1. Introduction
Cancer is a pressing global public health concern and ranks notably as the second most common cause of death in the United States [
1,
2]. The year 2023 has presented alarming statistics, as the US National Center for Health Statistics projected in collaboration with the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, that a staggering 81,800 new cases of kidney cancer have surfaced, culminating in approximately 14,890 deaths [
3]. An unsettling aspect of cancer treatment lies in the severe adverse effects of numerous anticancer drugs. These effects primarily stem from the drugs' inability to discern between regular and cancerous cells [
4]. Nevertheless, there is a silver lining. By adopting simple lifestyle modifications such as dietary changes, maintaining optimal body weight, and regular physical exercise, a significant portion of cancers (ranging from 30% to 40%) can be potentially thwarted [
5]. An encouraging revelation is that increased consumption of vegetables and fruits might hold the key to averting approximately 20% of annual cancer-related mortalities. The rationale lies in their intrinsic safety, minimal toxicity, potent antioxidant properties, and widespread acceptance as dietary supplements. Thus, in the current era of cancer research, the potential benefits of fruits and vegetables have become a focal point of scientific inquiry [
1]. This has spurred medical professionals worldwide to explore novel anticancer compounds sourced naturally intensively and to delve into complementary herbal therapies [
6,
7].
One such fruit garnering attention is the watermelon. Hailing from the Cucurbitaceae family, watermelon is a prominent horticultural crop cherished for its succulent fruits [
8]. While it is a natural diuretic and finds its way into various culinary delights, its rind (WR) is often discarded. Extracting bioactive compounds from this waste could revolutionize the agricultural food chain and present sustainable solutions [
7]. Previous research has illuminated the myriad of benefits WR holds, attributing its antioxidant, free radical scavenging, and anti-microbial capabilities to an array of phenolic compounds it houses, such as quercetin, myricetin, and more [
9,
10,
11]. Intriguingly, citrulline, a non-essential amino acid often likened to Viagra, is found in greater abundance in WR than the pulp, further underscoring its potential health benefits [
7,
12,
13].
1.1. Objectives
Given the potential benefits and therapeutic properties associated with watermelon, especially its rind, our study seeks to analyze the Watermelon rind waste using LC-MS to discern and comprehensively document the composition of Watermelon rind extract (WRE), to investigate the biological effects of WRE with a specific focus on its implications for cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell migration, and the global transcriptomic profile in HRAC-769-P cells, and to establish a comparative understanding between existing research findings on WRE's inhibitory effects on human cancer cell proliferation and its effects on HRAC-769-P cells. Through our research, we endeavor to bridge existing knowledge gaps, shed light on the implications of WRE on HRAC-769-P cells, and provide a comprehensive understanding of the therapeutic potential of watermelon rind.
Results
2.1. Metabolite analysis of phytoconstituents of watermelon rind extraction
WR metabolome analysis identified targeted citrulline (22.29 µg/mg) and untargeted other metabolites in our study, including amino acid derivatives, organic acid derivatives, sugar derivatives, and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives presented in the
Table 1.
2.2. HRAC-769-P cell proliferation was affected by concentration and duration of treatment
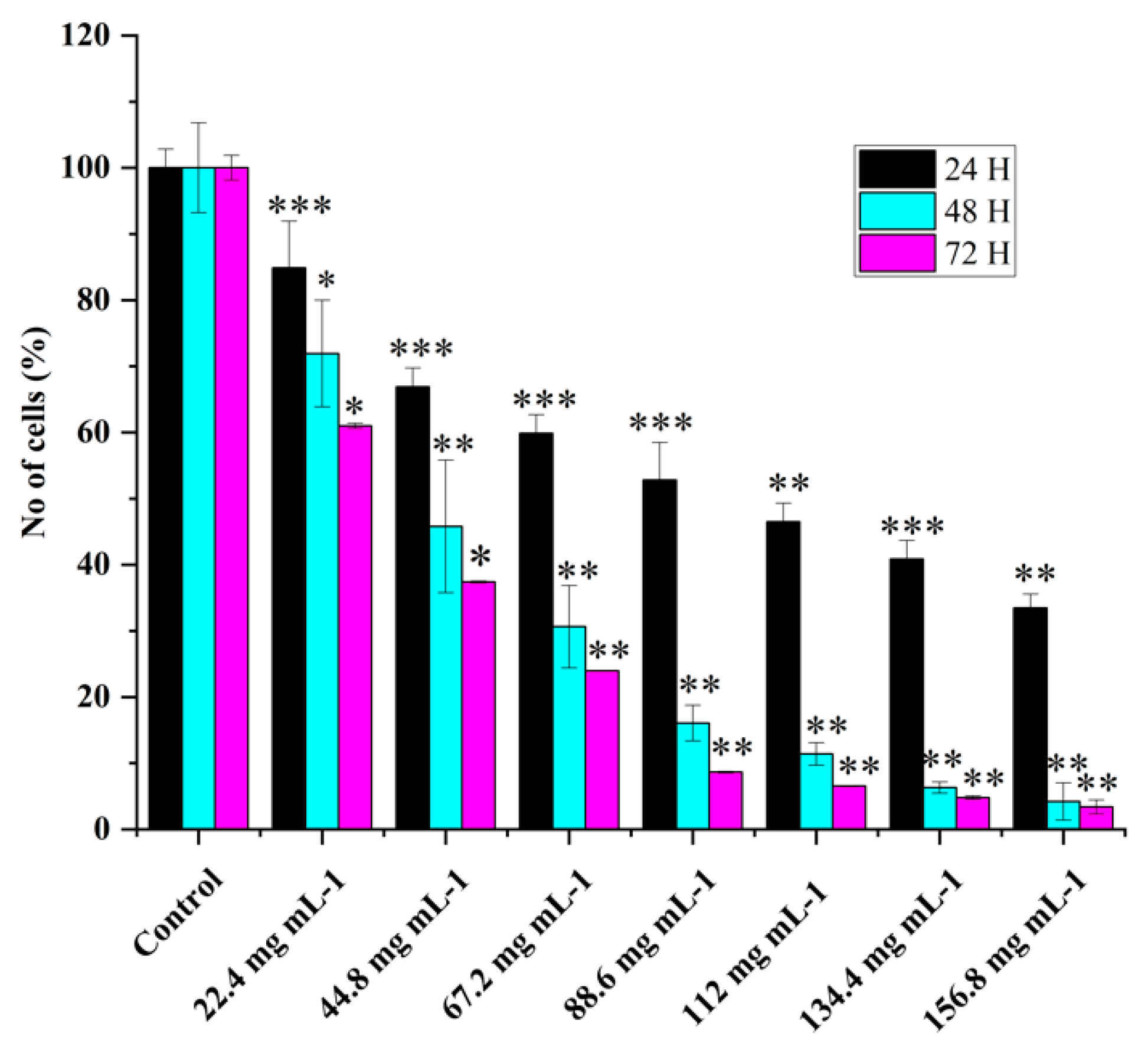
Various concentrations of WRE extract's effect on HRAC-769-P cell proliferation showed dose-dependent cell viability (
Figure 1). WRE chemical compounds could affect cell proliferation via L-Citrullin and other chemical constituents. In previous studies, it was observed that the anticancer effects of WRE in vitro were dependent on both the dose and time of exposure [
7]. The longer duration of exposure was found to increase the potency of WRE and enhance its stability under specific experimental conditions. The percentage of HRAC-769-P cells decreased as the concentration of WRE increased 24, 48, and 72 hours after treatment. (
Figure 1). At 24 hours after treatment, the proportion decreased to 15%, 33%, 40%, 47%, 53%, 59%, and 66%, respectively, compared with controls. Moreover, further cell growth was inhibited significantly at 48 and 72 hrs post=treatment, to 28%, 54%, 69%, 83%, 88%, 93%, 95% and 39%, 62%, 76%, 91%, 93%, 95% 96% respectively compared to control at various concentrations (
Figure 1). Control with culture media (0.96% ethanol) did not affect the cell proliferation as compared with culture media alone (Figure 3).
2.3. Apoptosis versus senescence
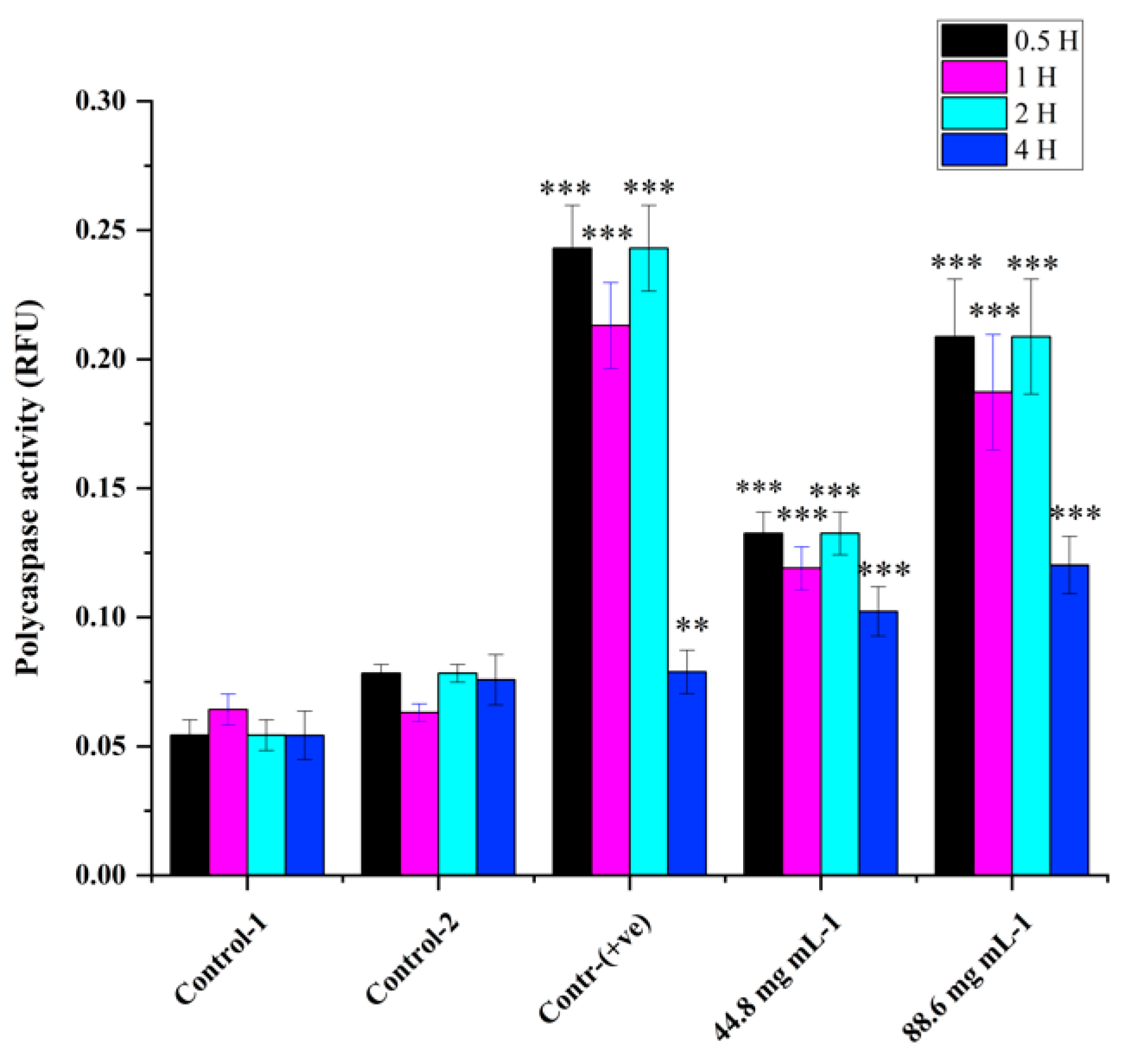
Poly caspase activity was noticed from 0.5 hr compared to the control in HRAC-769-P cells (
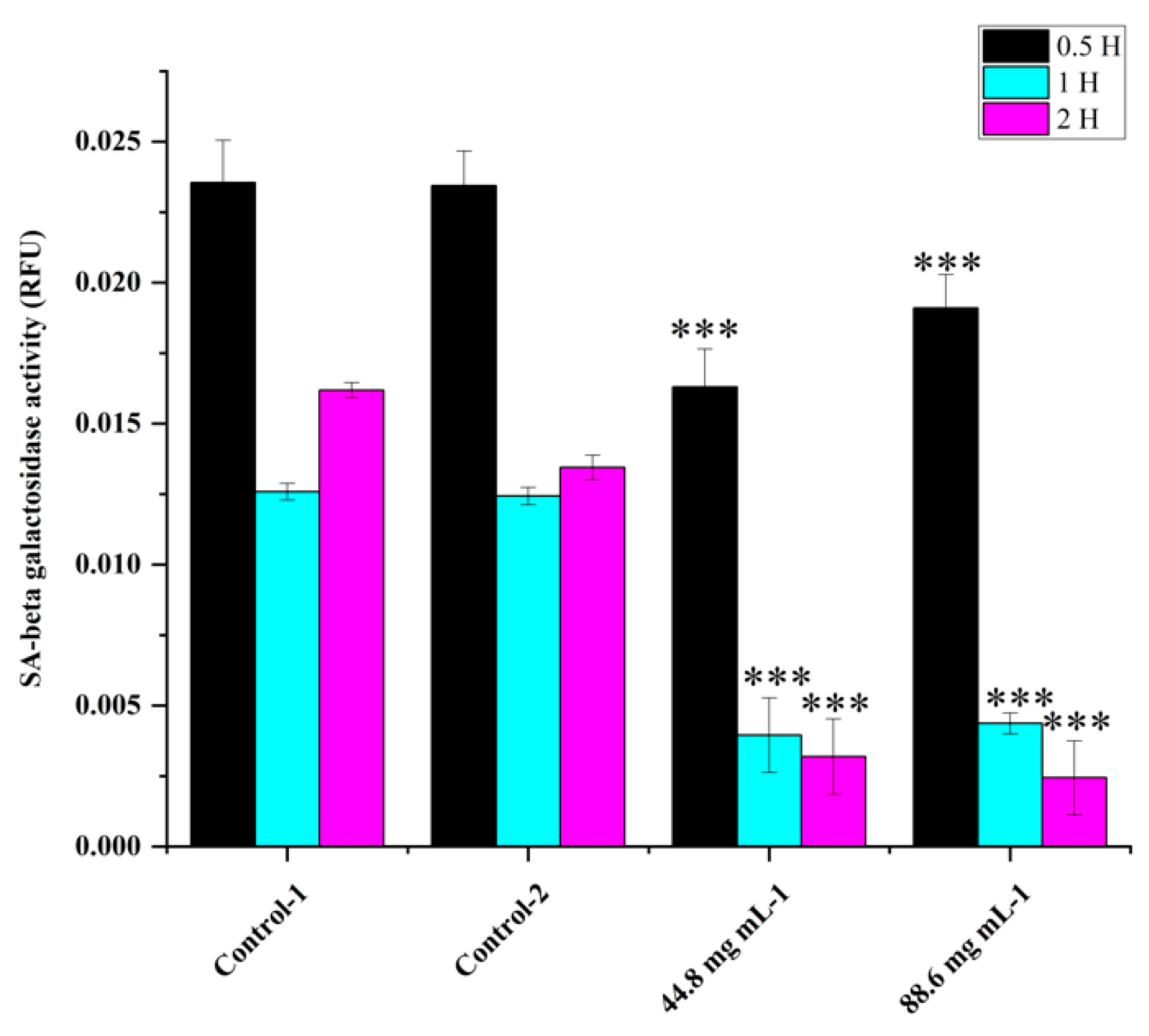
Figure 2). This trend continued up to 2 to 4 hr. Compared to the control, all concentrations of WRE (44.8 and 88.6 mg) exhibited caspase activity. Compared to the (ethanol-0.96%) control, peak poly caspase activity occurred with WRE (88 mg ml-1) at 2 hrs, followed by 1hr, respectively. Early induction of caspase activity was noticed, and it began to decrease at 4 h. SA-beta-gal activity with WRE 88.6 mg ml-1 treatment exhibited similarity to control(s) activity at 0.5 and 1 hr, followed by a decline (
Figure 3). Interestingly, the activity was significantly lower in other treatments between 0.5 and 2 hrs. Overall, SA-beta-gal activity began to decrease from 2 hrs with all treatments
2.4. Assessment of Cell Migration Inhibition and Metastasis Using Wound Healing Assay
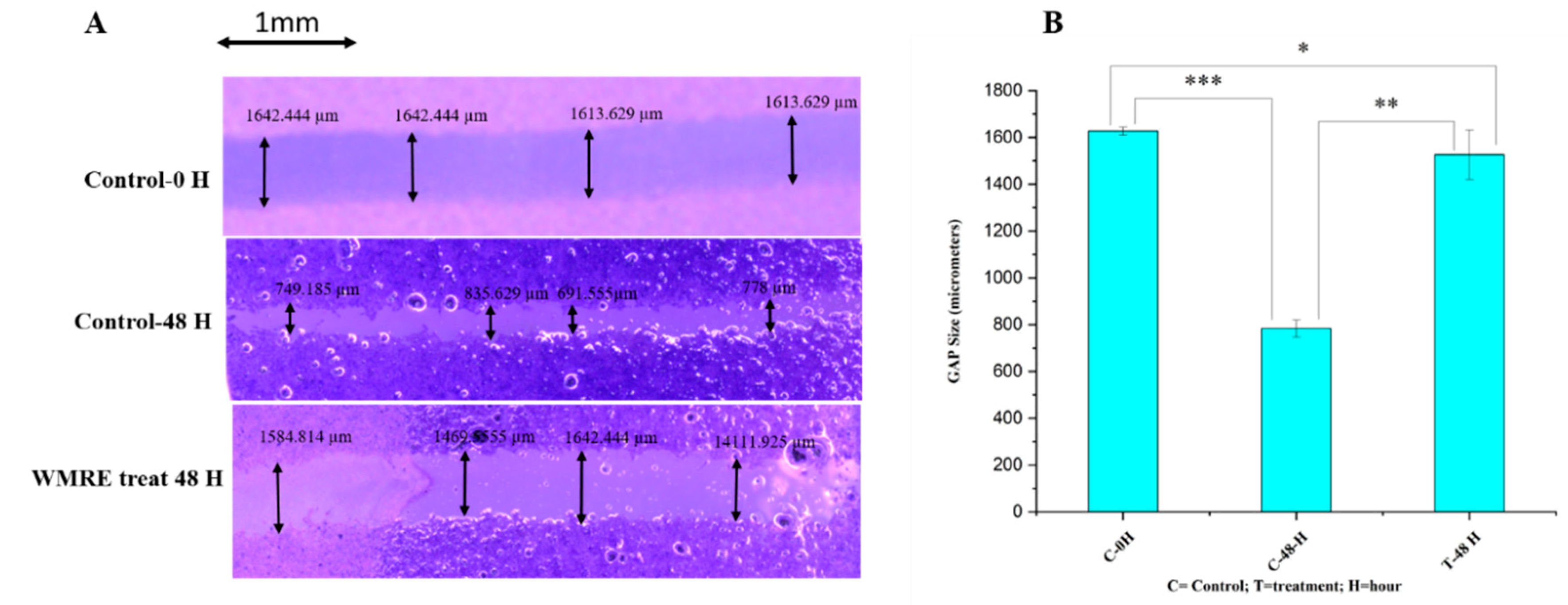
The effects of WRE on the progression and migration of HRAC-769-P cells were evaluated for 48 hrs. The wound in the control group was healed 48 hours after scratching a monolayer of cells. When cells were treated with WRE IC50, the wound healing of the scratched area was significantly delayed compared to untreated and WRE-treated cells (
Figure 4A). The WRE significantly decreased the wound closure by 93.14% (p < 0.00001) cells compared with that of the control group (
Figure 4B). In vitro cell migration analysis reveals metastatic potential. Cancer metastasis is the foremost reason for cancer death globally [
7,
14]. In our study, the WRE significantly inhibited cell migration and in HRAC-769-P cells. Therefore, WRE components may include potent anticancer agents in decreasing cancer metastasis.
2.5. RNAseq Assessment of Differentially Expressed Genes Between WRE-treated and Control Cells
A total of 26784649, 27470824, and 25,588,547 raw reads were generated from the control condition of HRAC-769-P cells, whereas 32424898, 27827568, and 31,744,771 reads were generated with WRE treatment (44.8 mg-ml-1), respectively. The raw reads were subjected to stringent quality filtering by using a trimmomatic tool, which resulted in 24702469, 25318621, 23597931, 29939262, 25713431, and 29,270,759 high-quality reads for control and treatment (44.8 mg), respectively. The Q30 percentage of reads in each library was >96%. The reads from the one controlled and two treatment conditions were aligned to the human reference genome (GRCh38.p13) using the STAR universal RNA sequence alignment tool with default parameters. 96.4, 96.3, 96.4, 96.5, 96.4, and 96.3 percent quality-filtered reads were mapped to the reference genomes for WRC and WRT44, respectively; ~3.6% of the reads remained unmapped (
Table 2).
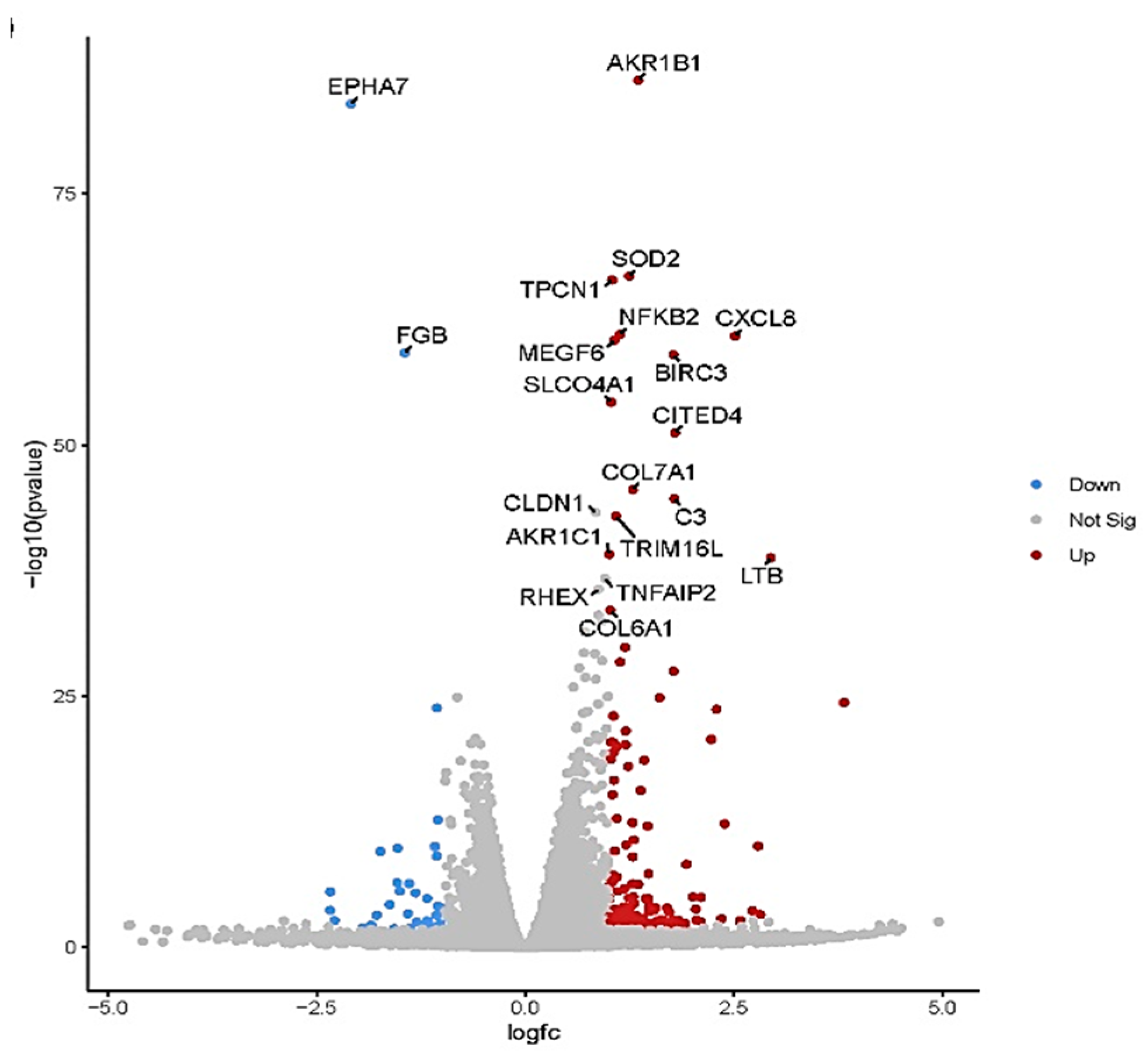
The volcano plot in (
Figure 5) shows each treatment's total up- and downregulated genes based on −log10 (p-value) and log2 fold change. It includes 149 upregulated and 37 downregulated genes. The top 10 up- and downregulated DEGs shared among the two treatments are presented in Supplementary
Table 1.
In total, 33 (up) and 24 (down) statistically significant differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified for WRET44.8 mg-ml-
1, that are known to be involved in tumor suppression and anti-cell proliferation (
Table 3).
2.6. Pathway Enrichment Analysis
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the DEGs from each ecotype showed different pathways enriched across the treatments. DEGs with WRE treatment revealed several enriched pathways such as NF-Kappa B Signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Leukocyte transendothelial migration, IL-17 signaling pathway, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Metabolic pathway, Calcium signaling pathway (Supplementary Figure. 1).
3. Discussion
3.1. Role of Nutraceutical Compounds
Watermelon, notably its rind, is rich in bioactive compounds like lycopene and L-citrulline, which are reported to exhibit antioxidant, anti-diabetic, and anticancer activities [
8]. Specifically, WRE has a high concentration of L-citrulline, an amino acid serving as a L-arginine precursor. L-citrulline is an important factor in nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, contributing to various physiological effects, including anticancer activities [
7,
15]. Our study corroborates these anti-proliferative effects and reveals a 22.29 µg/mg citrullin concentration in WRE as quantified by LC-MS.
3.2. Differential Impact on Apoptosis and Senescence
In the present study, we focused on elucidating the effects of watermelon rind extract (WRE) on various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, senescence, and global transcriptomic alterations in HRAC-769-P cells in vitro. Our findings predominantly indicate that WRE initiates apoptosis rather than senescence in these cells. The poly caspase FLICA probe, FAM-VAD-FMK, utilized in our study, is instrumental in detecting the early stages of apoptosis by identifying activated caspases. Conversely, senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-beta-gal) is an established marker for cell senescence [
16]. Our results showed that SA-beta-gal activity remained unchanged or decreased upon treatment with WRE, underscoring a limited role for senescence in this context. These findings confirm that apoptosis and senescence are exclusive cellular outcomes [
17].
3.3. The Intricacies of Nitric Oxide Signaling
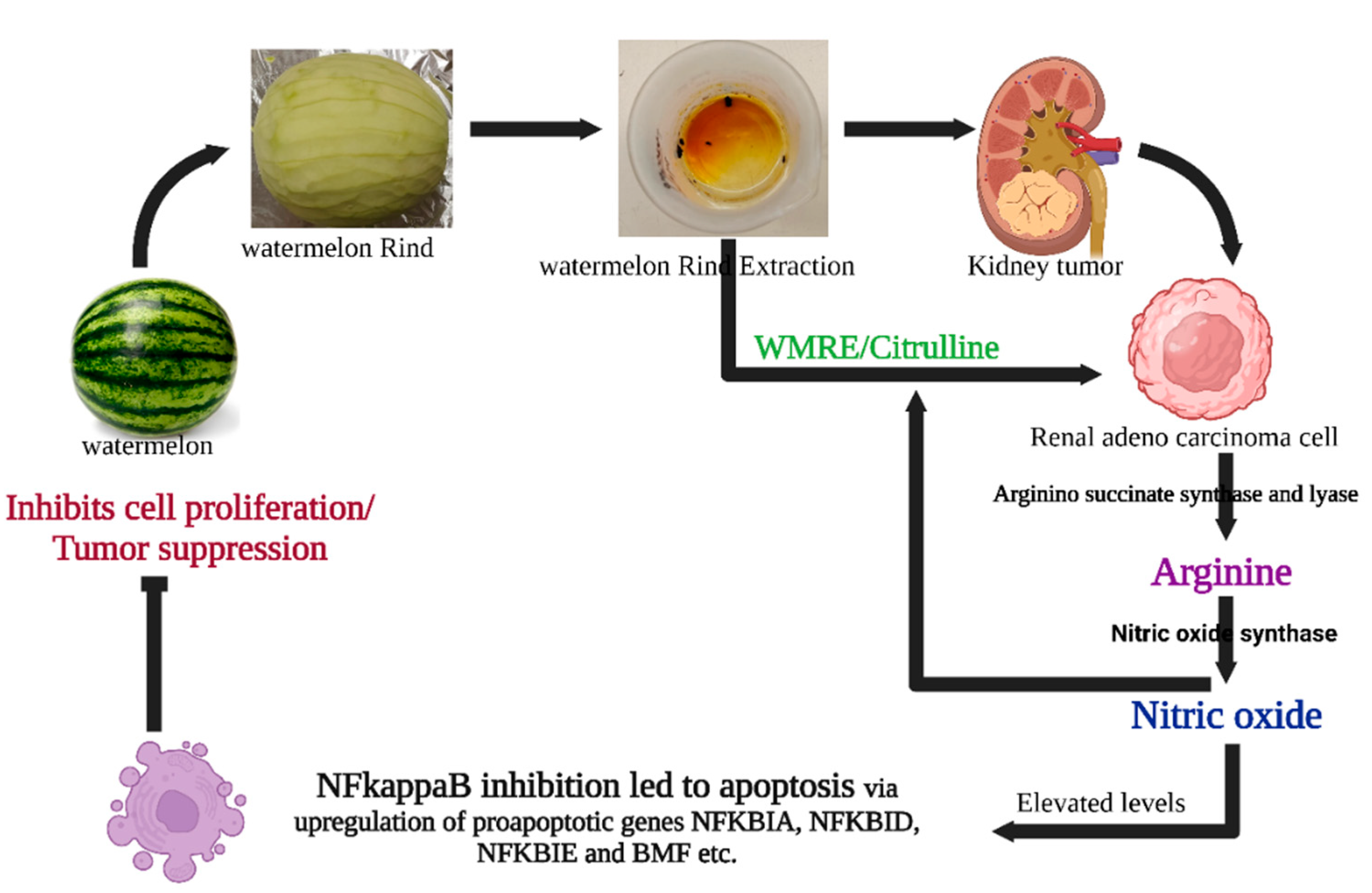
NO is a versatile signaling molecule that induces apoptosis in cancer cells through various mechanisms, including the caspase cascade [
18]. Additionally, NO can interact with reactive oxygen species (ROS) to produce peroxynitrite, which has been shown to inflict cellular damage and promote apoptosis [
19]. In our study, elevated citrulline levels could be postulated to enhance NO production, thereby triggering apoptosis in HRAC-769-P cells. However, the influence of NO in cellular mechanisms can be complex and context-dependent, necessitating further investigation. Apart from citrulline, alternative mechanisms might involve the inhibition of mitochondrial respiration, changes in cytochrome c levels, or suppression of anti-apoptotic genes like bcl-2. In summary, while our study establishes a promising link between WRE and induced apoptosis in HRAC-769-P cells, the precise mechanisms and the potential for therapeutic applications remain to be fully explored. The implications of citrulline and NO on different cancer types and cellular contexts also warrant comprehensive investigation.
3.4. Watermelon Rind Extract Modulates a Complex Network of Genes
Our study offers valuable insights into the transcriptomic landscape modulated by watermelon rind extract (WRE) in HRAC-769-P cells. The data illuminate how WRE affects various genes that could influence cell proliferation and apoptosis. This complexity underscores the necessity for a systems biology approach to understand the multifaceted gene networks regulated by WRE.
3.5. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Apoptotic Pathways
Apoptosis is a well-regulated process involving multiple pathways: the intrinsic (mitochondrial), extrinsic (death receptor), and perforin/granzyme pathways, all of which culminate in caspase-3 activation and cellular degradation [
20,
21,
22]. Our findings, precisely the differential expression of Bmf (Bcl-2-modifying factor) [
23] and NFKBIA [
24], suggest that WRE predominantly influences the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in HRAC-769-P cells.
3.6. Promising Effects of Upregulated Transcripts on Tumor Growth Inhibition
Our transcriptomic data align with existing studies that have identified genes like NPTX1, TRIM31, and CD82/KAI1 as potential therapeutic targets in various cancers [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. NPTX1 has been implicated in inhibiting tumor growth across multiple types of cancer, acting through distinct signaling pathways. Similarly, TRIM31 is a tumor suppressor gene in breast and ovarian cancer. ZC3H12A exhibits tumor-suppressive effects in colorectal cancer (CRC) by inducing apoptosis, inhibiting angiogenesis, and EMT signaling. Its expression is associated with chemokine ligands, indicating a potential role of immune response dysregulation in CRC development [
34]. Furthermore, MCPIP1, encoded by ZC3h12A-D, hinders cell migration and metastasis through TGF-β signaling inhibition [
35]. Linc00472 serves as a tumor suppressor in colorectal and pancreatic cancers. In colorectal cancer, it inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by releasing PDCD4 through miR-196a decoying. Linc00472 is a tumor suppressor in colorectal and pancreatic cancers [
36,
37]. Elevated levels of AATK1, RFN144A, βArr1, βArr2 KDF1 gene expression lead to various cancer cells inhibition [
38,
39,
40,
41,
42,
43].
3.7. Promising Effects of Downregulated Transcripts on Tumor Growth Inhibition
In addition to the upregulated transcripts, our study also sheds light on the significant downregulation of specific genes reported in various cancer forms. ENC1, SLAMF7 GREB1, EPHA7, CDH6, PKHD1, FBG, FLT3, ADAR2, and ANKRD1 are prominent in this category, suggesting their potential as therapeutic targets in various cancers [
44,
45,
46,
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62].
3.8. Multiple Gene Targets and Potential Therapeutic Avenues
Beyond the well-studied genes, our data indicated the potential roles of several other genes, including PAQR5, TRIM16, and ZC3H12A, in modulating cancer cell behavior [
34,
35,
63,
64,
65,
66]. These genes showed significant changes in expression upon WRE treatment, indicating their role in the anticancer effects of WRE. However, their specific anticancer mechanisms require further investigation.
3.9. NF-kappa B and TNF signaling pathway
NF-κB and TNF signaling pathways are pivotal in regulating immune responses, inflammation, and cellular processes [
67]. Our study suggests that WRE treatment in HRAC-769-P cells may influence these pathways, particularly the NF-κB pathway [
68,
69,
70,
71,
72], regulating chemokines, cytokines, and other signaling molecules, potentially leading to anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects.
Figure 6.
Possible mechanisms of WRE-mediated cell death in HRAC-769-P cells. WRE contains a high amount of citrulline and arginine. L-arginine is produced from L-citrulline to L-arginine by arginine succinate synthease and lyase. Meanwhile, cytokine-induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS or NOS2) converts arginine into nitric oxide while material is recycled. Nitric oxide can influence survival pathways in cancer cells, leading to a shift in the balance between cell survival and cell death signals in favor of apoptosis. WRE induces apoptosis by regulating the expression of critical genes involved in several cellular pathways, molecular mechanisms, and metabolism. Enzymatic assays and transcriptomic analysis suggested that WRE-induced apoptosis in HRAC-769-P cells was mediated through intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways and by inhibiting the NF Kappa B pathway and induction of BMF, suppressing anti-apoptotic genes.
Figure 6.
Possible mechanisms of WRE-mediated cell death in HRAC-769-P cells. WRE contains a high amount of citrulline and arginine. L-arginine is produced from L-citrulline to L-arginine by arginine succinate synthease and lyase. Meanwhile, cytokine-induced nitric oxide synthase (iNOS or NOS2) converts arginine into nitric oxide while material is recycled. Nitric oxide can influence survival pathways in cancer cells, leading to a shift in the balance between cell survival and cell death signals in favor of apoptosis. WRE induces apoptosis by regulating the expression of critical genes involved in several cellular pathways, molecular mechanisms, and metabolism. Enzymatic assays and transcriptomic analysis suggested that WRE-induced apoptosis in HRAC-769-P cells was mediated through intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways and by inhibiting the NF Kappa B pathway and induction of BMF, suppressing anti-apoptotic genes.
4. Material and methods
4.1 Plant Material and Extraction Process
A fresh fruit of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) was used in the study. The fruit rind or mesocarp was separated and dried. One kg of the dried rind was then finely powdered using a blender, and 100 grams of it was dissolved in 70% ethanol in four separate 500 mL aliquots. The derived mixture was filtered using a 0.22 µm bottle top filter (500 ml- CELLTREAT Scientific Products). The filtrate was subjected to evaporation at 50º C for a few hours to remove the ethanol. The extracted powder was initially dissolved in 0.1% ethanol, and the remaining volume was made up with water, sterilized by filtration, and preserved at -20ºC. The obtained samples were used for various biological and chemical investigations.
4.2. Chemical Characterization of Watermelon Rind Extract Using LC-MS
The phytoconstituents of WRE were identified using LC-MS. One ml methanol and 5 µl internal standard (4-Chloro-DL-phenylalanine, 25ug/mL) were added to the 100 mg WR sample. This was followed by vortexing for 1 min, centrifugation for 15 min at 20,000 rcf, and 100 µl of liquid fraction was transferred into a glass vial for subsequent analysis. For LC-MS metabolite profiling, a 5 µl sample was injected into the instrument. Samples were analyzed utilizing a Dionex Ultimate 3000 series UHPLC system (Thermo Scientific) with a Q-Exactive MS system (Thermo Scientific), as described previously [
73]. Metabolite assignments were made with citrulline as the target and also as an untargeted LC-MS metabolite profiling assay.
4.3. Cell culture
The HRAC-769-P cells (CRL-1933; American Type Cell Culture, Manassas, VA) were grown in cell culture T75 or T25 flasks (Greiner, Monroe, NC) using 10% FBS (Atlas, Biologicals, CO) containing RPMI-1640 media and 1% antibacterial-antimycotic solution (Gibco, Grand Island, NY). The cells were kept in a CO2 incubator at 37˚C with 90% humidity, using a gas mixture of 5% CO2 and 21% O2. When the cells reached around 90% confluence, the cells were sub-cultured by splitting them at ratios ranging from 1:4 to 1:12. To achieve this, a 0.25% Trypsin/0.53 mM EDTA solution in Hank's balanced salt solution (HBSS) without Ca2+ and Mg2+ (ATCC) was used for 10 min at 37ºC.
4.4. Treatments
Different concentrations of stock solutions of WRE were prepared in nuclease and microbial-free water, filter-sterilized, and stored at -20˚C. A stock media for various assays was prepared by adding RPMI-1640 media without phenol red (ATCC) along with FBS (10%), L-glutamine (0.3 g L-1; Gibco), and antibiotic-antimycotic solution (1%). The 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) was considered from dose–response curves using GraphPad Prism 8.4.2 (Supplementary Figure. 2). The IC50 value (88.6 mg ml-1) and another concentration, 44.8 mg ml-1, were combined with the stock media for assays. Corresponding controls were also prepared by mixing similar volumes with the stock media.
4.5. Cell proliferation assay
Cell proliferation was noted with the WST-8 cell proliferation assay kit (CCK8, Dojindo, Kumamoto, Kyushu, Japan) by using an orange fluorescent dye. WST-8 will be reduced by dehydrogenases abundant in viable cells and transformed to formazan, an orange-colored dye soluble in the culture medium. The amount of formazan dye produced by the activity of dehydrogenases in cells is directly correlated with the number of viable cells. Five hundred live cells were supplemented to each well, holding 100μL culture media in a 96-well flat black-bottomed plate (Greiner, Monroe, NC). After 24 hours of treatment, culture media was substituted with freshly prepared control or treatment media. Plates were collected by gently removing the culture media after 24, 48, and 72 hours of treatment and kept at -80˚C before further analysis. Plates were allowed to thaw for 0.5H at room temperature before starting the assay. In each well, 10μL of WST-8 (1x) solution was added and thoroughly mixed using a multichannel pipette. The absorbance was then measured at 450 nm (excitation/emission) using a microplate reader (SpectraMax iD3 Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (Molecular Devices, CA).
4.6. Poly caspase assay
The process of apoptosis was performed using the Poly caspase assay kit (FAM FLICA-ImmunoChemistry Technologies, Bloomington, MN). The probe FAM-VAD-FMK green fluorescent inhibitor binds to active cell caspase enzymes. Cells were grown in T25 flasks with phenol red-free media. Further cells were tested with different treatments when they reached 80% confluence. This study used staurosporine (6μM) (ImmunoChemistry Technologies) as a positive control. At various time intervals (0.5, 1, 2, and 4 h), floating cells were collected with media in a 15-mL centrifuge tube at 5000g for 5 min at room temperature. The supernatant was dispensed; cells were suspended with 600μL of 1x apoptosis wash buffer. Leftover adhered cells on the flask were spooled with trypsin and added to the cell suspension after removing the supernatant. The poly caspase inhibitor FAM-FLICA (1x) was added to the 500μL cell suspension and allowed for incubation at 37˚C for one hour with intermittent shaking. Simultaneously, some of the remaining cells were utilized to count cell numbers with a hemacytometer using trypan blue (0.04%). Subsequently to the incubation, cells were washed with 2mL of wash buffer, centrifuged, and the supernatant was eliminated. Following the washing step, the cells were incubated at 37˚C for 12 min to remove any excess FAM-FLICA reagent. Subsequently, the cells were collected through centrifugation, suspended in 500μl of wash buffer, and kept on ice. Ultimately,100μl of cell suspension was utilized for assessing poly-caspase activity in 96-well flat black bottom plates. The optical density (fluorescence) was measured in the microplate reader at 488/520nm (excitation/emission), and the resulting RFU (Relative Fluorescence Units) values were normalized.
4.7. SA-beta-gal assay
Senescence assay was carried out with SA-beta-gal activity with the 96-well cell senescence assay kit (Cell Biolabs, San Diego, CA). The procedure is almost similar to poly-caspase assay except for a few modifications. The activity readings were measured at 0.5, 1, and 2H. Following the cell collection, it was washed with PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) after the treatment. Subsequently, the cells were suspended in 400 μL of cell lysis buffer (1x) and kept on ice for 10 minutes. Further, the cell suspension was dissolved thoroughly by vertex, and 100 μl solution was taken out from this and frozen at -80˚C. Moreover, the leftover solution was utilized for the WST-8 cell proliferation assay. A 200μl solution was mixed with one volume of 2x reaction buffer containing SA-beta-gal substrate and grown at 37˚C for 60 minutes in the dark. The incubated solution was adequately mixed, and a 200 μl solution was combined with an 800μL stop solution. A 200 μl solution detected the SA-beta-gal activity in 96-well flat black-bottom plates. The optical density based on fluorescence was measured using a microplate reader at 360/465 nm (excitation/emission), and the resulting RFU (Relative Fluorescence Units) values were normalized or standardized to those obtained from the WST-8 cell proliferation assay.
4.8. Wound healing assay
The wound healing assay evaluated the effects of cell migration inhibition and metastasis. HRAC-769-P cells were cultured in 6-well plates until reaching 80-90% confluence. Subsequently, uniform scratches/wounds were created in each well using a 20-μL pipette tip. Afterward, the cells were carefully washed with sterile PBS to remove debris and treated with the WRE. The progress of wound closure was observed immediately (0 h) and after 48 h using an inverted microscope (DFC290, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Cells were stained with equal volumes
of 1% toluidine blue and 1% borax (LabChem Inc, PA) for photography. The experiments were conducted in triplicate to ensure reliability and reproducibility, as described by [
74].
4.9. RNA isolation and RNA-Seq library preparation
Total ribonucleic acid of control and treatment was extracted from the tissues of biological replicates using RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (QIAGEN). The RNA's quality and quantity were assessed using bioanalyzer the Agilent 2100 and Qubit 4 Fluorometer (Invitrogen, USA), respectively. The RNA sequencing libraries were developed using the NEBNext Ultra™ II RNA Library Prep Kit, following the manufacturer's protocol provided by NEB, USA. The mRNAs were enriched using Oligo (dT) beads, and subsequently, they were fragmented into shorter fragments using fragmentation buffer. The first-strand cDNA was synthesized from the fragmented mRNA using random hexamer primers and later converted into double-strand cDNA. The resulting double-strand cDNAs were end-repaired and added with Illumina sequencing adapters. The adapter-ligated libraries were amplified using sequencing primers for the enrichment. The library's quality and insert size were determined using a bioanalyzer (Invitrogen, USA), and the library was estimated using a Qubit fluorometer (Invitrogen, USA). The library was diluted to 4nM concentration and sequenced using Illumina's NextSeq 500 platform with paired-end sequencing chemistry. The resulting image files in the BCL format were converted to FASTQ with 2 × 150 bp reads using the bcl2fastq tool (Illumina, USA).
4.10. RNA-Seq analysis
In the analysis, sequencing adapters and low-quality reads (Phred score QV<30) were removed using Trimmomatic [
75]. The quality-filtered reads were then mapped to the Human (GRCh38.p13) reference genome (
https://www.gencodegenes.org/human/) using STAR RNA-Seq aligner [
76] to produce BAM alignment. A read count table was created from the BAM alignment file and genome annotation in GFF format using the HTSeq R package [
77]. Differential gene expression (DEG) analysis was carried out using DESeq2 [78], filtering DEGs based on a minimum log2FoldChange of 1 and a false discovery rate (FDR) of 0.05. Pathway Enrichment analyses were conducted using KOBAS. Gene Network analysis was done using Cytoscape and the STRING database.
5. Conclusions
Our study reveals that watermelon rind extract (WRE) holds high proportions of nutraceutical components and amino acid derivatives like citrulline and arginine. It demonstrates a dose- and time-dependent reduction in HRAC-769-P cell proliferation in vitro. The decrease in cell proliferation is primarily attributed to apoptosis, supported by upregulation of early poly-caspase activities and either normal or suppressed SA-beta-gal activity. Transcriptomic analyses suggest that the apoptotic effects may be mediated through both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways involving various key genes and molecular mechanisms. While our study presents a detailed overview, further in-depth research is required to validate these findings and explore clinical applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
UR: PN and GRH conceptualized the study. SC conducted experiments, SC and PUN performed data analysis, SC and UR drafted the manuscript, UR, PN, GRH, and PUN edited the manuscript.
Funding
USDA-NIFA CONTRACT/GRANT/AGREEMENT NO: 2022-38821-37343 and 2023-38821-39586.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Perla, V.; Nadimi, M.; Reddy, R.; Hankins, G.R.; Nimmakayala, P.; Harris, R.T.; Valluri, J.; Sirbu, C.; Reddy, U.K.; Effect of ghost pepper on cell proliferation, apoptosis, senescence and global proteomic profile in human renal adenocarcinoma cells. PloS one 2018, 31, 13, 10, 1e0206183. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. 2021, Cancer statistics, 2021. Ca Cancer J Clin, 71, 1, pp.7-33.
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 2023, 73, 1, 17-48.
- Nurgali, K.; Jagoe, R.T. Abalo, R. Editorial: Adverse effects of cancer chemotherapy: Anything new to improve tolerance and reduce sequelae? Front. Pharmacol 2018, 9, 245.
- Donaldson, Michael. S.; Nutrition and cancer: a review of the evidence for an anticancer diet. Nutrition journal 2004 3, 1, 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lu, J.J.; Ding, J. Natural Products in Cancer Therapy: Past, Present and Future. Nat. Products Bioprospect 2021, 11, 5–13. [CrossRef]
- El Gizawy, H.A.; El-Haddad, A. E., Attia, Y. M.; Fahim, S.A.; Zafer, M.M. Saadeldeen AM. In Vitro Cytotoxic Activity and Phytochemical Characterization (UPLC/T-TOF-MS/MS) of the Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) Rind Extract. Molecules 2022, 12, 27, 8, 2480. [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, A.; Lee, E.S.; Han. K.; Lee, H.E.; Kim, D.S. Versatile nutraceutical potentials of watermelon—A modest fruit loaded with pharmaceutically valuable phytochemicals. Molecules 2020, 11, 25, 22, 5258. [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G. M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman DJ. Impact of natural products on developing new anticancer agents. Chemical reviews 2009 8, 109, 7, 3012-43. [CrossRef]
- Al-Sayed, H.M.A.; Ahmed, A.R. Utilization of watermelon rinds and sharlyn melon peels as a natural source of dietary fiber and antioxidants in cake. Ann Agri. Sci 2013, 58, 83–95. [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, M.; Sultana, B.; Bhatti, H.N.; Asghar, M. RSM based optimized enzyme-assisted extraction of antioxidant phenolics from underutilized watermelon (Citrullus lanatus Thunb.) rind. J Food Sci Technol 2015, 52, 5048–5056. [CrossRef]
- Zamuz, S.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Gullón, B.; Rocchetti, G.; Montesano, D.; Lorenzo, J.M. Citrullus lanatus as source of bioactive components: An up-to-date review. Trends Food Sci. Technol 2021, 111, 208–222. [CrossRef]
- Rimando, Agnes, M., and Penelope, M. Perkins-Veazie. Determination of citrulline in watermelon rind. Journal of Chromatography A 2005, 1078, 1-2, 96-200. [CrossRef]
- Dillekås, H.; Rogers, M.S.; Straume, O. Are 90% of deaths from cancer caused by metastases? Cancer Med 2019, 8, 5574. [CrossRef]
- Fesseha, Meseret.; and Mee, Young, Hong. Effects of Watermelon Consumption on Cellular Proliferation, and Apoptosis in Rat Colon (P05-019-19). Current Developments in Nutrition 2019 3, nzz030-P05. [CrossRef]
- Itahana K, Campisi J, Dimri GP. Methods to detect biomarkers of cellular senescence: the senescenceassociatedβ-galactosidase assay. Biological Aging: Methods and Protocols. 2007:21–31. [CrossRef]
- Campisi, Judith.; and Fabrizio, d'Adda di Fagagna. Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2007, 8, 9, 729-740. [CrossRef]
- Mintz, Joel.; Anastasia, Vedenko.; Omar, Rosete.; Khushi, Shah.; Gabriella, Goldstein.; Joshua, M.; Hare, Ranjith Ramasamy.; and Himanshu, Arora. Current advances of nitric oxide in cancer and anticancer therapeutics. Vaccines 2021, 9, 2, 94. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Hyewon, and Navdeep, S. Chandel. Reactive oxygen species and cancer. In Oxidative Stress 2020, 619-637. Academic Press.
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicologic pathology 2007, 35, 4, 495–516. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R. A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. cell 2011; 144, 5, 646–74. [CrossRef]
- Vogler, M.; Dinsdale, D.; Dyer, M.J.; Cohen, G.M.; Bcl-2 inhibitors: small molecules with a big impact on cancer therapy. Cell Death and Differentiation 2009, 16, 3, 360–7. [CrossRef]
- Grespi, Francesca.; Claudia, Soratroi.; Gerhard, Krumschnabel.; Benedicte, Sohm.; Christian, Ploner.; Stephan, Geley.; Ludger, Hengst.; Georg, Häcker.; Andreas, Villunger. BH3-only protein Bmf mediates apoptosis upon inhibition of CAP-dependent protein synthesis. Cell Death and Differentiation 2010, 17, 11, 1672-1683. [CrossRef]
- Yan, W., Huang, J., Zhang, Q., & Zhang, J. (2021). Role of Metastasis Suppressor KAI1/CD82 in Different Cancers. Journal of Oncology, 2021, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Xiaofeng.; Kangming, Pan.; Wenli, Zhao.; Jianzhu, Zhang.; Shicheng, Yuan.; Xiang, Wen.; Wenquan, Zhou.; Zhijin, Yu. NPTX1 inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation through down-regulating cyclin A2 and CDK2 expression. Cell biology international 2018, 42, 5, 589-597. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Yue.; Yaqi, Yu.; Wenxiu, Zhao.; Song, You.; Min, Feng.; Chengrong, Xie.; Xiaoqin, Chi.; Yi, Zhang.; Xiaomin, Wang. As a downstream target of the AKT pathway, NPTX1 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioscience reports 2019, 39, 6. [CrossRef]
- Su, Xiaotong.; Jutong, Su.; Hua, He.; Yong, Zhan.; Haichao, Liu. Hsa_circ_0070269 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-182/NPTX1 axis. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2019, 120, 109497. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Jing.; Gaifang, Liu.; Kang, An.; Linping, Shi. NPTX1 inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity by targeting RBM10. Oncology Letters, 2022, 23, 5, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Huo, Leiming.; Bin, Wang.; Maohua, Zheng.; Yonghong, Zhang.; Jiguang, Xu.; Gang, Yang.; Quanlin, Guan. miR-128-3p inhibits glioma cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting NPTX1 through IRS-1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Experimental and therapeutic medicine 2019, 17, 4, 2921-2930. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Yafei.; Qin, Li.; Gang, Zhao.; Jie, Zhang.; Hang, Yuan.; Tianyu, Feng.; Deqiong, Ou. Loss of TRIM31 promotes breast cancer progression through regulating K48-and K63-linked ubiquitination of p53. Cell death & disease 2021, 12, 10, 945. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Zhentong.; Yan, Liu.; Yishu, Wang.; Yandong, Zhang.; Qinghua, Luo.; Xiaxia, Man.; Feng, Wei.; Xiaowei, Yu. Downregulation of Foxo3 and TRIM31 by miR-551b in side population promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and drug resistance of ovarian cancer. Medical oncology 2016, 33, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Viera, M.; Yip, G.S.; Shen, H.; Baeg, G.H.; Bay, B. Targeting CD82/KAI1 for Precision Therapeutics in Surmounting Metastatic Potential in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 2021 13, 17, 4486. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liang, C.; Hua, Y.; Miao, C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, A.; Zhao, K.; Liu, S.; Tian, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Su, S.; Qin, C.; Wang, Z. (2017). The metastasis suppressor CD82/KAI1 regulates cell migration and invasion via inhibiting TGF-β 1/Smad signaling in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget, 2017, 8, 31, 51559–51568. [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Du, D.; Chen, J.; Zhou, P.; Weinstein, J.N.; Yao, L.; Liu, Y. ZC3H12A Expression in Different Stages of Colorectal Cancer. Oncoscience, 2019, 6, 3–4, 301–311. [CrossRef]
- Miekus, K.; Kotlinowski, J.; Lichawska-Cieslar, A.; Rys, J.; Jura, J. Activity of MCPIP1 RNase in tumor associated processes. Clinical Cancer Research 2019, 38, 1. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Yafei.; Shengnan, Yang.; Yanping, Han.; Jingjing, Sun.; Lijuan, Xv.; Lina, Wu.; Yongfeng, Wang.; Liang, Ming. Linc00472 suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis through elevating PDCD4 expression by sponging miR-196a in colorectal cancer. Aging (Albany NY) 2018, 10, 6,1523.
- Bi, Cong.; Gang, Wang. LINC00472 suppressed by ZEB1 regulates the miR-23a-3p/FOXO3/BID axis to inhibit the progression of pancreatic cancer. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 2021, 25, 17, 8312-8328.
- Ma, Shuang.; Brian, P. Rubin. Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase 1 inhibits growth and migration and promotes apoptosis in melanoma. Laboratory investigation 2014, 94, 4, 430-438.
- Yang, Yin-Long.; Ye, Zhang.; Dou-Dou, Li.; Fang-Lin, Zhang.; Hong-Yi, Liu.; Xiao-Hong, Liao.; Hong-Yan.; Xie. RNF144A functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer through ubiquitin ligase activity-dependent regulation of stability and oncogenic functions of HSPA2. Cell Death and Differentiation 2020 27, 3,105-1118.
- Bostanabad, S. Yari.; Senem, Noyan.; Bala, G. Dedeoglu.; Hakan, Gurdal. Overexpression of β-Arrestins inhibits proliferation and motility in triple negative breast cancer cells. Scientific reports 2021, 11, 1, 1539.
- Peng, Yang.; Han, Li.; Yong, Fu.; Shipeng, Guo.; Chi, Qu.; Yingzi, Zhang.; Beige, Zong.; Shengchun Liu. JAM2 predicts a good prognosis and inhibits invasion and migration by suppressing EMT pathway in breast cancer. International immunopharmacology 2022, 103, 108430.
- Zheng, Jing-min.; Mei-Fu, Gan.; Hong-yuan, Yu.; Lu-xia, Ye.; Qing-xin, Yu.; Yu-Hui, Xia.; Han-xi, Zhou.; Jia-qian, Bao.; Yi-qing, Guo. KDF1, a novel tumor suppressor in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology 2021,11, 686678.
- Cui, Ying.; Corrigendum: Enc1 Facilitates Colorectal Carcinoma Tumorigenesis and Metastasis via JAK2/STAT5/Akt Axis-Mediated Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology, 2021, 9. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Haoyu.; Dawei, Liu.; Zhipeng, Li. Expression and clinical significance of ENC1 in gastrointestinal tumors: Bioinformatics analysis based on a public gene database. Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology 2023, 14, 2, 824.
- Malaer, Joseph, D. 2B4 (CD244, Slamf4) and CS1 (CD319, Slamf7) in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Cancer. Clinical Immunology 2019, 204, 50–56. [CrossRef]
- O'Connell, Patrick.; Sean, Hyslop.; Maja, K. Blake.; Sarah, Godbehere.; Andrea, Amalfitano.; Yasser, A. Aldhamen. SLAMF7 signaling reprograms T cells toward exhaustion in the tumor microenvironment. The Journal of Immunology 2021, 206, 1, 193-205.
- Cheng, Meng.; Stephanie, Michalski.; and Ramakrishna, Kommagani. Role for growth regulation by estrogen in breast cancer 1 (GREB1) in hormone-dependent cancers. International journal of molecular sciences 2018, 19, 9, 2543.
- Rae, J.M.; Michael, D.J.; Kevin, E., C.; Joshua, O.; José, M.L.; Marco M. G.; Kenneth, J.P.; Marc, E.L. GREB1 is a novel androgen-regulated gene required for prostate cancer growth. The Prostate 2006, 66, 8, 886-894.
- Guo, Y.; Shi, W.; Fang, R. miR-18a-5p promotes melanoma cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis and autophagy by targeting EPHA7 signaling. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2021, 23, 1, 1-1. [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, M.; Mori, H.; Bunai, T.; Kageyama, S.; Suzuki, M.; Okudela, K.; Takamochi, K.; Ogawa, H.; Niwa, H.; Shinmura, K.; Shinmura, K. Secreted form of EphA7 in lung cancer. Int J Oncol 2010, 36, 635-640. [CrossRef]
- Bartolomé, R.A.; Javier, Robles.; Ángela, Martin-Regalado.; Laura, Pintado-Berninches.; Miranda, Burdiel.; Marta, Jaén.; Carmen, Aizpurúa.; Juan, I.; Imbaud.; José Ignacio Casal. CDH6-activated αIIbβ3 crosstalks with α2β1 to trigger cellular adhesion and invasion in metastatic ovarian and renal cancers. Molecular Oncology, 2021, 15, 7, 1849-1865.
- Zhao, Zongxian.; Shuliang, Li.; Shilong, Li.; Jun, Wang.; Hai, Lin.; Weihua, Fu. High expression of oncogene cadherin-6 correlates with tumor progression and a poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell International 2021, 21,1, 1-9.
- Gugnoni, M.; Sancisi, V.; Gandolfi, G.; Manzotti, G.; Ragazzi, M.; Giordano, D.; Tamagnini, I.; Tigano, M.; Frasoldati, A.; Piana, S.; Ciarrocchi, A. Cadherin-6 promotes EMT and cancer metastasis by restraining autophagy. Oncogene, 2017 36, 5, 667-677. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, W.; Kayed, H.; Zheng, P.; Giese, N.A.; Friess, H.; Kleeff, J. Loss of ONECUT1 expression in human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncology reports, 2008, 19, 1, 157-163. [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.J.; Wu, Y.; Johnson, R.A.; Woollard, J.R.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Cicek, M.S.; Bakeberg, J.; Rossetti, S.; Heyer, C.M.; Petersen, G.M.; Lindor, N.M. 2011. Germline PKHD1 mutations are protective against colorectal cancer. Human genetics, 2011, 129, pp.345-349. [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk, B.J.; Simpson-Haidaris, P.J. 2000. Fibrinogen assembly, secretion, and deposition into extracellular matrix by MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Cancer research, 2000, 60, 7, 2033-2039.85.
- Knight, T.E.; Edwards, H.; Meshinchi, S.; Taub, J.W.; Ge, Y. FLipping the story: FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia and the evolving role of FLT3 inhibitors. Cancers, 2022, 14, 14, 3398. [CrossRef]
- Stirewalt, D.; Radich, J; The role of FLT3 in haematopoietic malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer 2003, 3, 650–665. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, B.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Dock2 in the development of inflammation and cancer. European journal of immunology, 2018, 48, 6, 915-922. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Yu.; Xiaoyuan, Yang.; Yalei, Cui.; Xiaobo Zhang. Suppression of RNA editing by miR-17 inhibits the stemness of melanoma stem cells. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids 2022, 27, 439-455.
- Lei, Y.; Henderson, B.R.; Emmanuel, C.; Harnett, P.R.; DeFazio, A. Inhibition of ANKRD1 sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis. Oncogene, 2015, 34, 4, 485-495. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Lu.; Yangyang, Yue.; Lu, Zhang.; Minxuan, Jing.; Minghai, Ma.; Chao, Liu.; Yan, Li. PAQR5 inhibits the growth and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by suppressing the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Cellular Oncology 2023, 1-16.
- Tao, Chang.; Wang, Liu.; Xiang, Yan.; Min, Yang.; Si, Yao.; Qiang, Shu.; Benyi, Li.; Runzhi Zhu. PAQR5 Expression is suppressed by TGFβ1 and associated with a poor survival outcome in renal clear cell carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022, 11, 827344.
- Ruan, L.; Liu, W.; Yang, Y.; Chu, Z.; Yang, C.; Yang, T.; Sun, J. TRIM16 overexpression inhibits the metastasis of colorectal cancer through mediating Snail degradation. Experimental Cell Research 2021, 406, 1, 112735. [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.M.; Bell, J.F.; Koach, J.; Tan, O.; Kim, P.Y.; Malyukova, A.; Thomas, W.K.; Sekyere, E.; Liu, T.; Cunningham, A.; Tobias, V.; Norris, M.D.; Haber, M.; Kavallaris, M.; Cheung, B.B. (2010). TRIM16 acts as a tumour suppressor by inhibitory effects on cytoplasmic vimentin and nuclear E2F1 in neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 46, 6172–6183. [CrossRef]
- Albensi.; Benedict C. What is nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) doing in and to the mitochondrion. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 2019, 7, 154.
- Zinatizadeh, M.R.; Schock, B.; Chalbatani, G.M.; Zarandi, P.K.; Jalali, S.A.; Miri, S.R. The Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-kB) signaling in cancer development and immune diseases. Genes and diseases, 2021, 8, 3, 287-297.
- González, Raúl.; Francisco, J.; Molina-Ruiz, J.; Antonio Bárcena, C.; Alicia, Padilla.; and Jordi, Muntané. Regulation of cell survival, apoptosis, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by nitric oxide-dependent post-translational modifications. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling 2018, 29, 13, 1312-1332.
- Della-Valle, V.; Roos-Weil, D.; Scourzic, L.; Mouly, E.; Aid, Z.; Darwiche, W.; Lécluse, Y.; Damm, F.; Mémet, S.; Mercher, T.; Aoufouchi, S.; Nguyen-Khac, F.; Bernard, O.; Ghamlouch, H. Nfkbie-deficiency leads to increased susceptibility to develop B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders in aged mice. Blood Cancer Journal 2020 10(3). [CrossRef]
- Olson, S.Y. and Garbán, H.J. Regulation of apoptosis-related genes by nitric oxide in cancer. Nitric Oxide 2008,19, 2, 170-176. [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; Cao, D. Role of the NFκB-signaling pathway in cancer. OncoTargets and therapy 2018, 2063-2073.
- Bonini, P.; Kind, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Retip: Retention Time Prediction for CompoundAnnotation in Untargeted Metabolomics. Anal Chem, 2020, 2, 92, 11, 7515-7522. [CrossRef]
- Stamm, A.; Reimers, K.; Strauß, S.; Vogt, P.; Scheper, T.; Pepelanova, I. In vitro wound healing assays—State of the art. BioNano-Materials 2016, 17, 79–87.
- Bolger, A.; Giorgi, F. Trimmomatic: a flexible read trimming tool for illumina NGS data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114-2120.
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15-21. [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166-169. [CrossRef]
- Love, M.; Anders, S.; and Huber, W. Differential analysis of count data–the DESeq2 package. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 10.1186.
Figure 1.
Effect of watermelon rind extract on HRAC-769-P cell proliferation. Percentage of cells at 24, 48, 72 hrs with various concentrations of WRE (mg ml−1). Control (media without any treatment compound) is adjusted to 100%. Values are means ± SD; n = 6; *p < 0.05 and * * p < 0.01 * * *p < 0.001 (as compared to control).
Figure 1.
Effect of watermelon rind extract on HRAC-769-P cell proliferation. Percentage of cells at 24, 48, 72 hrs with various concentrations of WRE (mg ml−1). Control (media without any treatment compound) is adjusted to 100%. Values are means ± SD; n = 6; *p < 0.05 and * * p < 0.01 * * *p < 0.001 (as compared to control).
Figure 2.
Cellular poly caspase activity in HRAC-769-P cells at 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 hrs. Control-1 contained culture media. Control-2 contained culture media with 0.96% ethanol. Control (+ve) contained staurosporine (6 μM). 44.8 and 88.6 (mg-ml−1) mg of WRE treatment. Values are means ± SD; n = 6; *p < 0.05 and * * p < 0.01 * * *p < 0.001 (as compared to control).
Figure 2.
Cellular poly caspase activity in HRAC-769-P cells at 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 hrs. Control-1 contained culture media. Control-2 contained culture media with 0.96% ethanol. Control (+ve) contained staurosporine (6 μM). 44.8 and 88.6 (mg-ml−1) mg of WRE treatment. Values are means ± SD; n = 6; *p < 0.05 and * * p < 0.01 * * *p < 0.001 (as compared to control).
Figure 3.
SA-beta-gal activity in HRAC-769-P cells at 0.5, 1, and 2 hrs. Control-1 contained culture media. Control-2 contained 0.96% ethanol. Control-2 was a corresponding control for WRE 44.8 and 88.6 mg ml−1 treatments. SA-beta-gal activities were normalized with relative fluorescence unit (RFU) values obtained with CyQUANT cell proliferation assay. Values are mean ± SD; n = 4; *p < 0.05 and * * p < 0.01 * * *p < 0.001 (as compared to control).
Figure 3.
SA-beta-gal activity in HRAC-769-P cells at 0.5, 1, and 2 hrs. Control-1 contained culture media. Control-2 contained 0.96% ethanol. Control-2 was a corresponding control for WRE 44.8 and 88.6 mg ml−1 treatments. SA-beta-gal activities were normalized with relative fluorescence unit (RFU) values obtained with CyQUANT cell proliferation assay. Values are mean ± SD; n = 4; *p < 0.05 and * * p < 0.01 * * *p < 0.001 (as compared to control).
Figure 4.
Effect of WRE (88.6 mg-ml−1) on cell migration in cells (A). Scratching was done with a 20-µL pipette tip. Quantitative representation of the migration of kidney cancer cells by the wound healing assay. B. The data was presented as the mean and standard deviation. The one-way ANOVA test was used to examine statistical differences. * Significant at p < 0.05, ** significant at p < 0.001, *** significant at p < 0.0001.
Figure 4.
Effect of WRE (88.6 mg-ml−1) on cell migration in cells (A). Scratching was done with a 20-µL pipette tip. Quantitative representation of the migration of kidney cancer cells by the wound healing assay. B. The data was presented as the mean and standard deviation. The one-way ANOVA test was used to examine statistical differences. * Significant at p < 0.05, ** significant at p < 0.001, *** significant at p < 0.0001.
Figure 5.
Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The volcano plots from control vs. treatment conditions 44.8 mg ml−1. The volcano plot illustrates the association between the fold change (log2) and statistical significance (-log10(p-value)) of DEGs. The log2 fold change is represented along the x-axis, with upregulated genes to the right and downregulated genes to the left. The y-axis represents the -log10(p-value), with more significant DEGs at the top of the graph. Points on the graph represent individual genes, with color-coding indicating the significance level and fold change: red points represent significantly upregulated genes, blue points represent significantly downregulated genes, and gray points represent non-significant genes.
Figure 5.
Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The volcano plots from control vs. treatment conditions 44.8 mg ml−1. The volcano plot illustrates the association between the fold change (log2) and statistical significance (-log10(p-value)) of DEGs. The log2 fold change is represented along the x-axis, with upregulated genes to the right and downregulated genes to the left. The y-axis represents the -log10(p-value), with more significant DEGs at the top of the graph. Points on the graph represent individual genes, with color-coding indicating the significance level and fold change: red points represent significantly upregulated genes, blue points represent significantly downregulated genes, and gray points represent non-significant genes.
Table 1.
Tentatively identified metabolites via LC-MS from watermelon rind aqueous extract using negative ionization mode. Rt: retention time.
Table 1.
Tentatively identified metabolites via LC-MS from watermelon rind aqueous extract using negative ionization mode. Rt: retention time.
| S. No |
Proposed Compounds |
Formula |
Rt [M-H] |
Peak Area |
| |
Amino acid derivatives |
| 1 |
4-Methyleneglutamine |
C6 H10 N2 O3 |
0.877 |
2360952958 |
| 2 |
D-(+)-Pyroglutamic Acid |
C5 H7 N O3 |
1.901 |
816414433.5 |
| 3 |
(2S)-3-(1H-Imidazol-4-yl) |
C12 H19 N3 O7 |
1.709 |
601125246 |
| 4 |
DL-Arginine |
C6 H14 N4 O2 |
0.85 |
549758768 |
| 5 |
DL-Histidine |
C6 H9 N3 O2 |
0.851 |
432774848.5 |
| 6 |
DL-Arginine |
C6 H14 N4 O2 |
0.85 |
549758768 |
| 7 |
Ornithine |
C5 H12 N2 O2 |
0.882 |
260397275 |
| 8 |
D-(-)-Glutamine |
C5 H10 N2 O3 |
9.389 |
249168133.5 |
| 9 |
N-Acetyl-L-Citrulline |
C8 H15 N3 O4 |
0.911 |
13964667.5 |
| 10 |
L-(+)-Citrulline |
C6 H13 N3 O3 |
3.383 |
10651743 |
| 11 |
Isoleucine |
C6 H13 N O2 |
2.54 |
244248729 |
| 12 |
L-Phenylalanine |
C9 H11 N O2 |
3.718 |
133133714 |
| 13 |
L-Glutamic acid, 5-[2-(4-carboxyphenyl)hydrazide] |
C12 H15 N3 O5 |
1.71 |
149760416 |
| 14 |
L-(+)-Lactic acid |
C3 H6 O3 |
10.516 |
89115500 |
| 15 |
D-PANTOTHENIC ACID |
C9 H17 N O5 |
3.845 |
143296593.5 |
| 16 |
Valine |
C5 H11 N O2 |
0.996 |
143149592 |
| 17 |
L-Histidine |
C6 H9 N3 O2 |
0.837 |
18285235.5 |
| 18 |
(2S)-2-Piperazinecarboxylic acid |
C5 H10 N2 O2 |
2.65 |
29609897.5 |
| 19 |
N-Acetylglucosaminitol |
C8 H17 N O6 |
0.858 |
23771288.5 |
| 20 |
N-Acetyl-L-glutamic acid |
C7 H11 N O5 |
1.983 |
22064841.5 |
| |
Acetylcarnitine |
C9 H17 N O4 |
8.78 |
21886355.5 |
| 21 |
N-Acetyl-L-phenylalanine |
C11 H13 N O3 |
5.26 |
5322091 |
| 22 |
organic derivatives |
| 23 |
DL-Malic acid |
C4 H6 O5 |
0.98 |
3630710449 |
| 24 |
Isocitric acid |
C6 H8 O7 |
1.822 |
1381987018 |
| 25 |
D-(+)-Pyroglutamic Acid |
C5 H7 N O3 |
1.901 |
816414433.5 |
| 26 |
Anthranilic acid |
C7 H7 N O2 |
0.912 |
651974104 |
| 27 |
2-(alpha-D-mannosyl)-D-glyceric acid |
C9 H16 O9 |
9.792 |
271529954.5 |
| 28 |
2-Formyl-1H-pyrrole |
C5 H5 N O |
0.879 |
261140066.5 |
| 29 |
2-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-4,5,6,7-tetramethyl-1H-benzimidazole |
C18 H18 N2 O2 |
8.301 |
86427528 |
| 30 |
Gluconic acid |
C6 H12 O7 |
0.881 |
219928281.5 |
| 31 |
2-Furoic acid |
C5 H4 O3 |
1.433 |
136738393.5 |
| 32 |
Citric acid |
C6 H8 O7 |
1.822 |
1381987018 |
| 33 |
Glutarylcarnitine |
C12 H21 N O6 |
2.963 |
209483451.5 |
| 34 |
Benzyl ë?-primeveroside |
C18 H26 O10 |
4.177 |
170786527 |
| 35 |
Glucoheptonic Acid |
C7 H14 O8 |
8.76 |
43076366 |
| 36 |
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid |
C7 H6 O3 |
4.279 |
42979188 |
| 37 |
Succinic anhydride |
C4 H4 O3 |
2.332 |
33805020.5 |
| 38 |
Itaconic acid |
C5 H6 O4 |
1.451 |
24903345.5 |
| 39 |
Mesaconic acid |
C5 H6 O4 |
1.824 |
28480332 |
| 40 |
Sorbic acid |
C6 H8 O2 |
0.974 |
27447509.5 |
| 41 |
Malondialdehyde |
C3 H4 O2 |
0.859 |
21556194.5 |
| 42 |
2,6-Dimethoxybenzoquinone |
C8 H8 O4 |
0.894 |
32512334 |
| 43 |
Acetonedicarboxylic Acid |
C5 H6 O5 |
|
|
| 44 |
6-Oxo-pipecolinic acid |
C6 H9 N O3 |
1.702 |
23925387 |
| 45 |
N-Acetyl-L-glutamic acid |
C7 H11 N O5 |
1.983 |
22064841.5 |
| 46 |
Acetylcarnitine |
C9 H17 N O4 |
8.78 |
21886355.5 |
| 47 |
Mevalonic acid |
C6 H12 O4 |
6.95 |
21755237.5 |
| 48 |
Malonic acid |
|
|
|
| 49 |
1,3,7-Trimethyluric acid |
C8 H10 N4 O3 |
10.067 |
18133176.5 |
| 50 |
5-Hydroxy-2-furoic acid |
C5 H4 O4 |
1.805 |
50812245.5 |
| 51 |
(±)-Malic Acid |
C4 H6 O5 |
1.209 |
50383480 |
| 52 |
Glucoheptonic Acid |
C7 H14 O8 |
8.76 |
43076366 |
| 53 |
Acetylcarnitine |
C9 H17 N O4 |
8.78 |
21886355.5 |
| 54 |
Itaconic acid |
C5 H6 O4 |
1.451 |
24903345.5 |
| 55 |
Mesaconic acid |
C5 H6 O4 |
1.824 |
28480332 |
| 56 |
Sorbic acid |
C6 H8 O2 |
0.974 |
27447509.5 |
| |
Malondialdehyde |
C3 H4 O2 |
0.859 |
21556194.5 |
| 57 |
Malonic acid |
|
|
|
| 58 |
Sugar Derivatives |
| 59 |
N-Acetylglucosamine |
C17 H27 N3 O17 P2 |
1.264 |
2146760 |
| 60 |
Maltose |
C12 H22 O11 |
3.179 |
10386453 |
| |
Lactose |
C12 H22 O11 |
0.981 |
289280035.5 |
| 61 |
Sucrose |
C12 H22 O11 |
10.781 |
1531407 |
| |
Trehalose |
C12 H22 O11 |
0.943 |
103537815 |
| 62 |
Raffinose |
C18 H32 O16 |
1.32 |
5170093 |
| 63 |
Hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives |
| 64 |
Caffeic acid |
C9 H8 O4 |
4.098 |
4166656 |
| 65 |
p-Coumaric acid |
C9 H8 O3 |
5.414 |
773133 |
Table 2.
Watermelon rind extract treated HRAC-769-P cells induced transcripts (upregulated and down regulated) mapped to human genome mapping percentage of uniquely mapped reads.
Table 2.
Watermelon rind extract treated HRAC-769-P cells induced transcripts (upregulated and down regulated) mapped to human genome mapping percentage of uniquely mapped reads.
| Sample |
No. of raw PE reads |
No. of filtered PE reads |
No. of uniquely mapped PE reads |
Mapping percentage of uniquely mapped reads |
| WMRC1 |
26784649 |
25630111 |
24702469 |
96.4 |
| WMRC2 |
27470824 |
26302571 |
25318621 |
96.3 |
| WMRC3 |
25588547 |
24467830 |
23597931 |
96.4 |
| WMRT1 |
32424898 |
31024773 |
29939262 |
96.5 |
| WMRT2 |
27827568 |
26668858 |
25713431 |
96.4 |
| WMRT3 |
31744771 |
30391428 |
29270759 |
96.3 |
| Pair-wise comparison |
Total DEGs |
UPregulated |
Down-Regulated |
| Control vs. 44.8 MG |
186 |
149 |
37 |
Table 3.
Differentially expressed transcripts of HRAC cells treated with WMR. Fold change of a transcript is a ratio of its expression in control and WMR-treated cells (n = 3). The fold change' indicates up (highlighted in blue) or downregulation (highlighted in green) of that transcript, respectively, in WRE-treated cells compared to control.
Table 3.
Differentially expressed transcripts of HRAC cells treated with WMR. Fold change of a transcript is a ratio of its expression in control and WMR-treated cells (n = 3). The fold change' indicates up (highlighted in blue) or downregulation (highlighted in green) of that transcript, respectively, in WRE-treated cells compared to control.
| S. No |
Gene ID |
FoldChange |
P adj |
Regulation |
Annotation |
| 1 |
NPTX1 |
3.822151586 |
1.40205E-22 |
UP |
neuronal pentraxin 1(NPTX1) |
| 2 |
JMA2 |
3.654043227 |
6.50348E-07 |
UP |
junctional adhesion molecule 2(JAM2) |
| 3 |
HMOX1 |
2.791739716 |
3.72984E-09 |
UP |
heme oxygenase 1(HMOX1) |
| 4 |
TRIM31 |
2.578310857 |
0.014206294 |
UP |
tripartite motif containing 31(TRIM31) |
| 5 |
CXCL2 |
2.390913463 |
3.41557E-11 |
UP |
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2(CXCL2) |
| 6 |
KDF1 |
1.864605173 |
0.049178644 |
UP |
keratinocyte differentiation factor 1(KDF1) |
| 7 |
TNFAIP3 |
1.77972605 |
1.3479E-25 |
UP |
TNF alpha induced protein 3(TNFAIP3) |
| 8 |
EFEMP2 |
1.753814923 |
0.045380994 |
UP |
EGF containing fibulin extracellular matrix protein 2(EFEMP2) |
| 9 |
LINC00887 |
1.604240482 |
0.045386292 |
UP |
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 887(LINC00887) |
| 10 |
NFKBID |
1.4789834 |
1.08647E-06 |
UP |
NFKB inhibitor delta(NFKBID) |
| 11 |
LINC00472 |
1.467452434 |
0.000148121 |
UP |
long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 472(LINC00472) |
| 12 |
PAQR5 |
1.355607471 |
9.19446E-06 |
UP |
progestin and adipoQ receptor family member 5(PAQR5) |
| 13 |
COL7A1 |
1.292376567 |
2.89259E-43 |
UP |
collagen type VII alpha 1 chain(COL7A1) |
| 14 |
RNF144B |
1.287668834 |
8.06605E-06 |
UP |
ring finger protein 144B(RNF144B) |
| 15 |
SOD2 |
1.24731498 |
6.67748E-64 |
UP |
superoxide dismutase 2(SOD2) |
| 16 |
ARRB1 |
1.244050952 |
0.00013318 |
UP |
arrestin beta 1(ARRB1) |
| 17 |
BMF |
1.183513353 |
0.000755165 |
UP |
Bcl2 modifying factor(BMF) |
| 18 |
NFKBIA |
1.140983535 |
1.77033E-26 |
UP |
NFKB inhibitor alpha(NFKBIA) |
| 19 |
TPD52L1 |
1.162282589 |
0.007265863 |
UP |
TPD52 like 1(TPD52L1) |
| 20 |
RHBDL1 |
1.127426241 |
0.039940739 |
UP |
rhomboid like 1(RHBDL1) |
| 21 |
CD82 |
1.109222868 |
3.56575E-05 |
UP |
CD82 molecule(CD82) |
| 22 |
CLIP4 |
1.105718912 |
0.004748612 |
UP |
CAP-Gly domain containing linker protein family member 4(CLIP4) |
| 23 |
TRIM16L |
1.088105329 |
9.69946E-41 |
UP |
tripartite motif containing 16 like(TRIM16L) |
| 24 |
NFKBIE |
1.065145553 |
3.25882E-15 |
UP |
NFKB inhibitor epsilon(NFKBIE) |
| 25 |
TMEM158 |
1.061667088 |
1.49615E-06 |
UP |
transmembrane protein 158(TMEM158) |
| 26 |
ZC3H12A |
1.058928366 |
7.96899E-18 |
UP |
s100 calcium binding protein A4(S100A4) |
| 27 |
HSF4 |
1.058853794 |
0.005924004 |
UP |
heat shock transcription factor 4(HSF4) |
| 28 |
AKR1C2 |
1.058573734 |
2.63416E-21 |
UP |
aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C2(AKR1C2) |
| 29 |
ADAMTS7 |
1.047212012 |
7.15087E-14 |
UP |
ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 7(ADAMTS7) |
| 30 |
KCNK3 |
1.026865059 |
3.68494E-17 |
UP |
potassium two pore domain channel subfamily K member 3(KCNK3) |
| 31 |
PGGHG |
1.026377088 |
9.09732E-19 |
UP |
protein-glucosylgalactosylhydroxylysine glucosidase(PGGHG) |
| 32 |
LACTB |
1.007908666 |
0.004812089 |
UP |
lactamase beta(LACTB) |
| 33 |
ATG16L2 |
1.001999864 |
1.37778E-05 |
UP |
autophagy related 16 like 2(ATG16L2) |
| 34 |
CELF2 |
-1.012165448 |
0.00091243 |
DOWN |
CUGBP Elav-like family member 2(CELF2) |
| 35 |
KCNH1 |
-1.01380309 |
0.020077479 |
DOWN |
potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily H member 1(KCNH1) |
| 36 |
CDH6 |
-1.044599459 |
1.57671E-11 |
DOWN |
cadherin 6(CDH6) |
| 37 |
DOCK2 |
-1.058742034 |
4.76266E-22 |
DOWN |
dedicator of cytokinesis 2(DOCK2) |
| 38 |
PAX8-AS1 |
-1.058885169 |
2.95114E-08 |
DOWN |
PAX8 antisense RNA 1(PAX8-AS1) |
| 39 |
ANKRD1 |
-1.080370398 |
4.09198E-09 |
DOWN |
ankyrin repeat domain 1(ANKRD1) |
| 40 |
TAF1A-AS1 |
-1.086638886 |
0.038122062 |
DOWN |
TAF1A antisense RNA 1(TAF1A-AS1) |
| 41 |
RHOU |
-1.10777548 |
0.048963406 |
DOWN |
ras homolog family member U(RHOU) |
| 42 |
SLC16A9 |
-1.1715508 |
0.010549451 |
DOWN |
solute carrier family 16 member 9(SLC16A9) |
| 43 |
ENC1 |
-1.17558341 |
0.000148121 |
DOWN |
ectodermal-neural cortex 1(ENC1) |
| 44 |
GREB1 |
-1.200291699 |
0.038699026 |
DOWN |
growth regulating estrogen receptor binding 1(GREB1) |
| 45 |
PKHD1 |
-1.311859039 |
4.96206E-05 |
DOWN |
PKHD1 ciliary IPT domain containing fibrocystin/polyductin(PKHD1) |
| 46 |
HORMAD2-AS1 |
-1.375725708 |
0.042051375 |
DOWN |
HORMAD2 and MTMR3 antisense RNA 1(HORMAD2-AS1) |
| 47 |
FGB |
-1.441683784 |
1.07928E-56 |
DOWN |
fibrinogen beta chain(FGB) |
| 48 |
SLCO4C1 |
-1.500449851 |
3.46892E-05 |
DOWN |
solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 4C1(SLCO4C1) |
| 49 |
NPNT |
-1.529088042 |
5.81654E-09 |
DOWN |
nephronectin(NPNT) |
| 50 |
ARHGAP28 |
-1.53301957 |
6.57424E-06 |
DOWN |
Rho GTPase activating protein 28(ARHGAP28) |
| 51 |
C1orf116 |
-1.56932167 |
0.045320324 |
DOWN |
chromosome 1 open reading frame 116(C1orf116) |
| 52 |
SLAMF7 |
-1.840054142 |
0.024930087 |
DOWN |
SLAM family member 7(SLAMF7) |
| 53 |
UNC13C |
-1.944259269 |
0.03671916 |
DOWN |
unc-13 homolog C(UNC13C) |
| 54 |
EPHA7 |
-2.087931878 |
7.25051E-81 |
DOWN |
EPH receptor A7(EPHA7) |
| 55 |
SLC26A5-AS1 |
-2.285084696 |
0.010311261 |
DOWN |
SLC26A5 antisense RNA 1(SLC26A5-AS1) |
| 56 |
SULT1B1 |
-2.333807748 |
3.9407E-05 |
DOWN |
sulfotransferase family 1B member 1(SULT1B1) |
| 57 |
FLT3 |
-2.335935596 |
0.001480949 |
DOWN |
fms related receptor tyrosine kinase 3(FLT3) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).