Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
18 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Life Cycle Systainability Assessment
2.1.1. Study Sites
2.1.2. Goal and Scope
2.1.3. System Boundaries
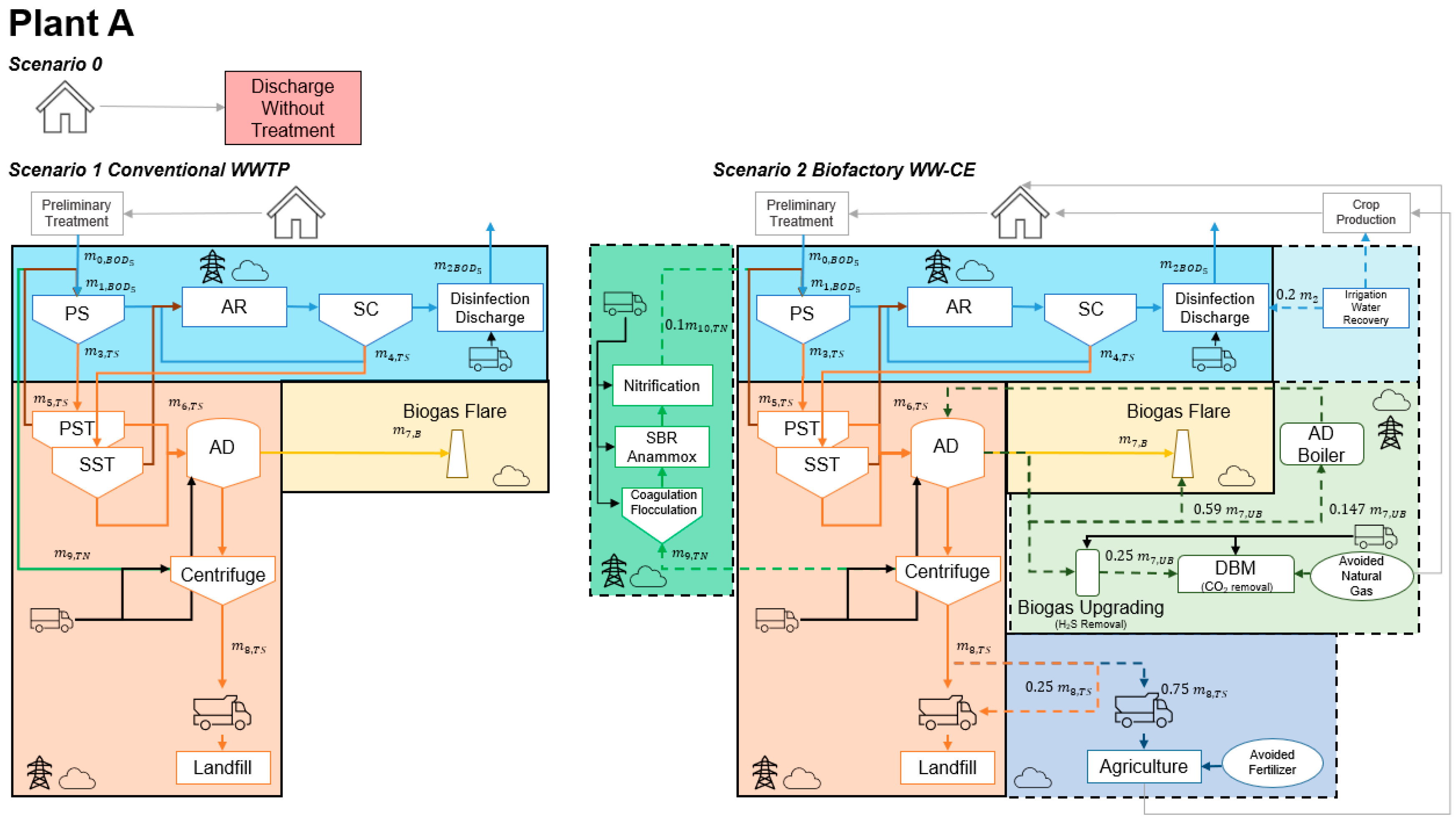
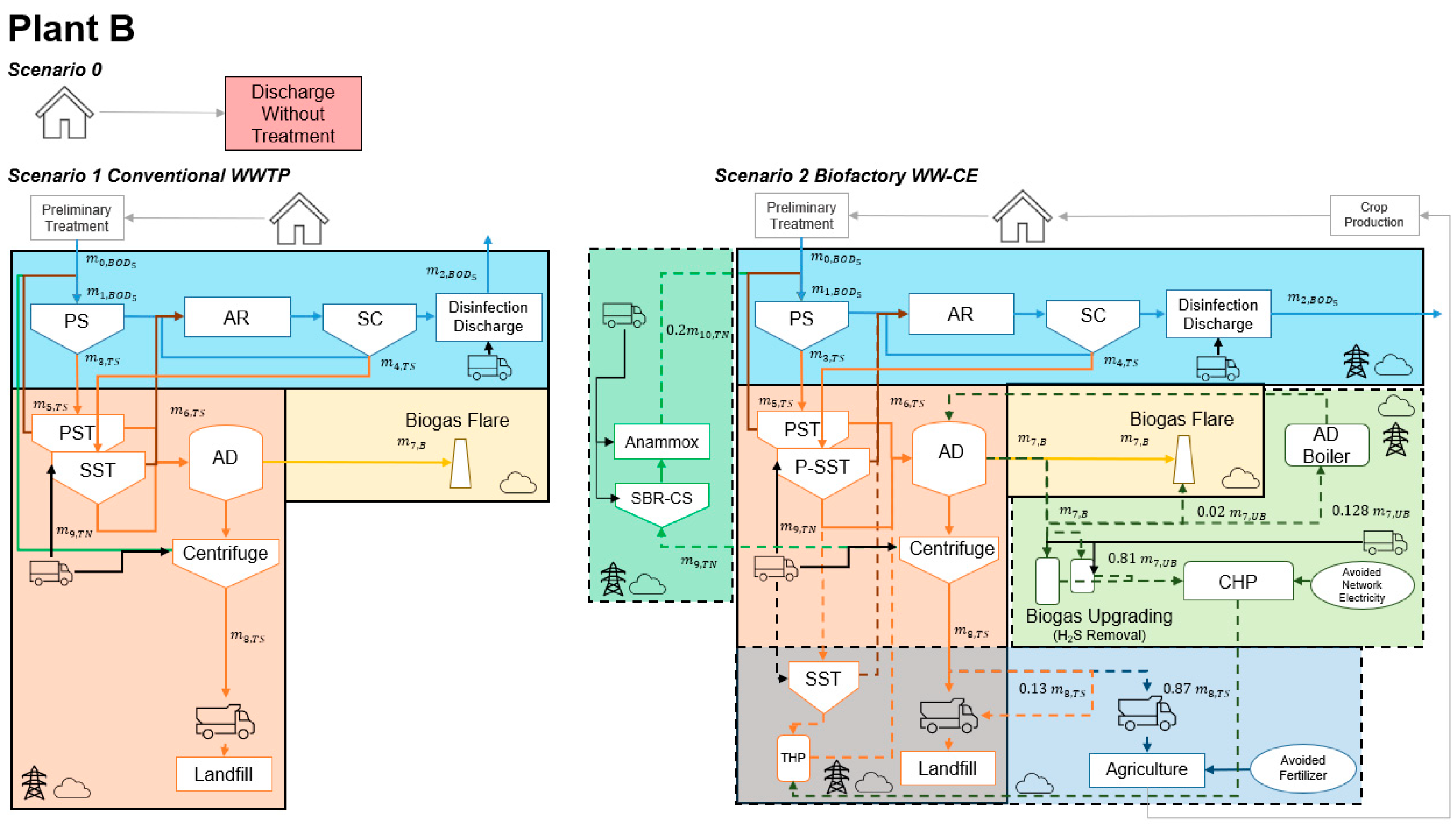
2.1.4. Integrated Life Cycle Inventories
2.1.3. Impact Characterization
2.2. Interpretation with Multi-ctieria Assessment of Sustainability Impacts
2.2.1. Overview of Decision Criteria
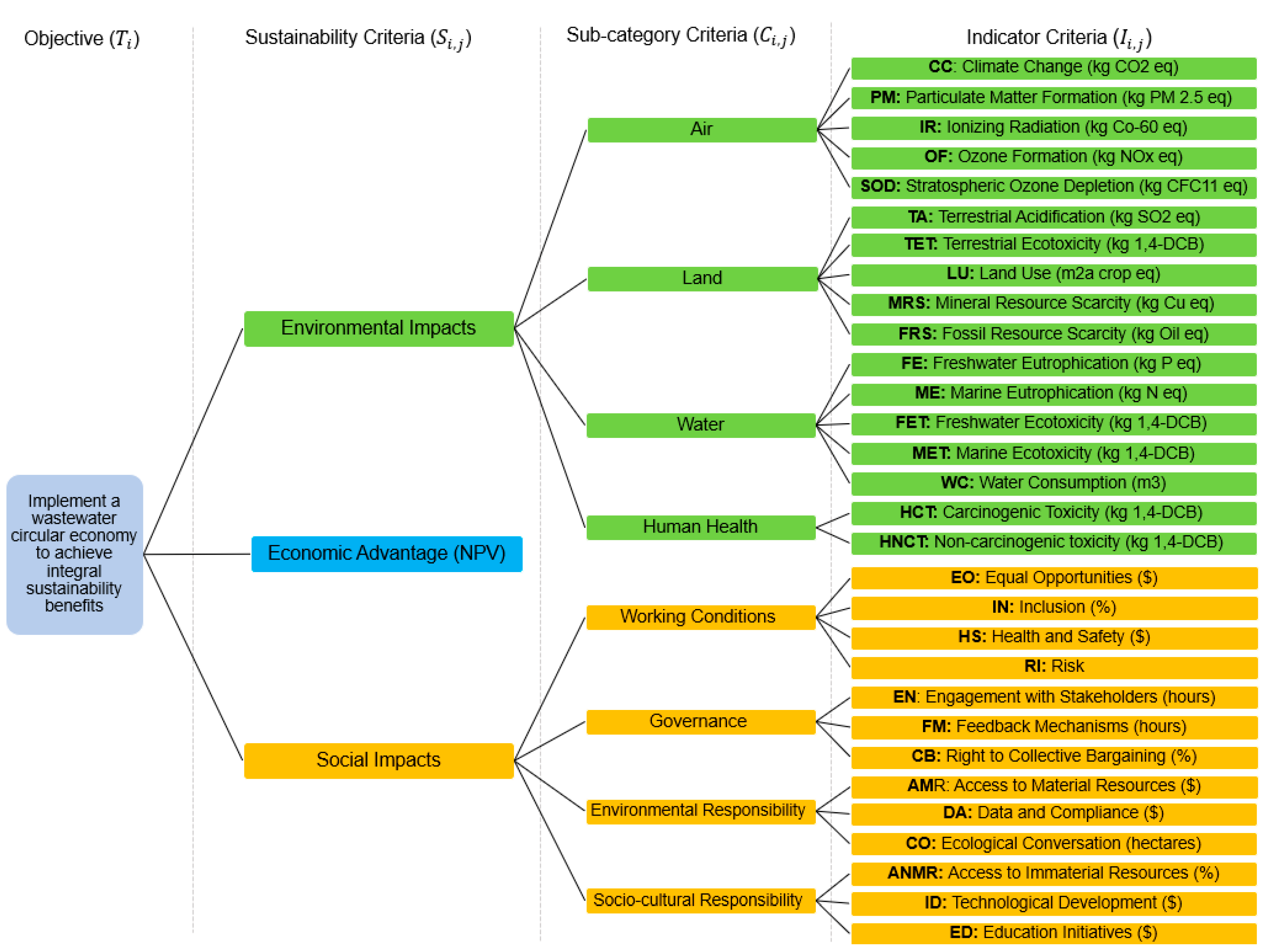
2.2.2. Criteria Weighting
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental and Social Indicators
3.1.1. Normalized LCA and SLCA Indicators
3.1.2. Indicator Criteria Weighted Sum Scores
3.2. Environmental and Social Sub-categories
3.2.1. Normalized LCA and SLCA Sub-categories
3.2.1. Sub-category Criteria Weighted Sum Scores
3.2. Environmental and Social Sub-categories
3.3.1. Normalized LCSA Performance Indicators
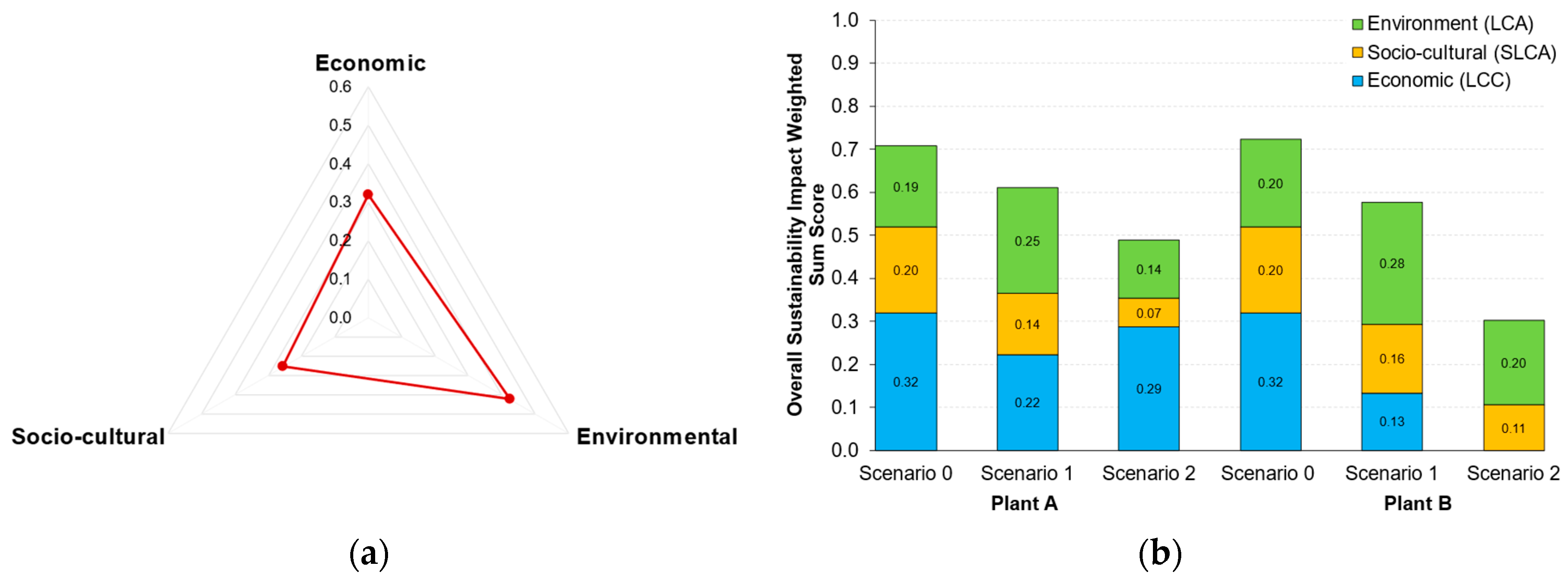
3.3.2. Overall Sustainability Impact Weighted Sum Scores
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Limitations
4.1. Reccomendations and Global Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN-Water, “Summary Progress Update 2021 : SDG 6 — water and sanitation for all,” UN-Water Integr. Monit. Initiat., pp. 1–58, 2021, [Online]. Available: https://www.unwater.org/new-data-on-global-progress-towards-ensuring-water-and-sanitation-for-all-by-2030/.
- UN DESA, “The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2022,” 2022. [Online]. Available: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2022.pdf.
- C. A. Ruggerio, “Sustainability and sustainable development: A review of principles and definitions,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 786, p. 147481, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Boretti and L. Rosa, “Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report,” npj Clean Water, vol. 2, no. 1, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Rashid, S. N. Harun, M. M. Hanafiah, K. K. Razman, Y. Q. Liu, and D. A. Tholibon, “Life Cycle Assessment and Its Application in Wastewater Treatment: A Brief Overview,” Processes, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 1–31, 2023. [CrossRef]
- E. G. Andary, C. Abi Shdid, A. Chowdhury, and I. Ahmad, “Integrated project delivery implementation framework for water and wastewater treatment plant projects,” Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag., vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 609–633, 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. R. Z. Tarpani and A. Azapagic, “Life cycle costs of advanced treatment techniques for wastewater reuse and resource recovery from sewage sludge,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 204, pp. 832–847, 2018. [CrossRef]
- SuSanA, “Contribution of Sustainable Sanitation to the Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development,” no. 1, pp. 1–4, 2017.
- G. Mannina, T. F. Rebouças, A. Cosenza, M. Sànchez-Marrè, and K. Gibert, “Decision support systems (DSS) for wastewater treatment plants – A review of the state of the art,” Bioresour. Technol., vol. 290, p. 121814, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Hosseinian-Far, M. Ramachandran, and D. Sarwar, Strategic Engineering for Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics. 2017. [CrossRef]
- T. S. Brinsmead, “Integrated Sustainability Assessment: Identifying Methodological Options Australian Energy View project Safe Switching in Control View project,” no. May, 2019, [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/333413032.
- U. Ghimire, G. Sarpong, and V. G. Gude, “Transitioning wastewater treatment plants toward circular economy and energy sustainability,” ACS Omega, vol. 6, no. 18, pp. 11794–11803, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Salgot and M. Folch, “Wastewater treatment and water reuse,” Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Heal., vol. 2, pp. 64–74, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. C. Collivignarelli, M. Canato, A. Abbà, and M. Carnevale Miino, “Biosolids: What are the different types of reuse?,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 238, 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. Ardolino, F. Parrillo, and U. Arena, “Biowaste-to-biomethane or biowaste-to-energy? An LCA study on anaerobic digestion of organic waste,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 174, pp. 462–476, 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Kehrein, M. Van Loosdrecht, P. Osseweijer, M. Garfí, J. Dewulf, and J. Posada, “A critical review of resource recovery from municipal wastewater treatment plants-market supply potentials, technologies and bottlenecks,” Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 877–910, 2020. [CrossRef]
- E. Walling and C. Vaneeckhaute, “Developing successful environmental decision support systems: Challenges and best practices,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 264, no. April, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Taherdoost and M. Madanchian, “Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) Methods and Concepts,” Encyclopedia, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 77–87, 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. Rezaei, N. Diaz-Elsayed, S. Mohebbi, X. Xie, and Q. Zhang, “A multi-criteria sustainability assessment of water reuse applications: a case study in Lakeland, Florida,” Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 102–118, 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. A. C. Lohman et al., “DMsan: A Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Framework and Package to Characterize Contextualized Sustainability of Sanitation and Resource Recovery Technologies,” ACS Environ. Au, 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. Ddiba, K. Andersson, S. Dickin, E. Ekener, and G. Finnveden, “A review of how decision support tools address resource recovery in sanitation systems,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 342, no. March, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Valdivia, J. Gerta, B. Marzia, T. Guido, and S. Stefano, “Principles for the application of life cycle sustainability assessment,” Int. J. Life Cycle Assess., no. 0123456789, 2021. [CrossRef]
- ISO 14040, “Environmental management — Life cycle assessment — Principles and framework,” 2006.
- UNEP, “Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products,” Management, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 104, 2020, [Online]. Available: http://www.unep.fr/shared/publications/pdf/DTIx1164xPA-guidelines_sLCA.pdf.
- G. Rebitze, D. Hunkeler, and O. Jollie, “LCC-The Economic Pillar of Sustainability: Methodology and Application to Watewater Treatment,” Environ. Prog., vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 241–249, 2003.
- T. Opher, “Comparative life cycle sustainability assessment of urban water reuse at various centralization scales,” pp. 1319–1332, 2019.
- H. Safarpour, M. Tabesh, S. A. Shahangian, M. Hajibabaei, and R. Sitzenfrei, “Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Wastewater Systems under Applying Water Demand Management Policies,” Sustain., vol. 14, no. 13, pp. 1–18, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu and J. Ren, “Developing a sustainability-oriented multi-criteria game theoretical decision analysis framework: A case study of sludge management,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 354, no. March, p. 131807, 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. R. Z. Tarpani and A. Azapagic, “Life cycle sustainability assessment of advanced treatment techniques for urban wastewater reuse and sewage sludge resource recovery,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 869, no. January, p. 161771, 2023. [CrossRef]
- SETAC, “Guidelines for Social Life Cycle Assessment of Products,” Management, vol. 15, no. 2, p. 104, 2020, [Online]. Available: http://www.unep.fr/shared/publications/pdf/DTIx1164xPA-guidelines_sLCA.pdf.
- Padilla-Rivera and L. P. Güereca, “A proposal metric for sustainability evaluations of wastewater treatment systems (SEWATS),” Ecol. Indic., vol. 103, no. March, pp. 22–33, 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Rathore, D. J. Killedar, D. Parde, and A. Sahare, “Life cycle cost analysis of wastewater treatment technologies,” IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 1032, no. 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Traverso et al., “Methodological Sheets for Subcategories in Social Life Cycle Assessment (S-LCA),” p. 150, 2021, [Online]. Available: https://www.lifecycleinitiative.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Methodological-Sheets_2021_final.pdf.
- LWC, “Intregrated Report 2022,” Santiago, 2022.
- R. Lauer, “Is Social Ontology Prior to Social Scientific Methodology?,” Philos. Soc. Sci., vol. 49, no. 3, pp. 171–189, 2019. [CrossRef]
- E. Roszkowska, “Rank Ordering Criteria Weighting Methods – a Comparative Overview,” Optimum. Stud. Ekon., vol. 5, no. 5(65), pp. 14–33, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Gherghel, C. Teodosiu, M. Notarnicola, and S. De Gisi, “Sustainable design of large wastewater treatment plants considering multi-criteria decision analysis and stakeholders’ involvement,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 261, no. August 2019, 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. De Feo and C. Ferrara, “Investigation of the environmental impacts of municipal wastewater treatment plants through a Life Cycle Assessment software tool,” Environ. Technol. (United Kingdom), vol. 38, no. 15, pp. 1943–1948, 2017. [CrossRef]
- N. C. Onat, M. Kucukvar, and O. Tatari, “Uncertainty-embedded dynamic life cycle sustainability assessment framework: An ex-ante perspective on the impacts of alternative vehicle options,” Energy, vol. 112, pp. 715–728, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Al-Gheethi, A. N. Efaq, J. D. Bala, I. Norli, M. O. Abdel-Monem, and M. O. Ab. Kadir, “Removal of pathogenic bacteria from sewage-treated effluent and biosolids for agricultural purposes,” Appl. Water Sci., vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 1–25, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhang, “Using Biosolids as a Plant Nutrient Source,” Oklahoma, 2017. [Online]. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20864901.
- R. Andreas, S. Serenella, and N. Jungbluth, “Normalization and weighting: the open challenge in LCA,” Int. J. Life Cycle Assess., vol. 25, no. 9, pp. 1859–1865, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. D. Orner et al., “Environmental and Economic Impacts of Managing Nutrients in Digestate Derived from Sewage Sludge and High-Strength Organic Waste,” Environ. Sci. Technol., vol. 56, no. 23, pp. 17256–17265, 2022. [CrossRef]
- de S. M. Gonçalves, F. L. de Carvalho, and P. de C. Fiorini, “Circular Economy and Financial Aspects: A Systematic Review of the Literature,” Sustain., vol. 14, no. 5, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Á. Mayor, S. Vinardell, K. Ganesan, C. Bacardí, J. L. Cortina, and C. Valderrama, “Life-cycle assessment and techno-economic evaluation of the value chain in nutrient recovery from wastewater treatment plants for agricultural application,” Sci. Total Environ., vol. 892, no. May, 2023. [CrossRef]
- OECD, Implementing the OECD Principles on Water Governance Indicator Framework and Evolving Practices: Indicator Framework and Evolving Practices. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://books.google.co.nz/books?id=7WJSDwAAQBAJ.
- K. Sjöstrand, A. Lindhe, T. Söderqvist, and L. Rosén, “Sustainability assessments of regional water supply interventions – Combining cost-benefit and multi-criteria decision analyses,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 225, no. March, pp. 313–324, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Cordella et al., “Addressing sustainable development goals in life cycle sustainable assessment: Synergies, challenges and needs,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 415, no. March 2022, p. 137719, 2023. [CrossRef]
- LWC, “Operational Data,” Santiago, 2019.
- Vineyard, A. Hicks, K. G. Karthikeyan, and P. Barak, “Economic analysis of electrodialysis, denitrification, and anammox for nitrogen removal in municipal wastewater treatment,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 262, p. 121145, 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Mills et al., “Second Generation Thermal Hydrolysis Processes,” Proc. Water Environ. Fed., vol. 2014, no. 2, pp. 1–13, 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. C. Maggi, “Implementacion de Tecnologias Anammox en Biofactorias,” Valparaiso, 2017.
- F. Ardolino, G. F. Cardamone, F. Parrillo, and U. Arena, “Biogas-to-biomethane upgrading: A comparative review and assessment in a life cycle perspective,” Renew. \& Sustain. ENERGY Rev., vol. 139, 2021. [CrossRef]
- ODEPA, “Evolucion de precios de fertilizantes internacional, importacion y nacional al mes de junio 2023,” Reporte Interactivo de Precios de Fertilizantes, 2023. https://apps.odepa.gob.cl/powerBI/reporte_fertilizantes.html (accessed Aug. 11, 2023).
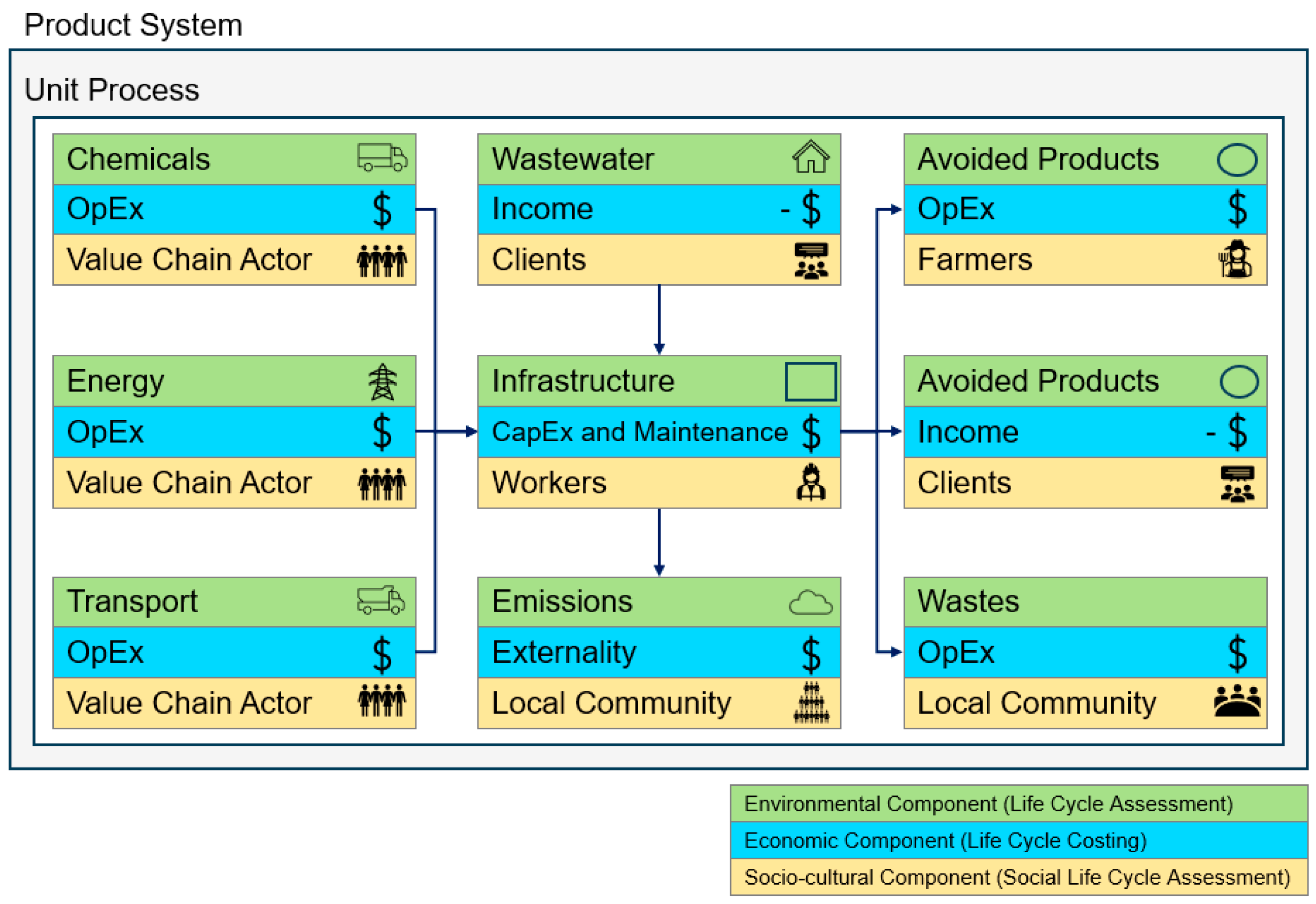
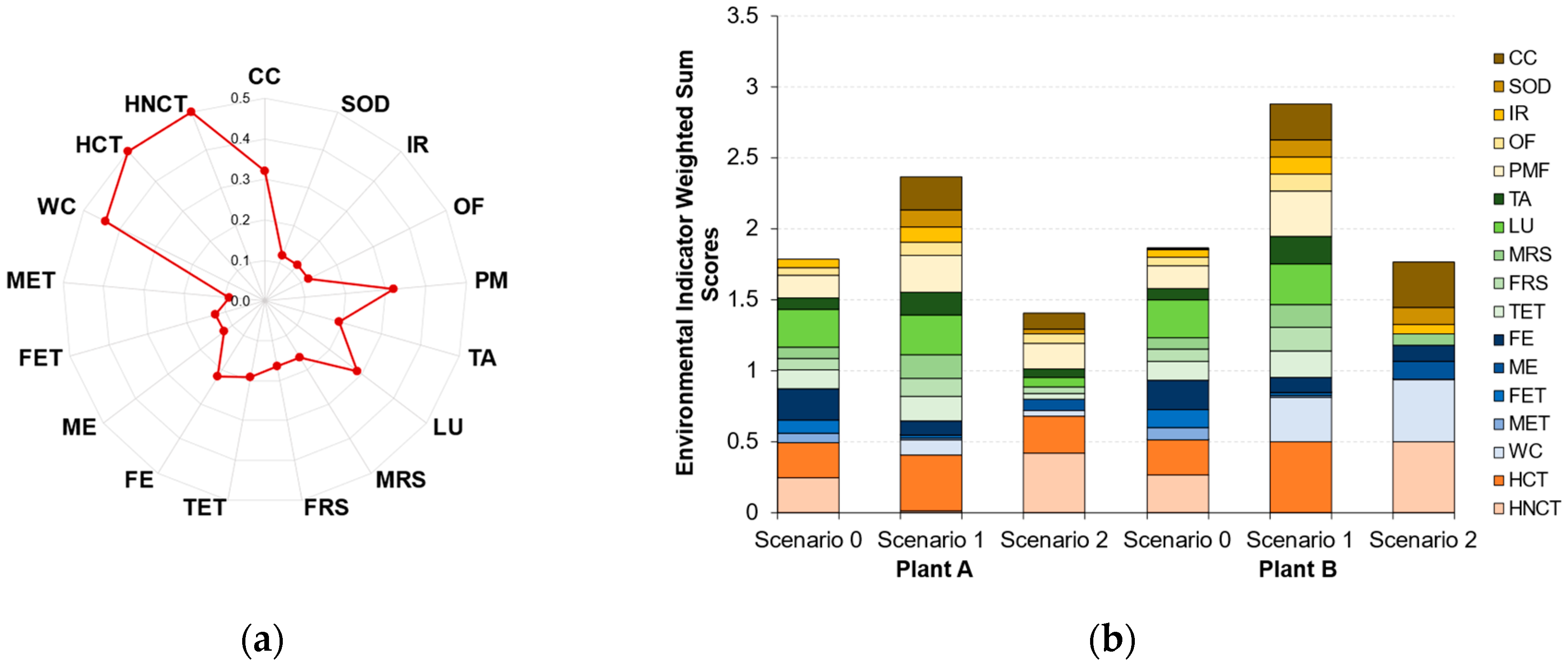
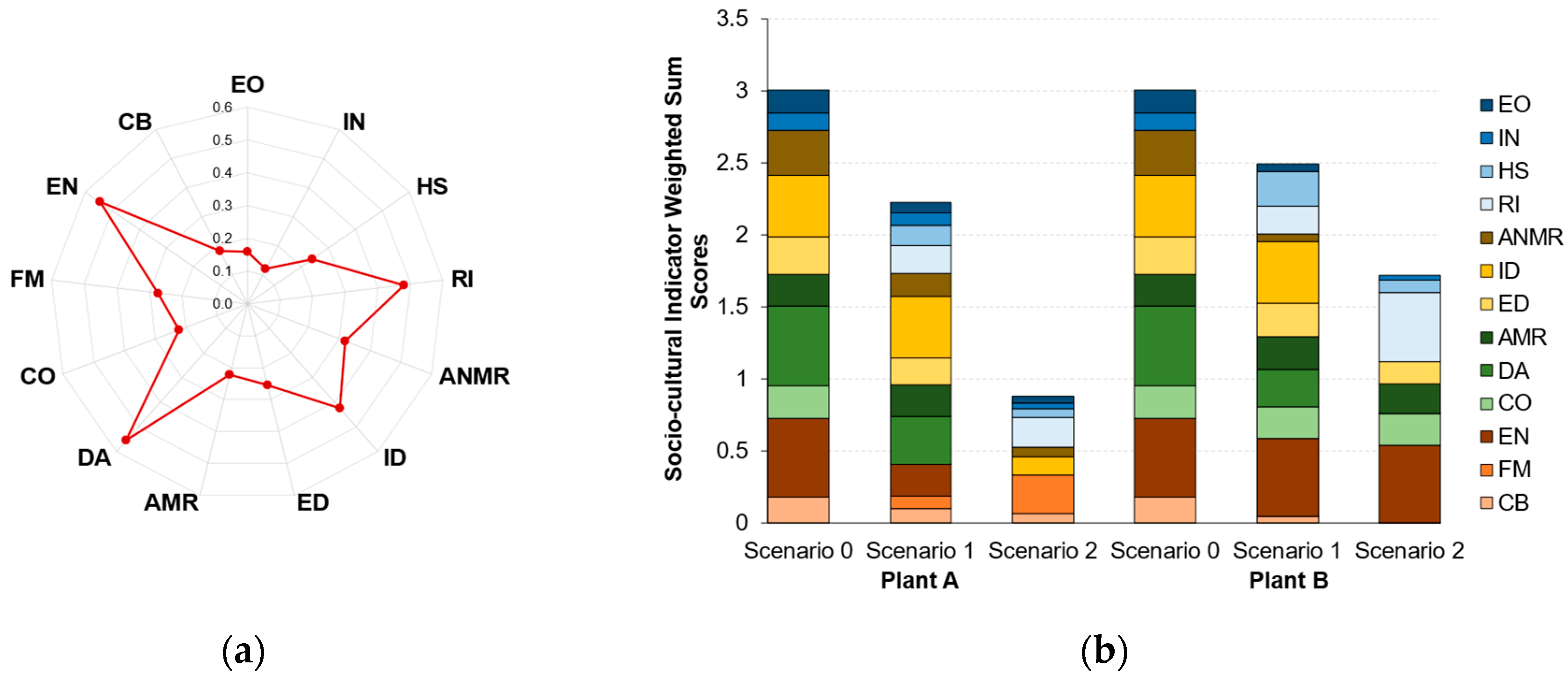
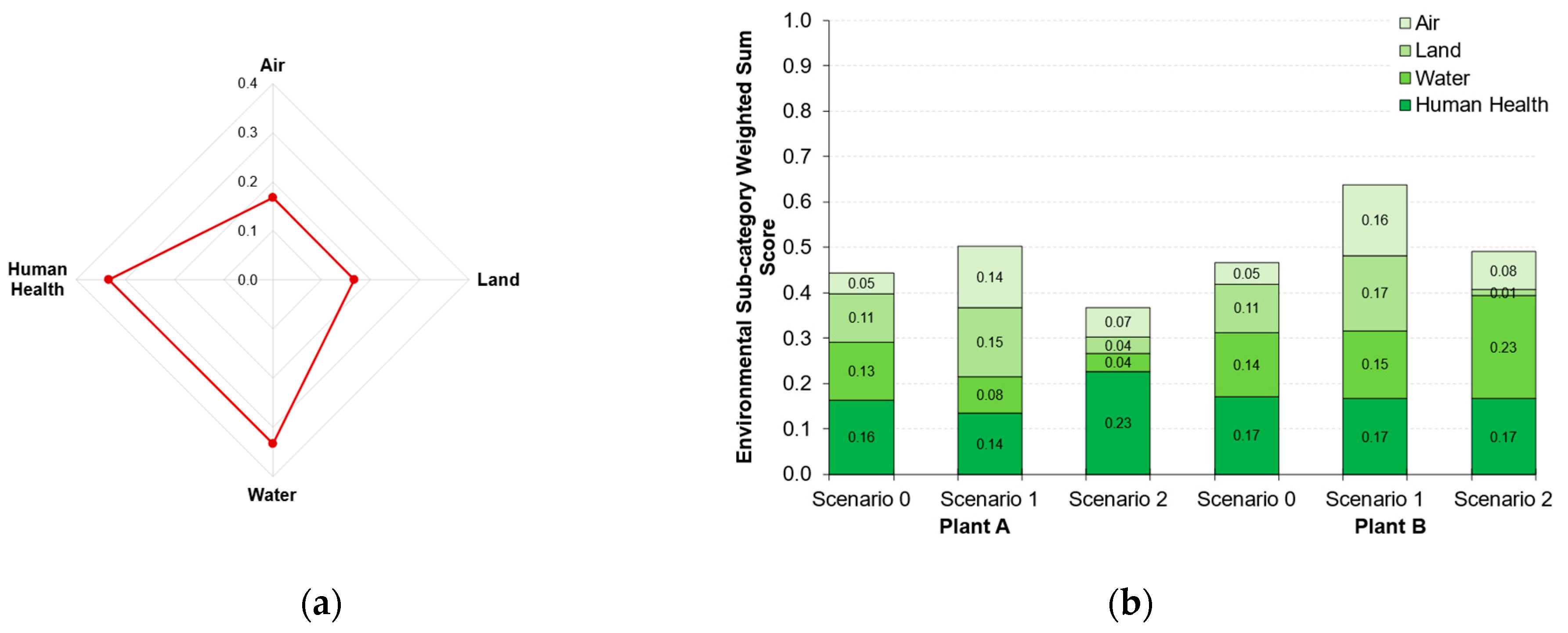
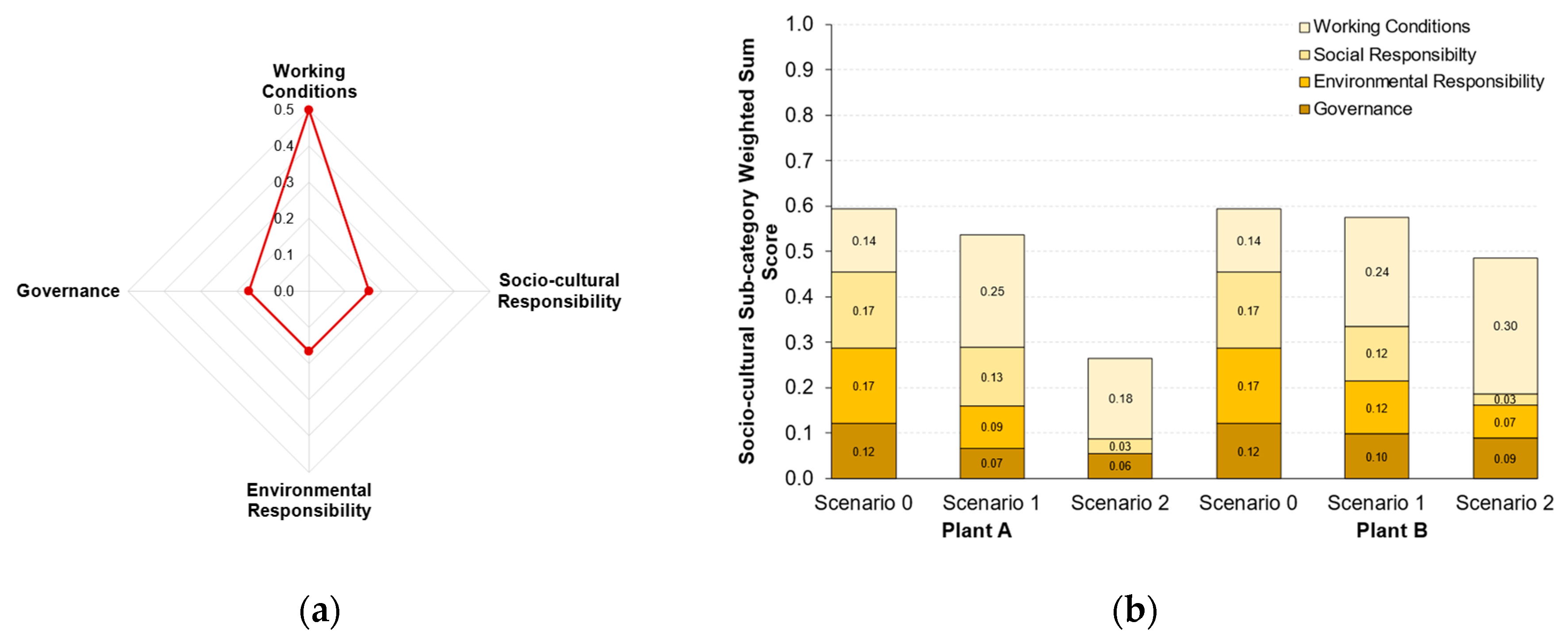
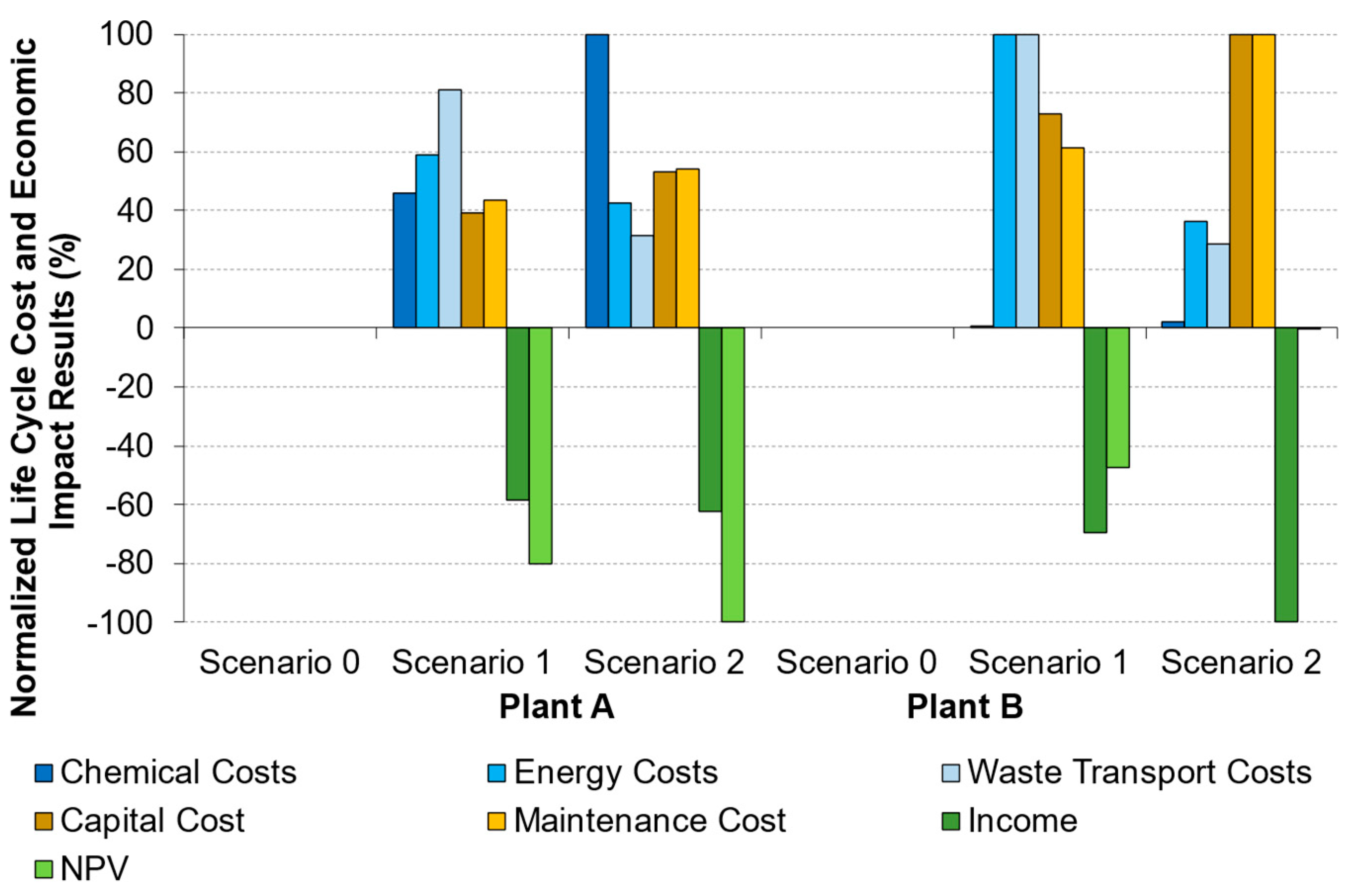
| Plant A | Plant B | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria Sub-category |
Indicator | S0 | S1 | S2 | S0 | S1 | S2 | |
| Environmental (LCA) | Air | CC | 0.00 | 0.74 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.78 | 1.00 |
| SOD | 0.00 | 0.97 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 1.00 | 0.97 | ||
| IR | 0.48 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.56 | ||
| OF | 0.49 | 0.79 | 0.53 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 0.00 | ||
| PM | 0.49 | 0.81 | 0.56 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 0.00 | ||
| Land | TA | 0.42 | 0.84 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.00 | |
| TET | 0.69 | 0.89 | 0.23 | 0.69 | 1.00 | 0.00 | ||
| LU | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.93 | 1.00 | 0.00 | ||
| MRS | 0.48 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.52 | 0.97 | 0.48 | ||
| FRS | 0.51 | 0.80 | 0.28 | 0.51 | 1.00 | 0.00 | ||
| Water | FE | 1.00 | 0.45 | 0.00 | 0.94 | 0.47 | 0.51 | |
| ME | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 1.00 | ||
| FET | 0.74 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.14 | 0.01 | ||
| MET | 0.76 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 0.00 | ||
| WC | 0.00 | 0.25 | 0.09 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 1.00 | ||
| Human Health | HCT | 0.49 | 0.79 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 1.00 | 0.00 | |
| HNCT | 0.50 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.53 | 0.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Socio-cultural (SLCA) | Working Conditions | EO | 1.00 | 0.49 | 0.29 | 1.00 | 0.32 | 0.00 |
| IN | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.37 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.28 | ||
| HS | 0.00 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.35 | ||
| RI | 0.00 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 1.00 | ||
| Social Responsibility | ANMR | 1.00 | 0.51 | 0.22 | 1.00 | 0.19 | 0.00 | |
| ID | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.29 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | ||
| ED | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.60 | ||
| Environmental Responsibility | AMR | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.93 | |
| DA | 1.00 | 0.60 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.47 | 0.01 | ||
| CO | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.98 | ||
| Governance | FM | 0.00 | 0.30 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| EN | 1.00 | 0.40 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 | ||
| CB | 1.00 | 0.56 | 0.35 | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.00 | ||
| Plant A | Plant B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria Sub-category |
S0 | S1 | S2 | S0 | S1 | S2 | |
| Environmental (LCA) |
Air | 0.27 | 0.81 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.93 | 0.50 |
| Land | 0.64 | 0.91 | 0.22 | 0.65 | 1.00 | 0.08 | |
| Water | 0.38 | 0.24 | 0.12 | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.68 | |
| Human Health | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 0.50 | |
| Socio-cultural (SLCA) | Working Conditions | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.33 | 0.50 | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| Social Responsibility | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.20 | |
| Environmental Responsibility | 1.00 | 0.53 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.64 | |
| Governance | 0.67 | 0.42 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.42 | 0.33 | |
| Plant A | Plant B | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Criteria | S0 | S1 | S2 | S0 | S1 | S2 |
| Environmental (LCA) | 0.44 | 0.58 | 0.32 | 0.48 | 0.67 | 0.46 |
| Socio-cultural (SLCA) | 0.79 | 0.57 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.70 | 0.29 |
| Economic (LCC) | 1.00 | 0.62 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 0.42 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





