Submitted:
14 September 2023
Posted:
15 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Single Antiseptics
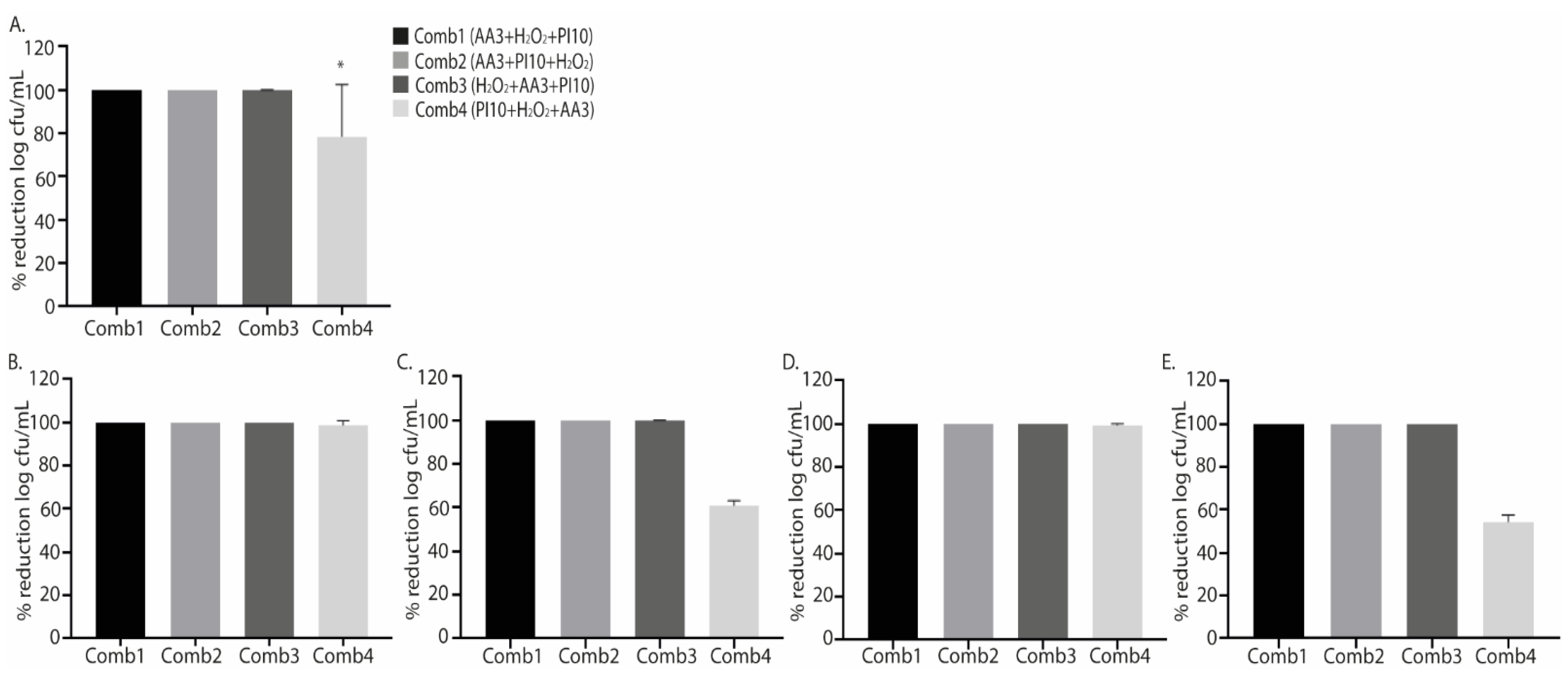
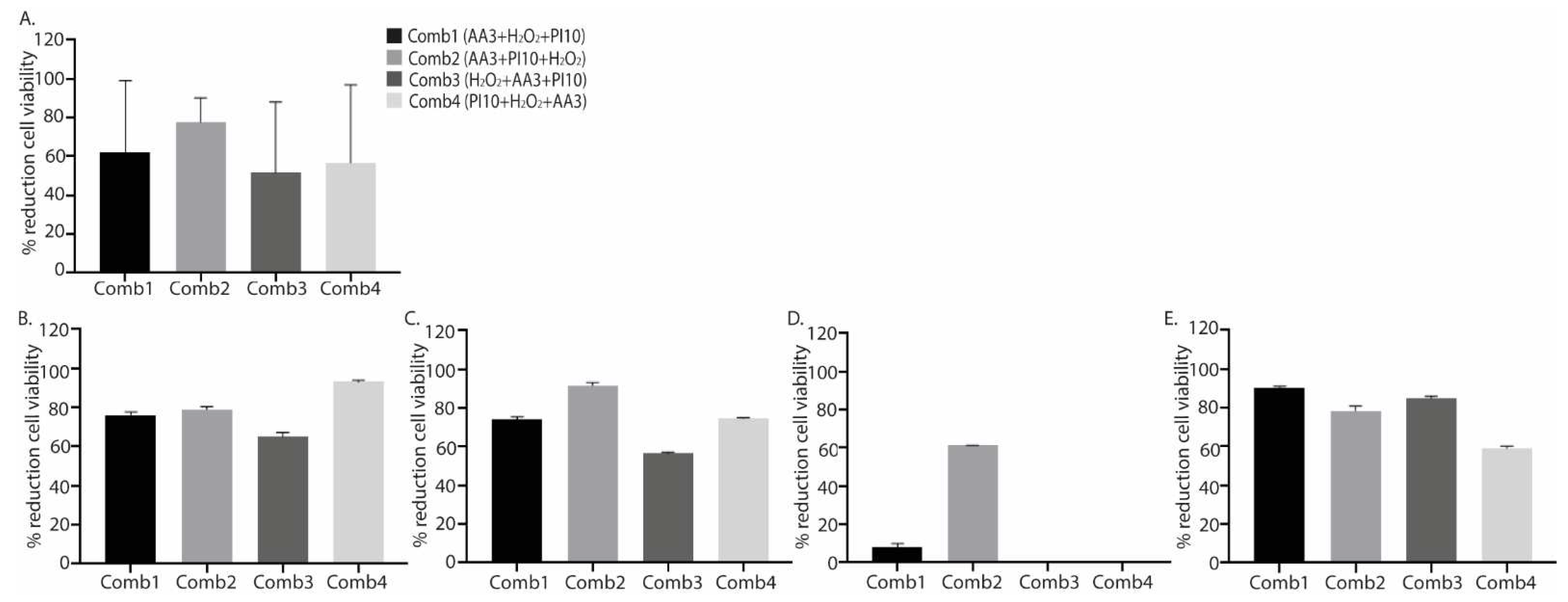
2.2. Combination of Antiseptics
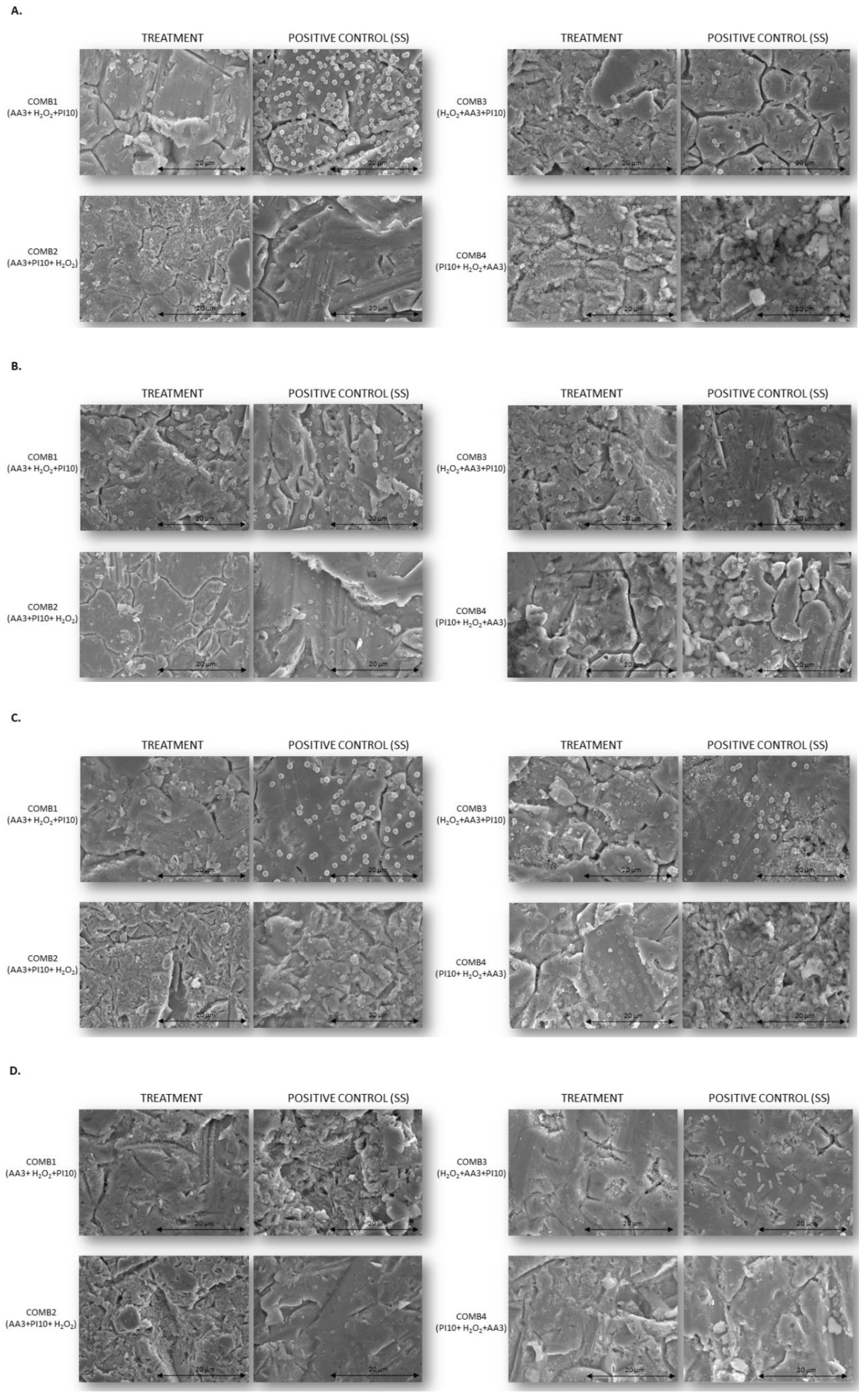
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Setting
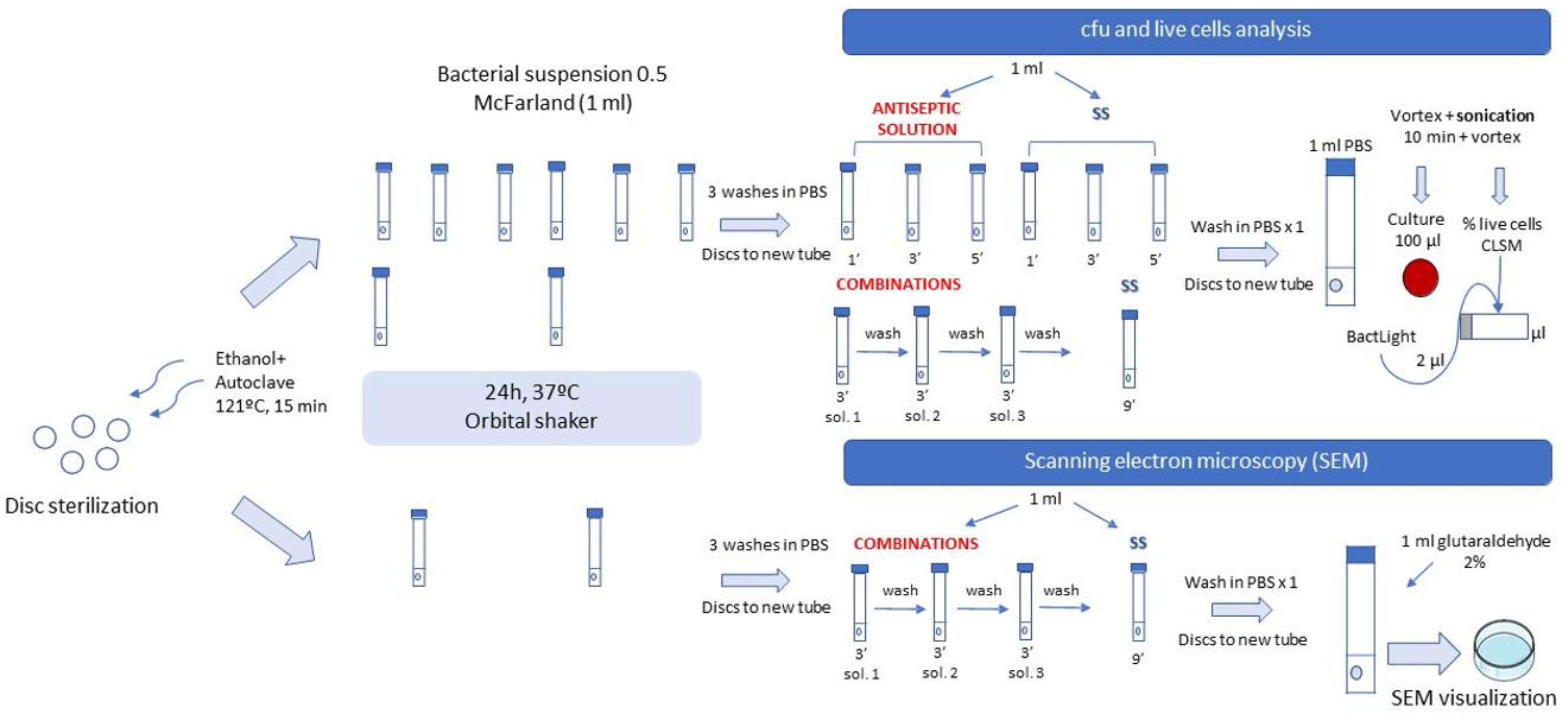
4.2. Laboratory Procedure
4.2.1. Strains:
4.2.2. Antiseptics:
- 0.3% povidone iodine (PI0.3)
- 10% povidone iodine (PI10)
- Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
- 3% acetic acid (AA3)
- Bactisure™ (ethanol [solvent], acetic acid [pH modifier], sodium acetate [buffer], benzalkonium chloride [surfactant], and water)
4.2.3. Combinations:
- Combination 1, AA3+H2O2+PI10
- Combination 2, AA3+PI10+H2O2
- Combination 3, H2O2+AA3+PI10
- Combination 4, PI10+H2O2+AA3
4.2.4. Methodology
4.2.5. Statistical Analysis
4.3. Availability of Data and Material
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic joint infection: Current concepts and outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitridis, D.; Tsikopoulos, K.; Givissis, P.; Chalidis, B. Mortality and complication rates in nonagenarians and octogenarians undergoing total hip and knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2022, 13, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, M.; Premkumar, A.; Sheth, N.P. Projected Volume of Primary Total Joint Arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2018, 100, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcos, M.W.; Kooner, P.; Marsh, J.; Howard, J.; Lanting, B.; Vasarhelyi, E. The economic impact of periprosthetic infection in total knee arthroplasty. Can. J. Surg. 2021, 64, E144–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akindolire, J.; Morcos, M.W.; Marsh, J.D.; Howard, J.L.; Lanting, B.A.; Vasarhelyi, E.M. The economic impact of periprosthetic infection in total hip arthroplasty. Can. J. Surg. 2020, 63, E52–E56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbejuade, H.O.; Lovering, A.M.; Webb, J.C. The role of microbial biofilms in prosthetic joint infections. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staats, A.; Li, D.; Sullivan, A.C.; Stoodley, P. Biofilm formation in periprosthetic joint infections. Ann. Jt. 2021, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, L.H.; Barbosa, T.A.; Esteves, J.; Abreu, M.; Soares, D.; Sousa, R. Early Debridement, antibiotics and implant retention (DAIR) in patients with suspected acute infection after hip or knee arthroplasty—Safe, effective and without negative functional impact. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2019, 4, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, K.; Cho, J.; Foltz, C.; Manrique, J.; Tan, T.L.; Fillingham, Y.; et al. Polymyxin and Bacitracin in the Irrigation Solution Provide No Benefit for Bacterial Killing in Vitro. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2019, 101, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, B.D.; White, D.W.; Wenke, J.C. Comparison of Irrigation Solutions and Devices in a Contaminated Musculoskeletal Wound Survival Model. J. Bone Jt. Surg. -Am. Vol. 2009, 91, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruckenhauser, E.-M.; Nogler, M.; Coraça-Huber, D. Use of Lavage Fluids in Arthroplasty to Prevent Postoperative Infections. Drug Res (Stuttg) 2013, 64, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premkumar, A.; Nishtala, S.N.; Nguyen, J.T.; Bostrom, M.P.G.; Carli, A.V. The AAHKS Best Podium Presentation Research Award: Comparing the Efficacy of Irrigation Solutions on Staphylococcal Biofilm Formed on Arthroplasty Surfaces. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, S26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, A.; Abdo, Z.E.; Rossman, S.R.; Kelly, M.A.; Piuzzi, N.S.; Higuera, C.A.; et al. What Is the Optimal Irrigation Solution in the Management of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Joint Infections? J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 3570–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kia, C.; Cusano, A.; Messina, J.; Muench, L.N.; Chadayammuri, V.; McCarthy, M.B.; et al. Effectiveness of topical adjuvants in reducing biofilm formation on orthopedic implants: An in vitro analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2021, 30, 2177–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.A.; Wu, M.; Cochrane, N.H.; Belay, E.; Myntti, M.F.; James, G.A.; et al. Efficacy of common antiseptic solutions against clinically relevant microorganisms in biofilm. Bone Joint J. 2021, 103-B, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, A.; Cho, J.; Fleischman, A.; Goswami, K.; Ketonis, C.; Kunutsor, S.K.; et al. General Assembly, Prevention, Antiseptic Irrigation Solution: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, S131–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduwole, K.O.; Glynn, A.A.; Molony, D.C.; Murray, D.; Rowe, S.; Holland, L.M.; et al. Anti-biofilm activity of sub-inhibitory povidone-iodine concentrations against Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernest, E.P.; Machi, A.S.; Karolcik, B.A.; LaSala, P.R.; Dietz, M.J. Topical adjuvants incompletely remove adherent Staphylococcus aureus from implant materials: TOPICAL ADJUVANTS AND BIOFILM REDUCTION. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohat, N.; Goh, G.S.; Harrer, S.L.; Brown, S. Dilute Povidone-Iodine Irrigation Reduces the Rate of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Following Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: An Analysis of 31,331 Cases. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, V.; Di Gennaro, D.; Sacco, A.M.; Festa, E.; Roscetto, E.; Basso, M.A.; et al. Cell Toxicity Study of Antiseptic Solutions Containing Povidone–Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, A.; Abdo, Z.E.; Springer, B.D.; Chen, A.F. Pursuit of the ideal antiseptic irrigation solution in the management of periprosthetic joint infections. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2021, 6, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ibarburu, B.; Díaz-Navarro, M.; Ibarra, G.; Rivera, A.; Hafian, R.; Irigoyen, Ã.; et al. Efficacy of Povidone Iodine Against Microbial Biofilms in Breast Implants With Different Textures: Results From an in vitro Study. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 868347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzam, K.A.; Seeley, M.; Ghanem, E.; Austin, M.S.; Purtill, J.J.; Parvizi, J. Irrigation and debridement in the management of prosthetic joint infection: Traditional indications revisited. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
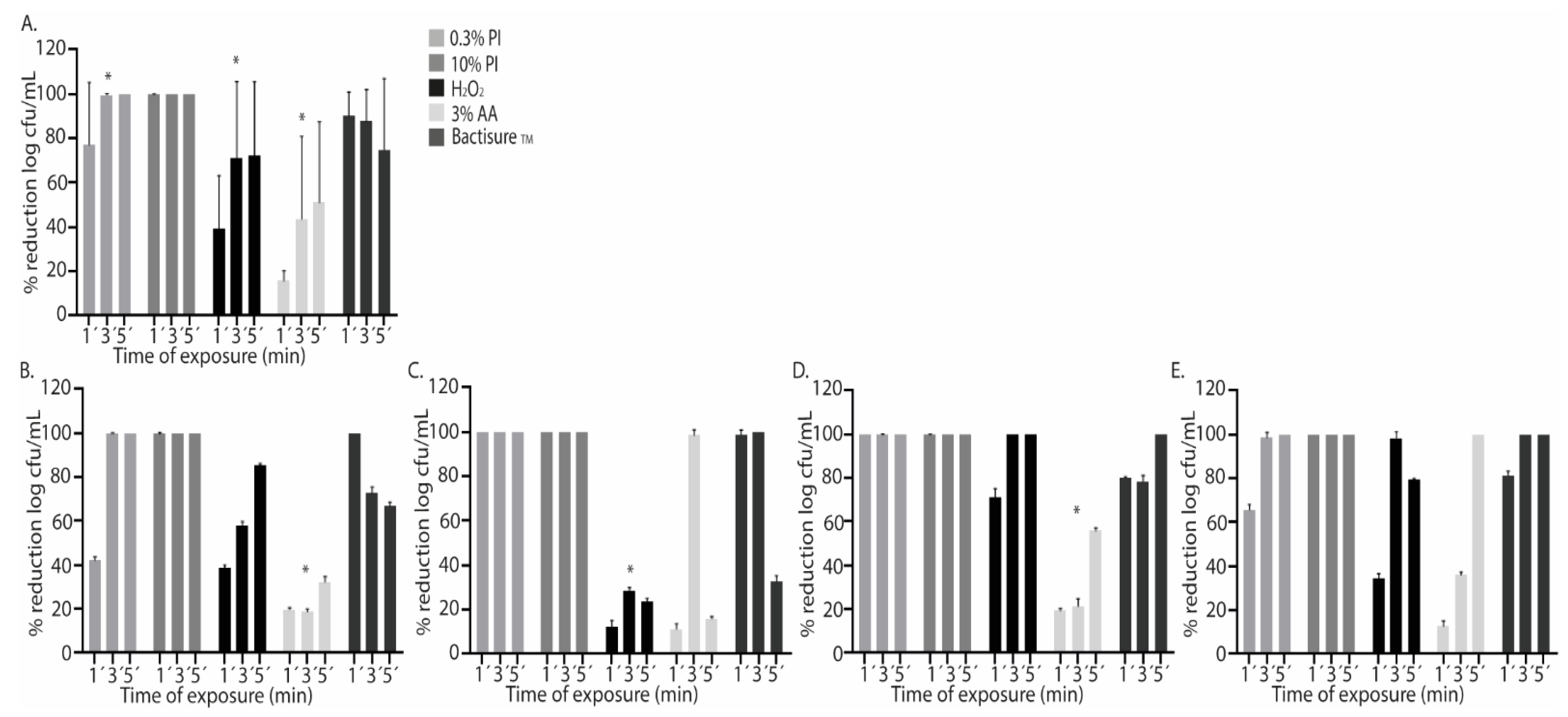
| Antiseptic solution | Treatment | Median (IQR) log cfu/ml | p* |
|---|---|---|---|
| PI0.3 | SS 1´ | 5.56 (5.13-6.05) | <0.001 |
| PI0.3 1´ | 1.08 (0.00-3.01) | ||
| SS 3´ | 5.64 (4.86-5.98) | <0.001 | |
| PI0.3 3´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||
| SS 5´ | 5.64 (5.36-6.05) | <0.001 | |
| PI0.3 5´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||
| PI10 | SS 1´ | 4.99 (4.08-5.49) | <0.001 |
| PI10 1´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||
| SS 3´ | 5.17 (4.65-5.72) | <0.001 | |
| PI10 3´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||
| SS 5´ | 5.51 (4.55-5.85) | <0.001 | |
| PI10 5´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||
| H2O2 | SS 1´ | 5.69 (4.97-6.53) | <0.001 |
| H2O2 1´ | 4.08 (2.13-4.29) | ||
| SS 3´ | 5.95 (5.01-7.04) | <0.001 | |
| H2O2 3´ | 1.40 (0.00-3.38) | ||
| SS 5´ | 5.78 (4.84-6.94) | <0.001 | |
| H2O2 5´ | 1.24 (0.25-3.07) | ||
| AA3 | SS 1´ | 5.59 (5.11-6.34) | 0.002 |
| AA3 1´ | 4.09 (4.23-5.45) | ||
| SS 3´ | 5.28 (4.78-6.1) | <0.001 | |
| AA3 3´ | 3.86 (0.93-4.36) | ||
| SS 5´ | 5.56 (5.21-6.40) | <0.001 | |
| AA3 5´ | 3.15 (0.58-4.23) | ||
| BactisureTM | SS 1´ | 3.84 (5.21-6.40) | <0.001 |
| BactisureTM 1´ | 0.50 (0.00-1.00) | ||
| SS 3´ | 6.12 (5.27-6.42) | <0.001 | |
| BactisureTM 3´ | 0.50 (0.00-1.59) | ||
| SS 5´ | 6.18 (5.45-6.48) | <0.001 | |
| BactisureTM 5´ | 1.10 (0.00-3.55) |
| Treatment | Median (IQR) log cfu/ml |
p* | Median (IQR) % live cells |
p* | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI0.3 vs. PI10 | PI0.3 1’ | 1.08 (0.00-3.01) | 0.006 | NA | NA |
| PI10 1’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||||
| PI0.3 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | NA | |||
| PI10 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||||
| PI0.3 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | NA | |||
| PI10 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | ||||
| PI0.3 vs. H2O2 | PI0.3 1’ | 1.08 (0.00-3.01) | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| H2O2 1’ | 4.08 (2.13-4.29) | ||||
| PI0.3 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.006 | |||
| H2O2 3’ | 1.40 (0.00-3.38) | ||||
| PI0.3 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | |||
| H2O2 5’ | 1.24 (0.25-3.07) | ||||
| PI0.3 vs. AA3 | PI0.3 1’ | 1.08 (0.00-3.01) | 0.001 | NA | NA |
| AA3 1’ | 4.09 (4.23-5.45) | ||||
| PI0.3 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | |||
| AA3 3’ | 3.86 (0.93-4.36) | ||||
| PI0.3 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | |||
| AA3 5’ | 3.15 (0.58-4.23) | ||||
| PI0.3 vs. BactisureTM | PI03 1’ | 1.08 (0.00-3.01) | 0.262 | NA | NA |
| Bactisure™ 1’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.00) | ||||
| PI0.3 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.006 | |||
| Bactisure™ 3’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.59) | ||||
| PI0.3 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.002 | |||
| Bactisure™ 5’ | 1.10 (0.00-3.55) | ||||
| PI10 vs. H2O2 | PI10 1’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| H2O2 1’ | 4.08 (2.13-4.29) | ||||
| PI10 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.006 | |||
| H2O2 3’ | 1.40 (0.00-3.38) | ||||
| PI10 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | |||
| H2O2 5’ | 1.24 (0.25-3.07) | ||||
| PI0.3 vs. AA3 | PI10 1’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| AA3 1’ | 4.09 (4.23-5.45) | ||||
| PI10 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | |||
| AA3 3’ | 3.86 (0.93-4.36) | ||||
| PI10 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | <0.001 | |||
| AA3 5’ | 3.15 (0.58-4.23) | ||||
| PI10 vs. BactisureTM | PI10 1’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.006 | NA | NA |
| Bactisure™ 1’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.00) | ||||
| PI10 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.006 | |||
| Bactisure™ 3’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.59) | ||||
| PI10 5’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.006 | |||
| Bactisure™ 5’ | 1.10 (0.00-3.55) | ||||
| H2O2 vs. AA3 | H2O2 1’ | 4.08 (2.13-4.29) | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| AA3 1’ | 4.09 (4.23-5.45) | ||||
| H2O2 3’ | 1.40 (0.00-3.38) | 0.007 | |||
| AA3 3’ | 3.86 (0.93-4.36) | ||||
| H2O2 5’ | 1.24 (0.25-3.07) | 0.065 | |||
| AA3 5’ | 3.15 (0.58-4.23) | ||||
| H2O2 vs. BactisureTM | H2O2 1’ | 4.08 (2.13-4.29) | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| Bactisure™ 1’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.00) | ||||
| H2O2 3’ | 1.40 (0.00-3.38) | 0.265 | |||
| Bactisure™ 3’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.59) | ||||
| H2O2 5’ | 1.24 (0.25-3.07) | 1.000 | |||
| Bactisure™ 5’ | 1.10 (0.00-3.55) | ||||
| AA3 vs. BactisureTM | AA3 1’ | 4.09 (4.23-5.45) | <0.001 | NA | NA |
| Bactisure™ 1’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.00) | ||||
| AA3 3’ | 3.86 (0.93-4.36) | 0.007 | |||
| Bactisure™ 3’ | 0.50 (0.00-1.59) | ||||
| AA3 5’ | 3.15 (0.58-4.23) | 0.059 | |||
| Bactisure™ 5’ | 1.10 (0.00-3.55) |
| Treatment |
Median (IQR) log cfu/ml |
p* |
Median (IQR) % live cells |
p* | ||
| Combination 1 vs. Combination 2 |
AA3 3’+ H2O2 3’+PI10 3’ | 0.0 (0.00-0.00) 0.00 (0.00-0.00) |
NA | 10.89 (4.03-16.97) 6.04 (3.90-8.60) |
0.248 | |
| AA3 3’+PI10 3’+ H2O2 3’ | ||||||
| Combination 1 vs. Combination 3 |
AA3 3’+ H2O2 3’+PI10 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) 0.00 (0.00-0.00) |
NA | 10.89 (4.03-16.97) 16.89 (5.87-32.49) |
0.386 | |
| H2O2 3’+AA3 3’+PI10 3’ | ||||||
| Combination 1 vs. Combination 4 |
AA3 3’+ H2O2 3’+PI10 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) 1.19 (0.00-2.67) |
0.006 | 10.89 (4.03-16.97) 9.35 (4.04-26.85) |
0.773 | |
| PI10 3’+ H2O2 3’+AA3 3’ | ||||||
| Combination 2 vs. Combination 3 |
AA3 3’+PI10 3’+ H2O2 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) 0.00 (0.00-0.00) |
NA | 6.04 (3.90-8.60) 16.89 (5.87-32.49) |
0.248 | |
| H2O2 3’+AA3 3’+PI10 3’ | ||||||
| Combination 2 vs. Combination 4 |
AA3 3’+PI10 3’+ H2O2 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) 1.19 (0.00-2.67) |
0.006 | 6.04 (3.90-8.60) 9.35 (4.04-26.85) |
0.564 | |
| PI10 3’+ H2O2 3’+AA3 3’ | ||||||
| Combination 3 vs. Combination 4 |
H2O2 3’+AA3 3’+PI10 3’ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 0.006 | 16.89 (5.87-32.49) | 0.468 | |
| PI10 3’+ H2O2 3’+AA3 3’ |
| Treatment |
Median (IQR) log cfu/ml |
p* | Median (IQR) % live cells | p* |
Median (IQR) % reduction live cells1 |
p* | |
| SS 9´ | 6.43 (6.39-6.45) | <0.001 | 32.20 (19.29-43.74) | 0.042 | 75.00 (25.63-87.00) | 0.103 | |
| Combination 1 | AA3 3´+ H2O2 3´+PI10 3´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 10.89 (4.03-16.97) | ||||
| SS 9´ | 5.96 (5.48-6.10) | <0.001 | 32.20 (19.29-43.74) | 0.020 | 79.75 (65.08-87.95) |
||
| Combination 2 | AA3 3´+PI10 3´+ H2O2 3´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 6.04 (3.90-8.60) | ||||
| SS 9´ | 5.08 (5.08-5.08) | <0.001 | 32.20 (19.29-43.74) | 0.081 | 59.90 (13.95-79.70) |
||
| Combination 3 | H2O2 3´+AA3 3´+PI10 3´ | 0.00 (0.00-0.00) | 16.89 (5.87-32.49) | ||||
| SS 9´ | 6.40 (6.01-6.62) | <0.001 | 32.20 (19.29-43.74) | 0.081 | 67.10 (14.50-87.75) |
||
| Combination 4 | PI10 3´+ H2O2 3´+AA3 3´ | 1.19 (0.00-2.67) | 9.35 (4.04-26.85) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





