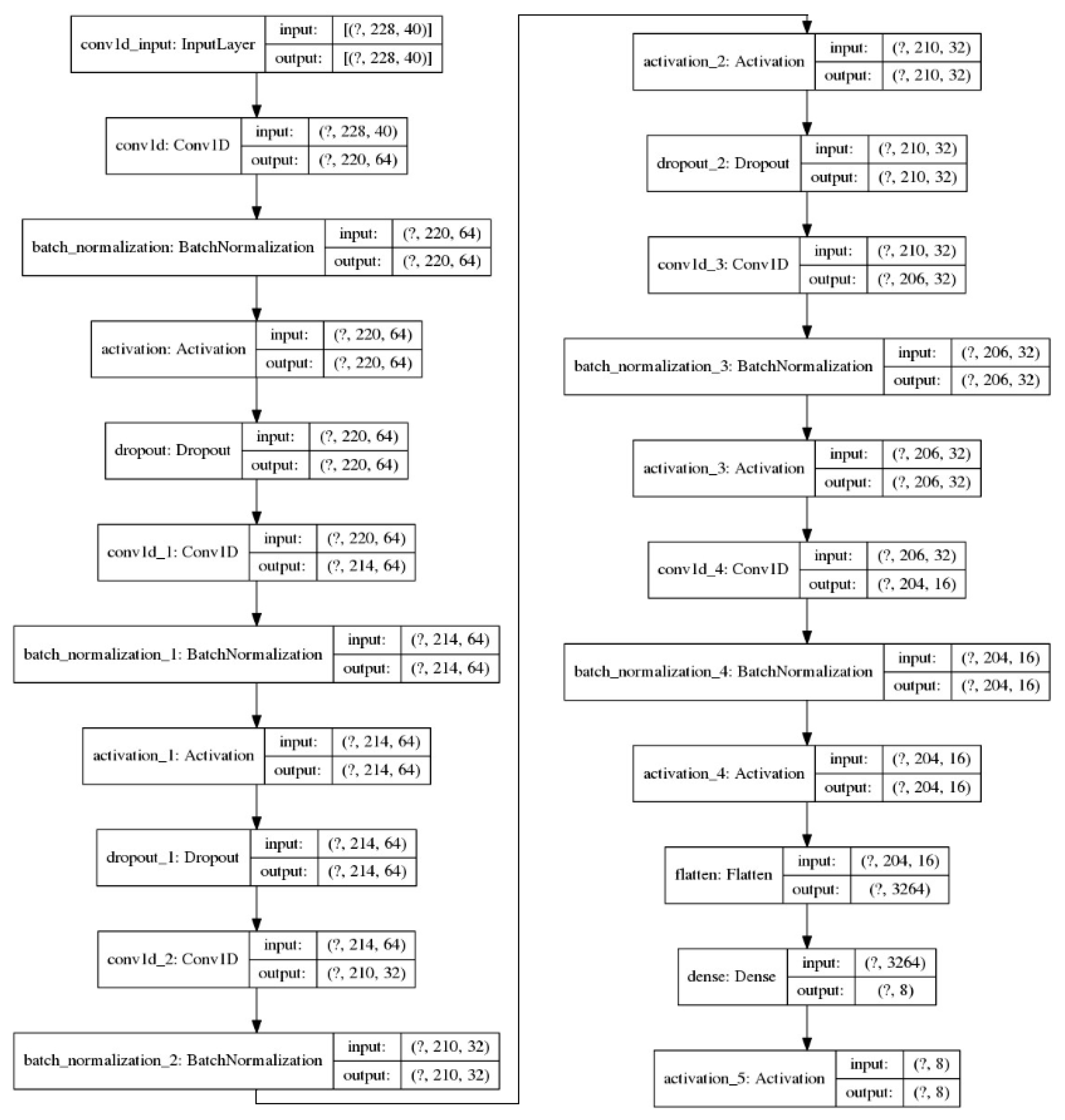
3.5. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
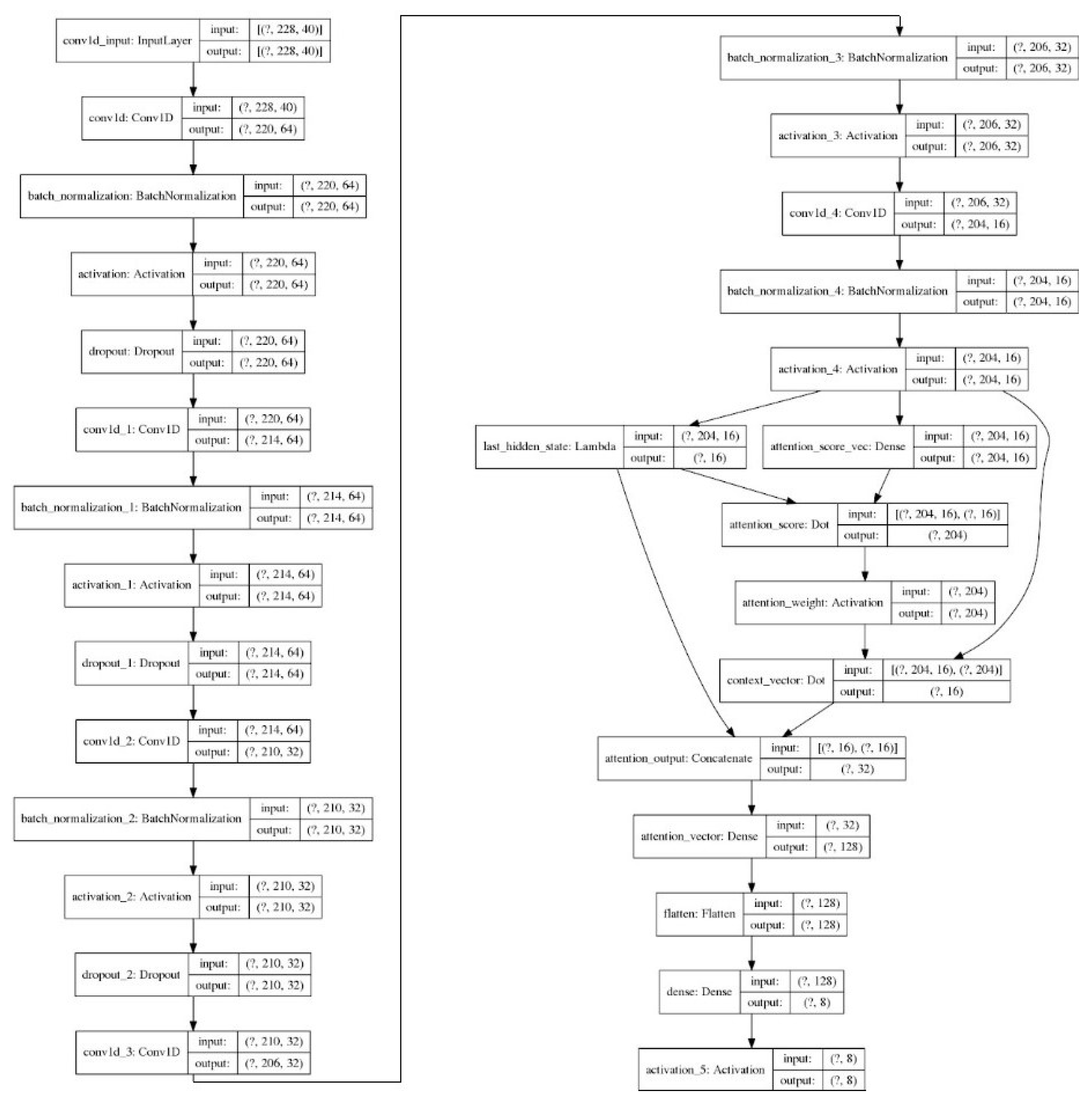
3.6. Convolutional Neural Network with Attention mechanism (CNN-ATN)
3.7. Implementation Tools
4. Experimental Study and Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Experimental Results-Accuracy and Loss Curves
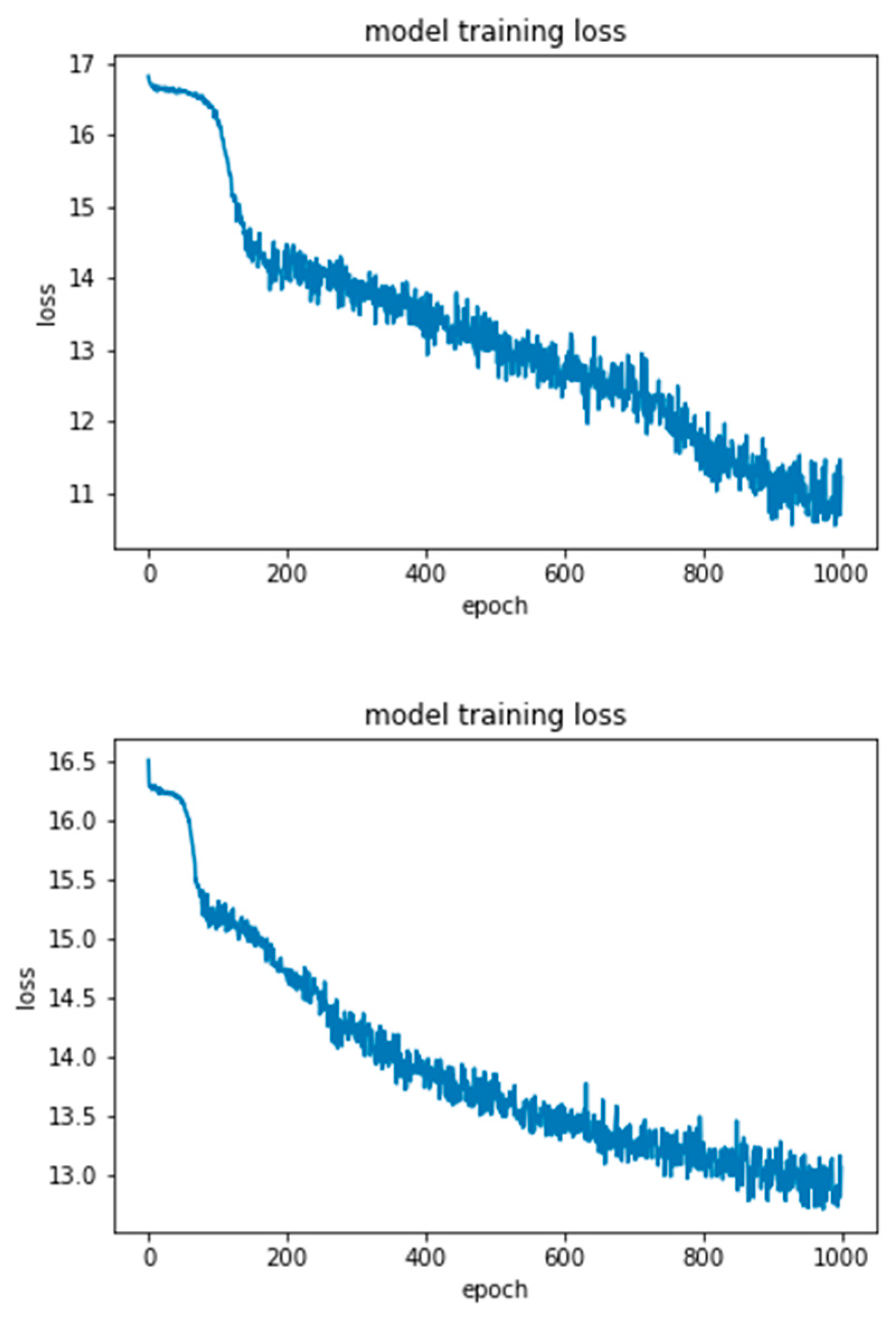
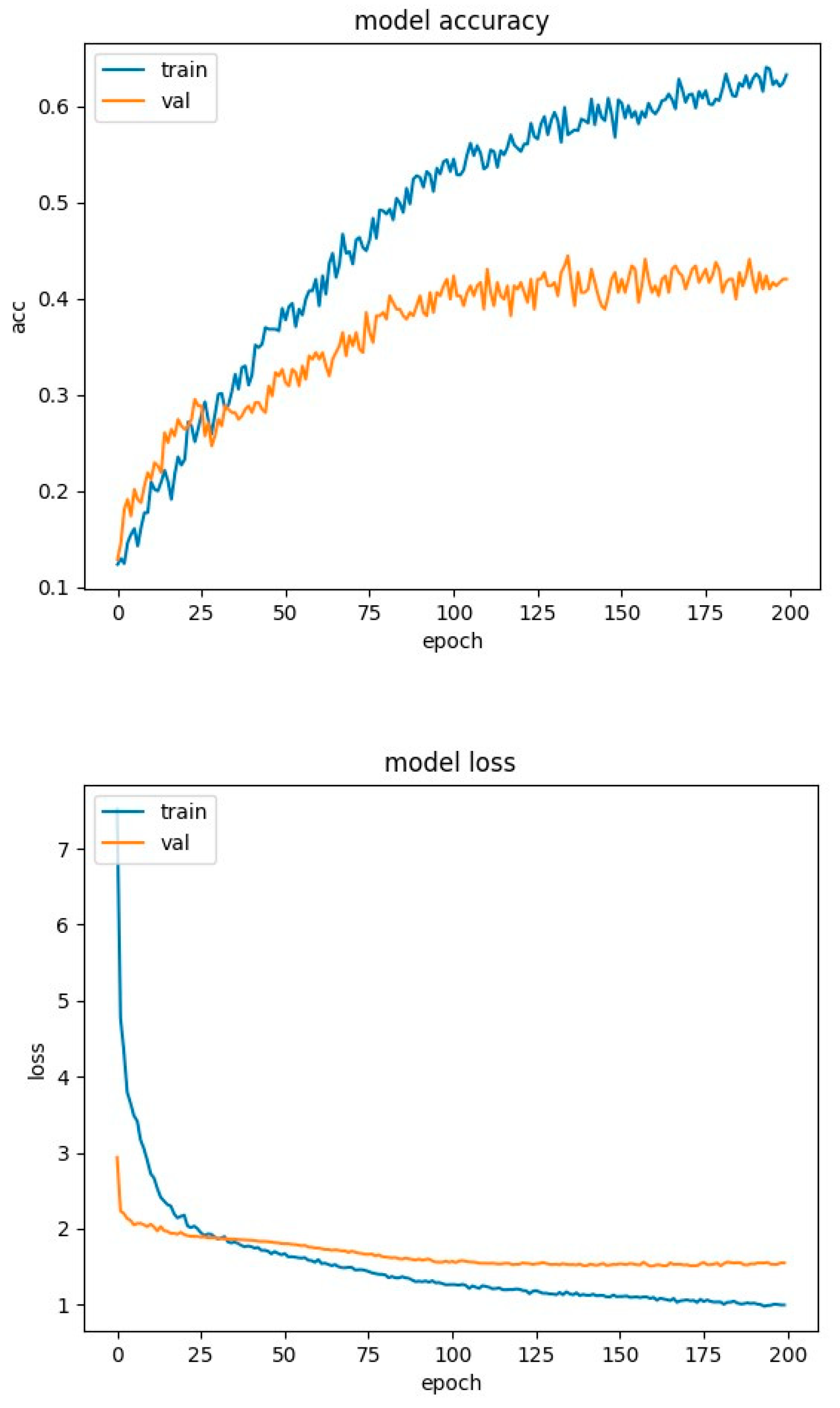
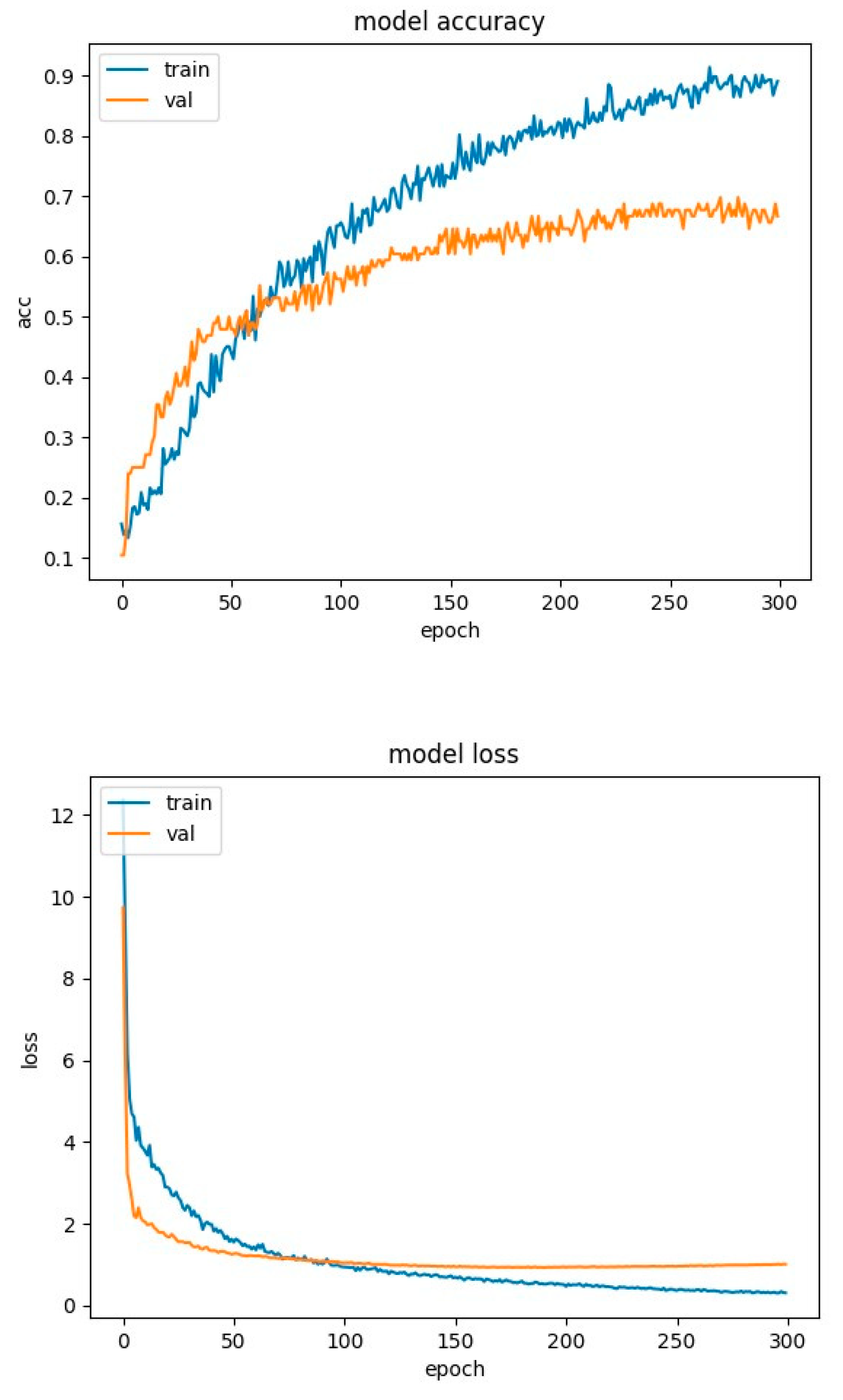
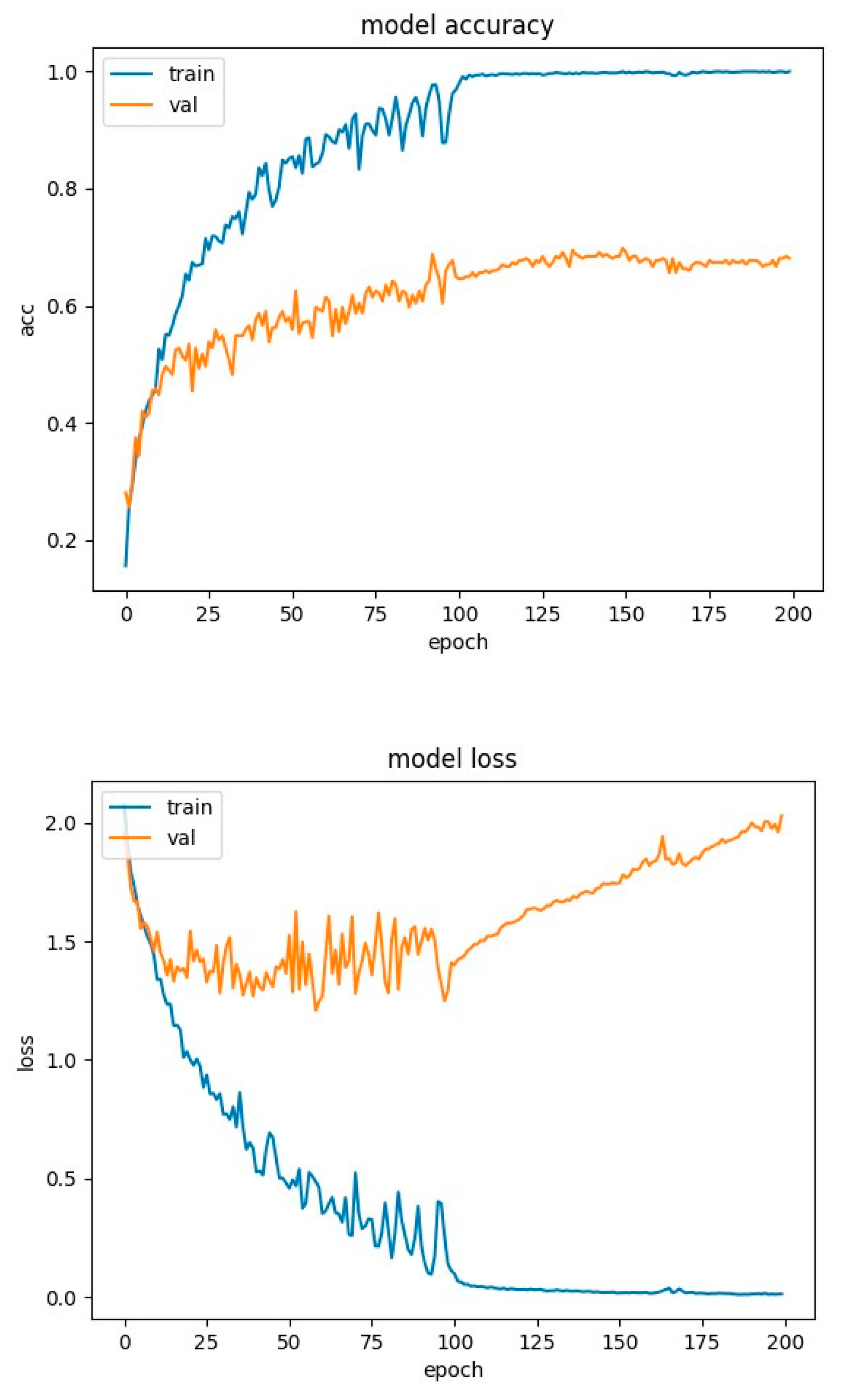
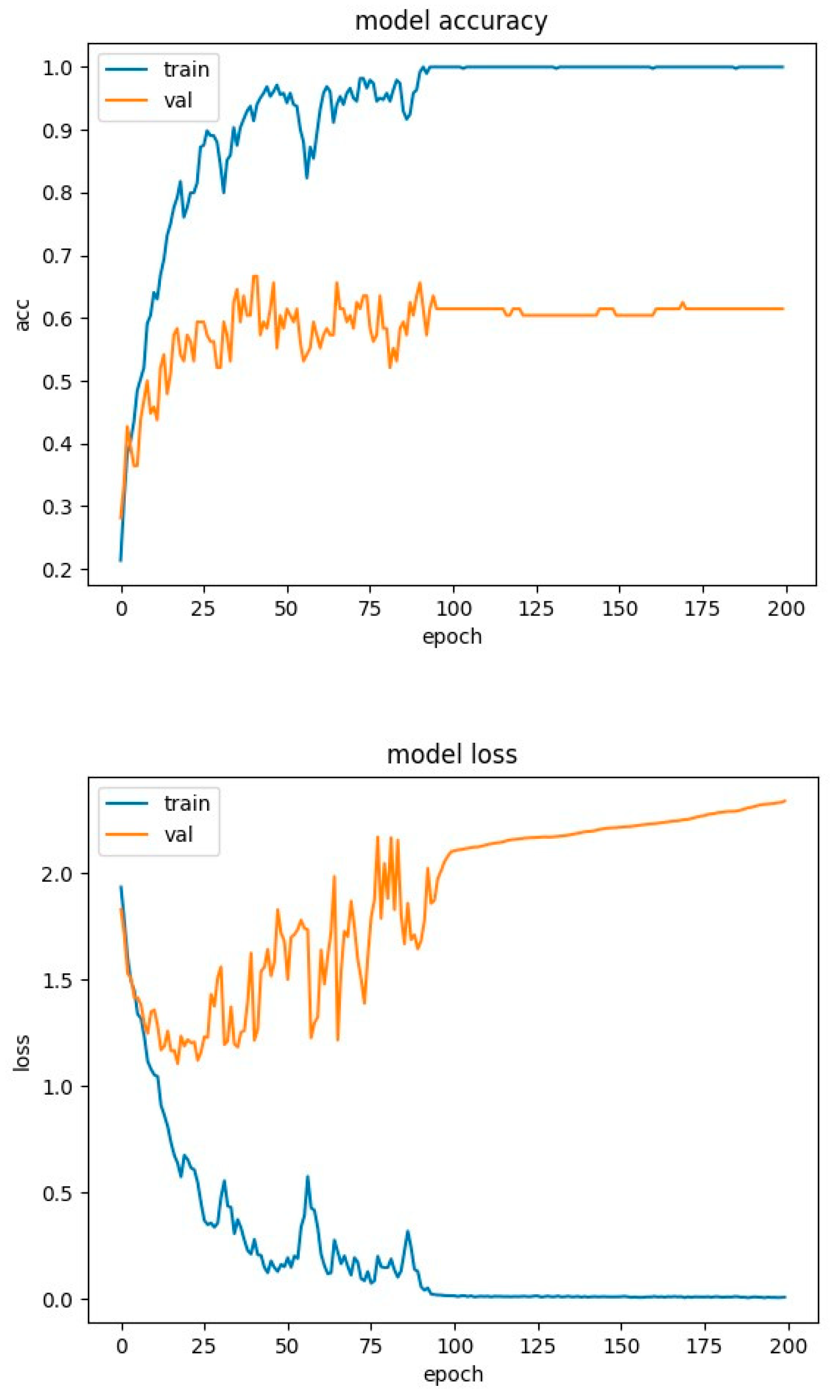
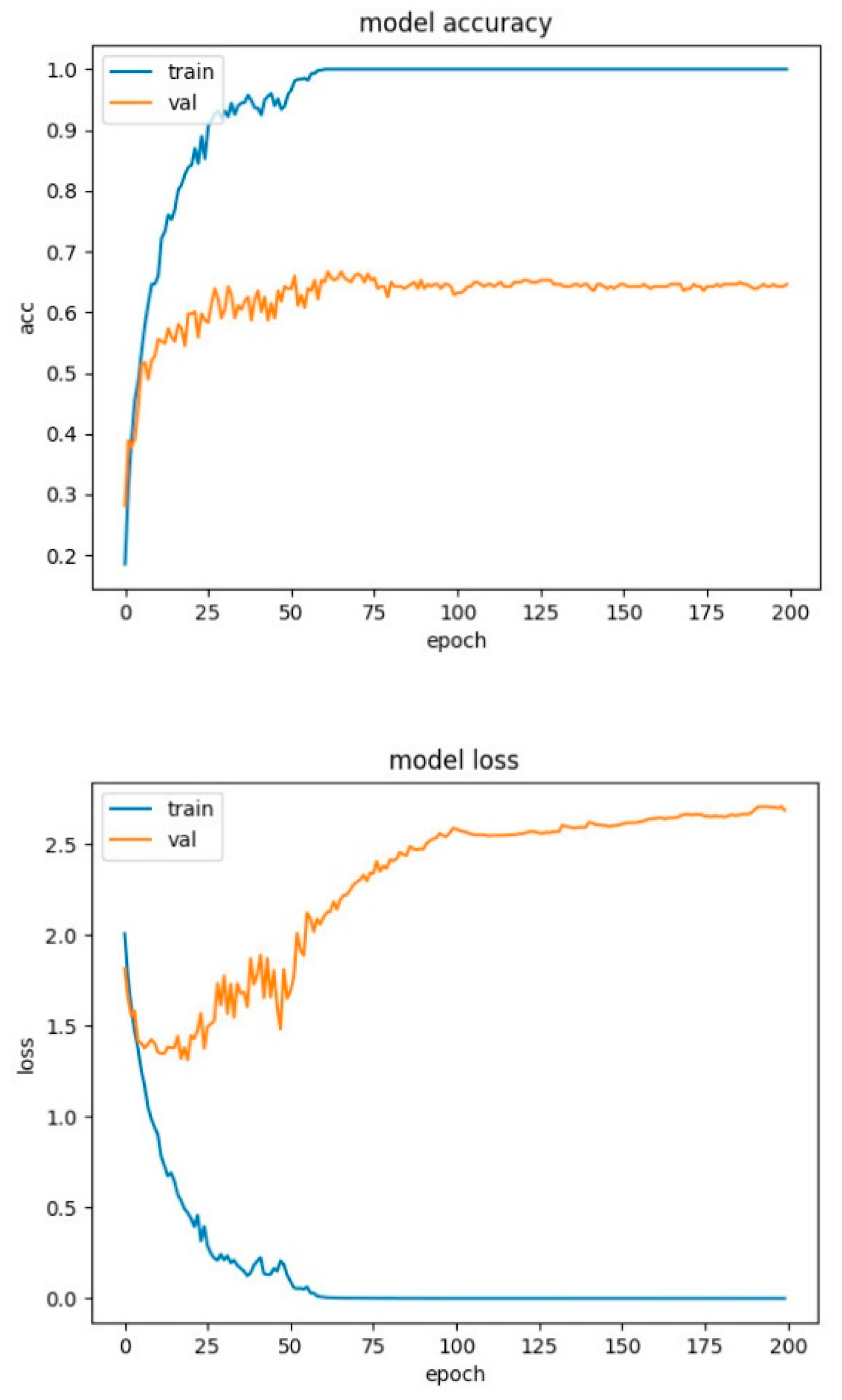
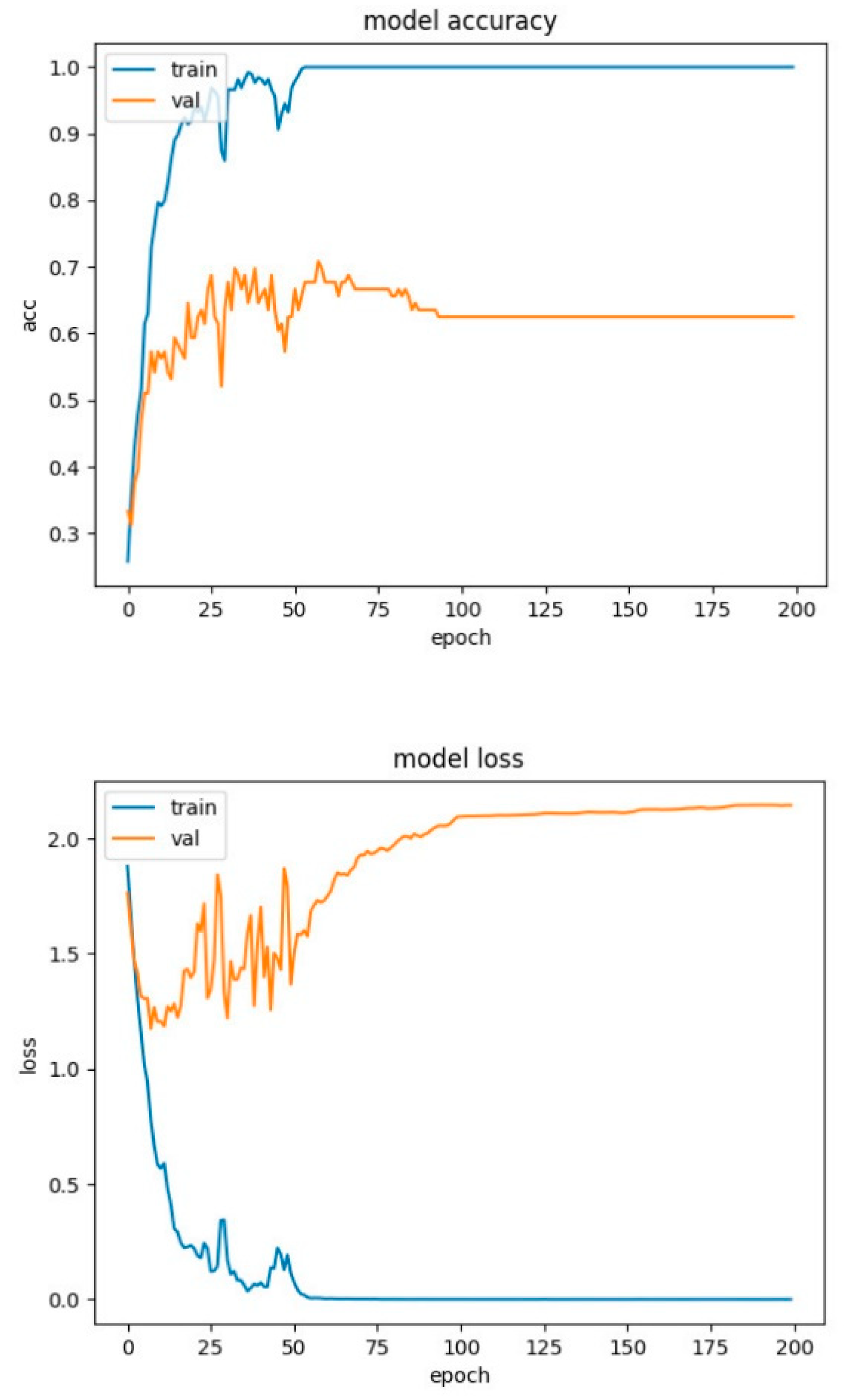
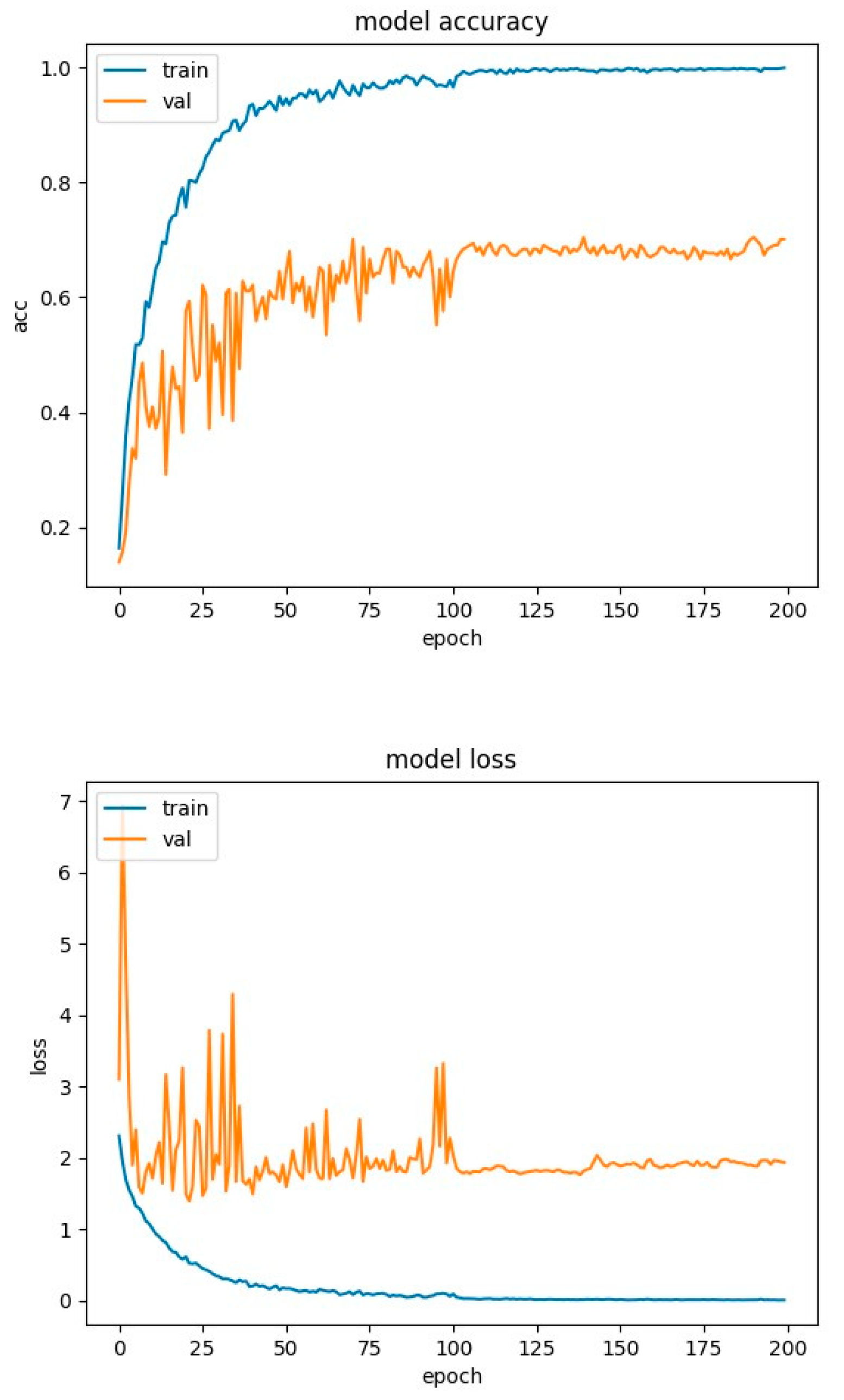
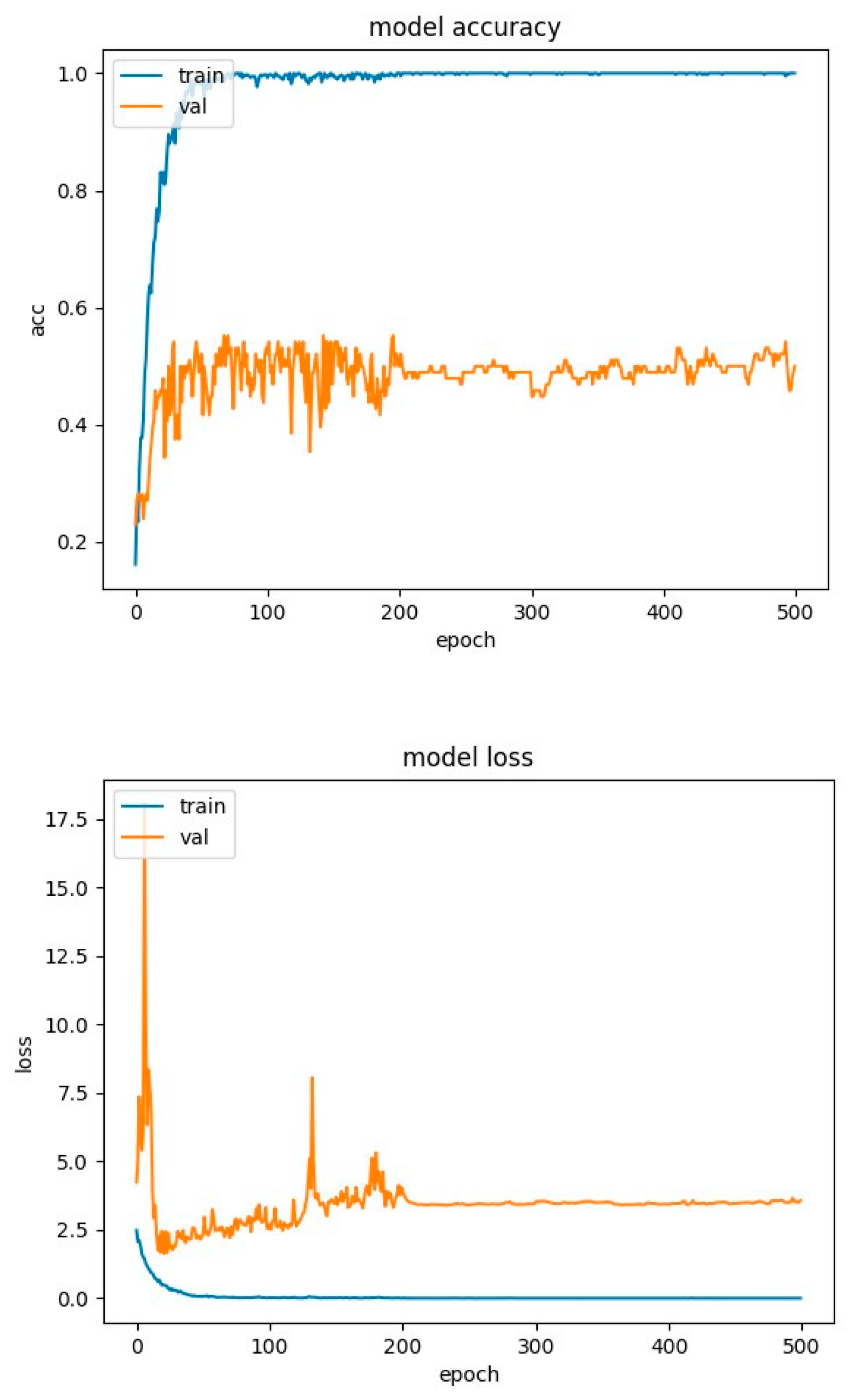
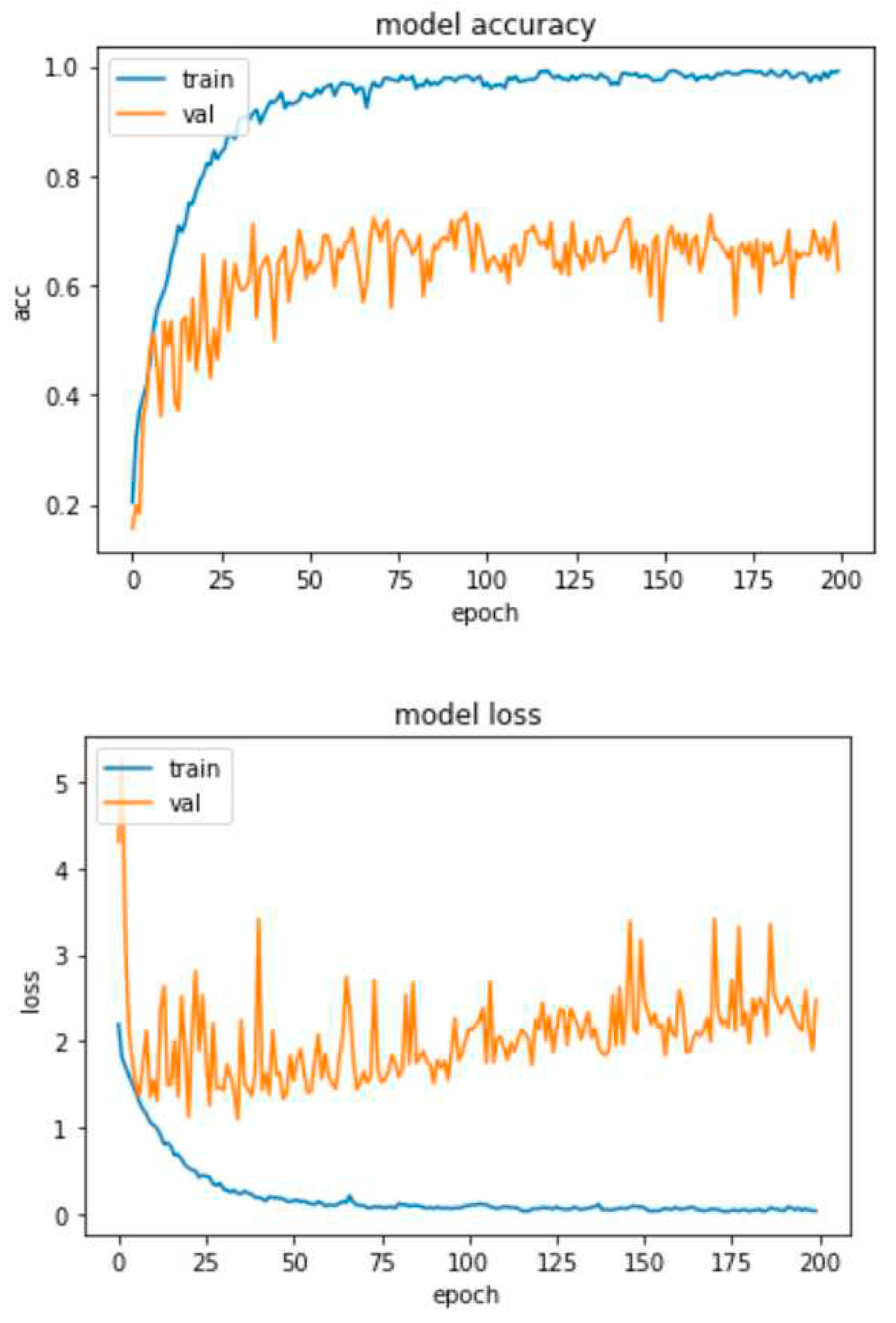
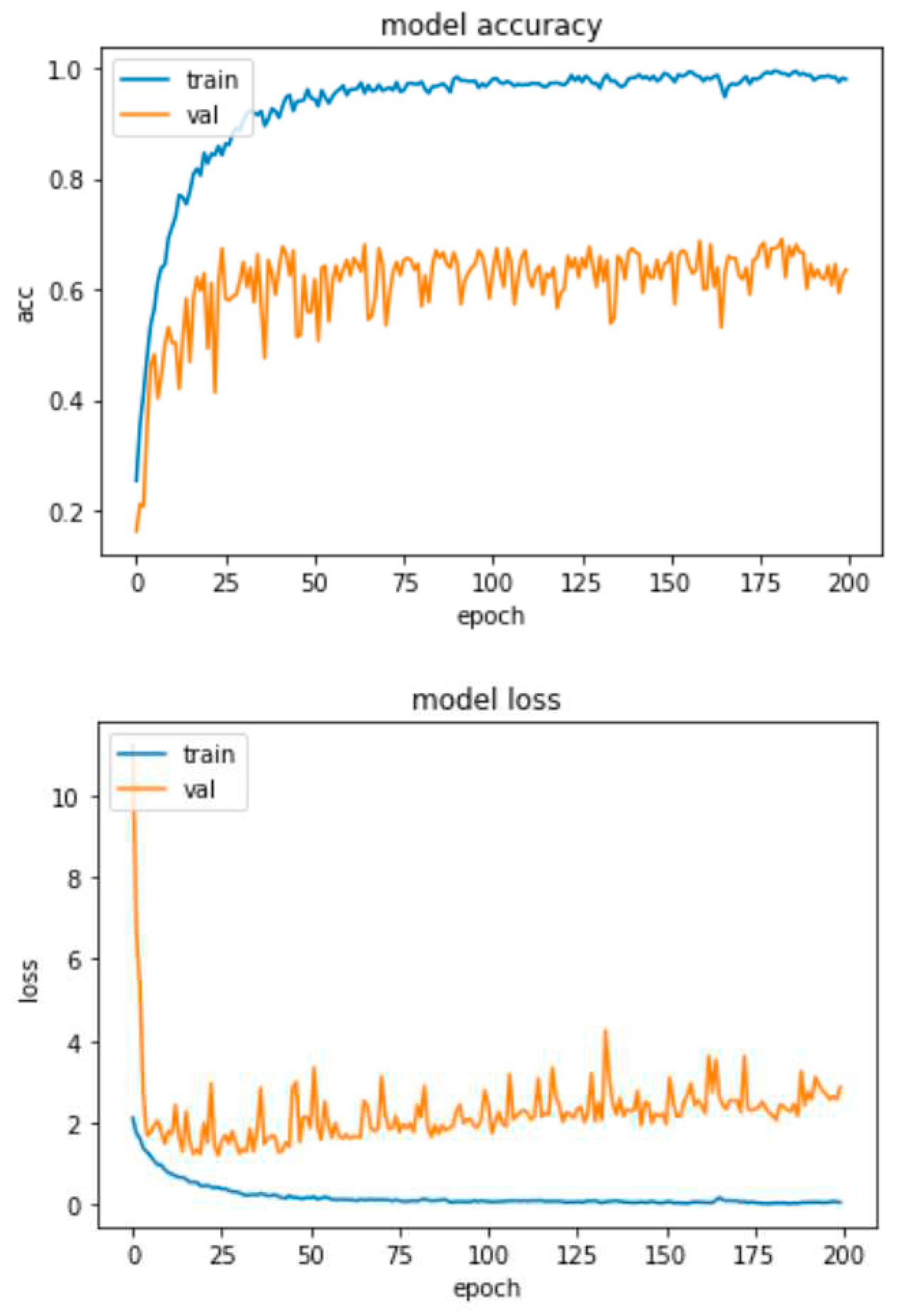
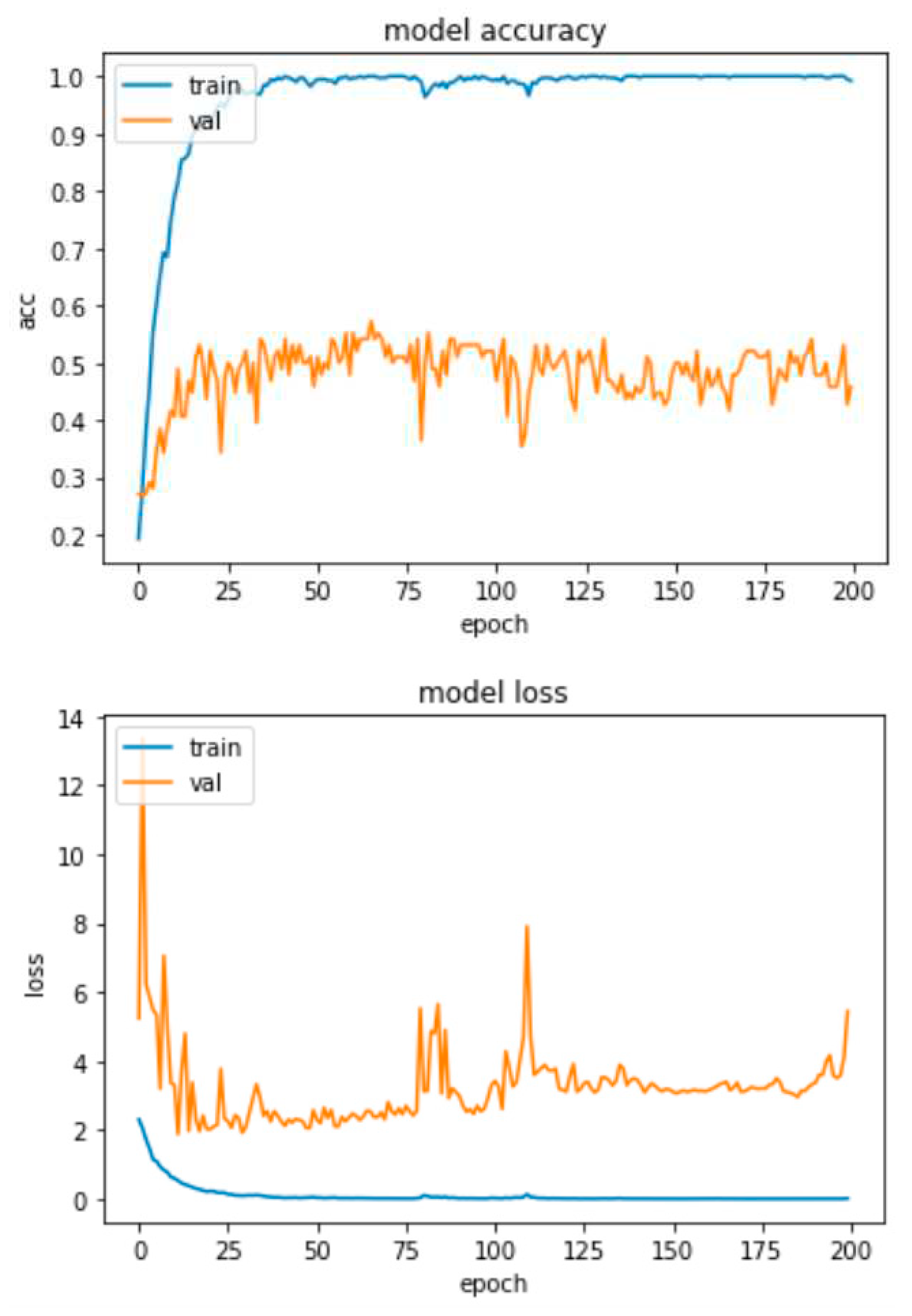
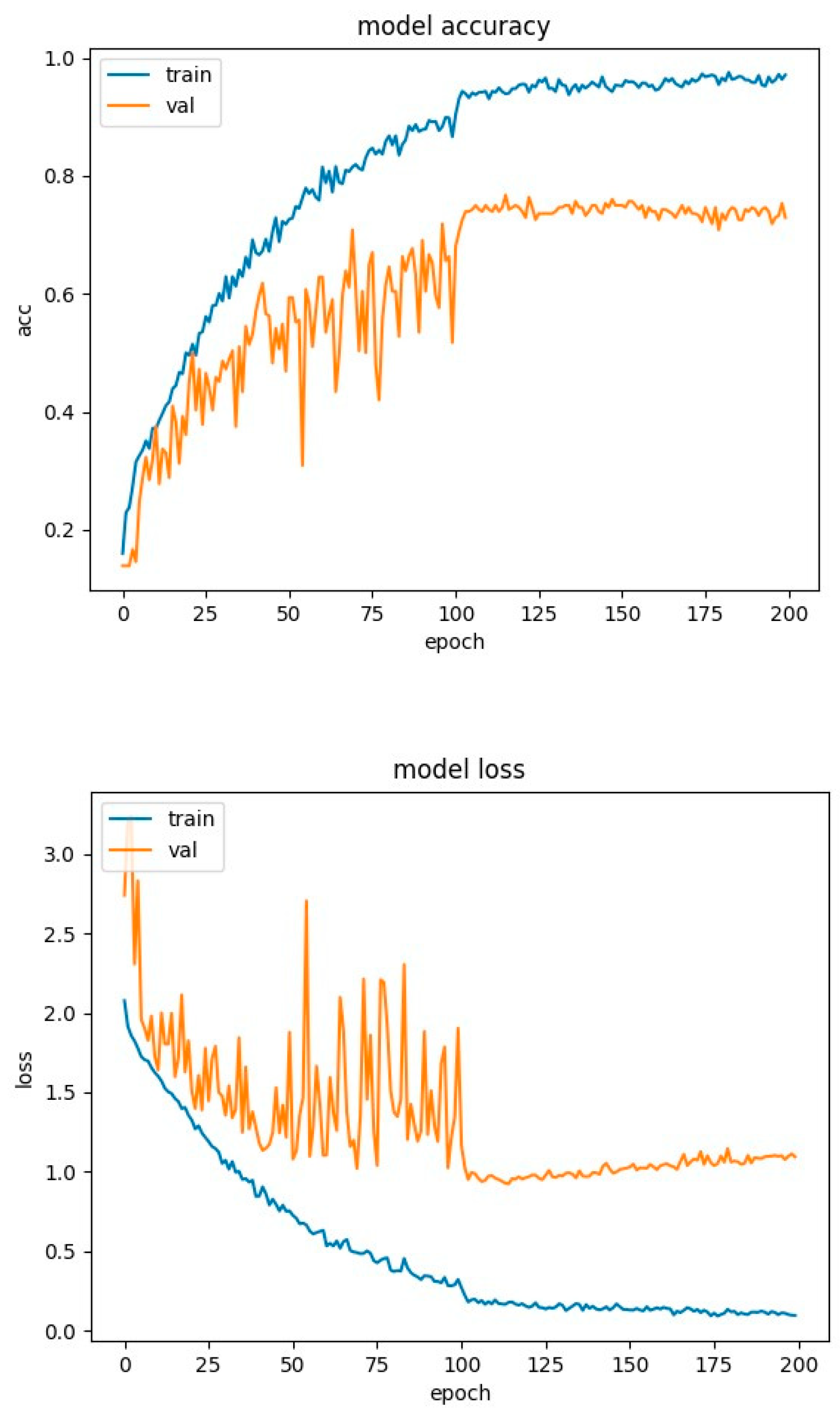
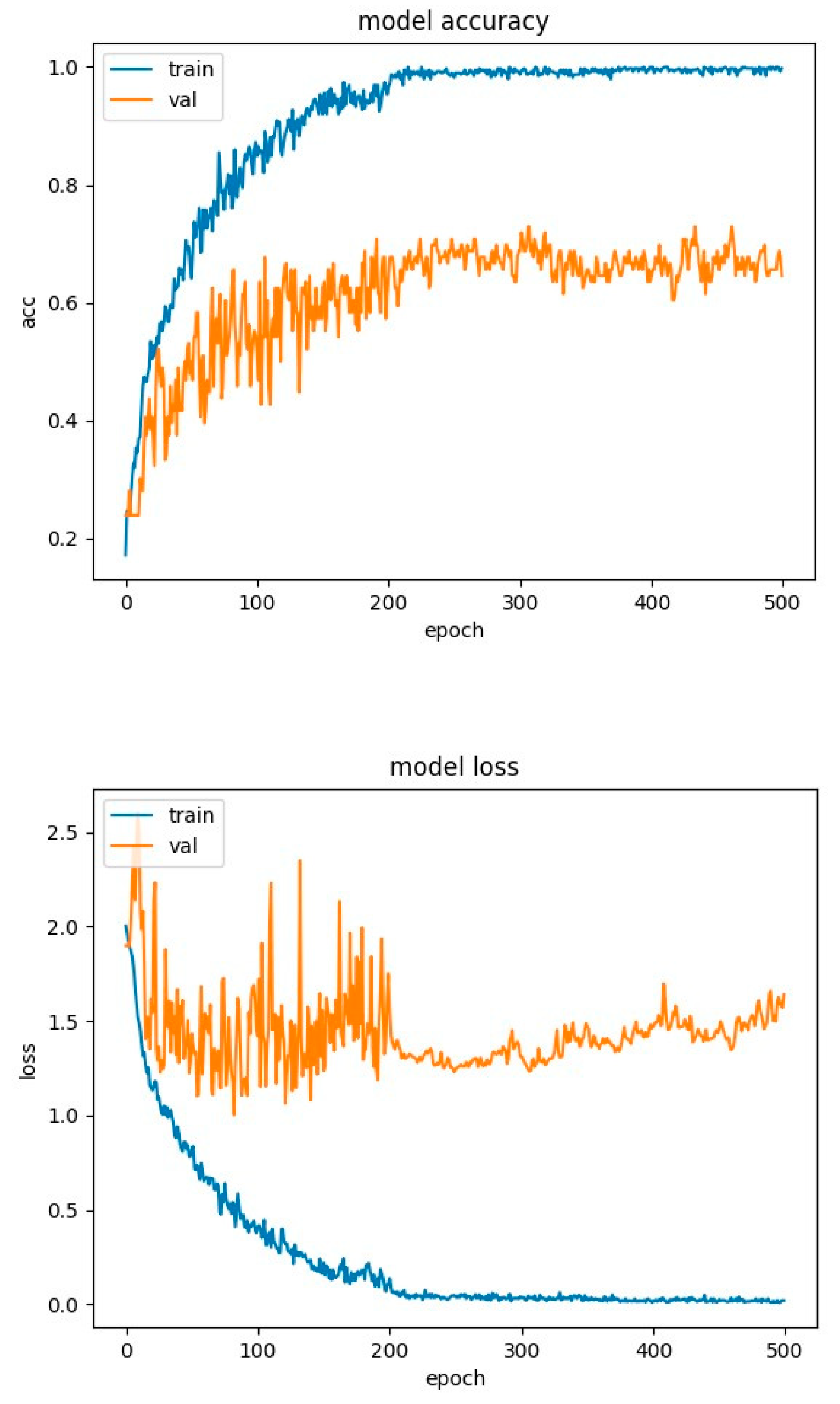
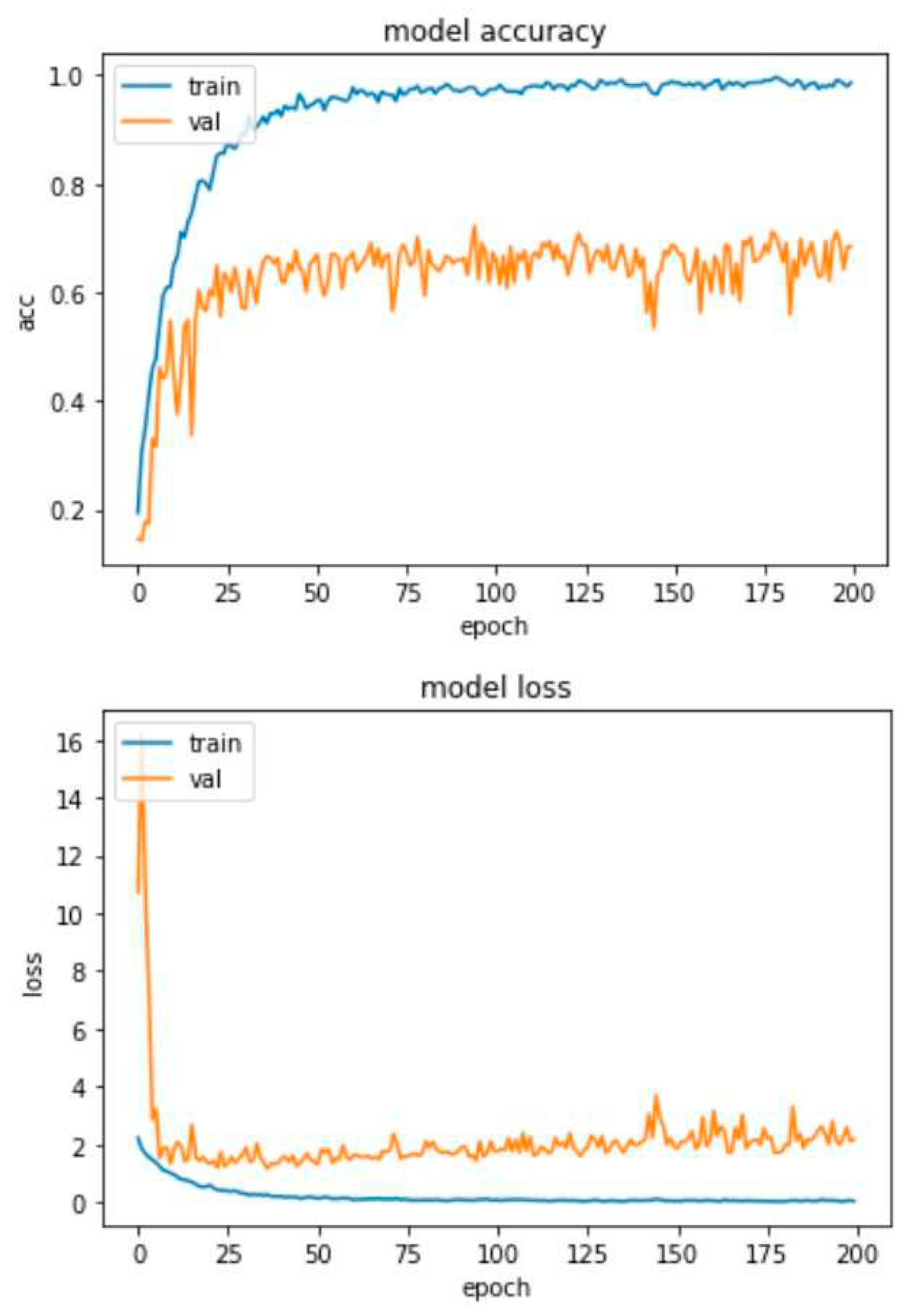
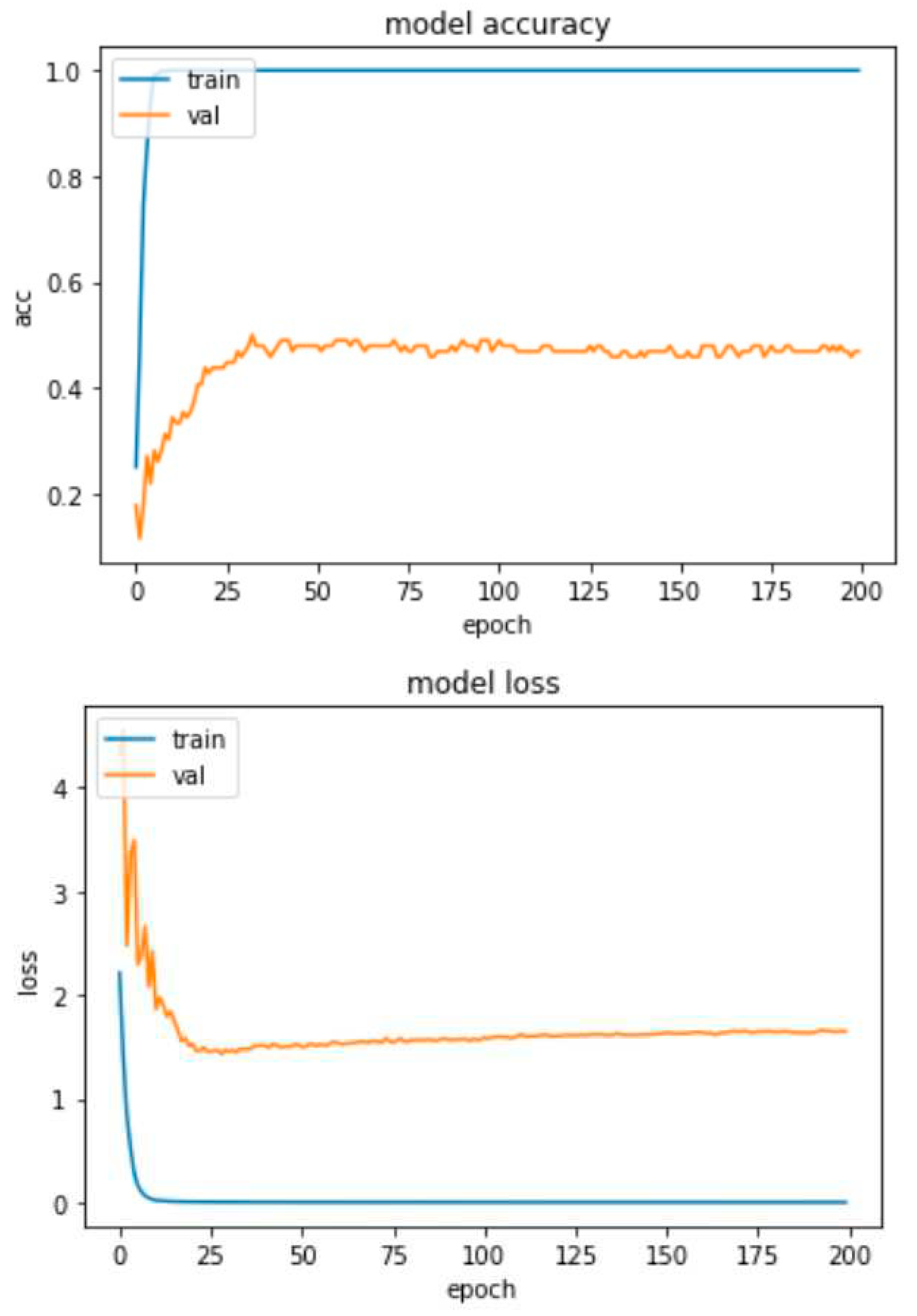
4.4. Experimental Results-Confusion Matrices
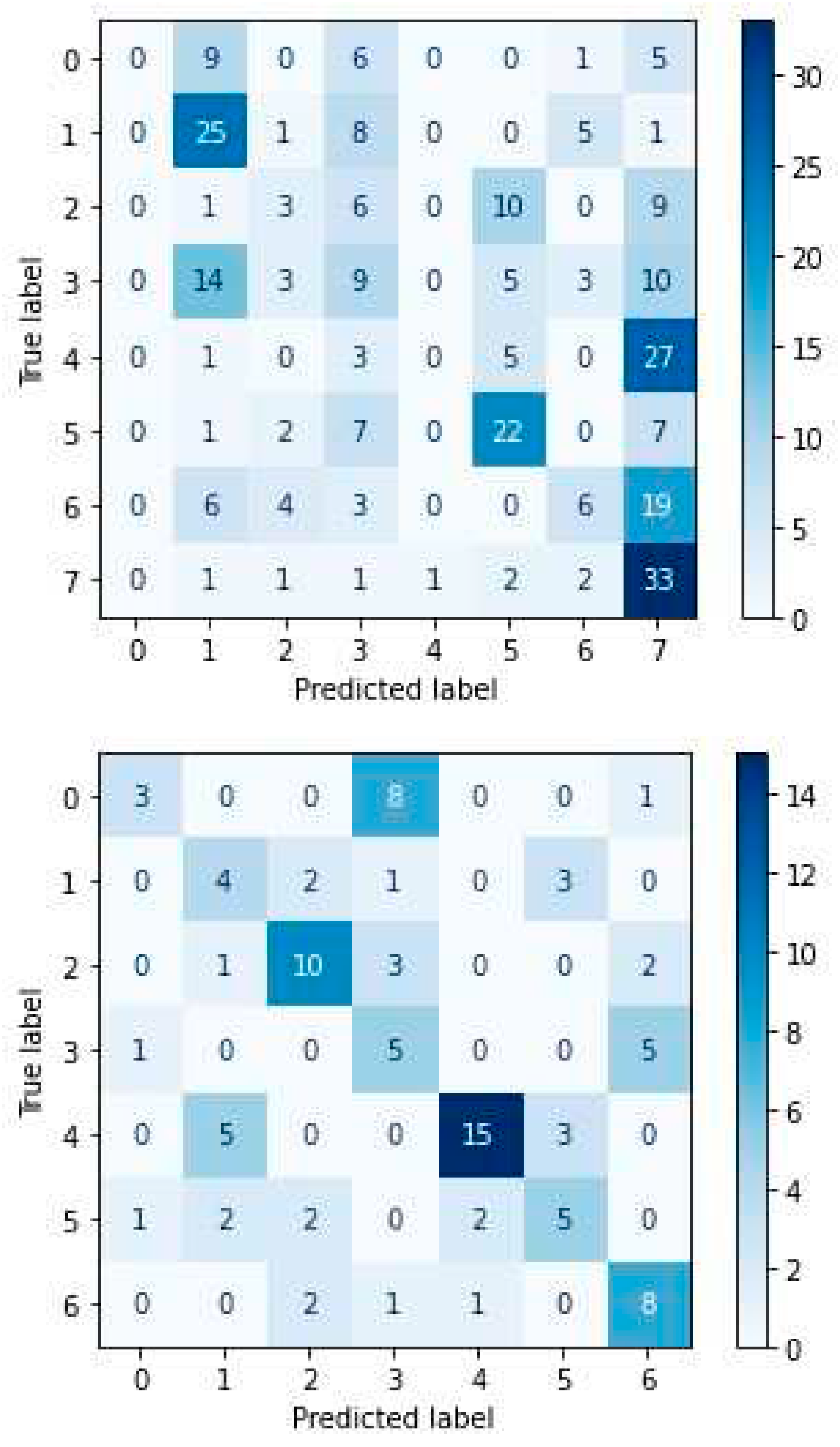
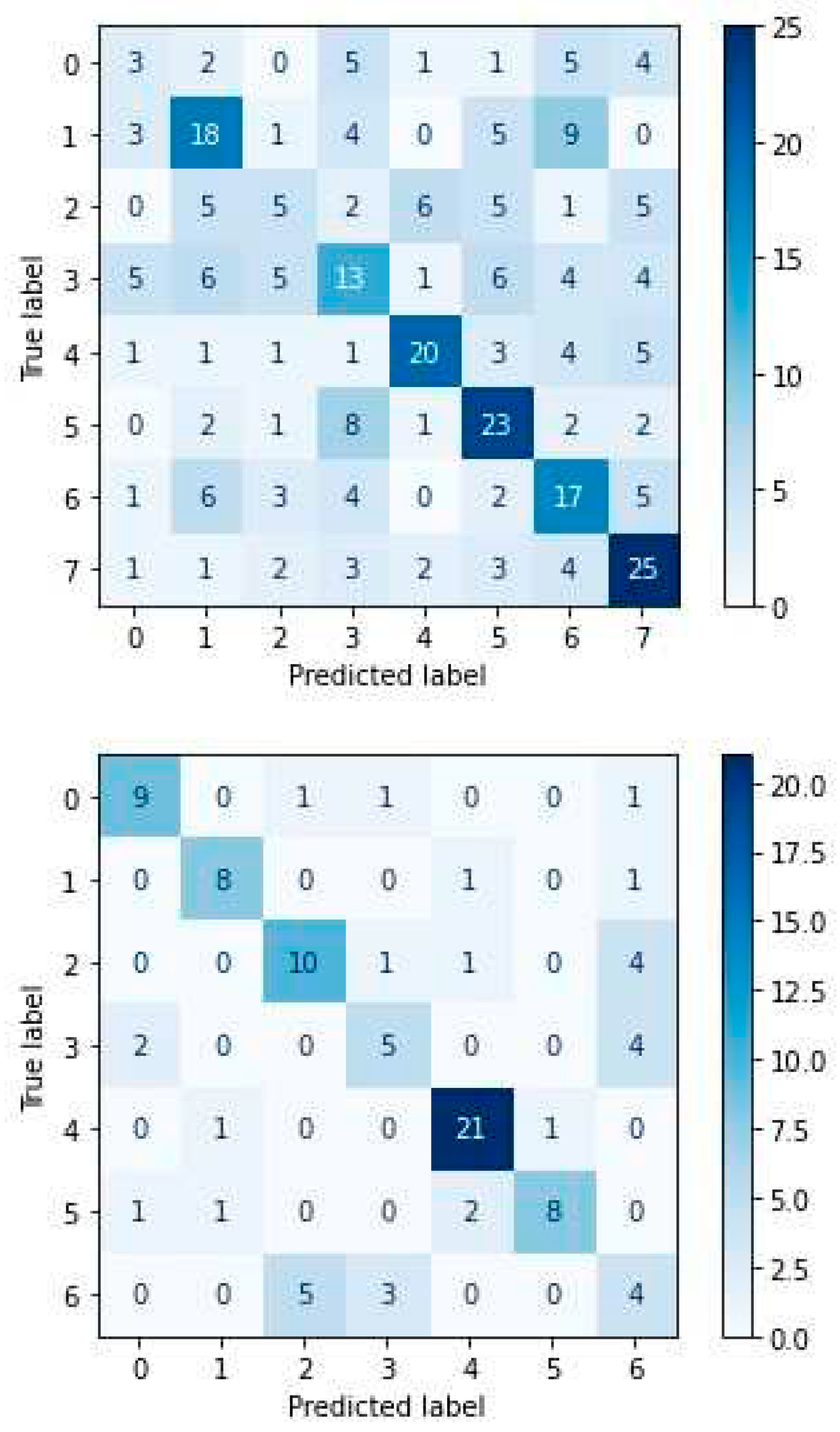
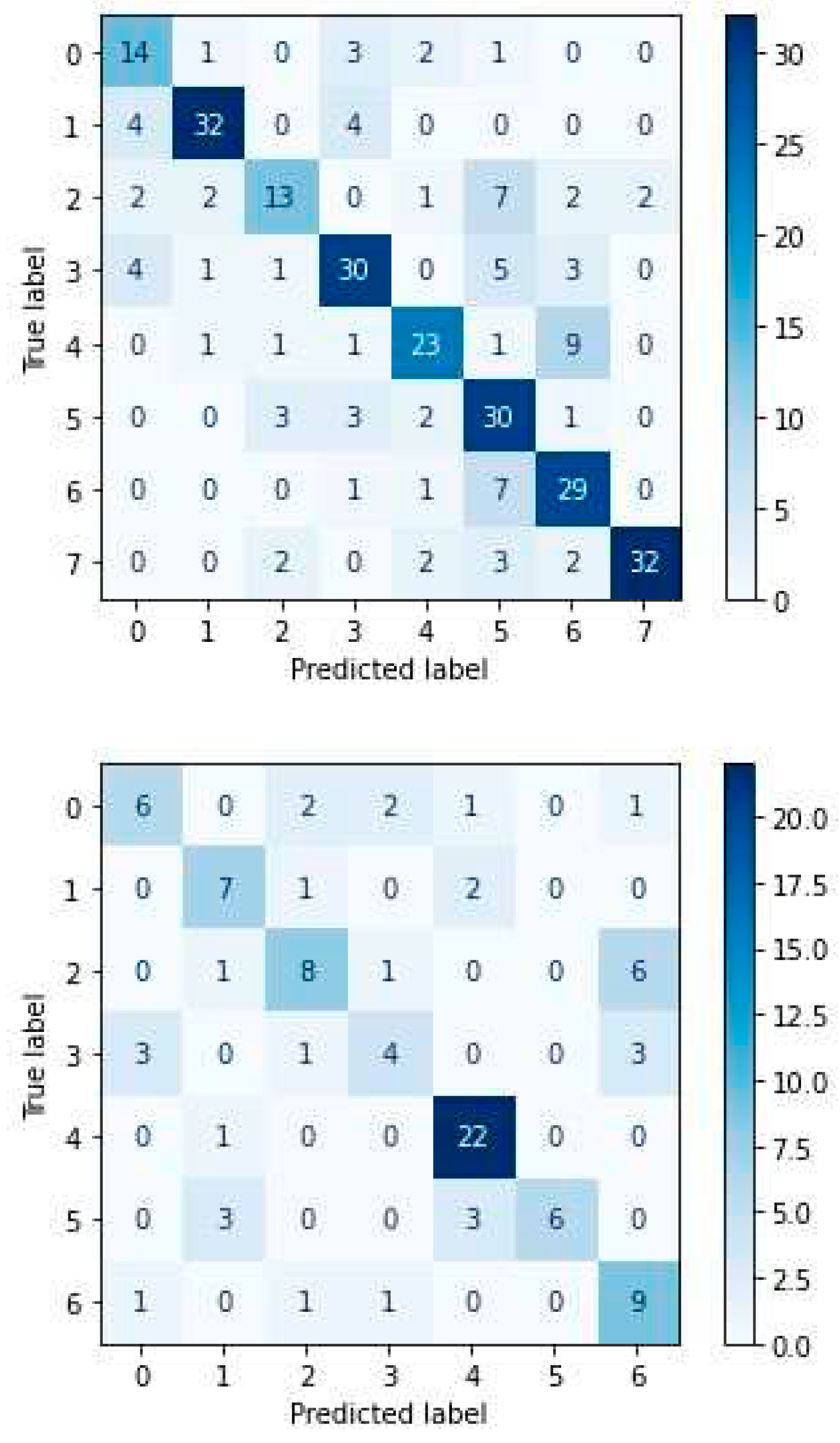
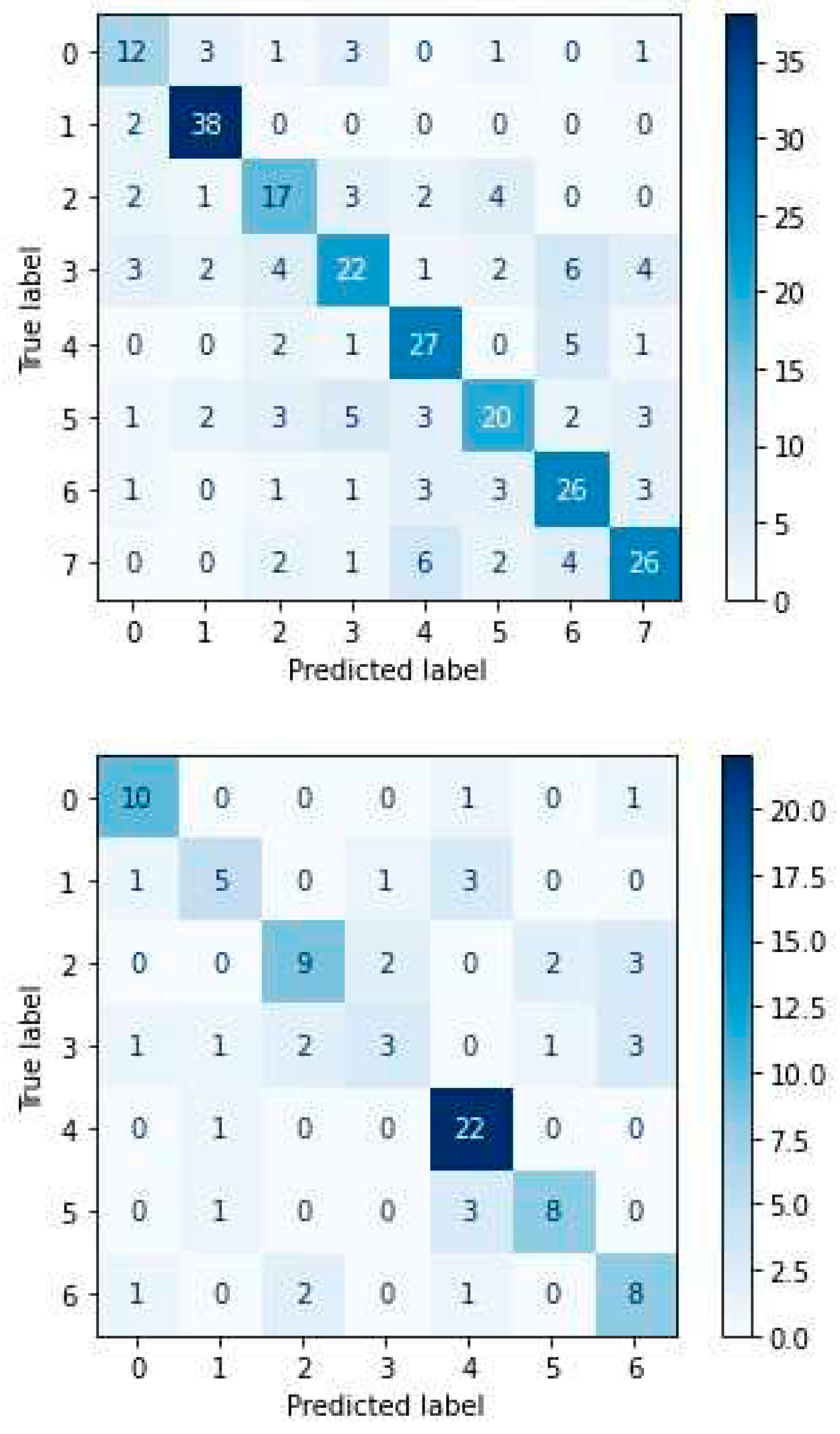
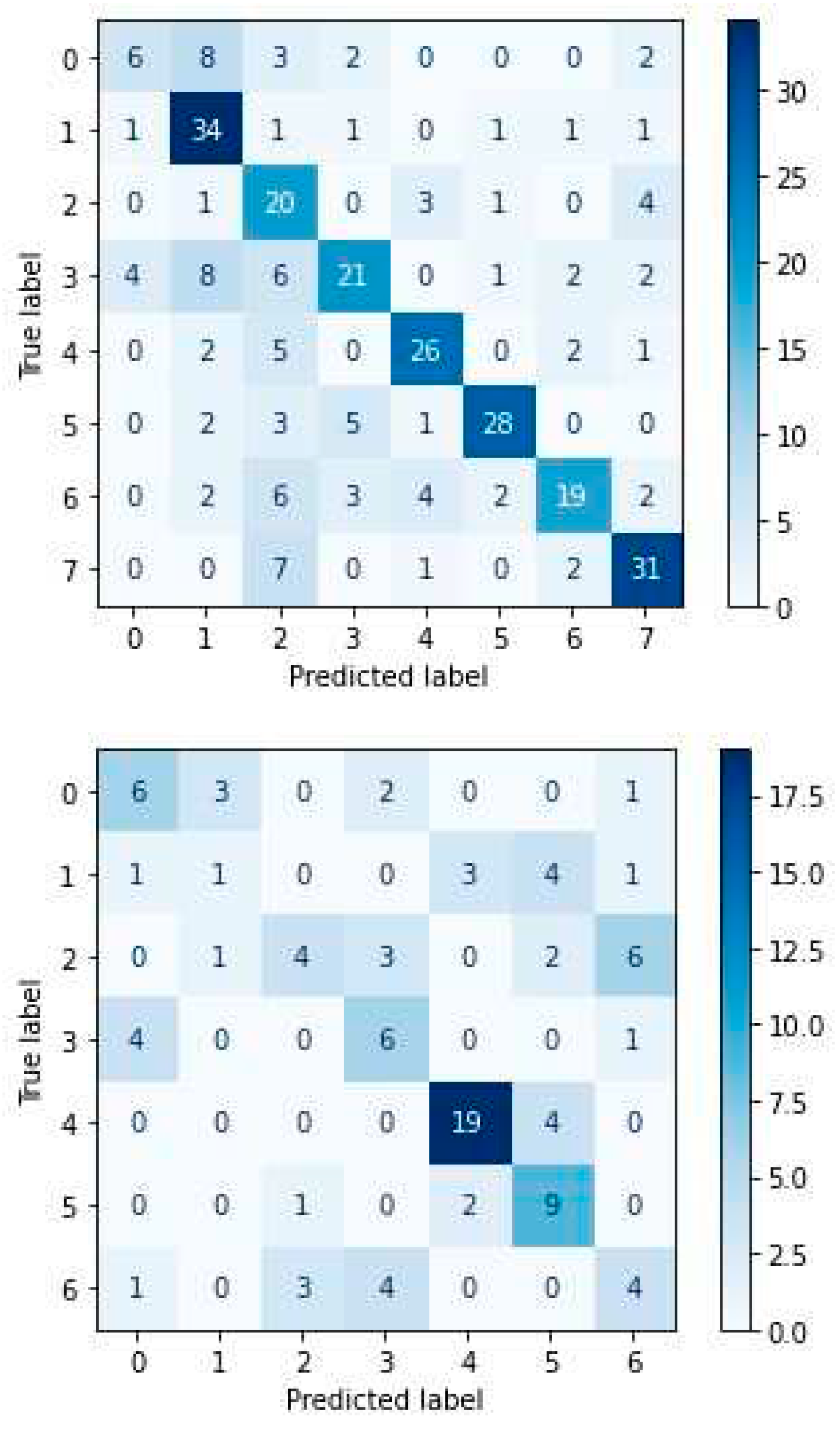
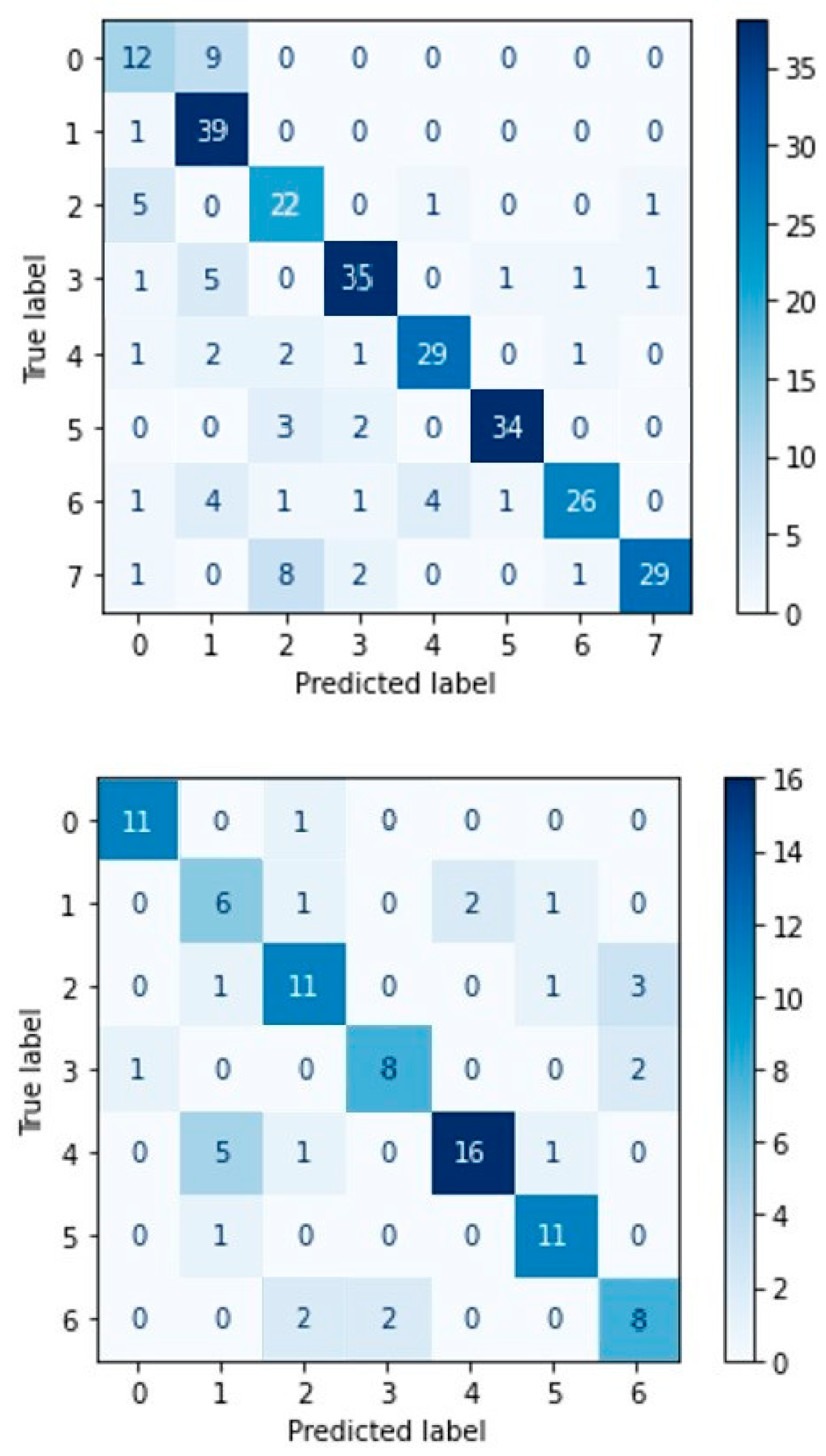
4. Discussion
| Models | Input Features | SAVEE | RAVDESS |
|---|---|---|---|
| DBN | Average of 40 MFCCs | 47.92 | 32.64 |
| DNN | Average of 40 MFCCs | 69.79 | 45.18 |
| LSTM | 40 MFCCs | 67 | 70 |
| LSTM-ATN | 40 MFCCs | 69.79 | 66 |
| CNN | 40 MFCCs | 55.2 | 70.5 |
| CNN-ATN | 40 MFCCs | 74 | 77 |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 |
References
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, F. E-learning recommendation framework based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC); 2017; pp. 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelena Gligorijevic, Djordje Gligorijevic, Martin Pavlovski, Elizabeth Milkovits, Lucas Glass, Kevin Grier, Praveen Vankireddy, Zoran Obradovic. Optimizing clinical trials recruitment via deep learning. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2019, 26, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davatzikos, C.; Ruparel, K.; Fan, Y.; Shen, D.; Acharyya, M.; Loughead, J.; Gur, R.; Langleben, D.D. Classifying spatial patterns of brain activity with machine learning methods: Application to lie detection. NeuroImage 2005, 28, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justesen, N.; Bontrager, P.; Togelius, J.; Risi, S. Deep Learning for Video Game Playing. IEEE Transactions on Games 2020, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentyeva, G.; Novoselov, S.; Malykh, E.; Kozlov, A.; Kudashev, O.; Shchemelinin, V. Audio Replay Attack Detection with Deep Learning Frameworks. Proc. Interspeech 2017, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchechukwu Ajuzieogu. The Role of AI In Modern Computing and Education”, Computer Education Seminar 2019, UNN, A seminar approach to understanding the underlying principles of AI and its relevance to Education, in the 21st Century, 2019.
- Jalal, M.A.; Loweimi, E.; Moore, R.K.; Hain, T. Learning Temporal Clusters Using Capsule Routing for Speech Emotion Recognition. Proc. Interspeech 2019, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustaqeem; Kwon, S. A CNN-Assisted Enhanced Audio Signal Processing for Speech Emotion Recognition. Sensors 2020, 20, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, Y.B.; Goel, S. A systematic literature review of speech emotion recognition approaches. Neurocomputing 2022, 492, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, T.M.; Gunawan, T.S.; Qadri, S.A.A.; Kartiwi, M.; Ambikairajah, E. A comprehensive review of speech emotion recognition systems. IEEE access 2021, 9, 47795–47814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.A.; Jones, E.; Babar, M.I.; Jan, T.; Zafar, M.H.; Alhussain, T. Speech emotion recognition using deep learning techniques: A review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 117327–117345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaschian, B.J.; Sierra-Sosa, D.; Elmaghraby, A. Deep learning techniques for speech emotion recognition, from databases to models. Sensors 2021, 21, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, G.; Li, H.; Huang, J.; Li, D.; Xun, E. Random Deep Belief Networks for Recognizing Emotions from Speech Signals. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2017, 2017, 1945630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, A.M.; Ahmad, J.; Rahim, N.; Baik, S.W. Speech Emotion Recognition from Spectrograms with Deep Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Platform Technology and Service (PlatCon); 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mao, X.; Chen, L. Speech emotion recognition using deep 1D & 2D CNN LSTM networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2019, 47, 312–323. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Song, K.Y.; Jeong, J.; Choi, W.Y. Convolutional Attention Networks for Multimodal Emotion Recognition from Speech and Text Data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1805.06606. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Zeng, J.; Li, M. An End-to-End Deep Learning Framework for Speech Emotion Recognition of Atypical Individuals. Proc. Interspeech 2018, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; He, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H. 3-D Convolutional Recurrent Neural Networks With Attention Model for Speech Emotion Recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 2018, 25, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Song, Y.; Mcloughlin, I.; Guo, W.; Dai, L. An Attention Pooling Based Representation Learning Method for Speech Emotion Recognition. Interspeech 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Z.; Jin, J.S.; Han, X.; Li, C. Speech Emotion Recognition with Heterogeneous Feature Unification of Deep Neural Network. Sensors 2019, 19, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Wu, C.; Hong, Q.; Su, M.; Chen, Y. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Neural Network Considering Verbal and Nonverbal Speech Sounds. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, United Kingdom; 2019; pp. 5866–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, D.; Demirci, M.; Yazici, A. Speech emotion recognition with deep convolutional neural networks. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2020, 59, 101894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhmudov, F.; Kutlimuratov, A.; Akhmedov, F.; Abdallah, M.S.; Cho, Y.I. Modeling Speech Emotion Recognition via Attention-Oriented Parallel CNN Encoders. Electronics 2022, 11, 4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, Z.K.; Al-Talabani, A.K. Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient and its applications: A Review. IEEE Access 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, M.T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective Approaches to Attention-based Neural Machine Translation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.04025. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, P.; Haq, S. Surrey Audio-Visual Expressed Emotion (SAVEE) database. 2011. Available online: http://kahlan.eps.surrey.ac.uk/savee/Database.html.
- Livingstone, S.R.; Russo, F.A. The Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS): A dynamic, multimodal set of facial and vocal expressions in North American English. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivanagaraja, T.; Ho, M.K.; Khong, A.W.H.; Wang, Y. End-to-end speech emotion recognition using multi-scale convolution networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA ASC), Kuala Lumpur; 2017; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Rana, R.; Younis, S.; Qadir, J.; Epps, J. Transfer Learning for Improving Speech Emotion Classification Accuracy. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.06353. [Google Scholar]
- HFayek, M.; Lech, M.; Cavedon, L. Towards real-time Speech Emotion Recognition using deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication Systems (ICSPCS), Cairns, QLD; 2015; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenchah, F.; Lachiri, Z. Acoustic Emotion Recognition Using Linear and Nonlinear Cepstral Coefficients. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA) 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajak, R.; Mall, R. Emotion recognition from audio, dimensional and discrete categorization using CNNs. In Proceedings of theTENCON 2019 - 2019 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON), Kochi, India; 2019; pp. 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramanan, K.; Rajamohan, H.R. Emotion Recognition from Speech. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.10458. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, H.; Budhvant, S.; Gawde, P.; Shelke, M. Implementation of Mood Detection through Voice Analysis using Librosa and CNN. In Proceedings of the International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET), Thane, Maharashtra, India, 6 June 2020; pp. 5876–5879. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, A.; Bao, P. Human Vocal Sentiment Analysis. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.08632. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.; et al. Dawn of the Transformer Era in Speech Emotion Recognition: Closing the Valence Gap. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2023, 45, 10745–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Label of Emotion | Emotion in SAVEE | Emotion in RAVDESS |
| [0] | anger | neutral |
| [1] | disgust | calm |
| [2] | fear | happy |
| [3] | happiness | sad |
| [4] | neutral | angry |
| [5] | sadness | fearful |
| [6] | surprise | disgust |
| [7] | - | surprise |
| Models | Input Features | SAVEE - Test accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| MCNN Sivanagaraja [28] | rawWav | 50.28 |
| DBN Latif [29] | eGeMAPS | 56.76 |
| DNN Fayek, Lech and Cavedon [30] | Spectrogram | 59.7 |
| HMM Chenchah and Lachiri [31] | LFCCs/MFCCs | 45/61.25 |
| Proposed method | MFCCs | 74 |
| Models | Input Features | RAVDESS - Test accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| CNN Rajak and Mall [32] | MFCCs | 47.92 |
| BLSTM-CNN-Capsule Network Jalal [7] | F0, MFCCs, Log Spectrogram augmented by delta and delta-delta | 56.2 |
| 2D CNN with Global Avg Pool Venkataramanan and Rajamohan [33] |
Log Mel Spectrogram | 69.79 |
| CNN Mohanty [34] | MFCCs | 67 |
| CNN Huang and Bao [35] | MFCCs | 69.79 |
| DSCNN Mustaqeem and Soonil Kwon [8] | Raw Spectrograms / Clean Spectrograms | 68 / 80 |
| 1D CNN Issa, Demicri and Yazici [22] | MFCCs, chromagram and Mel-Spectrogram | 71.61 |
| Proposed method | MFCCs | 77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





