1. Introduction
With the rapid development of sensor technology and computer technology, robotic autonomous navigation technology has been applied in orchards on a large scale [
1,
2,
3]. Autonomous navigation technology is the key technology to realize the intelligence of agricultural equipment in orchards, which is conducive to reducing the work intensity of operators, improving work efficiency and enhancing the quality of operations [
4,
5,
6].
Autonomous navigation technology mainly perceives the dynamic environment around the vehicle through a variety of sensors to plan and navigate the path and complete the operations such as orchard weeding [
7,
8], furrowing and fertilizing [
9,
10,
11], and picking [
12,
13].Commonly used navigation methods are classified as Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)/Global Positioning System (GPS) [
14,
15], Light Detection and Ranging (LIDAR) [
16,
17], vision sensors [
18,
19], and multi-sensor fusion navigation [
20].Wei Shuang et al [
21] proposed a pure tracking model based on GNSS autonomous navigation path search method for agricultural machines and pre-sighting point search, in straight line navigation, the root mean square error of navigation is 3.79, 4.28 and 5.39 cm when the speed is 0.8, 1.0 and 1.2m/s respectively. Luo Xiwen et al [
22] developed an automatic navigation control system based on DGPS, and the maximum error of this system is less than 15 cm and the average error is less than 3 cm in straight line navigation when the tractor is at a speed of 0.8 m/s. However, when the fruit tree branches and leaves are luxuriant and the canopy is closed, and the environment between the rows of the tree is almost close to the semi-closed state, the satellite signals are blocked by the canopy, which leads to a certain limitation of the positioning and navigation method based on GNSS/GPS. positioning and navigation methods are subject to certain limitations. Liu Weihong et al [
23] proposed an orchard inter-row navigation method based on 3D LiDAR, the method in the real pear orchard, mobile robot tracking tree rows at a speed of 1.35m/s, the maximum lateral deviation obtained is less than 22.1cm. 3D LiDAR is subject to weather conditions and expensive, greatly increasing the cost of inputs in orchard environments, and therefore difficult to be used universally. Han Zhenhao et al [
24] proposed an orchard visual navigation path recognition method based on U-Net network, which uses a camera to collect images and semantically segment the road information in the image to calculate the navigation path, using this method to drive in the orchard road with a width of about 3.1m, the average distance error ratio is 1.4%, which is about 4.4cm, and the average processing time of a single frame of image is 0.154s.
In recent years, deep learning has made breakthrough progress in image classification research, and also driven the rapid development of target visual detection [
25,
26,
27]. Deep learning-based target detection models, including two-stage target detection models and single-stage target detection models [
28,
29], two-stage target detection models have higher detection accuracy, but slower detection speed, therefore, most real-time detection tasks currently use single-stage target detection models. Typical single-stage detection models include the YOLO [
30,
31,
32] family of models and the SSD [
33] model. Xie Shuang et al. [
34] used an improved YOLOv8 model for tea recognition, which combines deformable convolution, an attention mechanism, and improved spatial pyramid pooling, thus enhancing the model's ability to learn complex target invariance, reducing the interference of irrelevant factors, and achieving multi-feature fusion, which improves the detection accuracy. Wang et al. [
35] constructed a model that fuses YOLO v5s and attention mechanism of convolutional neural network model YOLO_CBAM for the detection of spiny calyx lobelia weed. They devised a method for slicing high-resolution images. This method constructs the dataset by calculating the overlap rate to reduce the possibility of loss of details due to compression of high-resolution images during training, and the final accuracy is 92.72%. Tian et al. [
36,
37] successfully achieved detection of grape maturity and detection of weed identification and localization through the improved YOLOv4 algorithm. The experimental results show that this method has high accuracy.
This paper proposes a method based on binocular camera to determine the positional parameters of an orchard robot. When the orchard robot advances between rows, the binocular camera acquires images and transmits them to the improved YOLOv4 model for fruit tree trunk detection, obtains the camera coordinates of the trunks, and then obtains the ground projection coordinates of each trunk after coordinate conversion. The ground projection coordinates of different sides of the orchard robot are combined to take the midpoint and the least squares method is used to fit a straight line to the midpoint to obtain the navigation path, and the heading angle and lateral deviation values of the orchard robot are obtained through calculation.
2. Materials and Methods
In this paper, the proposed method for estimating the positional parameters between rows of orchard robots consists of four parts: fruit tree trunk detection, fruit tree trunk localization, navigation path calculation and calculation of positional parameters. The detection of fruit tree trunks is based on the improved YOLOv4 model to detect the trunks on both sides of the orchard robot; the positioning of fruit tree trunks is based on the parallax principle after the binocular camera acquires the image to obtain the camera coordinates of the fruit tree trunks; the calculation of the navigation path is based on the camera coordinates of the fruit tree trunks obtained from the previous step through the coordinate transformation to obtain the ground projection coordinates, the combination of projection coordinates of the different sides of the orchard robot to take the mid-point, and the mid-point is calculated using the least-squares method. The least squares method is used to fit the midpoint to a straight line; the attitude parameters are obtained by calculating the straight line relationship between the fitted straight line and the vehicle base coordinate system.
2.1. Hardware Composition
In this study, the electric-driven tracked orchard operation platform designed by the College of Engineering of Nanjing Agricultural University is used as the mobile carrier, which is driven by two 48V DC servo motors, and the motors are driven and controlled by one dual-channel servo motor driver; the upper computer is the New Creation Cloud Embedded Industrial Controller with an external display screen; STM32 is selected as the lower computer to control the servo motor driver of the mobile carrier; the vision sensor uses the ZED2i (polarized version) high-definition camera, the camera's focal length f is 1.8mm, the base distance b is 120mm, the camera captures the left and right images with a resolution of 1280×720. the overall scheme of the system is shown in
Figure 1:
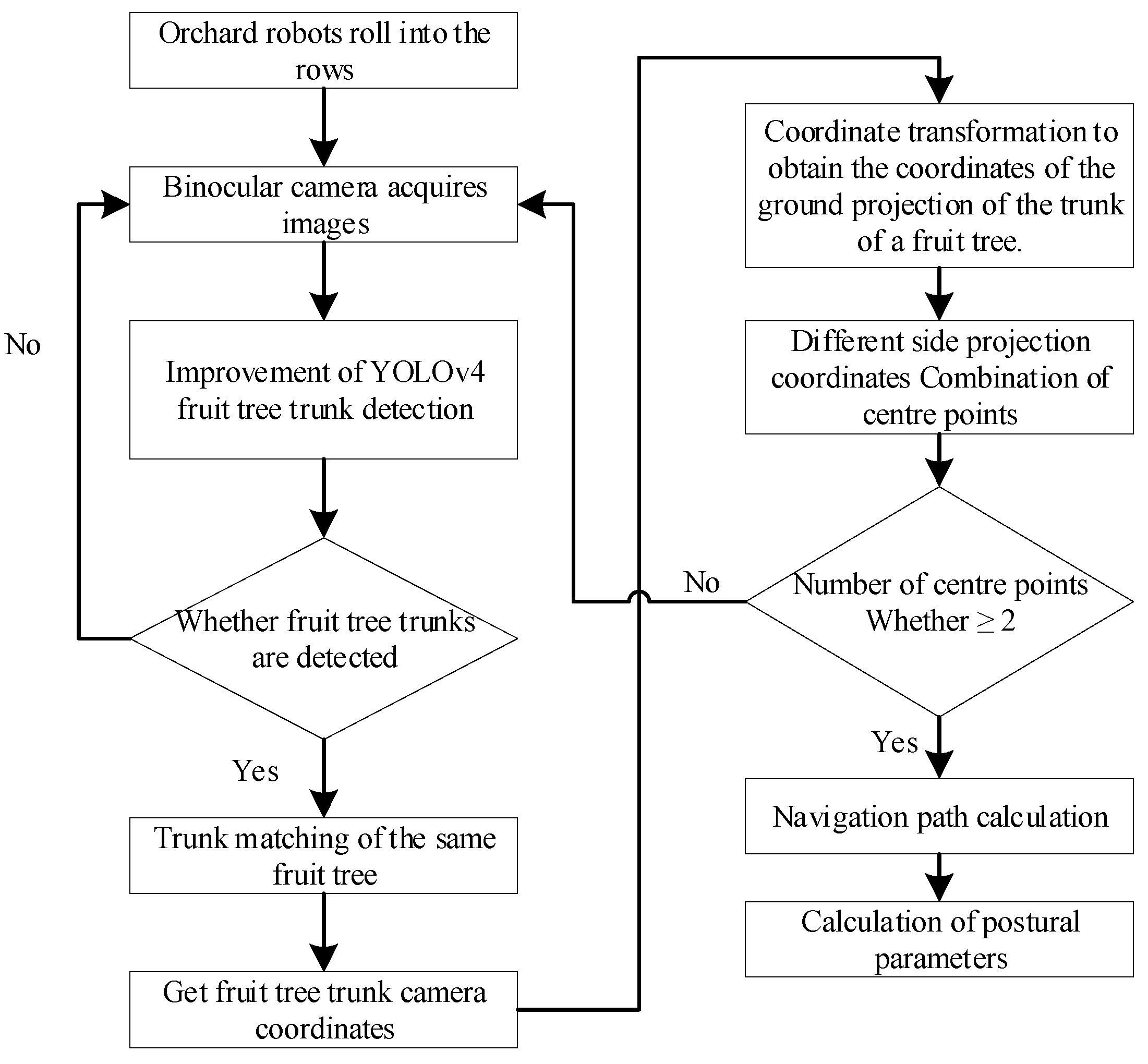
2.2. Technological Route
The technical flow of the machine vision based inter-row position estimation and navigation method for orchard robots at night is shown in
Figure 2.
2.3. Improvements to the YOLOv4 Algorithm
2.3.1. YOLOv4 Algorithm
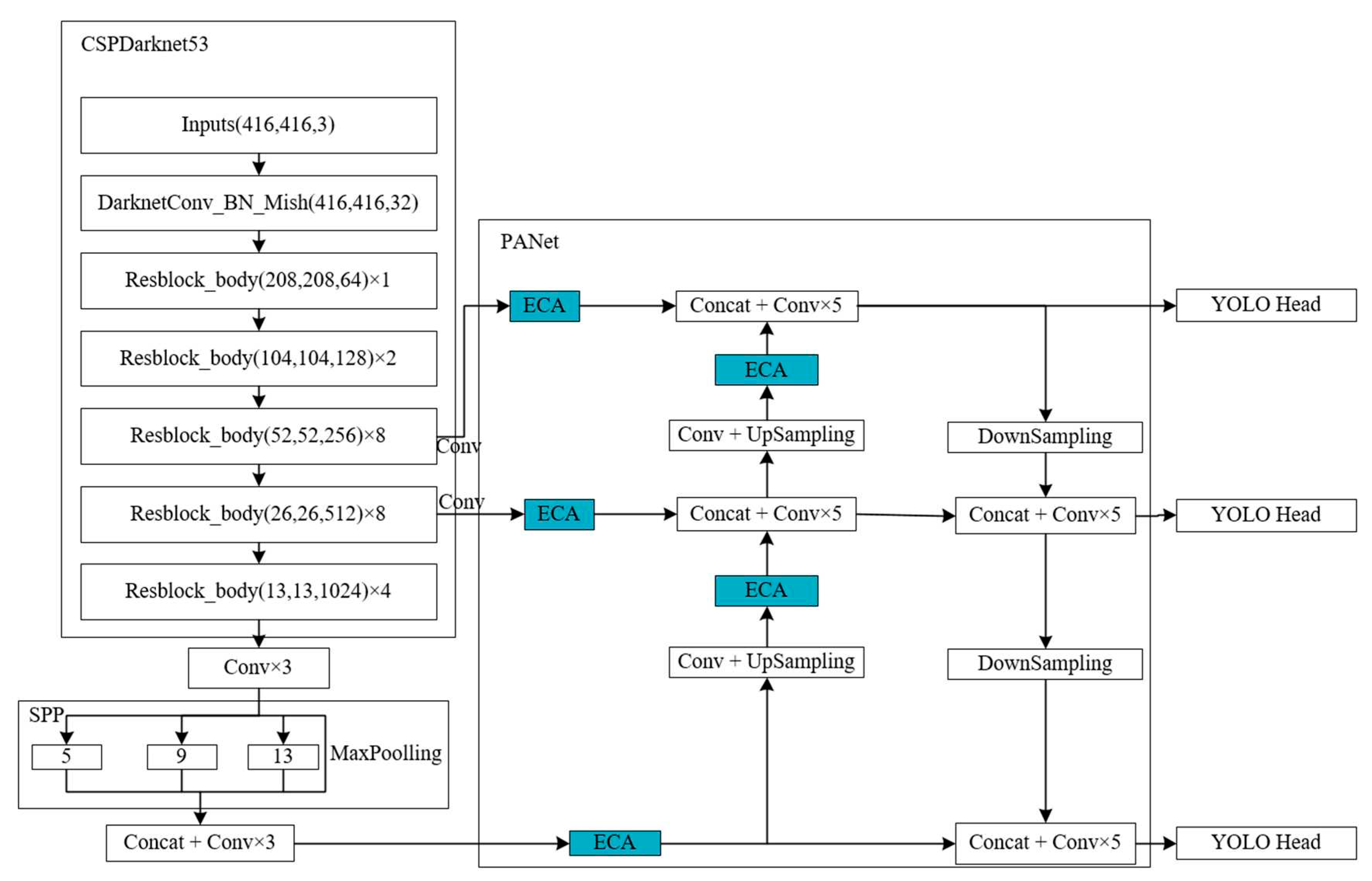
The YOLO family of algorithms is one of the advanced target detection algorithms in the world. The YOLOv4 algorithm uses the CSPDarknet53 as the backbone network for feature extraction, and uses the CBM (consisting of Convolution, Normalization, and Mish activation functions) module and CBL (consisting of Convolution, normalization, and LeakyReLU activation functions) module for feature extraction, and also joins the Spatial Pyramid Pooling Networks (SPPNet) and Path Aggregation Network (PANet) modules for feature extraction, while adding two network modules, Spatial Pyramid Pooling Networks (SPPNet) and Path Aggregation Network (PANet), so that the target detection accuracy of the YOLOv4 algorithm is better than that of the YOLOv3 algorithm. Meanwhile, YOLOv4 algorithm adds image enhancement during training, thus further expanding the dataset.
2.3.2. Improvement of the YOLOv4 Algorithm
In this paper, the YOLOv4 algorithm is used to detect fruit tree trunks. When the orchard robot travels between rows, the environment is relatively complex, and the detection accuracy of fruit tree trunks is an important prerequisite to ensure that the orchard robot can safely navigate, so it is necessary to carry out certain optimization of the YOLOv4 algorithm, so as to improve the detection accuracy of fruit tree trunks.
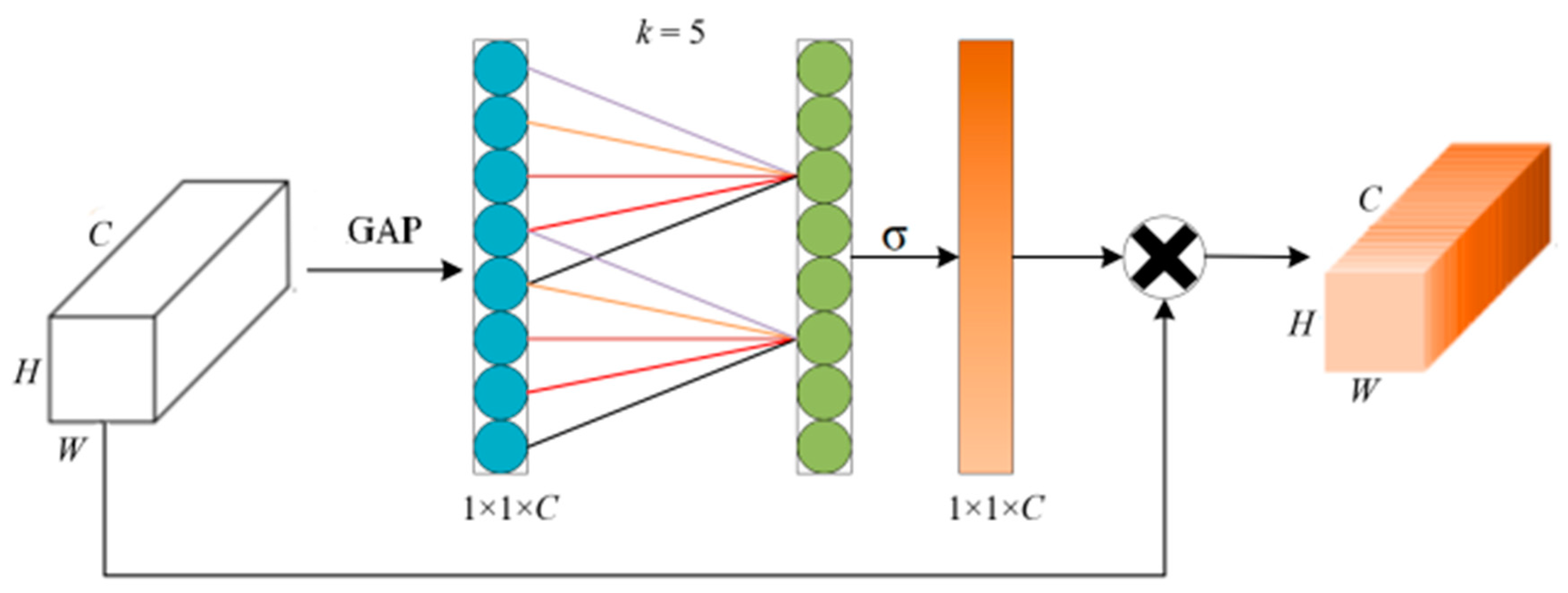
In this paper, we introduce an efficient channel attention mechanism ECA module, as shown in
Figure 3, where k=5 is used as an example. the ECA module maintains the dimensionality of the channel, performs a global average pooling (GAP) operation on the channel, generates the channel weights using a Sigmoid activation function (σ) after one-dimensional convolution, and finally multiplies the channel weights with the original feature layer one by one to obtain a new feature layer. Where the convolution kernel scale k can be adaptively determined and is proportional to the channel dimension. Therefore, if the channel dimension C is known, then the convolutional kernel scale k can be obtained by calculating equation (1). The ECA module adds little computational effort to the algorithm and improves performance in all aspects.
Where Ι*Ιodd denotes the nearest odd number toΙ*Ι, a and b are function coefficients, in this paper a takes the value of 2 and b takes the value of 1.
In the YOLOv4 algorithm, the input dataset outputs three kinds of feature layers, 52×52×256, 26×26×512 and 13×13×1024, after feature extraction by the backbone feature extraction network CSPDarknet53, where the 52×52×256 and 26×26×512 are inputted into the PANet module after one convolution and the 13×13×1024 feature layer is inputted into PANet after channel stacking and three convolutions after SPP module. In this paper, the channel attention mechanism ECA module is added to these three feature layers before channel stacking and five convolution operations in PANet. In the PANet module, there are 2 times of up-sampling of the feature layer, this paper adds ECA module after up-sampling, and performs enhanced feature extraction operation on the feature layer after up-sampling, so this paper adds 5 ECA modules to the original YOLOv4 algorithm, and obtains the optimised new algorithm ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm, and the network model of the ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm is shown in
Figure 4.
2.4. Fruit Tree Trunk Positioning
2.4.1. Fruit Tree Trunk Camera Coordinates
Fruit tree trunks are detected by improving the YOLOv4 model on the left and right images captured by the binocular camera. After detecting the fruit tree trunks, the fruit tree trunks are matched, and when the same fruit tree trunks in the left and right images are matched successfully, the pixel parallax
D and image parallax
d of the same fruit tree trunks in the left and right images are obtained; according to the principle of triangulation of the binocular camera, the camera coordinates of the fruit tree trunks are obtained
(Xc,Yc,Zc). The method in this paper is to project the ground, so the
Yc coordinates do not need to be solved to simplify the calculation process. The pixel coordinates of the geometric center of the fruit tree trunk in the left image are (u
L,v
L) and the image coordinates are (x
L,y
L); the pixel coordinates of the geometric center of the fruit tree trunk in the right image are (
uR,vR) and the image coordinates are (x
R,y
R).
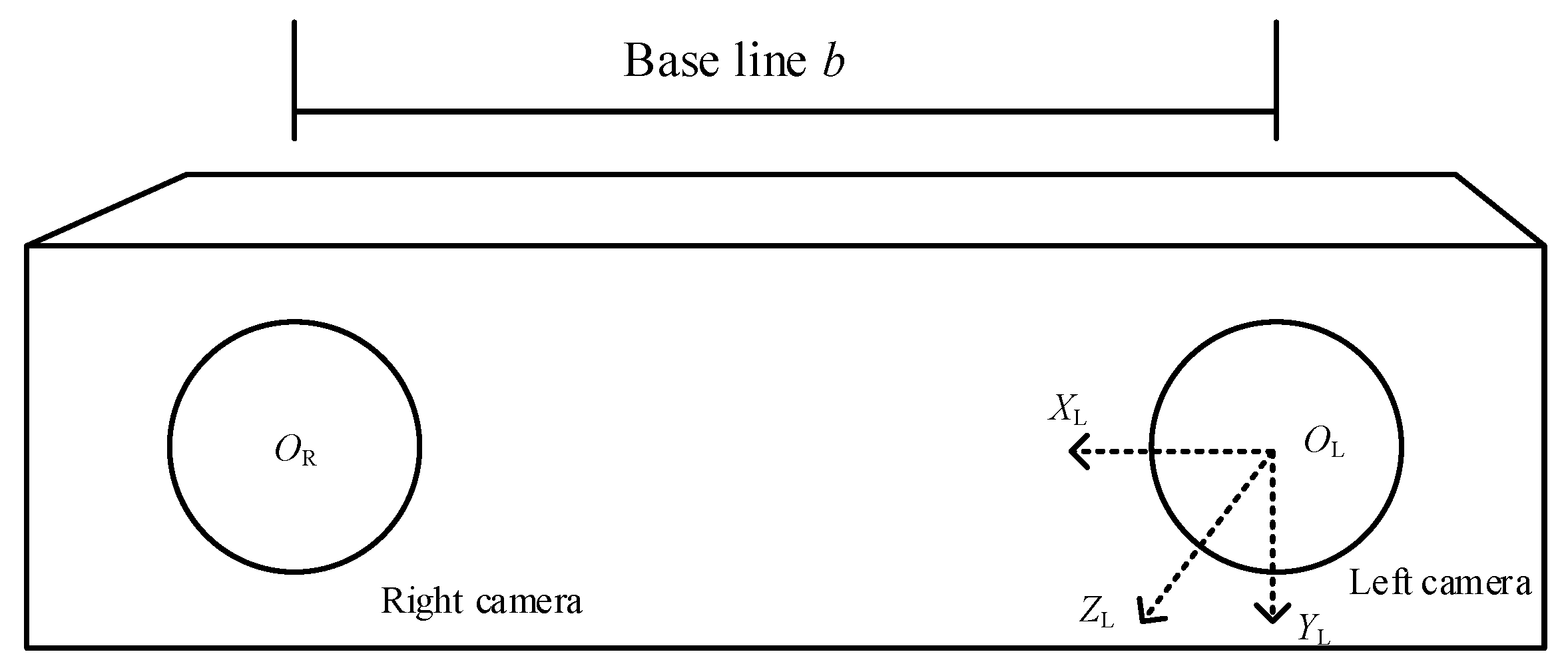
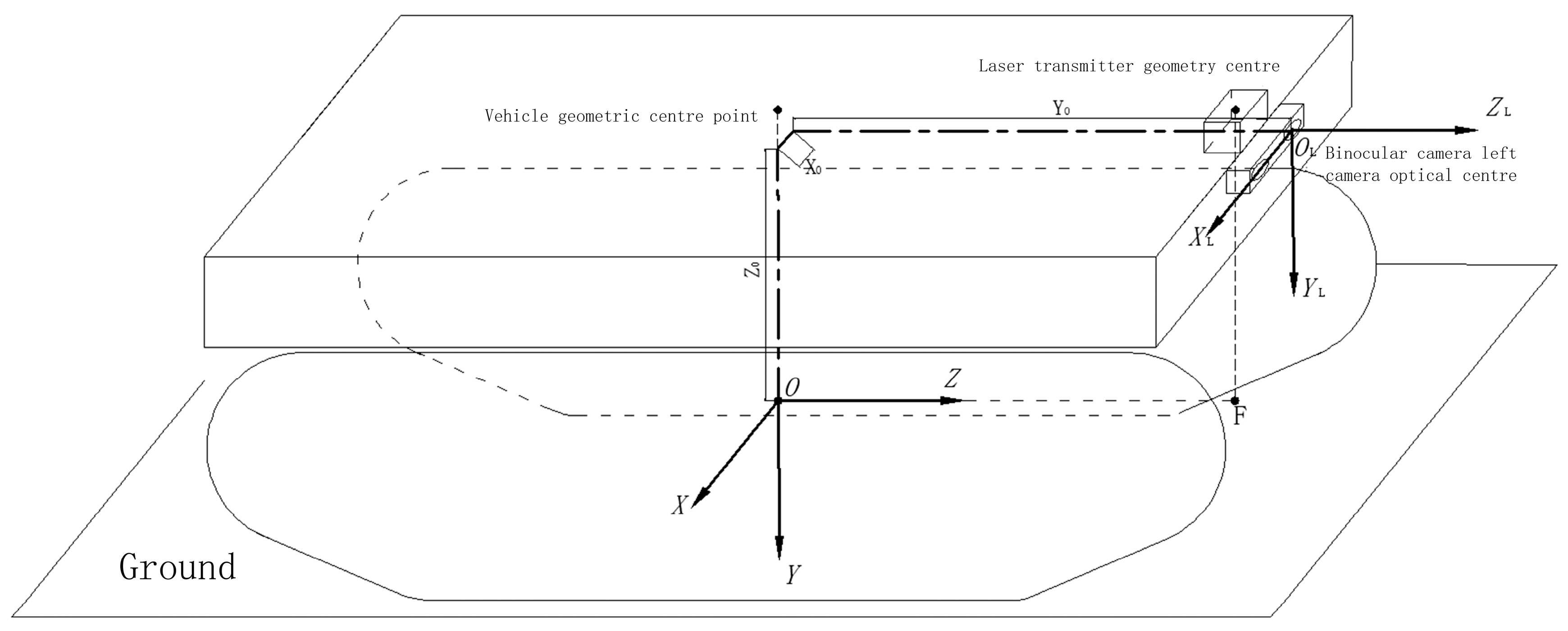
Binocular camera left and right camera optical center were expressed by
OL,
OR, and
OL as the origin, horizontally to the right for the axis
XL positive direction, vertically down for the axis Y
L positive direction, horizontally forward for the positive direction of the
ZL, the establishment of the camera coordinate system
OL-XLYLZL; f indicates the focal length of the binocular camera in mm;
b indicates the baseline of the left and right cameras in mm; the structure of the binocular camera is shown in
Figure 5:
According to the principle of conversion of pixel coordinates to image coordinates and the similarity triangle relationship between image coordinates and camera coordinates there:
where
denotes the pixel coordinate system u-axis scale factor, respectively; and
u0 denotes the amount of lateral translation of the image coordinate system origin in the pixel coordinate system.
According to the triangulation method there is:
The horizontal coordinates of the geometric center of the fruit tree trunk in the pixel coordinate system
uL,
uR in the left and right images, respectively:
From Eqs. (5) and (6), the depth
Zc is obtained as:
Substituting Eq. (7) into Eq. (4), there is:
The coordinates (Xc,Zc) of the fruit tree trunk in the planar coordinate system XLOLZL are obtained from equations (7) and (8). Where, b, u0, are camera internal parameters, which can be obtained by camera calibration.
2.4.2. Fruit Tree Trunk Coordinate Conversion
Coordinate system and conversion relationship shown in
Figure 6, this paper will be the orchard operation platform on the ground projection for the ground coordinate system origin
O; binocular camera installed in the front of the vehicle in the center, binocular camera geometric center of the projection of the ground for the point
F;
for the ground coordinate system axis
Z positive direction, horizontally to the right for the axis of the X-positive direction, the establishment of the ground coordinate system
XOZ. Ground coordinate system can be obtained by the camera coordinate system in the planar coordinate system
XLOLZL. The translation of
X and
Z direction is
X0 and
Z0 respectively. When the camera coordinates are converted to ground coordinates, the Y-axis direction is not to be calculated. Fruit tree trunk in the plane coordinate system
XLOLZL coordinates for (
Xc,Zc), in the ground coordinate system coordinates for (
Xg,Zg), the conversion relationship as shown in equation (9).
2.5. Calculation of Navigation Path and Attitude Parameters
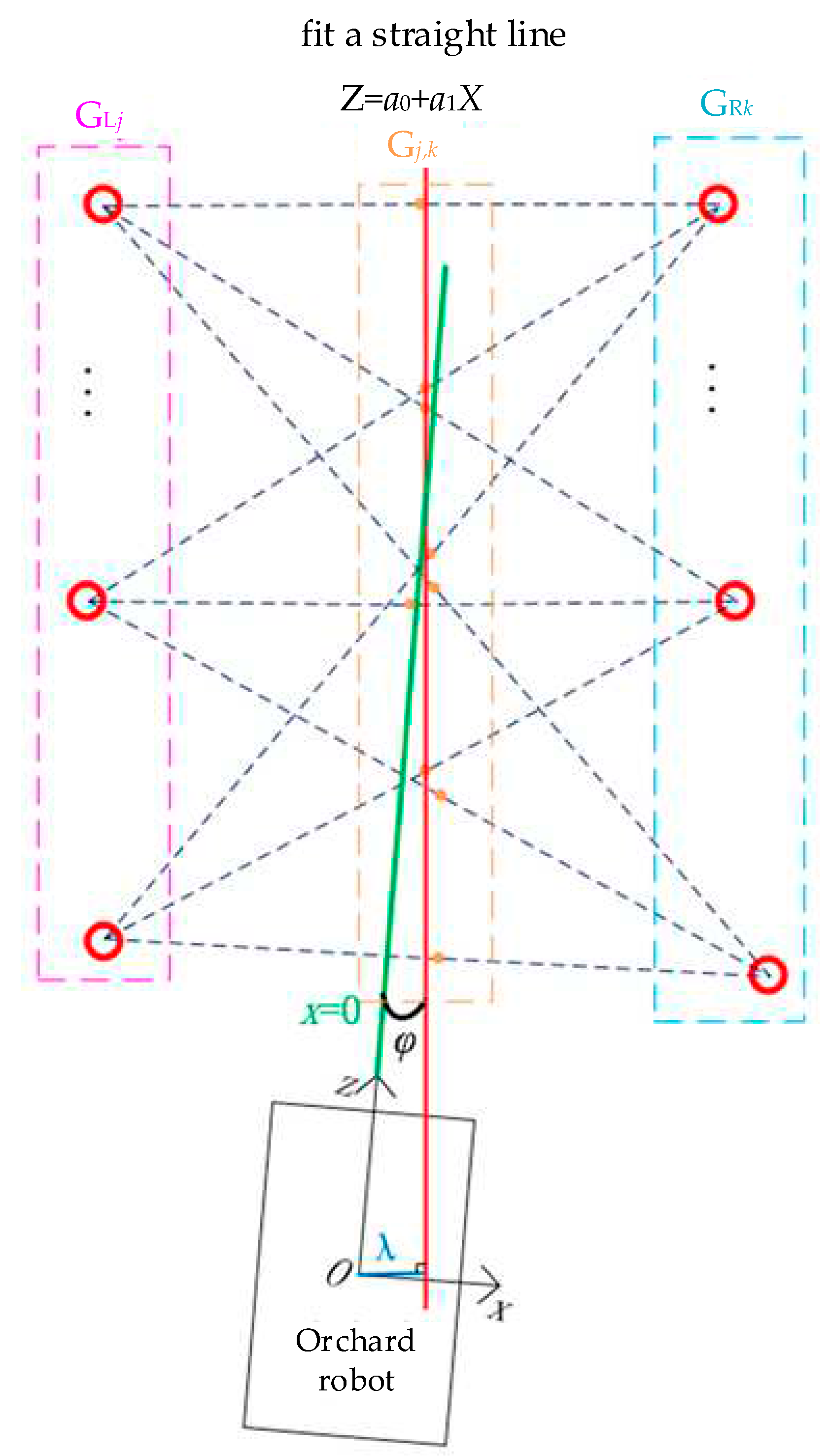
When the orchard robot is travelling between rows, the binocular camera is used to locate on the tree trunks, and then the coordinate conversion is used to obtain the sitting mark of a plurality of fruit tree trunks in the ground coordinate system as
Gi(Xgi,Zgi). Among them, the coordinate point of
Gi(Xgi,Zgi)<0 is regarded as being located on the left side of the orchard operation vehicle, and at this time, the left-side sitting mark is
GLj(Xglj,Zglj); the coordinate point of
Xgi≥0 is regarded as being located on the right side of the orchard operation vehicle, and at this time, the right-side sitting mark is
GRk(Xgrk,Zgrk).
The combination of points on the left and the right is taken to be the midpoint, with a total of
j × k midpoints, denoted
Cj,k(Xj,k,Zj,k).
2.5.1. Navigation Path Calculation
The obtained
j × k midpoints are fitted with a straight line using the least squares method, and the calculated straight line is the navigation path, noting that the fitted straight line is
Z = a1X + a0. The calculation process is as follows:
Find a
0 and a
1 from equation (12):
2.5.2. Calculation of Postural Parameters
The position relationship of the orchard operation platform when travelling between rows is shown in
Figure 7, and the travelling direction of the vehicle is the same as the positive direction of the
Z-axis, which can be expressed by
X=0. Therefore the heading angle
φ of the vehicle can be obtained by calculating the angle between
X=0 and
Z=a1X+a0; the lateral deviation
λ of the vehicle can be obtained by calculating the perpendicular distance from the origin
O to the fitted straight line
Z=a1X+a0. The calculation formulas are shown in (14) and (15):
3. Results
3.1. Data Acquisition and Model Training
The experimental dataset collection site was located in the College of Engineering, Nanjing Agricultural University, and 700 fruit tree trunk images were collected. Data enhancement was performed on the images by adding noise and flipping to expand the dataset to 1500 sheets, including 1200 sheets for the training set and 300 sheets for the validation set. The fruit tree trunk part was labelled using LabelImg tool with the category information: tree.
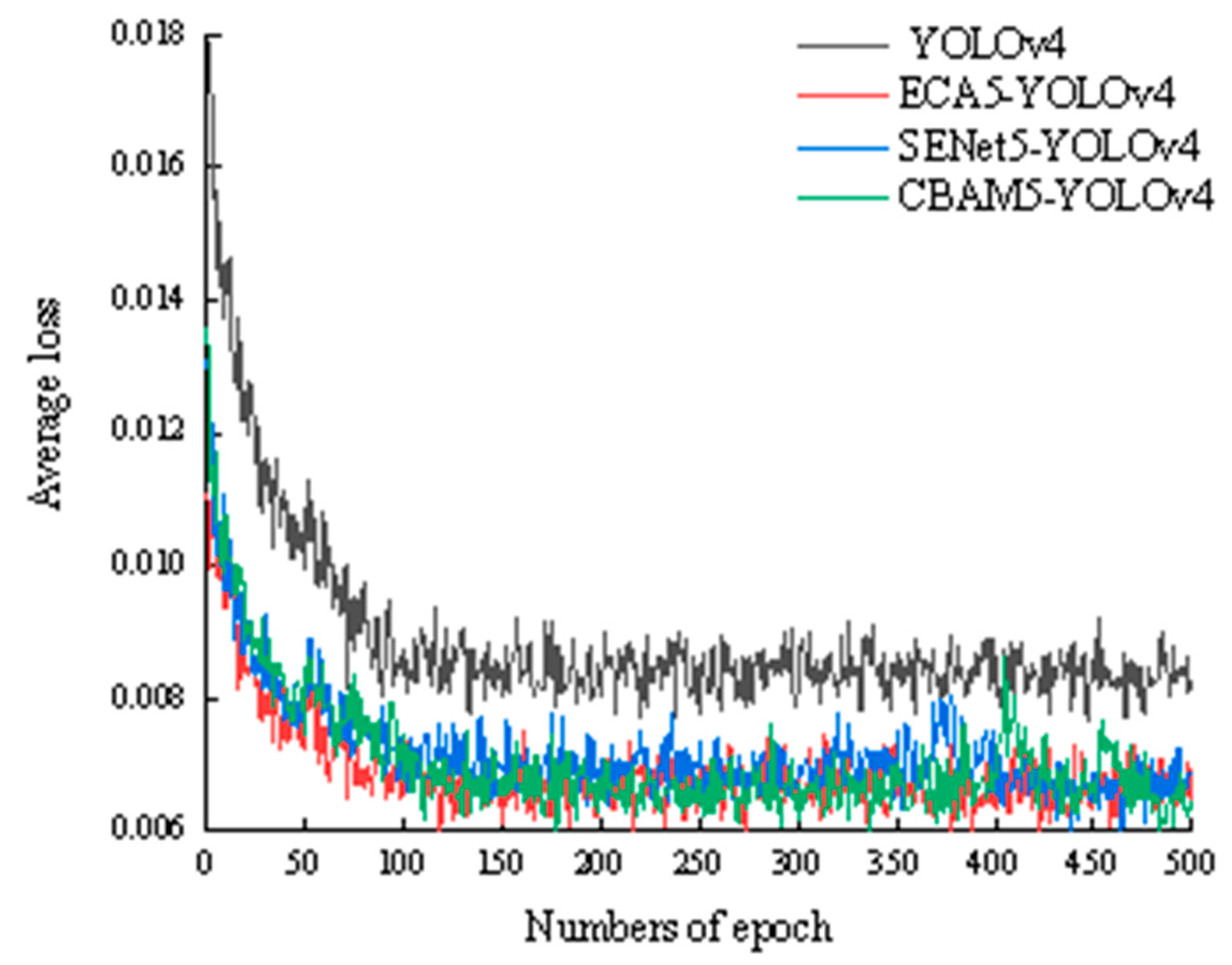
In order to verify the higher accuracy of the ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm, this paper replaces the five ECA modules in the model with the new attention mechanism modules SENet module and CBAM module. The original YOLOv4 algorithm, ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm, SENet5-YOLOv4 algorithm and CBAM5-YOLOv4 algorithm were trained for 500 generations using the same dataset respectively. The loss functions of the training models are shown in
Figure 8.
Training platform: Intel(R) Xeon(R) E5 2689 2.60GHz CPU, 32G RAM, NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070 8G graphics card.
The evaluation metrics of training results in this experiment include Precision (
P), Recall (
R) and Frame rate.
P and
R are calculated as:
Where TP denotes the number of correctly detected fruit tree trunks in the picture; FP denotes the number of detection errors in the picture; and FN denotes the number of missed targets in the picture
Table 1 shows the training results of the original YOLOv4 algorithm, the ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm, the SENet5-YOLOv4 algorithm and the CBAM5-YOLOv4 algorithm.
From the result analysis, the ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm, SENet5-YOLOv4 algorithm, and CBAM5-YOLOv4 algorithm have shown improvements in precision rate, recall rate, and frame rate compared to the original YOLOv4 algorithm. Among them, the ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm has the highest precision rate and recall rate of 97.05% and 95.42% respectively, which are improvements of 5.92%, 2.8%, and 0.22% in precision rate, and 7.91%, 4.41%, 0.28% in recall rate when compared to the YOLOv4 algorithm, SENet5-YOLOv4 algorithm, and CBAM5-YOLOv4 algorithm respectively. The SENet5-YOLOv4 algorithm has the highest frame rate, which is 2.56 fps, 0.44 fps, and 0.53 fps higher than the YOLOv4 algorithm, ECA5-YOLOv4 algorithm, and CBAM5-YOLOv4 algorithm respectively.
3.2. Posture Parameter Determination Test
3.2.1. Binocular Camera Internal Reference Measurement
In this experiment, a ZED2i (polarized version) HD camera was used, the focal length f of the binocular camera was 1.8mm, the base distance b was 120mm, and the resolution of the camera grabbing the left and right images was 1280×720.The internal parameters of the camera were calibrated by using the Software Development Kit (SDK) that comes with the binocular camera. According to the need of fruit tree trunk localization, u0 and result were obtained as 645.25 pixel and 529.88 pixel, respectively.
3.2.2. Experimental Design and Evaluation Indicators
This experiment was carried out in the College of Engineering of Nanjing Agricultural University, and the orchard robot was driven into the rows of fruit trees and stopped at any position in the rows, at which time the real values of the heading angle and lateral deviation of the orchard robot were measured and recorded as φ
t, λ
t; the values measured by the method in this paper are estimated values and recorded as φ
e, λ
e. The difference between the real values of the heading angle and lateral deviation and the estimated values are the error values and recorded as E
φ, E
λ, which were taken as the evaluation indexes of the present experiment. evaluation index, calculated as follows:
3.2.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
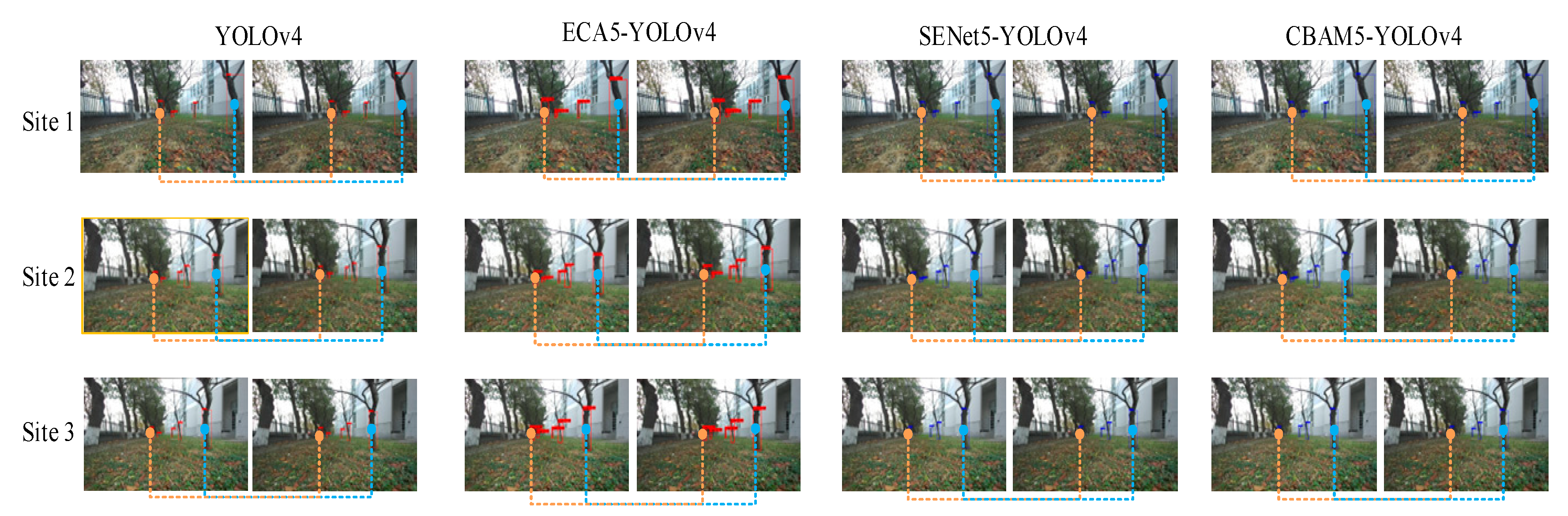
The fruit tree trunks are detected by different models and the positional parameters of the orchard robot are also calculated. The fruit tree trunk results are shown in
Figure 9, and the calculation results are shown in
Table 2. In
Figure 9, the actual heading angle and lateral deviation of the orchard robot from position 1 to position 3 are 150.2° and 0.53 m, 158.5° and 0.48 m, and 160.4° and 0.52 m, respectively. From
Table 2, it can be seen that the best estimation of the positional parameters of the orchard robot was made by the ECA5-YOLOv4 model, with the mean values of the errors of heading angle and lateral deviation being 0.57° and 0.02 m. The results were compared with those of the Original YOLOv4, SENet5-YOLOv4, and CBAM5-YOLOv4 models, the mean values of errors were reduced by 1.50° and 0.01m, 0.86° and 0.03m, and 0.60° and 0.03m, respectively.
4. Discussion
In this study, based on the YOLOv4 model, the ECA5-YOLOv4 model is obtained by introducing five ECA attention mechanism modules into the PANet module of the model, and the ECA5-YOLOv4 model can efficiently and accurately detect the trunks of fruit trees, which can provide a guarantee for obtaining the positional parameters of the orchard robot.
(1) Compared with the original YOLOv4, SENet5-YOLOv4, and CBAM5-YOLOv4 models, the accuracy of the ECA5-YOLOv4 model for fruit tree trunks improved by 5.92%, 2.8%, and 0.22%, respectively;
(2) The estimation method of inter-row position parameters of the orchard robot proposed in this paper obtains the mean values of the errors of heading angle and lateral deviation as 0.57° and 0.02m, with low errors, which can provide a theoretical basis for the orchard robot to navigate between the rows of fruit trees.
Author Contributions
B.G.: Conceptualization, methodology, data curation. Q.L.: software, validation, writing. Y.G.: translating and editing. G.T.: supervision, funding acquisition. B.Z.: resources, supervision. H.W.: reviewing and editing. H.L.: reviewing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the 10th Batch of Changzhou Science and Technology Planning Projects (International Science and Technology cooperation/Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan Science and Technology cooperation) (Grant No. CZ20220010) and Jiangsu Provincial Science and Technology Plan Special Fund (Innovation Support Plan International Science and Technology Cooperation/Hong Kong Macao Taiwan Science and Technology Cooperation) (Grant No. SBZ2022060024).
References
- Zhao, C.J. The development current situation and future outlook of smart agriculture. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2021, 42, 1–7.
- Hu, J.T.; Gao, L.; Bai, X.P.; Li, T.C.; Liu, X.G. Research progress in automatic navigation technology of Agricultural machinery. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31, 1–10.
- Zhou, J.; He, Y.Q. Research progress in agricultural machinery navigation path planning. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52, 1–14.
- Qi, F.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, X.Q.; Wei, X.M. Analysis of the relationship between agricultural engineering and China’s agricultural modernization. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31, 1–10.
- Luo, X.W.; Liao, J.; Hu, L.; Zang, Y.; Zhou, Z.Y. Improve the level of agricultural mechanization to promote sustainable agricultural development. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32, 1–11.
- Guo, C.Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J. Research on autonomous navigation system of orchard agricultural vehicles based on RTK-BDS. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2020, 42, 254–259.
- Li, X.J.; Wang, P.F.; Yang, X.; Li, J.P.; Liu, H.J.; Yang, X.V. Design and test of orchard ridge mower. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2019, 40, 47–52.
- Zhou, Z.K.; Hu, J.N.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Ren, Z.H. Design of Obstacle Avoidance Lawn Mower Control System Based on Image and LiDAR. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2022, 44, 80-84.
- Song, C.C.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wang, G.B.; Wang, X.W.; Zang, Y. Optimization of groove wheel structure parameters of groove wheel fertilizer ejector of fertilization UAV. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37, 1–10.
- Song, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.H.; Fan, G.Q.; Gao, D.S.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, X.H. Research status and development trend of orchard ditch fertilization machinery in China. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2019, 40, 7–12.
- Zhang, H.J.; Xu, C.B.; Liu, S.X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, C.F.; Wang, J.X. Design and Experiment of Double Row Ditching Fertilizer Applicator with Automatic Depth Adjustment. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52, 62–72.
- Hu, G.R.; Kong, W.Y.; Qi, C.; Zhang, S.; Bu, L.X.; Zhou, J.G.; Chen, J. Optimization of navigation path for mobile picking Robot in orchard Environment. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37, 175–184.
- Li, T.; Qiu, Q.; Zhao, C.J.; Xie, F. Task planning of multi-arm picking robot in dwarf dense planting orchard. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37, 1–10.
- Han, J.; Park, C. ; Park Y; Kwon J.H. Preliminary results of the development of a single-frequency GNSS RTK-based autonomous driving system for a speed sprayer. Journal of Sensors, 2019, 2019, 1–9.
- Yue, S.; Zhu H., P.; Ozkan H., E. Development of a variable-rate sprayer with laser scanning sensor to synchronize spray outputs to tree structures. Transactions of the ASABE, 2012, 55, 773–781.
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhou, J. Detection of orchard trunk based on lidar. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2015, 20, 249–255.
- Niu, R.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.W. A trunk detection algorithm based on agricultural robot orchard. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51, 21–27.
- Bi, S.; Wang, Y.H. Orchard robot visual navigation interline pose estimation and fruit tree target positioning method. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52, 16–26.
- Cai, S.P.; Sun, Z.M.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.X.; Zhang, Z.Z. Real-time detection method of orchard obstacles based on the modified YOLOv4. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37, 36–43.
- Zhong, Y.; Xue, M.Q.; Yuan, H.L. Design of GNSS/INS combined navigation System. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37, 40–46.
- Wei, S.; Li, S.C.; Zhang, M.; Ji, Y.H.; Xiang, M.; Li, M.Z. Agricultural machinery automatic navigation path search and steering control based on GNSS. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33, 70–77.
- Luo, X.W.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhao, Z.X.; Chen, B.; Hu, L.; Wu, X.P. DGPS automatic navigation control system of Dongfanghong X-804 tractor. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2009, 25, 139–145.
- Liu, W.H.; He, X.K.; Liu, Y.J.; Wu, Z.M.; Yuan, C.J.; Liu, L.M.; Qi, P.; Li, T. 3D LiDAR navigation method between orchard rows. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37, 165–174.
- Han, Z.H.; Li, J. , Yuan Y.W.; Fang X.F.; Zhao B.; Zhu L.C. Path recognition of orchard visual navigation based on U-Network. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52, 30–39.
- Feng, C.Y.; Nie, G.H.; Naveed, Q.N.; Potrich, E.; Sankaran, K.S.; Kaur, A.; Sammy, F. Optimization of sorting robot control system based on deep learning and machine vision. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2022, 2022.
- Nasirahmadi, A.; Sturm, B.; Edwards, S.; Jeppsson, K.; Olsson, A.C.; Müller, S.; Hensel, O. Deep Learning and Machine Vision Approaches for Posture Detection of Individual Pigs. Sensors, 2019, 19.
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, M.; Hu, Q. Brain-inspired filtering Network for small infrared target detection. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2023, 82.
- Huaming, Q.; Huilin, W.; Shuai, F.; Yan, S. FESSD:SSD target detection based on feature fusion and feature enhancement. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2023, 20.
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv arXiv:2004.10934, 2020.
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv arXiv:2207.02696, 2022.
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; SpringerInternational Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Sun, H. Tea-YOLOv8s: a tea bud detection model based on deep learning and computer vision. Sensors 2023, 23, 6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Cheng, M.; Huang, S.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, H. A deep learning approach incorporating YOLO v5 and attention mechanisms for field real-time detection of the invasive weed solanum rostratum dunal seedlings. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2022, 199, 0168–1699.
- Zhao, J.W.; Tian, G.Z.; Qiu, C.; Gu, B.X.; Zheng, K.; Liu, Q. Weed detection in potato fields based on improved YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of weed detection in potato fields. Electronics, 2022, 11, 3709.
- Qiu, C.; Tian, G.Z.; Zhao, J.W.; Liu, Q.; Xie, S.J.; Zheng, K. Grape maturity detection and visual pre-positioning based on improved YOLOv4. Electronics, 2022, 11, 2677.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).