Submitted:
14 September 2023
Posted:
15 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Drying Methodology
2.3. Aqueous Extract Preparation
2.4. Chemical Characterization of O. nervosum ssp. platylepis Aqueous Extracts
2.4.1. Dry Matter
2.4.2. Total Phenols Content
2.4.3. Flavonoids Content
2.4.4. Condensed Tannins
2.4.5. Proteins Content
2.5. Microbiological Characterization
2.6. Biological Activities
2.6.1. Clotting Milk Activity
2.6.2. Antioxidant Activity
DPPH Assay
ABTS Assay
FRAP
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Domestication and Drying Methodology on Chemical Composition and Microbiological Properties of O. nervosum platylepis Aqueous Extract
3.1.1. Dry Matter of Aqueous Extract
3.1.2. Phenolic Composition
3.1.3. Proteins Content
3.1.4. Microbiological Properties of O. nervosum platylepis Aqueous Extract
3.2. Effect of Domestication and Drying Methodology on Biological Activity of O. nervosum Platylepis Aqueous Extract
3.2.1. Clotting Milk Activity
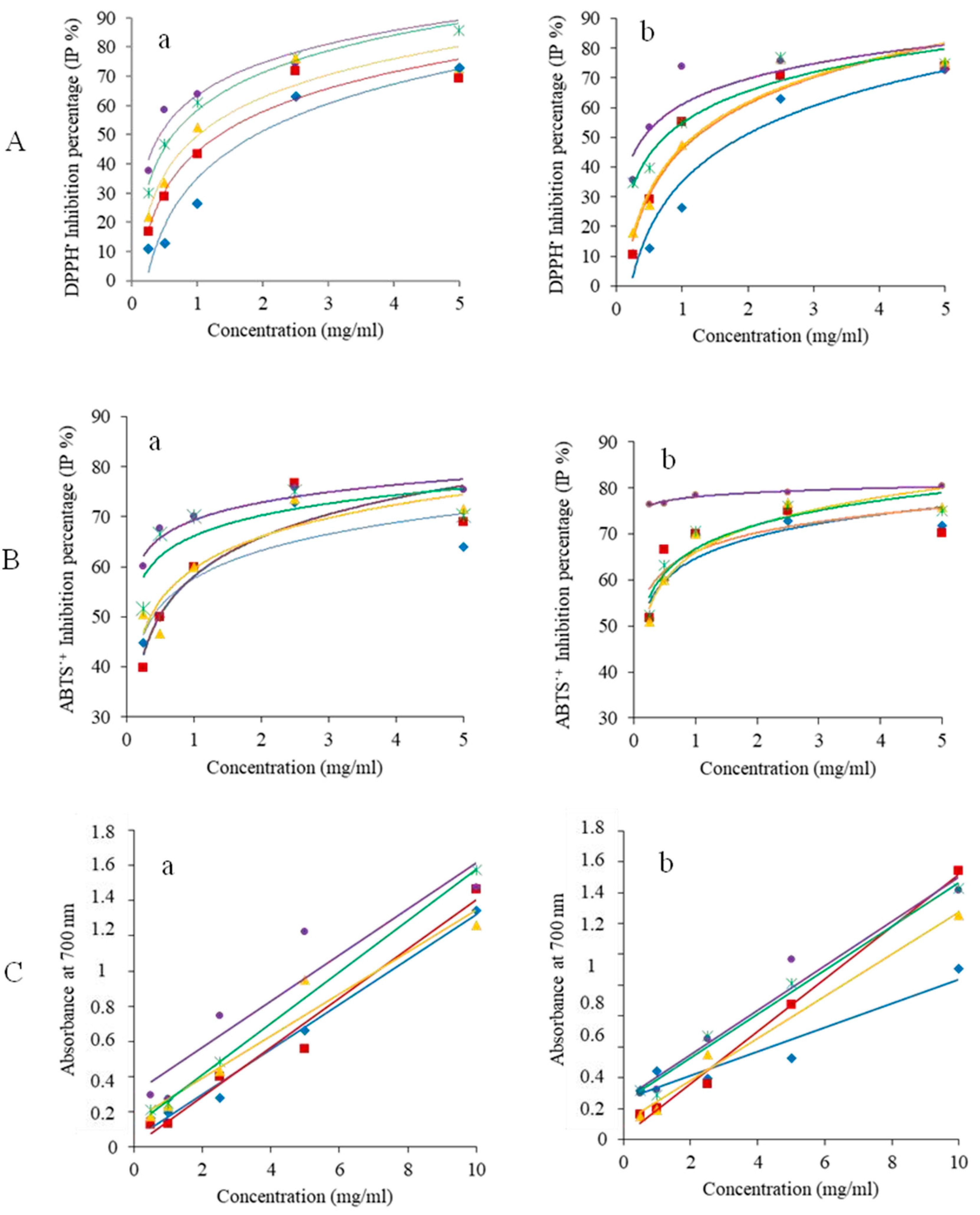
3.2.2. Antioxidant Activity
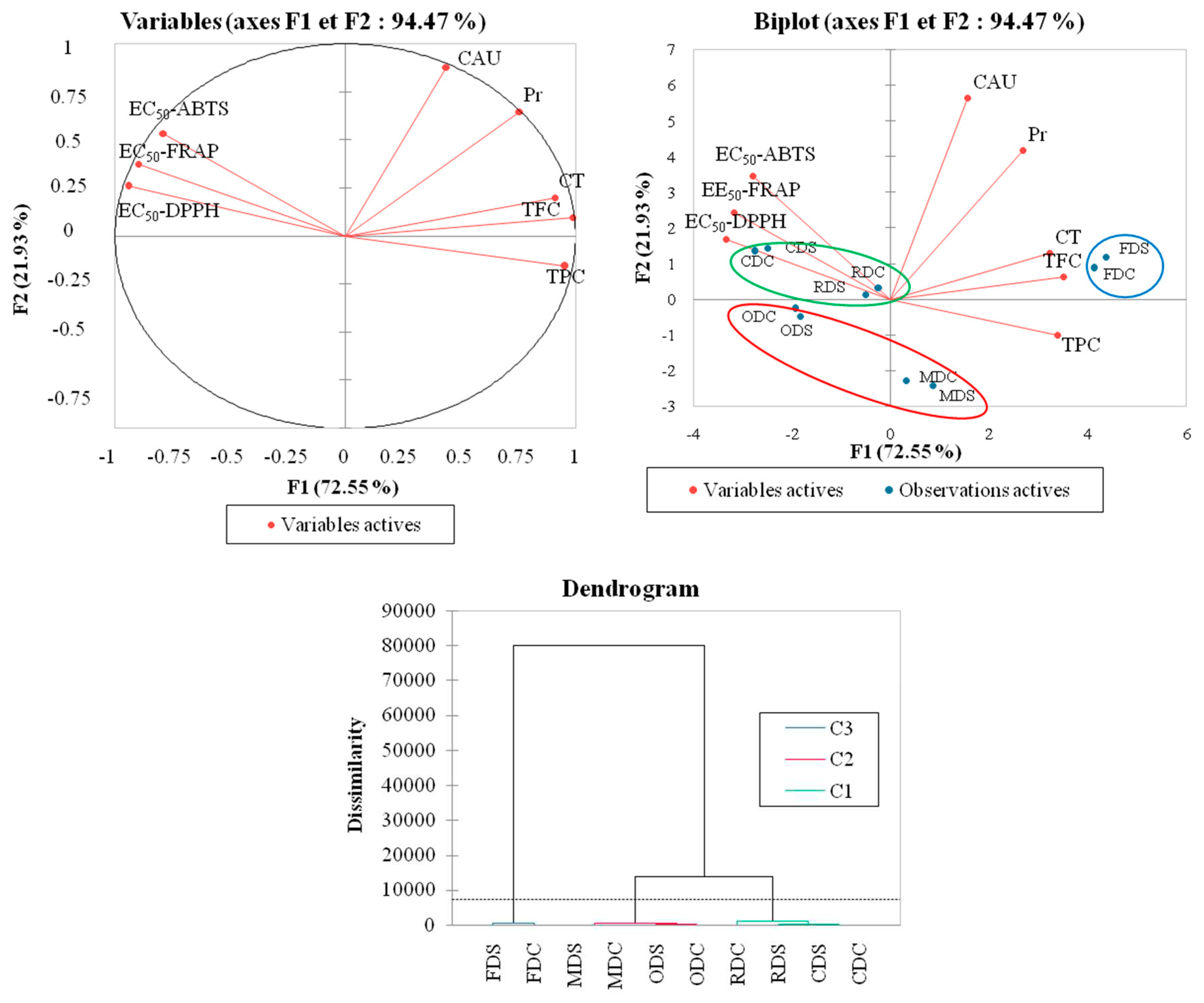
3.3. Correlation, PCA and Classification Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brutti, C.B.; Pardo, M.F.; Caffini, N.O.; Natalucci, C.L. Onopordum acanthium L. (Asteraceae) flowers as coagulating agent for cheesemaking LWT - Food Science and Technology 2012, 45, 172-179. [CrossRef]
- Mandim, F.; Petropoulos, S.A.; Santos-Buelgab, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L. Chemical composition of cardoon (Cynara cardunculus L. var altilis) petioles as affected by plant growth stage. Food Research International, 2022; 156, 111330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baştürk, A.; Peker, S. Antioxidant Capacity, Fatty Acid Profile and Volatile Components of the Onopordum Anatolicum and Onopordum Heteracanthum Species Seeds Grown in Van, Turkey. Journal of the Institute of Science and Technology 2021, 11, 2810–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachicha, S.F.; Barrek, S.; Skanji, T.; Ghrabi, Z.G.; Zarrouk, H. Composition chimique de l’huile des graines d’Onopordon nervosum subsp. platylepis Murb (Astéracées). Journal de la Société Chimique de Tunisie, 2007; 9, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Barman, M.; Soren, M.; Mishra, C.; Mitra, A. Dehydrated jasmine flowers obtained through natural convective solar drying retain scent volatiles and phenolics – A prospective for added-value utility. Industrial Crops & Products 2022, 114483. [CrossRef]
- Ziaa, M.P.; Alibas, I. Influence of the drying methods on color, vitamin C, anthocyanin, phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity, and in vitro bioaccessibility of blueberry fruits. Food Bioscience 2021, 42, 101179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Qin, L.; Shen, J.; He, Z.; Shao, Q.; Lin, D. (). Drying methods affect bioactive compound contents and antioxidant capacity of Bletilla striata (Thunb.) Reichb.f. flower. Industrial crops and products 2021,16,113388. doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021. 1133. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A. Colorimetry of Total Phenolics with Phosphomolybdic-Phosphotungstic Acid Reagent. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture 1965, 16,144-158. http://www.ajevonline.org/content/16/3/144.full.
- Kim, D.O.; Chun, O.K.; Kim, Y.J.; Moon, H.Y.; Lee, C.Y. Quantification of phenolics and their Antioxidant Capacity in Fresh Plums. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6509–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiitto, R.J. Phenolic constituents in the leaves of northem wiliows methods for the the analysis of certain phenolics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1985, 2, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal.Biochem. 1976, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NAFNOR Norm AFNOR. Microbiologie des aliments. Dénombrement des micro-organismes par comptage de colonies obtenues à 30°C-Méthodes de routines, 1992.
- Libouga, D.G.; Ngah, E.; Nono, Y.J.; Bitjoka, L. Clotting of cow (Bos taurus) and goat milk (Capra hircus) using calve and kid rennets. African Journal of Biotechnology 2008, 7(19), 3490–3496. [Google Scholar]
- Berridge, N.J. An improved method of observing the clotting of milk containing rennin. J. Dairy Res. 1952, 9: 328-329. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, W.I.; Lim, S.T. Antioxidant and anticancer activities of organic extracts from Platycodon grandiforum A. De Candolle roots. J Ethnopharmacol 2004, 93(2-3):409-415. [CrossRef]
- Re, R. , Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. () Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolourization assay. Free Radical Biol Med 1999, 26(9-10):1231–1237. [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Mavi, A.; Kara, A.A. Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rumex crispus L. extracts. J Agric Food Chem 2001, 49, 49,4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandino, G.; Lombardo, S.; Mauromicale, G.; Williamson, G. Profile of polyphenols and phenolic acids in bracts and receptacles of globe artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus) germplasm. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 2011, 24(2), 148-153. [CrossRef]
- Habibatni, S.; Zohra, A.F.; Khalida, H.; Anwar, S.; Mansi, I.; Ali, N. (). Antioxydant in-vitro, inhibiteur de la xanthine oxydase et in-vivo Activité anti-inflammatoire, analgésique, antipyrétique d'Onopordum acanthium. Journal international de phytomédecine 2017, 9, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, S.; Khali, M.; Mahmoudi, N. Etude de l’extraction des composés phénoliques de différentes parties de la fleur d’artichaut (Cynara scolymus L.). Nature & Technologie, B- Sciences Agronomiques et Biologiques 2013, 09, 35-40.
- Lim, Y.Y.; Murtijaya, J. Antioxidant properties of Phyllanthus amarus extracts as affected by different drying methods. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2007, 40(9), 1664-1669. [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Liu, J.; Gao, X.; Lu, F.; Yang, X. Effects of different drying methods on chemical compositions, antioxidant activity and anti-α-glucosidase activity of Coreopsis tinctoriaflower tea. ao). Heliyon 2022, e11784. [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Li, Y.; Si, D.; Yan, S.; Liu, J.; Si, J.; Zhang, X. Identification, quantitative and bioactivity analyses of aroma and alcohol-soluble components in flowers of Gardenia jasminoides and its variety during different drying processes, Food Chemistry 2023, 420, 135846.
- Maghsoudlou, Y.; Ghajari, M.A.; Tavasoli, S. Effects of heat treatment on the phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of quince fruit and its tisane’s sensory properties. J Food Sci Technol. 2019, 56(5), 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozzon, M.; Foligni, R.; Mannozzi, C.; Zamporlini, F.; Raffaelli, N.; Aquilanti, L. Clotting Properties of Onopordum tauricum (Willd.) Aqueous Extract in Milk of Different Species. Foods 2020, 9 (6), 692. [CrossRef]
- Michalak, J.; Czarnowska-Kujawska, M.; Klepacka, J.; Gujska, E. Effect of Microwave Heating on the Acrylamide Formation in Foods. Molecules 2020, 25, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Shoaib, S.M.A.; Abdel Salam, M.; Elsayed S., M. (). Efficient and fast removal of total and fecal coliform, BOD, COD and ammonia from raw water by microwave heating technique. Ground water for Sustainable Development 2022, 19, 100847. [CrossRef]
- Ben Amira, A.; Besbes, S.; Attia, H.; Blecker, C. (). Milk-clotting properties of plant rennets and their enzymatic, rheological, and sensory role in cheese making: A review. Int. J. Food Prop 2017, 20, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.C.; Cui, X.Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, X.D.; Liu, Y.L. Effect of drying pretreatment methods on structural features and antioxidant activities of Brauns native lignin extracted from Chinese quince fruit. Process Biochemistry 2021, 106, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL Hamdaoui, A.; Msanda, F.; Boubaker, H.; Leach, D.; Bombarda, I.; Vanloot, P.; Abbad, A.; Boudyach, H.; Achemchem, F. Essential oil composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of wild and cultivated Lavandula mairei Humbert. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 2018, 76, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drying methods | RD | OD | FD | MD | CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | SF | CF | SF | CF | SF | CF | SF | CF | SF | CF |
| DM (%) | 1.60±0.04b | 1.33±0.03b | 1.77±0.06a | 1.73±0.04a | 1.93±0.06a | 2.00±0.02a | 1.33±±0.06b | 1.67±±0.06b | 1.03±0.04c | 1.17±0.03c |
| TP (mg GAE/g | 4.15±0.50b | 4.14±0.77b | 3.62±0.21bc | 3.75±0.61bc | 6.19±0.50a | 5.54±0.67a | 4.94±0.15ab | 4.20±0.16ab | 3.01±0.32c | 2.96±0.22c |
| TF (mg QE/g) | 0.45±0.03c | 0.51±0.02c | 0.18±0.02d | 0.19±0.02d | 2.35±0.07a | 2.12±0.09a | 0.88±0.05b | 0.99±0.05b | 0.09±0.01d | 0.08±0.02d |
| CT (mg CE/g) | 0.013±0.002bc | 0.0130.001bc | 0.015±0.003bc | 0.017±0.002bc | 0.038±0.002a | 0.043±0.001a | 0.021±0.003b | 0.019±0.001b | 0.011±0.00c | 0.009±0.001c |
| PC (mg BSAE/g) | 84.53±10.41b | 99.84±9.84b | 29.85±1.16c | 28.99±3.60c | 263.05±18.67a | 261.23±16.38 a | 3.58±0.62d | 4.15±0.70d | 79.02±6.63b | 78.87±4.12b |
| TAMF(logUFC) | 1.82±0.20 a | 1.77±0.30 a | 1.62±0.16 b | 1.63±0.10 b | 1.38±0.12c | 1.35±0.14 c | abs d | abs d | 1.60±0.22 b | 1.57±0.25 b |
| Drying methods | RD | OD | FD | MD | CD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | SF | CF | SF | CF | SF | CF | SF | CF | SF | CF |
| ClT (s) | 180 | 180 | 490 | 480 | 120 | 120 | ND | ND | 180 | 190 |
| CAU | 0.556 b | 0.556 b | 0.204 c | 0.208 c | 0.833 a | 0.833 a | 0 d | 0 d | 0.556 b | 0.526 b |
| EC50_DPPH (mg/ml) | 0.78±0.08b | 0.91±0.04b | 1.02±0.02a | 1.20±0.02a | 0.48±0.02c | 0.41±0.03c | 0.67±0.09b | 0.73±0.04b | 1.34±0.08a | 1.16±0.01a |
| EC50_ABTS (mg/ml) | 0.20±0.02 b | 0.21±0.01 b | 0.39±0.03 a | 0.37±0.03 a | 0.16±0.04 b | 0.17±0.01 b | 0.14±0.01 b | 0.15±0.02 b | 0.51±0.01 a | 0.49±0.02 a |
| EC50_FRAP | 2.50±0.03d | 2.76±0.12d | 3.42±0.06b | 3.38±0.09b | 1.52±0.19c | 1.65±0.06c | 1.70±0.07c | 1.90±0.05c | 3.45±0.03 a | 3.98±0.09a |
| EC50_DPPH | EC50_ABTS | EC50_FRAP | ClT | CAU | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | Coefficient | -0.894** | -0.769** | -0.864** | -0.375 | 0.666** |
| Sig | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.071 | 0.000 | |
| TF | Coefficient | -0.876** | -0.750** | -0.848** | -0.560** | 0.803** |
| Sig | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.004 | 0.000 | |
| CT | Coefficient | -0.780** | -0.540** | -0.689** | -0.387 | 0.684** |
| Sig | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.000 | 0.062 | 0.000 | |
| PC | Coefficient | -0.530** | -0.275 | -0.432* | -0.733** | 0.921** |
| Sig | 0.003 | 0.141 | 0.017 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





