1. Introduction
Platelets are involved in a variety of physiologic and pathophysiologic processes including innate immune response, inflammation and atherosclerosis [
1,
2,
3]. Platelets can interact with innate immune cells and secrete cytokines and chemokines [
4]. In addition, platelets have significant impact on the course of many different tumor diseases [
5]. Upon contact with cancer cells or circulating tumor cells (CTCs) platelets get activated through a variety of interactions thereby promote cancer progression and metastasis [
6,
7]. The C-type lectin like receptor 2 (CLEC-2) mainly expressed on megakaryocytes and platelets is one of the key molecules that enables interaction with other cells such as innate immune cells and tumor cells [
8,
9].
CLEC-2 consists of a transmembrane domain, an extracellular lectin-like recognition domain and a short cytosolic tail, harboring a single YxxL sequence, a hem-immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (hemITAM) [
10]. Podoplanin (PDPN) is the most important endogenous ligand of CLEC-2 involved in the cell interaction mechanisms [
11]. This glycoprotein with a single transmembrane domain and four platelet aggregation stimulating domains (PLAG) is expressed on many different cells including lymphatic endothelial cells, kidney podocytes and tumor cells especially CTCs [
12,
13,
14]. Platelet aggregation induced by PDPN expressing tumor cells was shown to play a role in tumor growth and metastasis [
14,
15]. Blocking this interaction led to decreased metastatic herds, better survival and protection against venous thromboembolism (VTE).
Patients with ischemic stroke, acute coronary syndrome or coronary artery disease showed increased plasma concentration of soluble CLEC-2 (sCLEC-2) [
16,
17,
18]. Similar observations were reported for patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) or glioma [
19,
20]. It was hypothesized that sCLEC-2 is released upon platelet activation and, therefore, sCLEC-2 could serve as a plasma biomarker of platelet activation [
21]. However, the mechanism of sCLEC-2 release is still unclear. In contrast to the release of glycoprotein VI, CLEC-2 is not cleaved by ADAM10/17 [
22]. Furthermore, CLEC-2 is not shed or internalized following platelet activation and is maintained on microparticles from activated platelets [
23]. The antibody-induced downregulation of CLEC-2 was observed in mice platelets and megakaryocytes caused through internalization without evidence for ectodomain shedding [
24].
To further elucidate the effect of platelet activation and the mechanism of sCLEC-2 release we first performed in vitro studies on platelets from healthy individuals. We measured the CLEC-2 expression on platelets and the sCLEC-2 plasma concentration after stimulation of platelets using ADP and PDPN. Second, as an in vivo model for sCLEC-2 release, we measured sCLEC-2 in patients with different solid tumor entities including colorectal carcinoma, mamma carcinoma, melanoma and glioblastoma.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Blood Samples
Citrated blood samples from 20 healthy volunteer donors were used for aggregometry and the in vitro studies with flow cytometry, ELISA and Western blot analysis. At the time of blood collection, the donors had no medication affecting platelet function in the past 10 days. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was prepared from citrated blood by centrifugation for 15 minutes at 200 g in a swingout rotor within three hours after blood collection. For the in vitro platelet stimulation experiments 500 µL PRP from healthy donors was incubated without agonist or with 5 µM ADP ADP (möLab GmbH, Langenfeld, Germany) or PDPN (1 µg and 5 µg recombinant human glycosylated PDPN protein; Sino Biological Inc.; Biozol GmbH, Eiching, Germany) at room temperature for 30 minutes with slight agitation. The PRP samples were then directly subjected to flow cytometry, ELISA and Western blot analysis.
For the determination of the sCLEC-2 plasma level, EDTA blood samples were obtained from of 285 randomized healthy blood donors already used for a previous study [
25]. Plasma samples from patients with colorectal cancer (CRC; n=194), melanoma (160) and breast cancer (BC; 99) were provided by the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT) Heidelberg. Samples from 49 glioblastoma patients were collected at the Center for Neurooncology, Comprehensive Cancer Center, Tübingen. All donors and patients gave informed consent to provide blood samples for research purposes. The study protocols were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the ethical committee of the Medical Faculty Mannheim of the Heidelberg University (ethical approval codes: 2016-615N-MA, 2016-657N-MA).
2.2. Aggregometry
The platelet aggregation response was measured using light transmission aggregometry (LTA) in the PAP-8 system (möLab GmbH). In pilot experiments, we used PDPN in different concentrations and incubation times for the stimulation of platelets, which did not lead to a platelet aggregation response (results no shown). Therefore, PDPN was used as a co-agonist together with classical agonists ADP, arachidonic acid (AA) and collagen (COL) to stimulate platelet and determine the aggregation response for 10 minutes. As given in the results ADP, AA and COL were used in standard concentration and 5 times lower than standard. The primary aggregation (PA %) values were used for data analysis and statistical evaluation.
2.3. Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry was used to measure the expression of CLEC-2 and the activation marker CD62P (P-selectin) on platelets of healthy donors. Following antibodies were used: monoclonal anti-CD62P (PE-conjugated, clone AK-4, IgG1; BD Biosciences, Heidelberg, Germany) and monoclonal anti-CLEC-2 (FITC-conjugated, clone 17D9, IgG2b; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Darmstadt, Germany). For in vitro platelet stimulation we used ADP and recombinant human glycosylated PDPN protein. Unstimulated as well as ADP and PDPN stimulated PRP was assessed unstained and double-stained for CLEC-2 (FITC) and CD62P (PE) by using a FACS-Canto II system (BD Biosciences). All events detected in the stained samples were gated according to the side and forward scatter and further analyzed for mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in each fluorescence channel. The results were evaluated and processed for graphical presentation with the FlowJo software (FlowJo, LLC; Ashland, OR, USA).
2.4. ELISA for sCLEC-2
A commercial ELISA kit (RayBiotech; Hoelzel Diagnostika GmbH, Cologne, Germany) was used to measure the sCLEC-2 in plasma samples from the in vitro stimulation experiments and in the plasma samples from the healthy blood donors and the tumor patients. Unstimulated as well as ADP and PDPN stimulated PRP was centrifuged for 10 minutes at 1,000 g. The plasma in the supernatant was transferred to another tube and further processed for ELISA according to the standard protocol. The platelet pellet was further processed for Western blot analysis. The sCLEC-2 concentration was measured in all plasma samples in duplicate according to the standard protocol of the ELISA kit. Standardization of the optical density (OD) measured at 450 nm was achieved by using a dilution series of the recombinant CLEC-2 protein provided with the kit. The linear range of the standard curve was 0.1-48 ng/mL sCLEC 2 with a significant correlation (r2 = 0.9984).
2.5. Western Blot
Pellets of the unstimulated as well as ADP and PDPN stimulated platelets were resuspended in cold lysis buffer (RIPA buffer including protease inhibitor cocktail; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Heidelberg, Germany) followed by incubation on ice for 30 minutes. After shock freezing in liquid nitrogen followed by thawing, ultrasound treatment and centrifugation 10 minutes at 12,000 g, the supernatant (platelet lysate) was transferred to another tube. The total protein concentration of the lysates was determined by using a Bradford protein assay (Quick Start™ Bradford Protein Assay; Bio-Rad Laboratories GmbH, Feldkirchen, Germany). The sample volume corresponding to 25 µg total protein was calculated and mixed with electrophoresis sample buffer (Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.). After heat denaturation for 5 minutes at 100 °C the samples were loaded on 8.75 % polyacrylamid gels (PAGE) and electrophoresed for 50 minutes at 25 V/cm. The separated proteins were blotted onto nitrocellulose membranes (Bio-Rad) by electric field transfer. After incubation of the blots in blocking solution (UltraCruz® Blocking Reagent; Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.) for 1 hour, the primary antibody (goat anti-human CLEC1B polyclonal antibody; Invitrogen, Darmstadt, Germany) was added and incubated over night at 4 °C with constant agitation. Then, the blots were washed and incubated with the secondary antibody (mouse anti-goat HRP-conjugated; Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.) for one hour at room temperature. After repeated washing steps, we added Luminol and peroxide solution and measured our blots using the Epi Chemi II Darkroom (UVP laboratory products, Upland, California, USA). For relative quantification of the CLEC-2 protein band, the blots were stained for beta-actin (monoclonal anti-actin antibody, HRP-conjugated; Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc.) as reference protein. Quantitative analysis of the protein bands was accomplished by the ImageJ program.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
T-tests and further statistical analysis were performed using Excel (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) and PRISM 8 (GraphPad Software, Boston MA, USA). P values < 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
3. Results
First, we investigated the effect of PDPN on the platelet aggregation response of heathy donors. Second, ADP and PDPN were used as agonists for in vitro stimulation of platelets from healthy donors to analyze the expression of CLEC-2 on platelets, in plasma and in platelet lysates. The third part of our investigation included the measurement of sCLEC-2 in plasma samples from healthy controls and patients with different tumor entities.
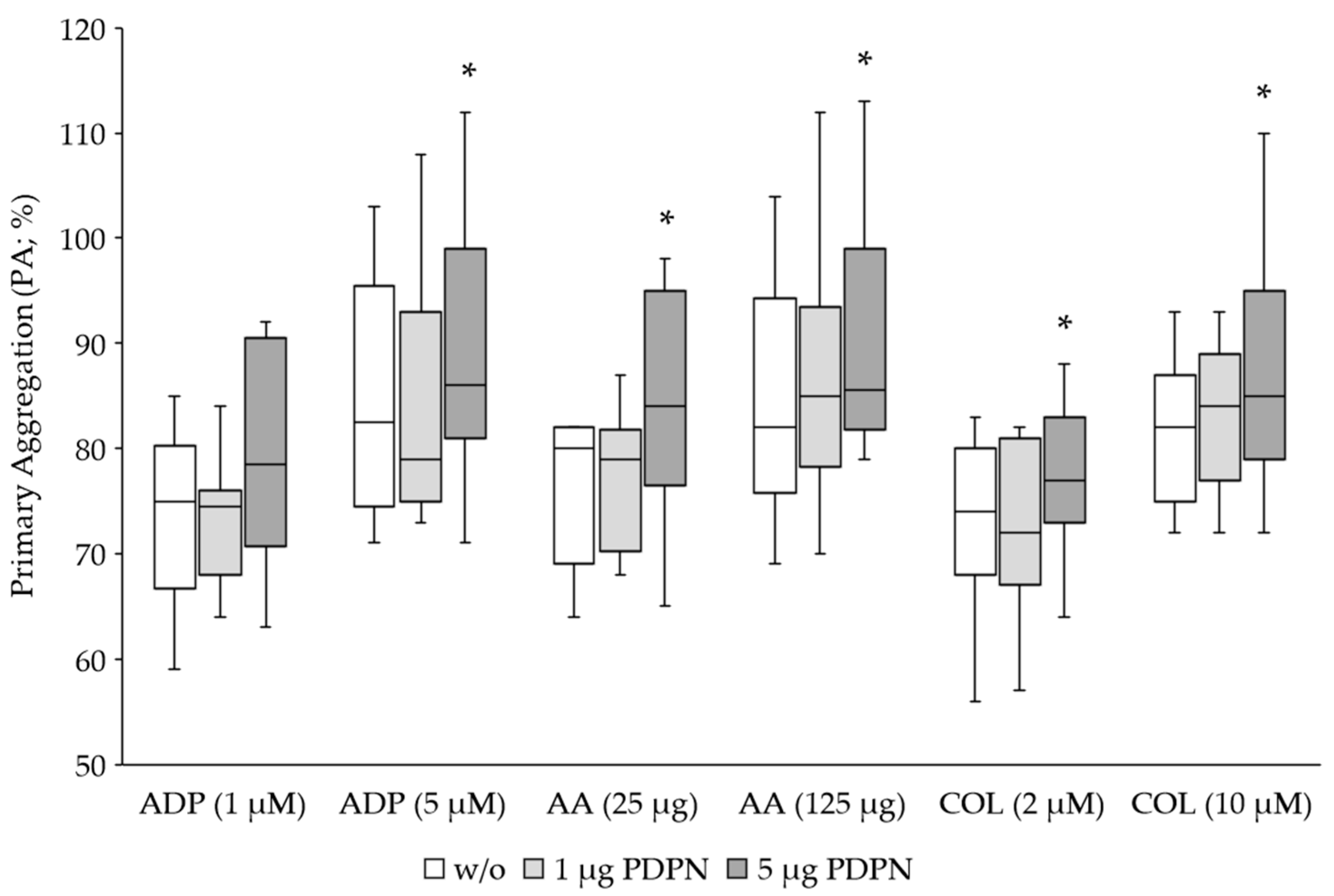
3.1. PDPN Is a Co-Agonist for Platelet Aggregation
Platelets from 20 healthy volunteer donors were stimulated for aggregation using classical agonists ADP, AA and COL at the corresponding standard concentration for LTA and 5 times lower concentration. To determine the effect of PDPN we applied 1 µg and 5 µg of the recombinant protein to the samples with 225 µL PRP. PDPN on its own did not induce a platelet aggregation response (data not shown). Only the classical agonists induced platelet aggregation (
Figure 1). As expected, the aggregation response was dose-dependently reduced when using the 5-fold lower agonist concentration. The co-stimulation with 5 µg PDPN caused a significant increase of the primary aggregation induced by all classical agonists, while 1 µg showed no effect (
Table 1).
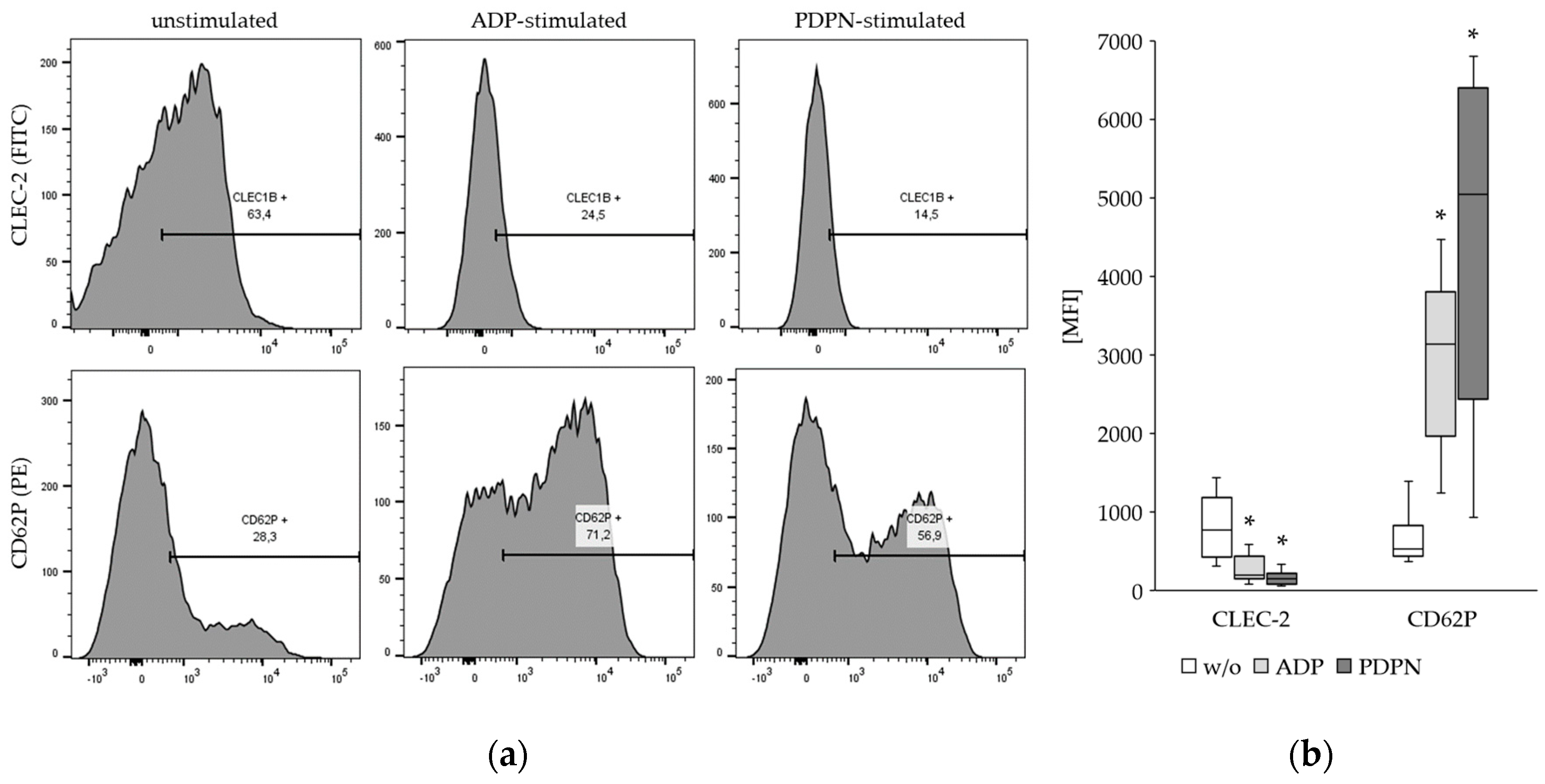
3.2. The CLEC-2 Expression Is Decreased upon Platelet Stimulation
The expression of CLEC-2 and the activation marker CD62P was determined on platelets without stimulation and after stimulation with ADP and PDPN. The results from flow cytometry revealed a significant decrease of the CLEC-2 expression upon ADP and PDPN stimulation of the platelets (
Figure 2). As expected, the CD62P expression was increased upon ADP and PDPN stimulation.
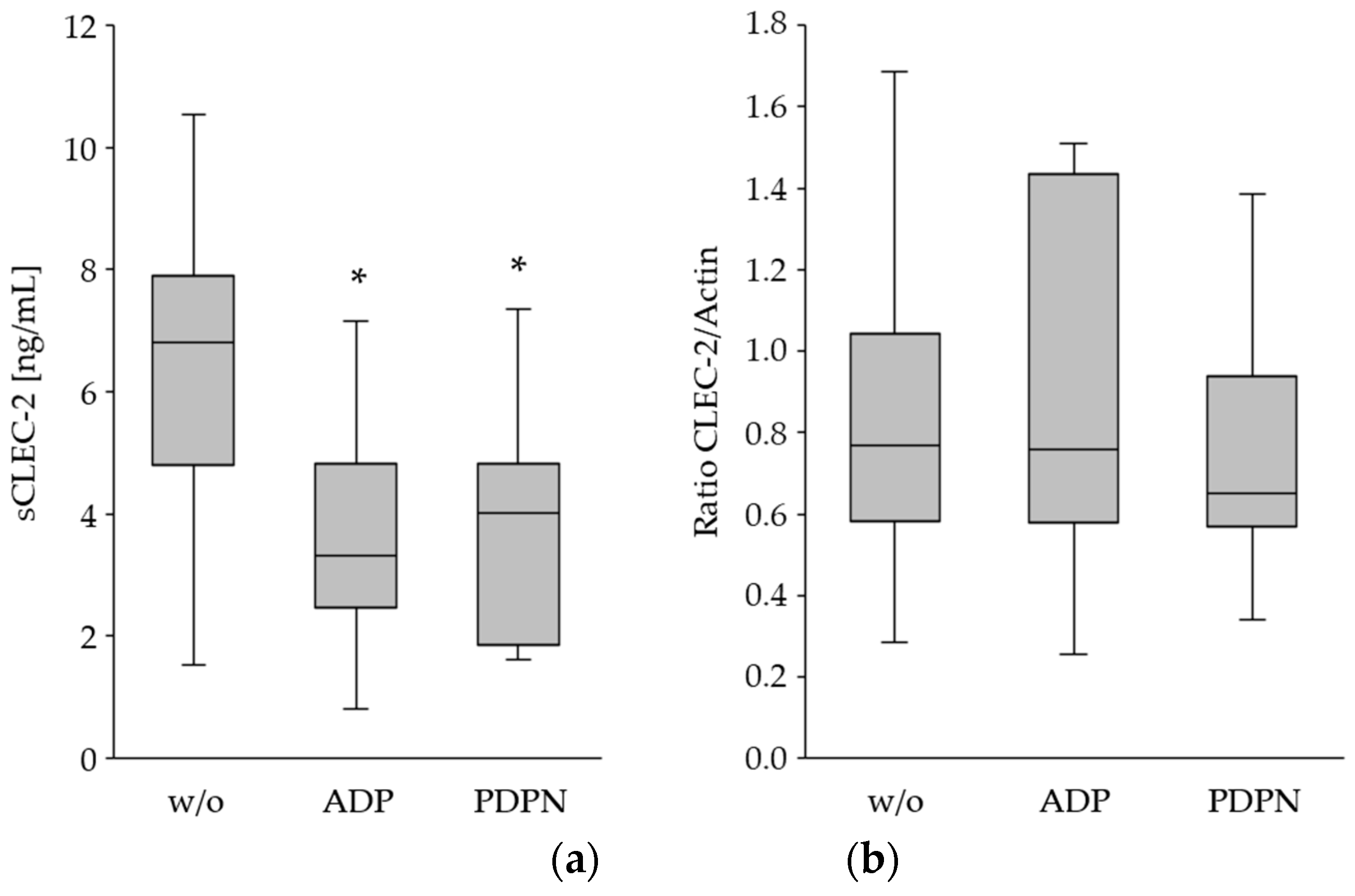
In order to prove whether the reduced CLEC-2 expression upon platelet activation was caused by shedding of CLEC-2 and release to the plasma, sCLEC-2 was measured in the supernatant of the ADP- and PDPN-stimulated PRP. Platelet activation was associated with a significant decrease of sCLEC-2 in the plasma (
Figure 3a). Whereas, the relative quantification of total CLEC-2 in the platelet lysates indicated a comparable protein concentration (
Figure 3b).
These data suggest that shedding and degradation of CLEC-2 upon platelet activation is rather unlikely (
Table 2). Given that overall expression levels do not change, internalization of CLEC-2 in platelets could be the cause.
3.3. The Plasma Level of sCLEC-2 Is Lower in Tumor Patients than in Healthy Controls
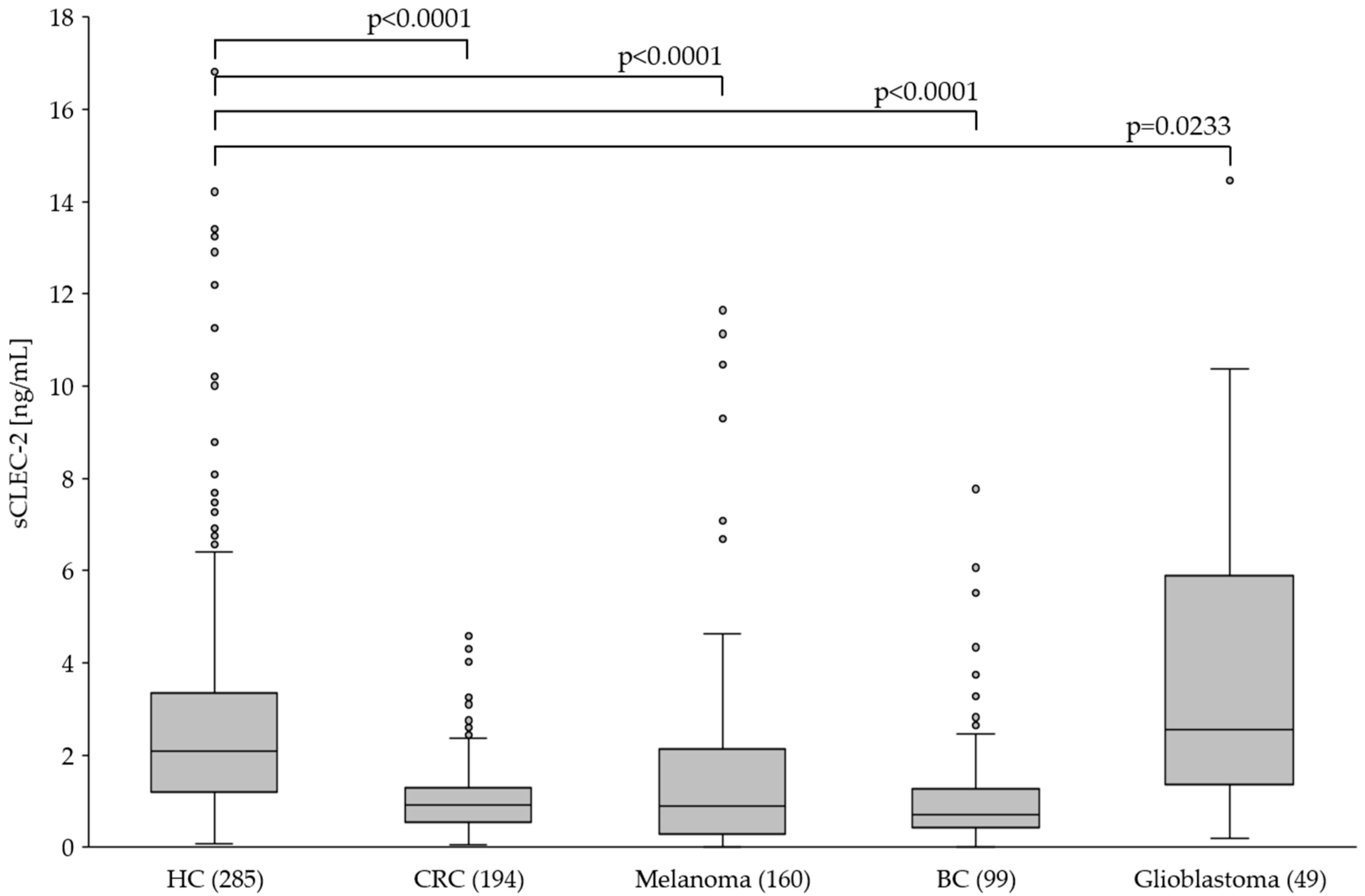
Previous studies reported increased sCLEC-2 plasma levels in patients with inflammatory and malignant disease and it was hypothesized that sCLEC-2 is released upon platelet activation. However, our in vitro studies indicated that platelet activation is not associated with increased but rather decreased CLEC-2 expression and sCLEC-2 level in the plasma. To further investigate this in vivo, we measured sCLEC-2 in plasma of healthy donors and patients with different solid tumors.
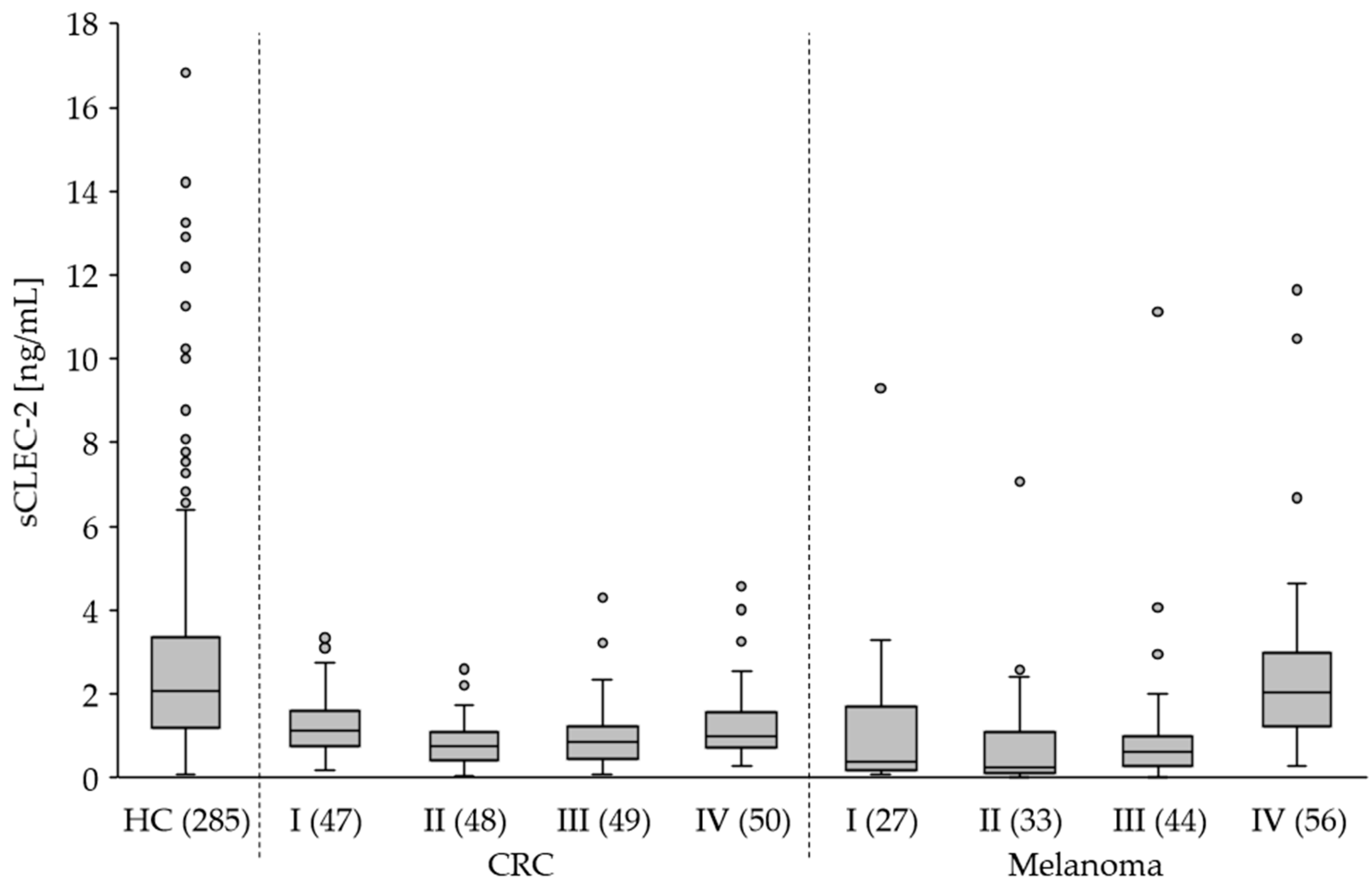
Compared to healthy controls (HC) we found significantly lower (p<0.0001) sCLEC-2 plasma levels in patients with CRC, melanoma and BC (
Figure 4). Interestingly, the sCLEC-2 level in glioblastoma patients was significantly higher (p=0.0233). A correlation to the tumor stages was assessed for CRC and melanoma. All CRC stages I to IV showed significantly lower sCLEC-2 levels than HC (
Figure 5,
Table 3). For the melanoma stages I to III we also found significantly lower sCLEC-2 levels, whereas, in patients with stage IV tumors the sCLEC-2 level was comparable with HC.
In summary, the in vivo data from patients revealed significantly lower sCLEC-2 plasma levels compared to heathy controls for all tumor entities analyzed except melanoma stage IV and glioblastoma. The latter displayed higher sCLEC-2 levels.
4. Discussion
It has been clearly demonstrated that binding of PDPN to CLEC-2 leads to an activation of platelets. However, with regard to platelet aggregation PDPN was only a weak agonist that enhanced stimulation by other agonists such as ADP, AA or collagen. In contrast to other platelet receptors such as CD62P or GPVI we showed that the CLEC-2 expression on platelets and the sCLEC-2 level in the plasma is decreased upon platelet activation. Thus, shedding of CLEC-2 upon platelet activation is rather excluded. We hypothesize that platelet activation cause the internalization of CLEC-2 including uptake of sCLEC-2 from the plasma. The reported antibody induced internalization of CLEC-2 in mouse platelets could represent a similar mechanism [
24]. However, the findings from our
in vitro studies are contradictory to reported increased sCLEC-2 plasma levels in patients with thromboinflammatory diseases that are associated with increased platelet activation [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22]. These studies proposed sCLEC-2 as plasma biomarker for platelet activation [
21]. It remains unclear whether the difference in the
in vitro conditions in our studies and the
in vivo conditions or the pathologic conditions account for the contradictory results.
Increased sCLEC-2 plasma levels were also reported for colorectal cancer and glioma [
19,
20]. The CLEC-2/PDPN-mediated binding of platelets to CTCs further promotes the crucial role of CLEC-2 in progression and metastasizing of tumors [
7,
12,
13]. The CLEC-2/PDPN axis was discussed as a promising drug target for cancer treatment [
26,
27]. Antibody-mediated inhibition of the interaction between tumor PDPN and platelet CLEC-2 blocked growth and pulmonary metastasis of human malignant melanoma [
28].
In contrast to previous reports, we observed significantly lower sCLEC-2 plasma levels in cancer patients compared to healthy donors. Zang
et al. showed higher sCLEC-2 levels in CRC patients compared to healthy controls [
19]. Moreover, the patients with liver metastases displayed higher CLEC-2 levels than patients without metastases. In our study, the sCLEC-2 level in patients with CRC at stage I to IV was significantly lower than in healthy controls. The same was true for melanoma stages I to III. The 56 patients with stage IV melanoma displayed sCLEC-2 levels comparable with healthy donors but significantly higher compared to stage I to III melanoma. Melanoma patients have a considerably higher risk of suffering from VTE than patients with CRC or BC [
29,
30,
31]. In stage IV melanoma a prevalence of VTE of 25 % was observed [
29]. Glioblastoma was the only tumor entity in our study that was associated with higher sCLEC-2 levels and confirmed the observation of previous reports [
20]. A correlation between sCLEC-2 levels and PDPN expression was reported in patients with high-grade gliomas [
32]. Interestingly, high PDPN expression in primary brain tumors induces platelet aggregation and is associated with increased risk of VTE [
33]. As shown in a mouse model blocking PDPN specifically on glioblastoma cells could represent a novel strategy to prevent platelet aggregation and thereby reduce the risk of VTE in glioma [
34]. However, tumor progression occurs independently of PDPN and blocking of PDPN does not represent a promising anti-cancer therapeutic approach [
35]. Taking the observations from our
in vitro platelet stimulation experiments into account, the significantly lower levels of sCLEC-2 in the plasma of cancer patients may result from the internalization of sCLEC-2 by activated platelets. Binding of sCLEC-2 to PDPN on CTC should also be considered.
Cancer-associated VTE is associated with an increased risk of mortality independent of the cancer characteristics. Nowadays, the use of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) is the most effective therapy for managing VTE in the general population and is also recommended for cancer patients [for review see 36]. Anti-platelet therapy using aspirin can reduce both the long-term risk of cancer and the risk of cancer metastasis for some solid tumors [
36,
37,
38]. The ADD-ASPIRIN trial is a phase III, double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized trial that investigates whether regular aspirin use after standard therapy prevents recurrence and prolongs survival in participants with non-metastatic CRC, BC, gastro-oesophageal or prostate cancer [
39]. A better understanding of the mechanisms how platelets promote tumor growth and progression is a prerequisite for the development of novel anti-cancer therapies.
5. Conclusions
Based on our in vitro studies on platelets from healthy individuals we showed that the CLEC-2 expression on platelets and the sCLEC-2 level in the plasma is decreased upon platelet activation. Uptake and internalization of the receptor is the proposed mechanism. Therefore, we conclude that an increased plasma level of sCLEC-2 is not a suitable biomarker of platelet activation. We also found decreased levels of sCLEC-2 plasma samples of patients with CRC, BC and melanoma stage I to III compared to healthy controls. Glioblastoma was the only tumor entity in our study with significantly higher sCLEC-2 levels. CLEC-2 and the ligand PDPN might play a significant role in the development and progression of glioblastoma as already hypothesized by other studies. The low sCLEC-2 plasma level observed in most of the tumor entities of our study, presumably, results from the internalization of sCLEC-2 by activated platelets or binding of sCLEC-2 to CTC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.B., H.K., P.B.; investigation, M.E., F.C., S.U.; resources, H.K., J.C.H., P.S.-K., H.B., C.M.U., K.B. and H.K.; data curation, M.E. and P.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.E. and F.C.; writing—review and editing, P.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg University (ethical approval code 2016-615N-MA from 2016-09-01 and 2016-657N-MA from 2016-12-29).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Ghazaleh Tabatabai for providing plasma samples from glioblastoma patients. The expert technical support by Gabi Rink is highly recognized.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rayes J, Bourne JH, Brill A, Watson SP. The dual role of platelet-innate immune cell interactions in thrombo-inflammation. Res Pract Thromb Haemost 2019, 4, :23-35. [CrossRef]
- Claushuis TA, van Vught LA, Scicluna BP, Wiewel MA, Klein Klouwenberg PM, Hoogendijk AJ, Ong DS, Cremer OL, Horn J, Franitza M, Toliat MR, Nürnberg P, Zwinderman AH, Bonten MJ, Schultz MJ, van der Poll T; Molecular Diagnosis and Risk Stratification of Sepsis Consortium. Thrombocytopenia is associated with a dysregulated host response in critically ill sepsis patients. Blood 2016, 127, 3062-3072. [CrossRef]
- Deppermann C, Kubes P. Start a fire, kill the bug: The role of platelets in inflammation and infection. Innate Immun 2018, 24, 335-348. [CrossRef]
- Martinod K, Deppermann C. Immunothrombosis and thromboinflammation in host defense and disease. Platelets 2021, 32, 314-324. [CrossRef]
- Gay LJ, Felding-Habermann B. Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2011, 11, 123-134. [CrossRef]
- Menter DG, Tucker SC, Kopetz S, Sood AK, Crissman JD, Honn KV. Platelets and cancer: a casual or causal relationship: revisited. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2014, 33, 231-269. [CrossRef]
- Takagi S, Sato S, Oh-hara T, Takami M, Koike S, Mishima Y, Hatake K, Fujita N. Platelets Promote Tumor Growth and Metastasis via Direct Interaction Between Aggrus/podoplanin and CLEC-2. PLoS One 2013, 8, e73609. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Inoue K, Osada M, Ozaki Y. Physiologic and pathophysiologic roles of interaction between C-type lectin-like receptor 2 and podoplanin: partners from in utero to adulthood. J Thromb Haemost 2017, 15, 219-229. [CrossRef]
- Meng D, Luo M, Liu B. The Role of CLEC-2 and Its Ligands in Thromboinflammation. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 688643. [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Inoue K, Fuller GL, García A, Eble JA, Pöhlmann S, Inoue O, Gartner TK, Hughan SC, Pearce AC, Laing GD, Theakston RD, Schweighoffer E, Zitzmann N, Morita T, Tybulewicz VL, Ozaki Y, Watson SP. A novel Syk-dependent mechanism of platelet activation by the C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2. Blood 2006, 107, 542-549.
- Ugorski M, Dziegiel P, Suchanski J. Podoplanin - a small glycoprotein with many faces. Am J Cancer Res 2016, 6, 370-386.
- Lowe KL, Navarro-Nunez L, Watson SP. Platelet CLEC-2 and podoplanin in cancer metastasis. Thromb Res 2012, 129, 30–37. [CrossRef]
- Leblanc R, Peyruchaud O. Metastasis: new functional implications of platelets and megakaryocytes. Blood 2016, 128, 24-31. [CrossRef]
- Takemoto A, Okitaka M, Takagi S, Takami M, Sato S, Nishio M, Okumura S, Fujita N. A critical role of platelet TGF-β release in podoplanin-mediated tumour invasion and metastasis. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 42186. [CrossRef]
- Shirai T, Inoue O, Tamura S, Tsukiji N, Sasaki T, Endo H, Satoh K, Osada M, Sato-Uchida H, Fujii H, Ozaki Y, Suzuki-Inoue K. C-type lectin-like receptor 2 promotes hematogenous tumor metastasis and prothrombotic state in tumor-bearing mice. J Thromb Haemost 2017, 15, 513-525. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Zhang W, Wu X, Li H, Zhang C, Huang Z, Shi R, You T, Shi J, Cao Y. Prognostic significance of plasma CLEC-2 (C-Type Lectin-Like Receptor 2) in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2018, 7, STROKEAHA118022563. [CrossRef]
- Yamashita Y, Suzuki K, Mastumoto T, Ikejiri M, Ohishi K, Katayama N, Suzuki-Inoue K, Wada H. Elevated plasma levels of soluble C-type lectin-like receptor 2 (CLEC2) in patients with thrombotic microangiopathy. Thromb Res 2019, 178, 54-58. [CrossRef]
- Fei M, Xiang L, Chai X, Jin J, You T, Zhao Y, Ruan C, Hao Y, Zhu L. Plasma soluble C-type lectin-like receptor-2 is associated with the risk of coronary artery disease. Front Med 2020, 14, 81-90. [CrossRef]
- Zhang ML, Huang WJ, Yue CX, Li MM, Li N, Wang RT, Xie R. Significant difference of c-type lectin-like receptor 2 between colorectal cancer and polyp subgroups. Cancer Biomark 2021, 31, 99-105. [CrossRef]
- Ando K, Natsumeda M, Kawamura M, Shirakawa K, Okada M, Tsukamoto Y, Eda T, Watanabe J, Saito S, Takahashi H, Kakita A, Oishi M, Fujii Y. Elevated ratio of C-type lectin-like receptor 2 level and platelet count (C2PAC) aids in the diagnosis of post-operative venous thromboembolism in IDH-wildtype gliomas. Thromb Res 2023, 223, 36-43. [CrossRef]
- Kazama F, Nakamura J, Osada M, Inoue O, Oosawa M, Tamura S, Tsukiji N, Aida K, Kawaguchi A, Takizawa S, Kaneshige M, Tanaka S, Suzuki-Inoue K, Ozaki Y. Measurement of soluble C-type lectin-like receptor 2 in human plasma. Platelets 2015, 26, 711-719. [CrossRef]
- Inoue O, Osada M, Nakamura J, Kazama F, Shirai T, Tsukiji N, Sasaki T, Yokomichi H, Dohi T, Kaneko M, Kurano M, Oosawa M, Tamura S, Satoh K, Takano K, Miyauchi K, Daida H, Yatomi Y, Ozaki Y, Suzuki-Inoue K. Soluble CLEC-2 is generated independently of ADAM10 and is increased in plasma in acute coronary syndrome: comparison with soluble GPVI. Int J Hematol 2019, 110, 285-294. [CrossRef]
- Gitz E, Pollitt AY, Gitz-Francois JJ, Alshehri O, Mori J, Montague S, Nash GB, Douglas MR, Gardiner EE, Andrews RK, Buckley CD, Harrison P, Watson SP. CLEC-2 expression is maintained on activated platelets and on platelet microparticles. Blood 2014, 124, 2262-2270. [CrossRef]
- Lorenz V, Stegner D, Stritt S, Vögtle T, Kiefer F, Witke W, Schymeinsky J, Watson SP, Walzog B, Nieswandt B. Targeted downregulation of platelet CLEC-2 occurs through Syk-independent internalization. Blood 2015, 125, 4069-4077. [CrossRef]
- Etemad M, Christodoulou F, Weiss C, Klüter H, Bugert P. Correlation of CLEC1B haplotypes with plasma levels of soluble CLEC-2 in healthy individuals. Platelets 2021, 32, 1103-1107. [CrossRef]
- Takemoto A, Miyata K, Fujita N. Platelet-activating factor podoplanin: from discovery to drug development. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2017, 36, 225-234. [CrossRef]
- Hwang BO, Park SY, Cho ES, Zhang X, Lee SK, Ahn HJ, Chun KS, Chung WY, Song NY. Platelet CLEC2-Podoplanin axis as a promising target for oral cancer treatment. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 807600. [CrossRef]
- Xu M, Wang X, Pan Y, Zhao X, Yan B, Ruan C, Xia L, Zhao Y. Blocking podoplanin suppresses growth and pulmonary metastasis of human malignant melanoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 599. [CrossRef]
- Sparsa A, Durox H, Doffoel-Hantz V, Munyangango EM, Bédane C, Cendras J, Gantois C, Boulinguez S, Bonnetblanc JM. High prevalence and risk factors of thromboembolism in stage IV melanoma. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2011, 25, 340-344. [CrossRef]
- Lundbech M, Krag AE, Iversen LH, Hvas AM. Postoperative bleeding and venous thromboembolism in colorectal cancer patients undergoing cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Colorectal Dis 2022, 37, 17-33. [CrossRef]
- Girardi L, Wang TF, Ageno W, Carrier M. Updates in the Incidence, Pathogenesis, and Management of Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2023, 43, 824-831. [CrossRef]
- Ando K, Natsumeda M, Kawamura M, Shirakawa K, Okada M, Tsukamoto Y, Eda T, Watanabe J, Saito S, Takahashi H, Kakita A, Oishi M, Fujii Y. Elevated ratio of C-type lectin-like receptor 2 level and platelet count (C2PAC) aids in the diagnosis of post-operative venous thromboembolism in IDH-wildtype gliomas. Thromb Res 2023, 223, 36-43. [CrossRef]
- Riedl J, Preusser M, Nazari PM, Posch F, Panzer S, Marosi C, Birner P, Thaler J, Brostjan C, Lötsch D, Berger W, Hainfellner JA, Pabinger I, Ay C. Podoplanin expression in primary brain tumors induces platelet aggregation and increases risk of venous thromboembolism. Blood 2017, 129, 1831-1839. [CrossRef]
- Costa B, Eisemann T, Strelau J, Spaan I, Korshunov A, Liu HK, Bugert P, Angel P, Peterziel H. Intratumoral platelet aggregate formation in a murine preclinical glioma model depends on podoplanin expression on tumor cells. Blood Adv 2019, 3, 1092-1102. [CrossRef]
- Eisemann T, Costa B, Harter PN, Wick W, Mittelbronn M, Angel P, Peterziel H. Podoplanin expression is a prognostic biomarker but may be dispensable for the malignancy of glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 2019, 21, 326-336.
- Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Price JF, Belch JF, Meade TW, Mehta Z. Effect of daily Aspirin on risk of cancer metastasis: a study of incident cancers during randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2012, 379, 1591-1601. [CrossRef]
- Rothwell PM, Price JF, Fowkes FG, Zanchetti A, Roncaglioni MC, Tognoni G, Lee R, Belch JF, Wilson M, Mehta Z, Meade TW. Short-term effects of daily aspirin on cancer incidence, mortality, and non-vascular death: analysis of the time course of risks and benefits in 51 randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2012, 379, 1602-1612. [CrossRef]
- Algra AM, Rothwell PM. Effects of regular Aspirin on long-term cancer incidence and metastasis: a systematic comparison of evidence from observational studies versus randomised trials. Lancet Oncol 2012, 13, 518-527. [CrossRef]
- Coyle C, Cafferty FH, Rowley S, MacKenzie M, Berkman L, Gupta S, Pramesh CS, Gilbert D, Kynaston H, Cameron D, Wilson RH, Ring A, Langley RE; Add-Aspirin investigators. ADD-ASPIRIN: A phase III, double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised trial assessing the effects of aspirin on disease recurrence and survival after primary therapy in common non-metastatic solid tumours. Contemp Clin Trials 2016, 51, 56-64. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).